Exploring the Coating of Gold Nanoparticles with Lipids
Abstract
1. Introduction
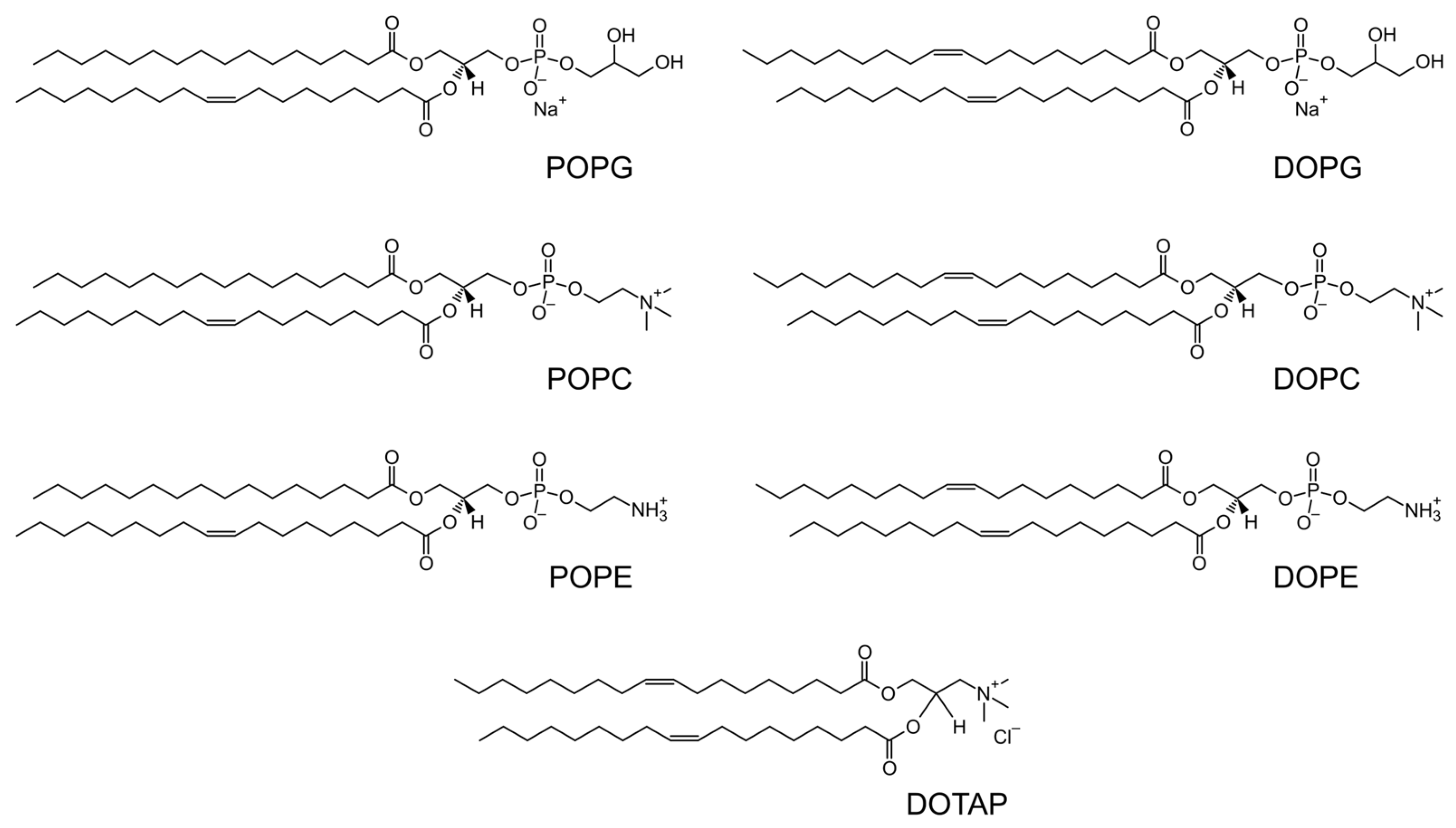
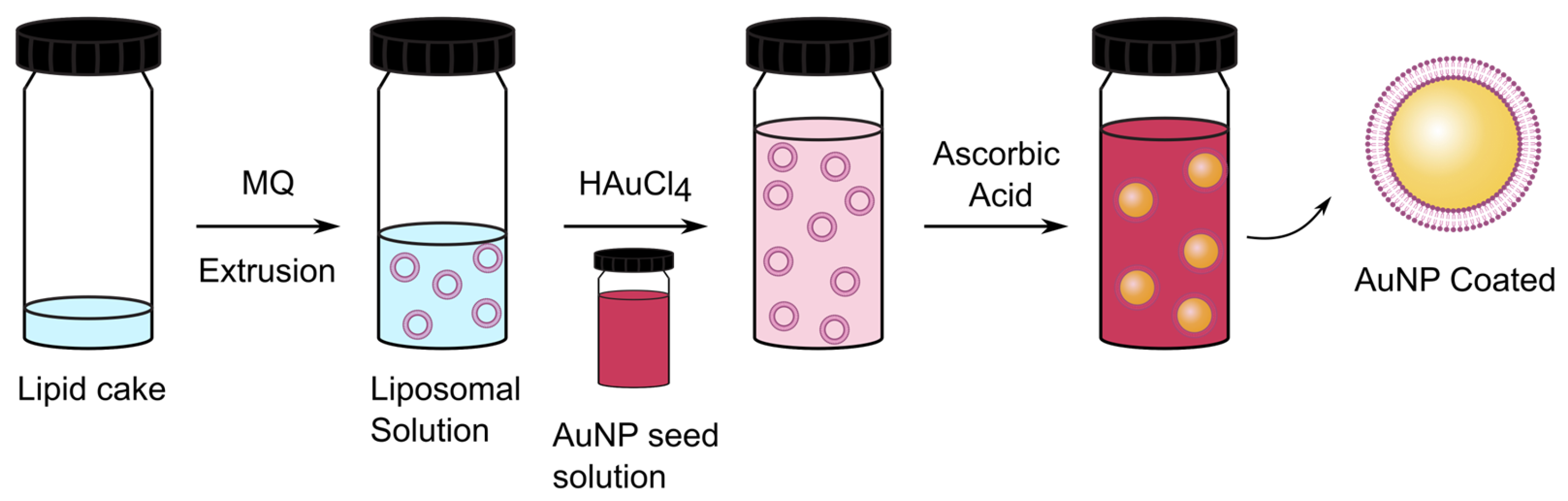
2. Materials and Methods
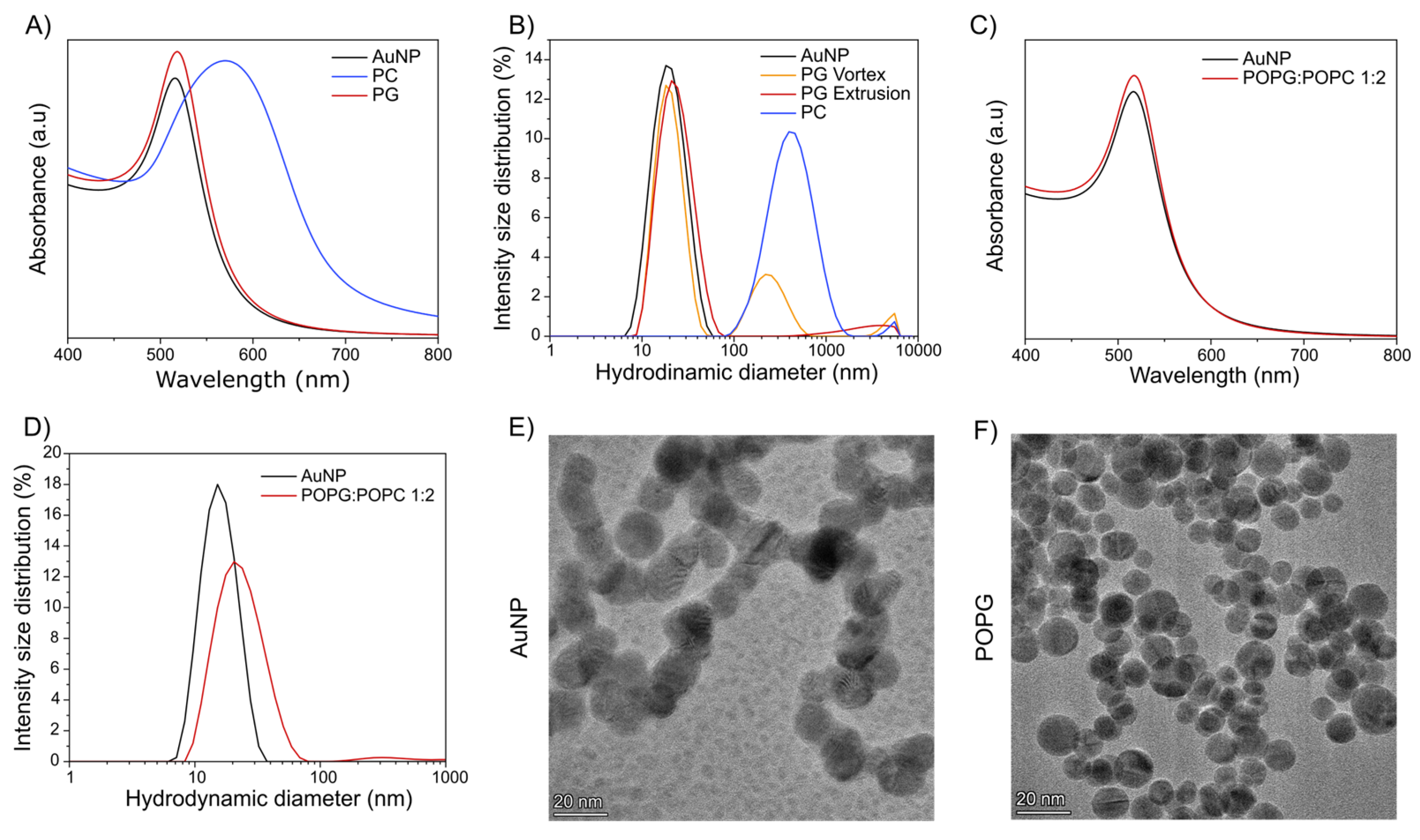
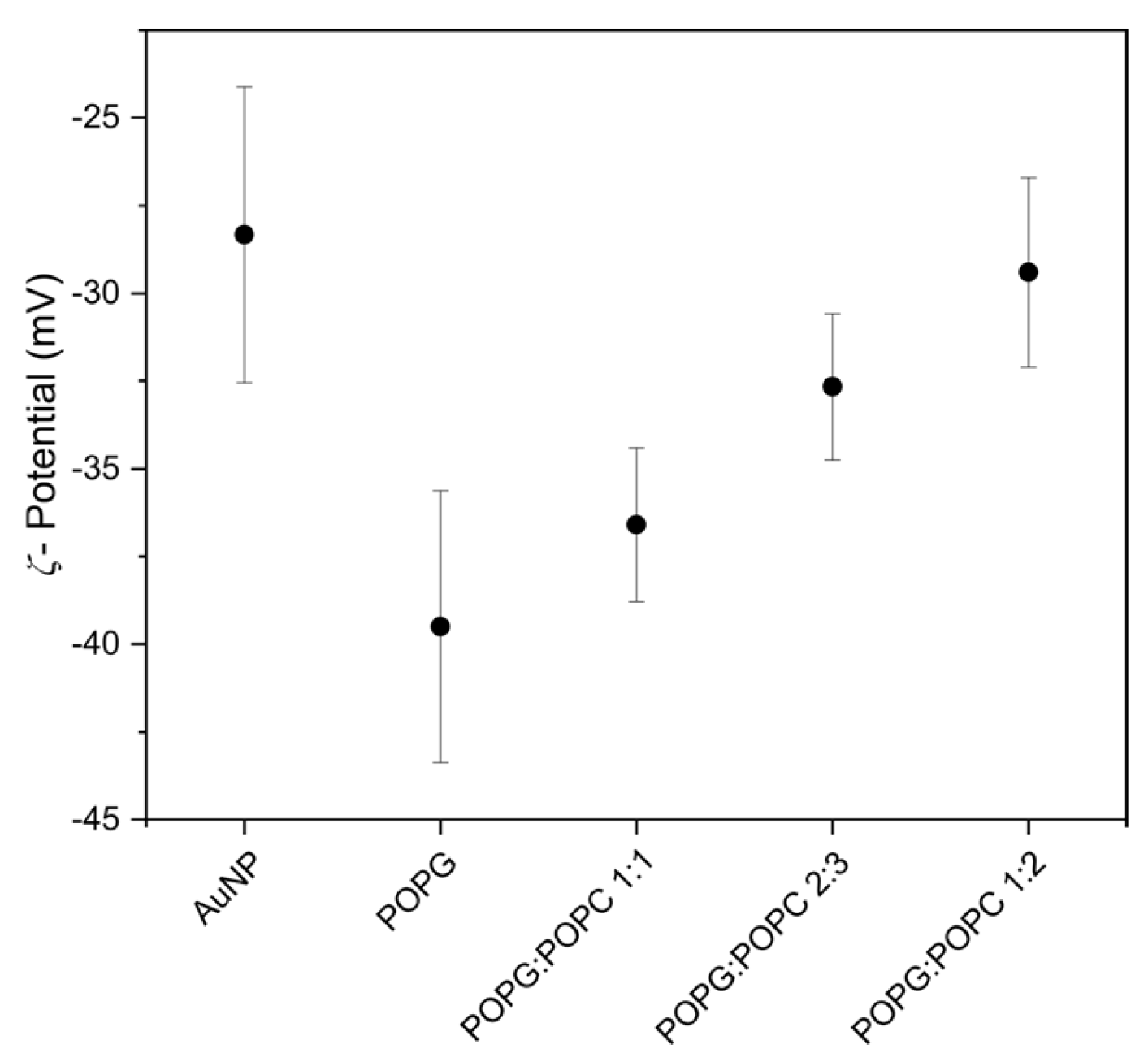
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P.; Hou, H.; Xu, S.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, F. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensing Based on Monometallic Gold Nanoparticles: From Material Preparation to Detection of Bioanalytes. Anal. Methods 2025, 17, 892–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouché, M.; Hsu, J.C.; Dong, Y.C.; Kim, J.; Taing, K.; Cormode, D.P. Recent Advances in Molecular Imaging with Gold Nanoparticles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 31, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ali, M.R.K.; Chen, K.; Fang, N.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanoparticles in Biological Optical Imaging. Nano Today 2019, 24, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vines, J.B.; Yoon, J.H.; Ryu, N.E.; Lim, D.J.; Park, H. Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 432792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauffred, L.; Samadi, A.; Klingberg, H.; Bendix, P.M.; Oddershede, L.B. Plasmonic Heating of Nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 8087–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Maragò, O.M.; Iatì, M.A. Surface Plasmon Resonance in Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Lee, K.S.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Calculated Absorption and Scattering Properties of Gold Nanoparticles of Different Size, Shape, and Composition: Applications in Biological Imaging and Biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Size and Temperature Dependence of the Plasmon Absorption of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 4212–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.R.; Walter, D.G.; Natan, M.J. Seeding of Colloidal Au Nanoparticle Solutions. 2. Improved Control of Particle Size and Shape. Chem. Mat. 2000, 12, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction Coefficient of Gold Nanoparticles with Different Sizes and Different Capping Ligands. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushki, E. Effect of Conjugation with Organic Molecules on the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Gold Nanoparticles and Application in Optical Biosensing. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 23390–23399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Griffith, B.; Bhomkar, P.; Wishart, D.S.; McDermott, M.T. Functionalized Gold Nanoparticle-Enhanced Competitive Assay for Sensitive Small-Molecule Metabolite Detection Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Analyst 2018, 143, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Huang, R.; Yu, Y.; Su, R.; Qi, W.; He, Z. Gold Nanoparticle-Aptamer-Based LSPR Sensing of Ochratoxin A at a Widened Detection Range by Double Calibration Curve Method. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, E.; Nicol, J.R.; Macias-Montero, M.; Burke, G.A.; Coulter, J.A.; Meenan, B.J.; Dixon, D. A Comparison of Gold Nanoparticle Surface Co-Functionalization Approaches Using Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) and the Effect on Stability, Non-Specific Protein Adsorption and Internalization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Morovati, V.; Dargazany, R. PEGylation on Mixed Monolayer Gold Nanoparticles: Effect of Grafting Density, Chain Length, and Surface Curvature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 504, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Quinsaat, J.E.Q.; Ono, T.; Maeki, M.; Tokeshi, M.; Isono, T.; Tajima, K.; Satoh, T.; Sato, S.; Miura, Y.; et al. Enhanced Dispersion Stability of Gold Nanoparticles by the Physisorption of Cyclic Poly(Ethylene Glycol). Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Tang, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, Q. Effects of Polyethylene Glycol on the Surface of Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 10748–10764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, X. Synthesis of Chitosan-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles in the Absence/Presence of Tripolyphosphate. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beik, J.; Khateri, M.; Khosravi, Z.; Kamrava, S.K.; Kooranifar, S.; Ghaznavi, H.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A. Gold Nanoparticles in Combinatorial Cancer Therapy Strategies. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 387, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdeperez, D.; Wutke, N.; Ackermann, L.M.; Parak, W.J.; Klapper, M.; Pelaz, B. Colloidal Stability of Polymer Coated Zwitterionic Au Nanoparticles in Biological Media. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2022, 534, 120820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.J.; Fang, R.H.; Wang, K.C.; Luk, B.T.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Dehaini, D.; Nguyen, P.; Angsantikul, P.; Wen, C.H.; Kroll, A.V.; et al. Nanoparticle Biointerfacing by Platelet Membrane Cloaking. Nature 2015, 526, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Liu, S.J.; Tang, L.J.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, J.H. Gold Nanoparticle Supported Phospholipid Membranes as a Biomimetic Biosensor Platform for Phosphoinositide Signaling Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meer, G. Cellular Lipidomics. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligtenberg, L.J.W.; Rabou, N.C.A.; Goulas, C.; Duinmeijer, W.C.; Halfwerk, F.R.; Arens, J.; Lomme, R.; Magdanz, V.; Klingner, A.; Klein Rot, E.A.M.; et al. Ex Vivo Validation of Magnetically Actuated Intravascular Untethered Robots in a Clinical Setting. Comms. Eng. 2024, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Weerd, J.; Karperien, M.; Jonkheijm, P.; Van Weerd, J.; Jonkheijm, P.; Karperien, M. Supported Lipid Bilayers for the Generation of Dynamic Cell–Material Interfaces. Adv Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 2743–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, J.; Cavatorta, E.; Sankaran, S.; Schmidt, B.; Van Weerd, J.; Jonkheijm, P. About Supramolecular Systems for Dynamically Probing Cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4449–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Caselli, L.; Paolini, L.; Fong, W.K.; Montis, C.; Zendrini, A.; Cardellini, J.; Bergese, P.; Berti, D. The Gold Nanoparticle–Lipid Membrane Synergy for Nanomedical Applications. Nanoscale Horiz. 2025, 10, 1863–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Ko, Y.T. Lipid-Coated Gold Nanocomposites for Enhanced Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKiewicz, M.R.; Hodges, H.L.; Reed, S.M. C-Reactive Protein Induced Rearrangement of Phosphatidylcholine on Nanoparticle Mimics of Lipoprotein Particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 5556–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.A.; Murphy, C.J. Evidence for Patchy Lipid Layers on Gold Nanoparticle Surfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 5404–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, S.M.; Milchberg, M.H.; Rienstra, C.M.; Murphy, C.J. Biologically Representative Lipid-Coated Gold Nanoparticles and Phospholipid Vesicles for the Study of Alpha-Synuclein/Membrane Interactions. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 20387–20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Wang, E. Cationic Lipid Bilayer Coated Gold Nanoparticles-Mediated Transfection of Mammalian Cells. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Gu, X.; Han, X.; Ding, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, E.; Wang, J. Lipid-Coated Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized by Folic Acid as Gene Vectors for Targeted Gene Delivery in Vitro and in Vivo. Chem. Med. Chem. 2017, 12, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Didodecyldimethylammonium Bromide Lipid Bilayer-Protected Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Self-Assembly. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2838–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Shin, Y.; Lee, W.; Whang, K.; Kim, D.; Lee, L.P.; Choi, J.W.; Kang, T. General and Programmable Synthesis of Hybrid Liposome/Metal Nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzigmann, D.; Sieber, S.; Porta, F.; Grossen, P.; Bieri, A.; Strelnikova, N.; Pfohl, T.; Prescianotto-Baschong, C.; Huwyler, J. Formation of Lipid and Polymer Based Gold Nanohybrids Using a Nanoreactor Approach. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74320–74328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, M.S.; Possmayer, F.; Petersen, N.O. Role of Different Phospholipids in the Synthesis of Pearl-Necklace-Type Gold-Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles as Bioconjugate Materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14113–14124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhu, X. Phospholipid-Assisted Synthesis of Size-Controlled Gold Nanoparticles. Mater Res. Bull. 2007, 42, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Petersen, N.O. Characterization of Phospholipid-Encapsulated Gold Nanoparticles: A Versatile Platform to Study Drug Delivery and Cellular Uptake Mechanisms. Can. J. Chem. 2015, 93, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.; Dobó, Z.; Palotás, A.B.; Kovács, H. A review of Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis: Transitioning from Conventional Techniques to Plant-Mediated Green Nanofabrication. Mater. Today Chem. 2025, 48, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.E.F.; Pereira, A.C.; Resende, M.A.C.; Ferreira, L.F. Gold Nanoparticles: A Didactic Step-by-Step of the Synthesis Using the Turkevich Method, Mechanisms, and Characterizations. Analytica 2023, 4, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-marza, L.M.; Giersig, M.; Mulvaney, P. Synthesis of Nanosized Gold–Silica Core–Shell Particles. Langmuir 1996, 7463, 4329–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudo-Canalejo, J.; Lipowsky, R. Critical Particle Sizes for the Engulfment of Nanoparticles by Membranes and Vesicles with Bilayer Asymmetry. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3704–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, J.A.; Kim, M.C.; Zhdanov, V.P.; Cho, N.J. Relationship between Vesicle Size and Steric Hindrance Influences Vesicle Rupture on Solid Supports. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lipid | PC | PE |
|---|---|---|
| PG | 1:0 1 | 0:1 1 |
| 9:1 1 | 9:1 1 | |
| 1:1 1 | 1:1 | |
| 2:3 | ||
| 1:2 | ||
| 1:3 | ||
| 0:1 1 | ||
| PC | PG | |
| DOTAP | 1:0 2 | |
| 1:1 2 | 1:1 2 | |
| 1:1:1 2 | ||
| Lipid Ratio | UV–Vis Shift | Diameter (nm) | PDI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POPG:POPC | 1:0 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 26 ± 1 | 0.20 ± 0.05 |
| 1:1 | 1 ± 0.9 | 25.5 ± 5 | 0.36 ± 0.09 | |
| 2:3 | 1 ± 0.5 | 36.5 ± 13.5 | 0.35 ± 0.09 | |
| 1:2 | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 44 ± 20.5 | 0.36 ± 0.13 | |
| 0:1 * |
| Lipid Ratio | UV–Vis Shift | Diameter (nm) | PDI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOPC:DOTAP | 0:1 | 48 | 136 ± 1 | 0.17 ± 0.02 |
| DOPC:DOTAP | 1:1 | 60 | 153 ± 7 | 0.41 ± 0.01 |
| DOPG:DOTAP | 1:1 | 0.5 | 162 ± 9 | 0.29 ± 0.02 |
| DOPC:DOPG:DOTAP | 1:1:1 | 17 | 211 ± 5 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vilar-Hernández, M.; van Weerd, J.; Jonkheijm, P. Exploring the Coating of Gold Nanoparticles with Lipids. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191516
Vilar-Hernández M, van Weerd J, Jonkheijm P. Exploring the Coating of Gold Nanoparticles with Lipids. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(19):1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191516
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilar-Hernández, Mireia, Jasper van Weerd, and Pascal Jonkheijm. 2025. "Exploring the Coating of Gold Nanoparticles with Lipids" Nanomaterials 15, no. 19: 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191516
APA StyleVilar-Hernández, M., van Weerd, J., & Jonkheijm, P. (2025). Exploring the Coating of Gold Nanoparticles with Lipids. Nanomaterials, 15(19), 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191516








