Synthesis of Antibacterial Copper Oxide Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids: Potential Application against Foodborne Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
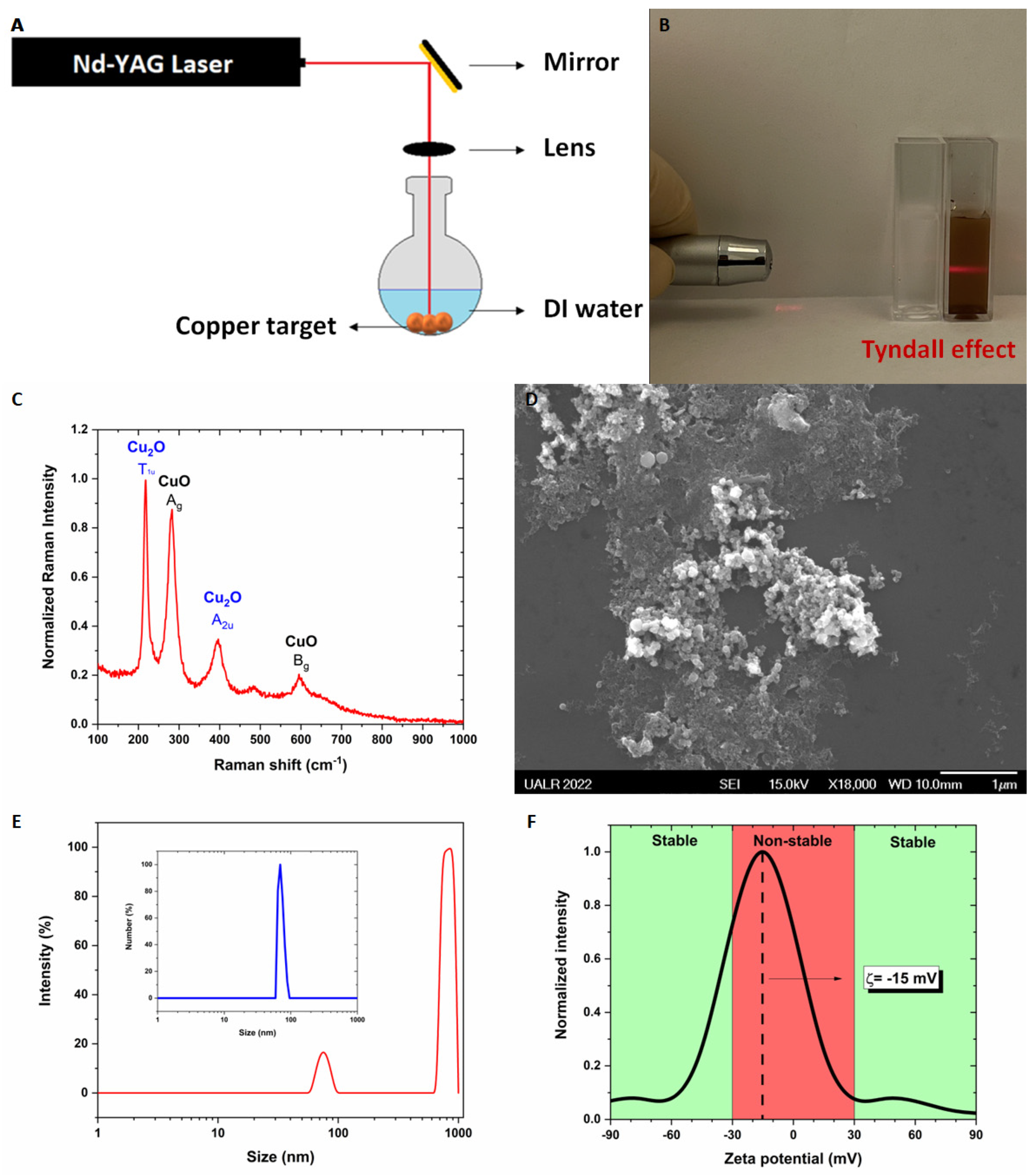
2.1. Synthesis of the CuO/Cu2O NPs
2.2. Physico-Chemical Characterization of CuO/Cu2O NPs
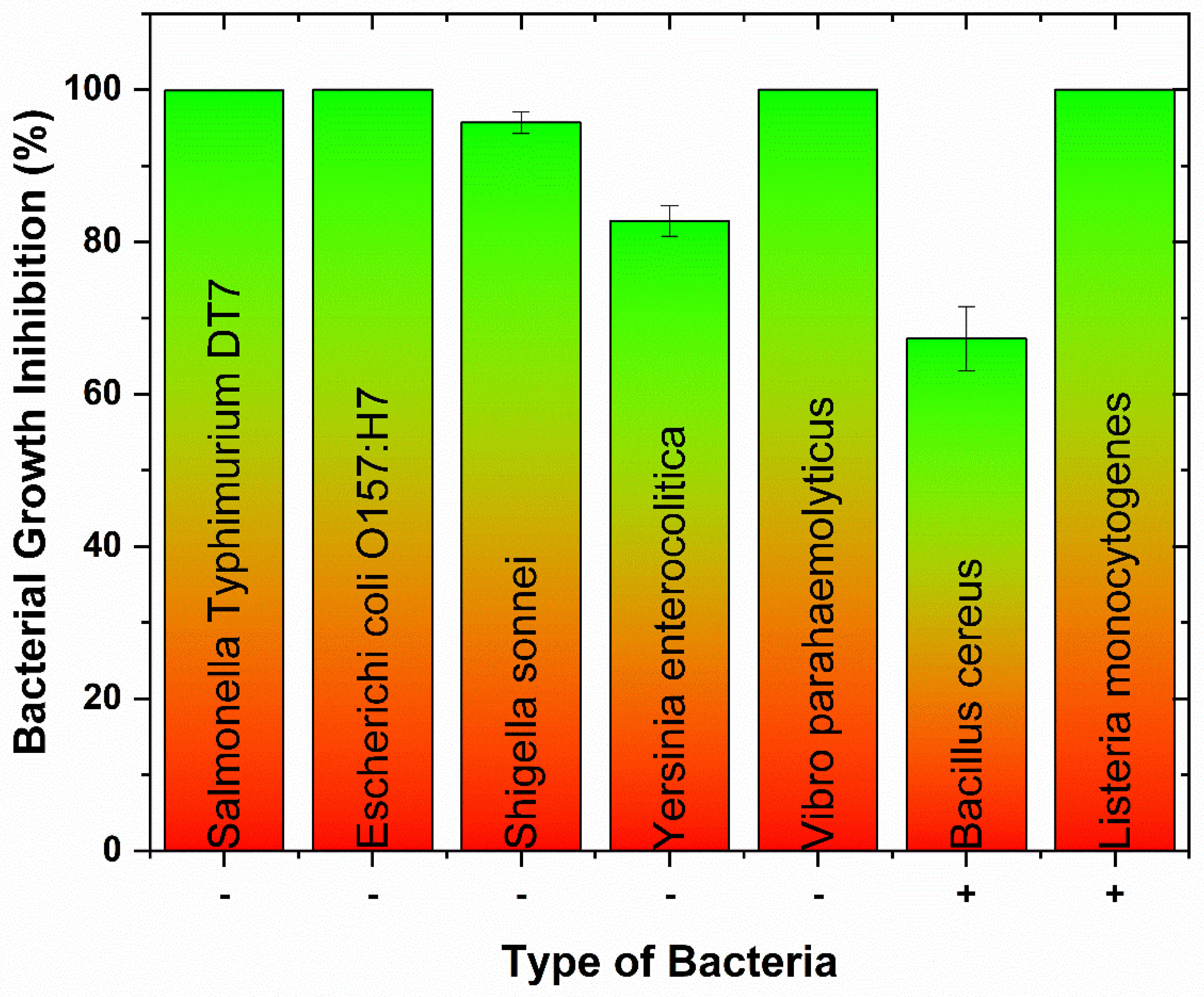
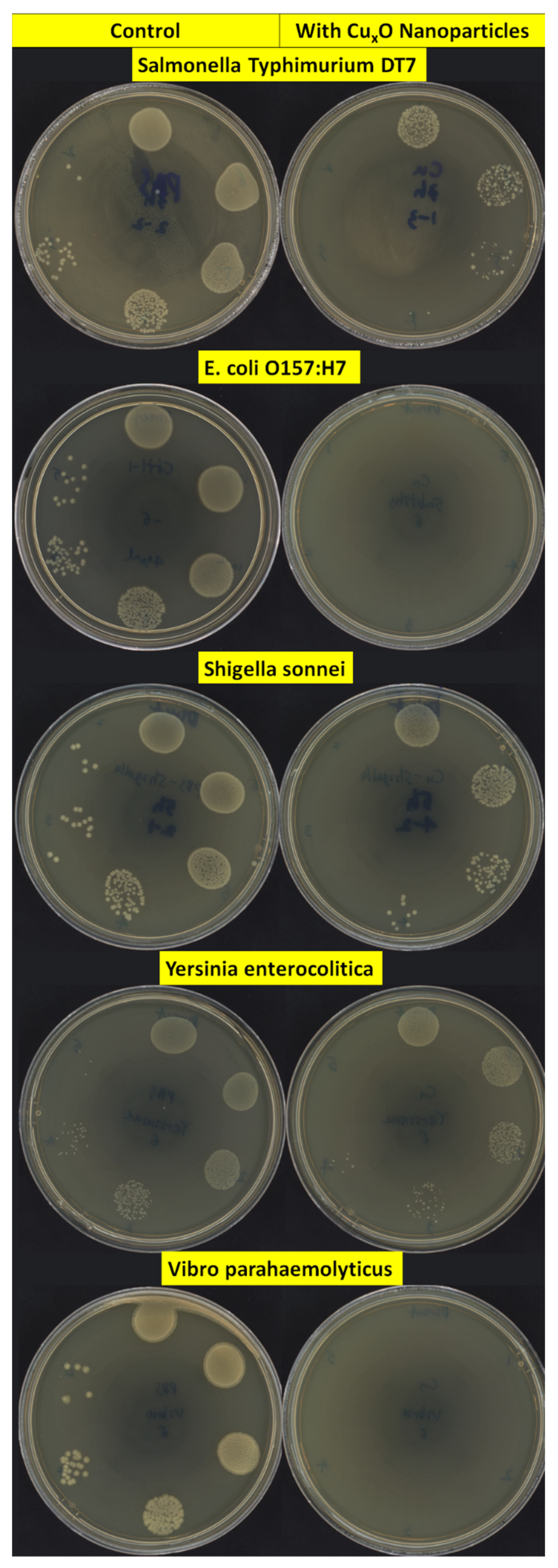
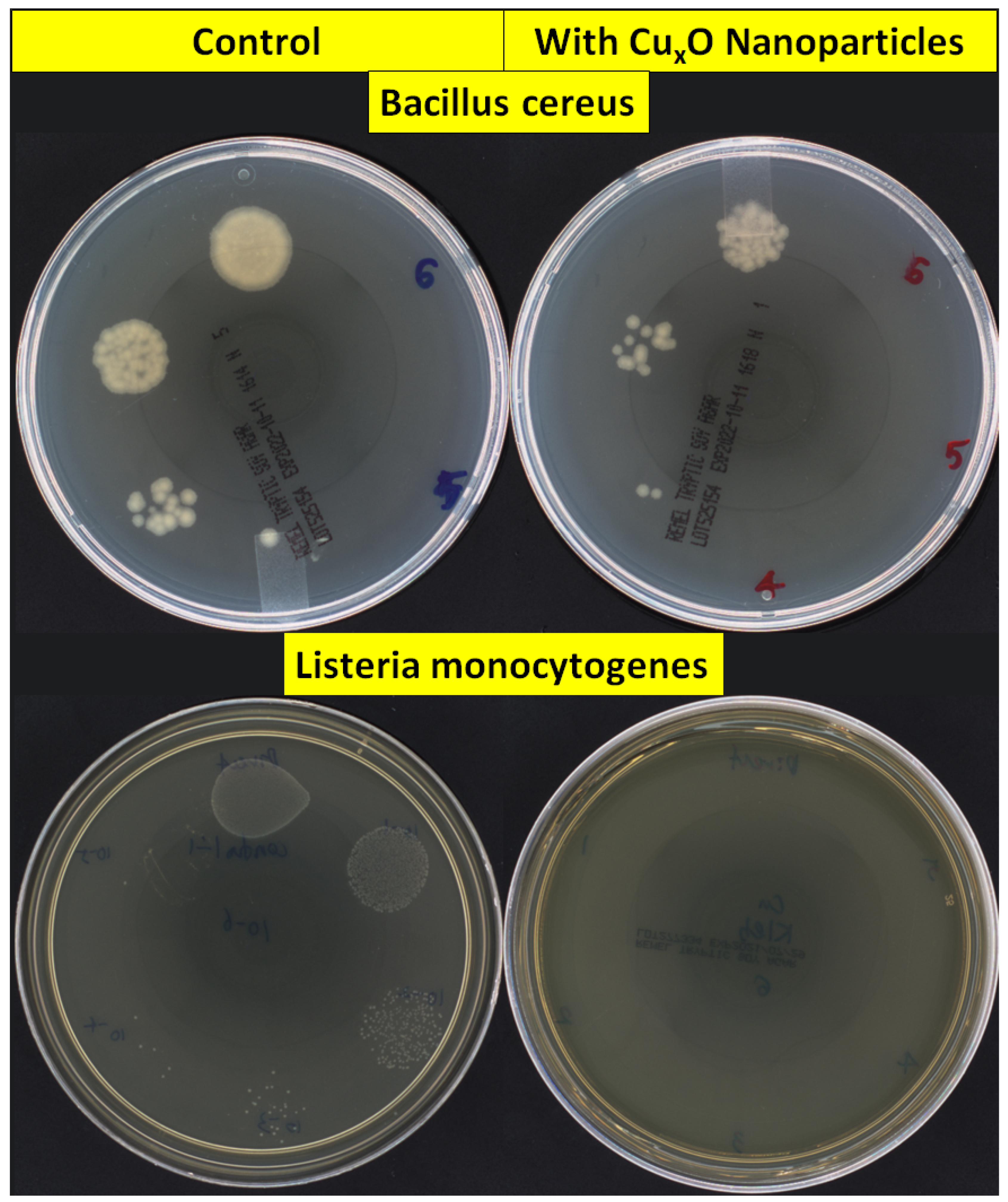
2.3. Antimicrobial Test of CuO/Cu2O NPs
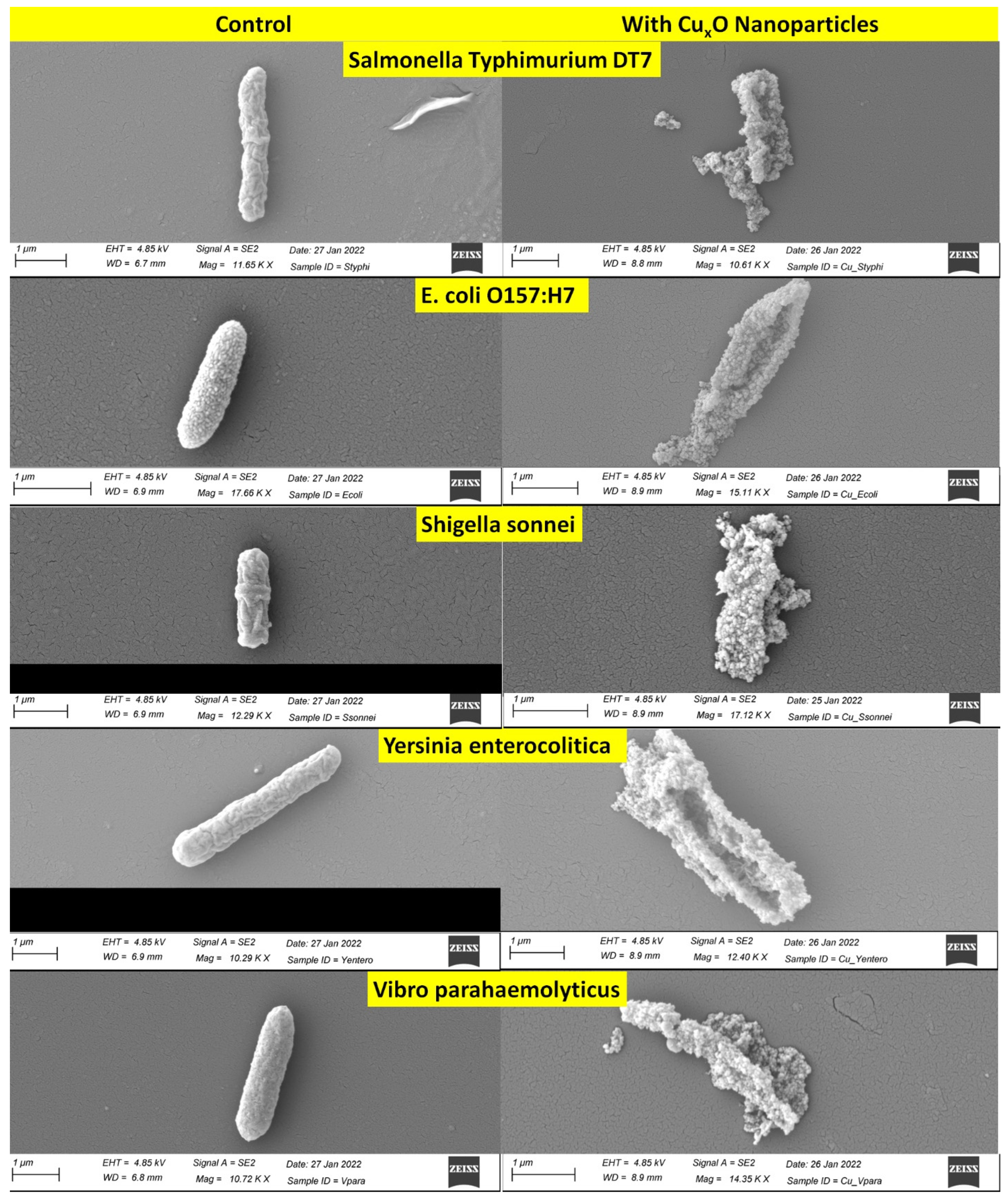
2.4. Observations of NP-Bacteria’s Interactions by Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bintsis, T. Foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 529–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne Illness Acquired in the United States—Major Pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- (CDC). C. F. D. C. A. P. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodborneburden/2011-foodborne-estimates.html (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Anvar, A.A.; Ahari, H.; Ataee, M. Antimicrobial Properties of Food Nanopackaging: A New Focus on Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 690706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Ahn, J.-W. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/amber-waves/2021/april/economic-cost-of-major-foodborne-illnesses-increased-2-billion-from-2013-to-2018/ (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Wang, H.; McEntire, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Doyle, M. The transfer of antibiotic resistance from food to humans: Facts, implications and future directions. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. 2012, 31, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (CDC). C. F. D. C. A. P. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Vimbela, G.V.; Ngo, S.M.; Fraze, C.; Yang, L.; Stout, D.A. Antibacterial properties and toxicity from metallic nanomaterials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3941–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.I.; Dias, A.M.; Zille, A. Synergistic Effects Between Metal Nanoparticles and Commercial Antimicrobial Agents: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 3030–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roduner, E. Size matters: Why nanomaterials are different. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perreault, F.; Melegari, S.P.; da Costa, C.H.; de Oliveira Franco Rossetto, A.L.; Popovic, R.; Matias, W.G. Genotoxic effects of copper oxide nanoparticles in Neuro 2A cell cultures. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 441, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasso-Robledo, J.L.; Torres, B.; Peralta-Videa, J.R. Do all Cu nanoparticles have similar applications in nano-enabled agriculture? Plant Nano Biol. 2022, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmani, A.; Kovačević, D.; Bohinc, K. Nanoparticles: From synthesis to applications and beyond. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 303, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Chung, I.-M.; Gomathi, T.; Ansari, M.A.; Khanna, V.G.; Babu, V.; Rajakumar, G. Synthesis, characterization and pharmacological potential of green synthesized copper nanoparticles. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 42, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahari, H.; Anvar, A.A.; Ataee, M.; Naeimabadi, M. Employing Nanosilver, Nanocopper, and Nanoclays in Food Packaging Production: A Systematic Review. Coatings 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Birla, S.; Yadav, A.; Dos Santos, C.A. Strategic role of selected noble metal nanoparticles in medicine. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Arias, M.; Boutinguiza, M.; Del Val, J.; Covarrubias, C.; Bastias, F.; Gomez, L.; Maureira, M.; Arias-Gonzalez, F.; Riveiro, A.; Pou, J. Copper nanoparticles obtained by laser ablation in liquids as bactericidal agent for dental applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 507, 145032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Gabbay, J. Putting copper into action: Copper-impregnated products with potent biocidal activities. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1728–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.A.; Ku, J.W.K.; Zhang, H.; Salim, T.; Oo, G.; Zinn, A.A.; Boothroyd, C.; Tang, R.M.Y.; Gan, C.L.; Gan, Y.-H.; et al. Copper-Nanoparticle-Coated Fabrics for Rapid and Sustained Antibacterial Activity Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 12876–12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintelu, S.A.; Folorunso, A.S.; Folorunso, F.A.; Oyebamiji, A.K. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for biomedical application and environmental remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Chrisey, D.B. Pulsed laser ablation in liquid for micro-/nanostructure generation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2012, 13, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Gökce, B.; De Giacomo, A.; Meneghetti, M.; Compagnini, G.; Tommasini, M.; Waag, F.; Lucotti, A.; Zanchi, C.G.; Ossi, P.M.; et al. Nanoparticles Engineering by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids: Concepts and Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesabizadeh, T.; Jebari, N.; Madouri, A.; Hallais, G.; Clark, T.E.; Behura, S.K.; Herth, E.; Guisbiers, G. Electric-Field-Induced Phase Change in Copper Oxide Nanostructures. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 33130–33140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yussof, A.; Cammalleri, B.; Fayemiwo, O.; Lopez, S.; Chu, T. Antibacterial and sporicidal activity evaluation of theaflavin-3,3′-digallate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meghana, S.; Kabra, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Padmavathy, N. Understanding the pathway of antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12293–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffrion, L.D.; Hesabizadeh, T.; Medina-Cruz, D.; Kusper, M.; Taylor, P.; Vernet-Crua, A.; Chen, J.; Ajo, A.; Webster, T.J.; Guisbiers, G. Naked selenium nanoparticles for antibacterial and anticancer treatments. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisbiers, G.; Lara, H.H.; Mendoza-Cruz, R.; Naranjo, G.; Vincent, B.A.; Peralta, X.G.; Nash, K.L. Inhibition of Candida albicans biofilm by pure selenium nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in liquids. Nanomed.-Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffrion, L.D.; Medina-Cruz, D.; Kusper, M.; Elsaidi, S.; Watanabe, F.; Parajuli, P.; Ponce, A.; Hoang, T.B.; Brintlinger, T.H.; Webster, T.J.; et al. Bi2O3 nano-flakes as a cost-effective antibacterial agent. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4106–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loss, G.; Martins Simões, P.; Valour, F.; Farrel Cortês, M.; Gonzaga, L.; Bergot, M.; Trouillet-Assant, S.; Josse, J.; Diot, A.; Ricci, E.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants (SCVs): News from a chronic prosthetic joint infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, K.; Anwar, A.; Khan, A.M.; Siddiqui, R. Brain-eating amoebae: Silver nanoparticle conjugation enhanced efficacy of anti-amoebic drugs against Naegleria fowleri. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 2626–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.-Y.; Byeon, J.H.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, J. Susceptibility constants of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis to silver and copper nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 373, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadhesari, S.M.; Alipour, S.; Mohammadnejad, S.; Akbarpour, M.R. Antibacterial activity of ultra-small copper oxide (II) nanoparticles synthesized by mechanochemical processing against S. aureus and E. coli. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabila, M.I.; Kannabiran, K. Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) from actinomycetes. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 15, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Radhika, D.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Ojiaku, A.A.; Verma, U. Facile fabrication of CuO nanoparticles via microwave-assisted method: Photocatalytic, antimicrobial and anticancer enhancing performance. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, P.; Rekha, M.; Suvitha, A.; Kowsalya, M.; Steephen, A. Diamond morphology CuO nanomaterial’s elastic properties, ADMET, optical, structural studies, electrical conductivity and antibacterial activities analysis. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2022, 52, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaili, T.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Al-Nabulsi, A.A.; Alromi, R.F.; Olaimat, A.; Al-Holy, M.; Savvaidis, I.; Holley, R. Effects of metal oxide nanoparticles with plant extract on viability of foodborne pathogens. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Hu, D.; Cheng, E.C.W.; Vargas-Reus, M.A.; Reip, P.; Allaker, R.P. Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt-Galindo, R.; Reyes-Rodriguez, P.Y.; Puente-Urbina, B.A.; Avila-Orta, C.A.; Rodríguez-Fernández, O.S.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Lira-Saldivar, R.H.; García-Cerda, L.A. Synthesis of copper nanoparticles by thermal decomposition and their antimicrobial properties. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 980545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Habib, S.S.; Memic, A. Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: A comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 6003–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, A.; Ara, S.; Ishaq, M.T.; Sughra, K. Green Fabrication of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: A comparative antibacterial study against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative bacteria. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applerot, G.; Lellouche, J.; Lipovsky, A.; Nitzan, Y.; Lubart, R.; Gedanken, A.; Banin, E. Understanding the antibacterial mechanism of CuO nanoparticles: Revealing the route of induced oxidative stress. Small 2012, 8, 3326–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Memic, A. Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of CuO nanoparticles against Gram-positive and -negative bacterial strains. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3527–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, M.; Narayanan, K.; Thakar, M.B.; Jagani, H.V.; Rao, J.V. Biosynthesis and wound healing activity of copper nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 8, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size- and shape-dependent antibacterial studies of silver nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, R.; Riaz, M.; Farooq, N.; Qamar, A.; Anjum, S. Antibacterial activity of Ag and Cu nanoparticles synthesized by chemical reduction method: A comparative analysis. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 075012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpa Chakra, C.H.; Venkateswara Rao, K.; Pavani, T. Antimicrobial activity of pure Cu nano particles synthesized by surfactant varied chemical reduction method. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 6, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, S.; Sasidharan, A.; Divya Rani, V.V.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Manzoor, K.; Raina, S. Role of size scale of ZnO nanoparticles and microparticles on toxicity toward bacteria and osteoblast cancer cells. J. Mater. Science. Mater. Med. 2009, 20 (Suppl. S1), S235–S241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezza, F.A.; Tichapondwa, S.M.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Fabrication of monodispersed copper oxide nanoparticles with potential application as antimicrobial agents. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of the US Food and Drug Administration, MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and is not intended as approval, endorsement, or recommen-dation. |

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hesabizadeh, T.; Sung, K.; Park, M.; Foley, S.; Paredes, A.; Blissett, S.; Guisbiers, G. Synthesis of Antibacterial Copper Oxide Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids: Potential Application against Foodborne Pathogens. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152206
Hesabizadeh T, Sung K, Park M, Foley S, Paredes A, Blissett S, Guisbiers G. Synthesis of Antibacterial Copper Oxide Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids: Potential Application against Foodborne Pathogens. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(15):2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152206
Chicago/Turabian StyleHesabizadeh, Tina, Kidon Sung, Miseon Park, Steven Foley, Angel Paredes, Stephen Blissett, and Gregory Guisbiers. 2023. "Synthesis of Antibacterial Copper Oxide Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids: Potential Application against Foodborne Pathogens" Nanomaterials 13, no. 15: 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152206
APA StyleHesabizadeh, T., Sung, K., Park, M., Foley, S., Paredes, A., Blissett, S., & Guisbiers, G. (2023). Synthesis of Antibacterial Copper Oxide Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids: Potential Application against Foodborne Pathogens. Nanomaterials, 13(15), 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152206







