Preparation Methods and Multifunctional Applications of Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomedicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers
2.1. Main Parameters Affecting the Electrospinning Process
2.1.1. Solution Parameters
Polymer Concentration
Molecular Weight of Polymers
Viscosity
Conductivity
Surface Tension
2.1.2. Process Parameters
Applied Voltage
Flow Rate
Collecting Distance
2.1.3. Ambient Parameters
Temperature
Relative Humidity
2.2. Functionalization Methods of Electrospun Nanofibers
2.2.1. One-Step Functionalization
2.2.2. Post-Functionalization
3. Biomedical Applications of Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers
3.1. Antibacterial Activity
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effect
3.3. Tissue Regeneration and Repair
| Electrospun Polymers | Functional Additives | Application Area | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)/sodium alginate (CA) | Calcium chloride (CaCl2) | Skin tissue engineering | [132] |
| Pectin (Pec)/polyacrylic acid (PAA) | Platelet rich fibrin (PRF)/Simvastatin (SIM) | Skin tissue engineering | [138] |
| Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (PVDF-TrFE) | Hydroxyapatite (HAp) | Bone tissue engineering | [134] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) | Bone tissue engineering | [139] |
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) | Hydroxyapatite (HAP)/roxithromycin (ROX) | Bone tissue engineering | [140] |
| Polylactide (PLA) | Graphene oxide (GO)/parathyroid hormone (rhPTH(1–34)) | Bone tissue engineering | [141] |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene (P(VDF-TrFE)/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (pNIPAM) | Barium titanate piezoelectric nanoparticles (BTNPs)/nerve growth factor (NGF) | Nerve tissue engineering | [142] |
| Polylactic acid (PLA)/polyaniline (PAni) | - | Nerve tissue engineering | [143] |
| Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)/gelatin (Gel) | Laminin/polyaniline nanoparticles | Nerve tissue engineering | [137] |
| Silk fibroin (SF) | Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/transforming growth factor (TGF) inhibitor | Vascular tissue engineering | [144] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Bioactive glasses (BGs) | Vascular tissue engineering | [145] |
| Poly-D,L-lactide-co-glycolide (PLGA) | Small intestine submucosa (SIS) | Tendon tissue engineering | [146] |
| Poly(butyl cyanoacrylate) (PBCA) | Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs)/caseinphosphopeptides (CPP) | Tendon tissue engineering | [147] |
| Poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA) | L-Arginine (Arg)/hyaluronic acid (HA) | Tendon tissue engineering | [148] |
3.4. Drug Delivery Systems
| Electrospun Polymers | Functional Additives | Therapy Mode | Cancer Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(glycolide-ε-caprolactone)(PGCL)/poly(lactide-glycolide) (PLGA) | Paclitaxel (PTX)/docetaxel (DTX) | Chemotherapy | Prostate cancer | [164] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | Paclitaxel (PTX) | Chemotherapy | Cervicovaginal cancer | [153] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Irinotecan | Chemotherapy | Pancreatic cancer | [165] |
| Poly[(d,l)-lactide-co-glycolide] (PLGA) | Imiquimod/metronidazole | Chemotherapy | Cervical cancer | [166] |
| Cellulose acetate (CA)/poly (ethylene oxide) (PEO) | Disulfiram | Chemotherapy | Breast cancer/colon cancer | [167] |
| Poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA) | Bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3) nanoplates | Photothermal therapy | Skin fibroblast | [168] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Graphene oxide (GO) | Photothermal therapy | Breast cancer | [169] |
| poly (lactic acid) (PLA)/polycaprolactone (PCL) | Copper(I) sulfide (Cu2S) | Photothermal therapy | Skin cancer | [170] |
| Silk fibroin (SF)/poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) | Black phosphorus (BP) | Photothermal therapy | Liver cancer | [155] |
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)/poly(p-dioxanone) | Albumin–Ce6–MnO2 nanoparticles (ACM NPs) | Photodynamic therapy | Oesophageal cancer | [156] |
| Chitosan (CS) | SGP Photosens (PS) | Photodynamic therapy | Breast cancer | [171] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Doxorubicin (DOX)/curcumin (CUR)/Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) | Combination of chemotherapy and magnetic thermal therapy | Breast cancer | [172] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Doxorubicin (DOX)/iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) | Combination of chemotherapy and magnetic thermal therapy | Cervical cancer | [154] |
| Gelatin (Gel) | Dihydromyricetin (DMY)/Copper Sulfide (CuS) | Combination of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy | Liver cancer | [157] |
| Polyurethane urea (PolyCEGS) | paclitaxel (PTX)/gold nanorods (AuNRs) | Combination of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy | Breast cancer/colon cancer | [158] |
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)/poly (D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) | Doxorubicin (DOX)/pyrrole | Combination of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy | Breast cancer/colon cancer | [173] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL)/polylactic acid(PLA) | Curcumin (CUR)/polydopamine (PDA) | Combination of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | [159] |
| Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)/Eudragit L100-55 | Carmofur (CAR)/rose bengal (RB) | Combination of chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy | Colon cancer | [174] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Natural melanin nanoparticles (MNPs) | Combination of chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy | Malignant melanoma | [175] |
3.5. Sensors
3.5.1. Applications of Sensors in Biomarker Detection
3.5.2. Applications of Sensors in Wearable Devices
3.6. Other Special Functions
4. Challenges and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lian, S.; Lamprou, D.; Zhao, M. Electrospinning technologies for the delivery of biopharmaceuticals: Current status and future trends. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 651, 123641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, N.; Stanger, J.J.; Staiger, M.P.; Razzaq, H.; Hofman, K. The history of the science and technology of electrospinning from 1600 to 1995. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lu, Y.; Han, H.; Yan, Z.; Chen, J. Solid-state electrolytes by electrospinning techniques for lithium batteries. Small 2024, 20, e2309801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Wang, Z.; Reddy, V.S.; Nagy, Z.K.; Vass, P.; Buzgo, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Radacsi, N. The history of electrospinning: Past, present, and future developments. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owida, H.A.; Al-Nabulsi, J.I.; Alnaimat, F.; Al-Ayyad, M.; Turab, N.M.; Al Sharah, A.; Shakur, M. Recent applications of electrospun nanofibrous scaffold in tissue engineering. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2022, 2022, 1953861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serik, A.; Idrissov, N.; Baratov, A.; Dikov, A.; Kislitsin, S.; Daulbayev, C.; Kuspanov, Z. Recent progress in photocatalytic applications of electrospun nanofibers: A review. Molecules 2024, 29, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Roh, S.; Nguyen, M.T.N.; Lee, J.S. Structural control of nanofibers according to electrospinning process conditions and their applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramarkou, M.; Tzegiannakis, I.; Christoforidi, E.; Krokida, M. Use of electrospinning for sustainable production of nanofibers: A comparative assessment of smart textiles-related applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhljar, L.; Ambrus, R. Electrospinning of potential medical devices (wound dressings, tissue engineering scaffolds, face masks) and their regulatory approach. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Sanjay, M.R.; Srisuk, R.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. A comprehensive review on chemical properties and applications of biopolymers and their composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, M.H.; Khan, M.M.R.; Zahari, M.; Beg, M.D.H.; Abdullah, N. Current issues and potential solutions for the electrospinning of major polysaccharides and proteins: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.N.; Khan, M.Q.; Nguyen, N.T.; Phan, T.T.; Ullah, A.; Khatri, M.; Kien, N.N.; Kim, I.S. A review on the fabrication of several carbohydrate polymers into nanofibrous structures using electrospinning for removal of metal ions and dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Ma, B.; He, C.; Guo, X.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. A review: Current status and emerging developments on natural polymer-based electrospun fibers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, e2200456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Kuang, H.; You, Z.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering with drug loading and release. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phutane, P.; Telange, D.; Agrawal, S.; Gunde, M.; Kotkar, K.; Pethe, A. Biofunctionalization and applications of polymeric nanofibers in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Polymers 2023, 15, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Guan, M.; Bian, Y.; Yin, X. Multifunctional electrospun nanofibers for biosensing and biomedical engineering applications. Biosensors 2023, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Zhou, J.; Du, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Incorporating charged Ag@MOFs to boost the antibacterial and filtration properties of porous electrospinning polylactide films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Bai, T.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, D.; Yu, S.; Zheng, Y. Biomimetic AgNPs@antimicrobial peptide/silk fibroin coating for infection-trigger antibacterial capability and enhanced osseointegration. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, K.F.; Williams, R.J.; Nisbet, D.R. Dynamic and responsive growth factor delivery from electrospun and hydrogel tissue engineering materials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Chiu, C.-W. Facile fabrication of a stretchable and flexible nanofiber carbon film-sensing electrode by electrospinning and its application in smart clothing for ecg and emg monitoring. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Li, P.; Yang, Z.; Mi, Q.; Yu, L. Electrospinning of flexible poly(vinyl alcohol)/mxene nanofiber-based humidity sensor self-powered by monolayer molybdenum diselenide piezoelectric nanogenerator. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braghirolli, D.I.; Steffens, D.; Pranke, P. Electrospinning for regenerative medicine: A review of the main topics. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Lin, X.; Ee, L.Y.; Li, S.F.Y.; Huang, M. A review on electrospinning as versatile supports for diverse nanofibers and their applications in environmental sensing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2023, 5, 429–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, F.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ajayi, A.O.; Quick, Q.; Mu, R. Optimization of electrospinning parameters for lower molecular weight polymers: A case study on polyvinylpyrrolidone. Polymers 2024, 16, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuchaeva, A.A.; Timchenko, T.P.; Karpova, E.V.; Vladimirov, S.V.; Soynov, I.A.; Zhuravleva, I.Y. Effects of electrospinning parameter adjustment on the mechanical behavior of poly-ε-caprolactone vascular scaffolds. Polymers 2022, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, L.; Satpathy, M.; Duan, Y. Effect of electrospinning parameters on the fiber diameter and morphology of plga nanofibers. Dent. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2021, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; White, K.L.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning polymer nanofibers with controlled diameters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 5239–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, B.A.; Krishnaswamy, M.; Xu, H.; Hoque, M.E. Electrospinning of biomedical nanofibers/nanomembranes: Effects of process parameters. Polymers 2022, 14, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Baldursdottir, S.G.; Aho, J.; Qu, H.; Christensen, L.P.; Rantanen, J.; Yang, M. Electrospinnability of poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (plga): The role of solvent type and solvent composition. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 34, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigani, B.; Rossi, S.; Milanesi, G.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Sandri, G.; Bruni, G.; Ferrari, F. Electrospun alginate fibers: Mixing of two different poly(ethylene oxide) grades to improve fiber functional properties. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Aho, J.; Baldursdottir, S.; Bohr, A.; Qu, H.; Christensen, L.P.; Rantanen, J.; Yang, M. The effect of poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid composition on the mechanical properties of electrospun fibrous mats. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refate, A.; Mohamed, Y.; Mohamed, M.; Sobhy, M.; Samhy, K.; Khaled, O.; Eidaroos, K.; Batikh, H.; El-Kashif, E.; El-Khatib, S.; et al. Influence of electrospinning parameters on biopolymers nanofibers, with emphasis on cellulose & chitosan. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezarati, R.M.; Eifert, M.B.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Effects of humidity and solution viscosity on electrospun fiber morphology. Tissue Eng. Part C-Methods 2013, 19, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren Boncu, T.; Ozdemir, N.; Uskudar Guclu, A. Electrospinning of linezolid loaded plga nanofibers: Effect of solvents on its spinnability, drug delivery, mechanical properties, and antibacterial activities. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.Y.; Chang, N.Y.; Li, C.; Chan, V.; Hsieh, J.H.; Tsai, Y.H.; Lin, T. Fabrication of gelatin nanofibers by electrospinning-mixture of gelatin and polyvinyl alcohol. Polymers 2022, 14, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Janković, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oviedo, M.; Montoya, Y.; Agudelo, W.; García-García, A.; Bustamante, J. Effect of molecular weight and nanoarchitecture of chitosan and polycaprolactone electrospun membranes on physicochemical and hemocompatible properties for possible wound dressing. Polymers 2021, 13, 4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Herrero, M.; Gómez-Tejedor, J.A.; Vallés-Lluch, A. Role of electrospinning parameters on poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and poly(caprolactone-co-glycolic acid) membranes. Polymers 2021, 13, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítková, L.; Musilová, L.; Achbergerová, E.; Minařík, A.; Smolka, P.; Wrzecionko, E.; Mráček, A. Electrospinning of hyaluronan using polymer coelectrospinning and intermediate solvent. Polymers 2019, 11, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, M.A.; Khalil, B.I.; Hameed, A.A. Characterizing optimum electrospinning conditions for graft urethanized poly(vinyl alcohol)(u-pva). Heliyon 2022, 8, e11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.; Um, I.C. Effect of relative humidity on the electrospinning performance of regenerated silk solution. Polymers 2021, 13, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Stachewicz, U. The impact of relative humidity on electrospun polymer fibers: From structural changes to fiber morphology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Tailoring the grooved texture of electrospun polystyrene nanofibers by controlling the solvent system and relative humidity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Controlling the secondary surface morphology of electrospun pvdf nanofibers by regulating the solvent and relative humidity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Ma, K.; Wei, Z.; Ran, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes meet antibacterial nanomaterials: From preparation strategies to biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 42, 478–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. Antibacterial biohybrid nanofibers for wound dressings. Acta Biomater. 2020, 107, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzgo, M.; Mickova, A.; Rampichova, M.; Doupnik, M. Blend electrospinning, coaxial electrospinning, and emulsion electrospinning techniques. In Core-Shell Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Theranostics; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 325–347. [Google Scholar]
- Kutikov, A.B.; Song, J. An amphiphilic degradable polymer/hydroxyapatite composite with enhanced handling characteristics promotes osteogenic gene expression in bone marrow stromal cells. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8354–8364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, S.A.; Nadhim, B.A.; Kadhim, B.J.; Ktab, M.S.; Kadhim, A.J.; Murad, F.S. Improving the physical properties of nanofibers prepared by electrospinning from polyvinyl chloride and polyacrylonitrile at low concentrations. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2023, 2023, 1811577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tobías, H.; Morales, G.; Grande, D. Comprehensive review on electrospinning techniques as versatile approaches toward antimicrobial biopolymeric composite fibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 101, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, S.; Anyfantakis, M.; Honaker, L.W.; Basoli, F.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Stable electrospinning of core-functionalized coaxial fibers enabled by the minimum-energy interface given by partial core-sheath miscibility. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13265–13277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyuchyuk, S.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Core-sheath fibers via single-nozzle spinneret electrospinning of emulsions and homogeneous blend solutions. Materials 2024, 17, 5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Yang, X.; Che, X.; Yang, M.; Zhai, G. Biomedical application and controlled drug release of electrospun fibrous materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 90, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, A.J.; Germershaus, O.; Luhmann, T.; Merkle, H.P.; Meinel, L. Electrospun matrices for localized drug delivery: Current technologies and selected biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luraghi, A.; Peri, F.; Moroni, L. Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: A review. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Su, Q.; Liu, W.; Lim, M.; Venugopal, J.R.; Mo, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M. Controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein 2 and dexamethasone loaded in core-shell pllacl-collagen fibers for use in bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadian, M.; Chan, K.V.; Norouzi, M.; Grande, S.; Cools, P.; Morent, R.; De Geyter, N. Fabrication and plasma modification of nanofibrous tissue engineering scaffolds. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopuk, B.; Gunes, R.; Palabiyik, I. Cold plasma modification of food macromolecules and effects on related products. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cassan, D.; Sydow, S.; Schmidt, N.; Behrens, P.; Roger, Y.; Hoffmann, A.; Hoheisel, A.L.; Glasmacher, B.; Hänsch, R.; Menzel, H. Attachment of nanoparticulate drug-release systems on poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers via a graftpolymer as interlayer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 163, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, N.I.; Marincaș, L.; Barabás, R.; Bizo, L.; Ilea, A.; Turdean, G.L.; Toșa, M.; Cadar, O.; Barbu-Tudoran, L. Preparation and characterization of doxycycline-loaded electrospun pla/hap nanofibers as a drug delivery system. Materials 2022, 15, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aijaz, M.O.; Alnaser, I.A.; Haque Siddiqui, M.I.; Karim, M.R. The integration of microwave-synthesized silver colloidal nanoparticles into poly (lactic acid)-based textiles as antimicrobial agents via pre- and post-electrospinning processes. Polymers 2024, 16, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapossa, A.B.; da Silva Júnior, A.H.; de Oliveira, C.R.S.; Mhike, W. Thermal, morphological and mechanical properties of multifunctional composites based on biodegradable polymers/bentonite clay: A review. Polymers 2023, 15, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Gu, P.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Fan, J.; Bai, Y. Instant and multifunctional nanofibers loaded with proanthocyanidins and hyaluronic acid for skincare applications. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y. Application of electrospinning in antibacterial field. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, S.; Kaur, H.; Singh, J.; Matharu, A.S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Bechelany, M. Recent advances in green synthesis of ag nps for extenuating antimicrobial resistance. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Li, J.; Sun, Z. The combination of antibiotic and non-antibiotic compounds improves antibiotic efficacy against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.; Gallus, I.; Tegginamath, A.; Maryska, J.; Yalcinkaya, F. Electrospun antibacterial nanomaterials for wound dressings applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Hong, M.; Xie, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Xie, S. Progress and prospects of nanomaterials against resistant bacteria. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Qian, Y.; Haghayegh, M.; Xia, Y.; Yang, S.; Cao, R.; Zhu, M. Electrospun organic/inorganic hybrid nanofibers for accelerating wound healing: A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 3171–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Forghani, F.; Kong, X.; Liu, D.; Ye, X.; Chen, S.; Ding, T. Antibacterial applications of metal-organic frameworks and their composites. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1397–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, M.; Andishmand, H.; Assadpour, E.; Barzegar, A.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Jafari, S.M. Nanoliposomal delivery systems of natural antibacterial compounds; properties, applications, and recent advances. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 6498–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.; Lee, R.E.; Brötz-Oesterhelt, H.; Hiller, S.; Rodnina, M.V.; Schneider, T.; Weingarth, M.; Wohlgemuth, I. Sophisticated natural products as antibiotics. Nature 2024, 632, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Dhingra, S.; Banerjee, A.; Saha, S.; Bhattacharyya, J.; Satapathy, B.K. Designing suture-proof cell-attachable copolymer-mediated and curcumin- β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex loaded aliphatic polyester-based electrospun antibacterial constructs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Liu, J. Mechanistic understanding of the effect of zein-chlorogenic acid interaction on the properties of electrospun nanofiber films. Food Chem. 2022, 16, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlířová, R.; Langová, D.; Bendová, A.; Gross, M.; Skoumalová, P.; Márová, I. Antimicrobial activity of gelatin nanofibers enriched by essential oils against cutibacterium acnes and staphylococcus epidermidis. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Q.; Lee, H.; Khatri, Z.; Kharaghani, D.; Khatri, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Im, S.S.; Kim, I.S. Fabrication and characterization of nanofibers of honey/poly(1,4-cyclohexane dimethylene isosorbide trephthalate) by electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 81, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, B.; Bo, L.; Chen, Z.S.; Yang, H.; Sun, L. Antimicrobial peptides for combating drug-resistant bacterial infections. Drug Resist. Updates 2023, 68, 100954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Potentials and perspectives for active food packaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Huang, X.; Kou, X. Antibacterial aroma compounds as property modifiers for electrospun biopolymer nanofibers of proteins and polysaccharides: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameen, D.E.; Ahmed, S.; Lu, R.; Li, R.; Dai, J.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, Y. Electrospun nanofibers food packaging: Trends and applications in food systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6238–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allizond, V.; Banche, G.; Salvoni, M.; Malandrino, M.; Cecone, C.; Cuffini, A.M.; Bracco, P. Facile one-step electrospinning process to prepare agnps-loaded pla and pla/peo mats with antibacterial activity. Polymers 2023, 15, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Cui, C.; Sun, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, S.; Ma, J.; Li, C.M. Electrospun zno-loaded chitosan/pcl bilayer membranes with spatially designed structure for accelerated wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 282, 119131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Huang, C.L.; Lai, R.Y.; Zhuang, C.H.; Chiu, W.H.; Lee, K.M. Microstructure and biological properties of electrospun in situ polymerization of polycaprolactone-graft-polyacrylic acid nanofibers and its composite nanofiber dressings. Polymers 2021, 13, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, D.; Tang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, P.; Zhong, Q.; Ning, Y.; Lei, M.; et al. Nir-responsive electrospun nanofiber dressing promotes diabetic-infected wound healing with programmed combined temperature-coordinated photothermal therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, A.; Qin, Z.; Li, Y.; Xianyu, Y.; Zhang, H. Covalent organic framework-incorporated nanofibrous membrane as an intelligent platform for wound dressing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 8680–8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbhnsawi, N.A.; Elwakil, B.H.; Hassanin, A.H.; Shehata, N.; Elshewemi, S.S.; Hagar, M.; Olama, Z.A. Nano-chitosan/eucalyptus oil/cellulose acetate nanofibers: Manufacturing, antibacterial and wound healing activities. Membranes 2023, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xing, W.; Li, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Tang, J. In situ growth of zif-8 nanoparticles on pure chitosan nanofibrous membranes for efficient antimicrobial wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 297, 139921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lao, J.; Wang, L. Integrating porphyrinic metal-organic frameworks in nanofibrous carrier for photodynamic antimicrobial application. Polymers 2021, 13, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Fu, X.; Lucas, T.; Zhao, H.; Chen, C.; Dubail, I.; Chen, Y.; Patriarche, G.; Gateau, J.; Gazeau, F.; et al. Mof-enhanced phototherapeutic wound dressings against drug-resistant bacteria. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e2402418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Lv, X.; Chen, J.; Wei, M.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, C.; et al. Gelatin-based nanofiber membranes loaded with curcumin and borneol as a sustainable wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, C.; Girón-Hernández, J.; Honey, D.A.; Fox, E.M.; Cassa, M.A.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Camagnola, I.; Gentile, P. Synergistic nanocoating with layer-by-layer functionalized pcl membranes enhanced by manuka honey and essential oils for advanced wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lan, X.; Leung, P.H.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Xie, M.; Han, Y.; Lin, X. Composite membranes of recombinant silkworm antimicrobial peptide and poly (l-lactic acid) (plla) for biomedical application. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhao, P.; Song, W.; Wang, M.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun zein/polyoxyethylene core-sheath ultrathin fibers and their antibacterial food packaging applications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Dong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; He, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, W.; Hu, Z.; et al. Emerging starch composite nanofibrous films for food packaging: Facile construction, hydrophobic property, and antibacterial activity enhancement. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yu, M.; Ren, R.; Wang, H.; Kong, B. Thymol incorporation within chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers by concurrent coaxial electrospinning and in-situ crosslinking from core-out for active antibacterial packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Li, D.; Mai, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, W.; Lai, C.; Dong, X.; Tong, R.; Cao, Y.; Cao, Q.; et al. In-situ electrospinning pvb/camellia oil/ZnO-TiO2 nanofibrous membranes with synergistic antibacterial and degradation of ethylene applied in fruit preservation. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Dwibedi, V.; Huang, H.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, T. Preparation and antibacterial mechanism of cinnamaldehyde/tea polyphenol/polylactic acid coaxial nanofiber films with zinc oxide sol to shewanella putrefaciens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 237, 123932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.G.; Li, D.H.; Kong, Y.M.; Zhang, R.R.; Gu, Q.; Hu, M.X.; Tian, S.Y.; Jin, W.G. Enhanced antibacterial efficacy and mechanism of octyl gallate/beta-cyclodextrins against pseudomonas fluorescens and vibrio parahaemolyticus and incorporated electrospun nanofibers for chinese giant salamander fillets preservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 361, 109460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Guo, X.; Duo, Y.; Qian, X. Preparation and characterization of a one-step electrospun poly(lactic acid)/wormwood oil antibacterial nanofiber membrane. Polymers 2023, 15, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Wang, W.; Peng, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.; Sun, H.; Duan, X. Electrospun Fe3O4-chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous film for improved capture and elimination of foodborne pathogens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, S.; Sengodan, P.; Saravanan, A.; Vickram, S.; Chopra, H. Antibacterial food packaging using biocompatible nickel oxide-infused cellulose acetate electrospun nanofibers. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, K.R.; Mahajan, U.B.; Unger, B.S.; Goyal, S.N.; Belemkar, S.; Surana, S.J.; Ojha, S.; Patil, C.R. Animal models of inflammation for screening of anti-inflammatory drugs: Implications for the discovery and development of phytopharmaceuticals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, F.; Luo, H.; Xu, G.; Wang, D. Inflammatory microenvironment of skin wounds. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 789274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, L.; Bai, L.; Li, M.; Guo, T.; Tian, B.; He, Z.; Fu, Q. Inflammatory microenvironment-targeted nanotherapies. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, H.; Su, M.; Wang, Y. Macrophage polarization: An important role in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadomoto, S.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. Macrophage polarity and disease control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, L. Electrospun nanofiber membranes with various structures for wound dressing. Materials 2023, 16, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.; Ni, D.; Wu, J.; Peng, X. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative electrospun nanofiber membrane promotes diabetic wound healing via macrophage modulation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, D.; Huang, X.; Wei, Y.; Tang, F.; Qin, X.; Liang, W.; Liang, Z.; Jin, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Puerarin-loaded electrospun patches with anti-inflammatory and pro-collagen synthesis properties for pelvic floor reconstruction. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2308590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, L.M.; de Carvalho, A.B.G.; Anselmi, C.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Dal-Fabbro, R.; Basso, F.G.; Bottino, M.C. Bifunctional naringenin-laden gelatin methacryloyl scaffolds with osteogenic and anti-inflammatory properties. Dent. Mater. 2024, 40, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, B.; El-Newehy, M.; Abdulhameed, M.M.; Fang, B.; Mo, X. Aspirin-loaded anti-inflammatory zno-sio(2) aerogel scaffolds for bone regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 17092–17108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paymanpour, P.; Anselmi, C.; Cardoso, L.M.; de Carvalho, A.B.G.; Soares, I.P.M.; Hebling, J.; Dal-Fabbro, R.; Bottino, M.C. Anti-inflammatory potential of casein enzymatic hydrolysate/gelatin methacryloyl scaffolds for vital pulp therapy. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Huang, W.; Shen, B.; Qi, D.; Mao, Z.; Wu, J. Composite nanofibrous dressing loaded with prussian blue and heparin for anti-inflammation therapy and diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Hu, Y.; Chang, L.; Xu, S.; Mei, X.; Chen, Z. Electrospinning of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory Ag@hesperidin core-shell nanoparticles into nanofibers used for promoting infected wound healing. Regen. Biomater. 2022, 9, rbac012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte-Werning, L.V.; Murugaiah, A.; Singh, B.; Johannessen, M.; Engstad, R.E.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; Holsæter, A.M. Multifunctional nanofibrous dressing with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties prepared by needle-free electrospinning. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Salinas, S.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Gámez-Herrera, E.; Arruebo, M.; Irusta, S.; Taraballi, F.; Mendoza, G.; Tasciotti, E. Electrospun anti-inflammatory patch loaded with essential oils for wound healing. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 577, 119067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.N.; Peng, Z.X.; Chen, N.B.; Liu, C.B.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.Q. Multifunctional electrospinning polyhydroxyalkanoate fibrous scaffolds with antibacterial and angiogenesis effects for accelerating wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Ding, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Ma, S.; Ding, Q.; Liu, W. Polyvinylpyrrolidone/chitosan-loaded dihydromyricetin-based nanofiber membrane promotes diabetic wound healing by anti-inflammatory and regulating autophagy-associated protein expression. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. A straightforward approach towards antibacterial and anti-inflammatory multifunctional nanofiber membranes with sustained drug release profiles. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, e2200150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, J.; Bao, Y.; Cheng, B.; Chen, S.; Du, J.; Hu, S. Magnolol hybrid nanofibrous mat with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and microvascularized properties for wound treatment. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Liang, S.; Lin, P.; Lai, X.; Lan, X.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y.; Gao, B. Phase change material-embedded multifunctional janus nanofiber dressing with directional moisture transport, controlled release of anti-inflammatory drugs, and synergistic antibacterial properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 52244–52261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Ren, X.; Yuan, H.; Lv, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Multifunctional porous poly (l-lactic acid) nanofiber membranes with enhanced anti-inflammation, angiogenesis and antibacterial properties for diabetic wound healing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, M.Z.A.; Nordin, D.; Shaari, N.; Kamarudin, S.K. Overview of electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Yeo, M.; Yang, G.H.; Kim, G. Cell-electrospinning and its application for tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yu, X.; Shen, Y.; Sun, B.; Guo, W.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Shafiq, M.; et al. Electrospinning inorganic nanomaterials to fabricate bionanocomposites for soft and hard tissue repair. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.B.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shah, A.H.; Husain, S.; Rehman, I.U. Electrospinning of chitosan-based solutions for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Mele, E. Electrospinning and additive manufacturing: Adding three-dimensionality to electrospun scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 674738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottoli, E.M.; Dorati, R.; Genta, I.; Chiesa, E.; Pisani, S.; Conti, B. Skin wound healing process and new emerging technologies for skin wound care and regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria Molina, M.I.; Chen, C.A.; Martinez, J.; Tran, P.; Komvopoulos, K. Novel electrospun polycaprolactone/calcium alginate scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Materials 2022, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Nie, M.; Li, Y. Current advances and future perspectives of advanced polymer processing for bone and tissue engineering: Morphological control and applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 895766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, F.; Garrudo, F.F.F.; Alberte, P.S.; Resina, L.; Carvalho, M.S.; Jain, A.; Marques, A.C.; Estrany, F.; Rawson, F.J.; Aléman, C.; et al. Hydroxyapatite-filled osteoinductive and piezoelectric nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2023, 24, 2242242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Sun, B.; Wu, T.; Li, D. Electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering. In Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 719–734. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Jiang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, L. Electrospun gelatin-based biomimetic scaffold with spatially aligned and three-layer architectures for vascular tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamanifard, M.; Khorasani, M.T.; Daliri, M. Hybrid electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate/gelatin/laminin/polyaniline scaffold for nerve tissue engineering application: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro assay. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, M.; Al-Musawi, M.H.; Kalali, A.; Shekarchizadeh, A.; Kaviani, Y.; Mansouri, A.; Nasiri-Harchegani, S.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Sharifianjazi, F.; Sattar, M.; et al. Platelet rich fibrin and simvastatin-loaded pectin-based 3d printed-electrospun bilayer scaffold for skin tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica Oprea, A.E.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Gherasim, O.; Ficai, A.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Oprea, O.C.; Vasile, B.; Balta, C.; Andronescu, E.; Hermenean, A.O. Electrospun fibrous silica for bone tissue engineering applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tang, L.; Gao, B.; Tang, Y. Antibacterial and osteogenic dual-functional micronano composite scaffold fabricated via melt electrowriting and solution electrospinning for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 37707–37721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Yao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J. Graphene oxide/rhpth(1-34)/polylactide composite nanofibrous scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Fu, S.; Zhang, H.; Lu, W.; Xie, J.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, R. Ultrasound-responsive aligned piezoelectric nanofibers derived hydrogel conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2307896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ghobeira, R.; Aliakbarshirazi, S.; Morent, R.; De Geyter, N. Polylactic acid/polyaniline nanofibers subjected to pre- and post-electrospinning plasma treatments for refined scaffold-based nerve tissue engineering applications. Polymers 2022, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Rütten, S.; Buhl, E.M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Rojas-González, D.M.; Mela, P. Development of a silk fibroin-small intestinal submucosa small-diameter vascular graft with sequential vegf and tgf-β1 inhibitor delivery for in situ tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, e2300184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasvand, N.; Behnamghader, A.; Milan, P.B.; Simorgh, S.; Mobasheri, A.; Mozafari, M. Tissue-engineered small-diameter vascular grafts containing novel copper-doped bioactive glass biomaterials to promote angiogenic activity and endothelial regeneration. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Do, S.; Kim, H. Potential of aligned electrospun plga/sis blended nanofibrous membrane for tendon tissue engineering. Polymers 2023, 15, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, E.; Vigani, B.; Ruggeri, M.; Del Favero, E.; Ricci, C.; Grisoli, P.; Ferraretto, A.; Rossi, S.; Viseras, C.; Sandri, G. Electrospun scaffolds based on poly(butyl cyanoacrylate) for tendon tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Li, N.; Sun, L.; Xue, Y.; Guan, H.; Yuan, H. Dual-bioactive molecules loaded aligned core-shell microfibers for tendon tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 228, 113416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Ramakrishna, S. Advances in drug delivery via electrospun and electrosprayed nanomaterials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2997–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadi, M.; Forootanfar, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Regenerative medicine and drug delivery: Progress via electrospun biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 109, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebian, S.; Foroughi, J.; Wade, S.J.; Vine, K.L.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Mehrali, M.; Conde, J.; Wallace, G.G. Biopolymers for antitumor implantable drug delivery systems: Recent advances and future outlook. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liang, Z.; Guo, J.; Chen, B.; Zhou, S.; Yu, D. Application of electrospun drug-loaded nanofibers in cancer therapy. Polymers 2024, 16, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Chen, H.; Qi, C.; Lv, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. A novel electrospun nanofiber system with pegylated paclitaxel nanocrystals enhancing the transmucus permeability and in situ retention for an efficient cervicovaginal cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 650, 123660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serio, F.; Silvestri, N.; Kumar Avugadda, S.; Nucci, G.E.P.; Nitti, S.; Onesto, V.; Catalano, F.; D’Amone, E.; Gigli, G.; Del Mercato, L.L.; et al. Co-loading of doxorubicin and iron oxide nanocubes in polycaprolactone fibers for combining magneto-thermal and chemotherapeutic effects on cancer cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H.; Dai, F.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Electrospun silk fibroin/polylactic-co-glycolic acid/black phosphorus nanosheets nanofibrous membrane with photothermal therapy potential for cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Cheng, L.; Fang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, R.; Tang, W.; Zhong, X.; Lu, Y.; Deng, L.; et al. Nanoparticle-embedded electrospun fiber-covered stent to assist intraluminal photodynamic treatment of oesophageal cancer. Small 2019, 15, e1904979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, T.; Xing, J.; Ge, R.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun medicated gelatin/polycaprolactone janus fibers for photothermal-chem combined therapy of liver cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 132113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorana, A.; Puleo, G.; Miceli, G.C.; Cancilla, F.; Licciardi, M.; Pitarresi, G.; Tranchina, L.; Marrale, M.; Palumbo, F.S. Redox/nir dual-responsive glutathione extended polyurethane urea electrospun membranes for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 669, 125108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lei, S.; Ning, Y.; Zhou, L.; Guo, Y.; Xu, R.; Wu, J. Injectable polydopamine/curcumin dual-modified polylactic acid/polycaprolactone coaxial staple fibers for chronotropic treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhl, D.L.; Mohanraj, D.; Nelson, D.W.; Gilbert, R.J. Designing electrospun fiber platforms for efficient delivery of genetic material and genome editing tools. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 183, 114161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, M.; Tang, S. Co-delivery of sirna and cisplatin via electrospun nanofibrous membranes for synergistic treatment of malignant melanoma. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Sun, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, G.; et al. Genetically engineered electrospinning contributes to spinal cord injury repair by regulating the immune microenvironment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1415527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, Z.; Tao, Z.; Pavel, V.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Cui, W.; Liu, S. Unidirectional gene delivery electrospun fibrous membrane via charge repulsion for tendon repair. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 37, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska, J.; Orchel, A.; Kaps, A.; Jaworska-Kik, M.; Hercog, A.; Stojko, M.; Włodarczyk, J.; Musiał-Kulik, M.; Pastusiak, M.; Bochenek, M.; et al. Bioresorbable nonwoven patches as taxane delivery systems for prostate cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeda-Franco, C.; Mitxelena-Iribarren, O.; Calero-Castro, F.J.; Astigarraga, M.; Castillo-Tuñon, J.M.; Laga, I.; Pereira, S.; Arana, S.; Mujika, M.; Padillo-Ruiz, J. Tartessus: A customized electrospun drug delivery system loaded with irinotecan for local and sustained chemotherapy release in pancreatic cancer. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Chiu, C.F.; Wang, C.N.; Lin, C.C.; Shen, C.R.; Yao, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Liu, S.J. Conglomerated imiquimod and metronidazole incorporated biodegradable nanofibrous mats for potential therapy of cervical cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Fawal, G.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; El-Gendi, H.; El-Fakharany, E.M. Fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation of disulfiram-loaded cellulose acetate/poly(ethylene oxide) nanofiber scaffold for breast and colon cancer cell lines treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 204, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Luo, Q.; Yu, X.F.; Chu, P.K. 2d material-based nanofibrous membrane for photothermal cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, N.; Scialabba, C.; Pitarresi, G.; Giammona, G. Enhanced adhesion and in situ photothermal ablation of cancer cells in surface-functionalized electrospun microfiber scaffold with graphene oxide. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lv, F.; Li, T.; Han, Y.; Yi, Z.; Liu, M.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Electrospun micropatterned nanocomposites incorporated with cu(2)s nanoflowers for skin tumor therapy and wound healing. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11337–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severyukhina, A.N.; Petrova, N.V.; Smuda, K.; Terentyuk, G.S.; Klebtsov, B.N.; Georgieva, R.; Bäumler, H.; Gorin, D.A. Photosensitizer-loaded electrospun chitosan-based scaffolds for photodynamic therapy and tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 144, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Nabil, A.; Fujisawa, N.; Oe, E.; Li, K.; Ebara, M. A facile, flexible, and multifunctional thermo-chemotherapy system for customized treatment of drug-resistant breast cancer. J. Control. Release 2023, 363, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanom, J.; Rezk, A.I.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Near-infrared responsive synergistic chemo-phototherapy from surface-functionalized poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) composite nanofibers for postsurgical cancer treatment. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sanchez-Vazquez, B.; Trindade, R.P.; Zou, Q.; Mai, Y.; Dou, L.; Zhu, L.M.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun oral formulations for combined photo-chemotherapy of colon cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabay, G.; Meydan, A.E.; Eom, T.; Shim, B.S.; Mutlu, M.; Kaleli-Can, G. Stimuli-responsive nanoparticle-nanofiber hybrids for drug delivery and photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulanicki, A.; Glab, S.; Ingman, F. Chemical sensors: Definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi-Khorrami, V.; Rahmanian-Devin, P.; Fadaei, M.R.; Movaffagh, J.; Askari, V.R. Advanced applications of smart electrospun nanofibers in cancer therapy: With insight into material capabilities and electrospinning parameters. Int. J. Pharm. X 2024, 8, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J. Fabrication of Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers with Diverse Morphologies. Molecules 2019, 24, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Fusco, G.; Tortolini, C.; Sanzò, G.; Favero, G.; Gorton, L.; Antiochia, R. Beyond graphene: Electrochemical sensors and biosensors for biomarkers detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paimard, G.; Shahlaei, M.; Moradipour, P.; Akbari, H.; Jafari, M.; Arkan, E. An impedimetric immunosensor modified with electrospun core-shell nanofibers for determination of the carcinoma embryonic antigen. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 311, 127928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobalu, K.; Vasudevan, M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Perumal, V.; Ovinis, M. Molybdenum disulphide/cellulose acetate nanofiber composite on screen printed electrodes for detecting cardiac troponin by electrical impedance spectroscopy. Cellulose 2021, 28, 5761–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.; Dong, H.; Chu, Z. Freestanding nanofiber-assembled aptasensor for precisely and ultrafast electrochemical detection of alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2304355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Li, M.; Li, D.; Shi, B.; Zhong, R.; Zhao, Y.; Tai, Q.; He, S.; Dong, Q. Schottky interface enabled electrospun rhodium oxide doped gold for both ph sensing and glucose measurements in neutral buffer and human serum. Langmuir 2024, 40, 20797–20810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-Y.; Song, J.; Jiang, R.-L.; Dai, J.; Xu, K.; Yang, X.-L.; Xie, M.-H. Construction of TiO2@ZnO nanofibers with beads-on-a-string heterostructures for photoelectrochemical detection of lactic acid. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, T.R.; Choi, J.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Krishnan, S.; Gutruf, P.; Tian, L.; Ghaffari, R.; Rogers, J.A. Bio-Integrated Wearable Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5461–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Pradhan, G.B.; Jeong, S.; Zhang, S.; Song, H.; Park, J.Y. Stretchable and all-directional strain- insensitive electronic glove for robotic skins and human-machine interfacing. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 8355–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Shin, H.S.; Kim, J.-W. Convolution neural networks for motion detection with electrospun reversibly-cross-linkable polymers and encapsulated ag nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 47591–47603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preda, M.D.; Popa, M.L.; Neacșu, I.A.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Ginghină, O. Antimicrobial Clothing Based on Electrospun Fibers with ZnO Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ahmed, A.; Xu, L. Electrospun Nanofibers for Functional Food Packaging Application. Materials 2023, 16, 5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y. Photocatalytic and photoelectrocatalytic reduction of CO2 using heterogeneous catalysts with controlled nanostructures. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błachowicz, T.; Hütten, A.; Ehrmann, A.J.F. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with Electrospun Nanofiber Mats—A Review of Production, Physical Properties and Performance. Fibers 2022, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Deng, L.; Zhang, T.; Shen, K.; Wang, X. Facile fabrication of environmentally friendly, waterproof, and breathable nanofibrous membranes with high uv-resistant performance by one-step electrospinning. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 4447–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Guan, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Effect of a room-temperature ionic liquid on the structure and properties of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 4447–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, W.; Shi, L.; Sun, X. Directional vapor transported and water-proof nanofibrous membranes for liquid desiccant dehumidification systems. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 265702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Niu, Y.; Shi, X.; Pan, D.; Liu, H.; Qiu, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, B.B.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Hou, H.; et al. Mxene@c-mwcnt adhesive silica nanofiber membranes enhancing electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal insulation performance in extreme environments. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Jiang, S.; Shen, L.; Pun, E.Y.B.; Lin, H. Heterogeneous CuS QDs/BiVO4@Y2O2S nanoreactor for monitorable photocatalysis. Small 2024, 20, e2401335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beachley, V.; Wen, X. Effect of electrospinning parameters on the nanofiber diameter and length. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2009, 29, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanova, N.; Nachev, N.; Spasova, M. Innovative bioactive nanofibrous materials combining medicinal and aromatic plant extracts and electrospinning method. Membranes 2023, 13, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, W.; Tan, G. Stimuli-responsive electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery, cancer therapy, wound dressing, and tissue engineering. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Awuye, D.E.; Guan, M.; Zhu, Y. Electrospinning-based biosensors for health monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Lv, H.; Wang, C.; He, D.; Xu, E.; Jin, Z.; Yuan, C.; Guo, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, P.; et al. Organic solvent-free starch-based green electrospun nanofiber mats for curcumin encapsulation and delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Antibacterial activities of aliphatic polyester nanocomposites with silver nanoparticles and/or graphene oxide sheets. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, C.; Tjong, S.C. Synthetic biodegradable aliphatic polyester nanocomposites reinforced with nanohydroxyapatite and/or graphene oxide for bone tissue engineering applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herwig, G.; Batt, T.; Clement, P.; Wick, P.; Rossi, R.M. Sterilization and filter performance of nano- and microfibrous facemask filters-electrospinning and restoration of charges for competitive sustainable alternatives. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, e2400867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havlickova, K.; Kuzelova Kostakova, E.; Lisnenko, M.; Hauzerova, S.; Stuchlik, M.; Vrchovecka, S.; Vistejnova, L.; Molacek, J.; Lukas, D.; Prochazkova, R.; et al. The impacts of the sterilization method and the electrospinning conditions of nanofibrous biodegradable layers on their degradation and hemocompatibility behavior. Polymers 2024, 16, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Ou, W.; He, J.; Liu, M.; Lu, Z.; Hu, J.; Zheng, G.; Wu, D. Response surface methodology to explore the influence mechanism of fiber diameter in a new multi-needle electrospinning spinneret. Polymers 2024, 16, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; You, C.; Xu, Y.; Xie, T.; Wang, Y. Research advances in electrospun nanofiber membranes for non-invasive medical applications. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, B.; Peterfi, O.; Galata, D.L.; Nagy, Z.K.; Hirsch, E. Process analytical technology based quality assurance of api concentration and fiber diameter of electrospun amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2024, 204, 114529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Barquero, A.; Paulis, M.; Leiza, J.R. Fabrication of multifunctional composite nanofibers by green electrospinning. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2300011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Hao, L.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, R.; Liu, W. Intelligent electrospinning nanofibrous membranes for monitoring and promotion of wound healing. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 26, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
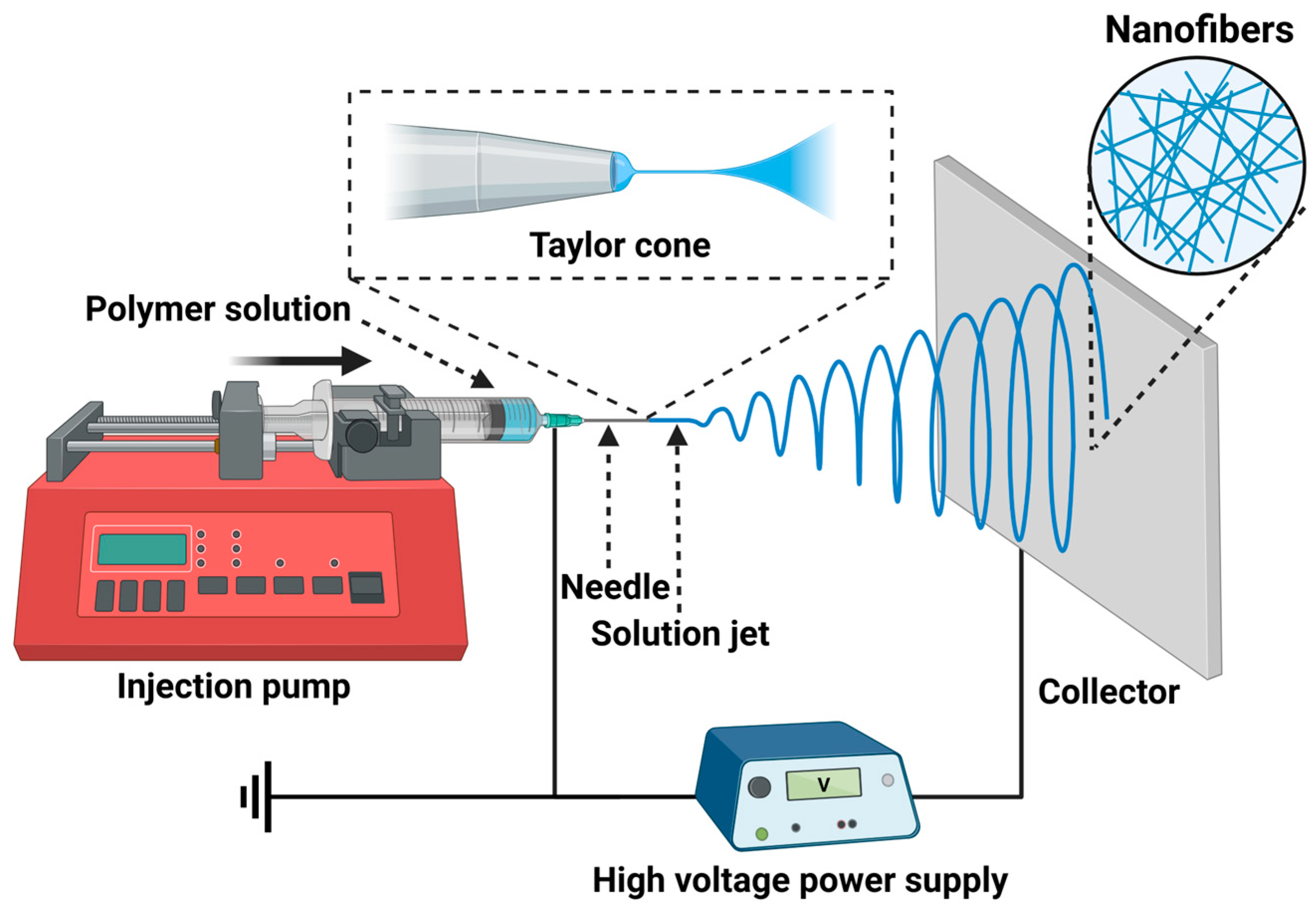
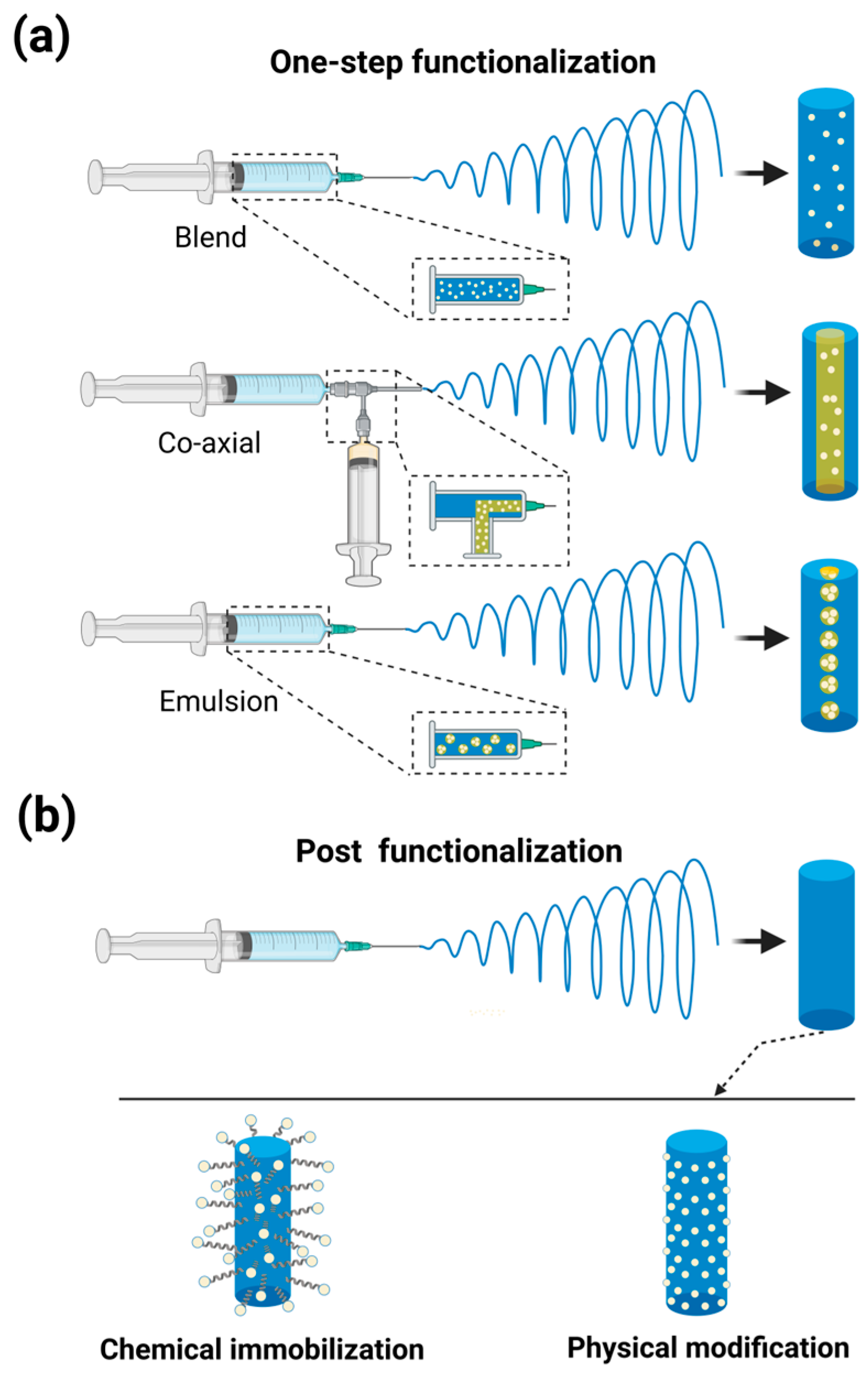
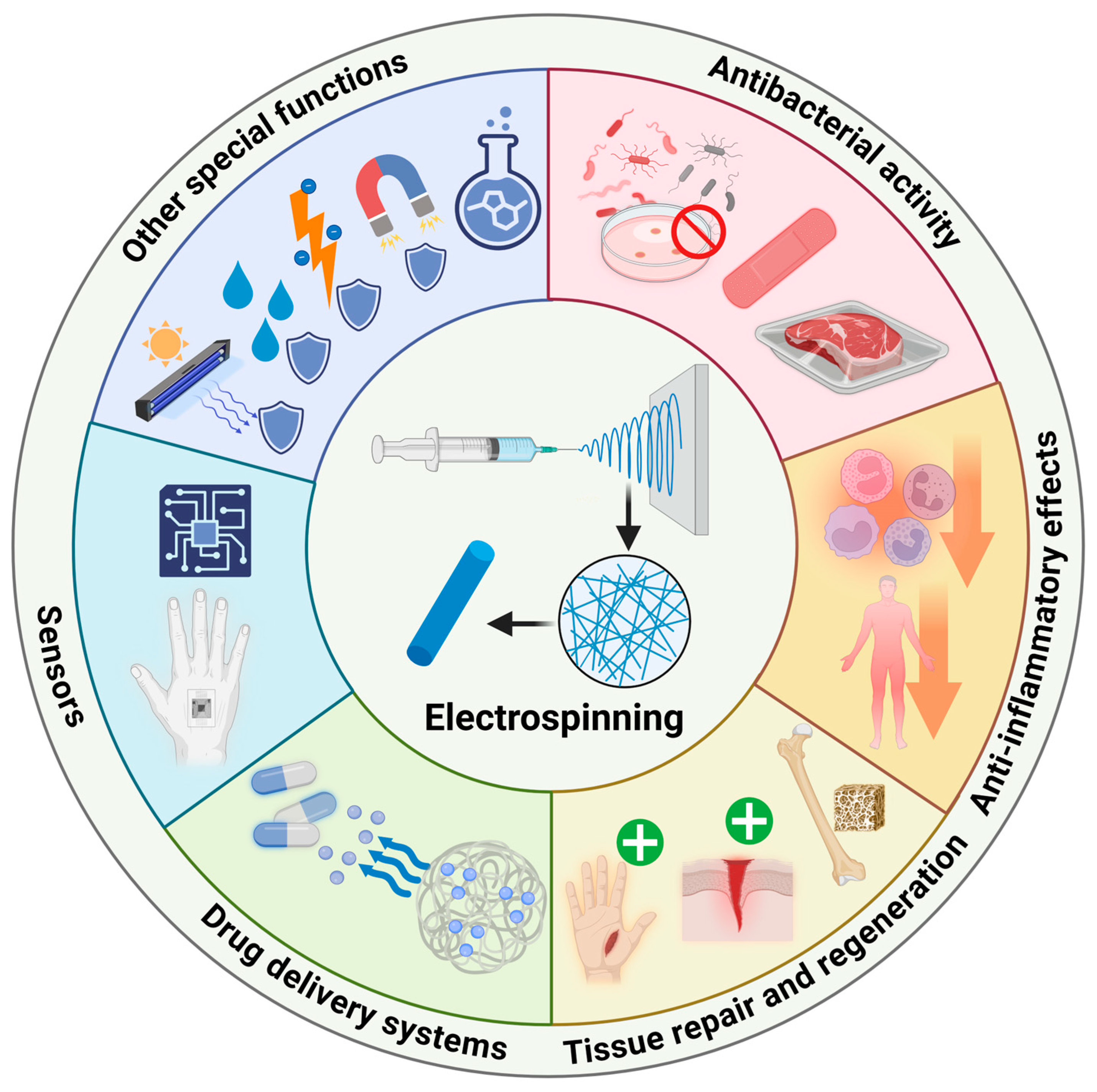
| Parameters | Effects on Other Parameters | Effects on Nanofiber Morphology |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer concentration | Viscosity ↑ Surface tension ↑ | Diameter ↑ Mechanical strengh ↑ |
| Molecular weight of polymer | Viscosity ↑ Surface tension ↓ Jet stability ↑ | Bead formation ↓ |
| Conductivity | Dielectric constant ↑ Charge density ↑ | Diameter ↓ |
| Viscosity | G’↑ G” ↑ G’/G” ↓ | Diameter ↑ Bead formation ↓ |
| Surface tension | Jet stability ↑ | Bead formation ↑ |
| Applied voltage | Size of Taylor Cone ↑ Charge density ↑ | The effect on diameter is under debate. |
| Flow rate | - | Diameter ↓ |
| Collecting distance | Evaporation rate ↓ Electric field intensity ↓ | Diameter ↑ Fiber uniformity ↓ |
| Temperature | Viscosity ↓ | Diameter ↓ |
| Relative humidity | Evaporation rate ↓ | The effect on diameter relies on polymer/solvent system. Porosity ↑ Bead formation ↑ |
| Electrospun Polymers | Antibacterial Additives | Types of Additives | Functionalization Methods | Application Area | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/poly(ethyleneoxide) (PEO) | Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) | Inorganic namomaterial | Blend electrospinning | Wound dressing | [83] |
| Chitosan (CS)/polycaprolactone (PCL) | Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) | Inorganic namomaterial | Co-axial electrospinning | Wound dressing | [84] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL)/poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) | Graphene oxides (GOs) | Inorganic namomaterial | Blend electrospinning/in situ polymerization | Wound dressing | [85] |
| Gelatin(Gel)/chitosan (CS) | Mxenes | Inorganic namomaterial | Blend electrospinning | Wound dressing | [86] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) Curcumin (CUR) | Organic nanomaterial/natural-derived compounds | Blend electrospinning | Wound dressing | [87] |
| Cellulose Acetate (CA) | Chitosan nanoparticles (CS NPs)/Eucalyptus Oil | Organic nanomaterial/natural-derived compounds | Blend electrospinning | Wound dressing | [88] |
| Chitosan (CS) | Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) | Inorganic-organic hybrid nanomaterial | In situ growth | Wound dressing | [89] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Porous coordination network−224 (PCN−224) | Inorganic-organic hybrid nanomaterial | Blend electrospinning | Wound dressing | [90] |
| Gelatin (Gel) | MIL-100(Fe)@IR775 | Inorganic-organic hybrid nanomaterial | Blend electrospinning | Wound dressing | [91] |
| Gelatin (Gel) | Curcumin (CUR)/borneol | Natural-derived compounds | Blend electrospinning | Wound dressing | [92] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Manuka honey/essential oils | Natural-derived compounds | Layer-by-layer assembly | Wound dressing | [93] |
| Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | AMP | Biofunctional agents | Blend electrospinning | Wound dressing | [94] |
| Zein/polyethylene oxide (PEO) | Resveratrol (RE)/Ag NPs | Inorganic namomaterial/natural-derived compounds | Co-axial electrospinning | Food package | [95] |
| Starch/(PVA) | Ag-ZrP | Inorganic namomaterial | Blend electrospinning/crosslinking | Food package | [96] |
| Chitosan (CS)/polyethylene oxide (PEO) | Thymol (Thy) | Natural-derived compounds | Co-axial electrospinning/in situ crosslinking | Food package | [97] |
| Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB) | Camellia oil (CO)/ZnO-TiO2 composite nanoparticles (ZT) | Inorganic namomaterial/natural-derived compounds | Blend electrospinning | Food package | [98] |
| Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | Cinnamaldehyde (CMA)/tea polyphenol (TP) | Natural-derived compounds | Co-axial electrospinning | Food package | [99] |
| Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | Octyl gallate (OG) | Natural-derived compounds | Blend electrospinning | Food package | [100] |
| Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | Wormwood Oil | Natural-derived compounds | Blend electrospinning | Food package | [101] |
| Chitosan(CS)/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | Fe3O4 | Inorganic namomaterial | Blend electrospinning | Food package | [102] |
| Cellulose Acetate (CA) | NiO | Inorganic namomaterial | Blend electrospinning | Food package | [103] |
| Electrospun Polymers | Anti-Inflammatory Materials | Anti-Inflammatory Strategy | Functionalization Methods | Application Area | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycaprolactone (PCL)/gelatin (Gel) | 4-Octyl itaconate (OI)/chitosan (CS) | Direct strategy | Blend electrospinning/covalent grafting | Wound healing | [111] |
| Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) | Puerarin (Pue) | Direct strategy | Blend electrospinning | Pelvic floor reconstruction | [112] |
| Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) | Naringenin (NA) | Direct strategy | Blend electrospinning | Bone tissue engineering | [113] |
| ZnO-SiO2/chitosan (CS) | Aspirin (ASA) | Direct strategy | Blend electrospinning/crosslinking | Bone tissue engineering | [114] |
| Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) | Casein enzymatic hydrolysate (CEH) | Direct strategy | Blend electrospinning/crosslinking | Vital pulp therapy | [115] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Prussian blue nanocrystals (PBNCs)/heparin sodium (Hep) | Direct strategy | Electrospraying/chemical deposition | Wound healing | [116] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/sodium alginate (SA) | Ag-Hes NPs (using hesperidin as reducing and capping agen) | Indirect strategy | Blend electrospinning | Wound healing | [117] |
| Polyethylene oxide (PEO)/hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) | Chloramphenicol (CAM)/beta-glucan (βG)/chitosan (CHI) | Indirect strategy | Blend electrospinning | Wound healing | [118] |
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) | Thymol (THY)/tyrosol (TYR) | Indirect strategy | Blend electrospinning | Wound healing | [119] |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) (P34HB) | Ciprofloxacin (CIP)/dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG) | Indirect strategy | Blend electrospinning | Wound healing | [120] |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)/chitosan (CS) | Dihydromyricetin (DHM) | Indirect strategy | Blend electrospinning | Wound healing | [121] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) | polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride (PHGC)/hydrophobic indomethacin (Indo) | Synergetic strategy | Blend electrospinning/bidirectional electrospinning | Wound healing | [122] |
| Poly(esterurethane)urea (PEUU)/silk fibroin (SF) | Magnolol (Mag) | Synergetic strategy | Blend electrospinning/post-hydrogen-bond crosslinking | Wound healing | [123] |
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)/polydopamine (PDA) | ε-polyL-lysine (ε-PL)/ibuprofen (IBU) | Synergetic strategy | Co-axial electrospinning/PDA-assisted assembly | Wound healing | [124] |
| Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) | Sulfated chitosan (SCS)/polydopamine (PDA)/gentamicin (GS) | Synergetic strategy | Blend electrospinning/PDA-assisted assembly | Wound healing | [125] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Jin, F.; Li, J.; Bin, Y.; Qian, X. Preparation Methods and Multifunctional Applications of Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomedicine. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120909
Liu J, Wang K, Jin F, Li J, Bin Y, Qian X. Preparation Methods and Multifunctional Applications of Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomedicine. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(12):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120909
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jingwen, Kai Wang, Fengying Jin, Jiayi Li, Yile Bin, and Xiaofei Qian. 2025. "Preparation Methods and Multifunctional Applications of Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomedicine" Nanomaterials 15, no. 12: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120909
APA StyleLiu, J., Wang, K., Jin, F., Li, J., Bin, Y., & Qian, X. (2025). Preparation Methods and Multifunctional Applications of Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomedicine. Nanomaterials, 15(12), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120909






