Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Garlic Peel Target NF-κB and Redox Imbalance: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Against Pyrogallol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Polyphenols Profile of Garlic Peel Extract (GPE) Determined by HPLC Analysis
2.2. UV–Vis Spectroscopic Analysis of GPE-Ag Nanoparticles
2.3. TEM, SEM and Size Analysis of GPE-Ag Nanoparticles
2.4. Elemental Composition Analysis of GPE-Ag Nanoparticles by Energy-Dispersive X-Ray (EDX) Spectroscopy
2.5. Zeta Potential Analysis of GPE-Ag Nanoparticles
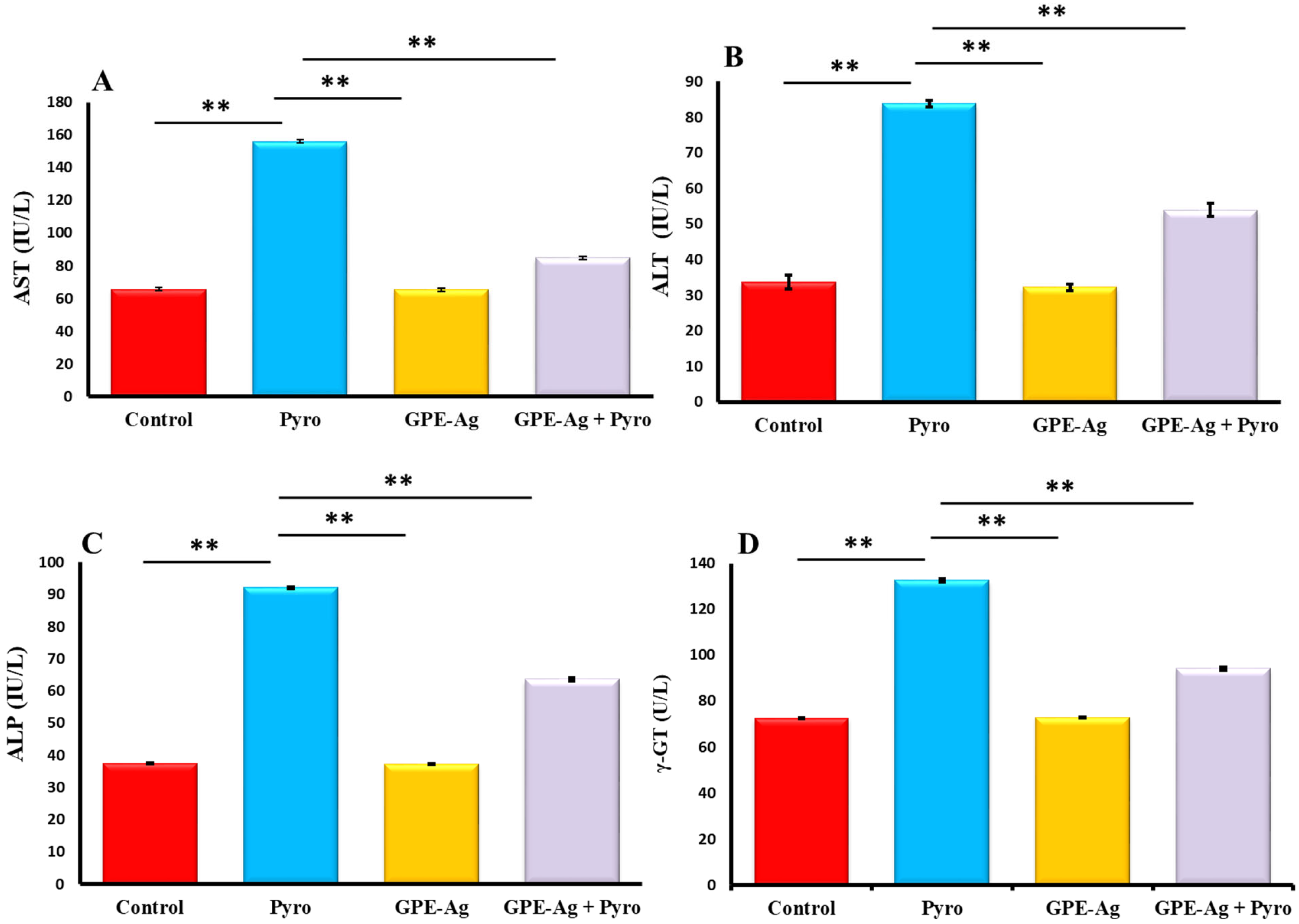
2.6. Effect of GPE-Ag Nanoparticles on Liver Function Enzymes in Pyrogallol-Intoxicated Rats
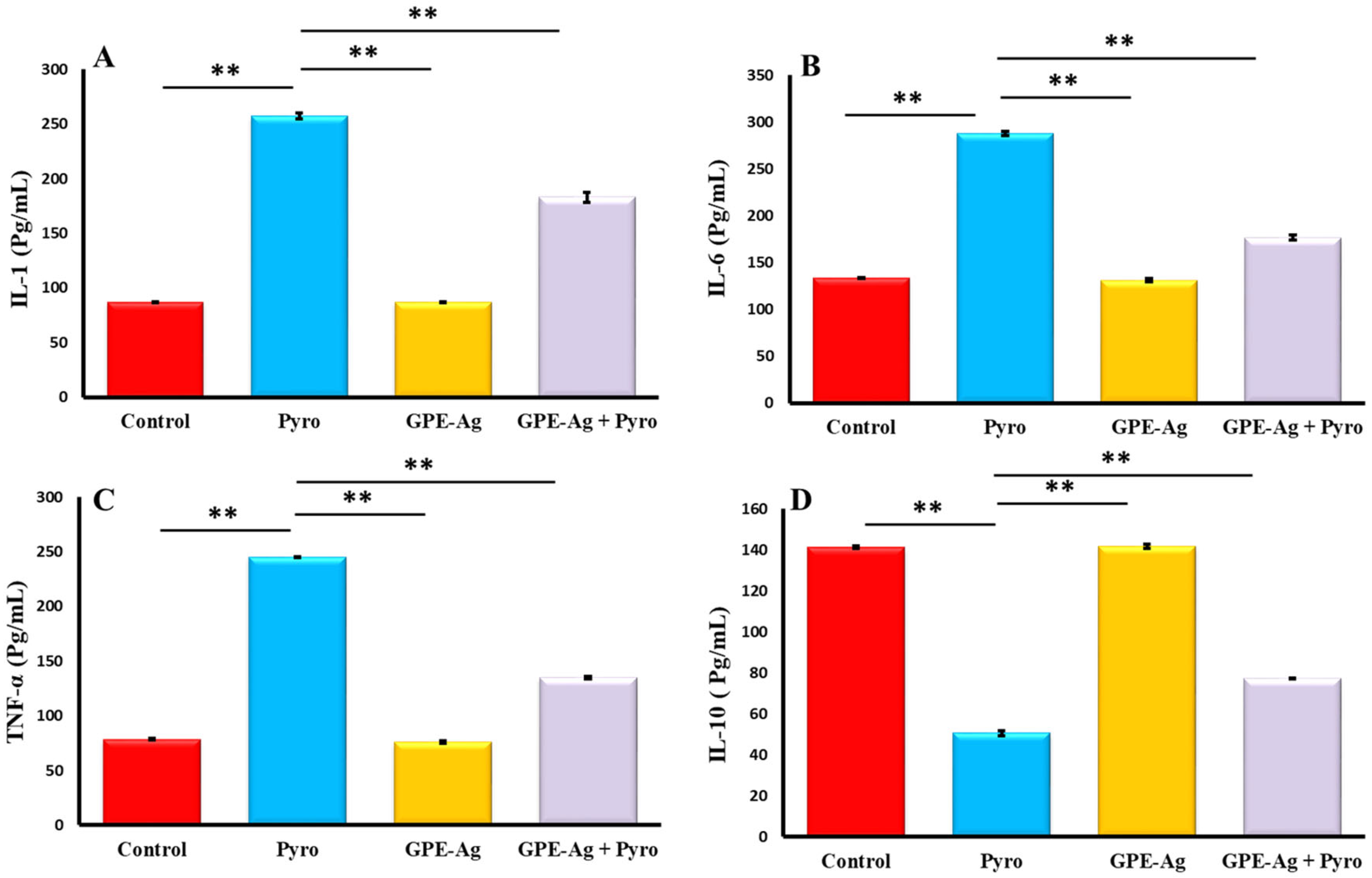
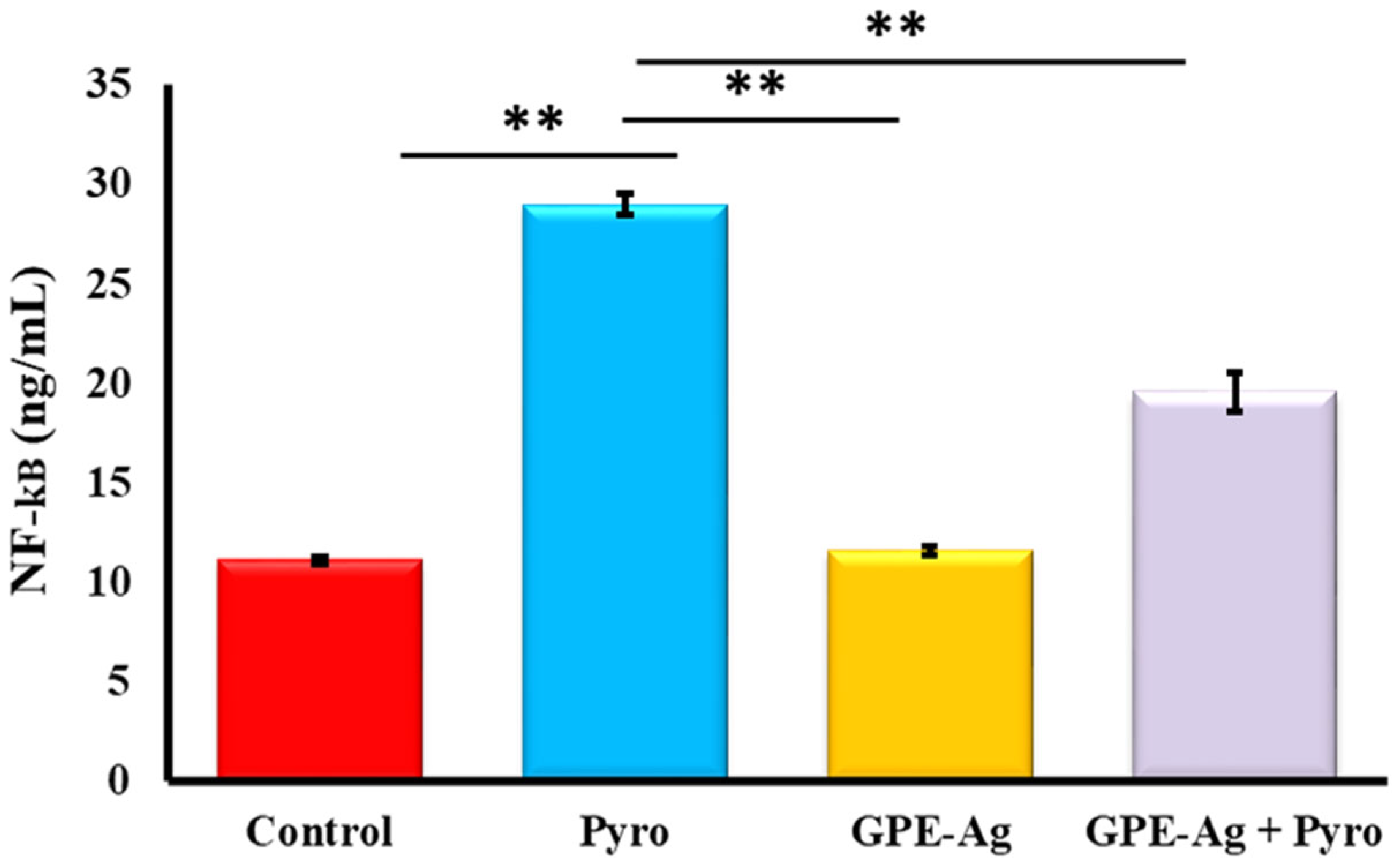
2.7. Effect of GPE-Ag Nanoparticles on Hepatic Inflammatory Markers in Pyrogallol-Intoxicated Rats
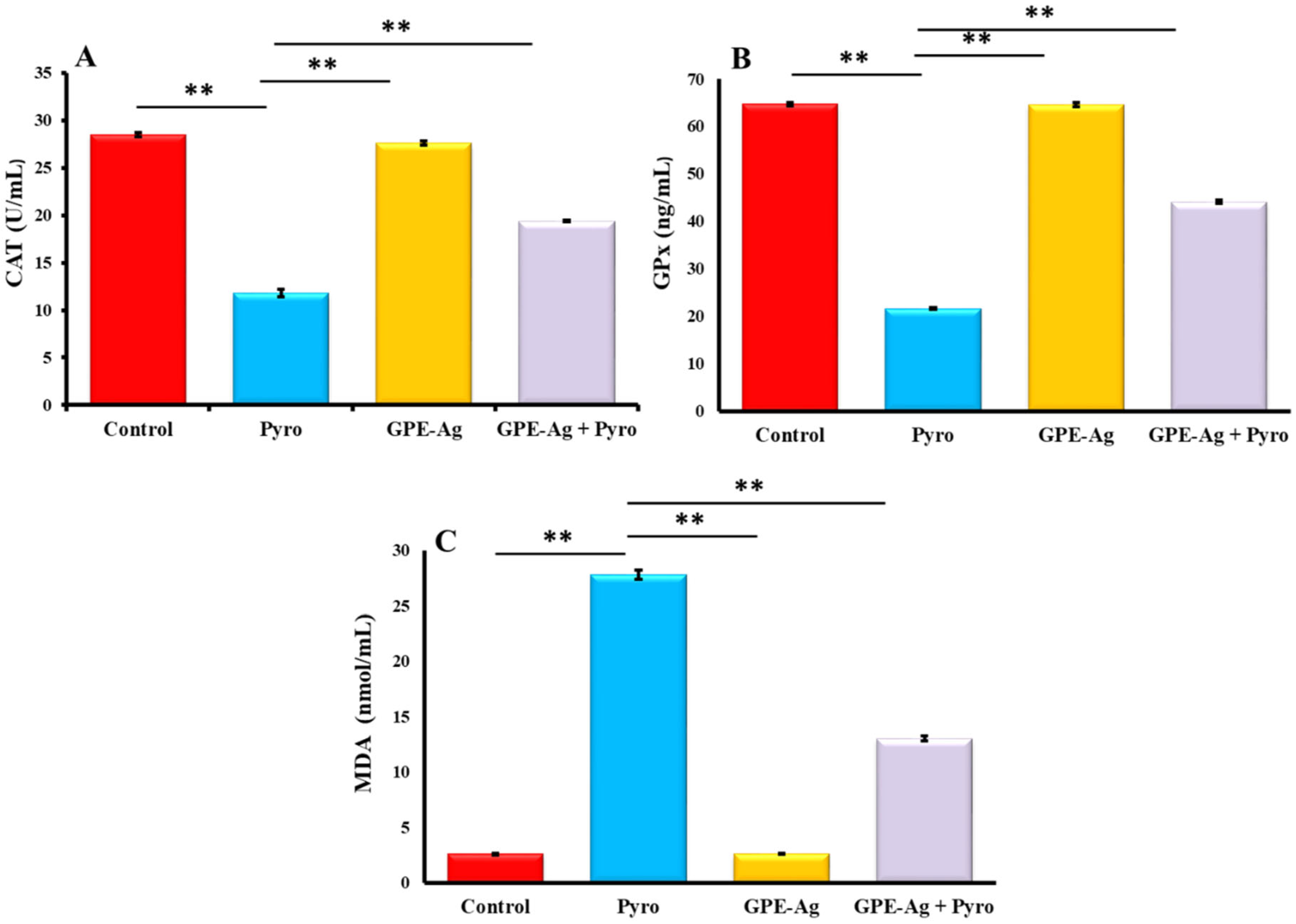
2.8. Effect of GPE-Ag Nanoparticles on Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Pyrogallol-Intoxicated Rats
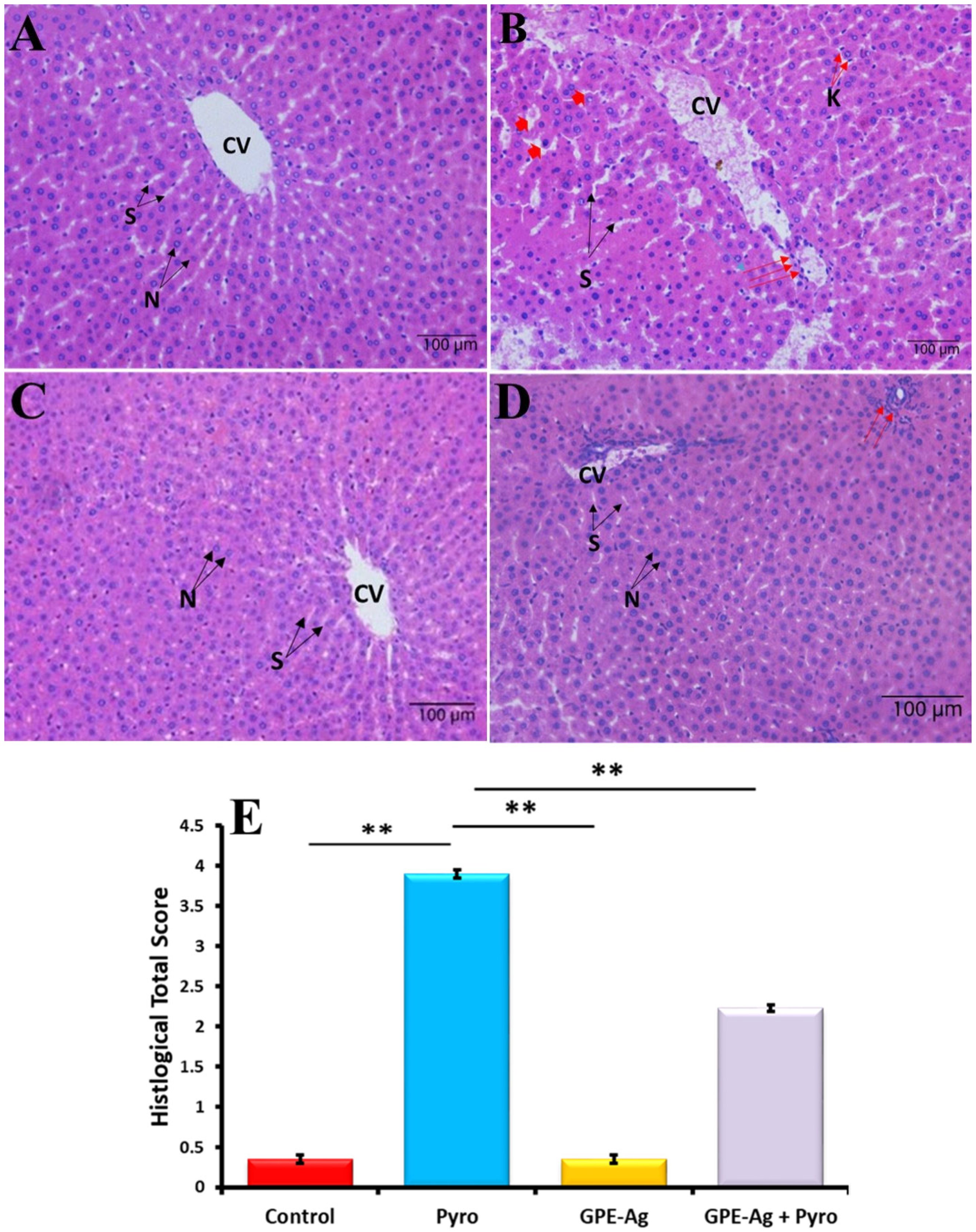
2.9. Effect of GPE-Ag Nanoparticles on Liver Histopathology in Pyrogallol-Intoxicated Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plants
4.2. Preparation of Garlic Peel Ethanolic Extract (GPE)
4.3. HPLC Analysis of Polyphenols in Garlic Peel Extract (GPE)
4.4. Synthesis of Garlic Peel Extract-Silver Nanoparticles (GPE–Ag)
4.5. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
4.6. Animals
4.7. Experimental Design
- Group 1 (Control): received oral saline (0.9%, 5 mL/kg) daily and a single intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of saline (0.9%, 1 mL/kg) on day 14.
- Group 2 (Pyro): received oral saline (0.9%, 5 mL/kg) daily and a single i.p. injection of pyrogallol (100 mg/kg in saline, 1 mL/kg) on day 14 to induce hepatotoxicity.
- Group 3 (GPE–Ag): received GPE-synthesized silver nanoparticles (GPE–Ag) orally at 50 mg/kg/day (suspended in saline, 0.9%, 5 mL/kg) for 28 days. On day 14, they received a single i.p. injection of saline (1 mL/kg) and continued GPE–Ag treatment for an additional 14 days.
- Group 4 (Pyro + GPE–Ag): received GPE–Ag orally at 50 mg/kg/day as in Group 3; on day 14, hepatotoxicity was induced by a single i.p. injection of pyrogallol (100 mg/kg in saline, 1 mL/kg), and GPE–Ag treatment continued for a further 14 days (total treatment period 28 days).
4.8. Sample Collection and Tissue Processing
4.9. Determination of Serum Liver Enzymes via Colorimetric Assay
4.10. Assessment of Hepatic Immunological and Molecular Markers Using ELISA
4.11. Assessment of Hepatic Redox Balance
4.12. Histological Assessment of Liver Architecture
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, G. Management of liver diseases: Current perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 5818–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, S.; Naraki, K.; Roohbakhsh, A.; Hayes, A.W.; Karimi, G. The protective effects of rutin on the liver, kidneys, and heart by counteracting organ toxicity caused by synthetic and natural compounds. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad-Hussein, A.; Ramadan, H.K.-A. Impacts of climate change on environmental toxins and pollutants causing liver health problems. In Impact of Climate Change on Health in Africa: A Focus on Liver and Gastrointestinal Tract; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 53–78. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Sun, J.; Li, D.; Hu, Y.; Yu, X.; Hua, H.; Jing, X.; Chen, F.; Jia, Z.; Xu, J. Shikonin attenuates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Huo, Y.; Yin, S.; Hu, H. Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.M.; Jhawer, A.; Frampton, G.; Troyanovskaya, E.; DeMorrow, S.; McMillin, M. Characterization of hepatic pathology during azoxymethane-induced acute liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 31, 103952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matić, S.; Stanić, S.; Bogojević, D.; Vidaković, M.; Grdović, N.; Arambašić, J.; Dinić, S.; Uskoković, A.; Poznanović, G.; Solujić, S. Extract of the plant Cotinus coggygria Scop. attenuates pyrogallol-induced hepatic oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 89, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarasakha, K.; Asawapanumas, T.; Suntivich, R.; Panya, A.; Phonsatta, N.; Thiennimitr, P.; Laoteng, K.; Tepaamorndech, S. Hatakabb, a herbal extract, contains pyrogallol as the novel mediator inhibiting LPS-induced TNF-α production by NF-κB inactivation and HMOX-1 upregulation. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 90, 104992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.-X.; Meng, X.-X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.-J.; He, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhao, S.-C.; Shi, Z.-M.; Zheng, L.-N. Targeting GPR65 alleviates hepatic inflammation and fibrosis by suppressing the JNK and NF-κB pathways. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Xue, H.; Zou, J.; Cai, J.; Shi, R.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis polysaccharide ameliorates cholestatic liver injury by alleviating gut microbiota dysbiosis and inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wu, G.; Libby, M.; Wu, K.; Jeong, K.J.; Kim, Y.J. Synthesis of biologically derived poly (pyrogallol) nanofibers for antibacterial applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 3356–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.; Sharma, M.; Chaudhary, G. Pyrogallol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: A model to evaluate antioxidant hepatoprotective agents. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekozin, A.; Otuechere, C.A.; Adewuyi, A. Apocynin loaded silver nanoparticles displays potent in vitro biological activities and mitigates pyrogallol-induced hepatotoxicity. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 365, 110069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, G.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, O.; Singh, M.P. Resveratrol modulates pyrogallol-induced changes in hepatic toxicity markers, xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes and oxidative stress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 596, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matić, S.; Stanić, S.; Bogojević, D.; Vidaković, M.; Grdović, N.; Dinić, S.; Solujić, S.; Mladenović, M.; Stanković, N.; Mihailović, M. Methanol extract from the stem of Cotinus coggygria Scop., and its major bioactive phytochemical constituent myricetin modulate pyrogallol-induced DNA damage and liver injury. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2013, 755, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, G.; Gupta, S.P.; Prakash, O.; Singh, M.P. Pyrogallol-mediated toxicity and natural antioxidants: Triumphs and pitfalls of preclinical findings and their translational limitations. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2010, 183, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleshchuk, O.; Datsko, V.; Loi, H.Y.; Datsko, T.; Mudra, A.Y.; Malanchuk, S.; Fedoniuk, L.Y. Hepatoprotective effects of L-ornithine-L-aspartate in toxic liver injury. Pharmacol. Online 2021, 3, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Pascale, R.M.; Simile, M.M.; Calvisi, D.F.; Feo, C.F.; Feo, F. S-adenosylmethionine: From the discovery of its inhibition of tumorigenesis to its use as a therapeutic agent. Cells 2022, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, D.; Usharani, P.; Paramjyothi, G.; Subbalaxmi, M.; Sireesha, K.; Ali, M.A. A study to evaluate the hepatoprotective effect of N-acetylcysteine on anti tuberculosis drug induced hepatotoxicity and quality of life. Indian J. Tuberc. 2023, 70, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessone, F.; Hillotte, G.L.; Tamagnone, N.; Arnedillo, D.; Roma, M.G. Ursodeoxycholic Acid for the Management of Drug-induced Liver Injury: Role of Hepatoprotective and Anti-cholestatic Mechanisms. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2025, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Ghosh, R.; Mandal, V.; Mandal, S.C. Recent advances in herbal medicine for treatment of liver diseases. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 970–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, V.; Delghandi, P.S.; Moallem, S.A.; Karimi, G. Safety and toxicity of silymarin, the major constituent of milk thistle extract: An updated review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraki, K.; Mousavi, S.H.; Etemad, L.; Rezazadeh-Shojaie, S.M.; Sadeghi, T.; Moshiri, M. N-acetylcysteine overdose: A case report. Int. J. Med. Toxicol. Forensic Med. 2021, 11, 32409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R.; Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Davis, R.M.; Xu, B. Natural product-based nanomedicine: Recent advances and issues. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6055–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heya, M.S.; García-Ponce, R.; Soto, B.A.M.; Verde-Star, M.J.; Soto-Domínguez, A.; García-Hernandez, D.G.; Saucedo-Cárdenas, O.; Hernández-Salazar, M.; Guillén-Meléndez, G.A. Green alternatives in treatment of liver diseases: The challenges of traditional medicine and green nanomedicine. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202300463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Shukla, S.; Behl, T.; Gupta, S.; Anwer, M.K.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; Bungau, S.G.; Brisc, C. Understanding the potential role of nanotechnology in liver fibrosis: A paradigm in therapeutics. Molecules 2023, 28, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Roy, H.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Patel, R.; Bohara, R. Advanced strategies in enhancing the hepatoprotective efficacy of natural products: Integrating nanotechnology, genomics, and mechanistic insights. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 11, 2528–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshi, M.S.; Uthra, C.; Yadav, D.; Sharma, S.; Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Jaswal, A.; Sinha, N.; Shrivastava, S.; Shukla, S. Silver nanoparticles protect acetaminophen induced acute hepatotoxicity: A biochemical and histopathological approach. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 90, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Ranjan, R.; Kumar, A.; Sinha, M.P.; Srivastava, R.; Subarna, S.; Mandal, S.K. Hepatoprotective activity of Silver Nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous leaf extract of Punica granatum against induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Nova Biol. Reper 2021, 7, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Dar, M.Y.; Nagar, D.P.; Tomar, R.S.; Shrivastava, S.; Shukla, S. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles for treatment of N-Nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatotoxicity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e22968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, Z.; Pervaiz, M.; Ejaz, A.; Hussain, S.; Shaheen, S.; Shehzad, B.; Younas, U. Garlic and ginger extracts mediated green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles: A review on recent advancements and prospective applications’. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 53, 102868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, N.; El Semary, N.; Mohamed, M. Silver nanoparticles green synthesis via cyanobacterium Phormidium sp.: Characterization, wound healing, antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 3083–3096. [Google Scholar]
- Bold, B.-E.; Urnukhsaikhan, E.; Mishig-Ochir, T. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory properties and their burn wound healing efficacy. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 972534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodeer, D.M.; Nasr, A.M.; Swidan, S.A.; Shabayek, S.; Khinkar, R.M.; Aldurdunji, M.M.; Ramadan, M.A.; Badr, J.M. Characterization, antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anti-inflammatory activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Phragmanthera austroarabica AG Mill and JA Nyberg extract. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1078061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, A.H.; Nasr, S.M.; Almaweri, A.H.; Sedky, D.; Mohamed, A.M.; Desouky, H.M.; Shalaby, M.A. Phytochemical, antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of different fractions of Moringa oleifera leaves methanol extract against liver injury in animal model. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 11, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, M.; Evan Prince, S. The potential effect of phytochemicals and herbal plant remedies for treating drug-induced hepatotoxicity: A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4767–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, B.; Ramezani Ahmadi, A.; Jafari, M.; Morshedzadeh, N. The association of dietary phytochemical index and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 4010–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, X.; Hu, X.; Li, C.; Wan, Y.; Yu, D. Amelioration of alcohol-induced acute liver injury in C57BL/6 mice by a mixture of TCM phytochemicals and probiotics with antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1144589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Dixit, S.; Ali, D.; Kumar, G. Synergistic Effect of Green Synthesized Nanoparticle from Combined Extract of Onion and Garlic Peel for Cytotoxicity. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 4011–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwuoke, K.C. Effects of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica on growth performance and liver function parameters in male albino rats. Cell Biol. Dev. 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.F.; Keskin, C.; Baran, A.; Hatipoğlu, A.; Yildiztekin, M.; Küçükaydin, S.; Kurt, K.; Hoşgören, H.; Sarker, M.M.R.; Sufianov, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Allium cepa L. Peel extract, their antioxidant, antipathogenic, and anticholinesterase activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Wang, J.; Yao, N.; Niu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, X. Hepatoprotective effect of lotus leaf against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via alteration of AMPK/SIRT1 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Acta Cirúrgica Bras. 2025, 40, e407025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cui, X.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, R.; Liu, B.; Xia, Y. Phenolic metabolites as therapeutic in inflammation and neoplasms: Molecular pathways explaining their efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 193, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqrad, M.A.; El-Agamy, D.S.; Ibrahim, S.R.; Sirwi, A.; Abdallah, H.M.; Abdel-Sattar, E.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Elsaed, W.M.; Mohamed, G.A. SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB signaling mediates anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activities of oleanolic acid in a mouse model of acute hepatorenal damage. Medicina 2023, 59, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmat, F.; Imran, A.; Islam, F.; Afzaal, M.; Zahoor, T.; Akram, R.; Aggarwal, S.; Rehman, M.; Naaz, S.; Ashraf, S. Valorization of the phytochemical profile, nutritional composition, and therapeutic potentials of garlic peel: A concurrent review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 2642–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreón-Delgado, D.F.; Hernández-Montesinos, I.Y.; Rivera-Hernández, K.N.; del Sugeyrol Villa-Ramírez, M.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E.; Ramírez-López, C. Evaluation of pretreatments and extraction conditions on the antifungal and antioxidant effects of garlic (Allium sativum) peel extracts. Plants 2023, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xie, A.; Yue, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, Q. Garlic peel extract as an antioxidant inhibits triple-negative breast tumor growth and angiogenesis by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 6886–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Jawed, J.J. Enzymatically Digested Garlic Waste Conserved Most of Its Polyphenols and Contributed to Nrf2 Activation: Bio-accessibility, Bioactivity, Gene Expression, and Genotoxicity Analysis. Waste Biomass Valorization 2024, 15, 4671–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althumairy, D.A.; Abu-Khudir, R.; Alandanoosi, A.I.; Badr, G.M. Garlic Peel-Derived Phytochemicals Using GC-MS: Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Effects in Ulcerative Colitis Rat Model. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Sirohi, R. Antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from peel of fruits and vegetables. Biol. Insights 2016, 1, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnasamy Sekar, R.; Sridhar, A.; Perumalsamy, B.; Manikandan, D.B.; Ramasamy, T. In vitro antioxidant, antipathogenicity and cytotoxicity effect of silver nanoparticles fabricated by onion (Allium cepa L.) peel extract. BioNanoScience 2020, 10, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, A.; Theertha, V.; Prakash, P.; Chandran, S.S. From waste to a value added product: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from onion peels together with its diverse applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 4460–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Dixit, S.; Almutairi, B.O.; Yadav, N. Synthesis and characterization of eco-friendly TiO2 nanoparticle from combine extract of onion and garlic peel. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoteleb, A.; Valdez-Salas, B.; Beltran-Partida, E.; Mendez-Trujillo, V.; González-Mendoza, D.; Tzintzun-Camacho, O.; Roumia, A.F. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Garlic Peel Extract and Their Antibacterial Potential. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espíndola, C. Some nanocarrier’s properties and chemical interaction mechanisms with flavones. Molecules 2023, 28, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, H.J.; Kim, H.-S.; Jun, S.H.; Kang, Y.-H.; Cho, S.; Park, Y. Biogenic silver nanoparticles with chlorogenic acid as a bioreducing agent. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 5787–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, E.; Amini, S.M. Green synthesis of stable and biocompatible silver nanoparticles with natural flavonoid apigenin. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 38, 101175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekrikaya, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Celik, C.; Demirbuga, S.; Ildiz, N.; Demirbas, A.; Ocsoy, I. Investigation of ellagic acid rich-berry extracts directed silver nanoparticles synthesis and their antimicrobial properties with potential mechanisms towards Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 341, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Banerjee, U.C. Quercetin and gallic acid mediated synthesis of bimetallic (silver and selenium) nanoparticles and their antitumor and antimicrobial potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 431, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.M.; Akbari, A. Metal nanoparticles synthesis through natural phenolic acids. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubavat, K.; Trivedi, P.; Ansari, H.; Kongor, A.; Panchal, M.; Jain, V.; Sindhav, G. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dietary antioxidant rutin and its biological contour. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, S.T.; Mobashir, M.; Fantoukh, O.I.; Khan, B.; Imtiyaz, K.; Naqvi, I.H.; Rizvi, M.M.A. Synthesis of silver nano particles using myricetin and the in-vitro assessment of anti-colorectal cancer activity: In-silico integration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Huang, C.Z. Detection of ferulic acid based on the plasmon resonance light scattering of silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2007, 72, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdar, G.; Gül Kılınç, G.; Mazlum Şen, T. Green One-Pot Synthesis of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Using Catechin Extracts: Influence of Temperature and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation. Plasmonics 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, N.M.; Alyami, H.M.; Almeer, R. Using green biosynthesized kaempferol-coated sliver nanoparticles to inhibit cancer cells growth: An in vitro study using hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2). Cancer Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Shin, H.-S.; Patra, J.K. Comparative assessment of antioxidant, anti-diabetic and cytotoxic effects of three peel/shell food waste extract-mediated silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9075–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of action and probable bio-application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Azeem, M.; Mumtaz, R.; Younas, M.; Adrees, M.; Zubair, E.; Khalid, A.; Hafeez, F.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Acacia nilotica and their anticancer, antidiabetic and antioxidant efficacy. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Ramirez, I.; Bashir, S.; Luo, Z.; Liu, J.L. Green synthesis and characterization of polymer-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; Shaikh, A. Green synthesis and zeta potential measurement of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Adv. Res. Innov. Ideas Educ. 2021, 7, 3448–3452. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, G.; Kumar, A.; Singh, M.P. Effect of silymarin on pyrogallol-and rifampicin-induced hepatotoxicity in mouse. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 565, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalas, M.A.; Chavez, L.; Leon, M.; Taweesedt, P.T.; Surani, S. Abnormal liver enzymes: A review for clinicians. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thagfan, F.A.; Dkhil, M.A.; Al-Shaebi, E.M.; Abdel-Gaber, R.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Elshanat, S. Biosynthesized nanosilver from ginger extract exhibits antioxidant and hepatic responses during Eimeria papillata infection. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 23806–23811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almatroodi, S.A.; Anwar, S.; Almatroudi, A.; Khan, A.A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Hepatoprotective effects of garlic extract against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury via modulation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities and hepatocyte architecture. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Patil, N.; Mohammed, A.; Hamzah, Z. Valorization of garlic (Allium sativum L.) byproducts: Bioactive compounds, biological properties, and applications. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunata, S.A.; Rahmawati, D.; Andika, D. Evaluation of phytochemical activities of aqueous and ethanolic garlic peel extract. J. Funct. Food Nutraceutical 2019, 1, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowska, A. Clinical insights into non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the therapeutic potential of flavonoids: An update. Nutrients 2025, 17, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Barky, A.R.; Mohamed, T.M.; Ali, E.M.M. Detoxifying and antioxidant effect of ellagic acid nano particles in rats intoxicated with sodium nitrites. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, B.; Elderdery, A.Y.; Alsrhani, A.; Alzerwi, N.A.; Althobiti, M.M.; Rayzah, M.; Idrees, B.; Elkhalifa, A.M.; Subbiah, S.K.; Mok, P.L. Effects of albumin–chlorogenic acid nanoparticles on apoptosis and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitory activity in MDA-MB-435s cells. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, H.A.; Ali, E.; Zahraa Abd EL Hakam, F.E.; Akl, E.M. Nano-encapsulated ferulic acid in sesame protein isolate alleviates acrylamide-induced liver toxicity and genotoxicity in rats via oxidative stress and DNA damage modulation. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2025, 26, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jacob, J.A.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, S.; Sun, K.; Zhong, Z.; Varadharaju, N.; Shanmugam, A. Hepatoprotective effect of silver nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous leaf extract of Rhizophora apiculata. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laib, I.; Ali, B.D.; Alsalme, A.; Croun, D.; Bechelany, M.; Barhoum, A. Therapeutic potential of silver nanoparticles from Helianthemum lippii extract for mitigating cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity: Liver function parameters, oxidative stress, and histopathology in wistar rats. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1400542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Pang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Q. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with high antimicrobial activity and low cytotoxicity using catechol-conjugated chitosan. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64357–64363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Biswas, S.; Al-Dayan, N.; Alhegaili, A.S.; Sarwat, M. Antioxidant Role of Kaempferol in Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghara, H.; Samanta, S.; Patel, M.; Chadha, P.; Patel, D.; Jha, A.; Mandal, P. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Enicostemma littorale Exhibit Gut Tight Junction Restoration and Hepatoprotective Activity via Regulation of the Inflammatory Pathway. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, S.; Gong, H.; Zhang, B.-K.; Yan, M. Dissecting the crosstalk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways in drug-induced toxicity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 809952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, E.T.; Ali, A.-S.A.; El-Shaarawy, F.; Mesbah, N.M.; Abo-Elmatty, D.M.; Aborehab, N.M. Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of lipopolysaccharide from Rhodobacter sphaeroides against ethanol-induced liver and kidney toxicity in experimental rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zha, X.; Ji, R.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, S. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extracts of ageratum conyzoides and their anti-inflammatory effects. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 13983–13992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.B.; Vasconcelos, A.G.; Silva de Carvalho, A.É.; Slompo, R.C.; Sá, B.S.; Gonçalves, M.J.L.; Lima Moura, L.N.R.d.C.; Brito, A.K.d.S.; França, J.V.d.S.; Martins, M.d.C.d.C.e. Lycopene from Red Guava (Psidium guajava L.): From hepatoprotective effect to its use as promising self-emulsifying drug delivery system for anti-inflammatory and antioxidant applications. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithiyanandam, S.; Prince, S.E. Caesalpinia bonducella counteracts paracetamol-instigated hepatic toxicity via modulating TNF-α and IL-6/10 expression and Bcl-2 and caspase-8/3 signalling. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 6256–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Majee, C.; Mazumder, R.; Padhi, S.; Khan, F.; Pal, R.S. Insight into the Regulation of Nrf2/Keap 1 Pathway by Flavonoids as an Approach for Treatment of Liver Diseases: A Review. Ind. J. Pharm. Edu. Res 2024, 58, s40–s57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z. Effects of flavonoids on alcoholic liver disease: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2025, 41, 173–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, T.; Lu, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Jin, M.; Ji, G.; Cao, Q. Apigenin prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating the SIRT1 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Ma, Q.; Hao, Z.; Tang, S.; Dai, C. Ellagic acid supplementation ameliorates cisplatin-induced liver injury in mice by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway and activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. One Health Adv. 2024, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xue, X.; Fan, G.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Ma, B.; Li, S. Ferulic acid ameliorates hepatic inflammation and fibrotic liver injury by inhibiting PTP1B activity and subsequent promoting AMPK phosphorylation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 754976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Emam, M.M.; Mostafa, M.; Farag, A.A.; Youssef, H.S.; El-Demerdash, A.S.; Bayoumi, H.; Gebba, M.A.; El-Halawani, S.M.; Saleh, A.M.; Badr, A.M. The potential effects of quercetin-loaded nanoliposomes on amoxicillin/clavulanate-induced hepatic damage: Targeting the SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway and microbiota modulation. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriel, P. NF-κB in liver diseases: A target for drug therapy. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2009, 29, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Karin, M. NF-κB signaling, liver disease and hepatoprotective agents. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6228–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; An, B.; Yu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. The hepatoprotective effect of myricetin against lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine-induced fulminant hepatitis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Qiu, Y.; Tian, W. Gallic Acid Alleviates Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Regulating Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Signaling Proteins. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanaraj, C.; Shah, M.D.; Makki, J.S.; Iqbal, M. Hepatoprotective effects of Flagellaria indica are mediated through the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.; Cheung, F.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Yuen, M.F.; Feng, Y. Hepatoprotective effects of Chinese medicinal herbs: A focus on anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.; Moldovan, B.; Baldea, I.; Olteanu, D.; Bolfa, P.; Clichici, S.; Filip, G.A. Modulatory effects of Cornus sanguinea L. mediated green synthesized silver nanoparticles on oxidative stress, COX-2/NOS2 and NFkB/pNFkB expressions in experimental inflammation in Wistar rats. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Atique Ullah, A.; Banik, S.; Sikder, M.T.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles-mediated cytotoxic effect in colorectal cancer cells: NF-κB signal induced apoptosis through autophagy. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 3272–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, Ç.; Karatoprak, G.Ş.; Açıkara, Ö.B.; Akkol, E.K.; Barak, T.H.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Aschner, M.; Shirooie, S. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory therapeutic potential of gingerols and their nanoformulations. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 902551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macit, M.; Duman, G.; Cumbul, A.; Sumer, E.; Macit, C. Formulation development of Silybum marianum seed extracts and silymarin nanoparticles, and evaluation of hepatoprotective effect. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 83, 104378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, H.M.; Al-Asmari, F.; Khan, F.A.; Rahim, M.A.; Zongo, E. Silymarin: Unveiling its pharmacological spectrum and therapeutic potential in liver diseases—A comprehensive narrative review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 3097–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Saeed, R.; Saeed, F.; Asghar, A.; Ghani, S.; Ateeq, H.; Ahmed, A.; Rasheed, A.; Afzaal, M.; Waheed, M. Silymarin: A review on paving the way towards promising pharmacological agent. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 2256–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Sayed, I.E.T.E.; El-Torgoman, A.M.A.; Kalam, A.; Wageh, S.; Kamel, M.A. Green synthesis of silymarin–chitosan nanoparticles as a new nano formulation with enhanced anti-fibrotic effects against liver fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbaf-Shandiz, M.; Adeli, S.; Faghfouri, A.H.; Khademi, F.; Jamilian, P.; Zarezadeh, M.; Ebrahimi-Mamaghani, M. The efficacy of N-acetylcysteine in improving liver function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. PharmaNutrition 2023, 24, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.; Bratu, A.; Agapie, M.; Borjog, T.; Jafal, M.; Sima, R.-M.; Orban, C. The use and potential benefits of N-acetylcysteine in non-acetaminophen acute liver failure: An etiology-based review. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharzadeh, J.; Derakhshan, L.; Asgharzadeh, N.; Mardani, M.; Shahrani, D.; Shahrani, M.; Shahrani Korrani, M. N-acetylcysteine reduces the hepatic complications of social isolation stress through modulation of interleukin 1 and 6 gene expression and liver enzymes in mice. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaprasad, H.N.; Gharabude, V.; Thimmannagari, S.; Krishnamani, M.; Soni, G. Silymarin: A Historical and Scientific Exploration of its Medicinal Properties. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2025, 19, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J.; Ahuja, A.; Vasudev, S.S.; Ahmad, S. Effects of silymarin nanoemulsion against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Heindl, A. Drying of medicinal plants. In Medicinal and Aromatic Plants; Bogers, R.J., Craker, L.E., Lange, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 237–252. [Google Scholar]
- Lala, P.K. Lab Manuals of Pharmacognosy; CSI Publishers and Distributors: Calcutta, India, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Juan, I.-M.; Chen, Y.-L.; Liang, Y.-C.; Lin, J.-K. Composition of polyphenols in fresh tea leaves and associations of their oxygen-radical-absorbing capacity with antiproliferative actions in fibroblast cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jini, D.; Sharmila, S.; Anitha, A.; Pandian, M.; Rajapaksha, R. In vitro and in silico studies of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) from Allium sativum against diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, K.; Mohan, G.K.; Hussain, M.A.; Jayarambabu, N.; Pravallika, P.L. Green biosynthesis, characterization, in vitro antidiabetic activity, and investigational acute toxicity studies of some herbal-mediated silver nanoparticles on animal models. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Elumalai, A.; Irfan, N.; Ahamed, H.N.; Prasad, M.; Ismail, Y.; Ashok Kumar, P.; Prabhu, D. Impact of Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticle in Wistar Rats: Behavioral, Biochemical, And Histopathological Insights from Acute and Sub-Acute Oral Exposure. Arch. Razi Inst. 2025, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Yagi, K. Simple assay for the level of total lipid peroxides in serum or plasma. In Free Radical and Antioxidant Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Cantiga-Silva, C.; Estrela, C.; Segura-Egea, J.; Azevedo, J.; de Oliveira, P.; Cardoso, C.; Pinheiro, T.; Ervolino, E.; Sivieri-Araújo, G.; Cintra, L. Inflammatory profile of apical periodontitis associated with liver fibrosis in rats: Histological and immunohistochemical analysis. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
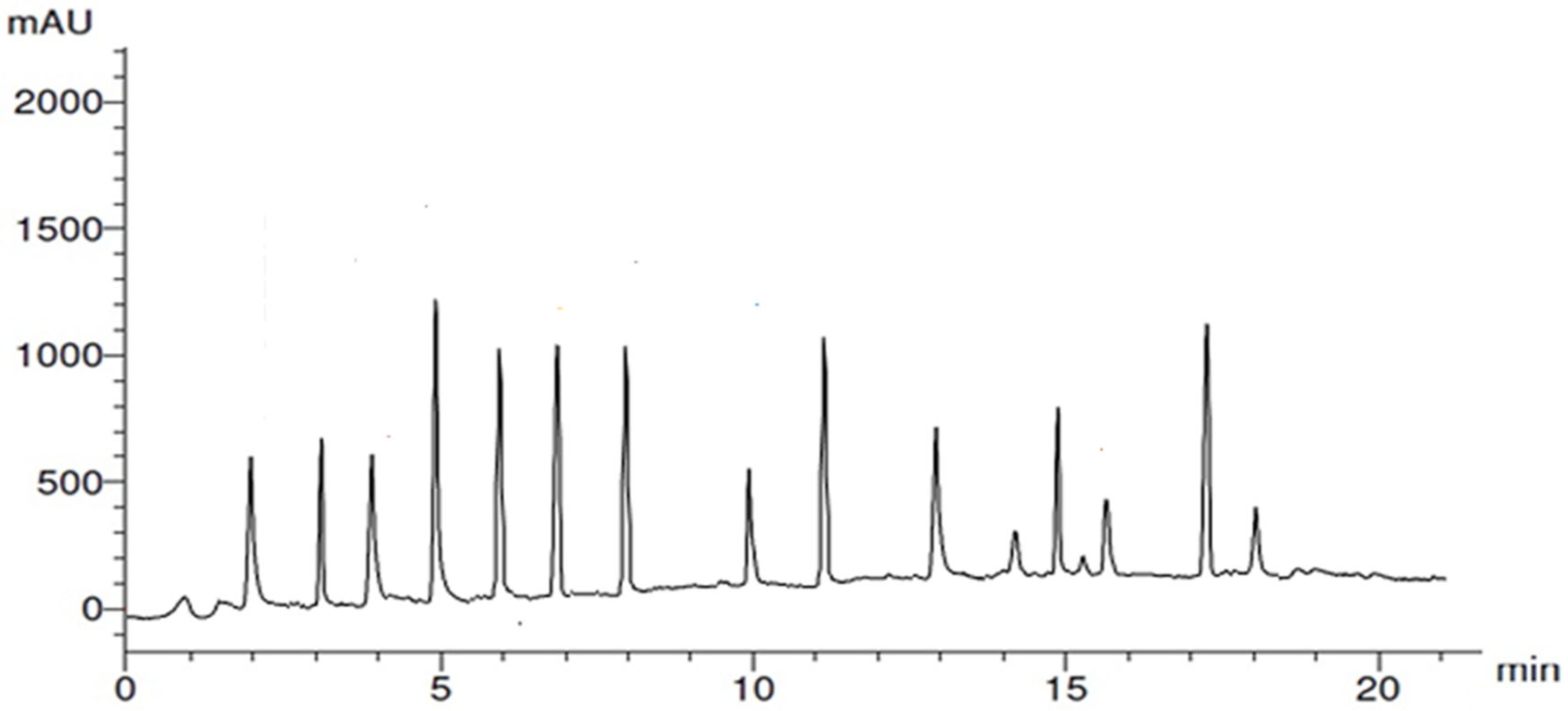

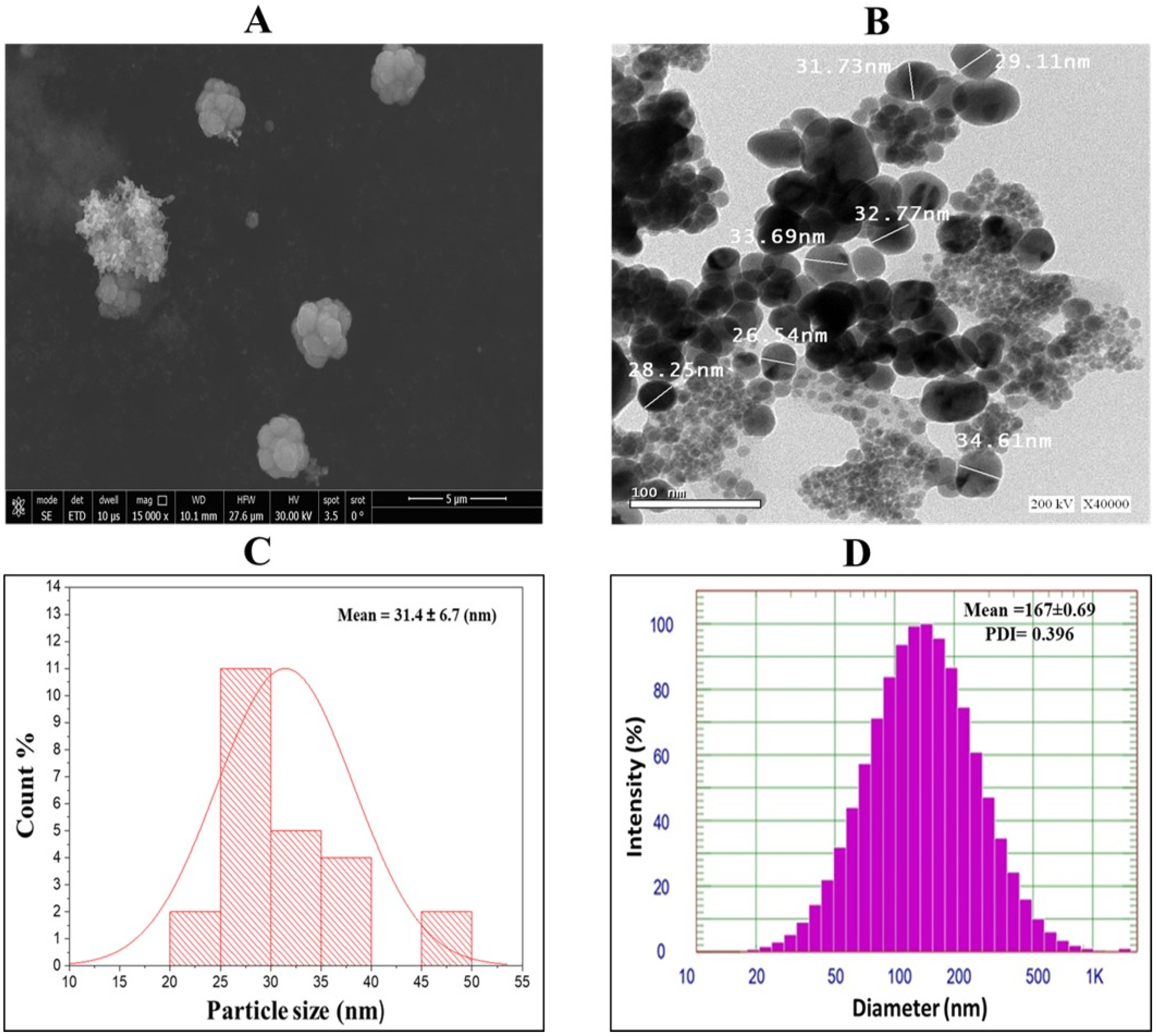
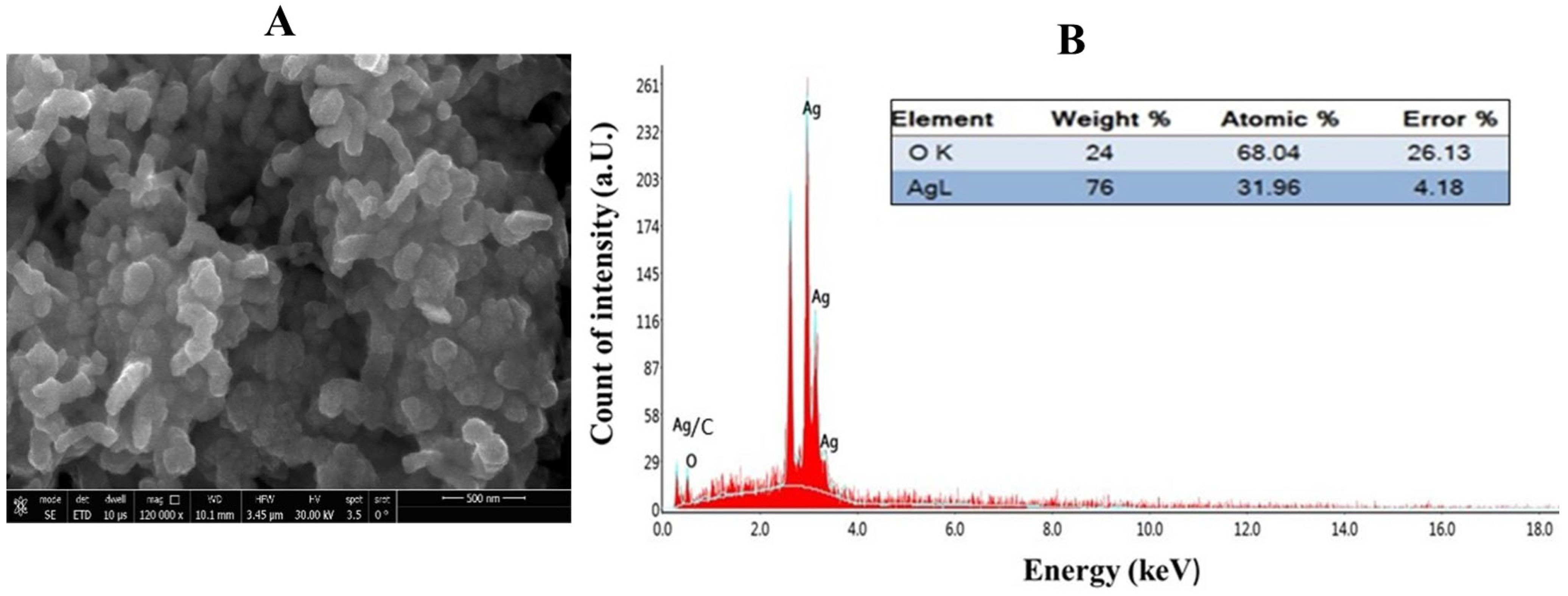
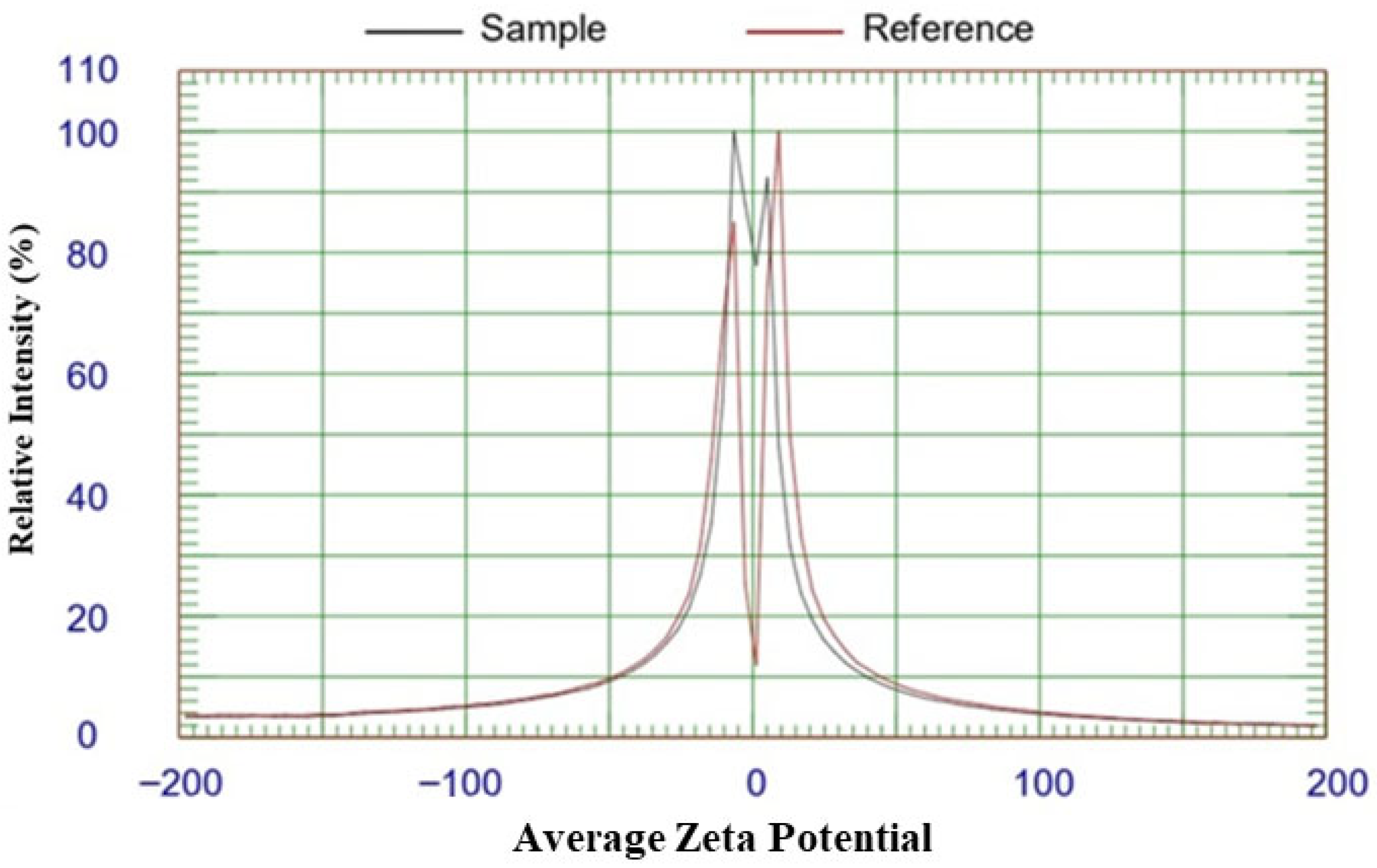
| Compound | R.T. | Class/Subclass | Conc. (µg/gm) | Caps/Stabilizes Ag-NPs (Ag+ → Ag0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-OH Flavone | 2.0 | Flavonoid/7-hydroxyflavone | 4.88 | [55] |
| Chlorogenic acid | 3.0 | Phenolic/phenolic acid ester | 6.20 | [56] |
| Apigenin | 4.0 | Flavonoid/trihydroxyflavone | 4.63 | [57] |
| Ellagic acid | 5.0 | Phenolic/polyphenolic lactone | 18.78 | [58] |
| Gallic acid | 6.0 | Phenolic/hydroxybenzoic acid | 15.20 | [59] |
| Quercetin | 7.0 | Flavonoid/pentahydroxyl flavonol | 14.77 | [59] |
| Syringic acid | 8.0 | Phenolic/hydroxybenzoic acid | 13.89 | [60] |
| Rutin | 10.0 | Flavonoid/flavonol glycoside | 4.25 | [61] |
| Myricetin | 11.0 | Flavonoid/hexahydroxyflavone | 13.76 | [62] |
| Ferulic acid | 13.0 | Phenolic/hydroxycinnamic acid | 7.94 | [63] |
| Cinnamic acid | 14.0 | Phenolic/cinnamic acid derivative | 2.04 | [60] |
| Benzoic acid | 15.0 | Phenolic-related/benzoic acid derivative | 7.64 | [60] |
| Catechin | 16.0 | Flavonoid/3-flavanol | 1.85 | [64] |
| Kaempferol | 17.0 | Flavonoid (flavonol) | 15.67 | [65] |
| Salicylic acid | 18.0 | Phenolic (benzoic acid derivative) | 3.08 | [60] |
| Category | Agent | Liver Function | Mechanisms | Adverse/Toxic Effects | Novelty | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Nanomedicine | GPE–Ag | ALT (35.7%) AST (45.7%) ALP (23.4%) | ↓ NF-κB (32.4%) | No systemic toxicity at 50 mg/kg; safe below reported LD50 (>2000 mg/kg) | Linking garlic peel–derived polyphenolic capping to antioxidant and NF-κB–mediated hepatoprotection; promotes sustainable agro-waste–based nanomedicine | Present study |
| ↓ IL-1 (28.9%) | ||||||
| ↓TNF-α (44.9%) | ||||||
| ↑ IL-10 (52.56%) | ||||||
| ↑ CAT (64.4%) | ||||||
| ↓ MDA (113%) | ||||||
| Synthetic Drug | N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) | ↓ ALT, ↓ AST | ↑ GSH, ↓ROS, ↓proinflammatory cytokine | Nausea, vomiting, possible hepatotoxicity at >200 mg/kg | Acts primarily via glutathione synthesis; lacks polyphenolic or cytokine-targeted effects | [23,110,112] |
| Natural Phytotherapeutic | Silymarin/nano | ↓ ALT, ↓ AST | ↓ lipid peroxidation, ↓proinflammatory cytokine | Mild gastrointestinal discomfort | Phytocomplex with known antioxidant activity; no NF-κB pathway assessment or green nanoplatform integration | [22,109,113,114] |
| Group | Designation | Oral Administration (Days 1–28) | Intraperitoneal (i.p.) Injection (Day 14) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Normal saline control | Saline (0.9%, 5 mL/kg/day) | Saline (0.9%, 1 mL/kg) |
| Pyro | Hepatotoxicity model | Saline (0.9%, 5 mL/kg/day) | Pyrogallol (100 mg/kg in saline) |
| GPE–Ag | Nanoparticles only | GPE–Ag nanoparticles (50 mg/kg/day) | Saline (0.9%, 1 mL/kg) |
| Pyro + GPE–Ag | Hepatotoxicity + treatment | GPE–Ag nanoparticles (50 mg/kg/day) | Pyrogallol (100 mg/kg in saline) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Althumairy, D.A. Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Garlic Peel Target NF-κB and Redox Imbalance: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Against Pyrogallol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15211610
Althumairy DA. Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Garlic Peel Target NF-κB and Redox Imbalance: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Against Pyrogallol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(21):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15211610
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlthumairy, Duaa A. 2025. "Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Garlic Peel Target NF-κB and Redox Imbalance: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Against Pyrogallol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats" Nanomaterials 15, no. 21: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15211610
APA StyleAlthumairy, D. A. (2025). Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Garlic Peel Target NF-κB and Redox Imbalance: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Against Pyrogallol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Nanomaterials, 15(21), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15211610







