Preparation of SiO2@Au Nanoparticle Photonic Crystal Array as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
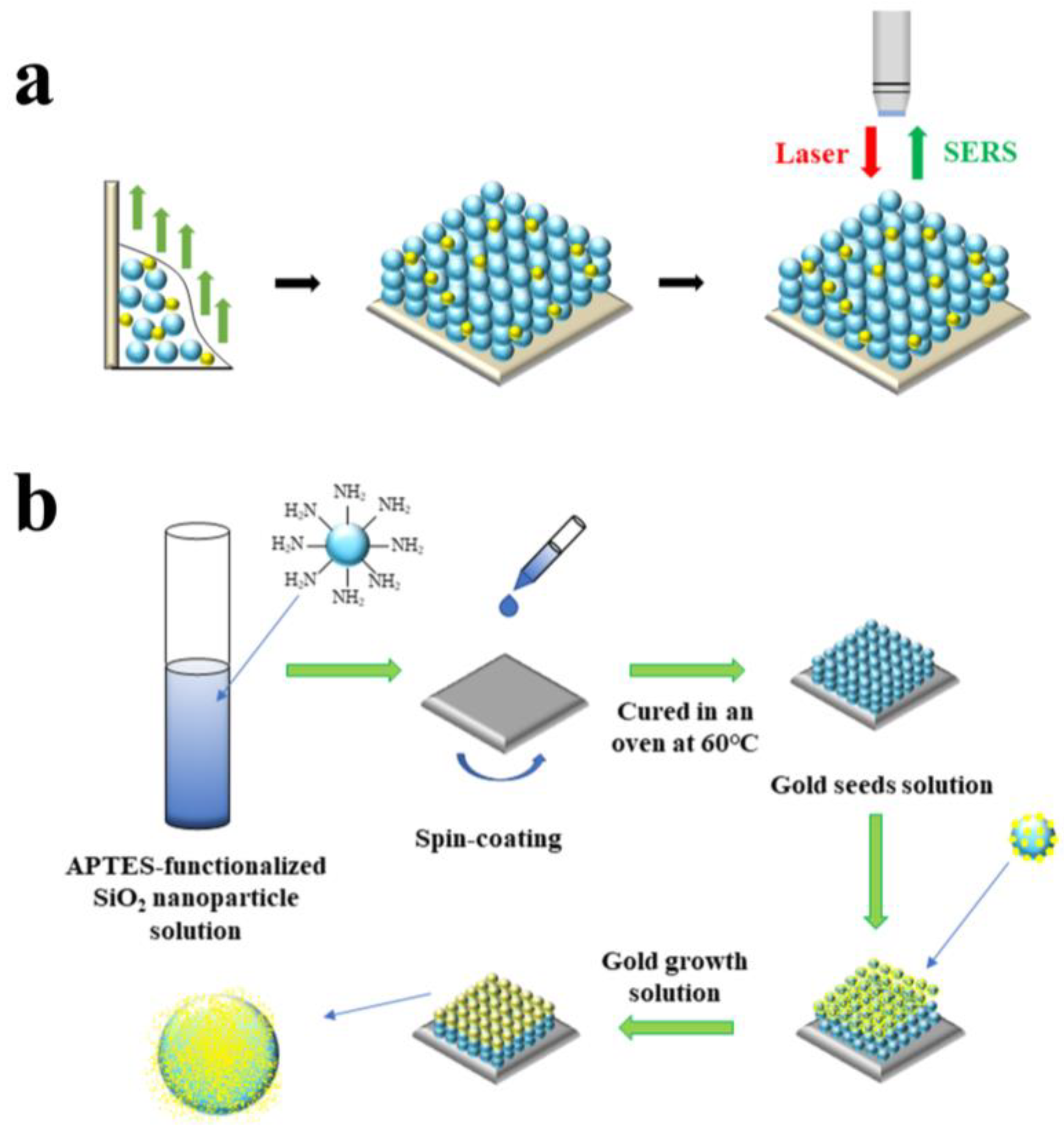
2.2. Preparation of Substrates
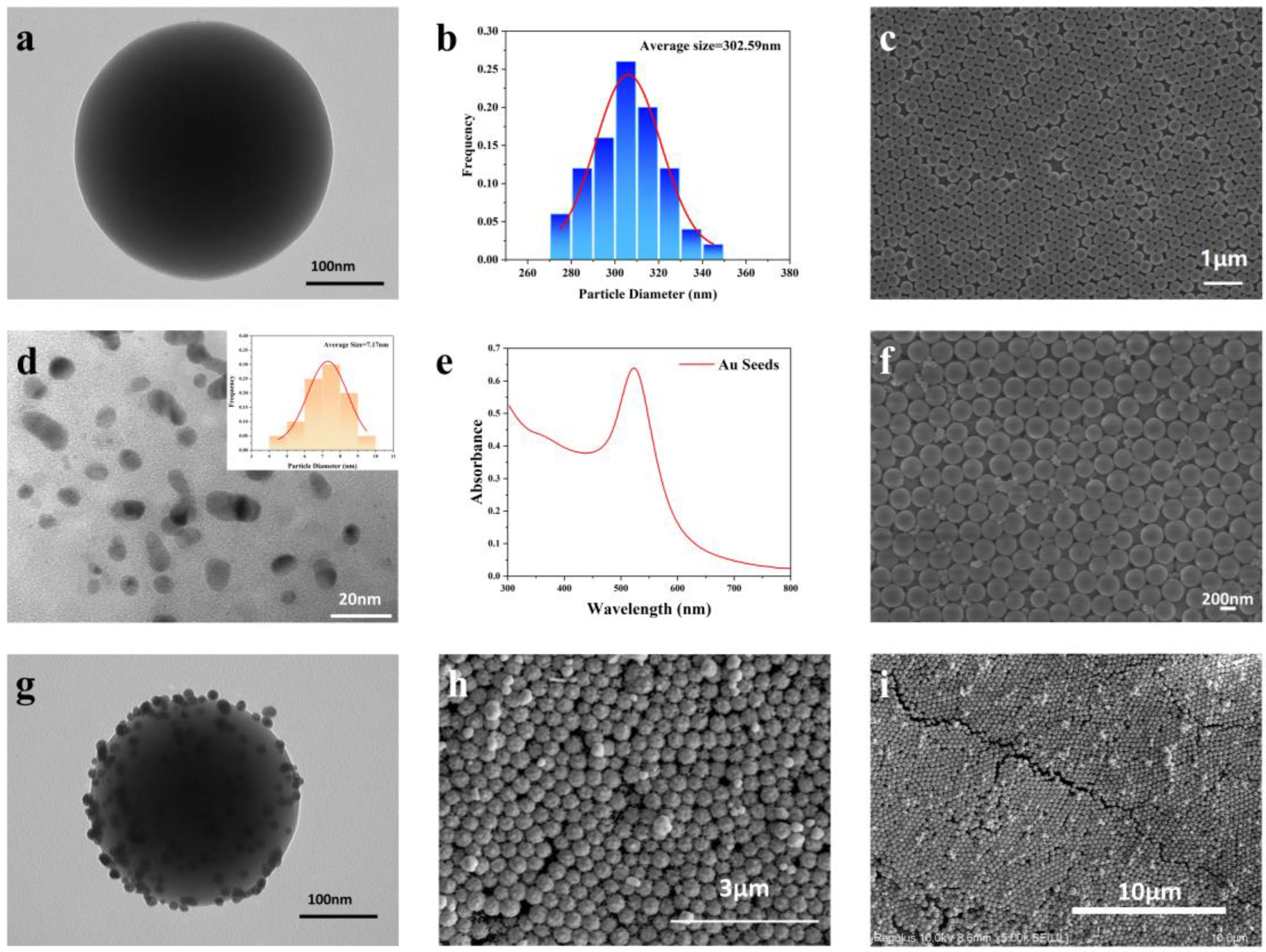
2.2.1. Preparation of APTES-Functionalized SiO2 NPs
2.2.2. Preparation of Gold Seed Solution
2.2.3. Preparation of Gold Growth Solution
2.2.4. SERS Substrate Preparation
2.2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
Enhancement Factor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nie, S.; Emory, S.R. Probing Single Molecules and Single Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Science 1997, 275, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kneipp, H.; Perelman, L.T.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S.; Kneipp, K. Single Molecule Detection Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Kneipp, J.; Kneipp, H.; Kneipp, K. SERS—A single-molecule and nanoscale tool for bioanalytics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, L.; Qi, J. Graphene oxide shell-isolated Ag nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Carbon 2015, 81, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, S.B.; Zhou, X.S.; Fan, F.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wu, D.Y.; et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, H.; Tan, X.; Lu, Z.; Han, H. Cauliflower-Inspired 3D SERS Substrate for Multiple Mycotoxins Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; You, T.; Yang, N.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yin, P. Hydrophobic paper-based SERS platform for direct-droplet quantitative determination of melamine. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hassan, M.M.; Ali, S.; Li, H.; Sheng, R.; Chen, Q. Evolving trends in SERS-based techniques for food quality and safety: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, G. Deciphering the microheterogeneous repartition effect of environmental matrix on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) analysis for pollutants in natural waters. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaw, S.L.; Birhan, Y.S.; Tsai, H. Plasmonic surface-enhanced Raman scattering nano-substrates for detection of anionic environmental contaminants: Current progress and future perspectives. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Qiu, P.; Mao, C. Bio-imaging, detection and analysis by using nanostructures as SERS substrates. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5190–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Teng, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, N. Droplet-Confined Electroless Deposition of Silver Nanoparticles on Ordered Superhydrophobic Structures for High Uniform SERS Measurements. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21548–21553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, J.R.; Birke, R.L. A Unified View of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, C.; Xu, M.; Xu, L.; Wei, T.; Ma, X.; Zheng, X.; Hu, R.; Ren, B. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Bioanalysis: Reliability and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4946–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, J.R.; Birke, R.L.; Sanchez, L.A.; Bernard, I.; Sun, S.C. The effect of molecular structure on voltage induced shifts of charge transfer excitation in surface enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1984, 104, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Susha, A.; Caruso, F. Gold nanoparticle-based core-shell and hollow spheres and ordered assemblies thereof. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wan, L.; Bai, C.; Jiang, L. Gold Hollow Nanospheres: Tunable Surface Plasmon Resonance Controlled by Interior-Cavity Sizes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 7795–7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, N.; Johan, M.R. Environmental modification of self-assembled plasmonic core-shell cluster (silica-gold nanoparticles) for surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xiao, T.; Luo, Z.; Kitahama, Y.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kishimoto, N.; Itoh, T.; Cheng, Z.; Goda, K. Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrabić, M.; Kosović, M.; Gotić, M.; Mikac, L.; Ivanda, M.; Gamulin, O. Near-Infrared Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering on Silver-Coated Porous Silicon Photonic Crystals. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ye, L.; Xiao, P.; Zhu, P.; Gui, X.; Zhuang, L. Dynamic modulation of a surface-enhanced Raman scattering signal by a varying magnetic field. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Wu, Z.; Guo, J.; Jia, D. Porous Silicon Photonic Crystals Coated with Ag Nanoparticles as Efficient Substrates for Detecting Trace Explosives Using SERS. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y. Preparation of Monolayer Photonic Crystals from Ag Nanobulge-Deposited SiO2 Particles as Substrates for Reproducible SERS Assay of Trace Thiol Pesticide. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, L.; Campopiano, S.; Pannico, M.; Giordano, M.; Musto, P.; Iadicicco, A. Photonic bandgap influence on the SERS effect in metal-dielectric colloidal crystals optical fiber probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyen, L.D.; Liu, A.C.; Huang, C.; Tsai, P.; Lin, J.H.; Wu, C.; Chau, L.; Yang, T.S.; Minh, L.Q.; Kan, H.; et al. Doubly resonant surface-enhanced Raman scattering on gold nanorod decorated inverse opal photonic crystals. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 29266–29275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Man, S.; Tang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Z. Preparation of a monolayer array of silica@gold core-shell nanoparticles as a SERS substrate. Optik 2020, 221, 165274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.Y.; You, E.M.; Tian, Z.Q.; Moskovits, M. Electromagnetic theories of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4042–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, C.; Man, S. Preparation of large-area surface-enhanced Raman scattering active Ag and Ag/Au nanocomposite films. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 111, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Schmedake, T.A.; Tsu, R. A comparative study of colloidal silica spheres: Photonic crystals versus Bragg’s law. Phys. Lett. A 2008, 372, 4517–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, P.; Ye, L.; Zhu, P.; Zhuang, L. Coupling Au-loaded magnetic frameworks to photonic crystal for the improvement of photothermal heating effect in SERS. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 5002–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, P.; Stockburger, M. Surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy of Rhodamine 6G adsorbed on colloidal silver. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 5935–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Cui, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Substrate-related issues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1729–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

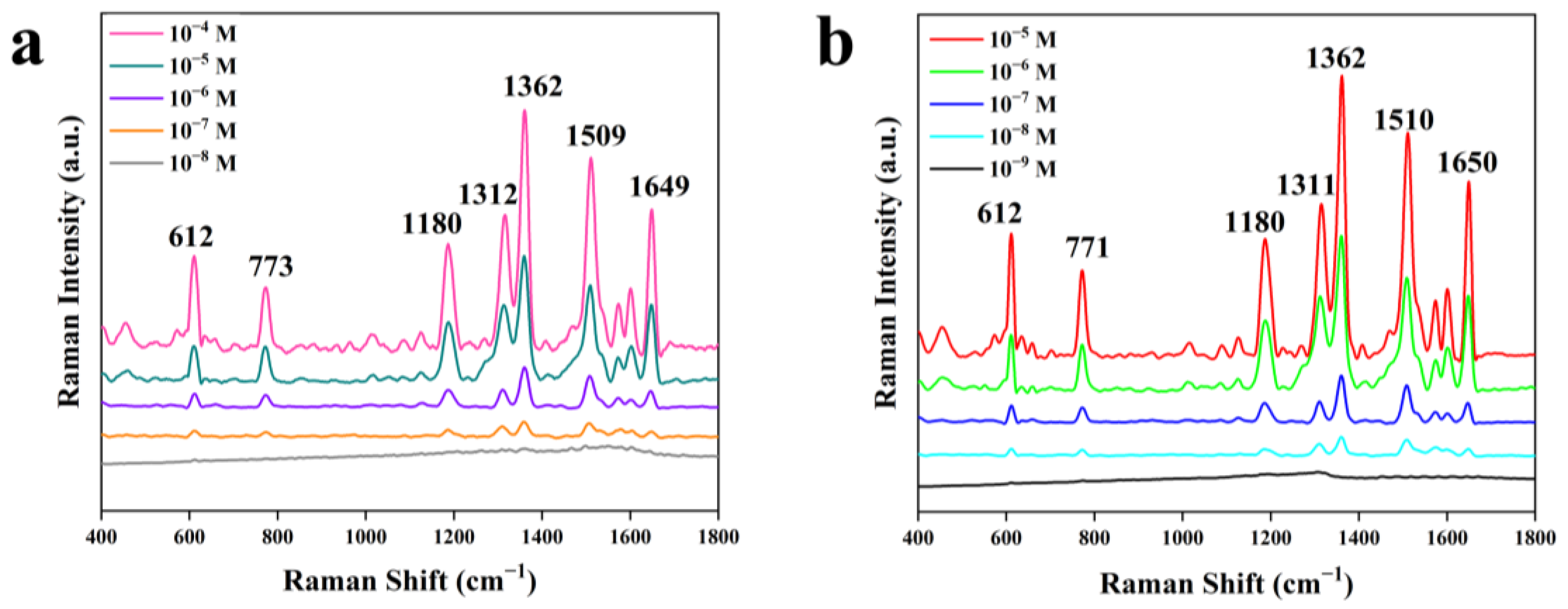
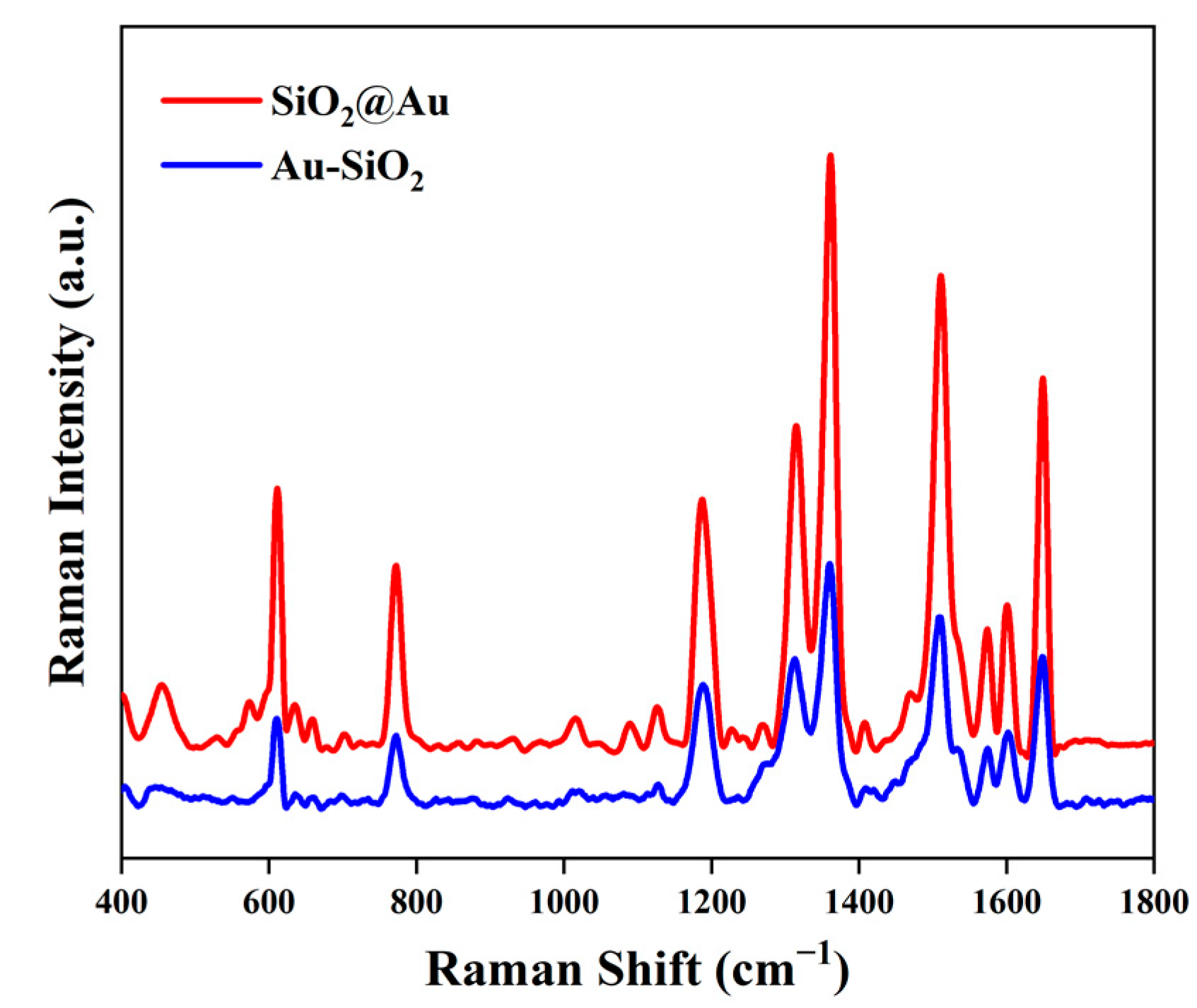
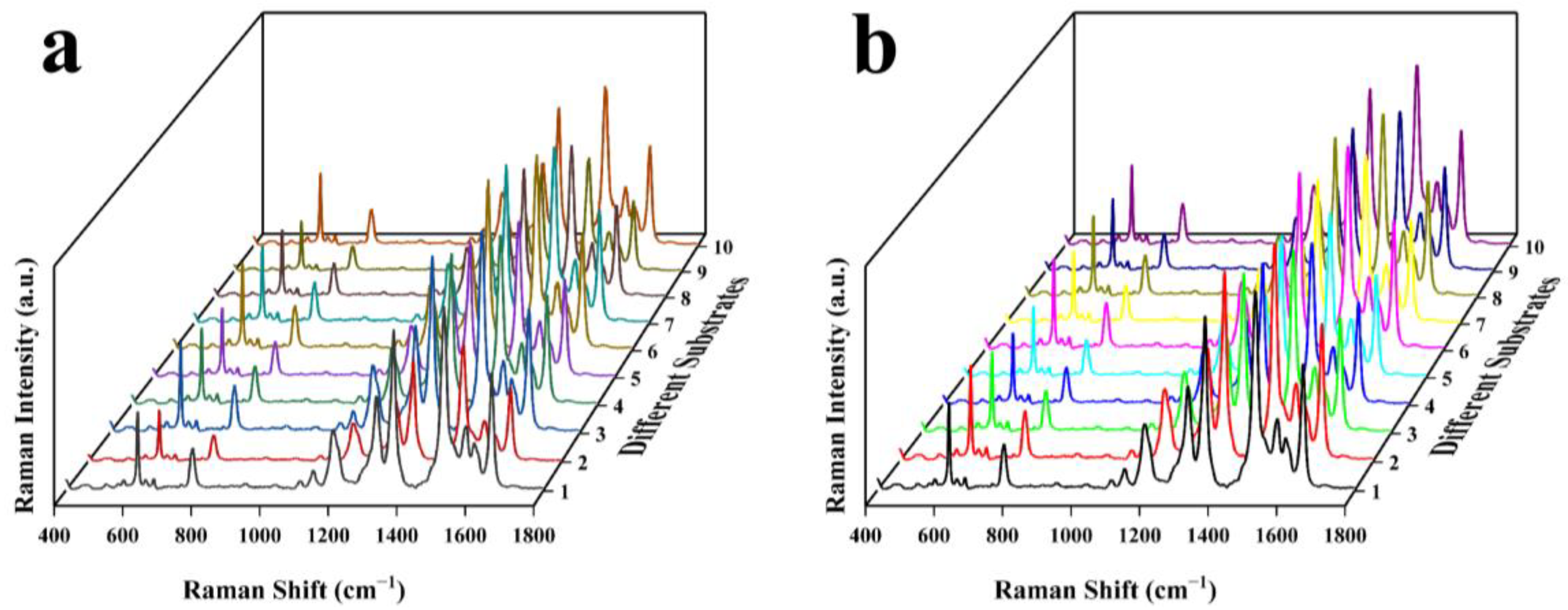
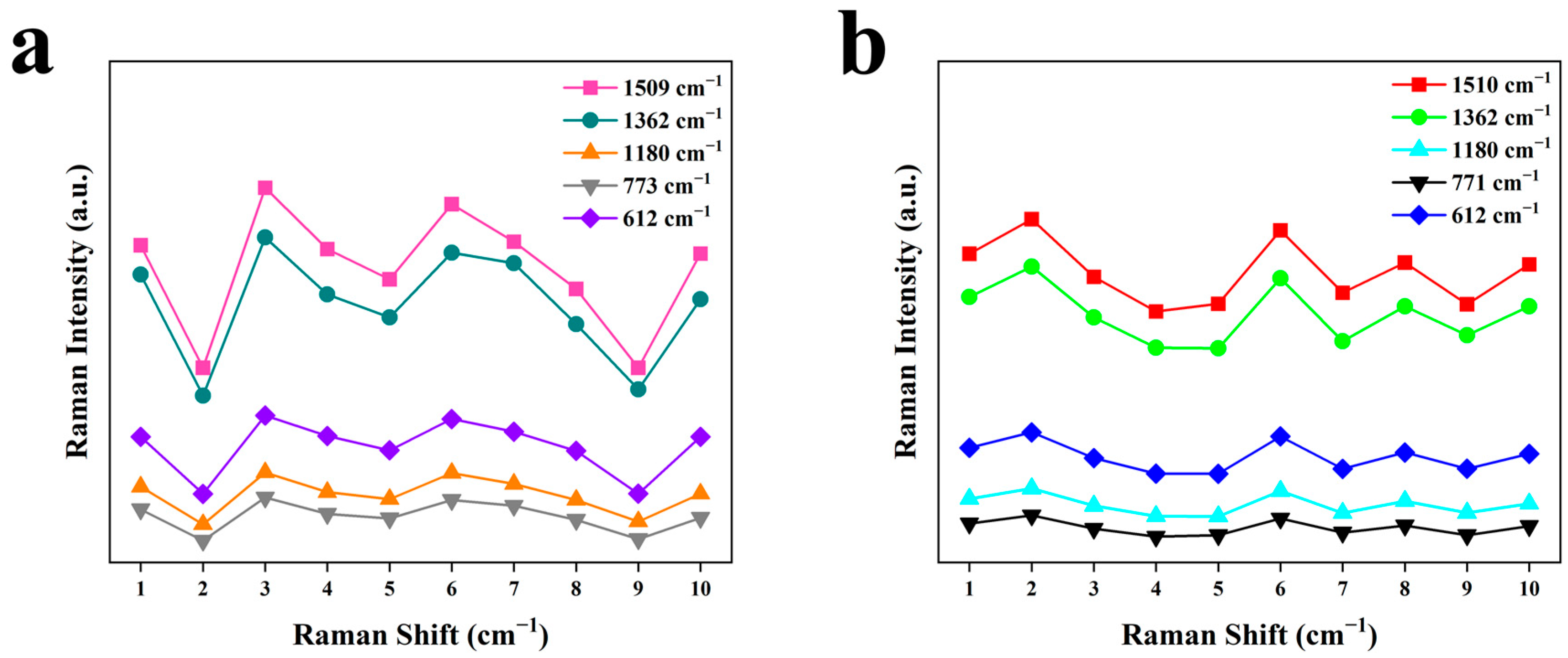
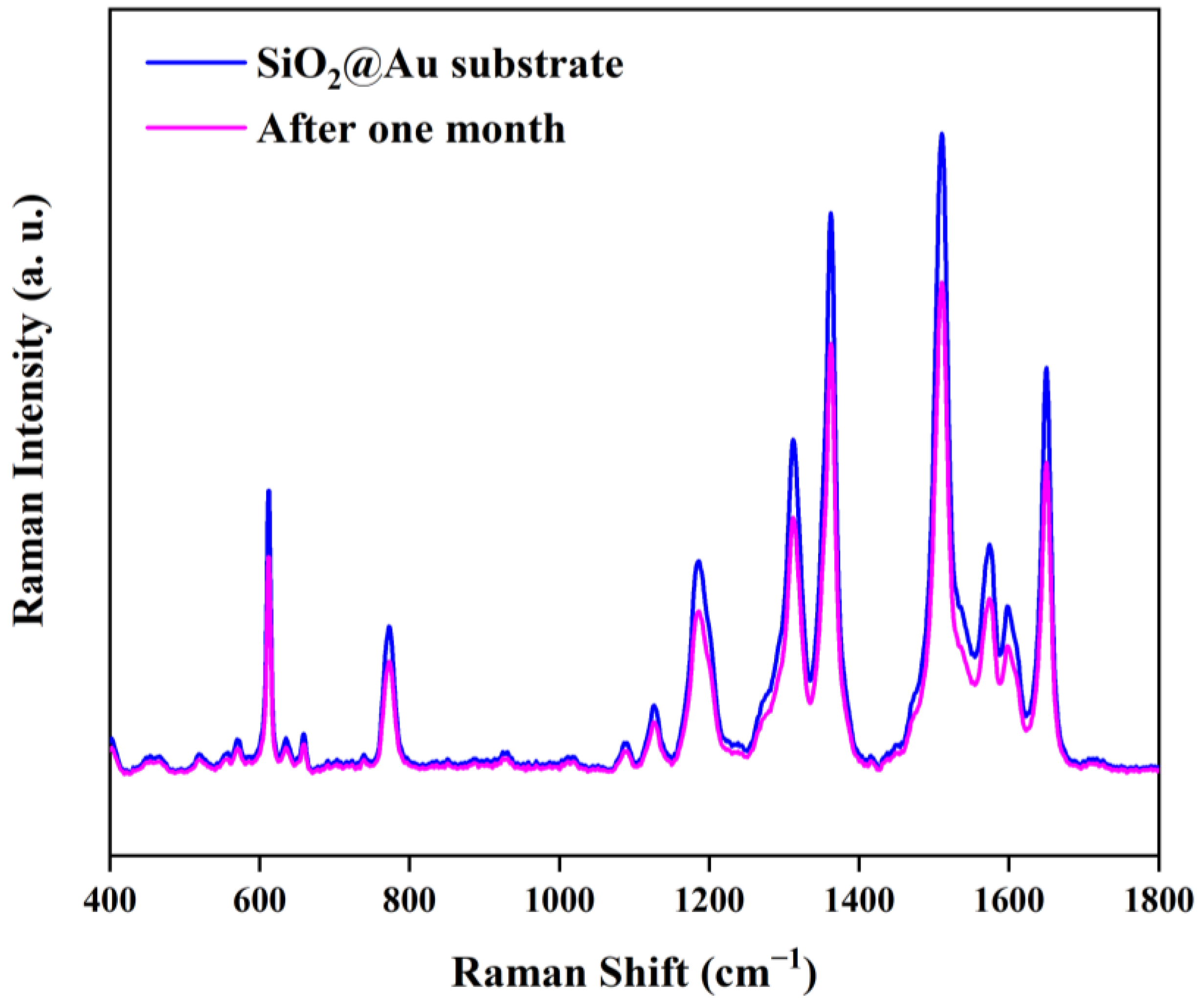
| Au-SiO2 | SiO2@Au | Reported Result [31] | Vibration Assignments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 612 | 612 | 614 | C-C-C ring ip bend |
| 773 | 771 | 773 | C-H op bend |
| 1180 | 1180 | 1181 | C-H ip bend |
| 1312 | 1311 | 1310 | Arom C-C str |
| 1362 | 1362 | 1363 | Arom C-C str |
| 1509 | 1510 | 1509 | Arom C-C str |
| 1649 | 1650 | 1650 | Arom C-C str |
| Substrate | 612 | 773/771 | 1180 | 1362 | 1509/1510 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au-SiO2 | 18.60% | 18.86% | 17.82% | 18.61% | 18.55% | 19.49% |
| SiO2@Au | 10.06% | 9.50% | 10.07% | 9.91% | 9.56% | 9.82% |
| Substrate | Detection Limit | Average RSD of Reproducibility | EF Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au-SiO2 | 1 × 10−7 M | 19.49% | 1.51 × 106 |
| SiO2@Au | 1 × 10−8 M | 9.82% | 1.06 × 106 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, D.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, L. Preparation of SiO2@Au Nanoparticle Photonic Crystal Array as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrate. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152156
Song D, Wang T, Zhuang L. Preparation of SiO2@Au Nanoparticle Photonic Crystal Array as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrate. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(15):2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152156
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Dingyu, Tianxing Wang, and Lin Zhuang. 2023. "Preparation of SiO2@Au Nanoparticle Photonic Crystal Array as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrate" Nanomaterials 13, no. 15: 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152156
APA StyleSong, D., Wang, T., & Zhuang, L. (2023). Preparation of SiO2@Au Nanoparticle Photonic Crystal Array as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrate. Nanomaterials, 13(15), 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152156





