Preparation of Remote Plasma Atomic Layer-Deposited HfO2 Thin Films with High Charge Trapping Densities and Their Application in Nonvolatile Memory Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Devices
2.2. Evaluation of Device Characteristics
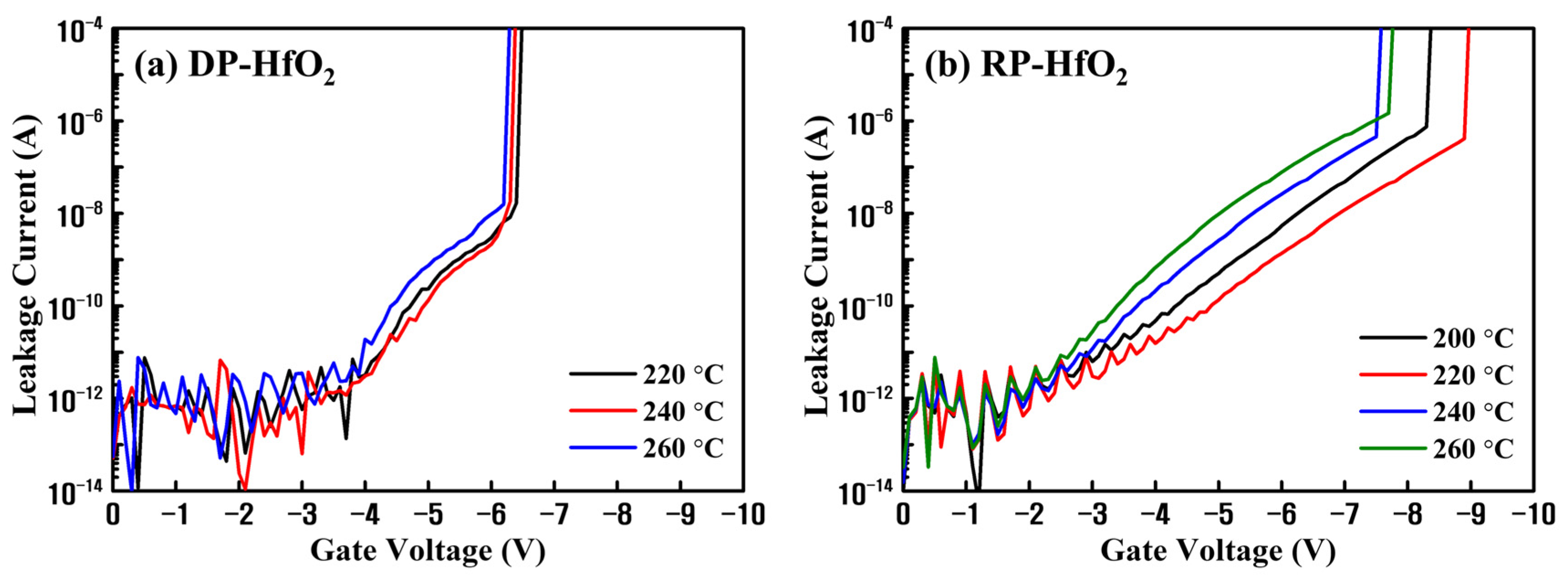
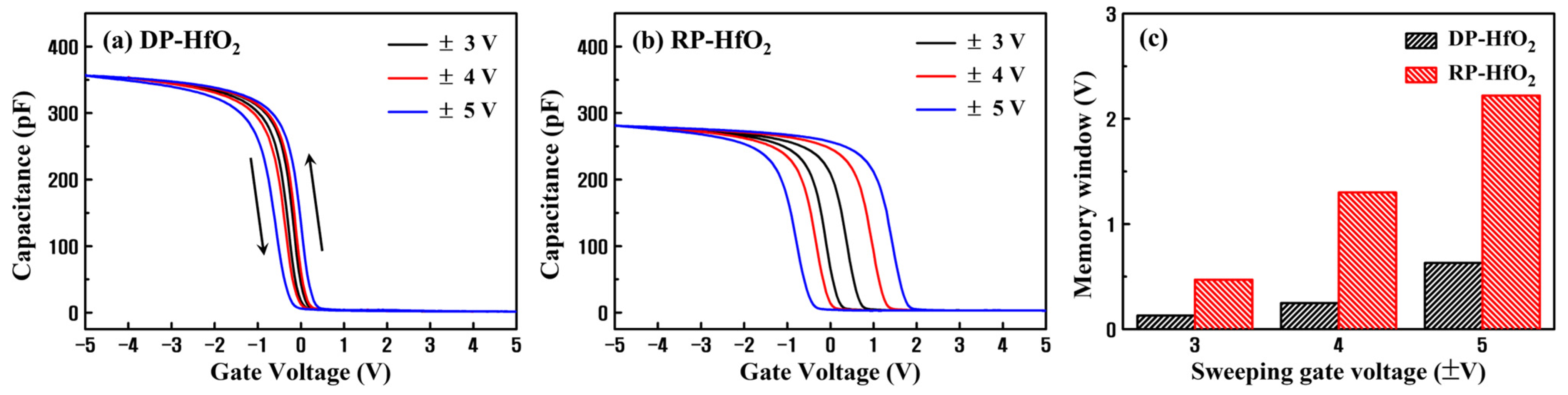
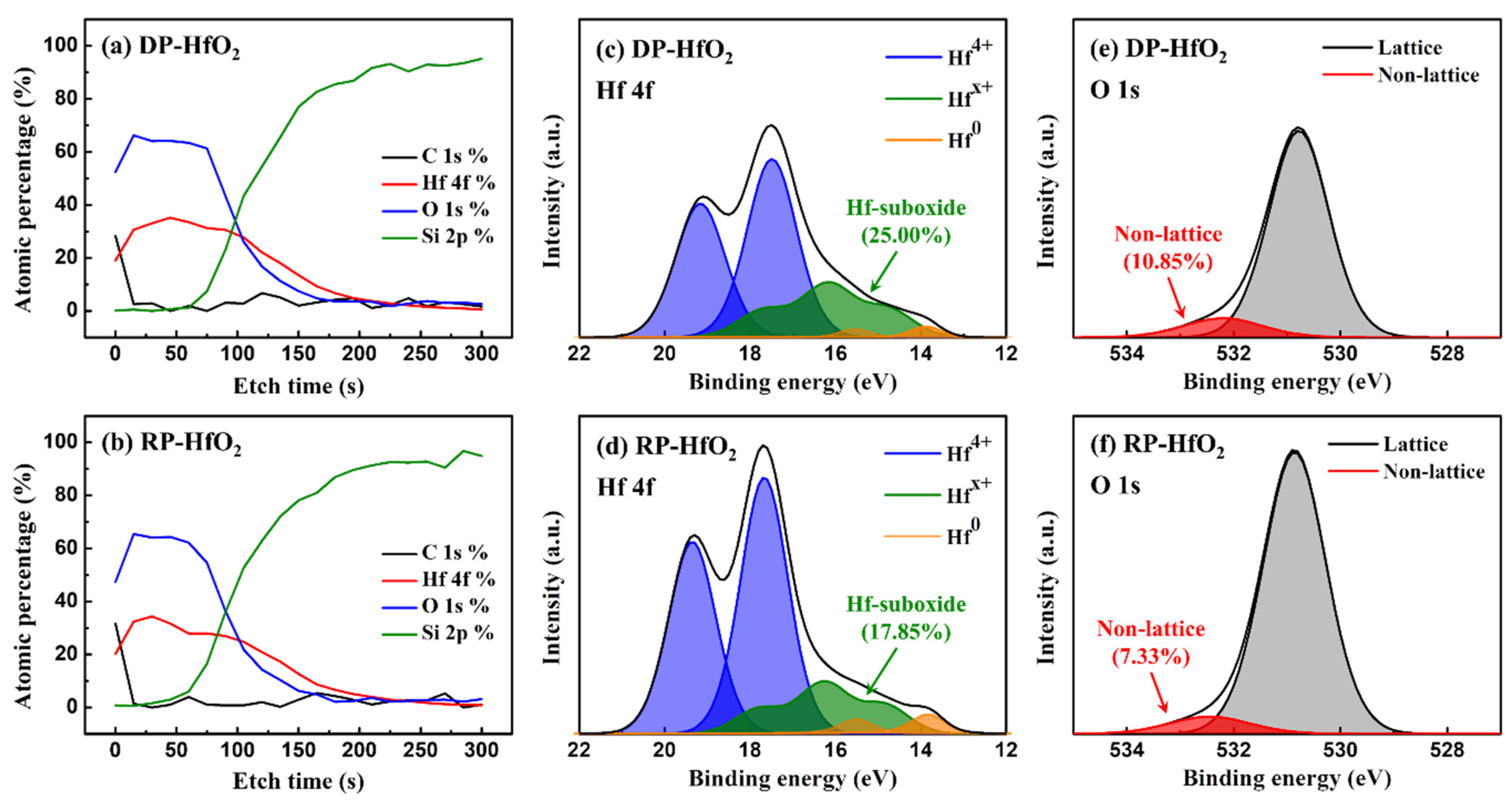
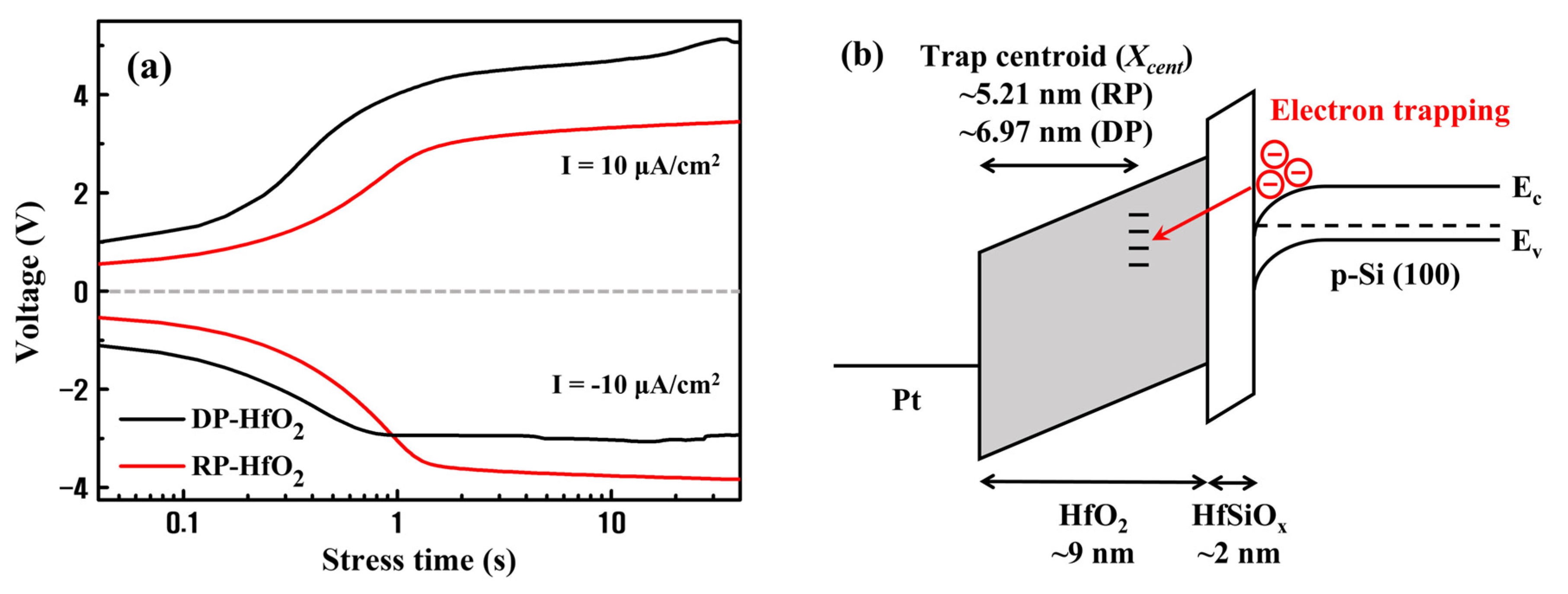
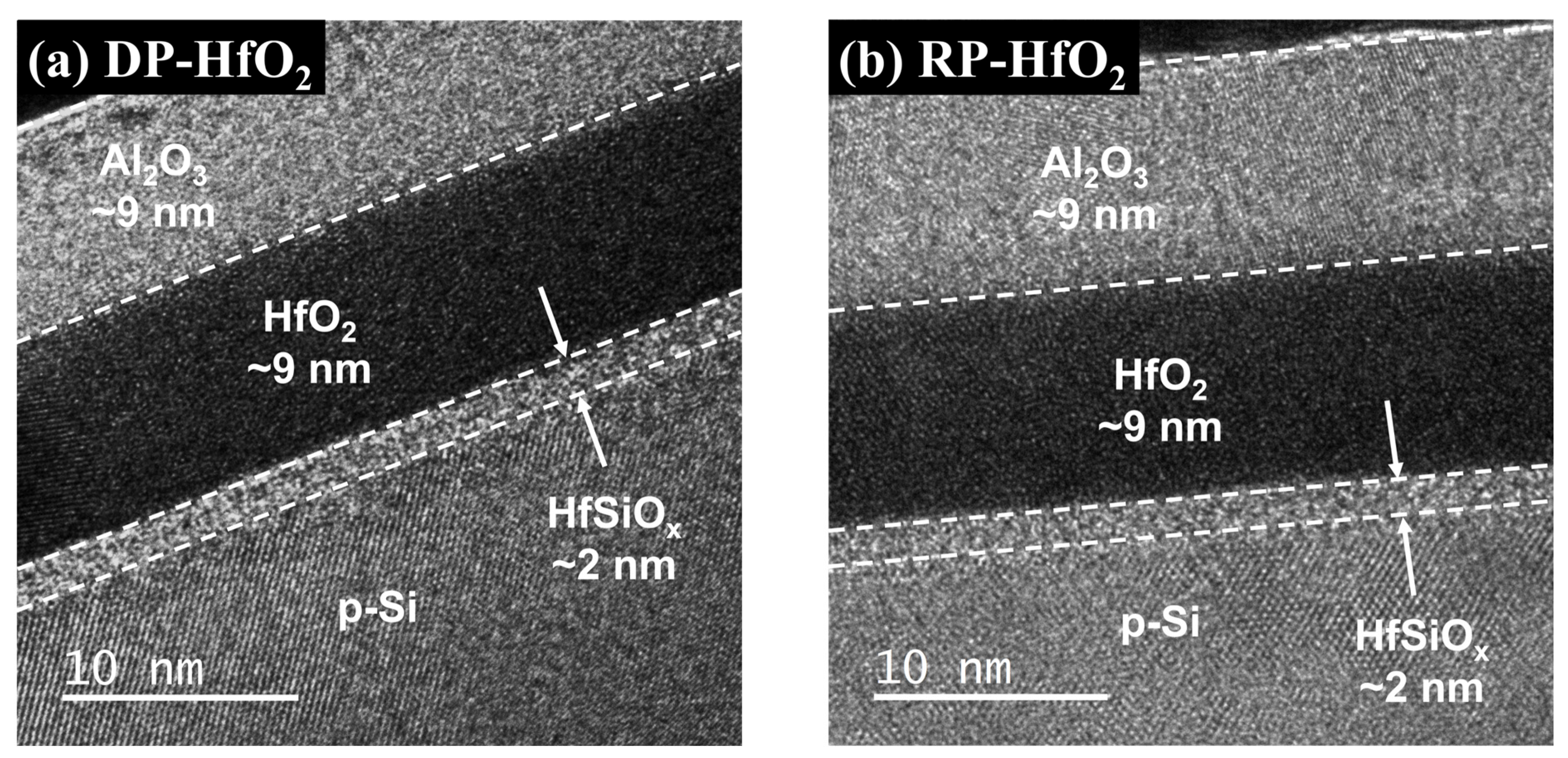
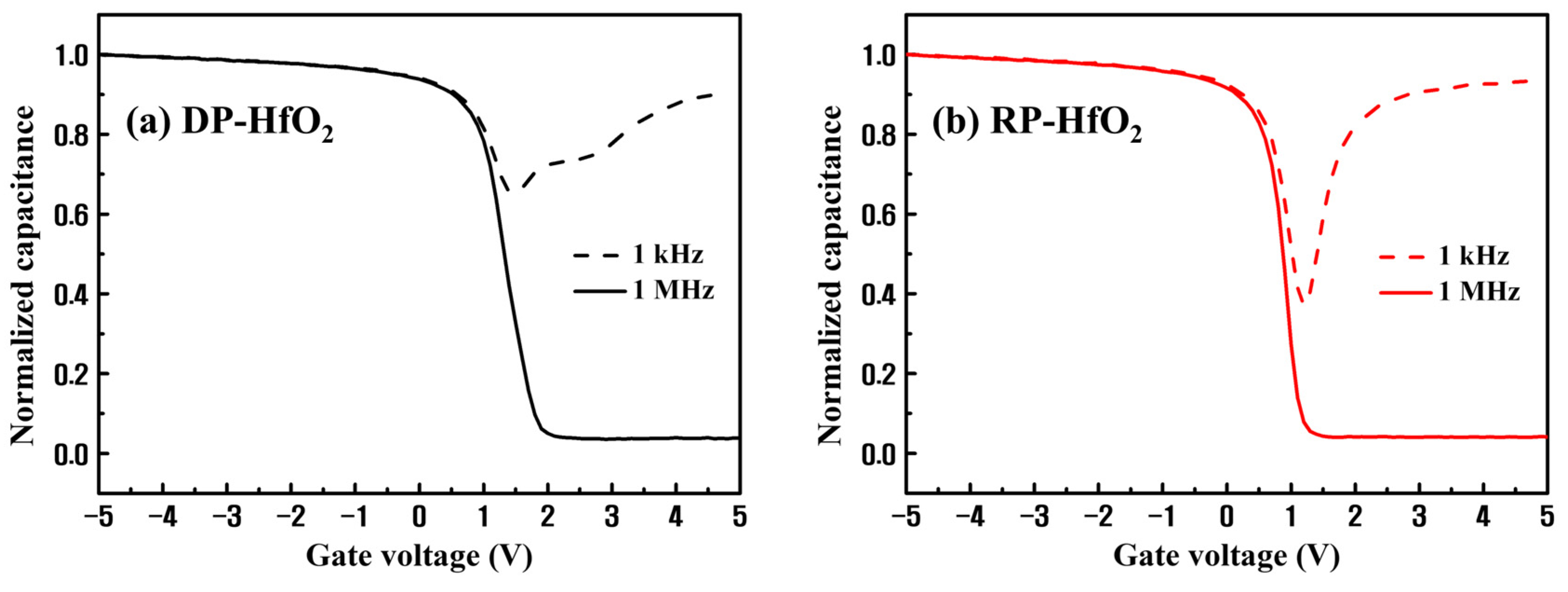
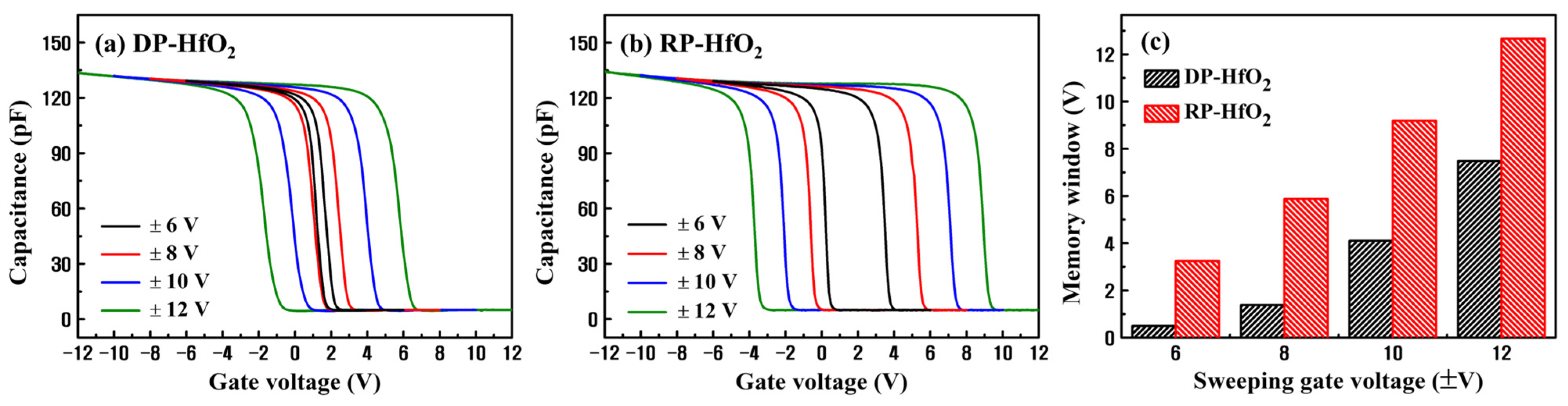
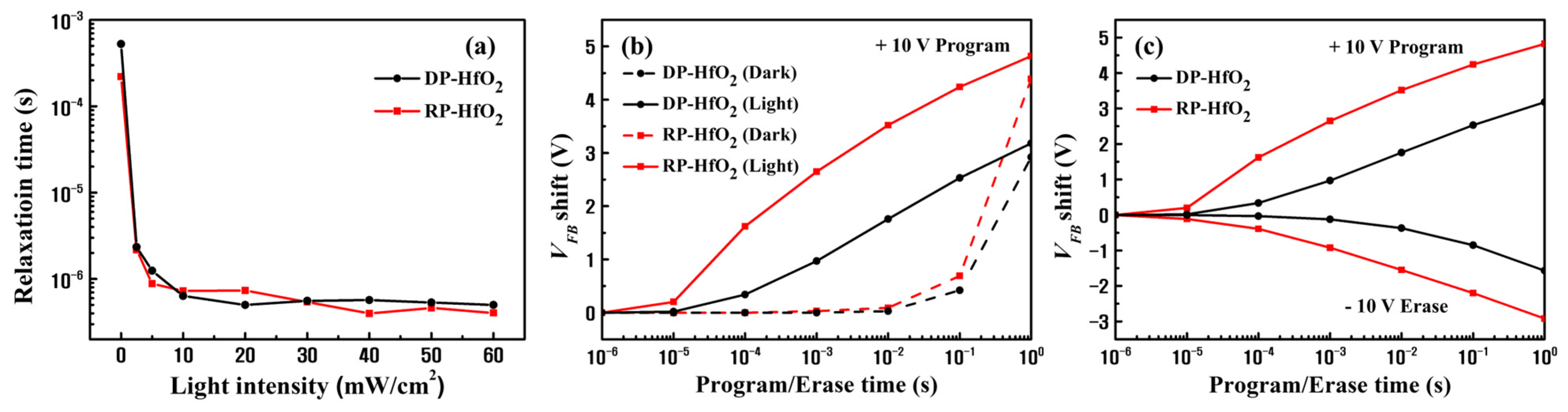
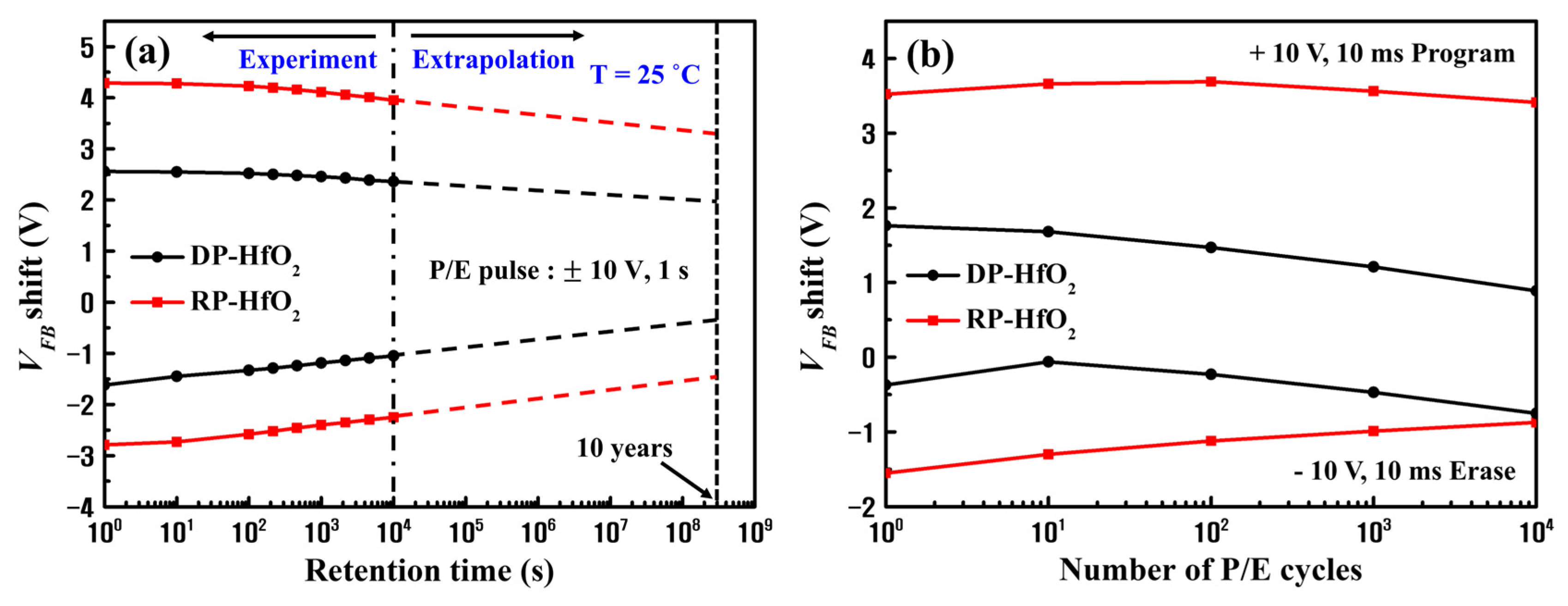
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, C.Z.; Taylor, S.; Chalker, P.R. Review on non-volatile memory with high-k dielectrics: Flash for generation beyond 32 nm. Materials 2014, 7, 5117–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.H.; Yun, J.-G.; Lee, J.H.; Park, B.-G. Scaling behaviors of silicon-nitride layer for charge-trapping memory. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2010, 28, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Park, G.-H.; Cho, W.-J. Dependence of charge trapping and tunneling on the silicon-nitride (Si3N4) thickness for tunnel barrier engineered nonvolatile memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 053508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melde, T.; Beug, M.F.; Bach, L.; Riedel, S.; Ludwig, C.; Mikolaijck, T. Nitride Thickness Scaling Limitations in TANOS Charge Trapping Devices. In Proceedings of the 2008 Joint Non-Volatile Semiconductor Memory Workshop and International Conference on Memory Technology and Design, Opio, France, 18–22 May 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, Y.Y.; Lu, X.B.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X.S.; Zhang, X.J.; Liu, J.-M.; Dai, J.Y. Defect states and charge trapping characteristics of HfO2 films for high performance nonvolatile memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 172902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, S.; Kato, T.; Ozaki, S.; Kawae, T.; Morimoto, A. Improvement of charge trapping characteristics of Al2O3/Al-rich Al2O3/SiO2 stacked films by thermal annealing. Thin Solid Films 2013, 542, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Ou, X.; Lan, X.X.; Cao, Z.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Lu, W.; Gong, C.J.; Xu, B.; Li, A.D.; Xia, Y.D.; et al. Remarkable charge-trapping efficiency of the memory device with (TiO2)0.8(Al2O3)0.1 composite charge-storage dielectric. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 263506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.-Y.; Yoon, S.-M. Impacts of HfO2/ZnO stack-structured charge-trap layers controlled by atomic layer deposition on nonvolatile memory characteristics of In-Ga-Zn-O channel charge-trap memory thin-film transistors. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2019, 7, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Long, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, M. A metal/Al2O3/ZrO2/SiO2/Si (MAZOS) structure for high-performance non-volatile memory application. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2010, 25, 055013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palade, C.; Slav, A.; Stavarache, I.; Maraloiu, V.A.; Negrila, C.; Ciurea, M.L. Memory properties of Zr doped ZrO2 MOS-like capacitor. Coatings 2022, 12, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, X. Progress of high-k dielectrics applicable to SONOS-type nonvolatile semiconductor memories. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2010, 11, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Woo, S.; Kim, H.; Bang, S.; Kim, Y.; Choi, D.; Jeon, H. Pt nanocrystals embedded in remote plasma atomic-layer-deposited HfO2 for nonvolatile memory devices. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2009, 12, H92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Recent progress in gold nanoparticle-based non-volatile memory devices. Gold Bull. 2010, 43, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, A.; Yan, F. Enhanced charge storage characteristics by ZrO2 nanocrystallites precipitated from amorphous (ZrO2)0.8(SiO2)0.2 charge trapping layer. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 3227–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.J.; Sahu, A.; Riedinger, A.; Norris, D.J.; Brandt, M.S.; Stutzmann, M.; Pereira, R.N. Charge trapping defects in CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 13763–13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavarache, I.; Cojocaru, O.; Maraloiu, V.A.; Teodorescu, V.S.; Stoica, T.; Ciurea, M.L. Effects of Ge-related storage centers formation in Al2O3 enhancing the performance of floating gate memories. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 542, 148702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palade, C.; Slav, A.; Lepadatu, A.M.; Stavarache, I.; Dascalescu, I.; Maraloiu, V.A.; Negrila, C.; Logafatu, C.; Stoica, T.; Teodorescu, V.S.; et al. Orthorhombic HfO2 with embedded Ge nanoparticles in nonvolatile memories used for the detection of ionizing radiation. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 065010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikap, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Tzeng, P.-J.; Wang, C.C.; Lee, L.S.; Liu, K.C.; Yang, J.-R.; Tsai, M.-J. Charge trapping characteristics of atomic-layer-deposited HfO2 films with Al2O3 as a blocking oxide for high-density non-volatile memory device applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2007, 22, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiga, S.; Driussi, F.; Lamperti, A.; Congedo, G.; Salicio, O. Effects of thermal treatments on the trapping properties of HfO2 films for charge trap memories. Appl. Phys. Express 2012, 5, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Puente, M.A.; Horley, P.; Aguirre-Tostado, F.S.; López-Medina, J.; Borbón-Nuñez, H.A.; Tiznado, H.; Susarrey-Arce, A.; Martínez-Guerra, E. ALD and PEALD deposition of HfO2 and its effects on the nature of oxygen vacancies. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2022, 285, 115964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.K.; Roh, J.-S.; Choi, B.H.; Kang, S.-W. Interfacial layer properties of HfO2 films formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition on silicon. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2006, 9, F34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Oh, I.-K.; Kim, H.; Lee, Z. Atomic-scale characterization of plasma-induced damage in plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.D.; Knaut, M.; Reif, J.; Nehm, F.; Albert, M.; Bartha, J.W. Direct plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition of aluminum nitride for water permeation barriers. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2020, 38, 022419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K.M.; Najmaei, S.; Ekuma, C.E.; Burke, R.A.; Dubey, M.; Franklin, A.D. Plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition of HfO2 on monolayer, bilayer, and trilayer MoS2 for the integration of high-κ dielectrics in two-dimensional devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 4085–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profijt, H.B.; Potts, S.E.; van de Sanden, M.C.M.; Kessels, W.M.M. Plasma-assisted atomic layer deposition: Basics, opportunities, and challenges. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2011, 29, 050801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, S.B.S.; van Hemmen, J.L.; Hodson, C.J.; Singh, N.; Klootwijk, J.H.; Roozeboom, F.; van de Sanden, M.C.M.; Kessels, W.M.M. Deposition of TiN and HfO2 in a commercial 200 mm remote plasma atomic layer deposition reactor. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2007, 25, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-G.; Hong, D.-H.; Yoo, J.-H.; Lee, H.-C. Effect of process temperature on density and electrical characteristics of Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 thin films prepared by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.H.; Yoo, J.H.; Park, W.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Uhm, S.H.; Lee, H.C. Characteristics of Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 thin films prepared by direct and remote plasma atomic layer deposition for application to ferroelectric memory. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.-W.; Cho, W.-J. Charge trapping properties of the HfO2 layer with various thicknesses for charge trap flash memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 093506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, F.; Yin, H.; Wei, Q.; Men, K. A Gd-doped HfO2 single film for a charge trapping memory device with a large memory window under a low voltage. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7812–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Robertson, J.; Gibson, M.C.; Clark, S.J. Defect energy levels in HfO2 high-dielectric-constant gate oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 183505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, G.H.; Farley, N.; Sherwood, P.M.A.; Linford, M.R.; Terry, J.; Fernandez, V.; Artyushkova, K. Practical guide for curve fitting in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2020, 38, 061203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morant, C.; Galán, L.; Sanz, J.M. An XPS study of the initial stages of oxidation of hafnium. Surf. Interface Anal. 1990, 16, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharath, S.U.; Kurian, J.; Komissinskiy, P.; Hildebrandt, E.; Bertaud, T.; Walczyk, C.; Calka, P.; Schroeder, T.; Alff, L. Thickness independent reduced forming voltage in oxygen engineered HfO2 based resistive switching memories. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 073505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driemeier, C.; Wallace, R.M.; Baumvol, I.J.R. Oxygen species in HfO2 films: An in situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study. J. Appl. Phys. Chem. 2007, 102, 024112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, M.K.; Maiti, C.K. Electrical properties of SiO2/TiO2 high-k gate dielectric stack. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2006, 9, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Lai, P.T.; Cheng, Y.C. Characterization of charge trapping and high-field endurance for 15-nm thermally nitrided oxides. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1991, 38, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-C.; Oh, S.-J.; Cho, M.; Hwang, C.S.; Jung, R. Chemical structure of the interface in ultrathin HfO2/Si films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Jeon, H.; Cho, M.-H.; Chung, K.-B.; Bae, C. Characteristics of HfO2 thin films grown by plasma atomic layer deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 053108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.-M.; Kim, H.-D.; Kim, T.G. Analysis of the energy distribution of interface traps related to tunnel oxide degradation using charge pumping techniques for 3D NAND flash applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 5084–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-S.; Chen, K.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Chen, T.-C.; Wu, Y.-H. Flash memory featuring low-voltage operation by crystalline ZrTiO4 charge-trapping layer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyns, L.; Ragnarsson, L.-Å.; Hall, L.; Delabie, A.; Heyns, M.; Van Elshocht, S.; Vinckier, C.; Zimmerman, P.; De Gendt, S. Silicon orientation effects in the atomic layer deposition of hafnium oxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, G9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, S.M.; Ng, K.K. Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Engel-Herbert, R.; Hwang, Y.; Stemmer, S. Comparison of methods to quantify interface trap densities at dielectric/III-V semiconductor interfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 124101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagné, R.; Vapaille, A. Description of the SiO2 Si interface properties by means of very low frequency MOS capacitance measurements. Surf. Sci. 1971, 28, 157–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Gong, C.; Ou, X.; Cao, Y.; Sun, C.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Xia, Y.; Li, A.; Yin, J.; et al. Enhancement of the charge trapping performances with HfAlO composite oxide thin films in SONOS-type nonvolatile memory. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 133, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, G.; Kim, T.; Agrawal, K.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.-H.; Cho, E.-C.; Yi, J. Optimization of MIS type non-volatile memory device with Al-doped HfO2 as charge trapping layer. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 075004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Kim, S.; Jeon, W.; Park, A.; Choi, D.; Choi, B. A study on the charge trapping characteristics of high-k laminated traps. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2019, 40, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, M.-H.; Huo, Z.-L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.-A.; Jiang, D.-D.; Chen, J.-N.; Liu, M. A simple and accurate method for measuring program/erase speed in a memory capacitor structure. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 018501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildenblat, G.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, W. Analytical expression for the bias and frequency-dependent capacitance of MOS varactors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2007, 54, 3107–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, S.-D.; Gwo, S. Charge trapping properties at silicon nitride/silicon oxide interface studied by variable-temperature electrostatic force microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 023711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, Z.; Wang, T.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Kang, J.; Du, G. Simulation on Endurance Characteristic of Charge Trapping Memory. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Simulation of Semiconductor Processes and Devices (SISPAD), Glasgow, UK, 3–5 September 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, N.; Ma, T.-P. A study of endurance issues in HfO2-based ferroelectric field effect transistors: Charge trapping and trap generation. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TO/CTL/BO | Thickness (nm) | Annealing Temp. (°C) | Operating Voltage (V) | Memory Window (V) | Charge Loss (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HfSiOX/RP-HfO2/Al2O3 | 2/9/9 | 400 | ±12 | 12.66 | 34.32 | This work |
| SiO2/HfO2/Al2O3 | 3/10/10 | 1000 | ±15 | 7.4 | 31 | [18] |
| SiO2/HfO2 | 3/55/0 | 800 | ±10 | 5.1 | - | [5] |
| Al2O3/HfAlO/Al2O3 | 2/9/12 | 600 | ±12 | 6.29 | 79 | [46] |
| Al2O3/HfAlO/Al2O3 | 2/10/15 | 450 | ±14 | 7.45 | 23.64 | [47] |
| SiO2/ZrO2/Al2O3 | 5/10/15 | 700 | ±11 | 7.1 | 16 | [9] |
| SiO2/HfAlO/Al2O3 | 3/9/8 | 800 | ±16 | 11.5 | 14.9 | [48] |
| SiO2/Al-rich Al2O3/Al2O3 | 3.4/5/6 | 400 | ±12 | 8.2 | - | [6] |
| (Al2O3/SiO2)/Ge/Al2O3 | (4/3)/15/10 | 700 | −1~14 | 5.41 | 11 (ON), 9.8 (OFF) | [16] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, J.-H.; Park, W.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, G.-R.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Uhm, S.-H.; Lee, H.-C. Preparation of Remote Plasma Atomic Layer-Deposited HfO2 Thin Films with High Charge Trapping Densities and Their Application in Nonvolatile Memory Devices. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111785
Yoo J-H, Park W-J, Kim S-W, Lee G-R, Kim J-H, Lee J-H, Uhm S-H, Lee H-C. Preparation of Remote Plasma Atomic Layer-Deposited HfO2 Thin Films with High Charge Trapping Densities and Their Application in Nonvolatile Memory Devices. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(11):1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111785
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Jae-Hoon, Won-Ji Park, So-Won Kim, Ga-Ram Lee, Jong-Hwan Kim, Joung-Ho Lee, Sae-Hoon Uhm, and Hee-Chul Lee. 2023. "Preparation of Remote Plasma Atomic Layer-Deposited HfO2 Thin Films with High Charge Trapping Densities and Their Application in Nonvolatile Memory Devices" Nanomaterials 13, no. 11: 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111785
APA StyleYoo, J.-H., Park, W.-J., Kim, S.-W., Lee, G.-R., Kim, J.-H., Lee, J.-H., Uhm, S.-H., & Lee, H.-C. (2023). Preparation of Remote Plasma Atomic Layer-Deposited HfO2 Thin Films with High Charge Trapping Densities and Their Application in Nonvolatile Memory Devices. Nanomaterials, 13(11), 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111785








