Exchange Bias in Nanostructures: An Update
Abstract
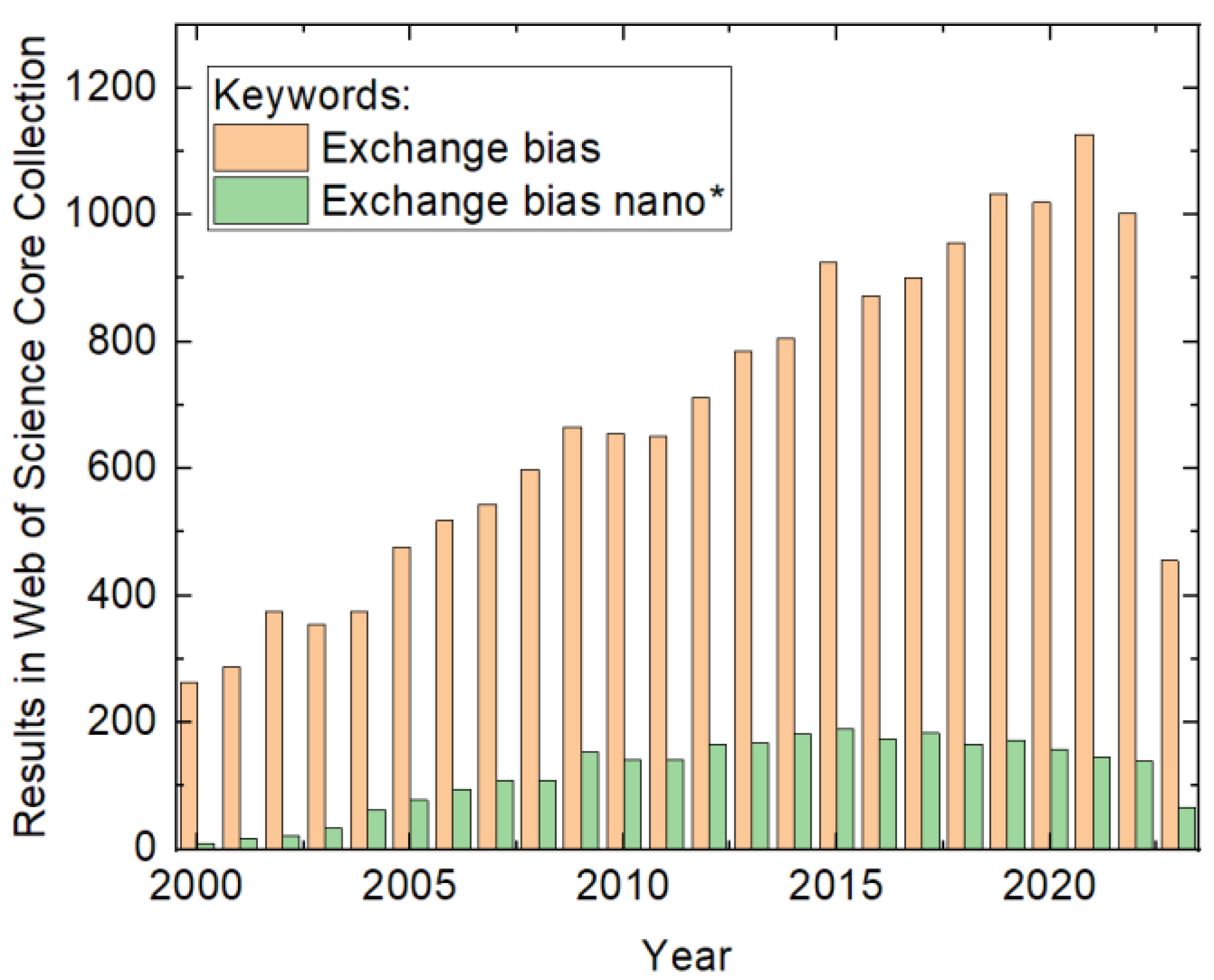
1. Introduction
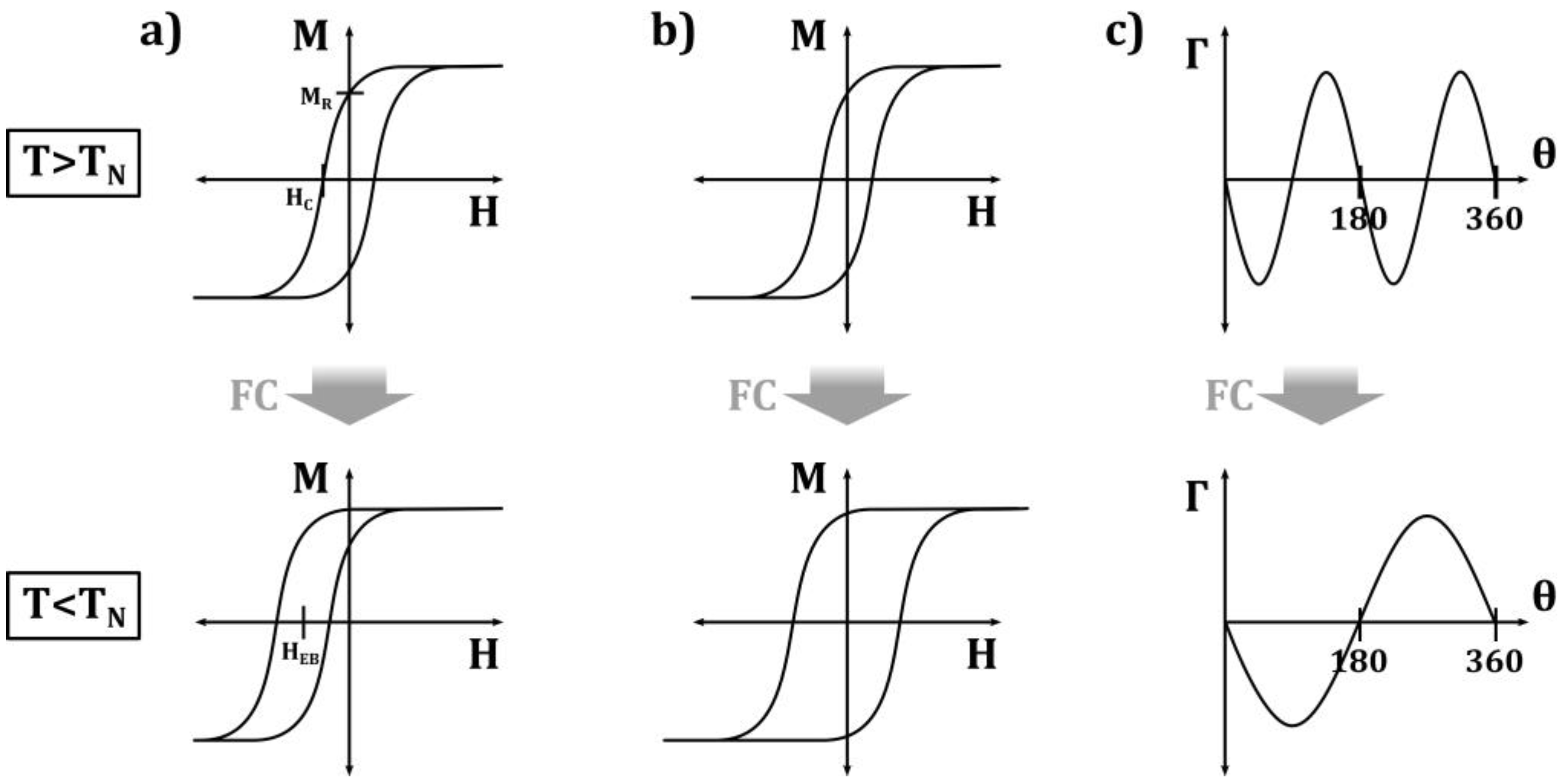
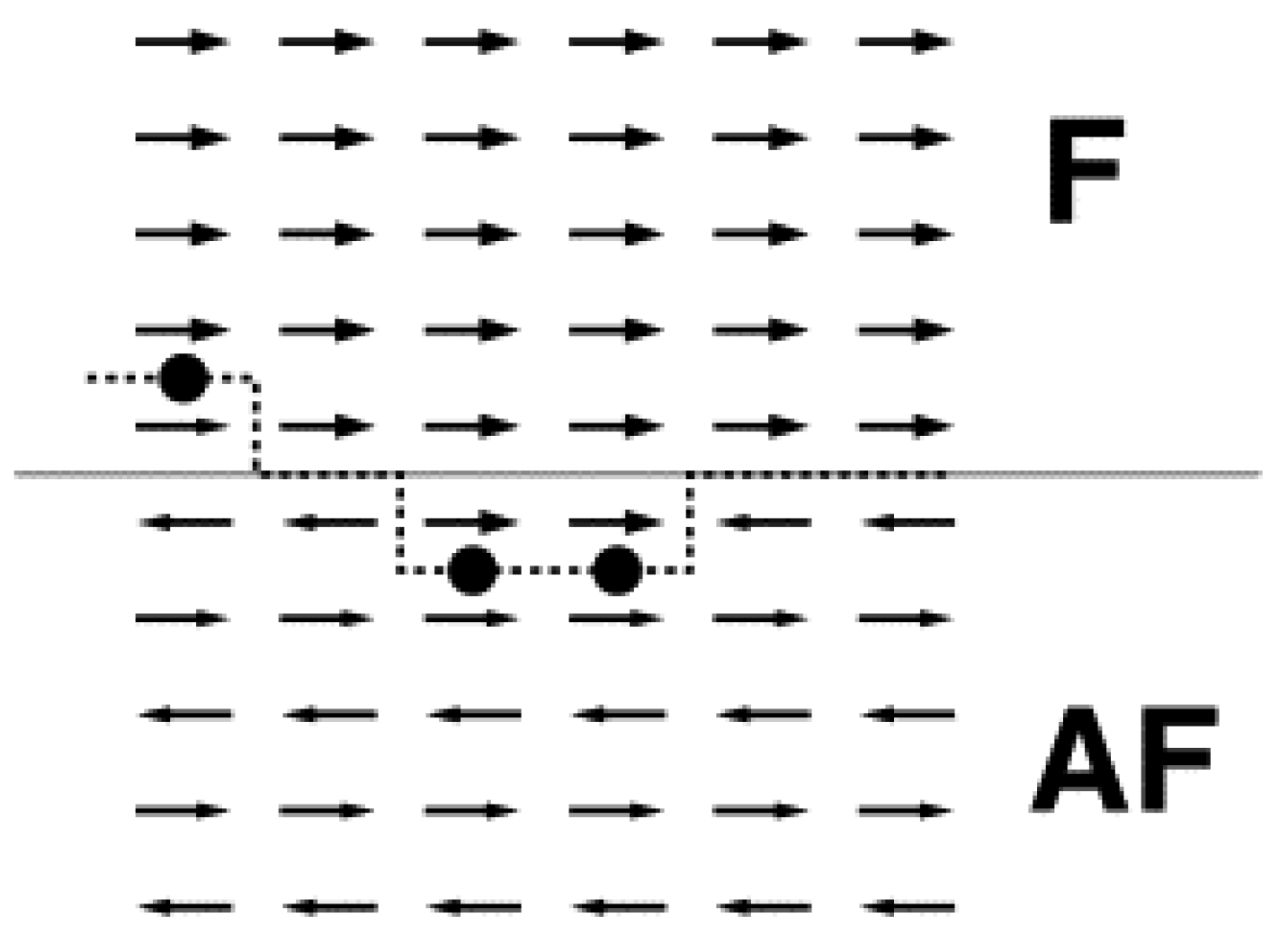
2. Properties of Exchange-Biased Nanostructures
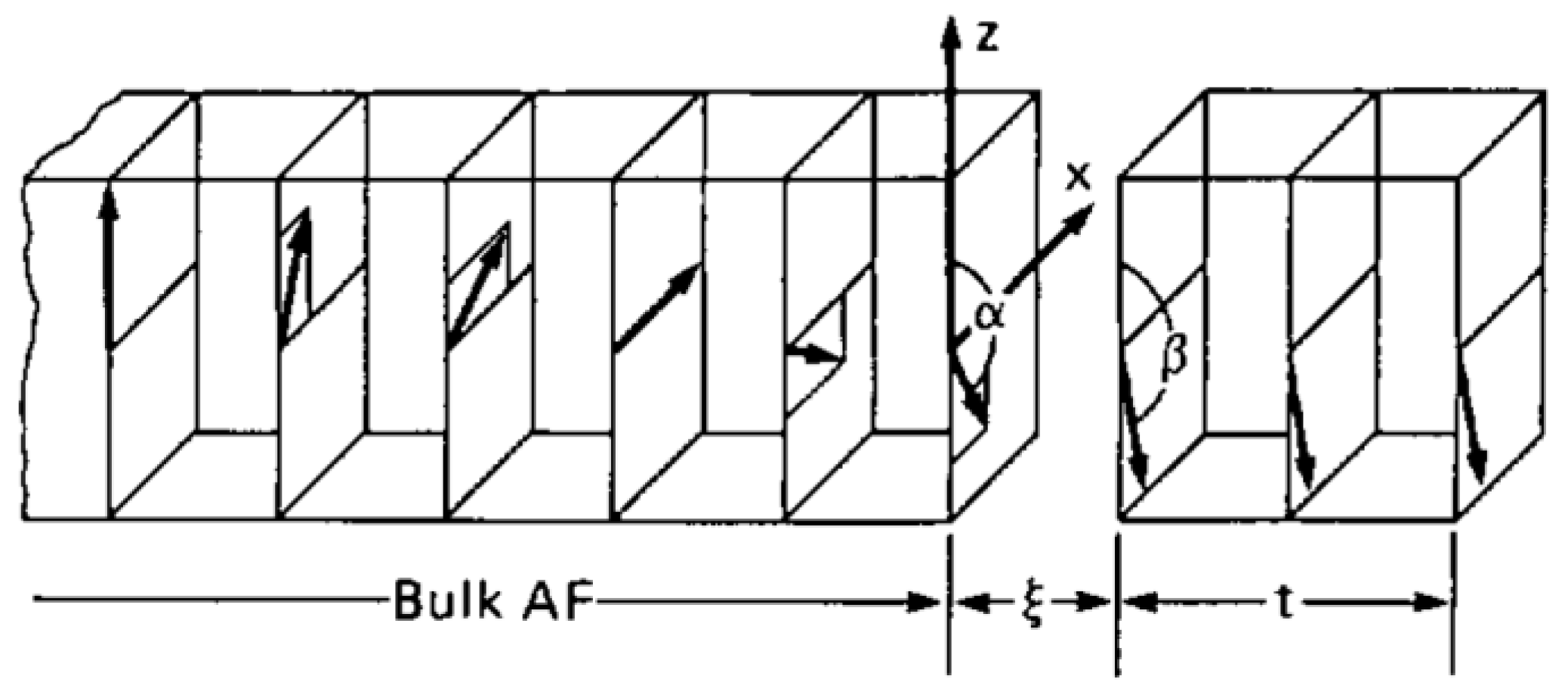
3. Modeling Exchange Bias in Nanostructures
4. Exchange Bias and Electronic Structure
5. Exchange Bias and Shape Anisotropy
6. Co/CoO Nanostructures
7. Other Exchange-Biased Nanostructures Containing Cobalt Oxides
8. Ni/NiO Nanostructures
9. Other Exchange-Biased Nanostructures Containing Nickel Oxides
10. FeO-Based Exchange-Biased Nanostructures
11. Other Iron-Oxide-Based Exchange-Biased Nanostructures
12. Other Exchange-Biased Nanostructures
12.1. Exchange-Biased Nanostructures Containing Fe
12.2. Exchange-Biased Nanostructures Containing Mn
12.3. Exchange-Biased Nanostructures Containing Other Materials
13. Pseudo-Exchange Bias
14. Conclusions
- -
- A positive EB, i.e., a horizontal shift opposite to the usual direction, was modeled [48,49,50] and simulated through Monte Carlo simulations [62]. Experimentally, it was found, e.g., in NiO/Fe3O4 core–shell nanoparticles [120], nanostructured FeMn/Co/FeMn networks [160], and α-MnO2 rectangular nanowires [178].
- -
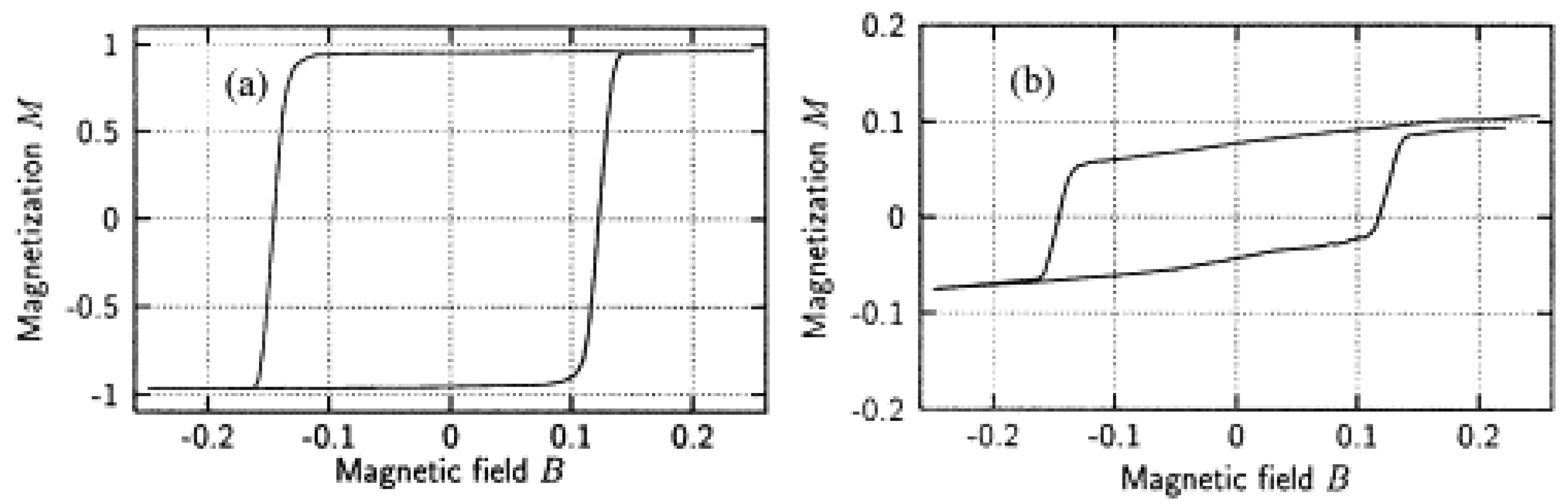
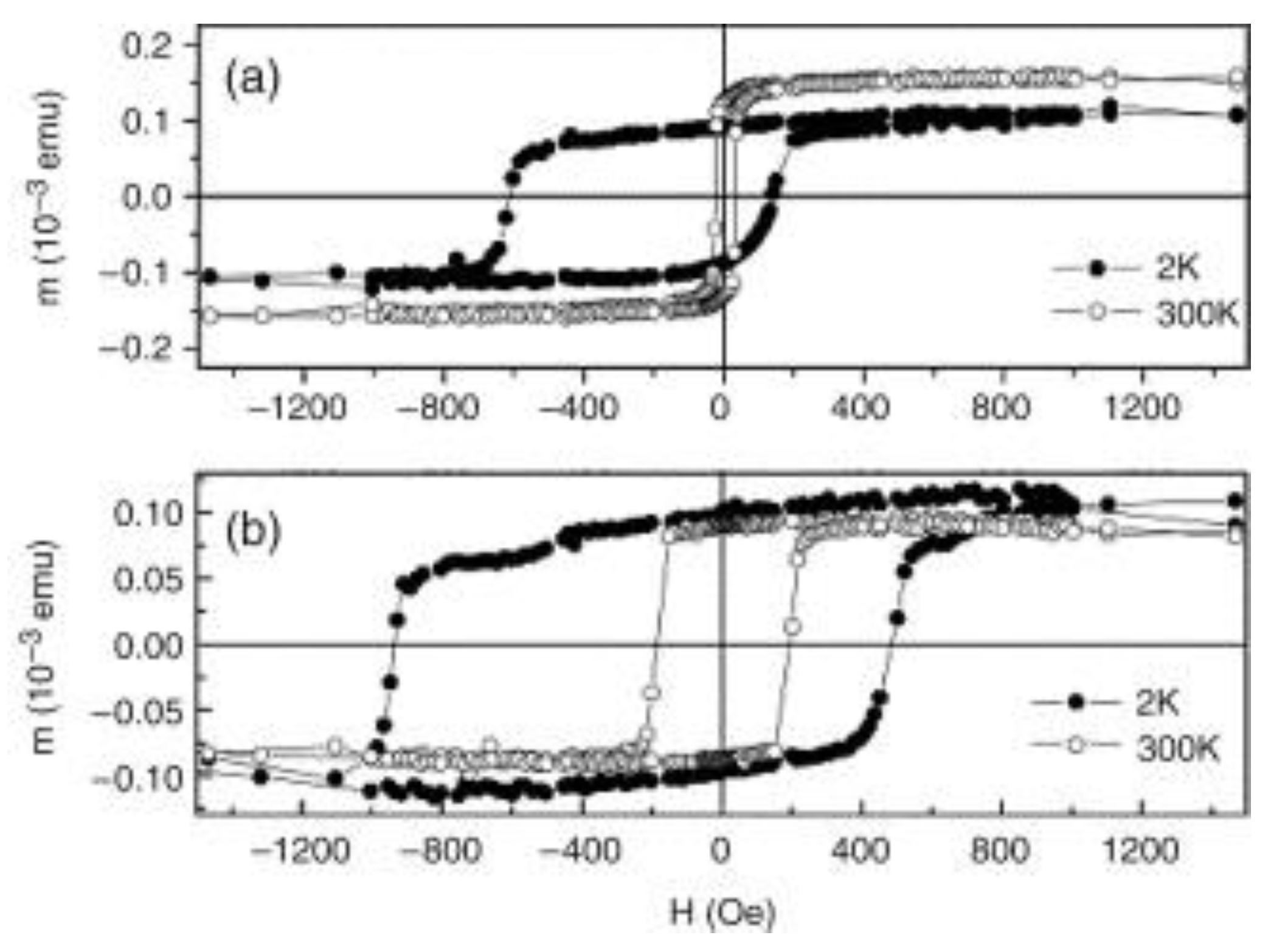
- A vertical shift of the hysteresis loop was often observed, in many cases relatively small and negligible for the evaluation of the coercive fields, but sometimes strikingly large. This effect was simulated, e.g., in the domain state model [41,42,43,44] or in other Monte Carlo simulations [59,61]. Experimentally, it was observed in Co/CoO nanostructures [97], Co3O4 nanowires [112], milled Fe/MnO2 containing 20% Fe [148], and in Co1−xNixFe2O4 [151] and Co0.33Fe0.67O nanoparticles [154], but also in manganite compounds, such as La0.2Ca0.8MnO3 [183], La0.25Ca0.75MnO3 [184], and Sm0.5Ca0.5MnO3 [185].
- -
- The exchange bias shift was usually higher at lower temperatures and, in some cases, described as especially large, e.g., for aligned Co/CoO core–shell nanowires systems [79], core–shell Co/CoO nanoparticles [98], Fe3−δO4@CoO core–shell nanoparticles [107], Co3O4 nanorods [113], Ni/NiO core/shell particles [115], Fe3O4/FeO core/shell nanoparticles [130], Fe/γ-Fe2O3 core–shell nanoparticles [135], or Zn0.3Ni0.7Fe2O4 as an example for a single-phase system [156].
- -
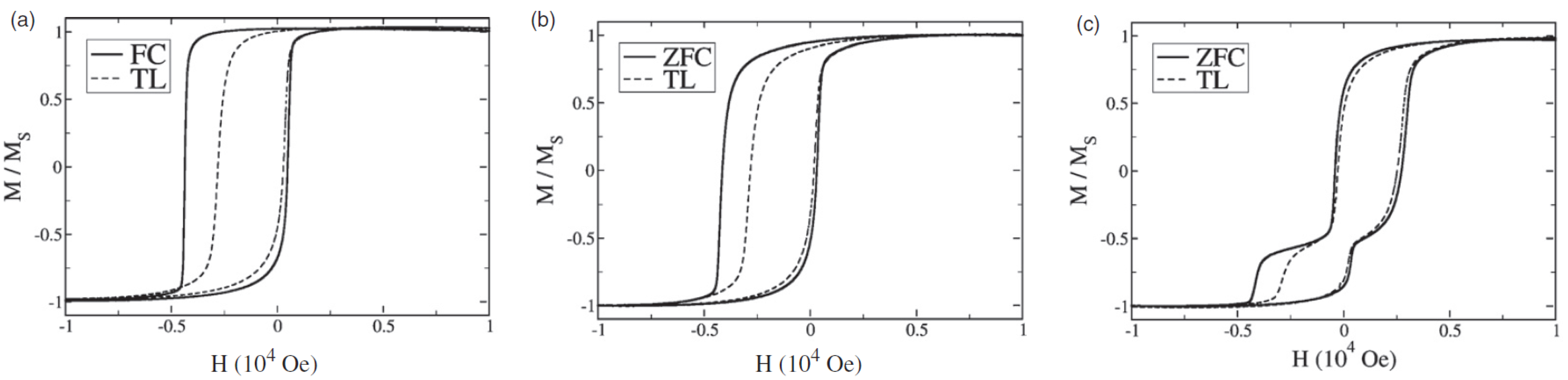
- Many exchange bias systems showed asymmetric hysteresis loops, often interpreted as different magnetization reversal mechanisms on either side of the loop, which could be modeled in the Monte Carlo simulations [58,59] and were found in diverse EB systems, such as Co/CoO core/shell particles [99] or FeO/Fe3O4 core/shell nanoparticles [130].
- -
- Surprisingly, an exchange bias could also be observed in some single-material systems, e.g., to interface layers forming between the substrate and material grown on it or the surface layers with different magnetic properties than the “bulk”. As some examples, CoFe2O4(111) grown on an Al2O3(0001) substrate can be mentioned [70], CoO nanoparticles [111], Co3O4 nanowires [112], Fe3O4 nanoparticles attached to Au seed particles [133], or Zn0.3Ni0.7Fe2O4 nanoparticles [156].
- -
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meiklejohn, W.H.; Bean, C.P. New magnetic anisotropy. Phys. Rev. 1956, 102, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiklejohn, W.H.; Bean, C.P. New magnetic anisotropy. Phys. Rev. 1957, 105, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogués, J.; Moran, T.J.; Lederman, D.; Schuller, I.K.; Rao, K.V. Role of interfacial structure on exchange-biased FeF2–Fe. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 6984–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Exchange bias in thin films—An update. Coatings 2021, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogués, J.; Schuller, I.K. Exchange bias. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 1999, 192, 203–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogués, J.; Sort, J.; Langlais, V.; Skumryev, V.; Surinach, S.; Munoz, J.S.; Baró, M.D. Exchange bias in nanostructures. Phys. Rep. 2005, 422, 65–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureti, S.; Suck, S.Y.; Haas, H.; Prestat, E.; Bourgeouis, O.; Givord, D. Size dependence of exchange bias in Co/CoO nanostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 077205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, K.; Li, W.J.; Ali, S.S.; Shi, D.W.; Khan, U.; Riaz, S.; Han, X.F. Enhanced exchange bias and improved ferromagnetic properties in Permalloy–BiFe0.95Co0.05O3 core–shell nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 18203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, V.; Reinholdt, A.; Kreibig, U.; Weirich, T.; Güntherodt, G.; Beschoten, B.; Tillmanns, A.; Krenn, H.; Rumpf, K.; Granitzer, P. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ni/NiOxide and Co/CoOxide Core/Shell Nanoparticles and their possible Use for Ferrofluids. Z. Phys. Chem. 2006, 220, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, A.; Oertker, S.; Beschoten, B.; Güntherodt, G.; Eisenmenger, J.; Schuller, I.K. Angular dependence and origin of asymmetric magnetization reversal in exchange-biased Fe/FeF2(110). Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 012401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, W.A.A.; Sahoo, B.; Kuncser, V.; Eisenmenger, J.; Felner, I.; Nogués, J.; Liu, K.; Keune, W.; Schuller, I.K. Changes in ferromagnetic spin structure induced by exchange bias in Fe/MnF2 films. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 224414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, A.; Oertker, S.; Beschoten, B.; Güntherodt, G.; Leighton, C.; Schuller, I.K.; Nogués, J. Magneto-optical study of magnetization reversal asymmetry in exchange bias. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 202512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Bera, A.K.; Dev, A.S.; Kumar, D.; Reddy, V.R. Exchange bias effect in Fe/LaAlO3: An interface induced effect. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 849, 156484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.M. Correlation of microstructure with magnetic properties in Pr0.67Sr0.33MnO3 thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 19875–19882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Tillmanns, A.; Fraune, M.; Beschoten, B.; Güntherodt, G. Exchange-bias in (110)-oriented CoO/Co bilayers with different magnetocrystalline anisotropies. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 054425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Adie, P.; Marrows, C.H.; Greig, D.; Hickey, B.J.; Stamps, R.L. Exchange bias using a spin glass. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, T.; Chien, C.L. Dependence of exchange field and coercitivity on cooling field in NiFe/CoO bilayers. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 7222–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, C.; Nogués, J.; Suhl, H.; Schuller, I.K. Competing interfacial exchange and Zeeman energies in exchange biases bilayers. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 12837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, T.J.; Gallego, J.M.; Schuller, I.K. Increased exchange anisotropy due to disorder at permalloy/CoO interfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 78, 1887–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demokritiv, S.O.; Hillebrands, B. Inelastic light scattering in magnetic dots and wires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, M.E.; Laughlin, E.E. Nano-scale materials development for future magnetic applications. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansmann, J.; Baker, S.H.; Binns, C.; Blackman, J.A.; Bucher, J.-P.; Dorantes-Dávila, J.; Dupuis, V.; Favre, L.; Kechrakos, D.; Kleibert, A.; et al. Magnetic and structural properties of isolated and assembled clusters. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2005, 56, 189–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.-F.; Xie, D.; Guo, M.-X.; Park, H.S.; Fujita, T. Size and shape effects on Curie temperature of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.S.; Chai, G.Z.; Li, X.L.; Fan, X.L. Effects of grain size distribution on coercivity and permeability of ferromagnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedke, M.O.; Potzger, K.; Bothmer, A.H.; Fassbender, J.; Hillebrands, B.; Rickart, M.; Freitas, P.P. Domain structure during magnetization reversal of PtMn/CoFe exchange bias micropatterned lines. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 043918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Reséndez, R.; Luna, C. Shape Anisotropy and Exchange Bias in Magnetic Flattened Nanospindles with Metallic/Oxide Core/Shell Structures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7577–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, A.; Reginka, M.; Huhnstock, R.; Merkel, M.; Holzinger, D.; Ehresmann, A. Magnetic textures in hemispherical thin film caps with in-plane exchange bias. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 015305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, S.; Schütz, G.; Goering, E.; Ji, X.S.; Krishnan, K.M. Uncompensated moments in the MnPd/Fe exchange bias system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 126402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiklejohn, W.H. Exchange anisotropy—A review. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 33, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Néel, L. Étude théorique du couplage ferro-antiferromagnétique dans les couches minces. Ann. Phys. 1967, 14, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwi, M. Exchange bias theory. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 234, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malozemoff, A.P. Random-field model of exchange bias anisotropy at rough ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic interfaces. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 35, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malozemoff, A.P. Mechanisms of exchange anisotropy. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 3874–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malozemoff, A.P. Heisenberg to Ising crossover in a random-field model with uniaxial anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 37, 7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, D.; Siegmann, H.C.; Bagus, P.S.; Kay, E. Simple model for thin ferromagnetic films exchange coupled to an antiferromagnetic substrate. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 62, 3047–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulthess, T.C.; Butler, W.H. Consequences of spin-flop coupling in exchange biased films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulthess, T.C.; Butler, W.H. Coupling mechanisms in exchange biased films. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 5510–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, K.; Kodama, R.H.; Berkowitz, A.E.; Cao, W.; Thomas, G. Interfacial uncompensated antiferromagnetic spins: Role in unidirectional anisotropy in polycrystalline Ni81F19/CoO bilayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, K.; Kodama, R.H.; Berkowitz, A.E.; Cao, W.; Thomas, G. Role of interfacial uncompensated antiferromagnetic spins in unidirectional anisotropy in Ni81F19/CoO bilayers. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 6888–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, M.D.; McMichael, R.D. Model for exchange bias in polycrystalline ferromagnet-antiferromagnet bilayers. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltényi, P.; Gierlings, M.; Keller, M.; Beschoten, B.; Güntherodt, G.; Nowak, U.; Usadel, K.D. Diluted antiferromagnets in exchange bias: Proof of the domain state model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, U.; Usadel, K.D.; Keller, J.; Miltényi, P.; Beschoten, B.; Güntherodt, G. Domain state model for exchange bias. I. Theory. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 014430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Miltényi, P.; Beschoten, B.; Güntherodt, G.; Nowak, U.; Usadel, K.D. Domain state model for exchange bias. II. Experiments. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 014431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beschoten, B.; Keller, J.; Tillmanns, A.; Miltényi, P.; Güntherodt, G. Domain state model for exchange bias: Training effect of diluted Co1−yO on exchange bias in Co/CoO. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 2744–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, U.; Misra, A.; Usadel, K.D. Modeling exchange bias microscopically. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 240, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwi, M.; Mejía-López, J.; Portugal, R.D.; Ramírez, R. Exchange bias model for Fe/FeF2: Role of domains in the ferromagnet. Europhys. Lett. 1999, 48, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwi, M.; Mejía-López, J.; Portugal, R.D.; Ramírez, R. Exchange-bias systems with compensated interfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 3995–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwi, M.; Mejía-López, J.; Portugal, R.D.; Ramírez, R. Positive exchange bias model: Fe/FeF2 and Fe/MnF2 bilayers. Solid State Commun. 2000, 116, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolting, F.; Scholl, A.; Stöhr, J.; Seo, J.W.; Fompeyrine, J.; Siegwart, H.; Locquet, J.-P.; Anders, S.; Lüning, J.; Fullerton, E.E.; et al. Direct observation of the alignment of ferromagnetic spins by antiferromagnetic spins. Nature 2000, 405, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Haginoya, C.; Koike, K. Microscopic imaging of Fe magnetic domains exchange coupled with those in a NiO(001) surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, F.; Westphalen, A.; Theis-Bröhl, K.; Zabel, H. Quantitative description of the azimuthal dependence of the exchange bias effect. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, L29–L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fita, I.; Markovich, V.; Moskvin, A.S.; Wisniewski, A.; Puzniak, R.; Iwanowski, P.; Martin, C.; Maignan, A.; Carbonio, R.E.; Gutowska, M.U.; et al. Reversed exchange-bias effect associated with magnetism reversal in the weak ferrimagnet LuFe0.5Cr0.5O3. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 104416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikov, A.G.; Stebliy, M.E.; Davydenko, A.V.; Kozlov, A.G.; Osmushko, I.S.; Korochentsev, V.V.; Ognev, A.V.; Gerasimenko, A.V.; Sadovnikov, A.V.; Gubanov, V.A.; et al. Magnetic properties and the interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction in exchange biased Pt/Co/NixOy films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 543, 148720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, V.; Kechrakos, D.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Tsiantos, V. Shape-dependent exchange bias effect in magnetic nanoparticles with core-shell morphology. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 064420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.F.L.; Bate, D.; Chantrell, R.W.; Yanes, R.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O. Influence of interfacial roughness on exchange bias in core-shell nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 092404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.F.L.; Fan, W.J.; Chureemart, P.; Ostler, T.A.; Ellis, M.O.A.; Chantrell, R.W. Atomistic spin model simulations of magnetic nanomaterials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.F.L.; Yanes, R.; Mryasov, O.; Chantrell, R.W.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O. On beating the superparamagnetic limit with exchange bias. Europhys. Lett. 2009, 88, 57004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iglesias, Ò.; Batlle, X.; Labarta, A. Microscopic origin of exchange bias in core/shell nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 212401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, Ò.; Labarta, A.; Batlle, X. Exchange bias phenomenology and models of core/shell nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2761–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftaxias, E.; Trohidou, K.N. Numerical study of the exchange bias effects in magnetic nanoparticles with core/shell morphology. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 134406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakaki, M.; Trohidou, K.N. Numerical study of the exchange-bias effect in nanoparticles with ferromagnetic core/ferrimagnetic disordered shell morphology. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 144402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Du, A. The effect of field-cooling strength and interfacial coupling on exchange bias in a granular system of ferromagnetic nanoparticles embedded in an antiferromagnetic matrix. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 113911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, O.G.; Schreiber, D.K.; Petford-Long, A.K. Micromagnetic modeling of spin-wave dynamics in exchange-biased permalloy disks. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 144407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-P.; Petracic, O.; Eisenmenger, J.; Schuller, I.K. Reversal behavior of exchange-biased submicron dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 072501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, E.; Faba, A.; Finocchio, G.; Azzerboni, B. Mathematical Modelling of Magnetic Hysteresis in Exchange-Bias Spin Valves. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3367–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, A.; Blachowicz, T.; Zghidi, H. Spreadsheet analysis of stability and meta-stability of low-dimensional magnetic particles using the Ising approach. Eur. J. Phys. 2015, 36, 035028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, T.; Koyama, T.; Chiba, D. Electric field modulation of exchange bias at the Co/CoOx interface. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 101, 014447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, C.A.F.; Altman, E.I.; Henrich, V.E. Exchange bias and interface electronic structure in Ni/Co3O4(011). Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 104428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.J.; Song, C.; Cui, B.; Li, F.; Mao, H.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, G.Y.; Pan, F. Exchange bias in a single LaMnO3 film induced by vertical electronic phase separation. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 165129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.T.; Yun, Y.; Subedi, A.; Rogers, N.E.; Cornelison, D.M.; Dowben, P.A.; Xu, X.S. Colossal intrinsic exchange bias from interfacial reconstruction in epitaxial CoFe2O4/Al2O3 thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2021, 103, 224405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffari, G.H.; Rumaiz, A.K.; Woicik, J.C.; Shah, S.I. Influence of oxygen vacancies on the electronic structure and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 093906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarveena; Shrivastava, N.; Singh, M.; Sharma, S.K. Multifunctional Magnetic Nanostructures: Exchange Bias Model and Applications. In Complex Magnetic Nanostructures; Sharma, S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 225–280. [Google Scholar]
- Tolea, F.; Sorescu, M.; Diamandescu, L.; Iacob, N.; Tolea, M.; Kuncser, V. Unidirectional Magnetic Anisotropy in Molybdenum Dioxide–Hematite Mixed-Oxide Nanostructures. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternst, K.; Girgis, E.; Portugal, R.D.; Loosvelt, H.; Poova, E.; van Bael, M.J.; van Haesendonck, C.; Fritzsche, H.; Gierlings, M.; Leunissen, L.H.A.; et al. Magnetization and polarized neutron reflectivity experiments on patterned exchange bias structures. Eur. Phys. J. B 2005, 45, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Mauc, C.; Perrier, T.; Moulin, J.; Kayer, P. Induced exchange bias in NiMn/CoFe multilayer thin films sputtered on a quartz substrate by field cooling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 544, 168649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temnst, K.; Popova, E.; Loosvelt, H.; van Bael, M.J.; Brems, S.; Bruynseraede, Y.; van Haesendonck, C.; Fritzsche, H.; Gierlings, M.; Leunissen, L.H.A.; et al. The influence of finite size and shape anisotropy on exchange bias: A study of patterned Co/CoO nanostructures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 304, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, E.; Loosvelt, H.; Gierlings, M.; Leunissen, L.H.A.; Jonckheere, R.; van Haesendonck, C.; Temst, K. Magnetization reversal in exchange biased Co/CoO patterns. Eur. Phys. J. B 2005, 44, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.; Adeyeye, A.O.; Chakrabarti, K.; Singh, N. Tuning the exchange bias in large area Co/CoO nanowire arrays. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09D705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandha, K.; Chaudhary, R.P.; Mohapatra, J.; Koymen, A.R.; Liu, J.P. Giant exchange bias and its angular dependence in Co/CoO core-shell nanowire assemblies. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 381, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, T.; Zighem, F.; Ott, F.; Chaboussant, G.; André, G.; Soumare, Y.; Piquemal, J.-Y.; Vian, G.; Gatel, C. Exhange bias in Co/CoO core-shell nanowires: Role of the antiferromagnetic superparamagnetic fluctuations. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 064427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koplak, O.V.; Morgunov, R.B. Exchange bias and spin-reorientation transition in α-Fe/PrDyCoFeB core/shell microwires. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 263, 114845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-P. Magnetoresistance and exchange bias effect of the periodically nanostructured cobalt filament arrays. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 185004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Li, W.J.; Javed, K.; Shi, D.W.; Riaz, S.; Zhai, G.J.; Han, X.F. Exchange bias in two-step artificially grown one-dimensional hybrid Co–BiFeO3 core–shell nanostructures. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 045708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Weiss, D.N.; Krishnan, K.M. Competing anisotropies and temperature dependence of exchange bias in Co_IrMn metallic wire arrays fabricated by nanoimprint lithography. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09D724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, W.O.; Knobel, M.; Cescato, L.; Gobbi, A.L.; Vázquez, M. Experimental magnetic study and evidence of the exchange bias effect in unidimensional Co arrays produced by interference lithography. Solid State Commun. 2007, 142, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.; Adeyeye, A.O.; Singh, N.; Stamps, R.L. Controlling the magnetization reversal in exchange-biased Co/CoO elongated nanorings. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 015304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenmenger, J.; Li, Z.-P.; Macedo, W.A.A.; Schuller, I.K. Exchange Bias and Asymmetric Reversal in Nanostructured Dot Arrays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 057203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.J.; Meng, X.G.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.Q.; Cao, J.F.; Tai, R.H. Vorticity of magnetic vortices controlled by exchange bias and shape anisotropy in polygonal nanomagnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 539, 168334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albisetti, E.; Calò, A.; Spieser, M.; Knoll, A.W.; Riedo, E.; Petti, D. Stabilization and control of topological magnetic solitons via magnetic nanopatterning of exchange bias systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 162401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moralejo, S.; Castano, F.J.; Ross, C.A.; Redondo, C.; Stano, F. Collective switching of single-layer and exchange bias coupled nanomagnet arrays. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 195003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donolato, M.; Dalslet, B.T.; Damsgaard, C.D.; Gunnarsson, K.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Svedlindth, P.; Hansen, M.F. Size-dependent effects in exchange-biased planar Hall effect sensor crosses. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 064511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candeloro, P.; Schultheiß, H.; Nembach, H.T.; Hillebrands, B.; Trellenkamp, S.; Dautermann, C.; Wolff, S. Orthogonal exchange bias field directions in exchange bias microstructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 192510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folven, E.; Scholl, A.; Young, A.; Retterer, S.T.; Boschker, J.E.; Tybell, T.; Takamura, Y.; Grepstad, J.K. Crossover from Spin-Flop Coupling to Collinear Spin Alignment in Antiferromagnetic/Ferromagnetic Nanostructures. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2386–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, J.B.; Weiss, D.N.; Dinega, D.P.; Bawendi, M.G. Exchange biasing and magnetic properties of partially and fully oxidized colloidal cobalt nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 064404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruyters, M. Spin-Glass-Like Behavior in CoO Nanoparticles and the Origin of Exchange Bias in Layered CoO/Ferromagnet Structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 077204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogués, J.; Skumryev, V.; Sort, J.; Stoyanov, S.; Givord, D. Shell-Driven Magnetic Stability in Core-Shell Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 157203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrynin, A.N.; Ternst, K.; Lievens, P.; Margueritat, J.; Gonzalo, J.; Afonso, C.N.; Piscopiello, E.; van Tendelo, G. Observation of Co/CoO nanoparticles below the critical size for exchange bias. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 113913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inderhees, S.E.; Borchers, J.A.; Green, K.S.; Kim, M.S.; Sun, K.; Strycker, G.L.; Aronson, M.C. Manipulating the Magnetic Structure of Co Core/CoO Shell Nanoparticles: Implications for Controlling the Exchange Bias. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 117202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Khurshid, H.; Phan, M.-H.; Srikanth, H. Asymmetric hysteresis loops and its dependence on magnetic anisotropy in exchange biased Co/CoO core-shell nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 232405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feygenson, M.; Yiu, Y.; Kou, A.; Kim, K.-S.; Aronson, M.C. Controlling the exchange bias field in Co core/CoO shell nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 195445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proenca, M.P.; Ventura, J.; Sousa, C.T.; Vazquez, M.; Araujo, J.P. Exchange bias, training effect, and bimodal distribution of blocking temperatures in electrodeposited core-shell nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 134404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrynin, A.N.; van Bael, M.J.; Temst, K.; Lievens, P. Evidence for coexistence of exchange bias and exchange spring effects in oxidized Co nanocluster assembled films. New J. Phys. 2007, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toro, J.A.; Andrés, J.P.; González, J.A.; Muniz, P.; Munoz, T.; Normile, P.S.; Riveiro, J.M. Exchange bias and nanoparticle magnetic stability in Co-CoO composites. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 094449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.; Adeyeye, A.O. Probing the exchange bias in Co/CoO nanoscale antidot arrays using anisotropic magnetoresistance. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 064413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Misra, V. Large-area long-range ordered anisotropic magnetic nanostructure fabrication by photolithography. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovylina, M.; García del Muro, M.; Konstantinovic, Z.; Varela, M.; Iglesias, O.; Labarta, M.; Batlle, X. Controlling exchange bias in Co–CoOx nanoparticles by oxygen content. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 175702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaziz, W.; Pichon, B.P.; Lefevre, C.; Ulhaq-Bouillet, C.; Greneche, J.-M.; Toumi, M.; Mhiri, T.; Bégin-Colin, S. High Exchange Bias in Fe3−δO4@CoO Core Shell Nanoparticles Synthesized by a One-Pot Seed-Mediated Growth Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11436–11443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, I.; Basina, G.; Alexandrakis, V.; Devlin, E.; Hadjipanayis, G.; Colak, L.; Niarchos, D.; Tzitzios, V. Synthesis and Exchange Bias in γ-Fe2O3/CoO and Reverse CoO/γ-Fe2O3 Binary Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14609–14614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorato, G.C.; Lima, E., Jr.; Troiani, H.E.; Zysler, R.D.; Winkler, E.L. Tuning the coercivity and exchange bias by controlling the interface coupling in bimagnetic core/shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10240–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomou, A.; Gournis, D.; Panagiotopoulos, I.; Huang, Y.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Kooi, B. Weak ferromagnetism and exchange biasing in cobalt oxide nanoparticle systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohldag, H.; Scholl, A.; Nolting, F.; Arenholz, E.; Maat, S.; Young, A.T.; Carey, M.; Stöhr, J. Correlation between Exchange Bias and Pinned Interfacial Spins. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 017203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salabas, E.L.; Rumplecker, A.; Kleitz, F.; Radu, F.; Schüth, F. Exchange Anisotropy in Nanocasted Co3O4 Nanowires. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2977–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.X.; Shen, X.P.; Horvat, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Wexler, D.; Yao, J. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Optical, Magnetic, and Supercapacitance Properties of Nanoporous Cobalt Oxide Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4357–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Seehra, M.S.; Thota, S.; Kumar, J. A comparative study of the magnetic properties of bulk and nanocrystalline Co3O4. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 015218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querejeta-Fernández, A.; Parras, M.; Varela, A.; del Monte, F.; García-Hernández, M.; González-Calbet, J.M. Urea-Melt Assisted Synthesis of Ni/NiO Nanoparticles Exhibiting Structural Disorder and Exchange Bias. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6529–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston-Peck, A.C.; Wang, J.W.; Tracy, J.B. Synthesis and Structural and Magnetic Characterization of Ni(Core)/NiO(Shell) Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Patra, M.; Majumdar, S.; Giri, S. Influence of cooling field on the magnetic properties of Ni/NiO nanostructure. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 480, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi-Montes, N.; Gorria, P.; Martínez-Blanco, D.; Amghouz, Z.; Fuertes, A.B.; Fernández Barquín, L.; de Pedro, I.; Olivi, L.; Blanco, J.A. Unravelling the onset of the exchange bias effect in Ni(core)@NiO(shell) nanoparticles embedded in a mesoporous carbon matrix. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5674–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremenovic, A.; Jancar, B.; Ristic, M.; Vucinic-Vasic, M.; Rogan, J.; Pacevski, A.; Antic, B. Exchange-Bias and Grain-Surface Relaxations in Nanostructured NiO/Ni Induced by a Particle Size Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 4356–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsopoe, S.P.; Borgohain, C.; Fopase, R.; Pandey, L.M.; Borah, J.P. A comparative investigation of normal and inverted exchange bias effect for magnetic fluid hyperthermia applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.M.; Yuan, S.L.; Yin, S.Y.; Liu, L.; He, J.H.; Duan, H.N.; Li, P.; Wang, C.H. Exchange bias effect in a granular system of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles embedded in an antiferromagnetic NiO matrix. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 222505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi-Montes, N.; Gorria, P.; Martínez-Blanco, D.; Fuertes, A.B.; Fernández Barquín, L.; Puente-Orench, I.; Blanco, J.A. Scrutinizing the role of size reduction on the exchange bias and dynamic magnetic behavior in NiO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 305705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, E.; Zysler, R.D.; Mansilla, M.V.; Fiorani, D. Surface anisotropy effects in NiO nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 132409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, S.A.; Al-Attar, H.; Kodama, R.H. Particle size and temperature dependence of exchange bias in NiO nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 2008, 145, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, R.K.; Li, C.-P.; Roshchin, I.V.; Schuller, I.K.; Liu, K. Deconvoluting reversal modes in exchange-biased nanodots. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 144410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboucas, G.O.G.; Silva, A.S.W.T.; Dantas, A.L.; Camley, R.E.; Carrico, A.S. Magnetic hysteresis of interface-biased flat iron dots. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Boubeta, C.; Simeonidis, K.; Angelakeris, M.; Pazos-Pérez, N.; Giersig, M.; Delimitis, A.; Nalbandian, L.; Alexandrakis, V.; Niarchos, D. Critical radius for exchange bias in naturally oxidized Fe nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 054430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unni, M.; Uhl, A.M.; Savliwala, S.; Savitzky, B.H.; Dhavalikar, R.; Garraud, N.; Arnold, D.P.; Kourkoutis, L.F.; Andrew, J.S.; Rinaldi, C. Thermal Decomposition Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Diminished Magnetic Dead Layer by Controlled Addition of Oxygen. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.; Loginova, E.; Mascaraque, A.; Schmid, A.K.; McCarty, K.F.; de la Figuera, J. Structure and magnetism in ultrathin iron oxides characterized by low energy electron microscopy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 314011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.L.; Frey Huls, N.; Sigdei, A.; Sun, S.H. Tuning Exchange Bias in Core/Shell FeO/Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatkowska-Warkocka, Z.; Kawaguchi, K.; Wang, H.Q.; Katou, Y.; Koshizaki, N. Controlling exchange bias in Fe3O4/FeO composite particles prepared by pulsed laser irradiation. Nano Express 2011, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, E.V.; Bodnarchuk, M.I.; Kovalenko, M.V.; Talapin, D.V.; Smith, R.K.; Aloni, S.; Heiss, W.; Alivisatos, A. Gold/Iron Oxide Core/Hollow-Shell Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Frey Huls, N.A.; Phan, M.H.; Srinath, S.; Garcia, M.A.; Lee, Y.M.; Wang, C.; Sun, S.H.; Iglesias, Ò.; Srikanth, H. Exchange bias effect in Au-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 055702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feygenson, M.; Bauer, J.C.; Gai, Z.; Marques, C.; Aronson, M.C.; Teng, X.W.; Su, D.; Stanic, V.; Urban, V.S.; Beyer, K.A.; et al. Exchange bias effect in Au-Fe3O4 dumbbell nanoparticles induced by the charge transfer from gold. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 054416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Khurshid, H.; Li, W.F.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Phan, M.H.; Srikanth, H. Spin dynamics and criteria for onset of exchange bias in superspin glass Fe/γ-Fe2O3 core-shell nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 014426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, H.; Phan, M.-H.; Mukherjee, P.; Srikanth, H. Tuning exchange bias in Fe/γ-Fe2O3 core-shell nanoparticles: Impacts of interface and surface spins. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 072407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabreira-Gomes, R.; Silva, F.G.; Aquino, R.; Bonville, P.; Tourinho, F.A.; Perzynski, R.; Depeyrot, J. Exchange bias of MnFe2O4@γFe2O3 and CoFe2O4@γFe2O3 core/shell nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 368, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltoni, P.; López-Martín, R.; Sánchez, E.; Normile, P.; Vasilakaki, M.; Lee, S.; Burgos, B.; López del Castillo, E.; Peddis, D.; Binns, C.; et al. Non-Exchange Bias in Binary Nanoparticle Systems. Preprint. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3125651/v1 (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Khurshid, H.; Li, W.F.; Phan, M.-H.; Mukherjee, P.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Srikanth, H. Surface spin disorder and exchange-bias in hollow maghemite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 022403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, R.N.; Saravanan, A. Surface magnetism, Morin transition, and magnetic dynamics in antiferromagnetic α-Fe2O3 (hematite) nanograins. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 053916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, X.J.; Jin, W.T.; Kashkarov, P.; Zhang, H. Synthesis and characterization of single-crystalline α-Fe2O3 nanoleaves. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2009, 41, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Q.K.; Wei, A.; Lin, X.-M. Exchange bias in Fe/Fe3O4 core-shell magnetic nanoparticles mediated by frozen interfacial spins. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 134418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, J.M.; Hettler, S.; Lima, E., Jr.; Goya, G.F.; Arenal, R.; Zysler, R.D.; Aguirre, M.H.; Winkler, E.L. Onion-like Fe3O4/MgO/CoFe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles: New Ways to Control Magnetic Coupling between Soft/Hard Phases. Preprint. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/371855160_Onion-like_Fe3O4MgOCoFe2O4_magnetic_nanoparticles_new_ways_to_control_magnetic_coupling_between_softhard_phases (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Estrader, M.; López-Ortega, A.; Estradé, S.; Golosovsky, I.V.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Vasilakaki, M.; Trohidou, K.N.; Varela, M.; Stanley, D.C.; Sinko, M.; et al. Robust antiferromagnetic coupling in hard-soft bi-magnetic core/shell nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Yang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Wie, M.B. Ferromagnetism and exchange bias in Fe-doped ZnO nanocrystals. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 112, 1021–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, A.C.; Saerbeck, T.; de la Venta, J.; Huckfeldt, H.; Ehresmann, A.; Schuller, I.K. Exchange bias: The antiferromagnetic bulk matters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 072403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.F.; Basaran, A.C.; Morales, R.; Kovylina, M.; Llobet, J.; Borrsé, X.; Marcus, M.A.; Scholl, A.; Schuller, I.K.; Batlle, X.; et al. Manipulation of competing ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic domains in exchange-biased nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 174417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamani, E.C.; Larica, C.; Marques, C.; Proveti, J.R.; Takeuchi, A.Y.; Sanchez, F.H. Exchange bias and anomalous vertical shift of the hysteresis loops in milled Fe/MnO2 material. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 299, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, C.; Qureshi, M.T.; Peddis, D.; Baker, S.H.; Howes, P.B.; Boatwright, A.; Cavill, S.A.; Dhesi, S.S.; Lari, L.; Kröger, R.; et al. Exchange Bias in Fe@Cr Core–Shell Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3334–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mumtaz, A.; Maaz, K.; Janjua, B.; Hasanain, S.K.; Bertino, M.F. Exchange bias and vertical shift in CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 313, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Khalid, W.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.K.; Liu, J.; Duan, J.L. Magnetic characterization of Co1−xNixFe2O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation route. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2009, 41, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.M.; Galdino, V.B.; Machado, F.L.A. Exchange-bias and exchange-spring coupling in magnetic core–shell nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 350, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masala, O.; Seshadri, R. Spinel Ferrite/MnO Core/Shell Nanoparticles: Chemical Synthesis of All-Oxide Exchange Biased Architectures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9354–9355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-J.; Chiang, R.-K.; Kamali, S.; Wang, S.-L. Synthesis and controllable oxidation of monodisperse cobalt-doped wüstite nanoparticles and their core–shell stability and exchange-bias stabilization. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14332–14343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.T.; Shams, N.N.; Wang, D.S.; Lai, C.-H. Enhanced exchange bias in sub-50-nm IrMn/CoFe nanostructure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 082503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Ghosh, M.P.; Mukherjee, S. Size dependent exchange bias in single-phase Zn0.3Ni0.7Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 458, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavra, M.; Zentková, M.; Mihalik, M.; Mihalik, M., Jr.; Lazúrová, J.; Girman, V.; Perovic, M.; Kusigerski, V.; Roupcova, P.; Jaglicic, Z. Exchange Bias Effect in NdFeO3 System of Nanoparticles. Act. Phys. Pol. A 2017, 131, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.M.; Manna, P.K.; Shirolkar, M.M.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Tewari, R.; Dey, G.K. A study of exchange bias in BiFeO3 core/NiFe2O4 shell nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 173906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizzo, F.; Bonfiglioli, E.; Tamisari, M.; Gerardino, A.; Barucca, G.; Notargiacomo, A.; Chinni, F.; del Bianco, L. Magnetic exchange coupling in IrMn/NiFe nanostructures: From the continuous film to dot arrays. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 064410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.J.; Xue, D.S.; Fan, X.L.; Guo, D.W.; Liu, Q.F. Anomalous positive exchange bias in nanostructured FeMn/Co/FeMn networks. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 335703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadvand, H.; Salamati, H.; Kameli, P.; Poddar, A.; Acet, M.; Zakeri, K. Exchange bias in LaFeO3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 245002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.K.; Yusuf, S.M.; Shukla, R.; Tyagi, A.K. Exchange bias in BiFe0.8Mn0.2O3 nanoparticles with an antiferromagnetic core and a diluted antiferromagnetic shell. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 184412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.-J.; Papaefthymiou, G.C.; Viescas, A.J.; Moodenbaugh, A.R.; Wong, S.S. Size-Dependent Magnetic Properties of Single-Crystalline Multiferroic BiFeO3 Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Z.; Xu, X.Y.; Lu, X.M.; Zhou, M.; Sang, H.; Zhu, J.S. The exchange bias behavior of BiFeO3 nanoparticles with natural core-shell structure. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, R.; Devi, P.S.; Bhattacharya, D.; Choudhury, P.; Sen, A.; Raja, M. Ferromagnetism in nanoscale BiFeO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 062510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, K.; Sarkar, B.; Ashok, V.D.; Das, K.; Chaudhuri, S.S.; De, S.K. Interfacial magnetism and exchange coupling in BiFeO3–CuO nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 505711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, T.; Goswami, S.; Bhattacharya, D.; Roy, S. Superspin Glass Mediated Giant Spontaneous Exchange Bias in a Nanocomposite of BiFeO3−Bi2Fe4O9. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, S.; Yadav, M.; Dehury, T.; Yadav, A.K.; Sahoo, P.K.; Rath, C. Coexistence of tetragonal and cubic phase induced complex magnetic behaviour in CoMn2O4 nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 425702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, T. Antiferromagnetism in γ-phase Mn-Ir alloys. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1974, 36, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suess, D.; Kirschner, M.; Schrefl, T.; Fidler, J.; Stamps, R.L.; Kim, J.-V. Exchange bias of polycrystalline antiferromagnets with perfectly compensated interfaces. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 054419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, V.; Sort, J.; Landis, S.; Rodmacq, B.; Dieny, B. Tailoring Size Effects on the Exchange Bias in Ferromagnetic-Antiferromagnetic <100 nm Nanostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 117201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baltz, V.; Sort, J.; Rodmacq, B.; Dieny, B.; Landis, S. Thermal activation effects on the exchange bias in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sort, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Chung, S.-H.; Buchanan, K.S.; Grimsditch, M.; Baró, M.D.; Dieny, B.; Nogués, J. Magnetization Reversal in Submicron Disks: Exchange Biased Vortices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 067201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerbanjiang, B.; Wiedwald, U.; Haering, F.; Biskupek, J.; Kaiser, U.; Ziemann, P.; Herr, U. Exchange bias of Ni nanoparticles embedded in an antiferromagnetic IrMn matrix. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 455702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowski, G.; Albrecht, M.; Guhr, I.L.; Coey, J.M.D.; van Dijken, S. Size-dependent scaling of perpendicular exchange bias in magnetic nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 012413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.B.; Yang, W.Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, S.; Yun, C.; Luo, Z.C.; Liu, S.Q.; Han, J.Z.; Du, H.L.; Xu, Q.; et al. Giant exchange bias in the nanostructured MnAl thin ribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 012402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Villacorta, F.; Marion, J.L.; Sepehrifar, T.; Daniil, M.; Willard, M.A.; Lewis, L.H. Exchange anisotropy in the nanostructured MnAl system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 112408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Zeng, R.; Sun, Z.Q.; Tian, D.L.; Dou, S.X. Uncoupled surface spin induced exchange bias in α-MnO2 nanowires. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, P.Z.; Li, D.; Choi, C.J.; Li, Y.B.; Geng, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.D. Large coercivity and small exchange bias in Mn3O4/MnO nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 2007, 142, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Sort, J.; Surinach, S.; Dolor Baro, M.; Nogués, J. Synthesis and Size-Dependent Exchange Bias in Inverted Core−Shell MnO|Mn3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9102–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, P.Z.; Li, D.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, C.J.; Zhang, Z.D.; Geng, D.Y.; Brück, E. Unconventional exchange bias in oxide-coated manganese nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 133122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dressel, M. Grain-size effects on the charge ordering and exchange bias in Pr0.5Ca0.5MnO3: The role of spin configuration. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 014435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovich, V.; Mogilyansky, d.; Wisniewski, A.; Fita, I.; Puzniak, R.; Iwanowski, P.; Wu, X.D.; Suzuki, K.; Chen, S.; Gorodetzky, G. Nanometer Size Effect on Structural and Magnetic Properties of La0.2Ca0.8MnO3. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 8607–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Ding, J.F.; Zhang, G.Q.; Hou, Y.; Yao, Y.P.; Li, X.G. Size-dependent exchange bias in La0.25Ca0.75MnO3 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 224408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.K.; Poddar, A.; Nath, T.K. Surface spin glass and exchange bias effect in Sm0.5Ca0.5MnO3 manganites nano particles. AIP Adv. 2011, 1, 032110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovich, V.; Fita, I.; Wisniewski, A.; Puzniak, R.; Mogilyansky, D.; Titelman, L.; Vradman, L.; Herskowitz, M.; Gorodetsky, G. Surface and exchange-bias effects in compacted CaMnO3−δ nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 054410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.W.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, W.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, H.R.; Wang, K.F. Spin-glassy behavior and exchange bias effect of hexagonal YMnO3 nanoparticles fabricated by hydrothermal process. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 053901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Guerra, C.; Vila, M.; Piqueras, J. Exchange bias in single-crystalline CuO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 193105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Gupta, P.; Bedanta, S.; Chakraborty, M.; De, D. Coexistence of exchange bias and memory effect in nanocrystalline CoCr2O4. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 890, 161916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.K.; Yusuf, S.M.; Shukla, R.; Tyagi, A.K. Coexistence of sign reversal of both magnetization and exchange bias field in the core-shell type La0.2Ce0.8CrO3 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 242508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.J.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, C.N.; Guo, D.H.; Zeng, S.Y.; Cheng, B.C.; Xiao, Y.H.; Zhou, L. General synthesis of rare-earth orthochromites with quasi-hollow nanostructures and their magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11982–11991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geshev, J. Comment on: “Exchange bias and vertical shift in coFe2O4 nanoparticles” [J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 313 (2007) 266]. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ömcü, E.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetization reversal in concave iron nano-superellipses. Condens. Matter 2021, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, A.; Komraus, S.; Blachowicz, T.; Domino, K.; Nees, M.K.; Jakobs, P.J.; Leiste, H.; Mathes, M.; Schaarschmidt, M. Pseudo exchange bias due to rotational anisotropy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 412, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detzmeier, J.; Königer, K.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Asymmetric Hysteresis Loops in Structured Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles with Hard/Soft Areas. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrmann, A.; Blachowicz, T. Magnetization reversal asymmetry in a structured ferromagnetic nanoparticle with varying shape anisotropy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 546, 168929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A.; Wortmann, M. Exchange Bias in Nanostructures: An Update. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172418
Blachowicz T, Ehrmann A, Wortmann M. Exchange Bias in Nanostructures: An Update. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(17):2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172418
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlachowicz, Tomasz, Andrea Ehrmann, and Martin Wortmann. 2023. "Exchange Bias in Nanostructures: An Update" Nanomaterials 13, no. 17: 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172418
APA StyleBlachowicz, T., Ehrmann, A., & Wortmann, M. (2023). Exchange Bias in Nanostructures: An Update. Nanomaterials, 13(17), 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172418






