Thickness and Wavelength Optimizations of a High-Performance SPR Sensor Employing a Silver Layer and Black Phosphorus in Principal Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure Characterization
2.1. Silver
2.2. Fused Silica, Titanium Dioxide
2.3. Black Phosphorus
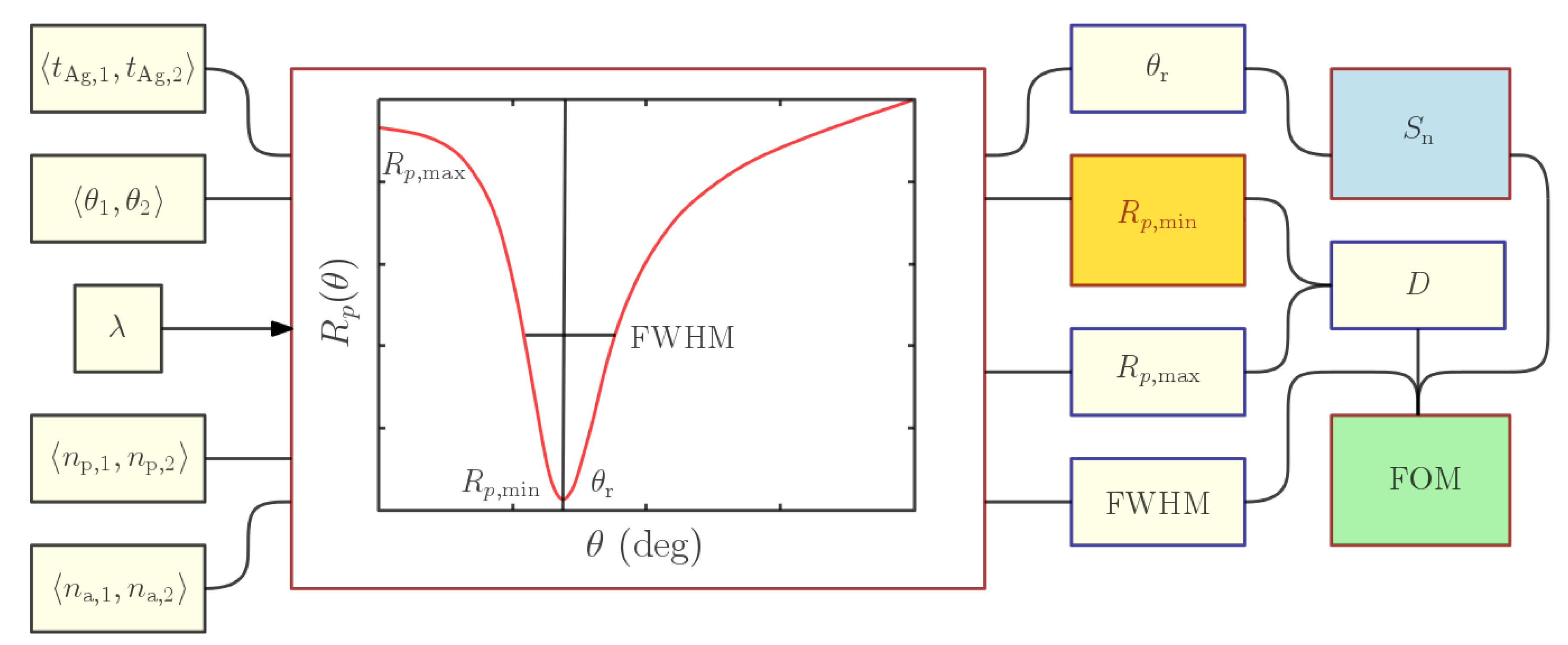
3. Methods
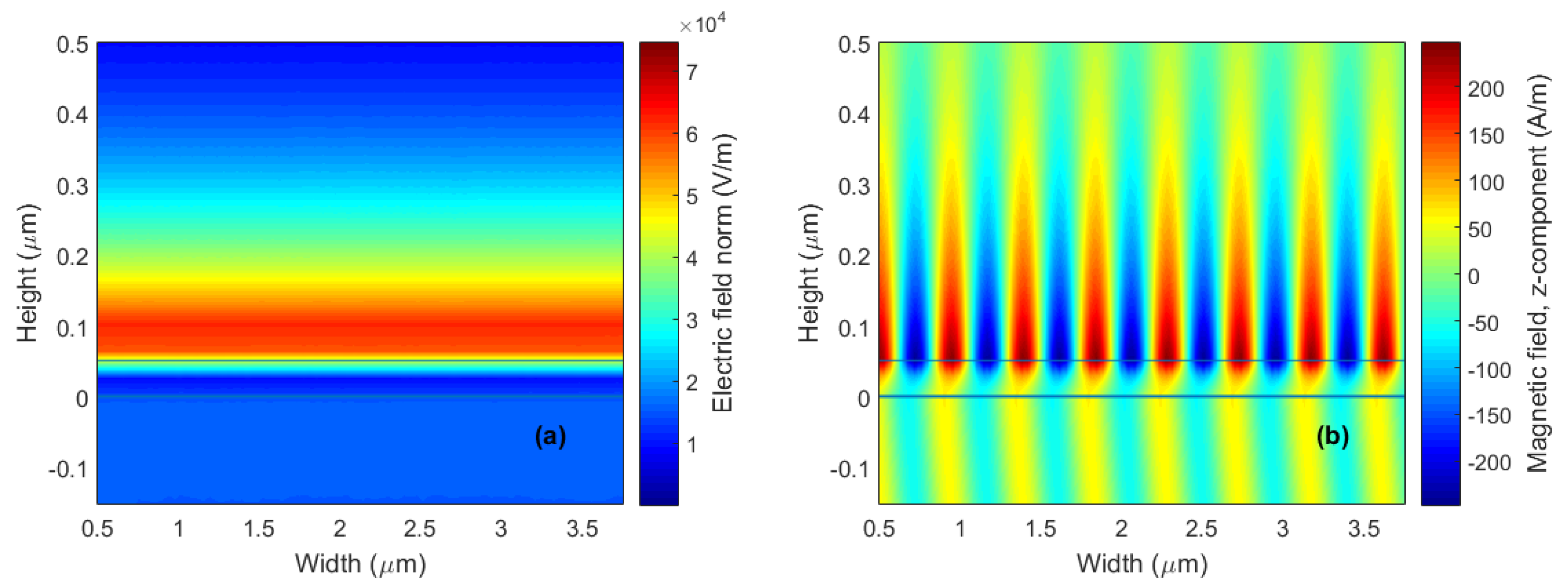
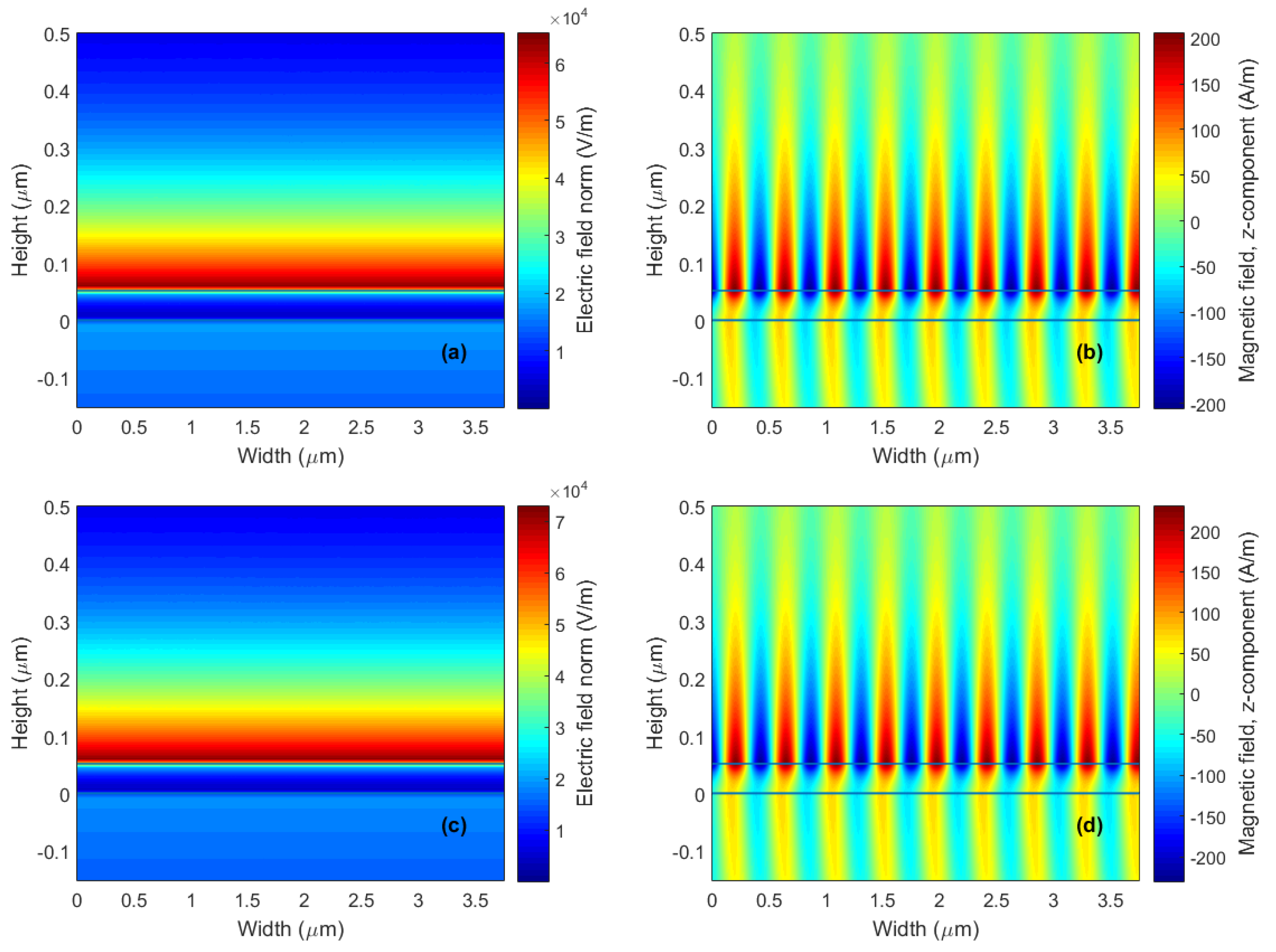
4. Results and Discussion
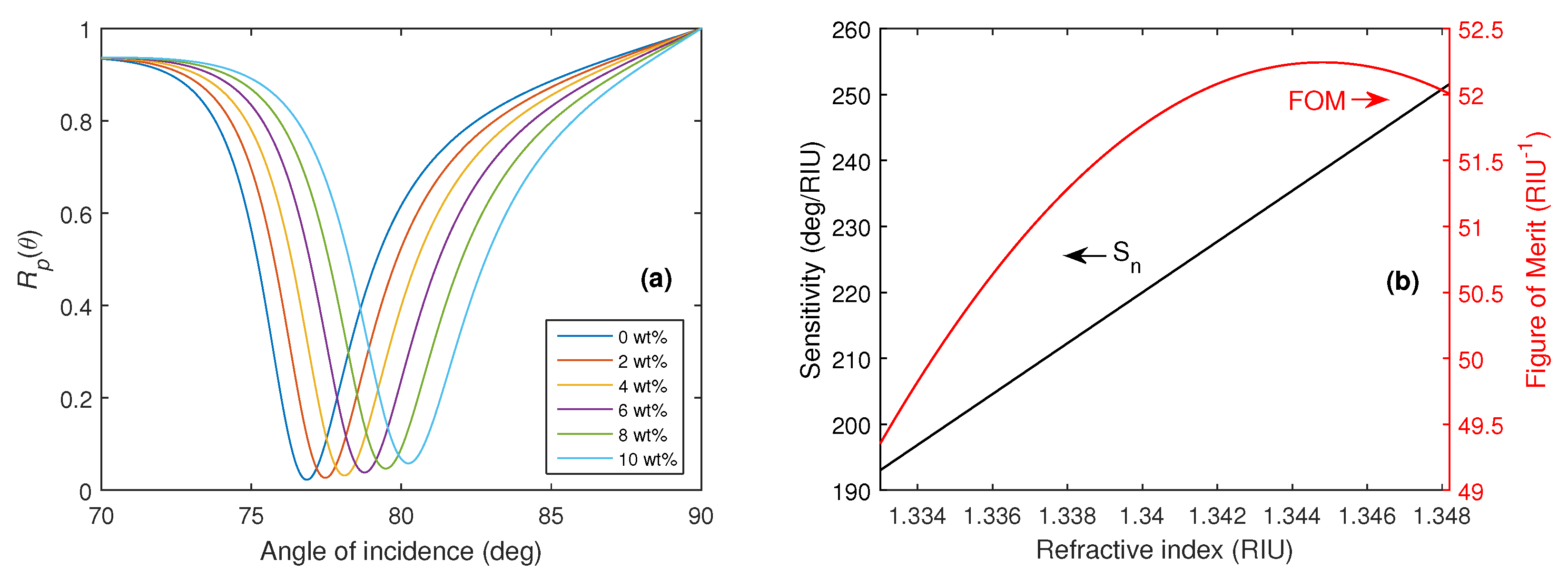
4.1. Prism Selection
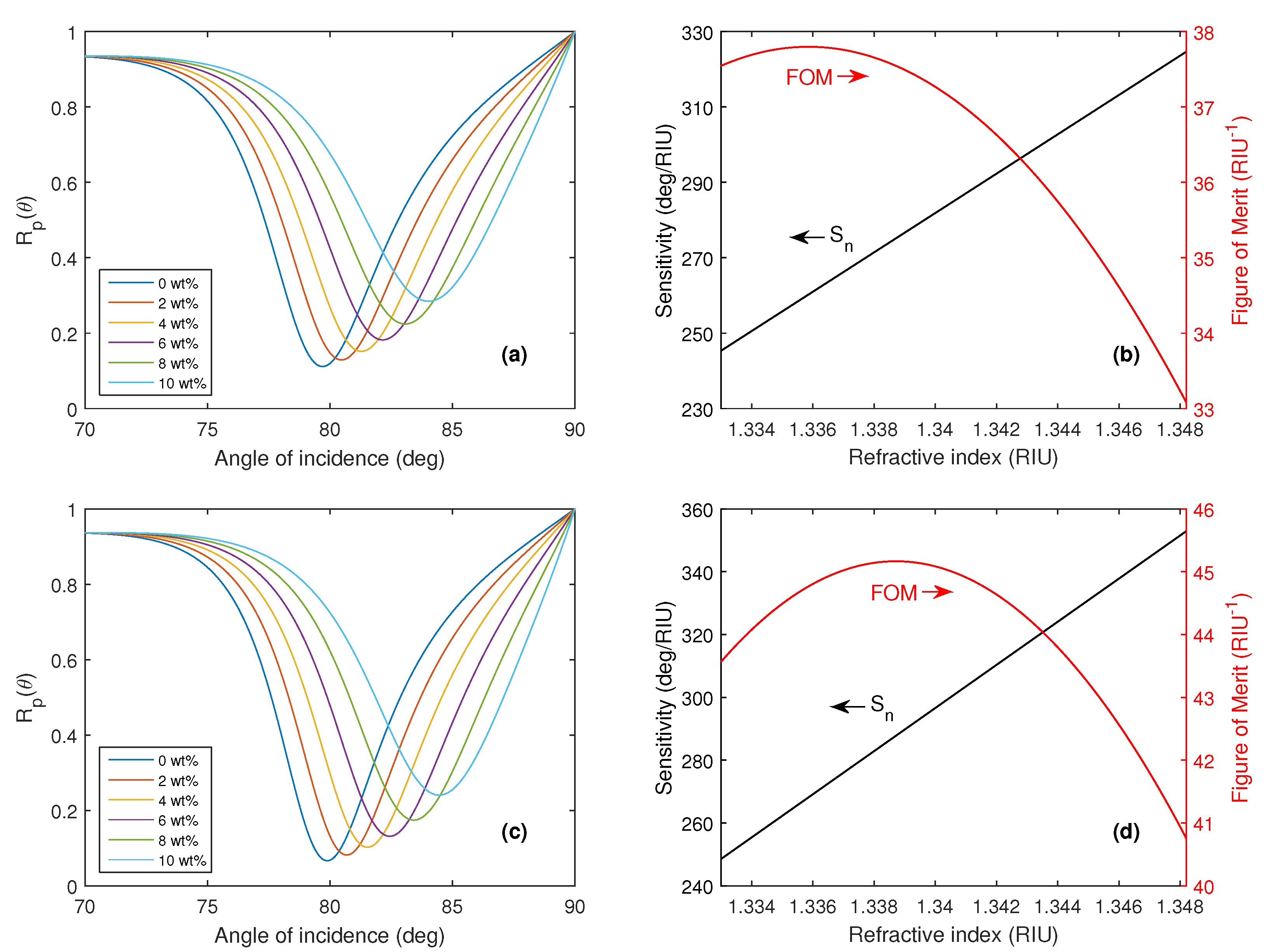
4.2. Black Phosphorus
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polman, A. Plasmonics applied. Science 2008, 322, 868–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretschmann, E.; Raether, H. Radiative decay of nonradiative surface plasmons excited by light. Z. Naturforschung 1968, A23, 2135–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raether, H. Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Homola, J.; Yee, S.; Gauglitz, G. Surface plasmon resonance sensors: Review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 54, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J. Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Sensors; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Manuel, M.; Vidal, B.; Lopéz, R.; Alegret, S.; Alonso-Chamarro, J.; Garces, I.; Mateo, J. Determination of probable alcohol yield in musts by means of an SPR optical sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1993, 11, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedberg, B.; Nylander, C.; Lundström, I. Principles of biosensing with an extended coupling matrix and surface plasmon resonance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1993, 11, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostálek, J.; Vaisocherova, H.; Homola, J. Multichannel surface plasmon resonance biosensor with wavelength division multiplexing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylek, J.; Maniakova, P.; Hlubina, P.; Sobota, J.; Pudis, D. Highly sensitive plasmonic structures utilizing a silicon dioxide overlayer. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, H.R.; Lee, S.H. Spectral and angular responses of surface plasmon resonance based on the Kretschmann prism configuration. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, P.; Beloglazov, A.; Kochergin, V.; Valeiko, M.; Ksenevich, T. Surface plasmon resonance interferometry for biological and chemical sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 54, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylek, J.; Ciprian, D.; Hlubina, P. Optimized film thicknesses for maximum refractive index sensitivity and figure of merit of a bimetallic film surface plasmon resonance sensor. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2024, 139, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Srivastava, S.K. High performance SPR sensor using 2-D materials: A treatise on design aspects, material choice and figure of merit. Sens. Actuators A Chem. 2024, 369, 115159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chu, H.S.; Koh, W.S.; Li, E.P. Highly sensitive graphene biosensors based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 14395–14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Q.; Loh, K.P. Graphene photonics, plasmonics, and broadband optoelectronic devices. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3677–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xing, F. Graphene optical biosensors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos-Gomez, A. Black phosphorus: Narrow gap, wide applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4280–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.N.; Liu, B.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; Cong, S.; Aroonyadet, N.; Kopf, M.; Nilges, T.; Zhou, C. Black phosphorus gas sensors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5618–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lan, S. Optical properties of black phosphorus. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2016, 8, 618–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ling, X. Black phosphorus: Optical characterization, properties and applications. Small 2017, 13, 1700823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venuthurumilli, P.K.; Ye, P.D.; Xu, X. Plasmonic resonance enhanced polarization-sensitive photodetection by black phosphorus in near infrared. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4861–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, K.; Yan, D.; Chen, R.; Zou, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. Recent advances on black phosphorus for energy storage, catalysis, and sensor applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Wu, L.; Xiang, Y. Ultrasensitive multiple guided-mode biosensor with few-layer black phosphorus. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 38, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Chu, P.K.; Yu, X.F. Optical and optoelectronic properties of black phosphorus and recent photonic and optoelectronic applications. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1900165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Chen, X.; Tang, L.; Yang, B.; Zou, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Fan, D. Black phosphorus (BP)–graphene guided-wave surface plasmon resonance (GWSPR) biosensor. Nanophotonics 2020, 9, 4265–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, S.C.; Perumal, S.; Atchudan, R.; Alagan, M.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Ramalingam, S.; Manoj, D.; Sambasivam, S. A critical review on black phosphorus and its utilization in the diverse range of sensors. Sens. Actuators A Chem. 2024, 377, 115719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, P.; Raghuwanshi, S.K.; Singh, Y. Enhancement of the sensitivity of a surface plasmon resonance sensor using a nobel structure based on barium titanate-graphene-silver. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 417. [Google Scholar]
- Karki, B.; Pal, A.; Singh, Y.; Sharma, S. Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensor using 2D material barium titanate and black phosphorus over the bimetallic layer of Au, Ag, and Cu. Opt. Commun. 2022, 508, 127616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, A.; Pal, A.; Srivastava, G.; Rana, M.M.; Taya, S.A.; Sharma, A.; Altahan, B.R.; Tomar, S.; Singh, Y.; Parajuli, D.; et al. Surface plasmon resonance biosensor sensitivity improvement employing of 2D materials and BaTiO3 with bimetallic layers of silver. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, X.; Xiang, Y. Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensors with 2D franckeite nanosheets. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Li, D.; Qi, W.; Elstner, M.; Fan, C.; Fang, H. Graphene on Au (111): A highly conductive material with excellent adsorption properties for high-resolution bio/nanodetection and identification. ChemPhysChem 2010, 11, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellán, G.; Wild, S.; Lloret, V.; Scheuschner, N.; Gillen, R.; Mundloch, U.; Maultzsch, J.; Varela, M.; Hauke, F.; Hirsch, A. Fundamental insights into the degradation and stabilization of thin layer black phosphorus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10432–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Lang, P.; Yuan, N.; Tang, J. Fabrication and applications of 2D black phosphorus in catalyst, sensing and electrochemical energy storage. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 850, 156580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Lee, Y.; Koh, H.J.; Jung, H.; Kim, J.S.; Yoo, H.W.; Kim, J.; Jung, H.T. Superior Chemical Sensing Performance of Black Phosphorus: Comparison with MoS2 and Graphene. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7020–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Dai, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, D. Sensitivity enhancement by using few-layer black phosphorus-graphene/TMDCs heterostructure in surface plasmon resonance biochemical sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, C.; Sun, Z.; Mao, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X. Black phosphorus based fiber optic biosensor for ultrasensitive cancer diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Nikam, A.N.; Fernandes, G.; Kulkarni, S.; Padya, B.S.; Prassl, R.; Das, S.; Joseph, A.; Deshmukh, P.K.; Patil, P.O.; et al. Black phosphorus as multifaceted advanced material nanoplatforms for potential biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalabney, A.; Abdulhalim, I. Sensitivity-enhancement methods for surface plasmon sensors. Laser Photonics Rev. 2011, 5, 571–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakayan, D.; Tuppurainen, J.; Albers, M.; van Lint, M.J.; van Iperen, D.J.; Weda, J.J.; Kuncova-Kallio, J.; Somsen, G.W.; Kool, J. Angular scanning and variable wavelength surface plasmon resonance allowing free sensor surface selection for optimum material-and bio-sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lin, C. Figure of merit analysis of graphene based surface plasmon resonance biosensor for visible and near infrared. Opt. Commun. 2019, 435, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, S.; Lin, C. Sensitivity improvement of a surface plasmon resonance sensor based on two-dimensional materials hybrid structure in visible region: A theoretical study. Sensors 2020, 20, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Laha, R.; Dantham, V.R. Wavelength-dependent angular shift and figure of merit of silver-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Sens. Actuators A Chem. 2020, 315, 112289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Dai, X.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Qu, J.; Ho, H.P.; et al. Wavelength sequential selection technique for high-throughput multi-channel phase interrogation surface plasmon resonance imaging sensing. Talanta 2023, 258, 124405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.B.; Wang, Y.; Blair, S.; Marques, J.L.; Moreira, C.S. Wavelength-dependent angular sensitivity signatures in SPR sensors: Is the 633 nm wavelength still optimal for the latest designs? IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 17653–17660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryga, M.; Ciprian, D.; Gembalova, L.; Hlubina, P. One-dimensional photonic crystal with a defect layer utilized as an optical filter in narrow linewidth LED-based sources. Crystals 2023, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakić, A.D.; Djurišić, A.B.; Elazar, J.M.; Majewski, M.L. Optical properties of metallic films for vertical-cavity optoelectronic devices. Optik 1998, 37, 5271–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitson, I.H. Interspecimen Comparison of the Refractive Index of Fused Silica. J. Opt. Soc. Amer. 1965, 55, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Aydin, K. Localized surface plasmons in nanostructured monolayer black phosphorus. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, L.; Xing, H.; Chen, X. Anisotropic plasmon induced transparency in black phosphorus nanostrip trimer. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xiong, L.; Hu, F.; Xiang, Y.; Dai, X.; Li, G. Ultrasensitive and tunable sensor based on plasmon-induced transparency in a black phosphorus metasurface. Plasmonics 2021, 16, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Yee, K.J. Black phosphorus phase retarder based on anisotropic refractive index dispersion. 2D Mater. 2021, 9, 015020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Lu, S.; Zeng, Q.; Han, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chai, G.; Xiang, B.; et al. High-responsivity and high-speed black phosphorus photodetectors integrated with proton exchanged thin-film lithium niobate waveguides. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 27962–27972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Jiang, H.B.; Sun, T.Q.; Gao, X.G.; Chen, S.N.; Zhao, B.; Yang, J.J.; Liu, Z.B.; Tian, J.G.; Guo, C.L. Optical anisotropy of black phosphorus by total internal reflection. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Ling, X.; Shu, W.; Luo, H.; Wen, S. Photonic spin Hall effect on the surface of anisotropic two-dimensional atomic crystals. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinibaldi, A.; Danz, N.; Descrovi, E.; Munzert, P.; Schulz, U.; Sonntag, F.; Dominici, L.; Michelotti, F. Direct comparison of the performance of Bloch surface wave and surface plasmon polariton sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P. Optical Waves in Layered Media; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, F.; Wang, H.; Jia, Y. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanok, R.; Abuleil, M.; Hlubina, P.; Abdulhalim, I. Bloch surface wave fast ellipsometric sensor utilizing a polarization camera with an improved detection limit. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 179, 111218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasib, M.H.H.; Nur, J.N.; Rizal, C.; Shushama, K.N. Improved transition metal dichalcogenides-based surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Condens. Matter 2019, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Mondol, N.; Kundu, D.; Meem, A.A.; Islam, M.R.; Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, M.B. Numerical investigation into impact of halide perovskite material on the optical performance of prism-loaded hybrid surface plasmon resonance biosensor: A strategy to increase sensitivity. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2024, 43, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Kushwaha, A.S.; Srivastava, S. A comparative study among WS2, MoS2 and graphene based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2020, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lin, C. Sensitivity comparison of graphene based surface plasmon resonance biosensor with Au, Ag and Cu in the visible region. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 056503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Pukhrambam, P.D. Modeling of high-performance SPR refractive index sensor employing novel 2D materials for detection of malaria pathogens. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2021, 21, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lin, Z.; Bai, G.; Lin, C. Comparative study on sensitivity enhancement of a graphene based nearly guided-wave surface plasmon resonance biosensor optimized using genetic algorithm in the visible region. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, M.; Jiao, L.; Wu, T.; Xia, F.; Liu, M.; Kong, W.; Dong, L.; Yun, M. Sensitivity enhancement of a graphene–barium titanate-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor with an Ag–Au bimetallic structure in the visible region. JOSA B 2019, 36, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Das, R.; Prajapati, Y.K. Effect of perovskite material on performance of surface plasmon resonance biosensor. IET Optoelectron. 2020, 14, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, B.; Dai, E.; Pan, W. Anisotropic Sensing Performance in a High-Sensitivity Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Based on Few-Layer Black Phosphorus. Sensors 2024, 24, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Structure | Wavelength (nm) | Sensitivity (deg/RIU) | FOM (RIU−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BK7/Ag/BP/Graphene | 633 | 217 | – | [35] |
| BK7/Ag/BP/WSe2 | 633 | 279 | – | [35] |
| BAK1/Ag/WS2/FASnI3/BP | 633 | 402 | 48.2 | [60] |
| BK7/ZnO/Ag/BaTiO3/WS2 | 633 | 235 | 63.51 | [61] |
| BK7/ZnO/Ag/BaTiO3/MoS2 | 633 | 195 | 20.67 | [61] |
| BK7/ZnO/Ag/BaTiO3/Graphene | 633 | 168 | 58.33 | [61] |
| BK7/Ag/Graphene | 457.5 | 300.26 | 33.25 | [62] |
| CaF2/TiO2/Ag/PtSe2/WS2 | 632.8 | 240.1 | 78.46 | [63] |
| BK7/Ag/TiO2/Graphene | 480 | 302.26 | 33.76 | [64] |
| CaF2/Ag/BP/WS2 | 633 | 375 | 65.78 | [59] |
| BK7/Ag/Au/BaTiO3/Graphene | 633 | 294 | 42.13 | [65] |
| BK7/Ag/WS2/BaTiO3/BP | 633 | 370 | 60 | [66] |
| BK7/Ag/12 layers BP (AC) | 633 | 211.1 | – | [67] |
| BK7/Ag/12 layers BP (ZZ) | 633 | 287.9 | – | [67] |
| FS/TiO2/Ag | 632.8 | 251.5 | 52.3 | This work |
| FS/TiO2/Ag/BP (AC) | 633 | 324.5 | 37.8 | This work |
| FS/TiO2/Ag/BP (ZZ) | 628 | 351.2 | 44.7 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chylek, J.; Ciprian, D.; Hlubina, P. Thickness and Wavelength Optimizations of a High-Performance SPR Sensor Employing a Silver Layer and Black Phosphorus in Principal Directions. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110790
Chylek J, Ciprian D, Hlubina P. Thickness and Wavelength Optimizations of a High-Performance SPR Sensor Employing a Silver Layer and Black Phosphorus in Principal Directions. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(11):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110790
Chicago/Turabian StyleChylek, Jakub, Dalibor Ciprian, and Petr Hlubina. 2025. "Thickness and Wavelength Optimizations of a High-Performance SPR Sensor Employing a Silver Layer and Black Phosphorus in Principal Directions" Nanomaterials 15, no. 11: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110790
APA StyleChylek, J., Ciprian, D., & Hlubina, P. (2025). Thickness and Wavelength Optimizations of a High-Performance SPR Sensor Employing a Silver Layer and Black Phosphorus in Principal Directions. Nanomaterials, 15(11), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110790





