Abstract
Deep-seated tumors present significant diagnostic challenges and pose substantial mortality risks due to their occult anatomical localization. Current diagnostic paradigms predominantly depend on conventional imaging modalities; nevertheless, inherent technical constraints persistently compromise diagnostic precision and therapeutic efficacy. In contrast to traditional methodologies, near-infrared (NIR; 700–1700 nm) fluorescence imaging (FLI) demonstrates superior sensitivity and spatiotemporal resolution, facilitating real-time intraoperative visualization and precision-guided surgical interventions. This paper explores fluorescence materials with tailored structures for tumors at different depths. We critically analyze optimization strategies for NIR fluorescence materials while evaluating their comparative advantages in stratified tissue imaging. This study presents a systematic evaluation of NIR fluorescence molecular tomography (FMT) systems and image reconstruction methodologies. These insights provide feasible ideas for detecting and treating tumors at varying depths in clinical practice. Furthermore, the application of NIR fluorescent materials in tumor diagnosis, navigation-guided surgery, and phototherapy (including photothermal, photodynamic, and immunomodulation therapies) is discussed. Finally, the prospects and challenges of clinical transformation are summarized.
1. Introduction
Evolving dietary patterns and lifestyle modifications have driven a global rise in malignant tumor incidence, establishing them as primary mortality determinants impacting global health [1]. Tumor morbidity and mortality persist at elevated levels, necessitating early detection and intervention for effective disease management. Beyond surgical resection, chemotherapy and radiotherapy remain the mainstays in oncology [2,3]. However, therapeutic resistance and severe treatment-related toxicities frequently contribute to tumor relapse and protracted patient morbidity [4].
Recent advances demonstrate tumor-targeting fluorophores as clinically translatable agents for imaging-guided oncotherapy. Developed NIR probes span methylene blue (MB), carbon nanotube (SWCNTs) [5], inorganic nanoparticles [6,7], quantum dots (QDs) [8,9,10], rare-earth nanomaterials [11,12], organic small molecules [13], fluorescent dyes [14], and conjugated polymers [15]. FLI modalities are categorized into visible VIS (400–700 nm), NIR-I (700–900 nm), and NIR-II (1000–1700 nm) regimes by emission spectra. In vitro murine models demonstrated that deep-tissue imaging is compromised by intrinsic autofluorescence, while NIR wavelengths exhibit significantly lower scattering coefficients compared to VIS [16]. As shown in Figure 1, we integrated NIR-responsive materials with combinatorial therapeutic strategies, including chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy (PDT), photothermal therapy (PTT), photoimmunotherapy (PIT), photoacoustic therapy (PA), chemodynamic therapy (CDT), and multimodal regimens, and achieved enhanced spatiotemporal precision in tumor targeting and treatment efficacy [17].
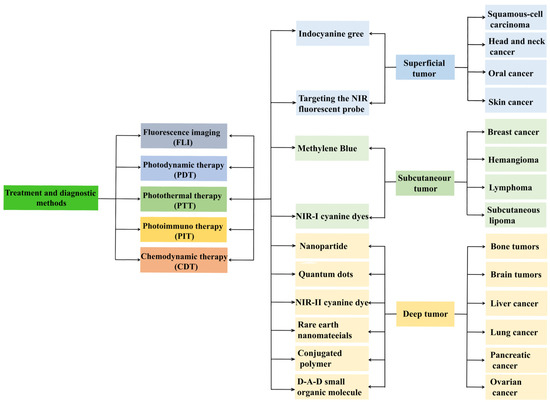
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the description of various NIR materials used for specific tumor sites at different depths.
In systematically reviewing advancements in NIR-II fluorescent probes for tumor surgery navigation, we identified critical limitations in existing review articles, notably their narrow analytical dimensions and restricted application scopes. For instance, Zia Ullah et al. comprehensively characterized NIR-II probes (e.g., QDs and organic small molecules) from a materials chemistry perspective, yet failed to establish comparative frameworks between NIR-II and NIR-I probes or to address anatomical tumor localization in probe selection [18]. Similarly, while Homan Kang’s team innovatively integrated cancer immunotherapy with NIR FLI, they omitted synergistic therapeutic modalities like PTT and PDT [19].
This research establishes a clinically stratified anatomical framework that correlates probe emission spectra (700–1700 nm) with malignant tissue penetration depth and spatial resolution across anatomical hierarchies. Employing an evidence-based analytical framework, we methodically evaluate NIR-guided surgical interventions integrated with combinatorial phototherapies (PTT/PDT/PIT), while synthesizing NIR fluorescence molecular tomography (FMT) architectures and computational reconstruction paradigms, bridging critical gaps in systematic investigations. Table 1 summarizes the applications of NIR fluorescent materials with different structures in tumor imaging and therapy at varying depths.

Table 1.
Application of NIR fluorescent materials with different structures in imaging and treatment of tumors of different depths.
2. Superficial Tumor
Superficial tumors comprise epithelial-origin malignancies primarily localized to cutaneous/submucosal layers, including squamous cell carcinoma, head-neck cancers, oral epidermoid carcinoma, and melanoma [40]. While early intervention mitigates metastatic dissemination, therapeutic management persists as a clinical challenge owing to surgical morbidity and chemotoxicity [41]. Current diagnostic armamentarium integrates computed tomography (CT), ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [42,43], positron emission tomography (PET) [44], and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). FLI surpasses conventional modalities through real-time capability, non-invasiveness, and superior target-to-background ratios, positioning it as a transformative diagnostic alternative [45]. Clinically validated NIR probes like indocyanine green (ICG) dominate superficial tumor imaging, while targeted NIR fluorophores exhibit enhanced tumor-specific accumulation.
2.1. Indocyanine Green (ICG) Fluorescent Dyes
ICG, an amphiphilic water-soluble fluorophore, exhibits excitation at 778–806 nm with 835 nm peak emission in biological matrices [46]. It is the sole U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved NIR contrast agent for surgical navigation [47]. This photosensitizer generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) under NIR irradiation, inducing cytotoxic effects against malignant and microbial targets [48]. Its clinical utility stems from its negligible systemic toxicity [49]. Integrated with NIR imaging, ICG enables early superficial tumor detection, sentinel node mapping, cervical lymphadenectomy, and chemotherapy targeting within the NIR-I window [50]. Wang et al. implemented ICG-guided NIR laparoscopy for precise esophagectomy with esophagogastric reconstruction [51]. This technique achieved intraoperative lesion demarcation, surgical margin preservation, lymphatic mapping, and anastomotic perfusion assessment. Although ICG has been approved by the FDA as a fluorescent imaging agent, certain inherent limitations persist that must be systematically addressed to optimize its clinical utility and advance surgical outcomes. For instance: (1) poor light stability, (2) rapid systemic clearance, (3) tumor-targeting deficiency [52], and (4) aqueous-phase aggregation causing quantum yield attenuation [53].
ICG-based FGS exhibits inherent limitations. To augment photostability, structural modifications of ICG via the incorporation of rigid moieties or electron donor-acceptor (D-A) substituents enable precise modulation of its excited-state energy distribution. This molecular engineering strategy suppresses non-radiative relaxation pathways and mitigates photobleaching by stabilizing the fluorophore’s electronically excited states, thereby preserving fluorescence intensity under prolonged illumination. Owing to self-quenching, ICG in solution displays reduced fluorescence quantum yield and rapid hepatic clearance post-intravenous injection [54]. Encapsulating ICG within nanoparticles addresses these constraints by improving stability, prolonging circulation, and enhancing tumor-specific accumulation [55].
To enhance targeting precision, covalent conjugation of ICG with molecular ligands (e.g., antibodies, peptides) enables the construction of ligand-functionalized ICG complexes. Ito et al. demonstrated ICG-conjugated anti-Podoplanin probes for NIR visualization of OSCC xenografts in murine models [22]. Albumin-conjugated ICG further demonstrates enhanced hydrolysis resistance and a 16.8% increase in photoluminescent quantum yield relative to unbound ICG [56]. This strategy exploits ligand-receptor molecular recognition mechanisms to achieve active accumulation in pathological regions, thereby amplifying signal-to-background ratios during fluorescence-guided interventions.
The encapsulation of ICG within inorganic or organic nanocarriers (e.g., silica nanoparticles, liposomes, or polymeric micelles) leverages the light-scattering or energy-absorption properties of the carrier matrix to mitigate photodegradation kinetics. This strategy not only prolongs the photostability of the fluorophore but also enhances photothermal conversion efficiency, thereby accelerating therapeutic efficacy in tumor ablation. For instance, Ledezma-DK et al. developed a nanoemulsion synthesis protocol to co-encapsulate ICG and Nexturastat A (NextA) within monodisperse poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA)-based nanoparticles (ICG-NextA-PLGA; INAPs) (Figure 2a). Therapeutic cohorts receiving epigenetic monotherapy exhibited tumor growth curves comparable to untreated tumor-bearing mice (Figure 2b). Compared with untreated controls, near-daily systemic NextA administration conferred no tumor progression benefit. In contrast, the ICG-PLGA-PTT group and the combinatorial INAPs-PTT + NextA-PLGA regimen demonstrated significantly attenuated tumor progression. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis revealed median survival durations of 18 days (INAPs-PTT + NextA-PLGA), 17 days (ICG-PLGA-PTT), and 14 days (untreated controls) (Figure 2c). These findings establish INAP as an epigenetic regulator whose combinatorial delivery platform delays tumorigenesis and extends median survival [51].
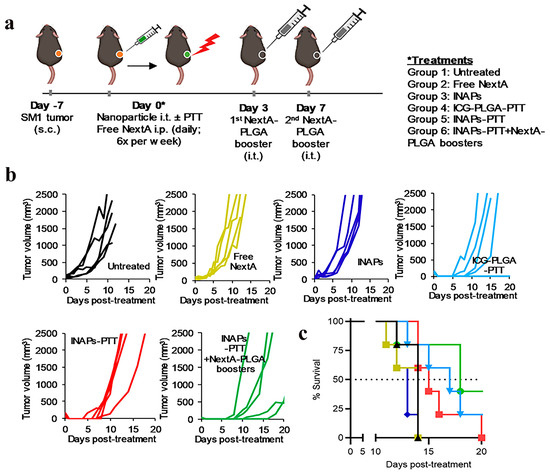
Figure 2.
Photothermal nanotherapy (INAP-PTT) inhibits melanoma progression and extends survival in B16-F10 murine models. (a) Therapeutic workflow for precision thermotherapy. (b) Longitudinal tumor volumetrics (n = 5) and (c) Kaplan–Meier analysis reveal extended recurrence-free survival with adjuvant epigenetic modulation (INAP-PTT + NextA-PLGA). Adapted with permission from references [51]. Copyright 2020, MDPI.
2.2. Targeting the NIR Fluorescent Probe
Owing to enhanced tumor target specificity, active targeting strategies and activatable probes present novel opportunities for intraoperative navigation. NIR-II fluorescent probes demonstrate superior efficacy in tumor imaging owing to their target selectivity, high spatial resolution, and deep-tissue penetration capabilities [57], as shown in Figure 3.
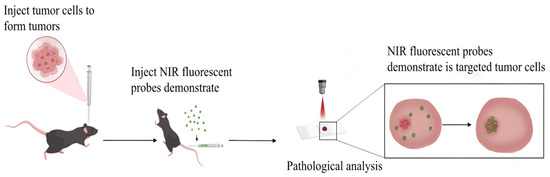
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of NIR fluorescent probe specifically targeting tumors.
ICG can be conjugated with functionalized nanoparticles through immobilization, doping, or covalent coupling strategies, enabling ligand-mediated tumor targeting [58]. Von Kiedrowski et al. [59] engineered an NIR fluorescent cyclic Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) peptide conjugate incorporating indocyanine dye, demonstrating melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R)-specific binding capacity for precision diagnosis of malignant melanoma. The NIR-II fluorophore Nd-Mn-MMP1Ab luminescent probe exhibited selective binding to Human Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma (Cal-27) cells, enabling precise OSCC tracking through targeted molecular recognition [60]. Notably, TM1-IR680 conjugated with gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR)-targeting peptides enabled intraoperative visualization of tumor margins and lymphatic metastases in orthotopic oral cancer murine models [61]. Furthermore, MC1R-directed fluorescent nanoprobes (MSH-TPE-BBT NPs) displayed enhanced tumor permeability, photophysical stability, biocompatibility, and specific accumulation in human/murine melanoma xenografts [62].
3. Subcutaneous Tumor
Multiple fluorophores have been developed for subcutaneous tumor imaging, yet VIS/NIR-I-based approaches remain suboptimal due to shallow tissue penetration and intense autofluorescence. Select NIR-I probes (such as MB, cyanine derivatives, ICG) achieve emission tailing beyond 1000 nm into the NIR-II regime, enabling enhanced imaging contrast and therapeutic efficacy in subcutaneous malignancies.
3.1. Methylene Blue (MB)
MB, a fluorescent dye first identified in 1876, has been applied across diverse scientific disciplines. Recently, MB has been utilized in intraoperative FLI, emitting NIR fluorescence at 700 nm. This dye is cost-effective, readily available, and demonstrates low systemic toxicity, achieving a maximal tissue penetration depth of 4 mm [63,64]. Current applications include intraoperative ureter visualization, parathyroid gland localization, pancreatic tumor delineation, breast cancer margin assessment, and sentinel lymph node mapping [65]. However, its limited diagnostic efficacy and shallow tissue penetration restrict its utility in subcutaneous tumor detection.
MB exhibits pronounced absorption and fluorescence emission within both the VIS NIR-I, enabling dual-modality visualization through FLI and photoacoustic imaging. MB demonstrates preferential biodistribution in endocrine tissues, serving as a surgical adjunct for thyroid/parathyroid procedures through high-dose intravenous administration (3–7.5 mg/kg), enabling visual identification of hyperplastic glands via chromatic differentiation [66]. Breast cancer exhibits metastatic tropism for pulmonary and cerebral tissues [67], and evidence confirms mortality reduction through early intervention strategies [68]. The high glandular density of breast parenchyma compromises mammographic sensitivity [69]. Intravenous MB administration enables NIR fluorescence-based tumor detection, with a radical mastectomy cohort (n = 12) achieving measurable fluorescence signals at 1 mg/kg dosing (mean TBR = 1.578 ± 0.36) [70]. Notably, Wu et al. [64] established MB’s efficacy in rodent sentinel lymph node mapping, demonstrating superior lymphatic mapping capability versus ICG.
3.2. NIR-I Cyanine Dyes
Cyanine-derived organic fluorophores exhibit elevated quantum yields, strong molar absorptivity, facile synthesis, and biocompatibility [71,72]. However, conventional NIR-I cyanine dyes (700–900 nm) exhibit inherent limitations in clinical oncology, primarily restricted to subcutaneous tumor applications due to their sub-optimal tissue penetration depth (<5 mm) and susceptibility to photon scattering/autofluorescence interference in deeper anatomical regions. These constraints arise from the rapid attenuation of NIR-I wavelengths in biological tissues and spectral overlap with endogenous chromophores (e.g., hemoglobin, melanin), which collectively compromise imaging contrast and therapeutic precision for visceral or orthotopic malignancies.
Breast cancer is the most common tumor. Early-stage intervention through screening and targeted therapies significantly improves survival outcomes [68,73]. To address ICG’s limited tissue penetration from short-wavelength emission, π-extended ICG derivatives conjugated with Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2+)/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR+) antibodies enable deep-tumor NIR imaging in HER2+/EGFR+ subtypes [74]. The ERα-targeted probe IRDye800CW-E2, which combines the cyanine fluorophore IRDye800CW with ethinylestradiol (ERα ligand), demonstrated rapid tumor accumulation (<4 h post-injection) with sustained tumor-to-background contrast (TBR 4–48 h) in murine models, validating its clinical potential for early detection [24]. Preclinical studies confirm HER2+ Affibody-IR700 conjugates mediate targeted ablation of HER2+ tumors in xenograft models, achieving 72% volume reduction within 24 h post-PIT [75].
IR-783, a commercial-grade NIR heptamethine dye, has been investigated in breast and prostate cancer research. Distinct from other commercial heptamethine cyanine dyes, IR-783 demonstrates unique physicochemical properties (Figure 4) [76]. Although structurally analogous to ICG, IR-783 shows minimal tumor uptake within 24 h post-injection (Figure 4a). Its heptamethine skeleton contains a chlorocyclohexenyl ring and dual sulfonate side chains (Figure 4b), improving aqueous solubility. A key structural divergence from ICG is the racemic chlorine atom on the heptamethine cyclohexene ring, which facilitates tumor-selective accumulation via albumin adduct formation. Owing to its hydrophilicity, IR-783 absorption and fluorescence spectra were characterized in PBS (pH 7.4) (Figure 4d), revealing a 776 nm absorption peak, 798 nm emission maximum, and 22 nm Stokes shift (Figure 4e). IR-783 also displays a moderate molar extinction coefficient (ε = 162,000 mol−1·cm−1) and quantum yield (Φ = 5.5%). These results confirm that IR-783 has great potential in the treatment of tumor cells.
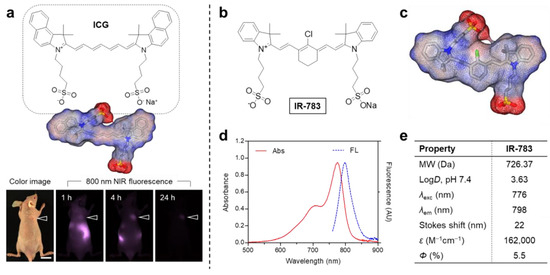
Figure 4.
(a) ICG chemical structure and in vivo tumor targeting (arrowheads indicate tumor sites; scale bar = 1 cm). (b) IR-783 chemical structure and (c) 3D electrostatic potential map (red: negative; blue: positive; gray: hydrophobic regions). (d) IR-783 absorption/emission spectra in PBS (pH 7.4). (e) Computed physicochemical properties of IR-783, including logD at pH 7.4 and surface charge distribution (calculated using Marvin/JChem plugins, ChemAxon, Budapest, Hungary). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [76]. Copyright 2024, MDPI.
4. Deep Tumor
Visceral tumors located in deep anatomical regions pose diagnostic challenges with high mortality upon clinical presentation, encompassing intracranial neoplasms, osseous malignancies, and visceral carcinomas (prostate, hepatic, pulmonary, etc.). Conventional VIS/NIR-I FLI suffers from tissue scattering and autofluorescence-induced compromised resolution and elevated false-positives [16]. Recent developments in NIR-II fluorescent materials have encompassed nanoparticles, QDs, cyanine dyes, rare-earth nanomaterials, conjugated polymers, and donor-acceptor-donor (D-A-D) organic small molecules, overcoming these aforementioned limitations. NIR-II FLI attenuates scattering effects, achieves ~10 mm tissue penetration, and suppresses autofluorescence, enabling precise tumor delineation [77]. This breakthrough facilitates deep-tissue visualization [78] and emerges as a transformative preclinical tool [79]. Its dual functionality spans contrast-enhanced cerebrovascular/cardiac imaging [80,81] to mechanistic investigations in neurodegeneration [82], bone repair [83], gastrointestinal diseases [84,85], kidney diseases [86], cervical diseases [87], diabetic angiopathies [88], and contrast-guided theranostic platforms. Despite their potential, all NIR-II fluorescent materials face inherent trade-offs. To objectively evaluate their clinical applicability, Table 2 provides a comparative analysis of their advantages (e.g., penetration depth, SNR) and limitations (e.g., toxicity, synthesis complexity) in imaging tumors located at deep tissue sites.

Table 2.
Advantages and limitations of NIR-II fluorescent materials for imaging deep-seated tumors.
4.1. Nanoparticle
Fluorescent nanoparticles demonstrate robust luminescence and stability, serving as effective cellular fluorophores. Surpassing conventional modalities, these nanoparticles provide enhanced biosafety through non-radioactive, non-invasive operation, establishing radiation-free diagnostic paradigms [102]. Their tumor imaging merits include: (1) Superior biocompatibility, (2) Extended circulatory half-lives, (3) Passive targeting via EPR-mediated tumor accumulation, (4) High payload capacity for hydrophobic therapeutics, and (5) Facile surface functionalization enabling receptor-specific targeting [89]. However, persistent challenges remain in probe design, stability, and clinical applicability, necessitating further breakthroughs to address critical limitations.
NIR-II nanoparticles enable synergistic integration of PTT, PDT, and CDT through wavelength-specific photoconversion, ROS generation, and Fenton/Fenton-like catalytic cascades. NIR-II-responsive Fe-doped carbon nanoparticles (FDCNs) were engineered via a one-pot hydrothermal method for combined PTT and CDT. Released iron ions catalyze H2O2-to-hydroxyl radical (OH) conversion, enabling CDT, while achieving a 36.3% photothermal efficiency [103]. Hydrophilic polymer-modified two perylene monoxide and one diaminoanthraquinone (2PMI-AQ) self-assembled into nanoparticles, synergizing PTT and PDT [104]. PDT clinically targets endoscopically accessible malignancies, including bladder and lung cancers [105]. Zhang X et al. [106] developed NIR-II-targeted nanoparticles (NPER/BO-PDT), which triggered immunogenic cell death, adaptive immunity, and tumor suppression under NIR irradiation, demonstrating effective PDT. PTT, a non-invasive modality, shows promise for tumor ablation with minimal invasiveness [107]. NIR-II-driven semiconductor polymer nanoparticles (SPNs) [108] enabled PA-guided U87 glioma PTT. Li et al. [109] engineered AE105 peptide-functionalized CH4T@MOF-PEG-AE nanoprobes, peaking in fluorescence intensity (TBR = 4.0) at 12 h post-injection with 30.4% photothermal efficiency. MR/NIR-II-guided PTT achieved complete glioma ablation.
Pancreatic malignancy, characterized by rapid metastasis and elusive early-stage detection, poses significant clinical challenges. The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment renders suboptimal therapeutic outcomes for conventional radio-chemotherapeutic regimens and immunotherapeutic approaches. NIR-II phototheranostics demonstrates unique advantages in pancreatic tumor resection and ablation [6]. Figure 5a illustrates the synthesis process of NIR-II fluorophore (IRNPs-SBA/PtIV), a cisplatin-prodrug nanoparticle exhibiting intense fluorescence emission at 980 nm excitation. Under 1064 nm irradiation, this system synergizes PTT and chemotherapy to suppress pancreatic tumor progression (Figure 5b) [7]. Engineered NIR-IIb AIE nanoparticles achieve 1550 nm-mediated high-precision glioblastoma delineation at 5.9 mm tissue depths [110]. Clinical trials now explore image-guided phototherapeutic modalities for enhanced precision and safety in neuro-oncological interventions.
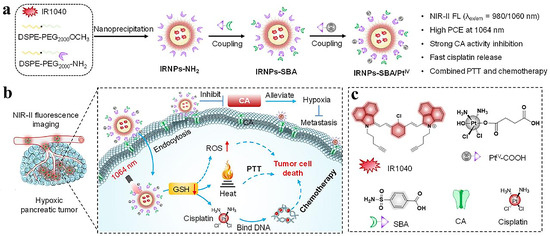
Figure 5.
(a) Synthesis scheme of IRNPs-SBA/PtIV. (b) Working mechanism of IRNPs-SBA/PtIV for NIR-II fluorescence-guided PTT/chemotherapy in pancreatic tumors (1064 nm excitation). (c) Molecular structures of IR1040, PtIV–COOH, SBA, cisplatin, and CA representation. Adapted with permission from Ref. [7]. Copyright 2024, Elsevier.
4.2. Quantum Dots (QDs)
QDs are considered ideal FGS nanoprobes due to their distinct optical properties and superior fluorescence performance, enabling high-fidelity tumor imaging. Nevertheless, intrinsic limitations of NIR-II QDs, which include inherent toxicity, suboptimal targeting efficiency, and limited solubility [91], pose critical barriers to advancing in vivo imaging contrast and spatiotemporal resolution, substantially constraining their clinical translation in FGS [111].
Intrinsic limitations of Ag2S QDs, which include suboptimal targeting and aqueous instability, demand structural optimization for theranostic implementation. Zebibula et al. engineered hydrophobic NIR-II PbS@CdS QDs via silica/amphiphilic polymer (Pluronic F-127) bilayer encapsulation [112]. The PbS@CdS@SiO2@F-127 nanocomposites demonstrated aqueous dispersibility (Φ = 5.79%) and enabled 950 µm-depth cerebral FLI in murine models. RCA-synthesized Programmed cell Death 1-ligand 1 (PD-L1) aptamer/C-rich DNA scaffolds templated Ag+-chelating pApt-Ag2S QDs for PD-L1 tumor targeting [91]. Ligand-exchange/amide-condensation strategies yielded tumor-targeting Ag2S@PEG-ABS probes functionalized with 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonamide, achieving precision FLI. PEGylation conferred enhanced hydrosolubility and photothermal stability (η = 45.17%), validating Ag2S@PEG-ABS as a potent colorectal cancer theranostic agent [38].
Intracranial neoplasms are histologically heterogeneous with infiltrative growth patterns, rendering complete resection technically challenging under visual guidance [94]. To overcome these constraints, Angiopep-2-functionalized Ag2S QDs were synthesized via carbodiimide-mediated conjugation, demonstrating biocompatibility at concentrations <100 μg/mL. In vivo studies using subcutaneous xenografts revealed preferential accumulation of Angiopep-2-QDs, suggesting active glioma-targeting properties [113]. FGS further provides multimodal surgical guidance for colorectal malignancies, integrating phototheranostic applications (PTT/PDT/PIT) with intraoperative navigation [114]. These findings collectively validate QDs as promising theranostic platforms for deep-tissue oncological imaging.
4.3. NIR-II Cyanine Dye
NIR-II cyanine dyes demonstrate advantageous properties such as low cytotoxicity, superior biocompatibility, negligible autofluorescence, and diminished background signals. Clinically relevant fluorophores, IR-1048, IR-1061, and IRDye800, have been utilized for preclinical imaging of deep-seated tumors [112]. Nevertheless, commercial NIR-II cyanine dyes are constrained by inherent limitations: (1) inadequate target specificity, (2) poor aqueous solubility, and (3) low photothermal efficiency [79,94].
Cyanine derivatives were functionalized with reactive moieties such as N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and maleimide (MAL) groups to enable covalent conjugation with targeting antibodies or peptides, thereby enhancing probe specificity (Figure 6). Lu et al. developed NIR-II fluorophore (H10@FSH), an NIR-II fluorophore demonstrating ovarian-specific targeting and dual-mode PA/FGS navigation for ovarian cancer lesions, enhancing patient theranostic efficacy [115]. Zhang et al. [116] developed a GRPR-targeted probe by conjugating RM26 with IRDye800CW, enabling NIR-II image-guided resection of malignant brain tumors. Novel bone-targeted fluorescent probes improve spatial resolution and specificity in noninvasive metastasis imaging. Sun et al. [31] engineered an NIR-II probe using IRDye800CW-NHS and trastuzumab, demonstrating that BTZ/Fe2+@BTF/ALD suppresses bone tumor progression via synergistic NIR-II PTT, chemotherapy, and CDT in a 4T1 murine model. Cy5.5-alendronate conjugates specifically target osteoblastic prostate cancer via NIR fluorescence [117].
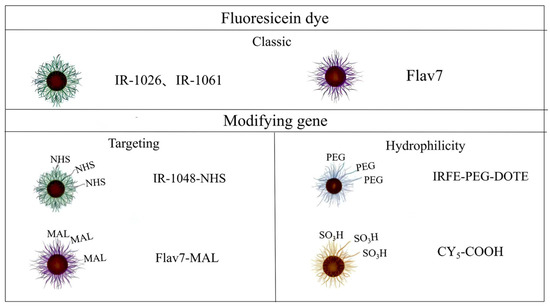
Figure 6.
Classification of NIR-II cyanine dyes modified by conventional and modifying groups.
Strategic incorporation of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) chains or sulfonic acid (-SO3H) groups further optimized aqueous solubility and biocompatibility profiles. The inherent hydrophobicity of squaraine (SQ) dyes was addressed through functionalization of each fluorene unit with azide-terminated alkyl side chains, enabling conjugation with poly(oligoethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate) (POEGMA) to yield water-soluble SQ-POEGMA conjugates with enhanced biocompatibility and photothermal efficacy [118]. Concurrently, Hongyun Qian et al. [119] developed hydrophilic quaternary sulfonate cyanine (HQS-Cy) dyes, where strategic incorporation of sulfonic acid groups and amphiphilic polypeptide encapsulation synergistically improved aqueous solubility while maintaining favorable biocompatibility profiles.
4.4. Rare Earth Nanomaterials
Rare-earth-doped nanoparticles have emerged as one of the most promising candidates for NIR-II bioimaging owing to their unique optical properties in this spectral region, including narrowband emission [120], exceptional photostability, deep-tissue penetration, prolonged luminescence lifetimes, and resistance to photobleaching [95,96]. However, the performance of rare-earth-based nanomaterials in NIR-II imaging exhibits significant divergence due to variations in dopant selection and structural engineering. Several limitations persist in current systems: (1) complex synthesis processes for multilayered core-shell architectures (e.g., NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4:Nd) requiring specialized techniques like thermal decomposition or co-assembly, posing scalability challenges [121]; (2) fluorescence quenching leading to diminished quantum yields; (3) unresolved biosafety concerns regarding long-term biocompatibility; and (4) intrinsic hydrophobicity necessitating surface modifications.
To address the limitations of rare-earth nanomaterials, strategic approaches such as dopant integration, surface functionalization, and protective shell encapsulation can be implemented. In Nd-Yb-Er co-doped NIR-II systems, multilayer core-shell architectures effectively suppress luminescence quenching [122]. Certain rare-earth ions demonstrate pronounced cytotoxicity, necessitating encapsulation within protective shells or coatings prior to biological applications to ensure biocompatibility. Notably, Yana Liu et al. developed a multifunctional platform (UCNPs@MIL-PEG) by coating PEG-functionalized metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) onto upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), which exhibited high biocompatibility in cytotoxicity assays for cancer theranostics [123]. To enhance aqueous dispersibility, surface modifiers such as PEG and Tween 20 (Tw) are typically grafted onto rare-earth nanoparticles (RENPs) [124].
Rare-earth luminescent probes exhibit versatile optical properties, encompassing both upconversion and downconversion emissions [125]. Energy upconversion, a nonlinear optical process, involves sequential absorption of multiple low-energy photons followed by intermediate energy-level transitions to emit higher-energy photons. This phenomenon primarily originates from the distinct electronic configurations and energy-transfer dynamics of lanthanide ions (e.g., Er3+, Tm3+, Ho3+, Pr3+, and Nd3+). The efficiency is governed by synergistic interactions between sensitizers and activators. Lanthanide-based nanoprobes represent an emerging class of NIR-II nanomaterials gaining prominence in bioimaging applications. As a primary dopant, Nd3+ exhibits optimal performance at 1–5% molar ratios, beyond which concentration quenching diminishes photoluminescence efficiency [126]. Precise tuning of Yb3+ and Er3+ content enhances local surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) absorption in low-aspect-ratio gold nanorods under 980 nm excitation, boosting PTT efficacy. Precise tuning of Yb3+ and Er3+ content enhances LSPR absorption in low-aspect-ratio gold nanorods under 980 nm excitation, boosting PTT efficacy [127]. Thus, rare-earth composition directly modulates emission wavelength and intensity. For deep-tumor imaging, surface modification with BSA, PEG, HA, or PLA improves blood circulation half-life, minimizes macrophage clearance, enhances tumor accumulation, and optimizes biocompatibility, solubility, and targeting [128]. Spatial separation of Nd3+ (sensitizer) and Er3+ (activator) across distinct layers maximizes 800 nm absorption while minimizing rare-earth cross-relaxation [129]. Yb/Ho/F-co-doped TiO2 generates ROS under 808 nm irradiation while exhibiting intensified upconversion fluorescence for deep-tissue imaging [130].
Skeletal metastases predominantly manifest in breast, prostate, and lung carcinomas via hematogenous dissemination [131]. Osteotropic malignancies present complex pathogenesis characterized by occult progression, elevated morbidity/mortality, and high recurrence rates, severely compromising terminal-stage patient prognosis [132]. He et al. engineered a ligand-free NIR-II fluorophore (RENPs@DSPE-mPEG) with intrinsic bone affinity, establishing a radiation-free diagnostic modality for skeletal mapping [133]. Antibody-functionalized rare-earth composites enable multimodal imaging (VIS/NIR-II down-/up-conversion) for precise lung adenocarcinoma delineation and intraoperative guidance [134]. Chen et al. developed NIR-II fluorophore (UiO-66-NH2@AuNS) core-shell nanostructures with NIR-II photothermal ablation capacity, where localized hyperthermia enhanced tumor perfusion while ameliorating hypoxic microenvironments [135].
4.5. Conjugated Polymer
Conjugated polymers have gained widespread application in NIR-II imaging owing to their advantageous properties, including high extinction coefficients, superior photothermal conversion efficiency, broad emission spectra, and facile synthesis [136,137]. Nevertheless, engineering conjugated polymers that simultaneously demonstrate optimal NIR-II fluorescence and PTT performance faces three key challenges: (1) limited aqueous solubility, (2) pronounced non-radiative decay causing substantial aggregation-caused quenching [138], and (3) inherently low NIR-II quantum yields in most developed systems, consistent with the energy gap law [98].
The above defects can be improved by optimizing conjugated polymer probes through post-polymerization modification or direct copolymerization to introduce polar/ionic groups and construct core-shell nanostructures. Structural integration of non-conjugated spacers yielded water-soluble nanoparticle (BTC12 NPs), enabling multimodal NIR-II FLI/PA/PTT imaging with 46.8% photothermal efficiency for tumor demarcation. To circumvent excessive non-radiative decay-induced fluorescence quenching, AIE-active NIR-II polymers were synthesized via Stille polycondensation. Dual structural engineering (AIE unit optimization and non-conjugated backbone incorporation) endowed BCT1 with αAIE = 3.27, 70.51% photothermal efficiency, and intense NIR-II emission [138]. Electron-donating moieties (thiophene derivatives) enhance conjugated polymer quantum yields [139]. Alkyl-functionalized bithiophene donors enabled the water-soluble nanoparticle (TTQ-2TC NPs) synthesis with organic solubility and bright NIR-II fluorescence [140]. Electron-acceptor density modulation through tetra-thiophene cores and alkyl side-chain engineering boosted radiative rates and NIR-II brightness [141].
A NIR-II-responsive conjugated polymer nanotheranostic platform (CPNPB) incorporating a nitric oxide (NO) donor has been developed to potentiate PTT (Figure 7). The system comprises three functional components: (1) a conjugated polymer backbone (IN-NDI), (2) a NO-releasing moiety (BNN6), and (3) an amphiphilic stabilizer (F127). This architecture demonstrates remarkable biocompatibility. The platform exhibits broad NIR-II absorption with 55.6% photothermal conversion efficiency, facilitating efficient heat generation at 1064 nm. Thermally induced BNN6 decomposition releases NO, synergistically enhancing the PTT efficacy [142].
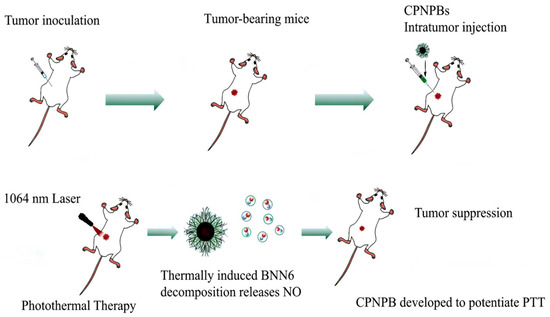
Figure 7.
The therapeutic effect of NIR-II conjugated polymer CPNPBs on PTT in tumor mice.
4.6. D-A-D Small Organic Molecule
D-A-D-type organic small molecules exhibit distinct advantages: well-defined structures, tunable optoelectronic properties, favorable metabolic profiles, substantial Stokes shifts, remarkable stability, and excellent biocompatibility. These characteristics render them particularly attractive for developing organic NIR-II fluorescent probes [100,101]. Nevertheless, fundamental limitations, including aggregation-caused quenching and the energy gap law, constrain their NIR-II quantum yields [143].
A D-π-A-π-D structured fluorophore (CED) was engineered into water-dispersible nanoparticles via DSPE-mPEG encapsulation, yielding a bright NIR-II emitter [144]. The D-A-D framework incorporated diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) as a strong acceptor to promote electron delocalization, complemented by cyclopentadithiophene (CPDT) as a secondary acceptor. The extended π-conjugation and intermolecular interactions risked aggregation-caused quenching. Isooctane side chains were grafted onto CPDT to suppress intermolecular interactions and prevent quenching. 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) π-bridges were introduced between CPDT and DPP to enhance quantum yield. This design extended conjugation, improved charge transfer, and induced molecular distortion. These fluorophores demonstrate intense absorption and bright NIR-II emission, permitting accurate tumor delineation and localized PTT [145].
D-A-D structured NIR-II fluorophores employing benzothiadiazole (BBTD) electron-accepting moieties have garnered considerable research interest, offering enhanced tissue penetration (>5 mm depth), minimized photon scattering, and favorable biosafety profiles [146]. COF-980, engineered with BBTD chromophores, demonstrates exceptional photoresistance, restricted molecular diffusion (logP = 3.2 ± 0.1), and depth-tunable ROS generation (~8 mm), enabling effective photodynamic tumor ablation through FLI-guided PDT in 4T1 models [147]. Pu et al. [14] developed BBTD/DSPE-PEG nanoprobes through solvent displacement synthesis, achieving passive tumor accumulation for intraoperative guidance in simulated ovarian tumor microenvironments (Figure 8a). Systemic administration via caudal vein enabled detection of 2-mm subclinical lesions with complete autofluorescence suppression in the NIR-I spectral regime (Figure 8b,c). Pre-laparotomy NIR-II mapping revealed fluorescent lymph node basins (cervical/axillary/iliac; Figure 8d), with ex vivo specimens confirming target specificity in adnexal structures (Figure 8e). Histopathological correlation (Figure 8f) validated the platform’s diagnostic accuracy for micron-scale ovarian malignancies. Multifunctional NIR-II fluorophore development thus critically advances colorectal cancer theranostics and FLI innovation.
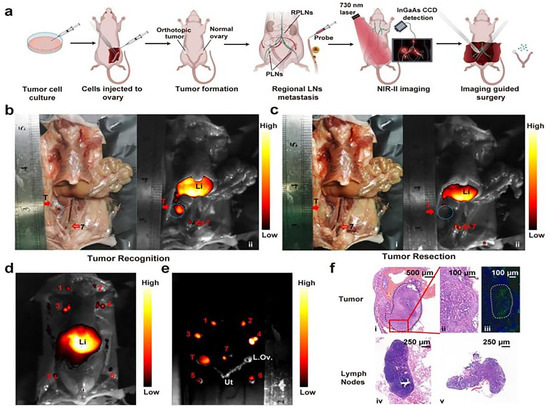
Figure 8.
NIR-II fluorescence imaging of orthotopic microtumors and lymph nodes. (a) S Experimental design for ovarian cancer modeling and imaging. (b,c) Surgical field visualization: (i) optical and (ii) NIR-II images (c: post-resection). (d) Pre-laparotomy lymph node imaging and guided resection. (e) Ex vivo imaging of resected tissues. (f) Histopathology: (i,ii) tumor H&E; (iii) CK-7+ tumor cells; (iv,v) lymph node H&E. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [14]. Copyright 2023, ACS.
5. NIR-Based FMT Systems and Reconstruction Algorithms
FMT is a non-invasive, highly sensitive imaging modality that enables 3D tumor visualization through reconstruction of NIR fluorescent probe distributions [148]. FMT systems and reconstruction algorithms represent active research frontiers in biomedical imaging, particularly when integrated with NIR-II technology to enhance imaging depth and resolution [149]. In the past few decades, NIR-I fluorophores dominated as the primary spectral window for FMT (NIR-I FMT). Conventional reconstruction frameworks employ photon transport models and inverse solving algorithms optimized for NIR-I parameters. Nevertheless, this spectral range exhibits pronounced scattering, precluding precise in vivo tumor localization. In contrast, the NIR-II window demonstrates reduced photon scattering, enabling NIR-II FMT to achieve superior reconstruction fidelity and spatial co-registration accuracy [150].
To enhance FMT performance, multiple computational strategies have been investigated. Conventional tomographic approaches employ Monte Carlo (MC) simulations or reduced-order radiative transfer equation (RTE) models to characterize forward photon transport. Yugo et al. [151] validated FMI-guided PDT for 9–15 mm tumors using ICG-C11-enhanced MC simulations in prone-position breast phantoms. Nevertheless, MC methods remain computationally prohibitive, severely limiting clinical translation. Simplified RTE frameworks implement diffusion equations with Robin boundary conditions to approximate photon propagation. Li et al. [152] integrated locality-preserving projection (LPP) with sparse regularization to mitigate reconstruction ill-posedness, demonstrating ICG-based high-resolution imaging in heterogeneous phantoms and murine models. The fast iterative contraction threshold algorithm (R-FISTA) achieves 30% faster convergence through adaptive step-size optimization without sacrificing precision [153]. Cai’s group [154] developed a Gaussian-weighted neighborhood fusion lasso (GWNFL) method for NIR-I/II FMT reconstruction in hepatoma-bearing mice, reporting localization errors of 2.13 mm (NIR-I) versus 0.84 mm (NIR-II) and Dice coefficients of 0.22 versus 0.76, respectively, confirming NIR-II’s superior accuracy through reduced scattering.
Advances in machine learning have driven the implementation of neural network-based reconstruction strategies to resolve these limitations. Cao et al. [155] developed an excitation-gated fully connected network (EFCN) modeling NIR-II photon transport in biological tissues. In vivo studies in glioma-bearing murine models demonstrated EFCN-enhanced NIR-II fluorescence imaging performance, achieving a mean centroid error of 0.26 mm and Dice coefficient of 0.78. Darwan et al. [156] further validated that laser-scan excitation synergized with artificial neural networks enables reliable depth imaging (>10 mm) in thick tissue sections across wide fields of view.
Contemporary FMT systems and algorithms exhibit a paradigm shift from conventional iterative approaches to deep learning integration, resulting in marked enhancements in both reconstruction velocity and precision. Nevertheless, practical implementations necessitate resolving persistent challenges including noise attenuation, multimodal data amalgamation, and real-time processing efficacy. Future advancements should focus on interdisciplinary integration of cutting-edge technologies and refinement of deep learning architectures to optimize imaging reconstruction efficacy and fidelity for clinical diagnostic precision.
6. Conclusions and Prospect
NIR fluorescent materials demonstrate significant advantages in tumor imaging, including deep tissue penetration, high signal-to-noise ratios, and real-time monitoring capabilities, yet face persistent technical limitations. NIR-I cyanine dyes (e.g., MB, ICG) exhibit limited penetration depths, rendering them ideal for superficial malignancies such as cutaneous and breast cancers. While these agents achieve emission tails > 1000 nm in the NIR-II window for subcutaneous tumor visualization, their quantum yields remain suboptimal due to aggregation-caused quenching from intermolecular π-π stacking. Commercially available NIR probes (e.g., IR806) predominantly lack tumor-specific targeting ligands, relying on passive accumulation via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, which induces nonspecific uptake and background interference. NIR-II nanomaterials, including nanoparticles, QDs, and rare-earth-doped materials, have a superior performance in penetration depth, signal-to-background ratio, and biocompatibility when compared to visible/NIR-I probes. However, QDs exhibit inherent heavy metal toxicity (Ag, Se, Pb), while rare-earth nanostructures show lower quantum yields compared to organic NIR-II dyes, compounded by aqueous solubility challenges and rapid photobleaching. Emerging organic NIR-II fluorophores, refined through surface engineering and core-shell architectures, demonstrate enhanced biocompatibility and safety profiles. Nevertheless, their clinical translation remains hindered by synthetic complexity and poor hydrophilicity. Furthermore, existing single-modality platforms fail to integrate synergistic therapeutic modalities such as PTT and PDT with real-time feedback.
To further improve the accuracy of NIR fluorescence image-guided surgery, several strategies can be adopted. The fluorescence wavelength and quantum yield can be regulated by extending the π-conjugated system or introducing electron-withdrawing/electron-donating groups to adjust the intramolecular torsion angle of the polymer. Develop activation-type nanoprobes to achieve the “OFF-to-ON” activation of NIR-II fluorescence. In addition, the persistent luminescence of nanoparticles is critical for advancing NIR bioimaging applications. The use of micelle and polymer coating can reduce the aggregation quenching effect and improve light stability at the same time. The penetration depth and signal-to-noise ratio are improved by designing a probe (NIR-III) that emits fluorescence within a longer wavelength range. The integration of multimodal synergistic therapy and imaging enables panoramic visualization from macroscopic anatomy to microscopic molecular level, thereby enhancing the therapeutic effect. For specific markers (such as pH, GSH, H2O2), intelligent probes that can provide real-time feedback on the metabolic status of tumors can be designed. Target-specific probes are crucial for the success of imaging applications. Developing NIR-II materials with multiple specific targets and stronger affinity may be a very promising research direction in the future. Future work should converge multidisciplinary technologies to engineer fluorescent probes with amplified signal intensity, synergized with advanced reconstruction algorithms for ultra-sensitive tumor imaging that addresses clinical precision medicine requirements.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, M.Y.; Writing—review and editing, X.L., S.W. and Z.Q.; Supervision, Z.L.; Project administration, B.H.; Funding acquisition, B.H. and S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Hebei Research Center of Pharmaceutical and Chemical Engineering (225676121H), the Higher Education Teaching Reform Research and Practice Project of Hebei Province (2022GJJG186), and the State Key Laboratory Breeding Base-Hebei Province Key Laboratory of Molecular Chemistry for Drug (No. 25).
Data Availability Statement
Raw data and images are available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, W.; Wu, C.; Qin, M.; Cai, F.; Huang, J. The aura of malignant tumor: Clinical analysis of malignant tumor-related pyogenic liver abscess. Medicine 2020, 99, e19282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Meng, Y.; Jiang, R.; Ge, S.; Song, M. Effect of Multimodal Exercise on Cancer-Related Fatigue in Patients Undergoing Simultaneous Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy: A Randomized Trial in Patients with Breast Cancer. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2023, 29, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.M.; Russell, R.G.G. Advances in the molecular pharmacology of bone and cancer-related bone diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1889–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donegan, W.L. Recent trends in the management of breast cancer. 3. Controversies in the use of adjuvant chemotherapy, hormonotherapy and radiotherapy for breast cancer. Can. J. Surg. 1992, 35, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, F.; Wei, X. Copolymerized carbon nitride nanoparticles for near-infrared II photoacoustic-guided synergistic photothermal/radiotherapy. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1124559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yin, B.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, B.; Zhou, N.; et al. Endoscopically guided interventional photodynamic therapy for orthotopic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on NIR-II fluorescent nanoparticles. Theranostics 2023, 13, 4469–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Weng, J.; Wen, X.; Liu, Y.; Ye, D. A carbonic anhydrase-targeted NIR-II fluorescent cisplatin theranostic nanoparticle for combined therapy of pancreatic tumors. Biomaterials 2024, 305, 122454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Hu, H.; Sun, Z.; He, P.; Zhu, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Wei, G. Assembling Ag2S quantum dots onto peptide nanosheet as a biomimetic two-dimensional nanoplatform for synergistic near infrared-II fluorescent imaging and photothermal therapy of tumor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 663, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Shao, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Xiong, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X.; Zeng, L.; Yang, Z.; et al. Near-infrared-II Ag2S quantum dot probes targeting podoplanin enhance immunotherapy in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Pharm. 2024, 170, 116011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Qian, Y.; Hu, L.; Fang, J.; Tong, W.; Nie, R.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H. Magnetic-induced graphene quantum dots for imaging-guided photothermal therapy in the second near-infrared window. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Pu, R.; Wang, B.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, K.; Wang, F.; Wei, W.; Liu, H.; Zhan, Q. The Spectroscopic Properties and Microscopic Imaging of Thulium-Doped Upconversion Nanoparticles Excited at Different NIR-II Light. Biosensors 2021, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Lv, J.; Fang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Lv, Z.; Li, P.; Yao, X.; et al. A multifunctional antibacterial coating on bone implants for osteosarcoma therapy and enhanced osteointegration. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 428, 131155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, A.; Zhang, S.; Wei, G.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Z.; Lu, W. Molecular Engineering of Near-Infrared-II Photosensitizers with Steric-Hindrance Effect for Image-Guided Cancer Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Peng, J.; Wang, Z.; Du, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, F.; Zhang, M.; Li, F.; et al. NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging for the Detection and Resection of Cancerous Foci and Lymph Nodes in Early-Stage Orthotopic and Advanced-Stage Metastatic Ovarian Cancer Models. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 32226–32239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Sun, B.; Li, M.; Han, T.; Yu, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Q. High-precision detection and navigation surgery of colorectal cancer micrometastases. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gao, S. Recent advances in fluorescence imaging-guided photothermal therapy and photodynamic therapy for cancer: From near-infrared-I to near-infrared-II. J. Control. Release 2023, 362, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bag, N.; Bardhan, S.; Hasan, I.; Guo, B. Recent progress in NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided drug delivery for cancer theranostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 197, 114821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Roy, S.; Gu, J.; Ko Soe, S.; Jin, J.; Guo, B. NIR-II Fluorescent Probes for Fluorescence-Imaging-Guided Tumor Surgery. Biosensors 2024, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Kang, M.-W.; Kashiwagi, S.; Choi, H.S. NIR fluorescence imaging and treatment for cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.A.; Franke, D.; Caram, J.R.; Perkinson, C.F.; Saif, M.; Askoxylakis, V.; Datta, M.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K.; Bawendi, M.G.; et al. Shortwave infrared fluorescence imaging with the clinically approved near-infrared dye indocyanine green. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4465–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Yang, F.; Han, R.; Yang, C.; Li, W.; Qian, Z. Near-infrared responsive 5-fluorouracil and indocyanine green loaded MPEG-PCL nanoparticle integrated with dissolvable microneedle for skin cancer therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 297–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Ohta, M.; Kato, Y.; Inada, S.; Kato, T.; Nakata, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Goto, M.; Kaneda, N.; Kurita, K.; et al. A Real-Time Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Method for the Detection of Oral Cancers in Mice Using an Indocyanine Green-Labeled Podoplanin Antibody. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.-C.; Hu, J.-L.; Bai, J.-W.; Zhang, G.-J. Detection of Sentinel Lymph Nodes with Near-Infrared Imaging in Malignancies. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 21, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Du, Y.; Liang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Tian, J. A Novel Estrogen Receptor α-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe for in Vivo Detection of Breast Tumor. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4702–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Du, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, C.; Fang, J.; Lu, W.; Guo, X.; Tian, J.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, J. Synergistic triple-combination therapy with hyaluronic acid-shelled PPy/CPT nanoparticles results in tumor regression and prevents tumor recurrence and metastasis in 4T1 breast cancer. Biomaterials 2019, 217, 119264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.W.; Teraphongphom, N.; de Boer, E.; van den Berg, N.S.; Divi, V.; Kaplan, M.J.; Oberhelman, N.J.; Hong, S.S.; Capes, E.; Colevas, A.D.; et al. Safety of panitumumab-IRDye800CW and cetuximab-IRDye800CW for fluorescence-guided surgical navigation in head and neck cancers. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2488–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Qiu, S.; Ma, Q.; Bai, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Near-infrared dye IRDye800CW-NHS coupled to Trastuzumab for near-infrared II fluorescence imaging in tumor xenograft models of HER-2-positive breast cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 10738–10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Chen, J.; Gao, R.; Chen, R.; Xue, Q.; Ren, Y.; Liu, L.; Tang, C.; Hu, H.; Zeng, N.; et al. NIR-II Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Oxygen Delivery and Controlled Release Improves Photodynamic Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Adv. Mater. 2023, 34, 2308780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Johnson, J.; Peck, A.; Xie, Q. Near infrared fluorescent imaging of brain tumor with IR780 dye incorporated phospholipid nanoparticles. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Li, K.; Kang, X.; Li, K.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Li, N.; Wu, G.; et al. Rational design of NIR-II molecule-engineered nanoplatform for preoperative downstaging and imaging-guided surgery of orthotopic hepatic tumor. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Qu, F.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, P.; Li, X.; Shen, Q.; Li, D.; Fan, Q. NIR-II Excitation Phototheranostic Platform for Synergistic Photothermal Therapy/Chemotherapy/Chemodynamic Therapy of Breast Cancer Bone Metastases. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2204718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zeng, X.; Li, A.; Zhou, W.; Tang, L.; Hu, W.; Fan, Q.; Meng, X.; Deng, H.; Duan, L.; et al. Upconversion NIR-II fluorophores for mitochondria-targeted cancer imaging and photothermal therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yan, D.; Wang, M.; Wu, Q.; Song, R.; Huang, Y.; Rao, J.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F.; Tang, B.Z. A Versatile 980 nm Absorbing Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen for NIR-II Imaging-Guided Synergistic Photo-Immunotherapy Against Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 9, 2204718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Ye, X.; Xie, M.; Feng, L.; Niu, X.; You, Z. Ultra-homogeneous Cu2−xSe nanoparticles as near-infrared II plasmonic phototheranstics for photothermal/chemodynamic synergistic therapy of liver cancer. Particuology 2022, 76, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Hu, H.; Mo, Z.; Chen, T.; He, Q.; Xu, Z. A multifunctional nanotheranostic agent based on Lenvatinib for multimodal synergistic hepatocellular carcinoma therapy with remarkably enhanced efficacy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 638, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Duan, G.; Huang, B.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, D.; Zeng, J.; Cui, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; Wen, L.; et al. Rapidly liver-clearable rare-earth core–shell nanoprobe for dual-modal breast cancer imaging in the second near-infrared window. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, K.-L.; Wang, P.-Y.; Yang, R.-Q.; Gao, Y.-Y.; Tian, H.-N.; Dang, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.-H.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.-L.; et al. Fabrication of tumor targeting rare-earth nanocrystals for real-time NIR-IIb fluorescence imaging-guided breast cancer precise surgery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 2, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, R.; Jiang, P.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Z. CA IX-targeted Ag2S quantum dots bioprobe for NIR-II imaging-guided hypoxia tumor chemo-photothermal therapy. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Du, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, J.; Zhou, B.; Dong, B.; Zhang, X.; Alifu, N. Ultrabright NIR-IIb Fluorescence Quantum Dots for Targeted Imaging-Guided Surgery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 32045–32057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Liu, F.; Muhammad, M.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S. Application of biomacromolecule-based passive penetration enhancement technique in superficial tumor therapy: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 272, 132745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, X.; Du, W.; Sun, M.; Ling, G.; Zhang, P. Microneedle-mediated treatment for superficial tumors by combining multiple strategies. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 1600–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, B.D.; Kuruva, M.; Shim, H.; Mullins, M.E. Clinical Applications of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Brain Tumors From Diagnosis to Treatment. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 59, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Ban, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Cao, P.; Yu, M.; Duan, X. MRI-visualized PTT/CDT for breast cancer ablation and distant metastasis prevention. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 36, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, M.; Pirayesh Islamian, J. Breast cancer: Early diagnosis and effective treatment by drug delivery tracing. Nucl. Med. Rev. Cent. East. Eur. 2017, 20, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhanova, A.; Ramos-Gomes, F.; Chames, P.; Sokolov, P.; Baty, D.; Alves, F.; Nabiev, I. Multiphoton Deep-Tissue Imaging of Micrometastases and Disseminated Cancer Cells Using Conjugates of Quantum Dots and Single-Domain Antibodies. Mol. Biol. 2021, 2350, 105–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, F.; Jiang, G.; Wang, J. Applications of indocyanine green based near-infrared fluorescence imaging in thoracic surgery. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, S738–S743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.W.; Huang, V.; Arguelles, G.R.; Zhou, C.; Cho, S.S.; Harmsen, S.; Lee, J.Y.K. Applications of indocyanine green in brain tumor surgery: Review of clinical evidence and emerging technologies. Neurosurg. Focus 2021, 50, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmut, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ruan, F.; Shi, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Tang, Z.; Dong, B.; Gao, D.; et al. Medical Applications and Advancement of Near Infrared Photosensitive Indocyanine Green Molecules. Molecules 2023, 28, 6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starosolski, Z.; Bhavane, R.; Ghaghada, K.B.; Vasudevan, S.A.; Kaay, A.; Annapragada, A. Indocyanine green fluorescence in second near-infrared (NIR-II) window. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Long, Y.; Sheng, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, B. Progress in application of near-infrared fluorescence imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of oral cancer. J. Cent. South Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2021, 46, 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Ledezma, D.K.; Balakrishnan, P.B.; Cano-Mejia, J.; Sweeney, E.E.; Hadley, M.; Bollard, C.M.; Villagra, A.; Fernandes, R. Indocyanine Green-Nexturastat A-PLGA Nanoparticles Combine Photothermal and Epigenetic Therapy for Melanoma. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egloff-Juras, C.; Bezdetnaya, L.; Dolivet, G.; Lassalle, H.-P. NIR fluorescence-guided tumor surgery: New strategies for the use of indocyanine green. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7823–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Ren, E.; Xu, D.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, G. Indocyanine green-based nanodrugs: A portfolio strategy for precision medicine. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Manen, L.; Handgraaf, H.J.M.; Diana, M.; Dijkstra, J.; Ishizawa, T.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; Mieog, J.S.D. A practical guide for the use of indocyanine green and methylene blue in fluorescence-guided abdominal surgery. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 118, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yan, L.; Amirshaghaghi, A.; Wei, Y.; You, T.; Singhal, S.; Tsourkas, A.; Cheng, Z. Indocyanine Green-Coated Polycaprolactone Micelles for Fluorescence Imaging of Tumors. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2344–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, M.; Mei, T.; Deng, G.; Guo, P.; Li, Y.; Sheng, R. Rationally assembled albumin/indocyanine green nanocomplex for enhanced tumor imaging to guide photothermal therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Bian, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H. The multifaceted roles of peptides in “always-on” near-infrared fluorescent probes for tumor imaging. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 129, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, C.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, X. Indocyanine Green Loaded Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as an Effective Photothermal Nanoplatform. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Kiedrowski, V.; Hübner, R.; Kail, D.; Cheng, X.; Schirrmacher, R.; Wängler, C.; Wängler, B. Synthesis, characterization and optimization of in vitro properties of NIR-fluorescent cyclic α-MSH peptides for melanoma imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10602–10608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Tao, X.; Lv, R. Nd-Mn Molecular Cluster with Searched Targets for Oral Cancer Imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2023, 25, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, S.A.A.; Johnson, K.K.; Nair, M.; Louis, J.M.; Sankaran, S.; Rajagopal, R.; Kumar, K.S.; Abraham, P.; Balagopal, P.G.; Sebastian, P.; et al. TM1-IR680 peptide for assessment of surgical margin and lymph node metastasis in murine orthotopic model of oral cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Pei, S.; Wen, K.; Peng, A.; Ma, H.; Huang, H. MC1R-targeted NIR-II aggregation-induced emission nanoparticles for melanoma imaging. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 66, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Kang, Y.F.; Mao, Q.Y.; Li, Z.M.; Shan, X.F.; Cai, Z.G. Application of methylene blue near-infrared fluorescence imaging for oral sentinel lymph node mapping in rats. J. Peking Univ. Health Sci. 2023, 55, 684–688. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-X.; Mao, Q.-Y.; Kang, Y.-F.; Xie, S.; Shan, X.-F.; Cai, Z.-G. In Vivo Oral Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping by Near-Infrared Fluorescent Methylene Blue in Rats. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwalinski, T.; Polom, W.; Marano, L.; Roviello, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Cwalina, N.; Matuszewski, M.; Roviello, F.; Jaskiewicz, J.; Polom, K. Methylene Blue—Current Knowledge, Fluorescent Properties, and Its Future Use. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillary, S.L.; Guillermet, S.; Brown, N.J.; Balasubramanian, S.P. Use of methylene blue and near-infrared fluorescence in thyroid and parathyroid surgery. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2017, 100, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonni, S.; Brindley, D.N.; Chamberlain, M.D.; Daneshvar-Baghbadorani, N.; Freywald, A.; Hemmings, D.G.; Hombach-Klonisch, S.; Klonisch, T.; Raouf, A.; Shemanko, C.S.; et al. Breast Tumor Metastasis and Its Microenvironment: It Takes Both Seed and Soil to Grow a Tumor and Target It for Treatment. Cancers 2024, 16, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinske, S.H.; Spellman, J.; Henry, L.; Shannon, M. Timeliness of Breast Cancer Treatment in Delaware. Del. J. Public Health 2017, 3, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturesdotter, L.; Larsson, A.-M.; Zackrisson, S.; Sartor, H. Investigating the prognostic value of mammographic breast density and mammographic tumor appearance in women with invasive breast cancer: The Malmo Diet and cancer study. Breast 2023, 70, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Mao, Y.; Wang, K.; Tian, J. The identification of breast cancer by Near-Infrared fluorescence imaging with methylene blue. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, E12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, S.G.; Krämer, R. Accessing Structurally Diverse Near-Infrared Cyanine Dyes for Folate Receptor-Targeted Cancer Cell Staining. Chem.—Eur. J. 2017, 23, 9306–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usama, S.M.; Lin, C.-M.; Burgess, K. On the Mechanisms of Uptake of Tumor-Seeking Cyanine Dyes. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3886–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Fan, D.; Shao, Z.; Xu, B.; Ren, G.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. CACA Guidelines for Holistic Integrative Management of Breast Cancer. Holist. Integr. Oncol. 2022, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, M.M.M.; Murai, Y.; Monde, K.; Tsuboi, S.; Jin, T. Shortwave-Infrared Fluorescent Molecular Imaging Probes Based on π-Conjugation Extended Indocyanine Green. Bioconjugate Chem. 2021, 32, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Pantarat, N.; Suzuki, T.; Evdokiou, A. Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Using a Small Protein Mimetic for HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Park, M.H.; Hyun, H. Structure-Inherent Tumor-Targeted IR-783 for Near-Infrared Fluorescence-Guided Photothermal Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yan, L.; Hu, Q.; Yin, D. NIR-II fluorescence imaging in liver tumor surgery: A narrative review. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2024, 17, 2330010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Fang, J.; Ye, S.; Wang, A.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, C.; He, L.; Shi, H. Smart On-Site Immobilizable Near-Infrared II Fluorescent Nanoprobes for Ultra-Long-Term Imaging-Guided Tumor Surgery and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 12857–12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Cheng, Z. Chapter 23—Near-Infrared II Optical Imaging. In Molecular Imaging, 2nd ed.; Ross, B.D., Gambhir, S.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 12, pp. 397–420. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Zhao, S.; Hong, G. Wireless deep-brain neuromodulation using photovoltaics in the second near-infrared spectrum. Device 2023, 1, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, n.; Wang, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, L.; Ye, J.; Sun, G. Progress of NIR-II fluorescence imaging technology applied to disease diagnosis and treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 267, 116173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ni, S.; Ma, Q.; Song, X.; Yang, H. Engineering NIR-II luminescent lanthanide nanoprobes for imaging brain diseases in vivo. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 496, 215401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Hu, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Ming, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, F. NIR-II Ratiometric Lanthanide-Dye Hybrid Nanoprobes Doped Bioscaffolds for In Situ Bone Repair Monitoring. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cao, K.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Chen, G.; Wang, Q. An oral ratiometric NIR-II fluorescent probe for reliable monitoring of gastrointestinal diseases in vivo. Biomaterials 2023, 293, 121956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhuang, P.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Sun, S.-K. Rational synthesis of IR820-albumin complex for NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided surgical treatment of tumors and gastrointestinal obstruction. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 12136–12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, G.; Pan, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.-K. Purification-free synthesis of bright lactoglobulin@dye nanoprobe for second near-infrared fluorescence imaging of kidney dysfunction in vivo. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 236, 113796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Tang, X.; Wang, M.; Du, Z.; Chen, S.; Heng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Alifu, N.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C. Clinical indocyanine green-based silk fibroin theranostic nanoprobes for in vivo NIR-I/II fluorescence imaging of cervical diseases. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2023, 47, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Sun, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Tian, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q. Precise Examination of Peripheral Vascular Disease for Diabetics with a Novel Multiplexed NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging Technology. Nano Today 2022, 43, 101378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Rustique, E.; Henry, M.; Guidetti, M.; Josserand, V.; Sancey, L.; Boutet, J.; Coll, J.-L. Targeting tumors with cyclic RGD-conjugated lipid nanoparticles loaded with an IR780 NIR dye: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2017, 532, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, M.; Gu, J.; Roy, S.; Jin, J.; Kuang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G.; Guo, B. Bright NIR-II emissive cyanine dye-loaded lipoprotein-mimicking nanoparticles for fluorescence imaging-guided and targeted NIR-II photothermal therapy of subcutaneous glioblastoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhu, J.; Dong, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. Polyvalent Aptamer-Functionalized NIR-II Quantum Dots for Targeted Theranostics in High PD-L1-Expressing Tumors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 21571–21581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-L.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Ren, M.; Kong, J.; Zong, X.; Luo, M.-Y.; Tang, B.; Xie, J.; Pang, D.-W.; et al. Acid-Resistant Near-Infrared II Ag2Se Quantum Dots for Gastrointestinal Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2023, 45, 15540–15548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, M.; Ma, P.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Lin, J. Assembling AgAuSe Quantum Dots with Peptidoglycan and Neutrophils to Realize Enhanced Tumor Targeting, NIR (II) Imaging, and Sonodynamic Therapy. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2201706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, D.; Gao, D.; Liu, C.; Zheng, H.; Sheng, Z. Miniature NIR-II Nanoprobes for Active-Targeted Phototheranostics of Brain Tumors. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 22023799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Li, G.; Yang, B.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Investigation of rare earth upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles in biomedical field. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2019, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y. Rare earth-doped nanocrystals for bioimaging in the near-infrared region. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 8596–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, H.; Liang, S.; Chen, D.; Xu, K.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. In Vivo NIR-II Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging of Whole-Body Vascular Using High Quantum Yield Lanthanide-Doped Nanoparticles. Small 2023, 19, 2300392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Yin, C.; Fan, Q. Size Modulation of Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles for Improved NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 4420–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Yang, Z.; Qu, F.; Du, X.; Shen, Q.; Fan, Q. Conjugated/nonconjugated alternating copolymers for enhanced NIR-II fluorescence imaging and NIR-II photothermal-ferrotherapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 9830–9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; He, C.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Chen, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Xiao, C. Regulating Electron Acceptor Unit to Construct Conjugated Polymer Probe for Raman Imaging of Tumor and Sentinel Lymph Nodes. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 19422–19429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terayama, K.; Habuchi, S.; Michinobu, T. Structural design of conjugated polymers for fluorescence bioimaging in the second near-infrared window. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 2276–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, D.; Ray, P.; Pan, D. Unlocking the power of optical imaging in the second biological window: Structuring near-infrared II materials from organic molecules to nanoparticles. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotech. 2021, 13, E1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, T.; Wu, X.; Lin, Y.; Shi, X.; Qian, J.; Nie, R.; Wang, H. NIR-II Responsive Fe-Doped Carbon Nanoparticles for Photothermal-Enhanced Chemodynamic Synergistic Oncotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 17, 7211–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, S.; Ma, R.; Ji, C.; Müllen, K.; Yin, M. NIR-triggered dual sensitization of nanoparticles for mild tumor phototherapy. Nano Today 2022, 42, 101363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, S.; Mansour, N.; Daher, C.F.; Elias, M.G.; Dagher, C.; Khnayzer, R.S. Drug-free phototherapy of superficial tumors: White light at the end of the tunnel. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2021, 224, 112324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, J.; Mo, F.; Tang, D.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Jia, J.; Liu, T. Targeting Bone Tumor and Subcellular Endoplasmic Reticulum via Near Infrared II Fluorescent Polymer for Photodynamic-Immunotherapy to Break the Step-Reduction Delivery Dilemma. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2201819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tang, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, L.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, H. Biodegradable Polymer with Effective Near-Infrared-II Absorption as a Photothermal Agent for Deep Tumor Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 112324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Chan, K.W.Y.; Lee, C.S.; Yin, C.; Bian, L.; et al. Effective Phototheranostics of Brain Tumor Assisted by Near-Infrared-II Light-Responsive Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33492–33499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Lian, X.; Xiong, C.; Tian, R.; Hu, L.; Xiong, X.; Tian, J. uPAR targeted phototheranostic metal-organic framework nanoprobes for MR/NIR-II imaging-guided therapy and surgical resection of glioblastoma. Mater. Des. 2021, 198, 109396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Morsch, M.; Lu, Y.; Shangguan, P.; Han, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Song, C.; Liu, S.; et al. Brain-Targeted Aggregation-Induced-Emission Nanoparticles with Near-Infrared Imaging at 1550 nm Boosts Orthotopic Glioblastoma Theranostics. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Tang, T.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.-H.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Zhang, M.; Cui, R. Quantum dots boost large-view NIR-II imaging with high fidelity for fluorescence-guided tumor surgery. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebibula, A.; Alifu, N.; Xia, L.; Sun, C.; Yu, X.; Xue, D.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Qian, J. Ultrastable and Biocompatible NIR-II Quantum Dots for Functional Bioimaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 28, 1703451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wang, L.; Fan, C.; Gao, J.; Sun, Y. Angiopep-2-conjugated Ag2S Quantum Dot for NIR-II Imaging of Brain Tumors. Acta Chim. Sin. 2018, 76, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, H.; Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Han, Z. Progress of near-infrared-II fluorescence in precision diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. Heliyon 2023, 9, e23209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Xue, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hong, X.; Wu, M.; Xiao, Y. NIR-II fluorescence/photoacoustic imaging of ovarian cancer and peritoneal metastasis. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, L.; Jin, S.; Zhou, W.; Guan, X.; Kang, P.; Zhang, C.; et al. Preclinical assessment of IRDye800CW-labeled gastrin-releasing peptide receptor-targeting peptide for near infrared-II imaging of brain malignancies. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, E10532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasco, J.A.; Yu, G.; Kumar, A.; Perez, J.; Lirag, R.C.M.; Whitley, E.M.; Lin, S.-H.; Melancon, M.P. Alendronate conjugate for targeted delivery to bone-forming prostate cancer. Talanta 2023, 256, 124308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, S.; Deng, W.; Wu, S.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y. Water-soluble polymer brush-substituted squaraine NIR-II dye for efficient photothermal therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 4389–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Cheng, Q.; Tian, Y.; Dang, H.; Teng, C.; Yan, L. An anti-aggregation NIR-II heptamethine-cyanine dye with a stereo-specific cyanine for imaging-guided photothermal therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2688–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Ting, Z.; Xiaojun, S.; Zuqiang, W.; Quli, F.; Wei, H. Rare-earth Doped Nanoparticles with Narrow NIR-II Emission for Optical Imaging with Reduced Autofluorescence. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2021, 37, 943–950. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yun, B.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Ren, F.; Li, Z. Dye-Sensitized Rare Earth Nanoparticles with Up/Down Conversion Luminescence for On-Demand Gas Therapy of Glioblastoma Guided by NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 11, 2102042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Feng, W. Fine-tuning of composition in multi-layered core-shell rare earth nanoparticles for the enhanced NIR-II emission. Mater. Res. Bull. 2024, 178, 112889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Whittaker, A. Controllable synthesis of up-conversion nanoparticles UCNPs@MIL-PEG for pH-responsive drug delivery and potential up-conversion luminescence/magnetic resonance dual-mode imaging. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 749, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.; Chen, J.-K.; Jain, V.; Agrawal, L.; Lin, C.-A.J.; Chen, M.-H. The Influence of Surface Modification on the Shortwave Infrared Emission of Rare-Earth-Doped Nanoparticles. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2023, 44, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Dai, H. A mini-review on rare-earth down-conversion nanoparticles for NIR-II imaging of biological systems. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Multifunctional NaYF4:Nd/NaDyF4 nanocrystals as a multimodal platform for NIR-II fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 3, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Liu, B.; Gai, S.; He, F.; Yang, P. Multimodal imaging and photothermal therapy were simultaneously achieved in the core–shell UCNR structure by using single near-infrared light. Dalton Trans. 2017, 36, 12147–12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, S.; Ding, B.; Qu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Fang, H.; Long, Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Rare Earth Doped Nanoparticles for Tumor Surgery Navigation in NIR-II Imaging Window. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 385, 123959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Ge, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhao, T.; Lu, X.; Fan, Q. Nd3+-sensitized multilayered rare-earth nanocrystals with enhanced NIR-IIb luminescence for high resolution optical imaging. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 25060–25067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Luo, P.; Sun, C.; Meng, L.; Ye, W.; Chen, S.; Du, B. A “win-win” nanoplatform: TiO2:Yb,Ho,F for NIR light-induced synergistic therapy and imaging. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4244–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, M.; Volpi, M.; Walejewska, E.; Olszewska, A.; Swieszkowski, W. Printing of 3D biomimetic structures for the study of bone metastasis: A review. Acta Biomater. 2024, 178, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, B.; Jiao, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Yu, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Application of advanced biomaterials in photothermal therapy for malignant bone tumors. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Song, J.; Liu, L.; Qu, J.; Cheng, Z. High Affinity to Skeleton Rare Earth Doped Nanoparticles for Near-Infrared II Imaging. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Wang, Y.; Lin, B.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Lu, W.-d.; Tian, J. Targeted Luminescent Probes for Precise Upconversion/NIR II Luminescence Diagnosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4984–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Peng, J.; Huang, N.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J. Biotin-decorated hollow gold nanoshells for dual-modal imaging-guided NIR-II photothermal and radiosensitizing therapy toward breast cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 10003–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yuan, P.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, P.; Huang, W.; Fan, Q. A highly water-soluble triblock conjugated polymer for in vivo NIR-II imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3118–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Duan, X.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Ding, D.; Deng, Y.; Han, Y.; Geng, Y. NIR-II-absorbing conjugated polymers based on tetra-fused isoindigo ribbons for photothermal conversion and photoacoustic imaging. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; He, J.; Xi, C.; Xu, S.; Shen, Q.; Chen, P.; Sun, P.; Fan, Q. Aggregation-Induced Emission Near-Infrared (NIR)-II-Conjugated Polymers Coupled With Nonconjugated Segments for NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging–Guided NIR-II Photothermal Therapy. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2024, 225, 2400268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zou, W.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. A design strategy for D–A conjugated polymers for NIR-II fluorescence imaging. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 4707–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Lu, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, H.; Sun, P.; Miao, H.; Fan, Q.; Huang, W. Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles with Absorption beyond 1000 nm for NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging System Guided NIR-II Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Jiang, X.; Sun, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Fan, Q.; Huang, W. Electron-acceptor density adjustments for preparation conjugated polymers with NIR-II absorption and brighter NIR-II fluorescence and 1064 nm active photothermal/gas therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 280, 121319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Sun, X.; Qi, Q.; Fu, M.; Han, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ni, T.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; et al. NIR-II Absorbing Conjugated Polymer Nanotheranostics for Thermal Initiated NO Enhanced Photothermal Therapy. Biosensors 2023, 13, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, L.; Sun, T.; Gong, M.; Zhang, D. Bright “D–A–D” semiconducting small molecule aggregates for NIR-II fluorescence bioimaging guiding photothermal therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 13, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, R.; Gao, J.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y. NIR-II organic small molecule probe for labeling lymph nodes and guiding tumor imaging. Talanta 2023, 266, 125123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Su, Y.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. D–A–D organic small molecules with AIE effect for fluorescence imaging guided photothermal therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 11, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Q.; Xu, X.-Y.; Cao, S.-Q.; Zou, Y.-Q. Structures and Applications of NIR-II AIEgens Containing Benzobisthiadiazole Derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 44, e202201131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dou, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, P.; Wen, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, R. Rationally Designed Benzobisthiadiazole-Based Covalent Organic Framework for High-Performance NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging-Guided Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2303842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Li, C.; Xiao, A.; Tian, Y.; Tian, J.; Hu, Z. TSPE: Reconstruction of multi-morphological tumors of NIR-II fluorescence molecular tomography based on positional encoding. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025, 261, 108554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Zhang, P.; Wu, H.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z.; Cai, R.; Feng, Y.; He, Y.; Dong, X.; Tian, Y.; et al. Advances of Fluorescence Molecular Imaging: NIR-II Window, Probes, and Tomography. Laser Photonics Rev. 2025, 19, 2400275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, C.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Nanoaggregate Probe for Breast Cancer Metastasis through Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography and Aggregation-Induced NIR-I/II Fluorescence Imaging. Angew. Chem. 2019, 59, 10111–10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minegishi, Y.; Nomura, Y. Fluorescence molecular imaging-guided photodynamic therapy for early breast cancer in the prone position: Feasibility evaluation with Monte Carlo simulations. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2025, 52, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Wu, J.; Lu, L.; Feng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Chen, W. Model-Based Optoacoustic Tomography Image Reconstruction With Non-local and Sparsity Regularizations. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 102136–102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Ye, J.; Tian, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, B.; Dai, M.; Xu, C.; Fu, F. Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm with Continuation for Brain Injury Monitoring Imaging Based on Electrical Impedance Tomography. Sensors 2022, 22, 9934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Hu, Z.; Tian, J. NIR-II/NIR-I Fluorescence Molecular Tomography of Heterogeneous Mice Based on Gaussian Weighted Neighborhood Fused Lasso Method. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xiao, A.; Cai, M.; Shen, B.; Guo, L.; Shi, X.; Tian, J.; Hu, Z. Excitation-based fully connected network for precise NIR-II fluorescence molecular tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 6284–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwan, D.; Lim, K.R.G.; Wijaya, H.; Lim, Z.C.; Wang, T.; Ang, W.H.; Tan, Z.-K. Deep Fluorescence Imaging by Laser-Scanning Excitation and Artificial Neural Network Processing. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 2000390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).