The Effect of Carbon Nanofibers on the Microstructure, Chemistry, and Pore Structure of Concrete Made with Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
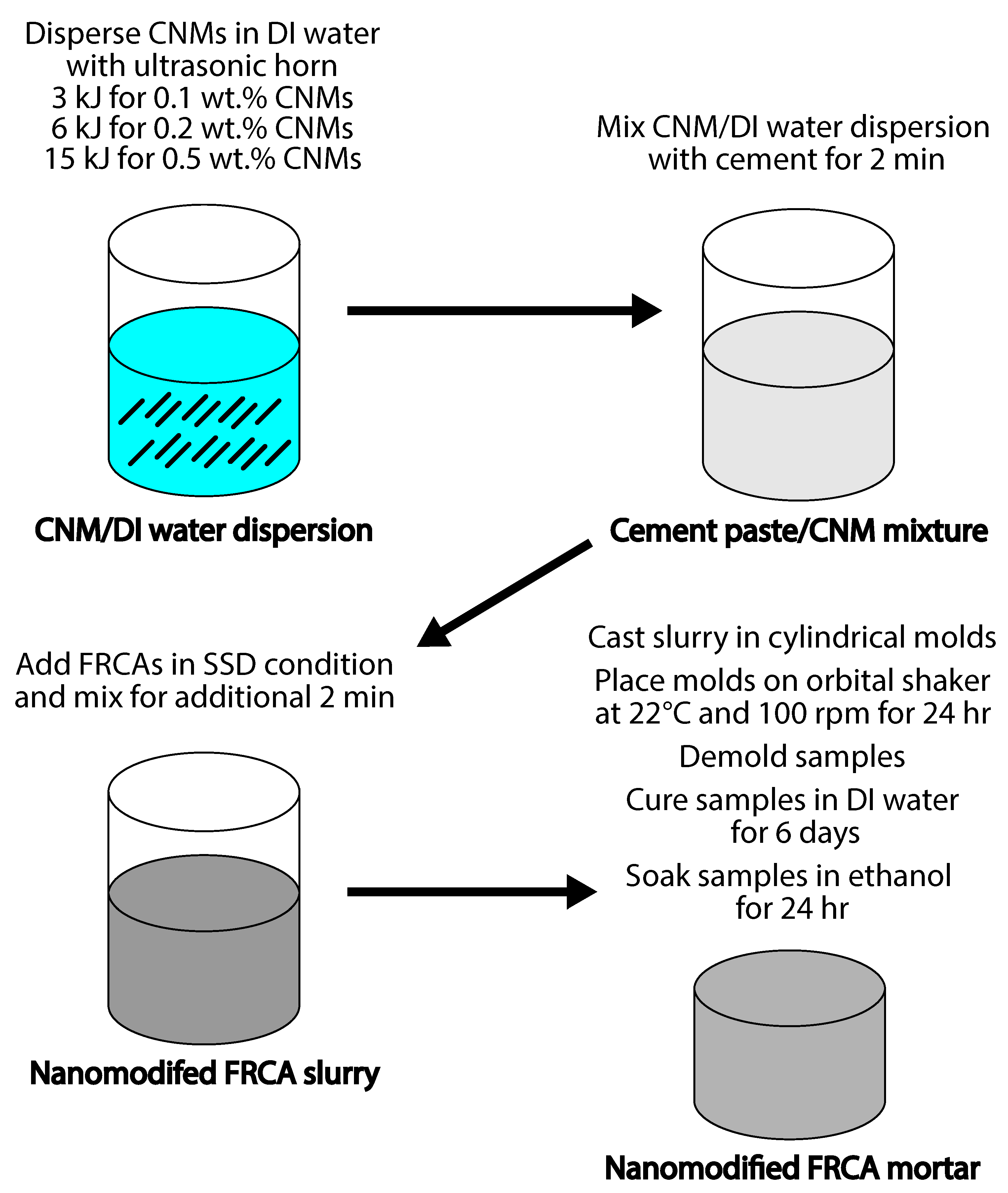
2.2. Sample Preparation
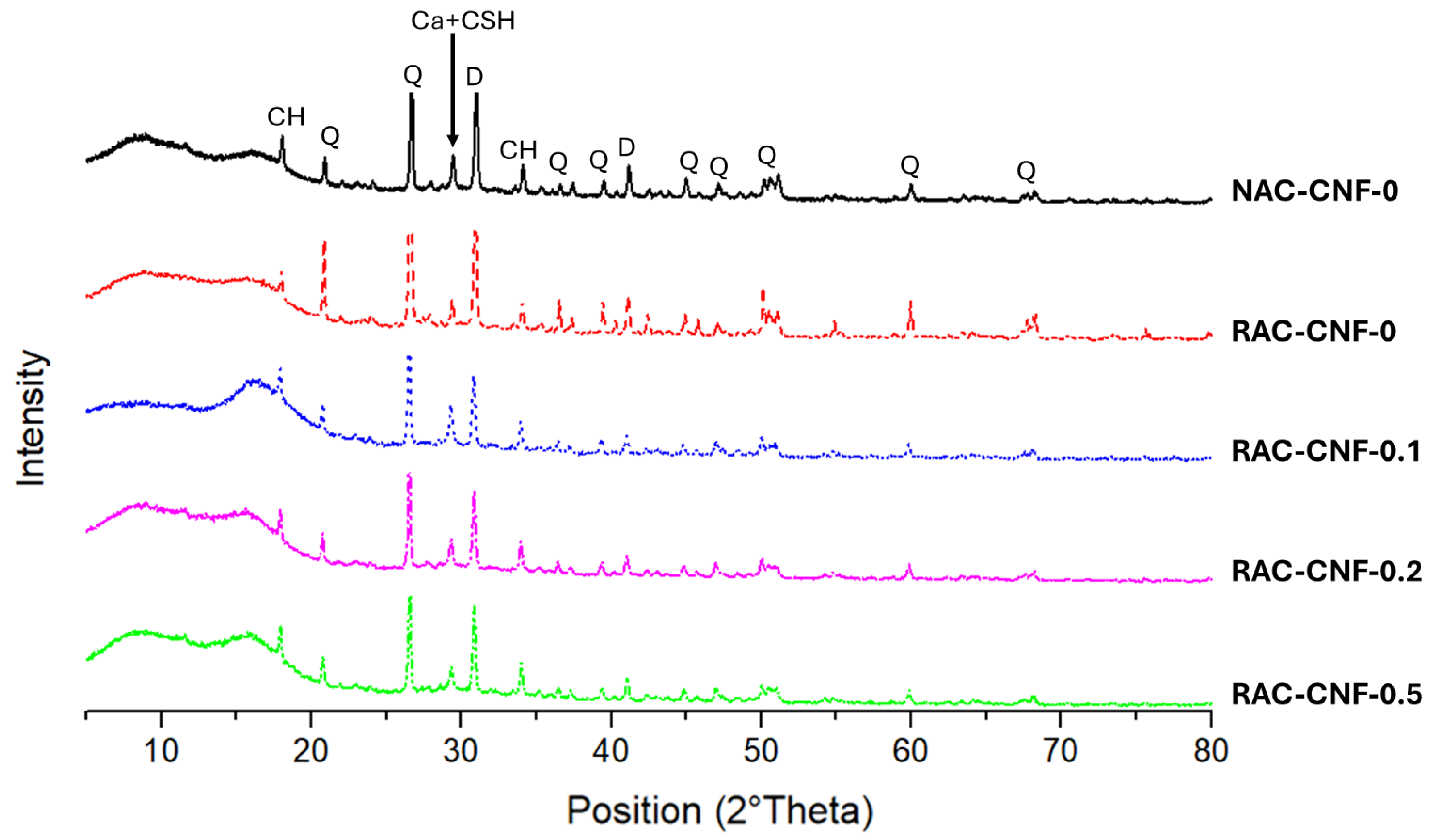
2.3. Mineralogical Composition
2.4. Microstructural Analysis
2.5. Permeability Analysis
3. Results
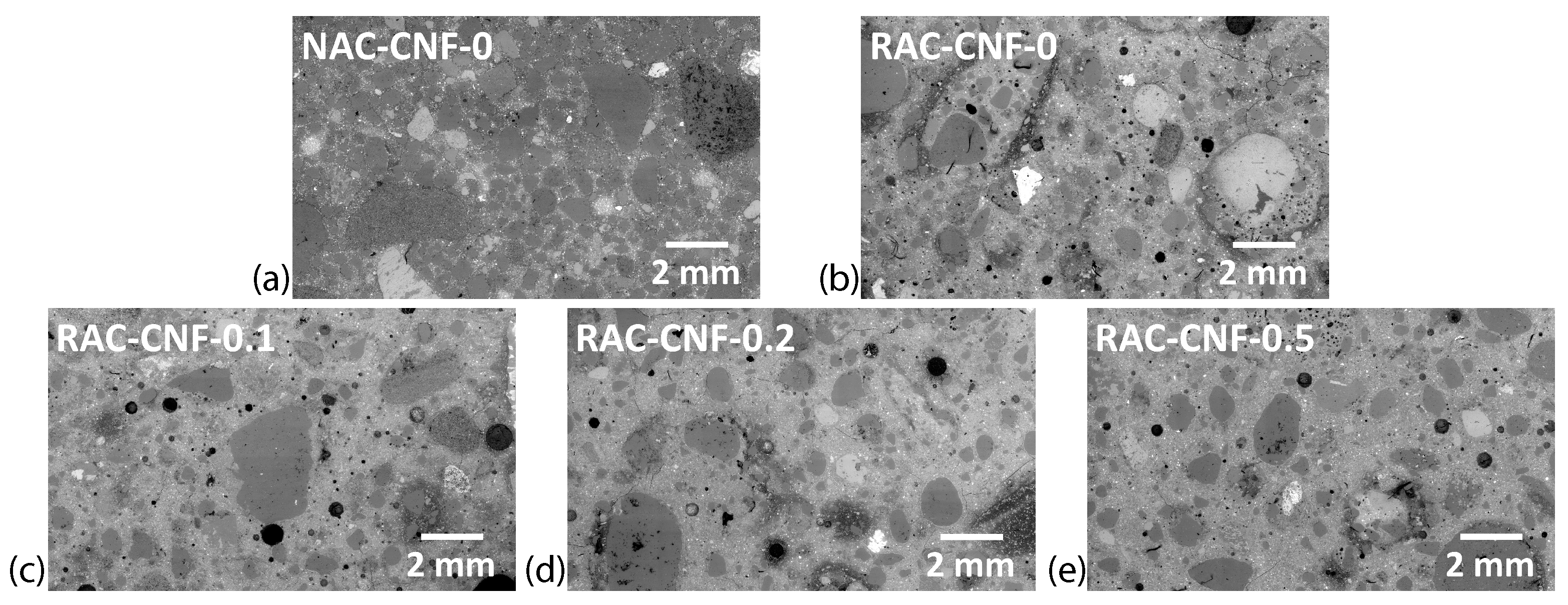
3.1. Microstructural Observation
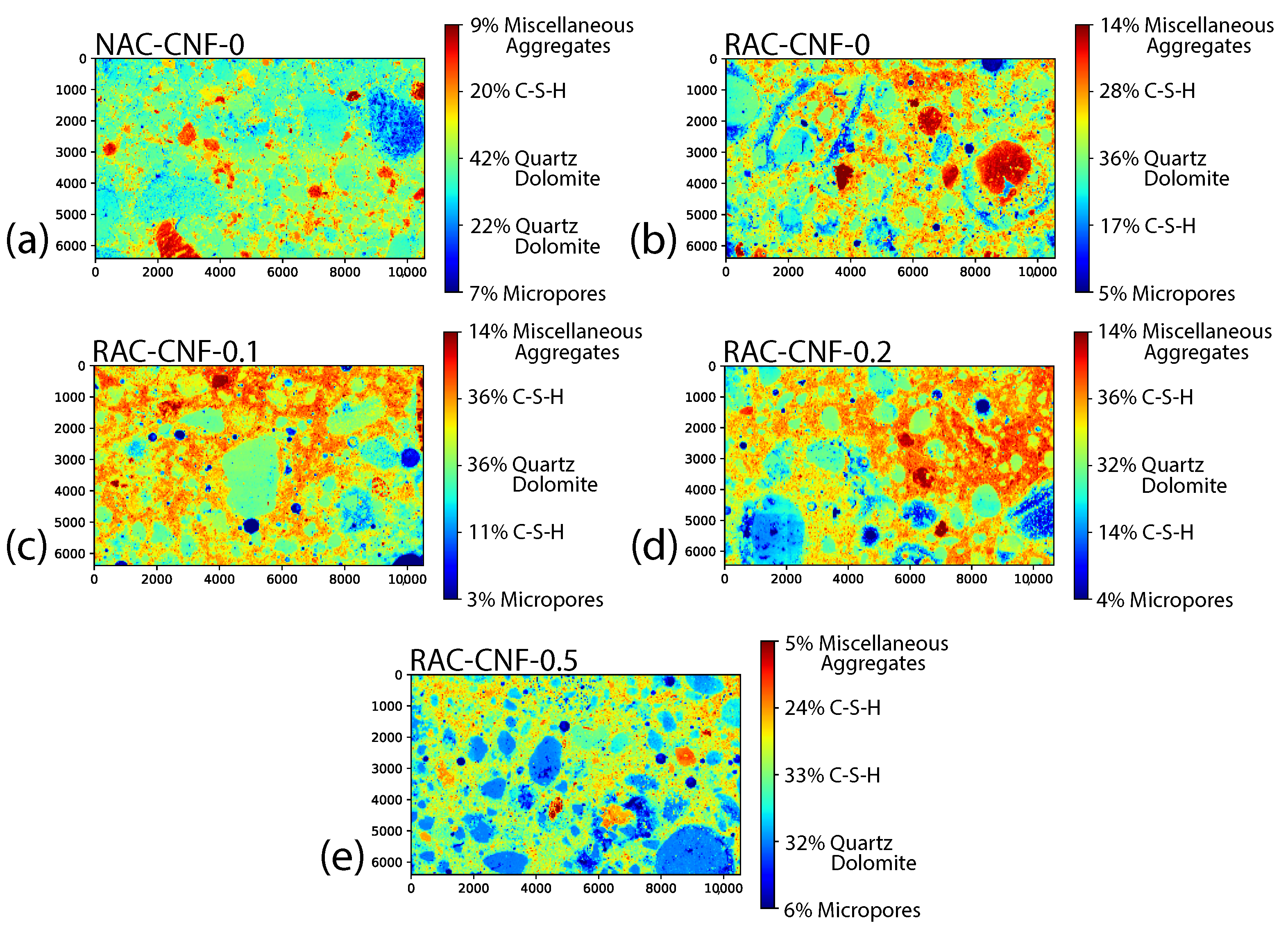
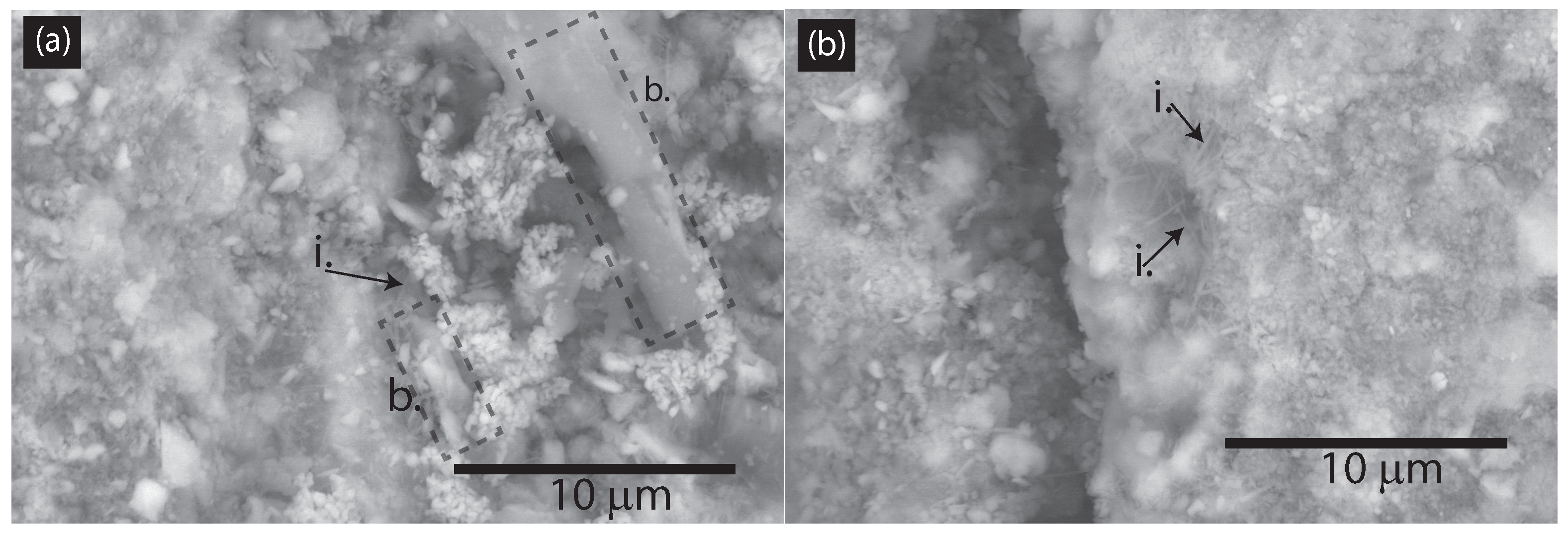
3.1.1. SEM and Digital Image Analysis
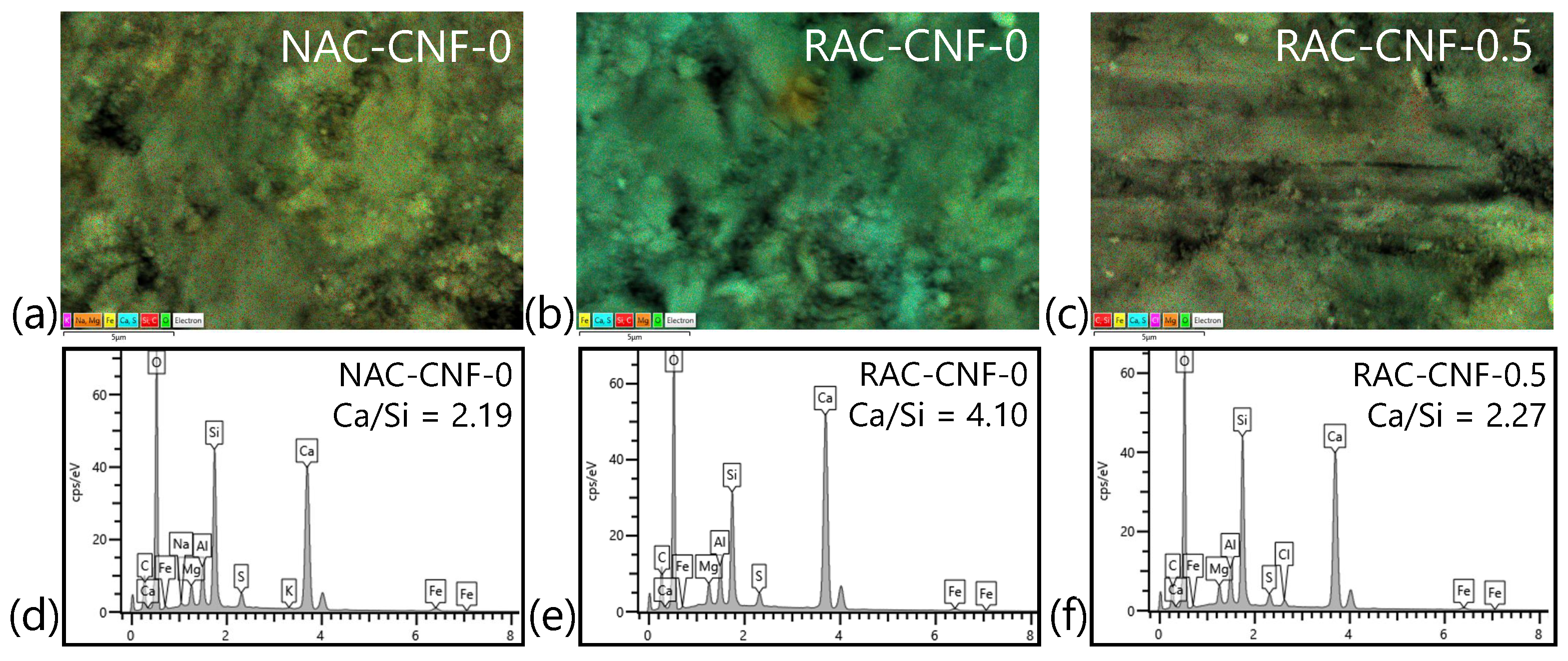
3.1.2. SEM-EDS
3.2. Pore Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- XRD analysis showed that CNFs increased the presence of calcium hydroxide (CH) within RAC.
- The CNFs increased the CH orientation index, indicating improved crystallinity and matrix reinforcement.
- SEM showed significant microstructural changes, with CNFs reducing the maximum pore size and promoting C-S-H gel formation.
- SEM-EDS showed a reduced Ca/Si ratio with 0.5 wt.% CNFs, suggesting that CNFs accelerate cement hydration within RAC.
- MIP showed that CNFs refined the pore structure and reduced the porosity, with the highest reduction in porosity, 8.9%, observed at a reinforcement level of 0.5 wt.%.
- MIP showed that CNFs reduced the water permeability, with the highest reduction in water permeability, 37.9%, observed at a reinforcement level of 0.5 wt.%.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghanbari, M.; Abbasi, A.M.; Ravanshadnia, M. Production of natural and recycled aggregates: The environmental impacts of energy consumption and CO2 emissions. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Deetman, S.; Tukker, A.; Behrens, P. Increasing material efficiencies of buildings to address the global sand crisis. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Zhu, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, B. An evaluation of the recycled aggregate characteristics and the recycled aggregate concrete mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, C.; Guan, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y.; Ling, T.C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete—A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 89, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhuo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P. Mechanical properties and meso-microscopic mechanism of basalt fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P. Review of mechanical properties and strengthening mechanism of fully recycled aggregate concrete under high temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhuo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P. Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 2169–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, J. Mechanical properties and durability of geopolymer recycled aggregate concrete: A review. Polymers 2023, 15, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.A.; Hayashi, T.; Endo, M.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Carbon nanofibers. In Springer Handbook of Nanomaterials; Vajtai, R., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 233–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kukovecz, A.; Kozma, G.; Kónya, Z. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes. In Springer Handbook of Nanomaterials; Vajtai, R., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 147–188. [Google Scholar]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Danoglidis, P.A.; Shah, S.P. High modulus concrete: Effects of low carbon nanotube and nanofiber additions. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2019, 103, 102295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gdoutos, E.E.; Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Danoglidis, P.A. Portland cement mortar nanocomposites at low carbon nanotube and carbon nanofiber content: A fracture mechanics experimental study. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 70, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Meng, B.; Peng, G. Experimental study on the effect of carbon nanofiber content on the durability of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriço, A.; Bogas, J.A.; Hawreen, A.; Guedes, M. Durability of multi-walled carbon nanotube reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, L.; Ma, H.; Pan, G.; Sun, Z. Spatial distribution characteristics and microscopic mechanisms for enhancing mechanical properties of MWCNTs in recycled coarse aggregate shotcrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 364, 129927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, N.; Iyacu, G.; Akono, A.T. Colloidal nanosilica promotes high-density calcium-silicate-hydrates in fine recycled concrete aggregate mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 180, 107498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akono, A.T.; Zhan, M.; Chen, J.; Shah, S.P. Nanostructure of calcium-silicate-hydrates in fine recycled aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 115, 103827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akono, A.T.; Chen, J.; Zhan, M.; Shah, S.P. Basic creep and fracture response of fine recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akono, A.T. Nanostructure and fracture behavior of carbon nanofiber-reinforced cement using nanoscale depth-sensing methods. Materials 2002, 13, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akono, A.T. Fracture toughness of one-and two-dimensional nanoreinforced cement via scratch testing. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20200288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagum, H.; Farooque, K.N. Analysis of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC). Barishal Univ. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 9, 231–242. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamadani, Y.A.; Chu, K.H.; Son, A.; Heo, J.; Her, N.; Jang, M.; Park, C.M.; Yoon, Y. Stabilization and dispersion of carbon nanomaterials in aqueous solutions: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L. The use of backscattered electron microscopy and image analysis to study the porosity of cement paste. MRS Online Proc. Libr. (OPL) 1988, 137, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, D.A.; Jennings, H.M.; Shah, S.P. Image analysis techniques for characterization of pore structure of cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 1994, 24, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.; She, W.; Miao, C.; Chang, H.; Gu, Y. Quantitative characterization of pore morphology in hardened cement paste via SEM-BSE image analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preibisch, S.; Saalfeld, S.; Tomancak, P. Globally optimal stitching of tiled 3D microscopic image acquisitions. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1463–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chityala, R.; Pudipeddi, S. Image Processing and Acquisition Using Python, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, A.J.; Thompson, A.H. Prediction of rock electrical conductivity from mercury injection measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1987, 92, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H. Mercury intrusion porosimetry in concrete technology: Tips in measurement, pore structure, parameter acquisition and application. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyame, B.K.; Illston, J.M. Relationships between permeability and pore structure of hardened cement paste. Mag. Concr. Res. 1981, 33, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, M.; Ulm, F.J. Nanoindentation investigation of creep properties of calcium-silicate-hydrates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 52, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arliguie, G.; Grandet, J.; Ollivier, J.P. Orientation de la portlandite dans les mortiers et bétons de ciment Portland: Influence de la nature et de l’état de surface du support de cristallisation. Mater. Struct. 1985, 18, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Nicolosi, V.; Rickard, D.; Bergin, S.D.; Aherne, D.; Coleman, J.N. Quantitative evaluation of surfactant-stabilized single-walled carbon nanotubes: Dispersion quality and its correlation with zeta potential. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 10692–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.; Brown, L.; Sanchez, F. Quantification of the re-agglomeration of carbon nanofiber aqueous dispersion in cement pastes and effect on the early age flexural response. Carbon 2016, 107, 482–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.G. The nature of CSH in hardened cements. Cem. Conr. Res. 1999, 29, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Liang, C.; Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Li, S. Alite hydration at the single grain level. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2023, 144, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehervari, A.; MacLeod, A.J.N.; Garcez, E.O.; Aldridge, L.; Gates, W.P.; Yang, Y.; Collins, F. On the mechanisms for improved strengths of carbon nanofiber-enriched mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 136, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Corr, D.J.; Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Shah, S.P. Characterization of the interfacial transition zone of CNF-reinforced cementitious composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 99, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | CNF wt.% | CNFs (g) | Water (g) | Cement (g) | FRCAs (g) | Sand (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAC-CNF-0 | 0 | 0 | 10.81 | 24.56 | - | 64.63 |
| RAC-CNF-0 | 0 | 0 | 10.81 | 24.56 | 64.63 | - |
| RAC-CNF-0.1 | 0.1 | 0.025 | 10.81 | 24.56 | 64.63 | - |
| RAC-CNF-0.2 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 10.81 | 24.56 | 64.63 | - |
| RAC-CNF-0.5 | 0.5 | 0.12 | 10.81 | 24.56 | 64.63 | - |
| Sample | Porosity | Skeletal Density | k | K at 20 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (g/cm3) | (nm) | (m2) | (m/s) | |
| NAC-CNF-0 | 16.7 | 2.47 | 164 | ||
| RAC-CNF-0 | 28.0 | 2.27 | 193 | ||
| RAC-CNF-0.1 | 30.3 | 2.27 | 203 | ||
| RAC-CNF-0.2 | 27.4 | 2.25 | 150 | ||
| RAC-CNF-0.5 | 25.5 | 2.24 | 155 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buettner, N.; Iyacu, G.; Dal Poggetto, G.; Akono, A.-T. The Effect of Carbon Nanofibers on the Microstructure, Chemistry, and Pore Structure of Concrete Made with Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15040253
Buettner N, Iyacu G, Dal Poggetto G, Akono A-T. The Effect of Carbon Nanofibers on the Microstructure, Chemistry, and Pore Structure of Concrete Made with Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(4):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15040253
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuettner, Nathanial, Gass Iyacu, Giovanni Dal Poggetto, and Ange-Therese Akono. 2025. "The Effect of Carbon Nanofibers on the Microstructure, Chemistry, and Pore Structure of Concrete Made with Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates" Nanomaterials 15, no. 4: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15040253
APA StyleBuettner, N., Iyacu, G., Dal Poggetto, G., & Akono, A.-T. (2025). The Effect of Carbon Nanofibers on the Microstructure, Chemistry, and Pore Structure of Concrete Made with Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Nanomaterials, 15(4), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15040253







