Phase and Valence State Engineering of MOFs-Derived Iron Oxide@Carbon Polyhedrons for Advanced Microwave Absorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
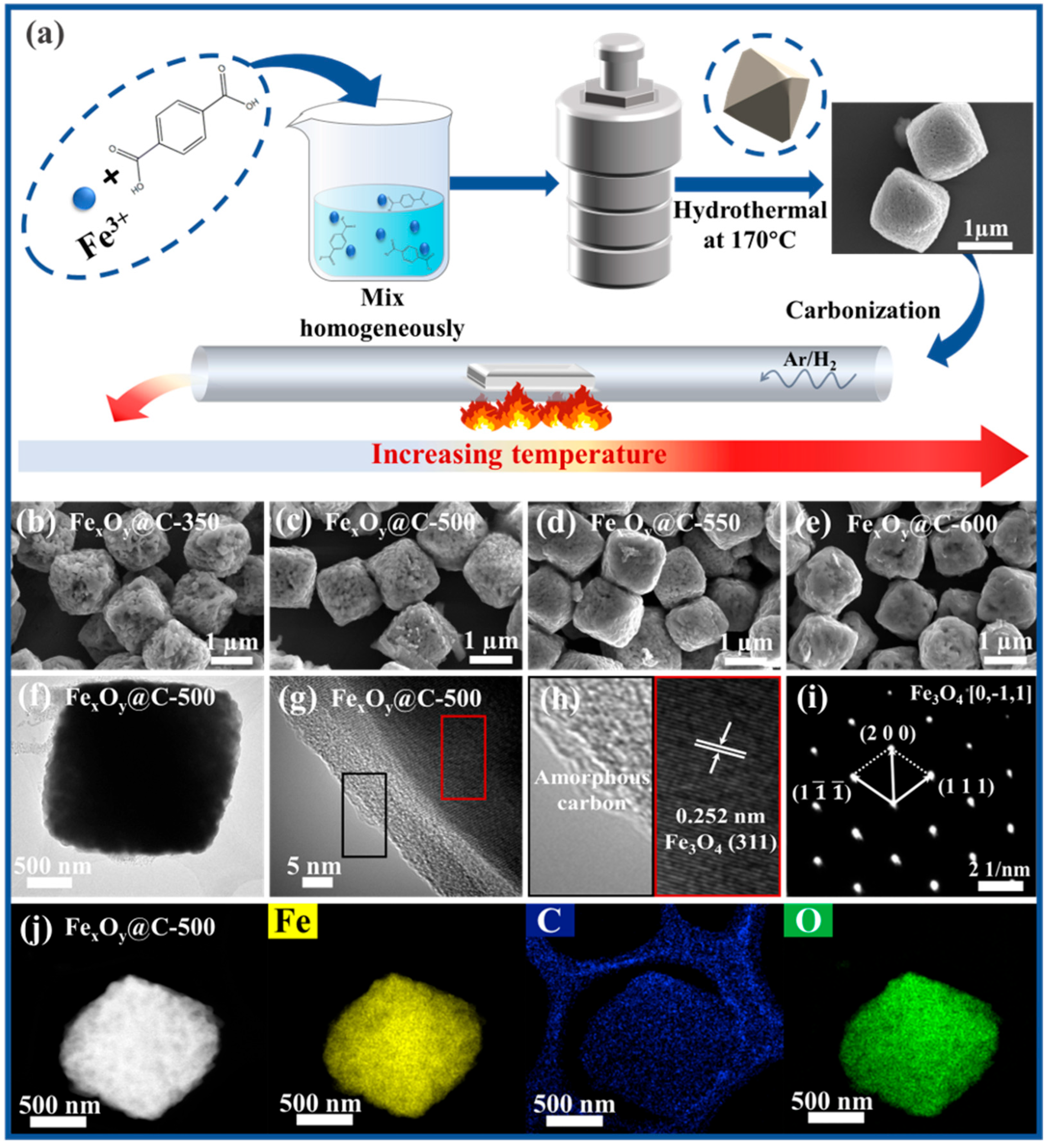
2.2. Preparation of Fe-Based MOFs Precursor
2.3. Preparation of Iron Oxide@Carbon Composites
2.4. Testing and Characterization
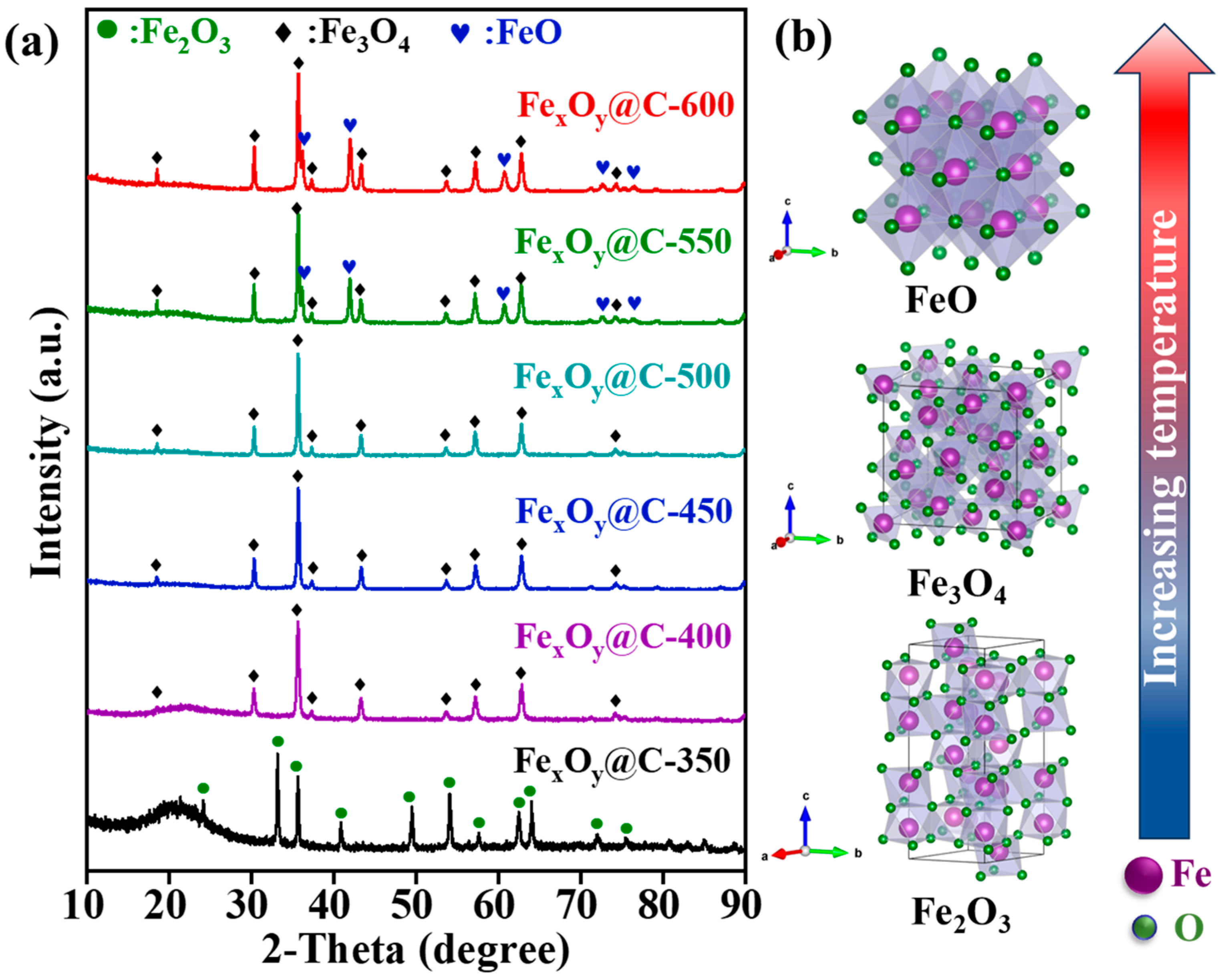
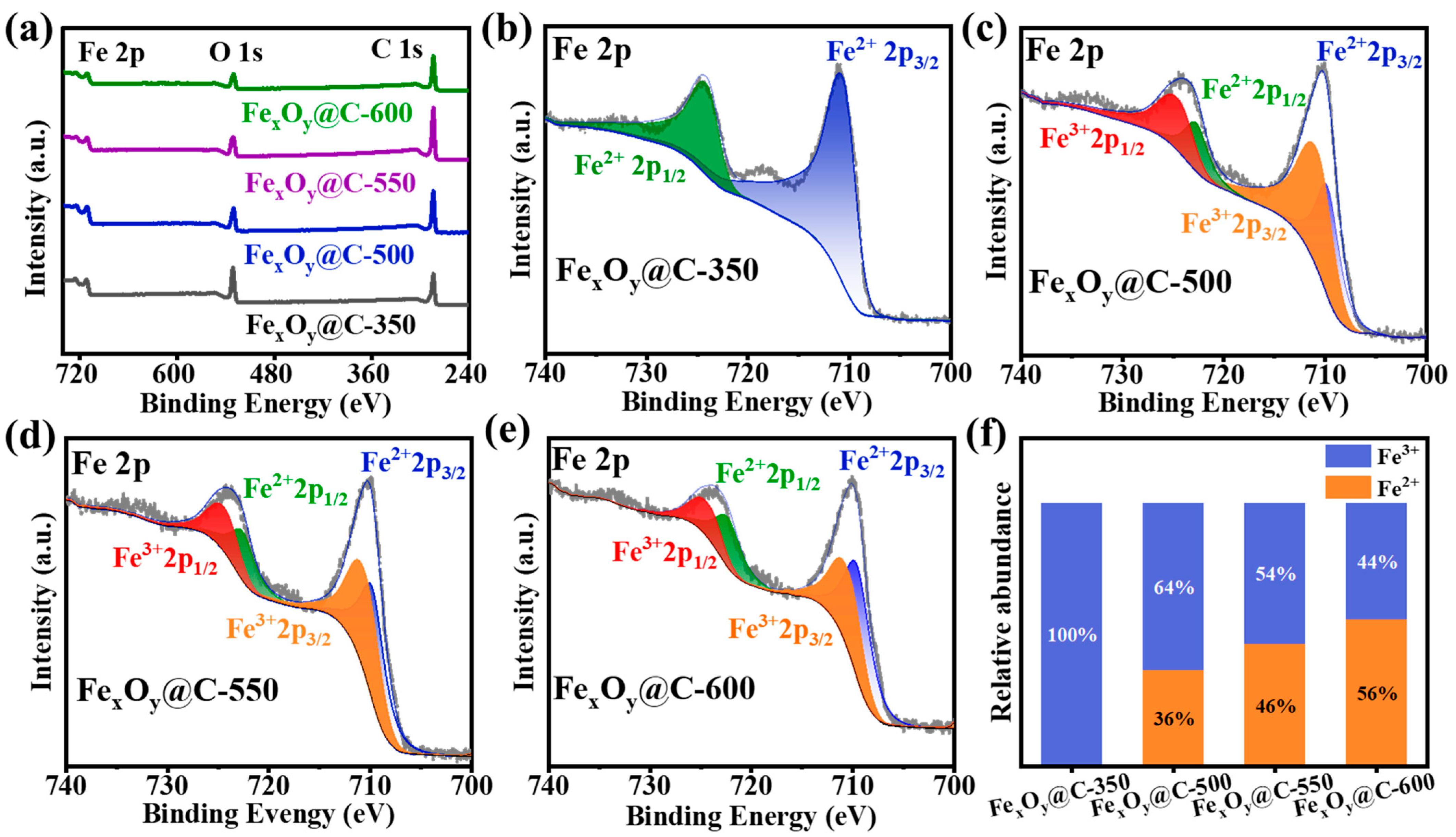
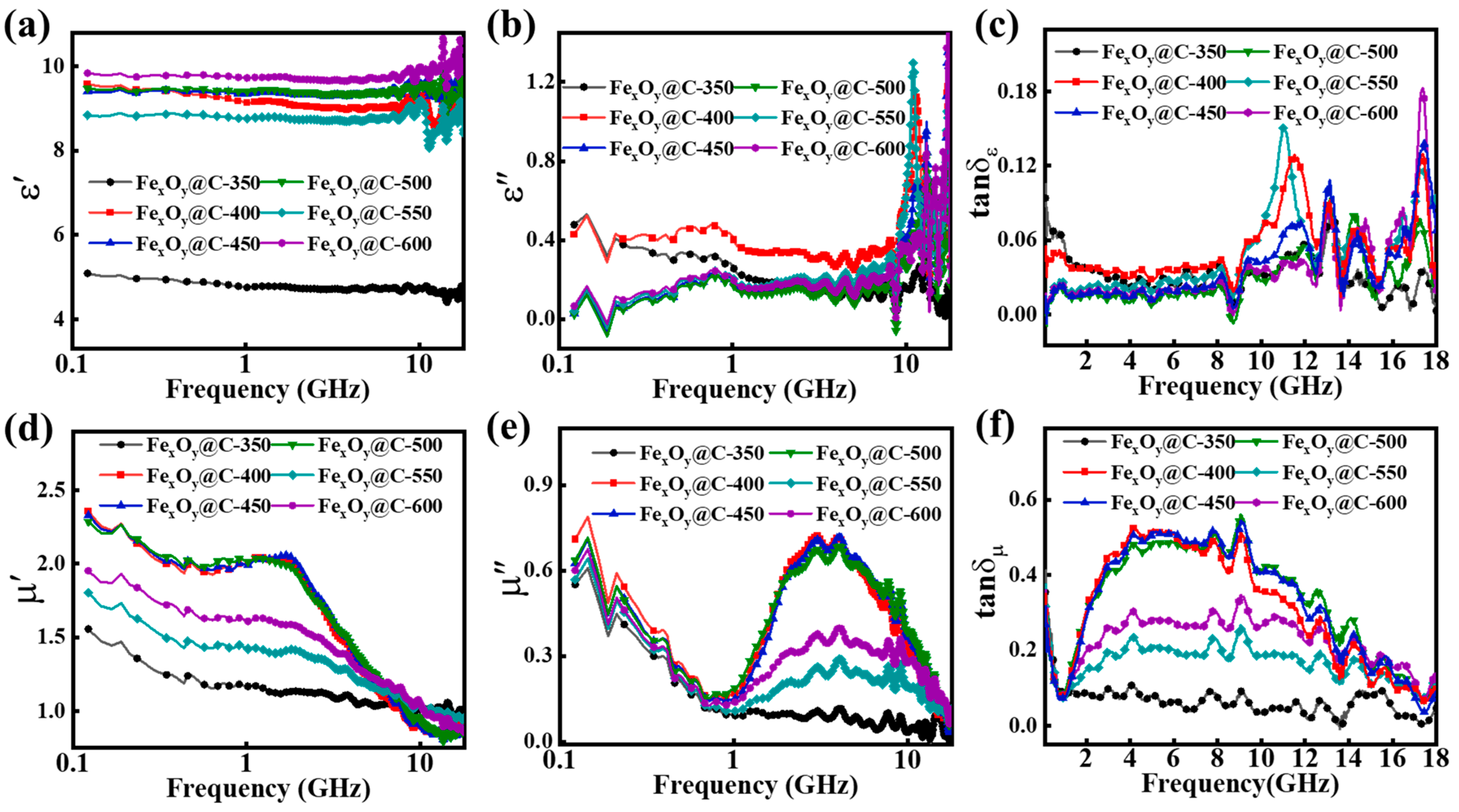
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Pei, K.; You, W.; Yu, X.; Wu, Z.; Che, R. Multidimension-Controllable Synthesis of MOF-Derived Co@N-Doped Carbon Composite with Magnetic-Dielectric Synergy toward Strong Microwave Absorption. Small 2020, 16, 200158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolanowska, A.; Janas, D.; Herman, A.P.; Jędrysiak, R.G.; Giżewski, T.; Boncel, S. From blackness to invisibility-Carbon nanotubes role in the attenuation of and shielding from radio waves for stealth technology. Carbon 2018, 126, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Lin, T.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Hong, Y.; Liu, J. State of the Art and Prospects in Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Microwave Absorption Materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 67–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusmaniar; Erdawati; Sosiati, H.; Budi, S.; Alaydrus, M.; Handoko, E. Microwave absorbing characteristics of Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell polyaniline-based composites. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 046101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhen, M.; Meng, F.; Meng, X.; Zhu, M. Progress, Challenges and Prospects of Biomass-Derived Lightweight Carbon-Based Microwave-Absorbing Materials. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Yi, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Piao, M. Exploring the Microstructural Effect of FeCo Alloy on Carbon Microsphere Deposition and Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liu, Y.; Bi, Y.; Su, X.; Lu, C.; Han, X.; Ma, Y.; Feng, C.; Ma, M. Recent advancement of magnetic MOF composites in microwave absorption. Synth. Met. 2023, 294, 117307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, H.; Huang, F.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hui, D.; Zhou, Z. Graphene-based microwave absorbing composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B 2018, 137, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, A. Microwave Radar Absorbing Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Polymer Composites: A Review. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2015, 36, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Haq, R.S.U.; Ahmed, S.; Siddiqui, F.; Yi, J. Recent advances in carbon nanotubes, graphene and carbon fibers-based microwave absorbers. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 970, 172625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chang, H.; Xiao, P.; Chen, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y. Broadband and Tunable High-Performance Microwave Absorption of an Ultralight and Highly Compressible Graphene Foam. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, Q.; Ye, F.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide Modified by Maghemite Colloidal Nanoparticle Clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 19701–19711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Q.; Fu, Y.; Liu, T. A review on carbon/magnetic metal composites for microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 86, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Chen, X. Recent progress of nanomaterials for microwave absorption. J. Mater. 2019, 5, 503–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, J.; Xing, H.; Lv, M.; Zong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Progress in the use of MoS2-based composites for microwave absorption. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2024, 161, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Peng, R.; Xing, H.; Xie, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Deng, X.; Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, X. Magnetic vortex configuration in Fe3O4 nanorings/nanotubes for aspect ratio and magnetic orientation regulated microwave absorption. Results Phys. 2024, 58, 107543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Wang, H.; Xing, H.; Wang, L.; Feng, J.; Zong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Bimagnetic CoxNi100−x Nanocrystals Anchored on MoS2 Nanosheets for Applications as Microwave Absorption Materials. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 24201–24212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Xu, Q. Bimetallic metal-organic frameworks and their derivatives. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 5369–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Qian, J. Interfacial Engineering of Heterogeneous Reactions for MOF-on-MOF Heterostructures. Small 2024, 20, 2308732–2308760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeggai, F.Z.; Ait-Touchente, Z.; Bachari, K.; Elaissari, A. Investigation of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Synthesis, Properties, and Applications-An In-Depth Review. Chem. Phys. Impact 2025, 10, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Xia, L.; Ma, S.; Yin, Z.; Huang, Y. A Review on Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Porous Carbon-Based Novel Microwave Absorption Materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 56–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Pereda, N.; Pané, S.; Puigmartí-Luis, J.; Ruiz-Molina, D. Conductive properties of triphenylene MOFs and COFs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 460, 214459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, X.; Qin, Y.; Qiao, J.; Pan, F.; Wu, N.; Wang, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W. Conductive Metal-Organic Frameworks with Tunable Dielectric Properties for Boosting Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 12510–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, J.; Cui, B.; Li, Y. Preparation and wave-absorbing properties of cobalt-chromium ferrite/carbon fiber composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Z.; Zou, J.; Gu, Z.; Wu, G. MOF-derived NiFe2S4/Porous carbon composites as electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, J.; Du, Y.; Bai, J.; Fan, H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, F. One-pot synthesis of CoFe2O4/graphene oxide hybrids and their conversion into FeCo/graphene hybrids for lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5535–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Pu, F.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Bai, J. Interfacial interactions and synergistic effect of CoNi nanocrystals and nitrogen-doped graphene in a composite microwave absorber. Carbon 2016, 104, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Feng, J.; Zong, Y.; Miao, H.; Hu, X.; Bai, J.; Li, X. Hydrophobic graphene nanosheets decorated by monodispersed superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals as synergistic electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 4452–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; Xu, C.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, M.; Yang, L.; You, W.; et al. Multi-interfacial 1D magnetic ferrite@C fibers for broadband microwave absorption. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 35, 101140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; He, M.; Xing, R.; Gu, J.; Kong, J. 2D/2D coupled MOF/Fe composite metamaterials enable robust ultra-broadband microwave absorption. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, M.; Yu, X.; You, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Che, R. MOF-Derived Ni1−xCox@Carbon with Tunable Nano-Microstructure as Lightweight and Highly Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorber. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, B.; Yan, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C. Hierarchically nitrogen-doped carbon hollow microspheres assembled with loose and porous magnetic carbon sheets for enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 212, 118165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, F.; Cui, L.; Xu, X.; Han, X.; Du, Y. Composition Optimization and Microstructure Design in MOFs-Derived Magnetic Carbon-Based Microwave Absorbers: A Review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshariazar, F.; Morsali, A. Mixed-valence metal-organic frameworks: Concepts, opportunities, and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 1318–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shi, L.; Sun, R.; Ding, L.; He, M.; Li, J.; Guo, H.; Gao, T.; Liu, P. Low-Temperature Oxidation Induced Phase Evolution with Gradient Magnetic Heterointerfaces for Superior Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Chai, X.; Qing, Y. Influence of synergistic effect of Mn valence state and oxygen vacancy concentration on microwave absorbing properties of CaMnO3. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 9882–9889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Ni, C.; Lin, Z.; Wu, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Du, W. Phase and morphology evolution of high dielectric CoO/Co3O4 particles with Co3O4 nanoneedles on surface for excellent microwave absorption application. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, T.; Yu, B.; Gao, H.; Xu, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Han, X. The electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption of mesoporous carbon. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 135, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, M.; Hayashi, M.; Lanagan, M.T.; Agrawal, D.K.; Nagata, K. Complex Permittivity of Graphite, Carbon Black and Coal Powders in the Ranges of X-band Frequencies (8.2 to 12.4 GHz) and between 1 and 10 GHz. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wu, D.; Wu, H.; Hou, C.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Du, W. Dielectric parameters of activated carbon derived from rosewood and corncob. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 18077–18084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Qi, C.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Recent advances of carbon-based electromagnetic wave absorption materials facing the actual situations. Carbon 2023, 208, 390–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Xue, Y.; Lu, X. Structural Engineering of Hierarchical Magnetic/Carbon Nanocomposites via In Situ Growth for High-Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Zhao, C.; Shindume, H.L.; Ren, J.; Chen, L.; Hou, H.; Ibrahim, M.M.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Guo, Z. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of magnetite-spinach derived carbon composite. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 694, 134149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Lu, W.; Chou, T.W. Flexible electromagnetic wave absorbing composite based on 3D rGO-CNT-Fe3O4 ternary films. Carbon 2018, 129, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Shah, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. Preparation of pleated RGO/MXene/Fe3O4 microsphere and its absorption properties for electromagnetic wave. Carbon 2021, 172, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Ding, S.; Ling, H.; Wang, T.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Meng, A.; Li, Q. Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 2020, 167, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Ye, W.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Xue, W. Construction of three-dimensional porous network Fe-rGO aerogels with monocrystal magnetic Fe3O4@C core-shell structure nanospheres for enhanced microwave absorption. Mater. Today Phys. 2024, 42, 101383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Song, Y.; Xiong, J.; Pan, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, R.; Yang, H.; Lu, W. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of nanoporous Fe3O4@carbon composites derived from metal-organic frameworks. Carbon 2019, 142, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Xing, H.; Feng, J.; Zong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Insight to the enhanced microwave absorption of porous N-doped carbon driven by ZIF-8: Competition between graphitization and porosity. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ye, W.; Wang, S.; Cao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Xue, W. A strategy based on composition control and structural design to prepare 3DOM RFCo composites with a 3D ordered macroporous structure for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 10748–10757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
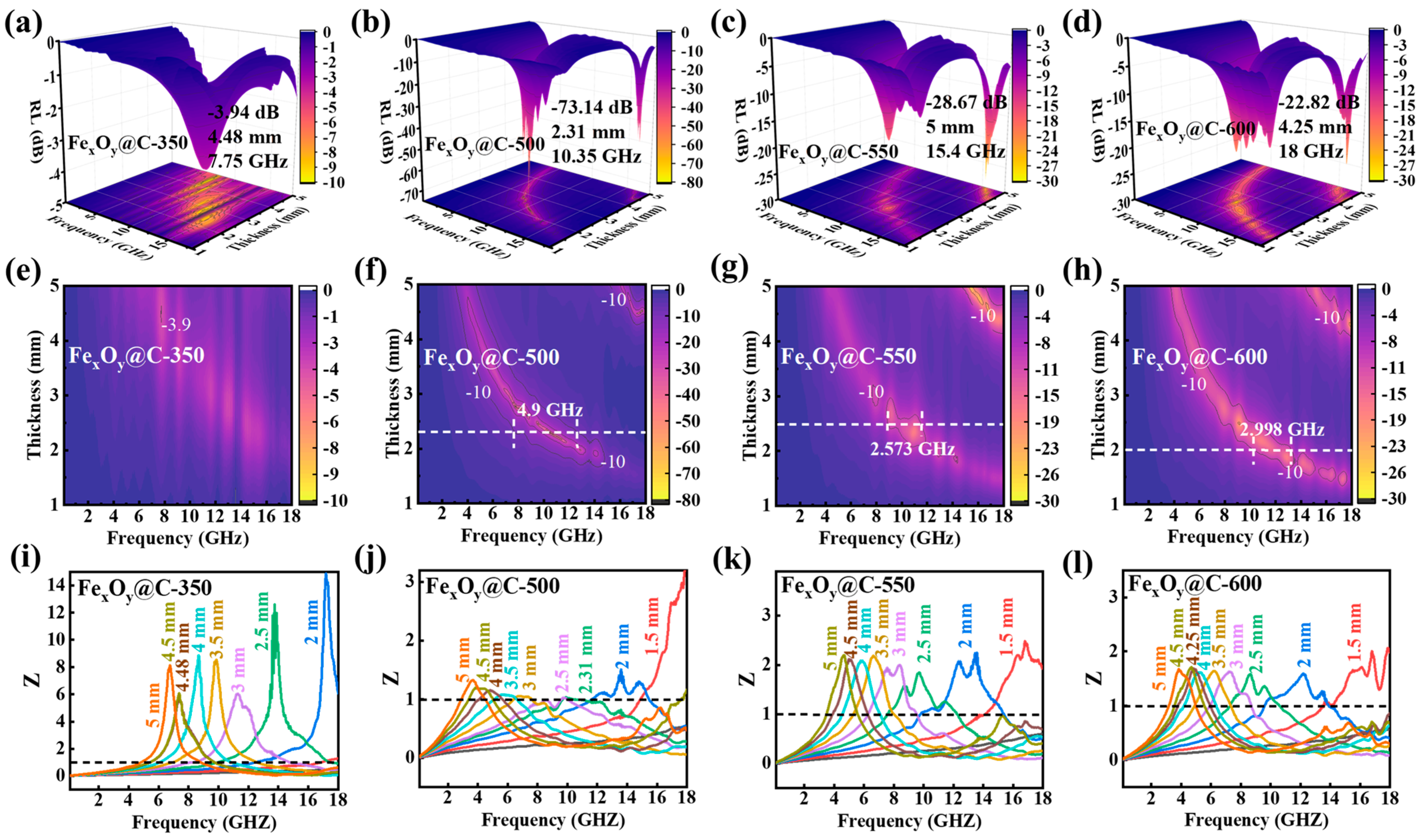
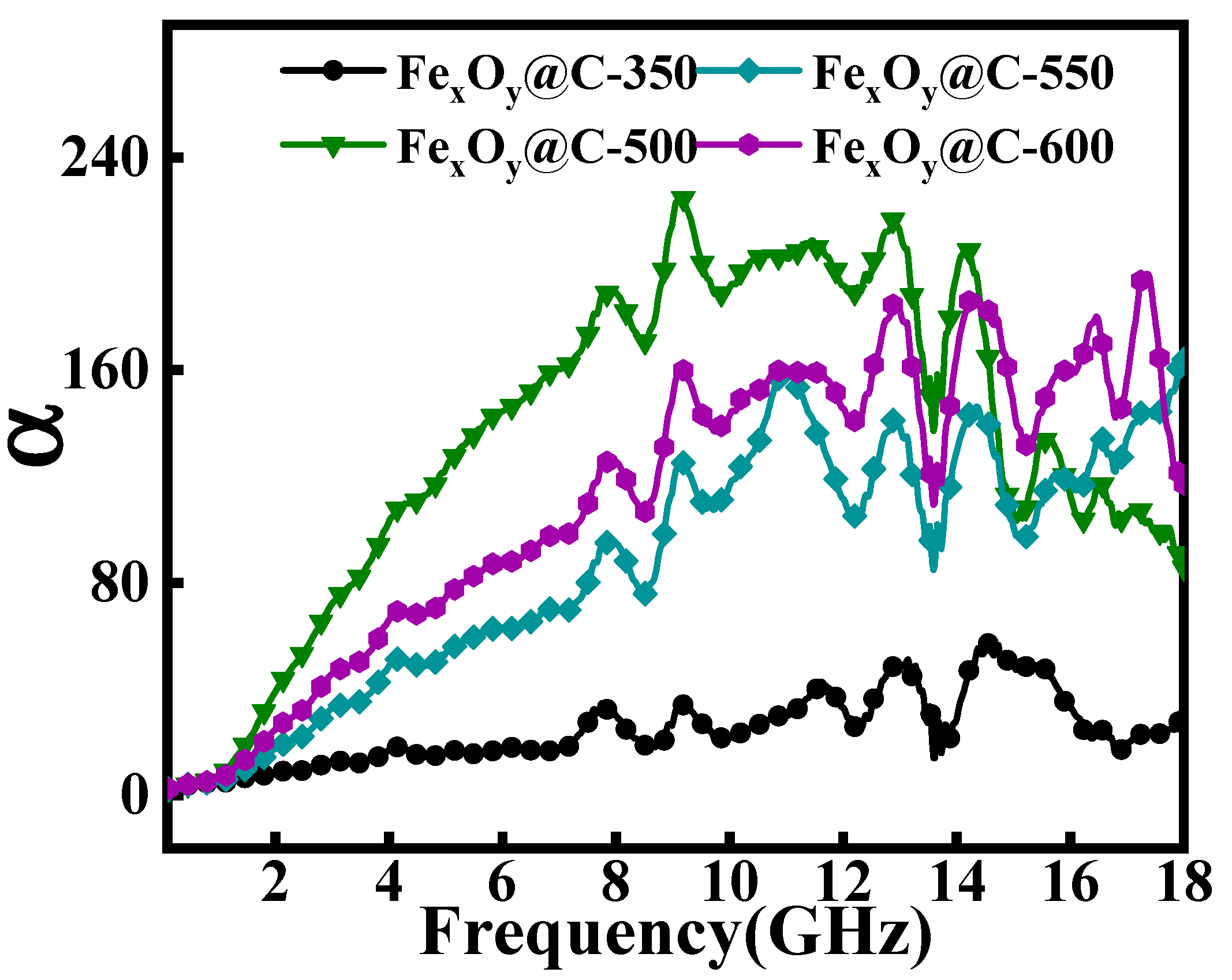

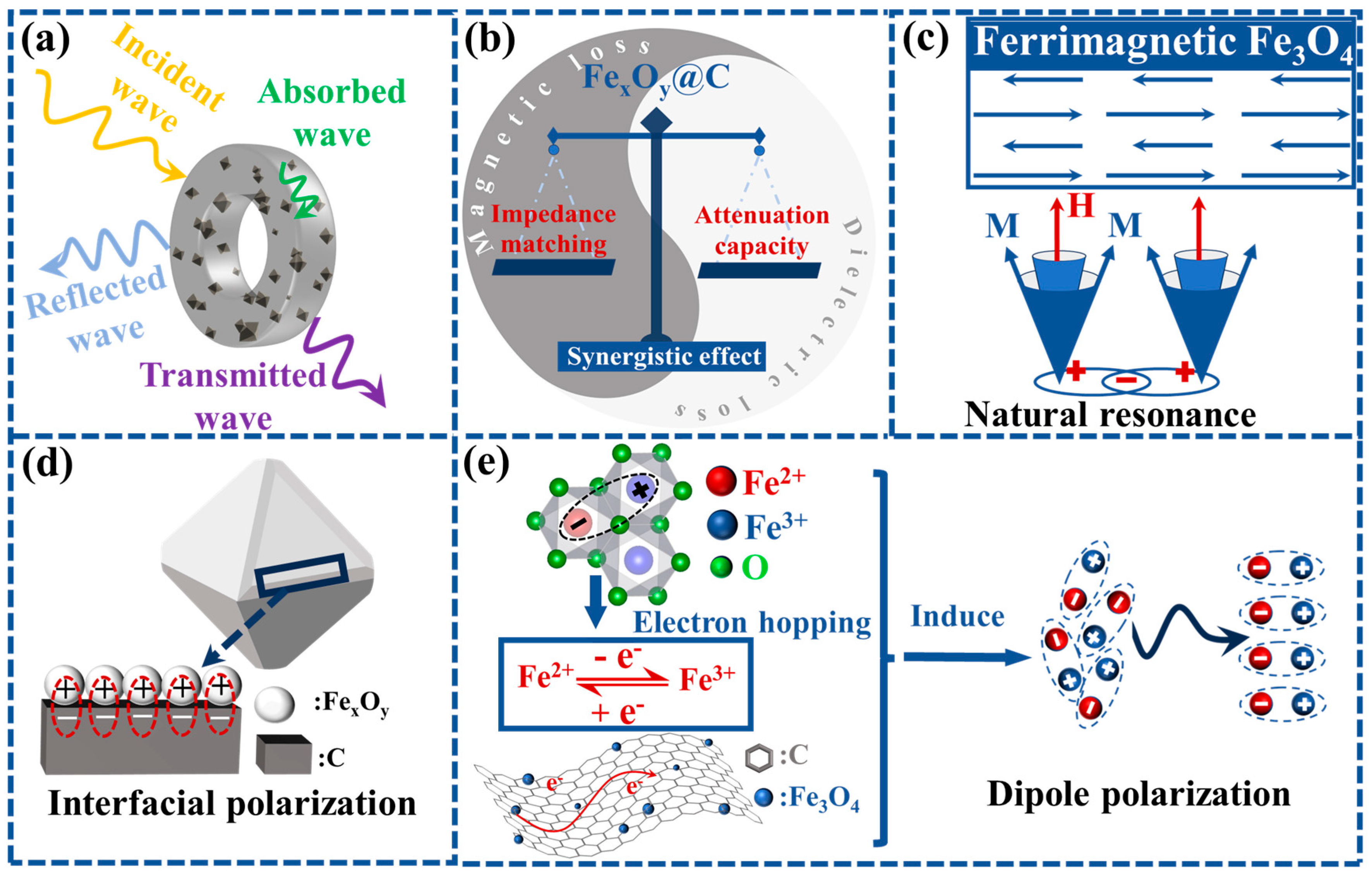
| Samples | Thickness (mm) | EAB (GHz) | RLmin (dB) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4-Fe@CNFs/Al-Fe3O4-Fe | 4.3 | 5.6 | −59.3 | [42] |
| Fe3O4@spinach-derived carbon | 4.5 | 4.73 | −48.81 | [43] |
| CNT film-Fe3O4-rGO-PDMS | 1.42 | 5.7 | −50.5 | [44] |
| 3D pleated RGO/MXene/Fe3O4 microspheres | 2.9 | 4.7 | −51.2 | [45] |
| Fe3O4@walnut shell-derived porous carbon | 2.46 | 2.72 | −56.61 | [46] |
| Fe3O4@C core-shell structure nanospheres | 2.9 | 6.96 | −64.89 | [47] |
| Fe3O4@NPC | 3.0 | 4.5 | −65.5 | [48] |
| Fe3O4@C-T | 2.31 | 4.9 | −73.14 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Han, S.; Xing, H.; Dong, Y.; Deng, X.; Zong, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Phase and Valence State Engineering of MOFs-Derived Iron Oxide@Carbon Polyhedrons for Advanced Microwave Absorption. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110806
Yang X, Han S, Xing H, Dong Y, Deng X, Zong Y, Feng J, Zhu X, Li X, Zheng X. Phase and Valence State Engineering of MOFs-Derived Iron Oxide@Carbon Polyhedrons for Advanced Microwave Absorption. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(11):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110806
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaojiao, Shuai Han, Hongna Xing, Yi Dong, Xia Deng, Yan Zong, Juan Feng, Xiuhong Zhu, Xinghua Li, and Xinliang Zheng. 2025. "Phase and Valence State Engineering of MOFs-Derived Iron Oxide@Carbon Polyhedrons for Advanced Microwave Absorption" Nanomaterials 15, no. 11: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110806
APA StyleYang, X., Han, S., Xing, H., Dong, Y., Deng, X., Zong, Y., Feng, J., Zhu, X., Li, X., & Zheng, X. (2025). Phase and Valence State Engineering of MOFs-Derived Iron Oxide@Carbon Polyhedrons for Advanced Microwave Absorption. Nanomaterials, 15(11), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110806






