Evaluation of Nanodiamond-in-Oil Emulsion with Snake Venom to Enhance Potent Antibody Induction in Mice and Rabbits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Venom and Material
2.2. Production of NDs
2.3. Binding Capacity of ND with Cobra Venom
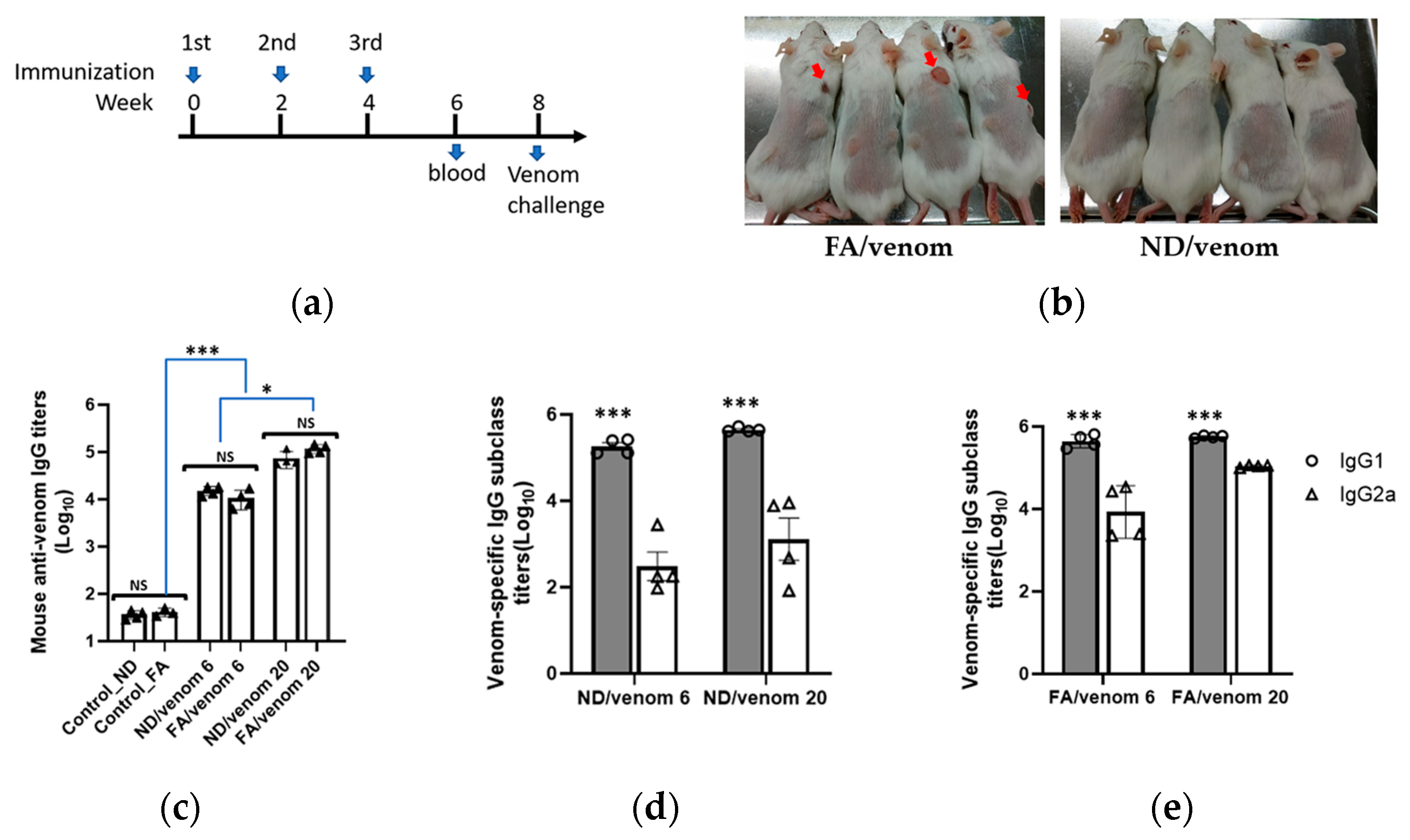
2.4. Animal Immunization
2.5. ELISA Analysis
2.6. Peptide-Based ELISA
2.7. Challenge Assay
2.8. Neutralization Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Venom-ND Conjugate
3.2. Induction of Specific Antibody Responses by ND/Venom Immunization in Mice
3.3. ND/Venom Immunization Induces Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Mice
3.4. ND/Venom Immunization Induces Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Rabbits
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NDs | Nanodiamonds |
| CFA | Complete Freund’s adjuvant |
| IFA | Incomplete Freund’s adjuvant |
| APCs | Antigen-presenting cells |
| sNTX | Short-chain neurotoxin |
| nAChRs | Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors |
| LD50 | Median lethal dose |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays |
References
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippaux, J.P. Guidelines for the production, control and regulation of snake antivenom immunoglobulins. Biol. Aujourdhui 2010, 204, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippaux, J.P.; Habib, A.G. Antivenom shortage is not circumstantial but structural. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 109, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Burnouf, T.; Harrison, R.A.; Calvete, J.J.; Kuch, U.; Warrell, D.A.; Williams, D.J. A multicomponent strategy to improve the availability of antivenom for treating snakebite envenoming. Bull. World Health Organ. 2014, 92, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.B.; Khandhar, A.P.; Khuu, L.; Phan, T.; Kinsey, R.; Cordero, D.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; León, G. Physicochemical and immunological effects of adjuvant formulations with snake venom antigens for immunization of horses for antivenom production. Toxicon 2023, 232, 107229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, H.; Herrera, M.; Rojas, L.; Villalta, M.; Vargas, M.; Leiguez, E.; Teixeira, C.; Estrada, R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; León, G.; et al. Comparison of the adjuvant activity of aluminum hydroxide and calcium phosphate on the antibody response towards Bothrops asper snake venom. J. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 11, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapsutthipas, S.; Leong, P.K.; Akesowan, S.; Pratanaphon, R.; Tan, N.H.; Ratanabanangkoon, K. Effective equine immunization protocol for production of potent poly-specific antisera against Calloselasma rhodostoma, Cryptelytrops albolabris and Daboia siamensis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, L.S.; Pascual, M.M.; Hernandez, D.; Vallecillo, M.F.S.; Arrieta, M.B.; Moron, G.; Palma, S.; Maletto, B.A.; Leiva, L.C. CpG-ODN formulated with a nanostructure as adjuvant for anticrotalic serum production. Studies in mice. Toxicon 2022, 215, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arguedas, M.; Umaña, D.; Moscoso, E.; García, A.; Pereira, C.; Sánchez, A.; Durán, G.; Cordero, D.; Sánchez, A.; Segura, Á.; et al. Comparison of adjuvant emulsions for their safety and ability to enhance the antibody response in horses immunized with African snake venoms. Vaccine X 2022, 12, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, T.V.; Frézard, F. Encapsulation of native crotoxin in liposomes: A safe approach for the production of antivenom and vaccination against Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Toxicon 1997, 35, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Vedelaar, T.A.; Sigaeva, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Olinga, P.; Wlodarzyk-Biegun, M.K.; Schirhagl, R. Fluorescent nanodiamonds for tracking single polymer particles in cells and tissues. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 13046–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahchamandi, S.Y.R.; Mirhadi, E.; Gheybi, F.; Kazemi-Beydokhti, A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Mostafavi, E.; Kesharwani, P.; Sahebkar, A.; Alavizadeh, S.H. Engineering carbon-based nanomaterials for the delivery of platinum compounds: An innovative cancer disarming frontier. Environ Res. 2024, 262, 119933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, S.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Hilmi Ismail, Z.; Subramaniam, S. Nanodiamond conjugated SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Electrochemical impedance immunosensing on a gold microelectrode. Mikrochim. Acta 2022, 189, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, M.F.S.; Brachtenbach Mitchell, A.J.; Moulder, K.R.; Van Slyke, G.; Larson, N.R.; Mantis, N.J.; Middaugh, C.R.; Forrest, M.L. Synthesis and characterization of modified nanodiamonds for use as a potential vaccine adjuvant delivery platform for a candidate ricin toxin vaccine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 114, 103900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsieh, F.J.; Liao, F.Z.; Su, Y.K.; Pham, M.D.; Lee, C.Y.; Chang, H.C.; Hsu, H.H. Nanodiamonds-in-oil emulsions elicit potent immune responses for effective vaccination and therapeutics. Nanomedicine 2023, 18, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.T.; Pham, V.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Trinh, V.T.; Vi, T.; Lin, H.H.; Nguyen, P.M.T.; Bui, H.T.; Pham, N.B.; Le, T.B.T.; et al. Effects of size and surface properties of nanodiamonds on the immunogenicity of plant-based H5 protein of A/H5N1 virus in mice. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Yang, C.O.; Hsu, C.P.; Liu, C.C.; Yu, J.S.; Lo, C.H.; Fann, W.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, C.C. Taiwan cobra envenoming: Serum venom concentration before and after specific treatment and relationship with debridement of necrotic wound tissue. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 29, e20220027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.W.; Liu, B.S.; Chien, K.Y.; Chiang, L.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Sung, W.C.; Wu, W.G. Cobra venom proteome and glycome determined from individual snakes of Naja atra reveal medically important dynamic range and systematic geographic variation. J. Proteom. 2015, 128, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.L.; Viegas, M.F.; da Silva, S.L.; Soares, A.M.; Ramos, M.J.; Fernandes, P.A. The chemistry of snake venom and its medicinal potential. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.S.; Chou, Y.C.; Lin, S.R.; Wu, B.N.; Lin, J.; Hong, E.; Sun, Y.J.; Hsiao, C.D. A novel neurotoxin, cobrotoxin b, from Naja naja atra (Taiwan cobra) venom: Purification, characterization, and gene organization. J. Biochem. 1997, 122, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanabanangkoon, K.; Tan, K.Y.; Eursakun, S.; Tan, C.H.; Simsiriwong, P.; Pamornsakda, T.; Wiriyarat, W.; Klinpayom, C.; Tan, N.H. A simple and novel strategy for the production of a pan-specific antiserum against elapid snakes of Asia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.S.; Jiang, B.R.; Hu, K.C.; Liu, C.H.; Hsieh, W.C.; Lin, M.H.; Sung, W.C. Development of a broad-spectrum antiserum against cobra venoms using recombinant three-finger toxins. Toxins 2021, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, R.J.; Marriott, A.E.; Stars, E.L.; Patel, R.N.; Wilkinson, M.C.; King, L.D.W.; Slagboom, J.; Tan, C.H.; Ratanabanangkoon, K.; Draper, S.J.; et al. Plug and play virus-like particles for the generation of anti-toxin antibodies. Toxicon X 2024, 23, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.R.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo Ide, L.; Novo, J.B.; Castro, K.; Duarte, C.G.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.A.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Ho, P.L. A heterologous multiepitope DNA prime/recombinant protein boost immunisation strategy for the development of an antiserum against micrurus corallinus (Coral snake) venom. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, H.; Corrales-García, L.L.; Bolaños, D.; Corzo, G.; Villegas, E. Immunogenic properties of recombinant enzymes from Bothrops ammodytoides towards the generation of neutralizing antibodies against Its own venom. Toxins 2019, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.S.; Wu, W.G.; Lin, M.H.; Li, C.H.; Jiang, B.R.; Wu, S.C.; Leng, C.H.; Sung, W.C. Identification of immunoreactive peptides of toxins to simultaneously assess the neutralization potency of antivenoms against neurotoxicity and cytotoxicity of Naja atra venom. Toxins 2017, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, V.C.; McKeon, R.M.; Brackin, M.N.; Miller, L.A.; Keating, R.; Brown, S.A.; Makarova, N.; Perez, D.R.; Macdonald, G.H.; McCullers, J.A. Distinct contributions of vaccine-induced immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) and IgG2a antibodies to protective immunity against influenza. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Jennings, G.T. Vaccine delivery: A matter of size, geometry, kinetics and molecular patterns. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melssen, M.M.; Fisher, C.T.; Slingluff, C.L.; Melief, C.J.M. Peptide emulsions in incomplete Freund’s adjuvant create effective nurseries promoting egress of systemic CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells for immunotherapy of cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, L.J.; Middaugh, C.R.; Berkland, C. Nanotechnology in vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa de Almeida, M.; Susnik, E.; Drasler, B.; Taladriz-Blanco, P.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Understanding nanoparticle endocytosis to improve targeting strategies in nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5397–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Gong, H.; Sun, Q.; Yang, J.; Yan, X.; Xu, F. Research progress on emulsion vaccine adjuvants. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekbossynova, A.; Zharylgap, A.; Filchakova, O. Venom-derived neurotoxins targeting nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Molecules 2021, 26, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, P.K.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Sim, S.M.; Tan, N.H. Immunological cross-reactivity and neutralization of the principal toxins of Naja sumatrana and related cobra venoms by a Thai polyvalent antivenom (Neuro Polyvalent Snake Antivenom). Acta Trop. 2015, 149, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Rabbit Antisera Group | Antibody Titers (Endpoint, Log10) | Neutralization Potency (3LD50 Cobra Venom) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Venom | Anti-sNTX | ED50 (mg) 1 | P (mg/g) 2 | |
| ND/venom | 5.14 ± 0.02 | 4.20 ± 0.01 | 2.31 (1.78–2.83) | 5.76 (4.03–10.08) |
| FA/venom | 5.93 ± 0.03 | 4.60 ± 0.02 | 5.56 (4.84–6.32) | 5.76 (4.03–10.08) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, M.-H.; Su, L.-J.; Lin, H.-H.; Chen, L.-Y.; Husna, A.; Sung, W.-C. Evaluation of Nanodiamond-in-Oil Emulsion with Snake Venom to Enhance Potent Antibody Induction in Mice and Rabbits. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191518
Lin M-H, Su L-J, Lin H-H, Chen L-Y, Husna A, Sung W-C. Evaluation of Nanodiamond-in-Oil Emulsion with Snake Venom to Enhance Potent Antibody Induction in Mice and Rabbits. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(19):1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191518
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Min-Han, Long-Jyun Su, Hsin-Hung Lin, Liang-Yu Chen, Asmaul Husna, and Wang-Chou Sung. 2025. "Evaluation of Nanodiamond-in-Oil Emulsion with Snake Venom to Enhance Potent Antibody Induction in Mice and Rabbits" Nanomaterials 15, no. 19: 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191518
APA StyleLin, M.-H., Su, L.-J., Lin, H.-H., Chen, L.-Y., Husna, A., & Sung, W.-C. (2025). Evaluation of Nanodiamond-in-Oil Emulsion with Snake Venom to Enhance Potent Antibody Induction in Mice and Rabbits. Nanomaterials, 15(19), 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191518






