Sterilization Effects on Liposomes with Varying Lipid Chains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Liposome
2.3. Liposomes Sterilization Methods
2.4. Liposome Characterization
2.4.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity, and Zeta Potential Determination
2.4.2. pH Measurements
2.4.3. Phospholipid Measurement
2.4.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.4.5. Raman Spectroscopy (RS)
2.5. Biological Evaluation
2.5.1. Cell Cultures
2.5.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Appearance and Physicochemical Characteristics
3.2. pH Values Before and After Sterilization
3.3. Influence of Sterilization on Chemical Characteristics of Liposomes
3.4. Comparison of Raman Spectra
3.5. Phospholipid Measurement
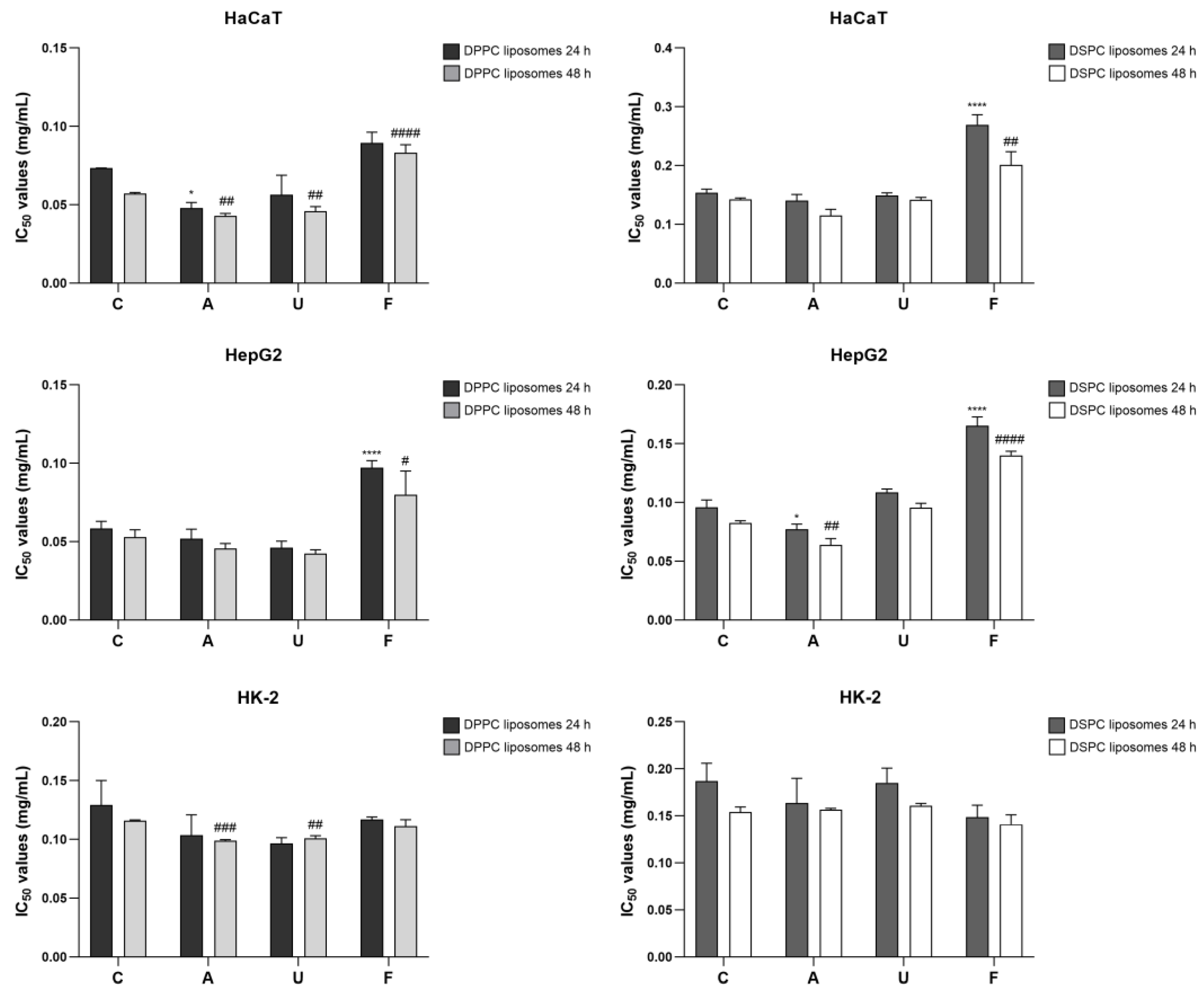
3.6. Effects of Sterilization on Cell Viability
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Sterilization on Physicochemical Properties
4.2. Chemical and Structural Alterations
4.3. Effects on Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A | Autoclaving |
| C | Non-sterilized liposomes |
| ATR | Attenuated total reflection |
| DDAB | Didecyldimethylammonium bromide |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium |
| DPPC | Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine |
| DSPC | Distearoylphosphatidylcholine |
| DTGS | Deuterated triglycine sulphate |
| EtO | Ethylene oxide |
| F | Filtration |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| IC50 | 50% Inhibitory Concentration |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| RS | Raman Spectroscopy |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| U | UV irradiation |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Huang, Q. Liposomes for Tumor Targeted Therapy: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymek, M.; Sikora, E. Liposomes as biocompatible and smart delivery systems—The current state. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 309, 102757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttasiddaiah, R.; Lakshminarayana, R.; Somashekar, N.L.; Gupta, V.K.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Usmani, Z.; Raghavendra, V.B.; Sridhar, K.; Sharma, M. Advances in Nanofabrication Technology for Nutraceuticals: New Insights and Future Trends. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, M.; Rana, R.; Sambhakar, S.; Chourasia, M.K. Nanocosmeceuticals: Trends and Recent Advancements in Self Care. Aaps Pharmscitech 2024, 25, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Thin-Film Hydration Followed by Extrusion Method for Liposome Preparation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1522, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, A.; Vorauer-Uhl, K. Liposome Technology for Industrial Purposes. J. Drug Deliv. 2011, 2011, 591325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Application of Response Surface Methodology in Development of Sirolimus Liposomes Prepared by Thin Film Hydration Technique. Bioimpacts 2013, 3, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duong, T.T.; Isomäki, A.; Paaver, U.; Laidmäe, I.; Tõnisoo, A.; Yen, T.T.H.; Kogermann, K.; Raal, A.; Heinämäki, J.; Pham, T.-M. Nanoformulation and Evaluation of Oral Berberine-Loaded Liposomes. Molecules 2021, 26, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsana, H.; Olusanya, T.O.B.; Carr-Wilkinson, J.; Darby, S.; Faheem, A.; Elkordy, A.A. Evaluation of novel cationic gene based liposomes with cyclodextrin prepared by thin film hydration and microfluidic systems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A. Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delma, K.L.; Lechanteur, A.; Evrard, B.; Semdé, R.; Piel, G. Sterilization methods of liposomes: Drawbacks of conventional methods and perspectives. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, Á.; Pelaz, B.; Moros, M.; Sánchez-Espinel, C.; Hernández, A.; Fernández-López, C.; Grazú, V.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; et al. Sterilization matters: Consequences of different sterilization techniques on gold nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetten, M.A.; Yah, C.S.; Singh, T.; Gulumian, M. Challenges facing sterilization and depyrogenation of nanoparticles: Effects on structural stability and biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S. Sterilization and Disinfection; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 929–944. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.; Ao, T.; Mao, X.; Yan, X.; Javed, R.; Hou, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Lin, S.; Yu, T.; et al. Sterilization and disinfection methods for decellularized matrix materials: Review, consideration and proposal. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2927–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, S.C.; Chonn, A.; Cullis, P.R. Influence of cholesterol on the association of plasma proteins with liposomes. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 2521–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Omri, A. The effect of different lipid components on the in vitro stability and release kinetics of liposome formulations. Drug Deliv. 2004, 11, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzielo, R.S.; Heberle, F.A.; Drazba, P.; Katsaras, J.; Feigenson, G.W. Phase behavior and domain size in sphingomyelin-containing lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonenko, Z.; Finot, E.; Ma, H.; Dahms, T.S.; Cramb, D. Investigation of temperature-induced phase transitions in DOPC and DPPC phospholipid bilayers using temperature-controlled scanning force microscopy. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 3783–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidorra, M.; Heimburg, T.; Seeger, H. Melting of individual lipid components in binary lipid mixtures studied by FTIR spectroscopy, DSC and Monte Carlo simulations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pietzyk, B.; Henschke, K. Degradation of phosphatidylcholine in liposomes containing carboplatin in dependence on composition and storage conditions. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 196, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongkow, M.; Rimsueb, N.; Jantimaporn, A.; Janyaphisan, T.; Woraprayote, W.; Visessanguan, W.; Ruktanonchai, U.R. Cationic liposome of hen egg white lysozyme for enhanced its stability, activity and accessibility in gastro-intestinal tract. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rodà, F.; Picciolini, S.; Mangolini, V.; Gualerzi, A.; Seneci, P.; Renda, A.; Sesana, S.; Re, F.; Bedoni, M. Raman Spectroscopy Characterization of Multi-Functionalized Liposomes as Drug-Delivery Systems for Neurological Disorders. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharib, R.; Najjar, A.; Auezova, L.; Charcosset, C.; Greige-Gerges, H. Interaction of Selected Phenylpropenes with Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine Membrane and Their Relevance to Antibacterial Activity. J. Membr. Biol. 2017, 250, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, B.; Nag, O.K.; Rogers, K.E.; Delehanty, J.B. Recent Progress in Bioconjugation Strategies for Liposome-Mediated Drug Delivery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Large, D.E.; Abdelmessih, R.G.; Fink, E.A.; Auguste, D.T. Liposome composition in drug delivery design, synthesis, characterization, and clinical application. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zylberberg, C.; Gaskill, K.; Pasley, S.; Matosevic, S. Engineering liposomal nanoparticles for targeted gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidam, N.J.; Lee, S.S.L.; Crommelin, D.J.A. Sterilization of liposomes by heat treatment. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, Â.L.; Valente, M.A.; Ferreira, J.M.; Fabris, J.D. Preparation of size-controlled nanoparticles of magnetite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1753–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mak, K.; Shi, J.; Wong, C.; Leung, C.; Mak, C.; Chan, K.; Chan, N.; Wu, E.; Pong, P. Sterilization on dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: Effects of autoclaving, filtration, UV irradiation, and ethanol treatment. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 111, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasarin, D.; Ghizdareanu, A.-I.; Enascuta, C.E.; Matei, C.B.; Bilbie, C.; Paraschiv-Palada, L.; Veres, P.-A. Coating Materials to Increase the Stability of Liposomes. Polymers 2023, 15, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.G.; Yianni, Y.P.; Sandhu, S.S.; Mitchell, A.C. Liposome fusion and lipid exchange on ultraviolet irradiation of liposomes containing a photochromic phospholipid. Photochem. Photobiol. 1995, 62, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntsche, J.; Bunjes, H. Influence of preparation conditions and heat treatment on the properties of supercooled smectic cholesteryl myristate nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, R.; Matsuzaki, T.; Nakamura, A.; Nakatani, D.; Sanada, S.; Fu, H.Y.; Okuda, K.; Yamato, M.; Tsuchida, S.; Sakata, Y.; et al. Development of a novel one-step production system for injectable liposomes under GMP. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldbach, P.; Brochart, H.; Wehrlé, P.; Stamm, A. Sterile filtration of liposomes: Retention of encapsulated carboxyfluorescein. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 117, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmendinger, A.; Mueller, R.; Huwyler, J.; Mahler, H.-C.; Fischer, S. Sterile Filtration of Highly Concentrated Protein Formulations: Impact of Protein Concentration, Formulation Composition, and Filter Material. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3319–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V.; Maurin, F.; Fessi, H.; Devissaguet, J. Influence of sterilization processes on poly(ε-caprolactone) nanospheres. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, D.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Nogueira, E. Design of liposomes as drug delivery system for therapeutic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.S.; Hussein, S.A.; Ali, A.H.; Korma, S.A.; Lipeng, Q.; Jinghua, C. Liposome: Composition, characterisation, preparation, and recent innovation in clinical applications. J. Drug Target 2019, 27, 742–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Abbas, S.; Feng, B.; Zhang, X.; Xia, W.; Xia, S. Biopolymer–Lipid Bilayer Interaction Modulates the Physical Properties of Liposomes: Mechanism and Structure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7277–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, D.R.; Rezler, E.M.; Lauer-Fields, J.; Fields, G.B. Effects of Drug Hydrophobicity on Liposomal Stability. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2008, 71, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


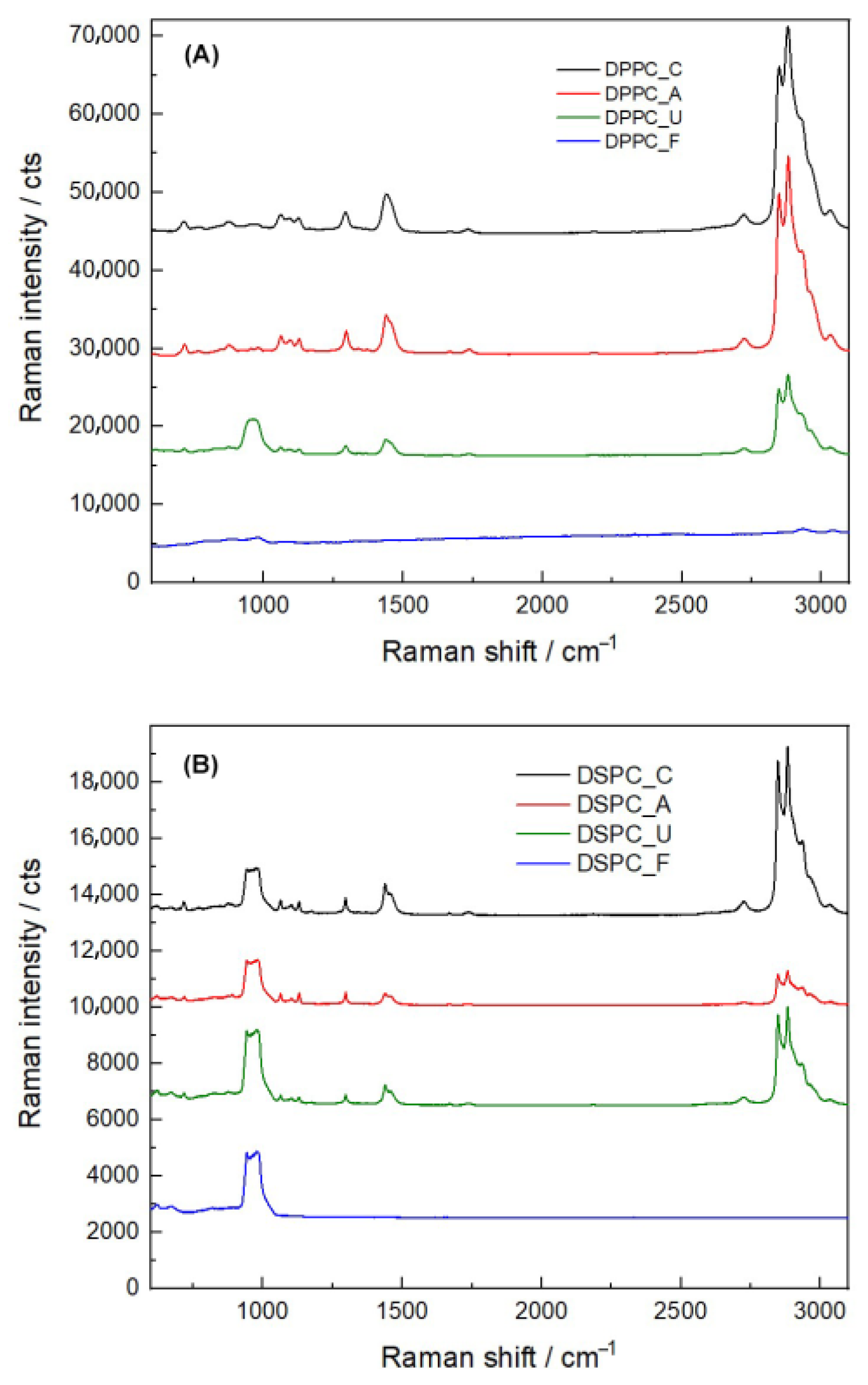
| Sterilization Treatments | Z-Average (d.nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPPC liposome | |||
| Control | 118.77 ± 0.65 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 43.92 ± 2.20 |
| Autoclaving | 103.80 ± 1.68 *** | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 44.17 ± 1.25 |
| UV irradiation | 117.83 ± 3.29 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 39.58 ± 7.89 |
| Filtration | 114.33 ± 2.38 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 28.21 ± 8.05 * |
| DSPC liposome | |||
| Control | 124.70 ± 1.82 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 56.67 ± 4.97 |
| Autoclaving | 108.10 ± 0.30 **** | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 57.98 ± 0.84 |
| UV irradiation | 128.10 ± 2.00 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 58.82 ± 1.09 |
| Filtration | 114.00 ± 1.71 *** | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 45.02 ± 0.40 ** |
| Sterilization Treatments | pH | |
|---|---|---|
| DPPC Liposomes | DSPC Liposome | |
| Control | 4.22 ± 0.02 | 4.68 ± 0.03 |
| Autoclaving | 4.06 ± 0.01 **** | 4.57 ± 0.03 ** |
| UV irradiation | 4.18 ± 0.01 * | 4.68 ± 0.02 |
| Filtration | 4.30 ± 0.02 *** | 4.52 ± 0.01 *** |
| Wavenumber (cm–1) | Assignment | |
|---|---|---|
| DPPC | DSPC | |
| 721 | 721 | CH2 rocking |
| 824 | 827 | P–O asymmetric stretching |
| 969 | 969 | CN asymmetric stretching, (CH3)3N+ |
| 1063 | 1062 | C–O–P stretching, CO–O–C symmetric stretching |
| 1089 | 1088 | PO2– symmetric stretching |
| 1163 | 1162 | CO–O–C asymmetric stretching |
| 1242 | 1236 | PO2– asymmetric stretching |
| 1377 | 1376 | CH3 symmetric bending |
| 1467 | 1467 | CH3 asymmetric bending, CH2 scissoring |
| 1734 | 1736 | C=O stretching |
| 2849 | 2849 | CH2 symmetric stretching |
| 2916 | 2915 | CH2 asymmetric stretching |
| 2955 | 2955 | CH3 asymmetric stretching |
| Sterilization Treatments | Phospholipid (mg/dL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPC Liposomes | Percentage (%) | DSPC Liposomes | Percentage (%) | |
| Control | 304.59 ± 7.47 | 100.00 | 251.36 ± 11.03 | 100.00 |
| Autoclaving | 268.89 ± 6.85 *** | 88.30 ± 2.52 | 248.92 ± 4.13 | 99.11 ± 2.73 |
| UV irradiation | 279.83 ± 1.38 ** | 91.91 ± 2.10 | 241.86 ± 2.97 | 96.32 ± 3.61 |
| Filtration | 181.27 ± 5.89 **** | 59.51 ± 1.04 | 58.70 ± 7.58 **** | 23.39 ± 3.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cherdchom, S.; Pongpirul, K.; Rimsueb, N.; Pienpinijtham, P.; Sereemaspun, A. Sterilization Effects on Liposomes with Varying Lipid Chains. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191478
Cherdchom S, Pongpirul K, Rimsueb N, Pienpinijtham P, Sereemaspun A. Sterilization Effects on Liposomes with Varying Lipid Chains. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(19):1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191478
Chicago/Turabian StyleCherdchom, Sarocha, Krit Pongpirul, Natchanon Rimsueb, Prompong Pienpinijtham, and Amornpun Sereemaspun. 2025. "Sterilization Effects on Liposomes with Varying Lipid Chains" Nanomaterials 15, no. 19: 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191478
APA StyleCherdchom, S., Pongpirul, K., Rimsueb, N., Pienpinijtham, P., & Sereemaspun, A. (2025). Sterilization Effects on Liposomes with Varying Lipid Chains. Nanomaterials, 15(19), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191478






