Nonlinear Magnetic Response Measurements in Study of Magnetic Nanoparticles Uptake by Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Coated by Dextran Shell
2.2. Study of the Structure of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by X-Ray Diffraction
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.5. Determination of MNP Concentration in Suspension
2.6. MSC Culture
2.7. Coincubation of MSCs with MNPs
2.8. NLR-M2 Measurements
2.9. Processing Nonlinear Response Data
2.10. Statistics
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Characterization of the MNPs
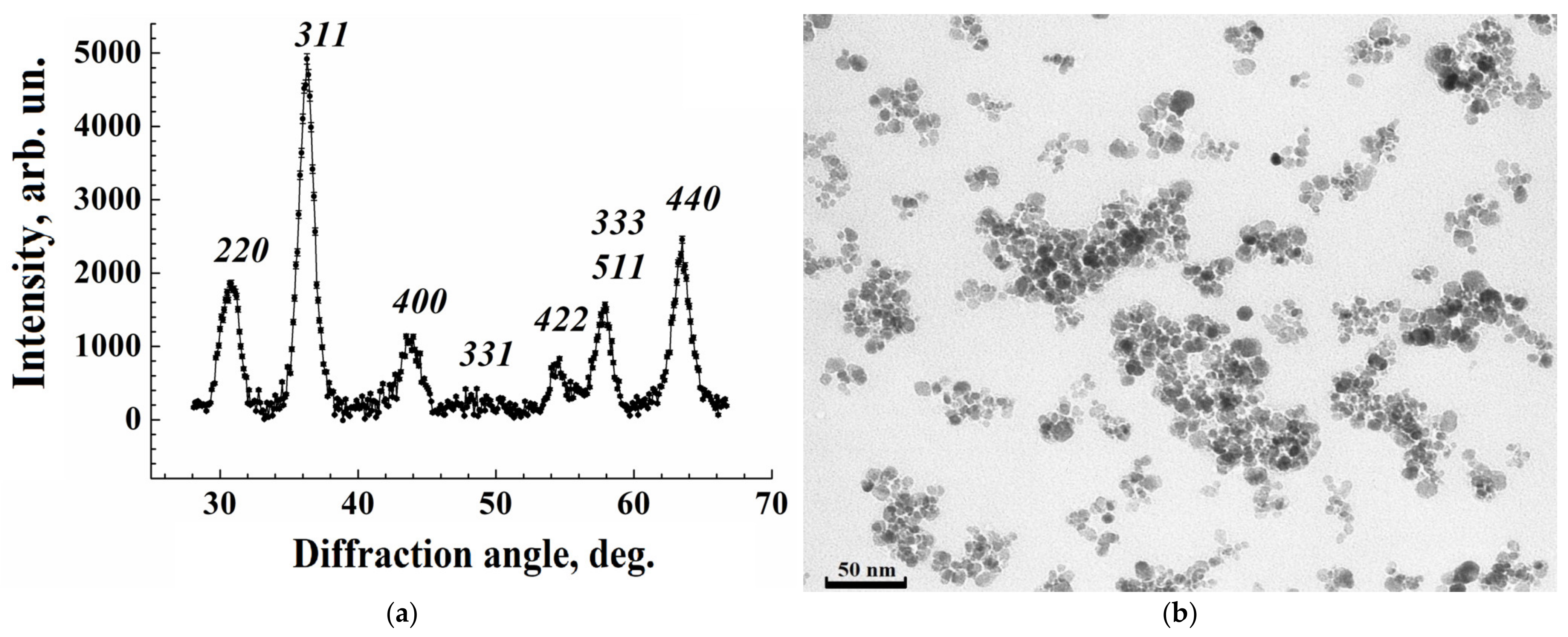
3.1.1. Structure of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles from X-Ray Diffraction
3.1.2. Examination by Transmission Electron Microscopy
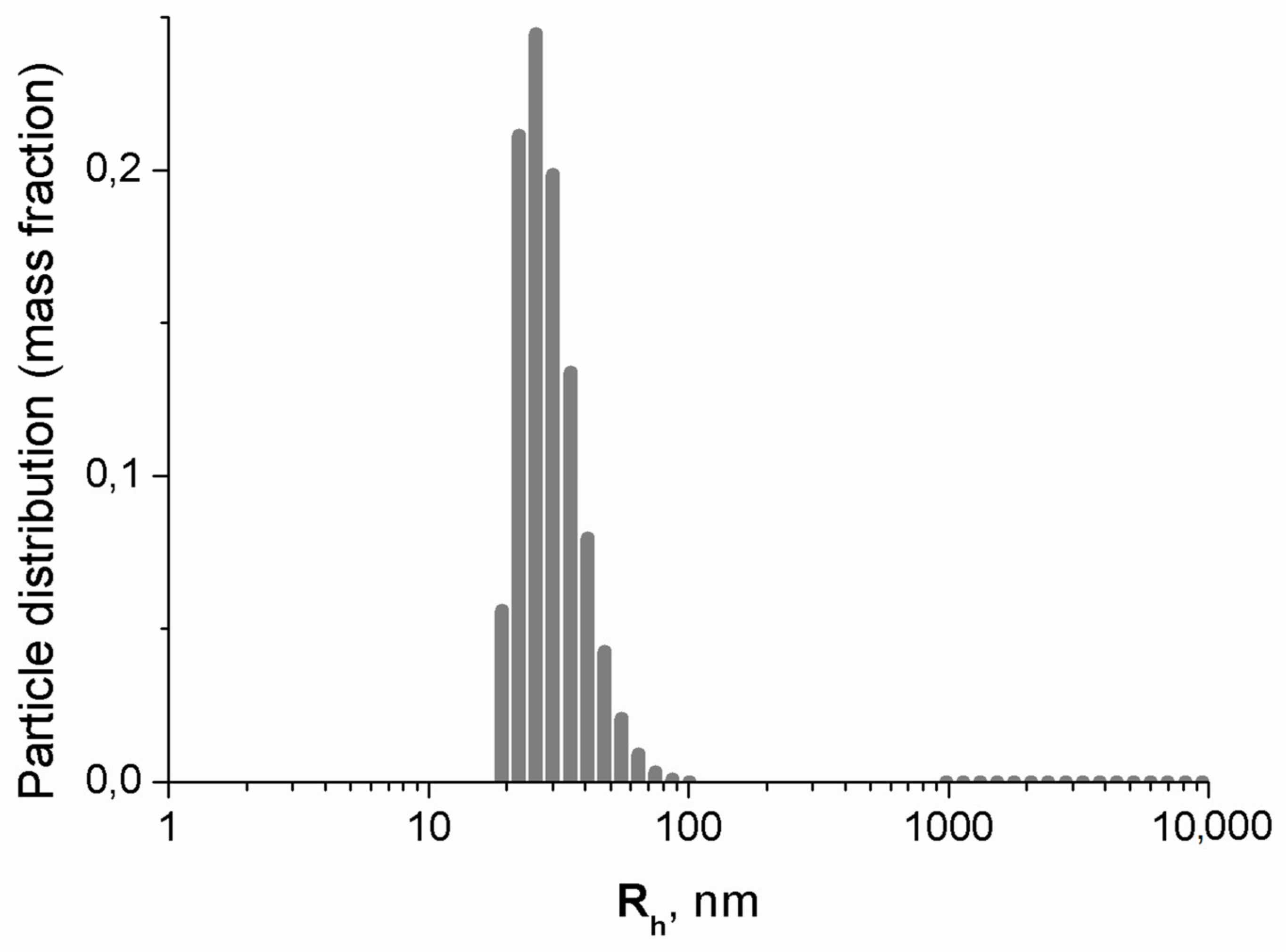
3.1.3. Dynamic Light Scattering Results
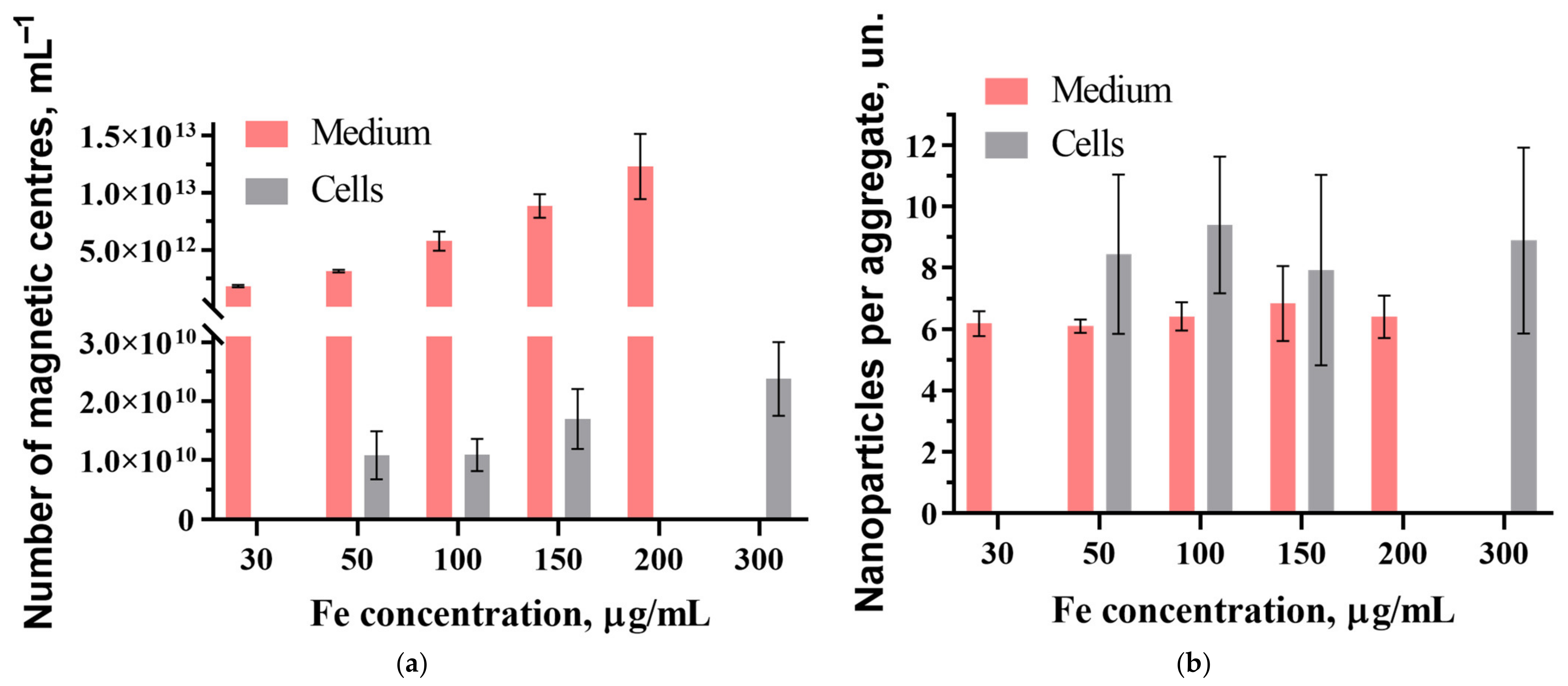
3.2. Evaluation of the Toxicity of Nanoparticles
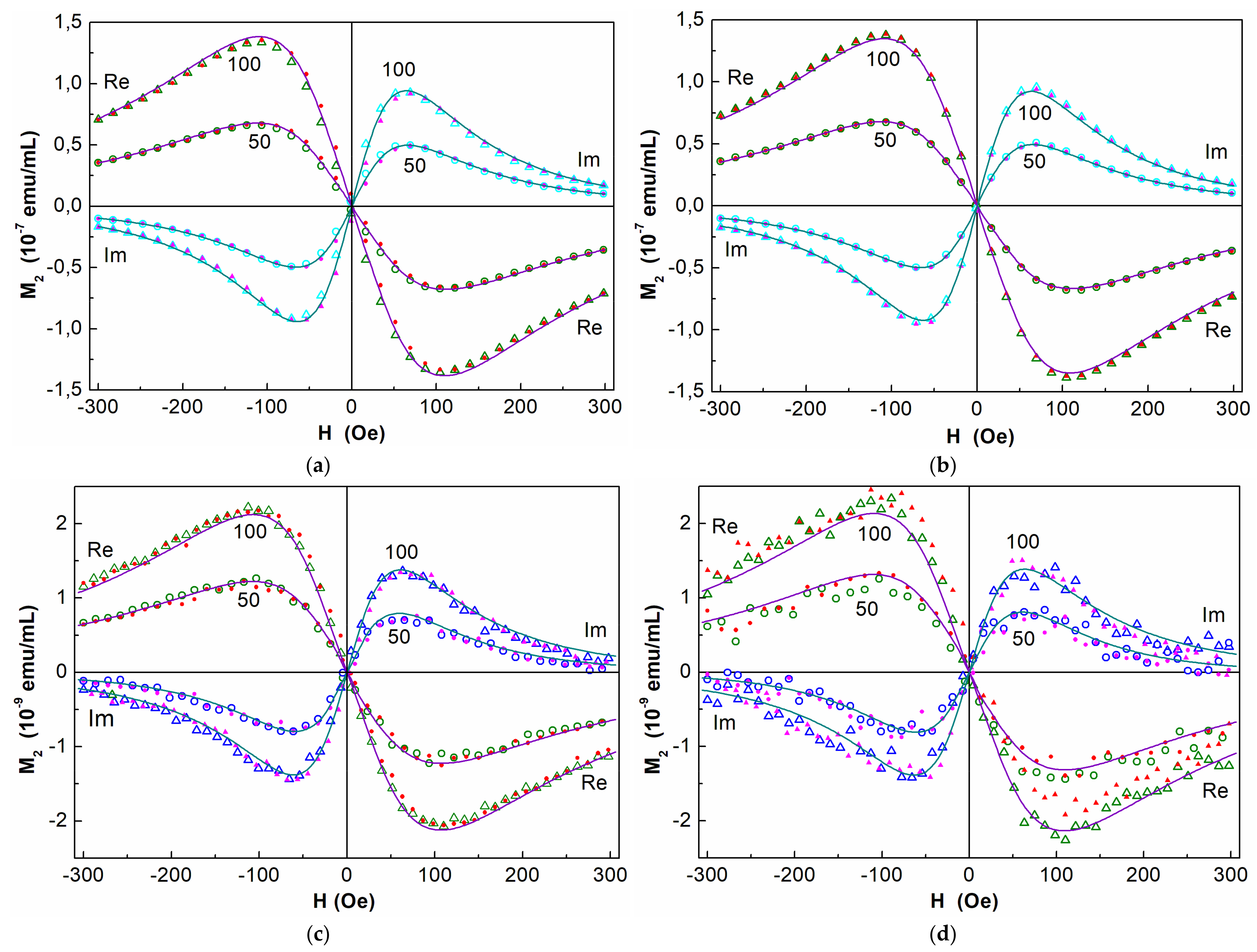
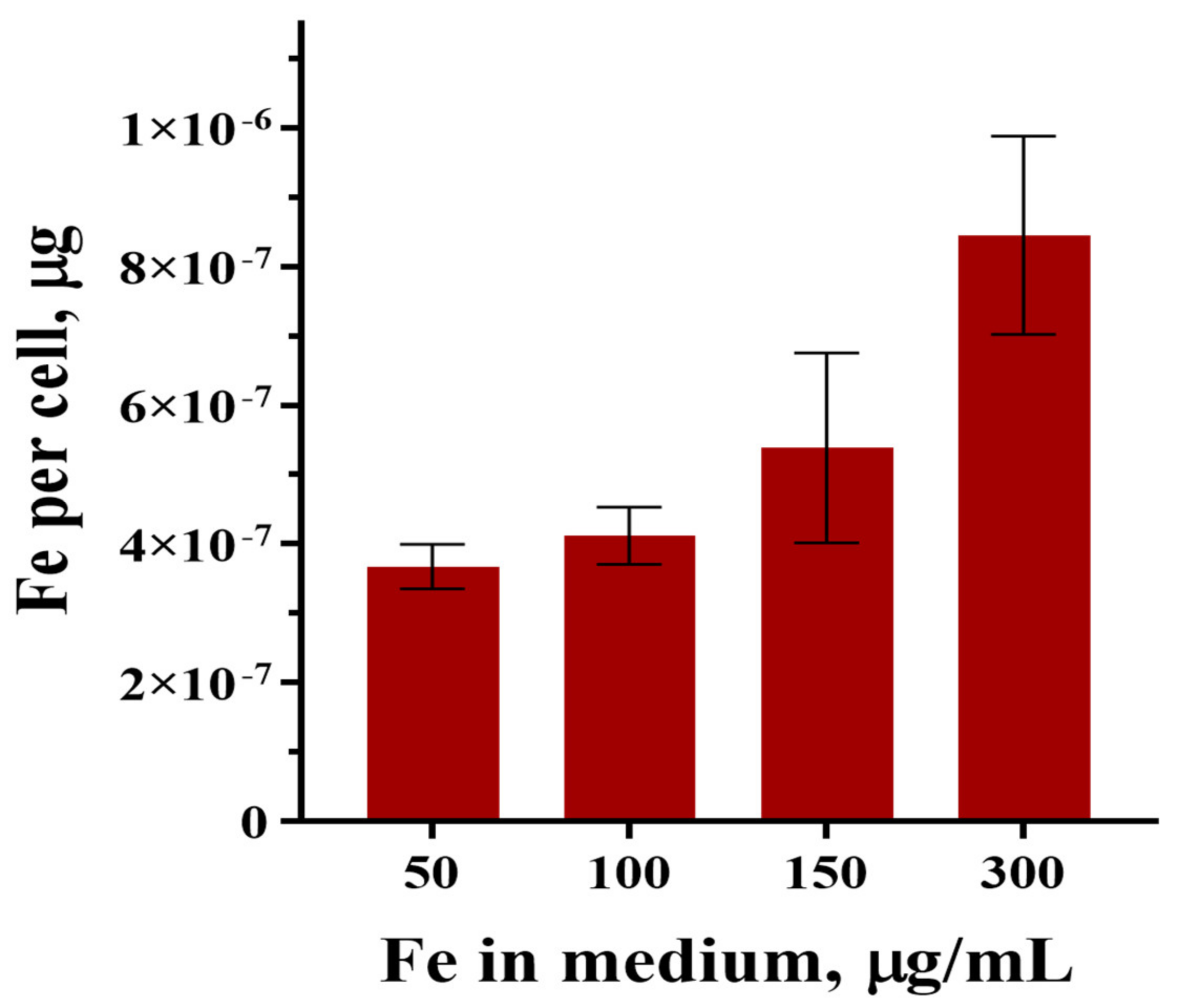
3.3. NLR-M2 Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MNP | Magnetic nanoparticle |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cell |
| SPM | Superparamagnetic |
| NLR-M2 | Nonlinear longitudinal response to weak ac magnetic fields with registration of the second harmonic of magnetization |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| ac | Alternating current |
| dc | Direct current |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
References
- Su, Z.; Dong, S.; Zhao, S.C.; Liu, K.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Qin, B.; Chen, Z.S.; Zou, C. Novel nanomedicines to overcome cancer multidrug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2021, 58, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veselov, V.V.; Nosyrev, A.E.; Jicsinszky, L.; Alyautdin, R.N.; Cravotto, G. Targeted Delivery Methods for Anticancer Drugs. Cancers 2022, 14, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Chen, G.; Xu, F.; Yang, F.; Yu, H.; Li, L.; Dong, X.; Han, J.; Cao, C.; et al. A Review on Drug Delivery System for Tumor Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 735446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareev, K.G.; Grouzdev, D.S.; Koziaeva, V.V.; Sitkov, N.O.; Gao, H.; Zimina, T.M.; Shevtsov, M. Biomimetic Nanomaterials: Diversity, Technology, and Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 2, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Erythrocyte-inspired delivery systems. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, K.K.; Boczkowski, D.; Dannull, J.; Pruitt, S.; Leong, K.W.; Nair, S.K. Whole blood cells loaded with messenger RNA as an anti-tumor vaccine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Williams, G.R.; Fan, Q.; Niu, S.; Wu, J.; Xie, X.; Zhu, L.M. Platelet-membrane-biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted antitumor drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnology 2019, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, X.; Mo, J.; Li, Q.; Cao, B.; Huang, J.; Lu, Y.; Lu, L.; Fan, M.; Lu, H. Targeted co-delivery of PD-L1 monoclonal antibody and sorafenib to circulating tumor cells via platelet-functionalized nanocarriers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 671, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Tang, W.; Wen, R.; Zhou, S.; Lee, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Delahunty, I.M.; Zhen, Z.; et al. Nanoparticle-Laden Macrophages for Tumor-Tropic Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1805557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z. Neutrophil-Mediated Delivery of Therapeutic Nanoparticles across Blood Vessel Barrier for Treatment of Inflammation and Infection. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11800–11811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, N.; Pishavar, E.; Baradaran, B.; Oroojalian, F.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Stem cell membrane, stem cell-derived exosomes and hybrid stem cell camouflaged nanoparticles: A promising biomimetic nanoplatforms for cancer theranostics. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2022, 348, 706–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, A.; Javius-Jones, K.; Hong, S.; Park, H. Cell-Based Drug Delivery Systems with Innate Homing Capability as a Novel Nanocarrier Platform. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shi, X.; Kuang, Y.; Wei, R.; Feng, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, X. Cell-nanocarrier drug delivery system: A promising strategy for cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Cao, R.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Ren, B.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.C. Blood-Brain Barrier Conquest in Glioblastoma Nanomedicine: Strategies, Clinical Advances, and Emerging Challenges. Cancers 2024, 16, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Xue, X.; Geng, J.; Chung, R.; Shi, B. Effective and Targeted Human Orthotopic Glioblastoma Xenograft Therapy via a Multifunctional Biomimetic Nanomedicine. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1803717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Kuang, L.; Yin, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, B.; Dong, Z.; Wang, W.; Yin, T.; et al. Tumor-Antigen Activated Dendritic Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles with Orchestrating Immune Responses Promote Therapeutic Efficacy against Glioma. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2341–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ji, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Ke, Y. Inflammatory responsive neutrophil-like membrane-based drug delivery system for post-surgical glioblastoma therapy. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2023, 362, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenberg, M.S.S.; Degeling, M.H.; Tannous, B.A. Advances in stem cell therapy against gliomas. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Chang, F.; Ding, J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Cells 2019, 8, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Song, S.U. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic applications. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2012, 35, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.; Yaseen, N.; Al-Joubory, A.; Abdullah, R.; Mahmood, N.; Ahmed, A.; Al-Shammari, A. Production of Neural Progenitors from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cell Discov. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K. Stem cell-based therapies for tumors in the brain: Are we there yet? Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laszlo Hajba, L.; Guttman, A. The use of magnetic nanoparticles in cancer theranostics: Toward handheld diagnostic devices. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.K.; Mitov, M.I.; Daley, E.F.; McGarry, R.C.; Anderson, K.W.; Zach Hilt, J. Targeted iron oxide nanoparticles for the enhancement of radiation therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 105, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Sommer, S.; Distel, L.V.R.; Neuhuber, W.; Kryschi, C. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as radiosensitizer via enhanced reactive oxygen species formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, E.; Dunne, V.; Russell, V.; Mohamud, H.; Ghita, M.; McMahon, S.J.; Butterworth, K.T.; Schettino, G.; McGarry, C.K.; Prise, K.M. Impact of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on in vitro and in vivo radiosensitisation of cancer cells. Radiat Oncol. 2021, 16, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Ryzhov, V.; Volnitskiy, A.; Amerkanov, D.; Pack, F.; Golubev, A.M.; Arutyunyan, A.; Spitsyna, A.; Burdakov, V.; Lebedev, D.; et al. Radiosensitizing Effect of Dextran-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on Malignant Glioma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altanerova, U.; Babincova, M.; Babinec, P.; Benejova, K.; Jakubechova, J.; Altanerova, V.; Zduriencikova, M.; Repiska, V.; Altaner, C. Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived iron oxide exosomes allow targeted ablation of tumor cells via magnetic hyperthermia. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7923–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, H.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Kim, K.-S. Fundamentals to Apply Magnetic Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Therapy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.J.; Agliardi, G.; Lin, F.-Y.; Ellis, M.; Jones, C.; Robson, M.; Richard-Londt, A.; Southern, P.; Lythgoe, M.; Thin, M.Z.; et al. Potential of Magnetic Hyperthermia to Stimulate Localized Immune Activation. Small 2021, 17, 2005241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudintceva, N.; Mikhailova, N.; Bobkov, D.; Yakovleva, L.; Nikolaev, B.; Krasavina, D.; Muraviov, A.; Vinogradova, T.; Yablonskiy, P.; Samusenko, I.; et al. Evaluation of the Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Pre-clinical Renal Tuberculosis Model by Non-linear Magnetic Response Measurements. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 625622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, D.; Park, J.Y.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Dang, M.; Dai, X.; Yang, J.; Yuan, M.; Li, M.; et al. Evaluation of the management of rotator cuff injuries utilising superparamagnetic iron oxide tracking stem cells. Tissue Cell 2025, 95, 102836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.S.; Niknam, Z.; Mojtaba-Zebarjad, S.; Mehrabani, D.; Jalli, R.; Saeedi Moghadam, M.; Behroozi, R.; Zare, S.; Jamhiri, I.; Derakhshanfar, A.; et al. Tracking the healing effect of human Wharton’s jelly stem cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles seeded onto polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan/carbon nanotubes in burn wounds by MRI and Prussian blue staining. Biomed. Mater. 2025, 20, 025037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhen, H.; Qi, M.; Luo, J.; Zhen, J. Macrophage tracking with USPIO imaging and T2 mapping predicts immune rejection of transplanted stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Chen, X.; Liu, D.; Bu, X.; Wang, G.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J. A multi-modality imaging strategy to determine the multiple in vivo fates of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells at different periods of acute liver injury treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 9213–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Majood, M.; Meena, R.; Mukherjee, M.; Dinda, A.K.; Kuanr, B.K.; Mohanty, S. Biocompatible poly-mer-coated magneto-fluorescent super nanoparticles for the homing of mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 132794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Tang, X.S.; Margel, S. Superparamagnetic Amine-Functionalized Maghemite Nanoparticles as a Thixotropy Promoter for Hydrogels and Magnetic Field-Driven Diffusion-Controlled Drug Release. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 5272–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Yoshitomi, T.; Takeguchi, M.; Kawazoe, N.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G. Smart composite scaffold to synchronize magnetic hyperthermia and chemotherapy for efficient breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2024, 307, 122511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharkova, I.I.; Alipkina, S.I.; Zeltzer, A.; Dudun, A.A.; Makhina, T.; Bonartseva, G.A.; Voinova, V.V.; Wagner, D.V.; Pariy, I.; Bonartsev, A.P.; et al. Magnetoactive Composite Conduits Based on Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Magnetite Nanoparticles for Repair of Peripheral Nerve Injury. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Minuti, A.E.; Stavila, C.; Herea, D.D.; Labusca, L.; Ababei, G.; Stoian, G.; Lupu, N. Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Trigger Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Magneto-Mechanical Actuation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, D. Exosomes from magnetic particles-primed mesenchymal stem cells enhance neural differentiation of PC12 cells. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevtsov, M.A.; Nikolaev, B.P.; Yakovleva, L.Y.; Marchenko, Y.Y.; Dobrodumov, A.V.; Mikhrina, A.L.; Martynova, M.G.; Bystrova, O.A.; Yakovenko, I.V.; Ischenko, A.M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with epidermal growth factor (SPION-EGF) for targeting brain tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiufiuc, G.F.; Stiufiuc, R.I. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Use in Biomedical Field. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrukhin, O.M. (Ed.) Analytical Chemistry. In Chemical Methods of Analysis; Chemistry: Moscow, Russia, 1992; 400p. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhov, V.A.; Larionov, I.I.; Fomichev, V.N. On the spurious signal in the longitudinal nonlinear magnetic susceptibility of magnets at the second harmonic of excitation frequency. Tech. Phys. 1996, 41, 620–626. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhov, V.A.; Zavatskii, E.I. Device for Studying Magnetic Properties of Magnets. Russian Patent 2507527, 20 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhov, V.A.; Kiselev, I.A.; Smirnov, O.P.; Chernenkov, Y.P.; Deriglazov, V.V.; Marchenko, Y.Y.; Yakovleva, L.Y.; Nikolaev, B.P.; Bogachev, Y.V. Comprehensive characterization of magnetite-based colloid for biomedical applications. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhov, V.A.; Deriglazov, V.V.; Tran, N.H.; Volnitskiy, A.V.; Shtam, T.A.; Arutyunyan, A.V.; Spitsyna, A.S.; Smirnov, O.P.; Chernenkov, Y.P.; Zinoviev, V.G.; et al. Study of dextran coated magnetic nanoparticles incorporation into glioblastoma cells. Nanobiotechnology Rep. 2024, 19, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Norton, M.G. X-Ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach; Plenum Press Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1998; 273p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kartikowati, C.W.; Horie, S.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Okuyama, K. Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9894–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudintceva, N.; Lomert, E.; Mikhailova, N.; Tolkunova, E.; Agadzhanian, N.; Samochernych, K.; Multhoff, G.; Timin, G.; Ryzhov, V.; Deriglazov, V.; et al. Targeting Brain Tumors with Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Experimental Model of the Orthotopic Glioblastoma in Rats. Biomedicine 2021, 9, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhirde, A.; Xie, J.; Swierczewska, M.; Chen, X. Nanoparticles for cell labeling. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.Y.; Greve, J.M.; Gheysens, O.; Willmann, J.K.; Rodriguez-Porcel, M.; Chu, P.; Sheikh, A.Y.; Faranesh, A.Z.; Paulmurugan, R.; Yang, P.C.; et al. Comparison of optical bioluminescence reporter gene and superparamagnetic iron oxide MR contrast agent as cell markers for noninvasive imaging of cardiac cell transplantation. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2009, 11, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De, A.; Lewis, X.Z.; Gambhir, S.S. Noninvasive imaging of lentiviral-mediated reporter gene expression in living mice. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Castaneda, R.T.; Khurana, A.; Khan, R.; Daldrup-Link, H.E. Labeling stem cells with ferumoxytol, an FDA-approved iron oxide nanoparticle. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2011, 57, e3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Cao, J.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Liu, G. Functional investigations on embryonic stem cells labeled with clinically translatable iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9025–9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.Q.; Shi, Y.N.; Zhu, Y.P.; Liu, Y.Q.; Gu, L.W.; Liu, D.D.; Ma, A.; Xia, F.; Guo, Q.Y.; Xu, C.C.; et al. Recent trends in preparation and biomedical applications of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazuel, F.; Espinosa, A.; Luciani, N.; Reffay, M.; Le Borgne, R.; Motte, L.; Desboeufs, K.; Michel, A.; Pellegrino, T.; Lalatonne, Y.; et al. Massive Intracellular Biodegradation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Evidenced Magnetically at Single-Endosome and Tissue Levels. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7627–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, Y.; Mulens-Arias, V.; Paradela, A.; Ramos-Fernández, A.; Pérez-Yagüe, S.; Morales, M.P.; Barber, D.F. The surface coating of iron oxide nanoparticles drives their intracellular trafficking and degradation in endolysosomes differently depending on the cell type. Biomaterials 2022, 281, 121365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costela Ruiz, V.J.; Melguizo Rodríguez, L.; Illescas Montes, R.; García Recio, E.; Arias Santiago, S.; Ruiz, C.; De Luna Bertos, E. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their phagocytic capacity. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, A.; Li, Z. Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Targeting 3WJ Nanoparticles and Reported Specific Delivery of Anti-miRNA 138 to Treat Osteoporosis. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 10633–10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Choi, H.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, S.H. Injectable Endoplasmin-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles-Hydrogel Composite for Cartilage Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Sample | Medium with MNPs Before Incubation | Cells with MNPs After Incubation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFe of MNPs, μg/mL | Mcenter, µB | σ | α | τN, ns | Mcenter, µB | σ | α | τN, ns |
| 50 | 3.5(2)∙104 | 0.65(1) | 0.18(1) | 1.26(3) | 3.0(2)·104 | 0.71(4) | 0.17(2) | 1.15(11) |
| 100 | 3.8(4)·104 | 0.6(1) | 0.18(3) | 1.49(26) | 3.4(3)·104 | 0.67(4) | 0.18(1) | 1.23(14) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryzhov, V.; Marchenko, Y.; Deriglazov, V.; Yudintceva, N.; Smirnov, O.; Arutyunyan, A.; Shtam, T.; Ivanov, E.; Combs, S.E.; Shevtsov, M. Nonlinear Magnetic Response Measurements in Study of Magnetic Nanoparticles Uptake by Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090675
Ryzhov V, Marchenko Y, Deriglazov V, Yudintceva N, Smirnov O, Arutyunyan A, Shtam T, Ivanov E, Combs SE, Shevtsov M. Nonlinear Magnetic Response Measurements in Study of Magnetic Nanoparticles Uptake by Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(9):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090675
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyzhov, Vyacheslav, Yaroslav Marchenko, Vladimir Deriglazov, Natalia Yudintceva, Oleg Smirnov, Alexandr Arutyunyan, Tatiana Shtam, Evgenii Ivanov, Stephanie E. Combs, and Maxim Shevtsov. 2025. "Nonlinear Magnetic Response Measurements in Study of Magnetic Nanoparticles Uptake by Mesenchymal Stem Cells" Nanomaterials 15, no. 9: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090675
APA StyleRyzhov, V., Marchenko, Y., Deriglazov, V., Yudintceva, N., Smirnov, O., Arutyunyan, A., Shtam, T., Ivanov, E., Combs, S. E., & Shevtsov, M. (2025). Nonlinear Magnetic Response Measurements in Study of Magnetic Nanoparticles Uptake by Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomaterials, 15(9), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090675







