Observation of Spin-Glass-like Behavior over a Wide Temperature Range in Single-Domain Nickel-Substituted Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
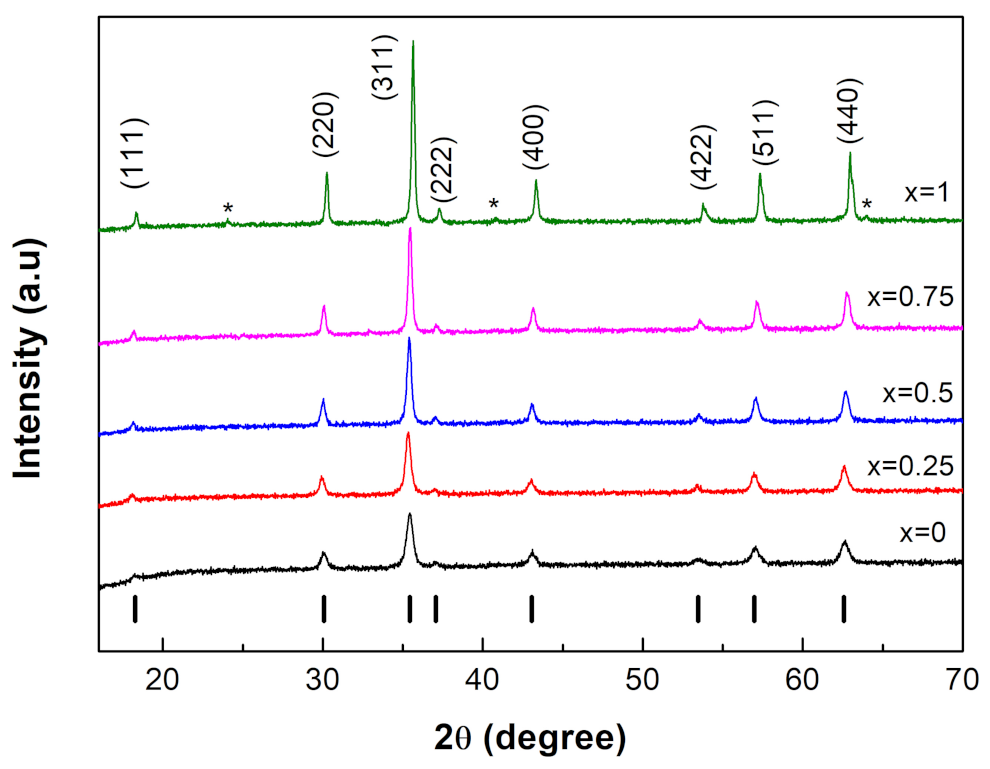
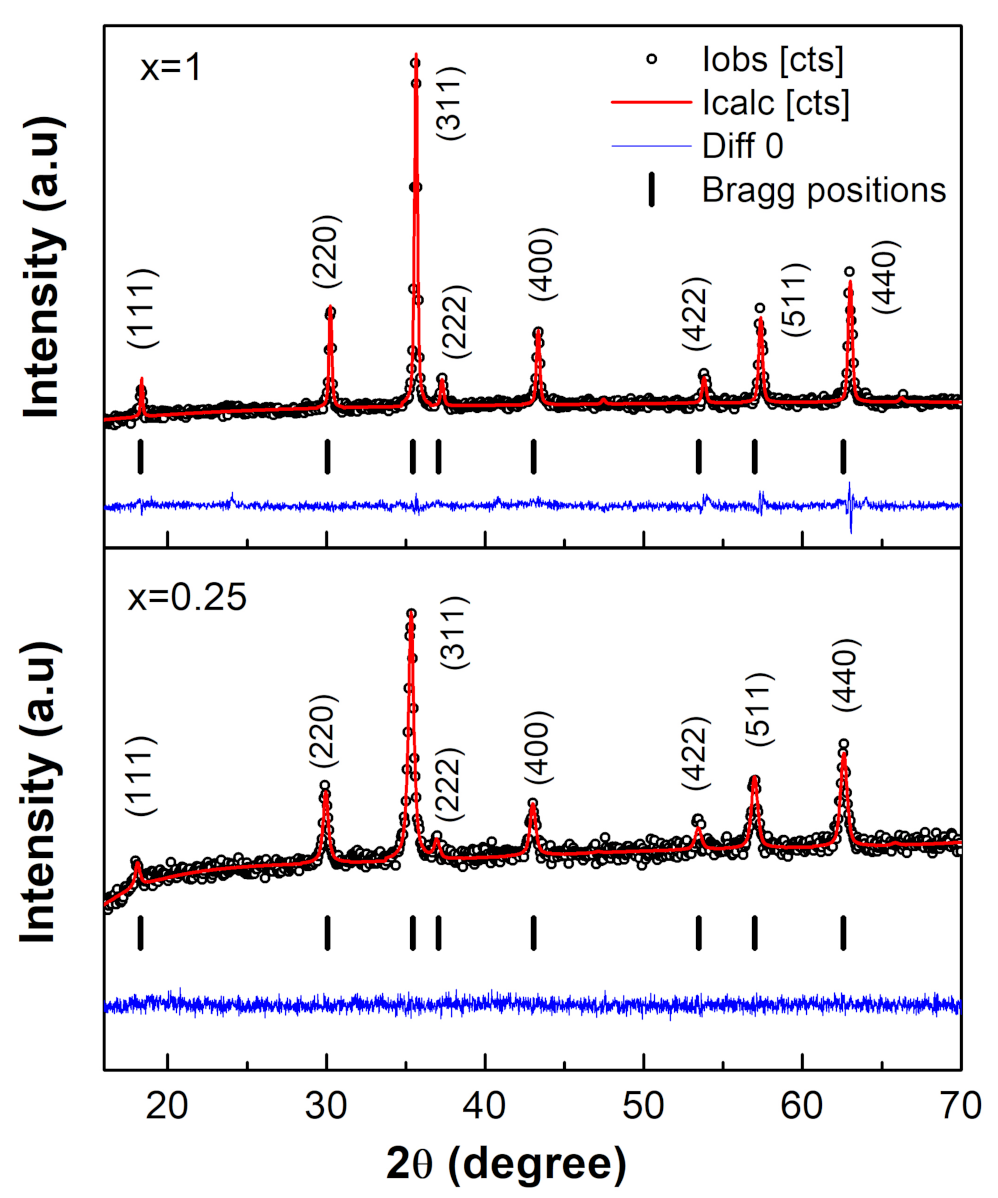
3.1. XRD Analysis
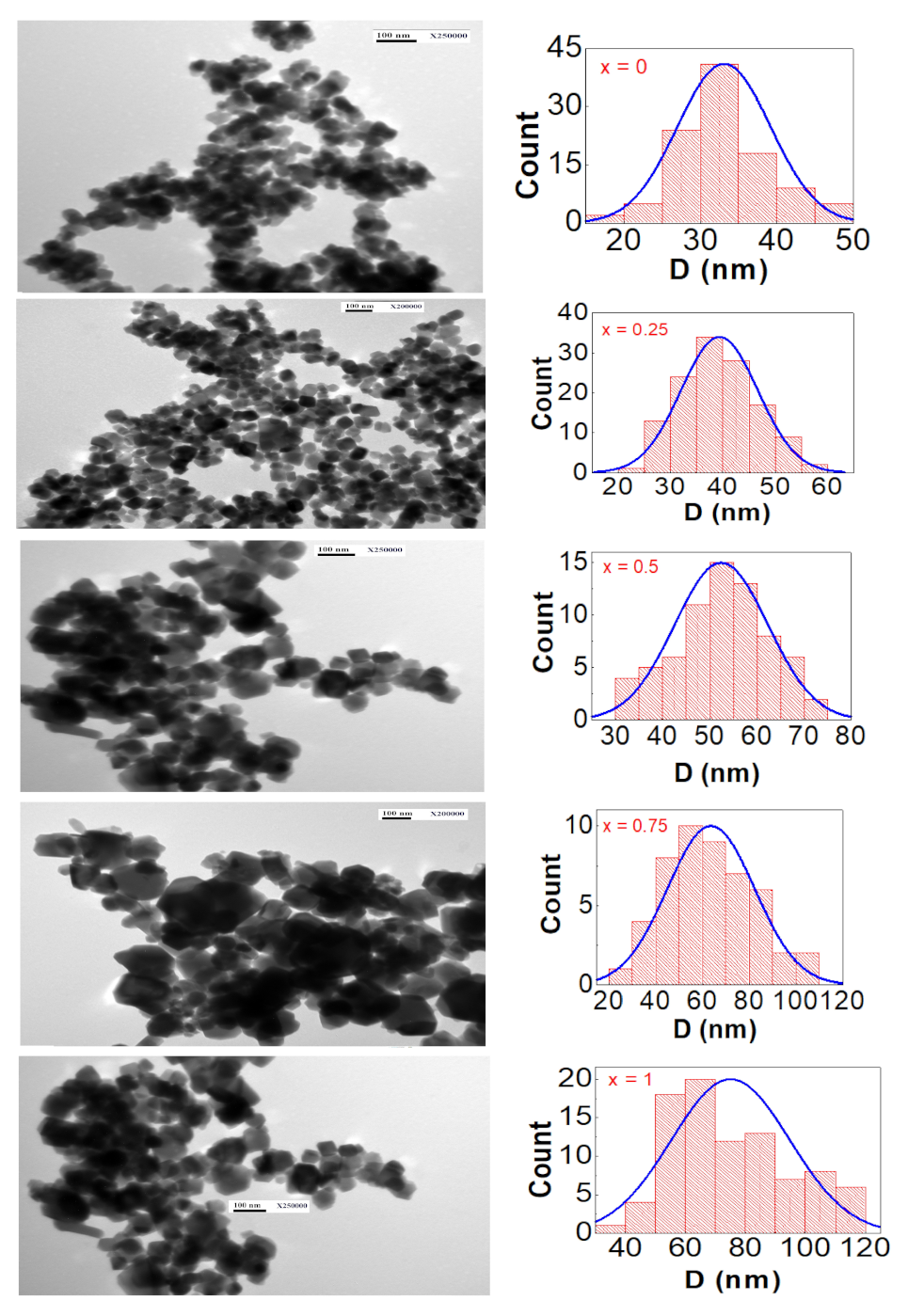
3.2. TEM Characterization
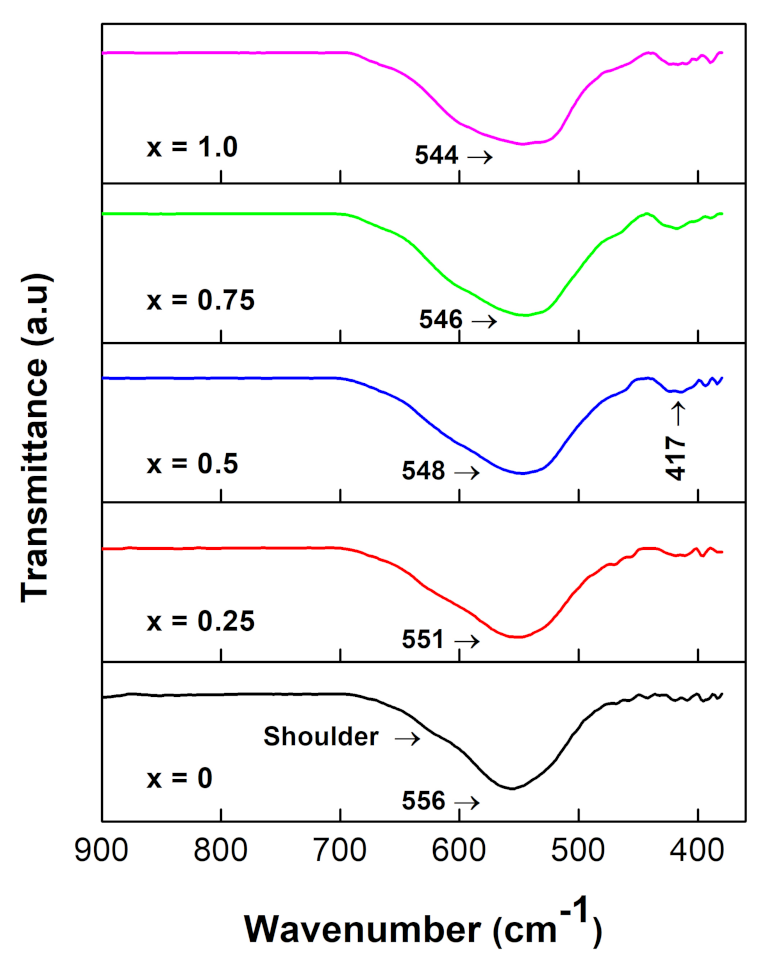
3.3. FT-IR Analysis
3.4. Magnetic Properties
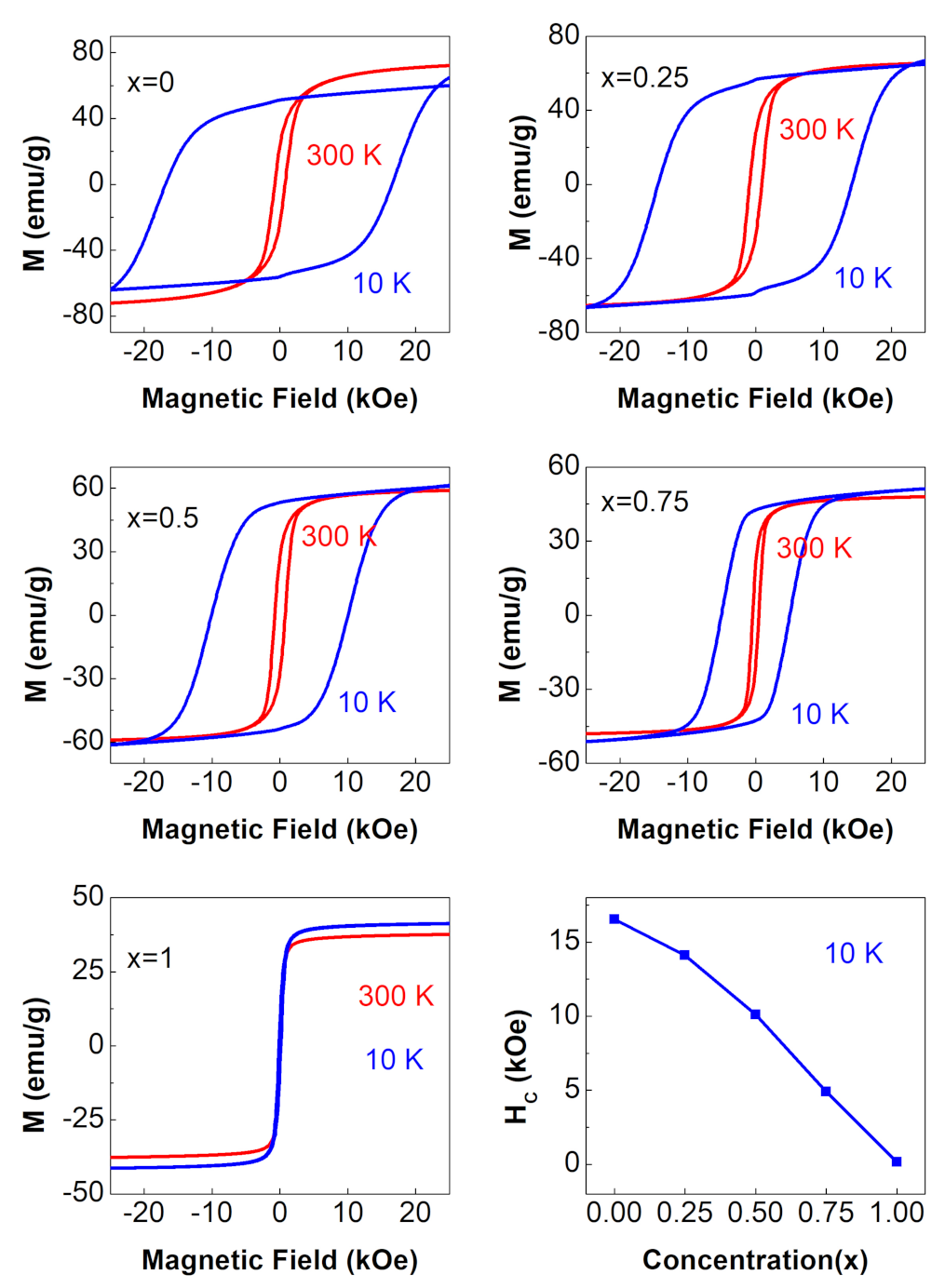
3.4.1. M vs. H Curves
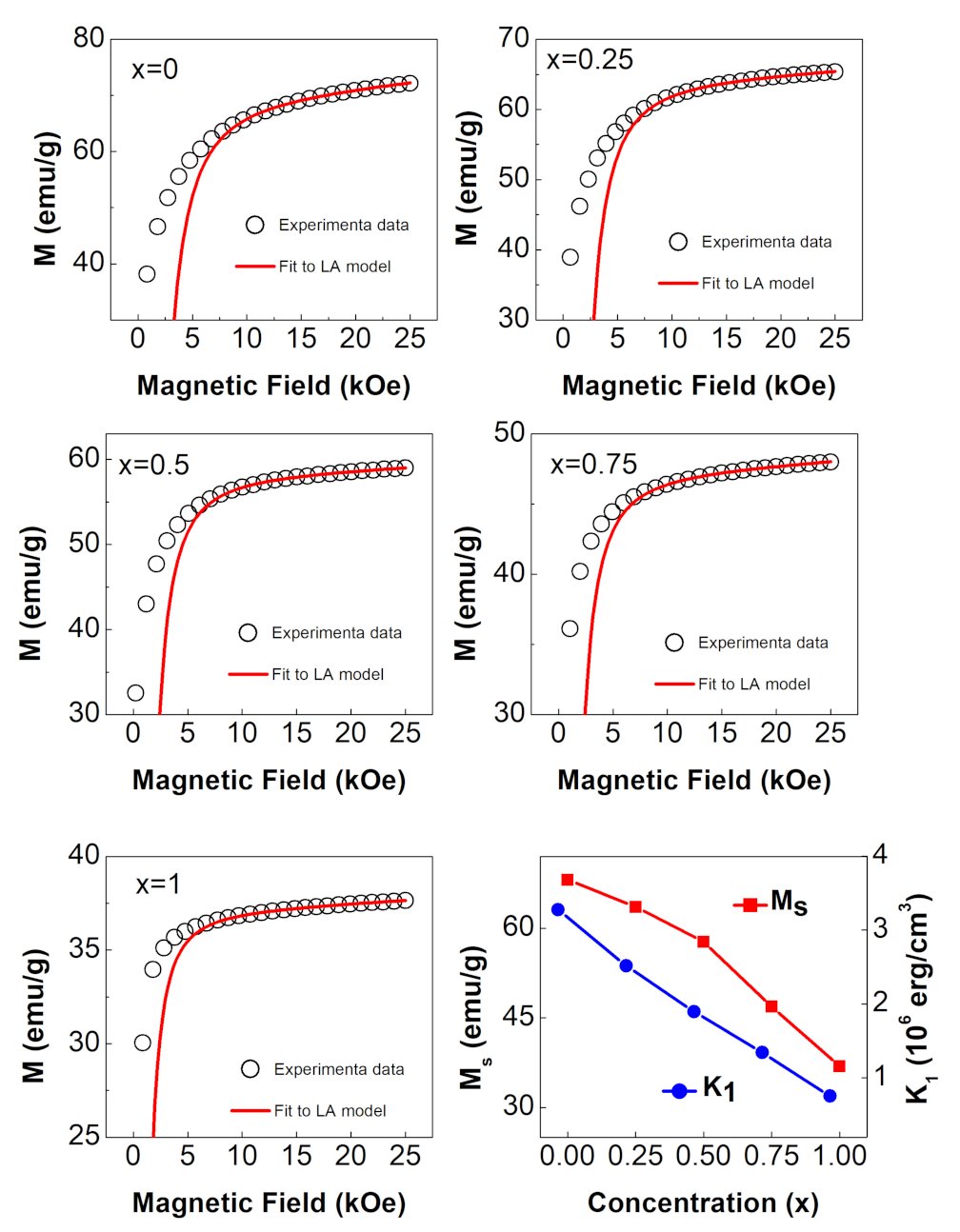
3.4.2. LA Approach
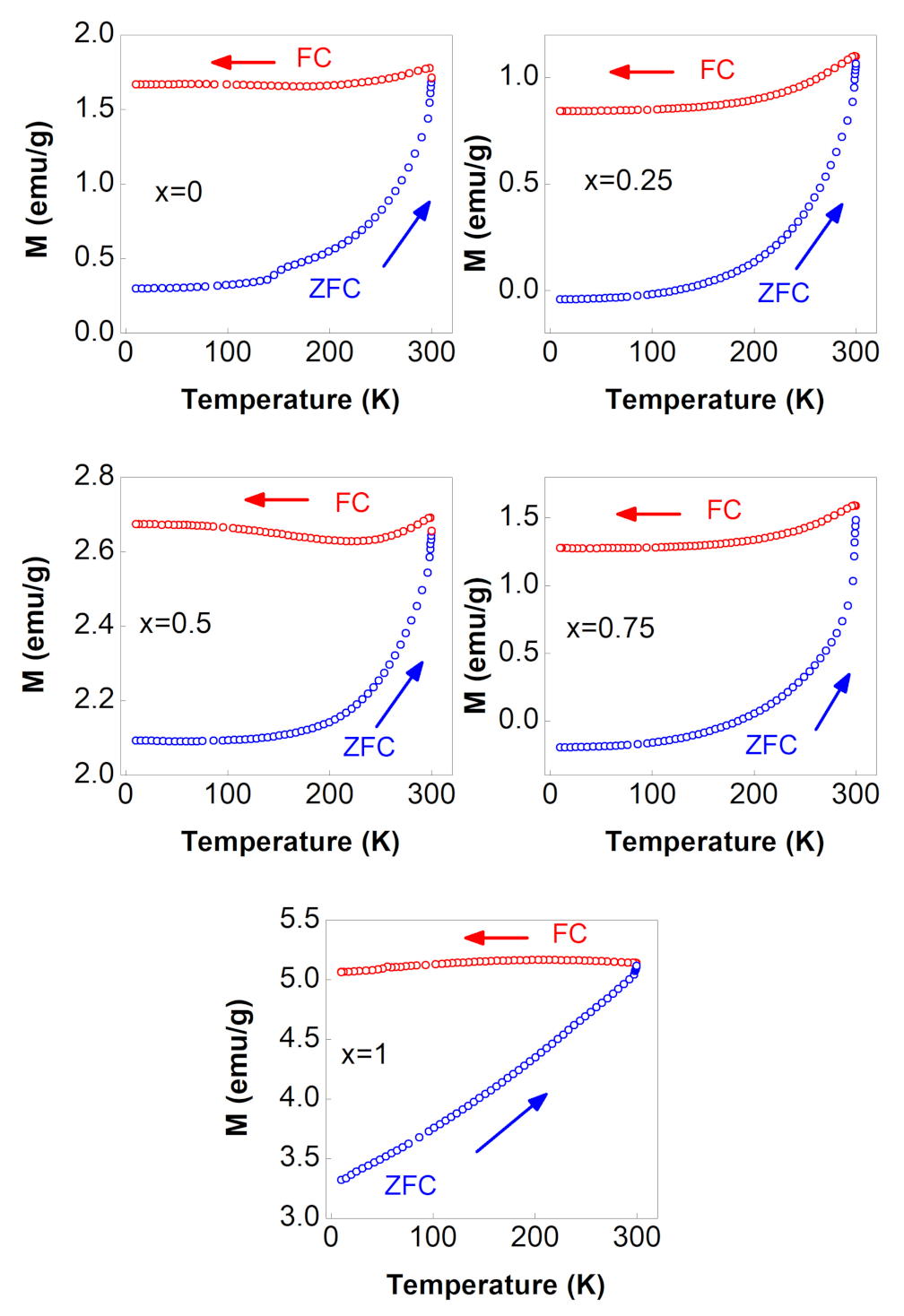
3.4.3. M vs. T Curves
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahanian, H.; Aliahmadi, M.; Faiz, J. Ferrite Permanent Magnets in Electrical Machines: Opportunities and Challenges of a Non-Rare-Earth Alternative. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šutka, A.; Gross, K.A. Spinel ferrite oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierlich, S.; Gellersen, F.; Jacob, A.; Töpfer, J. Low-temperature sintering and magnetic properties of Sc-and In-substituted M-type hexagonal barium ferrites for microwave applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 86, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.Y.; Paknikar, K.M.; Bodas, D.; Gajbhiye, V. Applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in biomedical nanotechnology. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzoubi, G.M.; Alsmadi, A.; Alna’washi, G.; Salameh, B.; Shatnawi, M.; Alnemrat, S.; Albiss, B.; Bsoul, I. Coexistence of superparamagnetism and spin-glass like behavior in zinc-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, R. Magnetic Ceramics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Alzoubi, G.M.; Albiss, B.; Shatnawi, M.; Bsoul, I.; Alsmadi, A.; Salameh, B.; Alna’washi, G. Influence of High-Temperature Annealing on Structural and Magnetic Properties of Crystalline Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles in the Single-Domain Regime. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2020, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, B.; Bhatnagar, M.; Kashyap, S.C. Cation distribution in nanocrystalline cobalt substituted nickel ferrites: X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopic investigations. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 129, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pubby, K.; Meena, S.; Yusuf, S.; Narang, S.B. Cobalt substituted nickel ferrites via Pechini’s sol–gel citrate route: X-band electromagnetic characterization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 466, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Levei, E.A.; Deac, I.G.; Neag, E.; Cadar, O. Influence of Cu2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ Ions Doping on the Structure, Morphology, and Magnetic Properties of Co-Ferrite Embedded in SiO2 Matrix Obtained by an Innovative Sol-Gel Route. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharambe, S.S.; Trimukhe, A.; Bhatia, P. Synthesis Techniques of Nickel Substituted Cobalt Ferrites—An Investigative Study Using Structural Data. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 23, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, G.M. Probing the structural and magnetic properties of small crystalline nickel ferrite nanoparticles near the upper size limit of the single-domain regime. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2020, 119, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, G.; Maji, P.; Sain, S.; Das, S.; Kar, T.; Pradhan, S. Microstructure, optical and electrical characterizations of nanocrystalline ZnAl2O4 spinel synthesized by mechanical alloying: Effect of sintering on microstructure and properties. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2019, 108, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, D.S.; Juang, R.S. An overview of the structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 129, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, C.; Jeyadevan, B.; Shinoda, K.; Tohji, K.; Djayaprawira, D.; Takahashi, M.; Joseyphus, R.J.; Narayanasamy, A. Unusually high coercivity and critical single-domain size of nearly monodispersed CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 2862–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, B.; Obaidat, I.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alijani, H.Q.; Pourseyedi, S.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Seifalian, A.; Khatami, M. Bimetallic nickel-ferrite nanorod particles: Greener synthesis using rosemary and its biomedical efficiency. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerdj, I. Rietveld Refinement in the Characterization of Crystalline Materials; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bujakiewicz-Koro ´nska, R.; Hetma ´nczyk, Ł.; Garbarz-Glos, B.; Budziak, A.; Kalvane, A.; Bormanis, K.; Druzbicki, K. Low temperature measurements by infrared spectroscopy in CoFe2O4 ceramic. Open Phys. 2012, 10, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, Y. Structural Rietveld Refinement of Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles Prepared by Chemical Method. J. Nanosci. Technol. 2019, 5, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Cryst. Phys. Diffr. Theor. Gen. Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toksha, B.; Shirsath, S.E.; Patange, S.; Jadhav, K. Structural investigations and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel auto combustion method. Solid State Commun. 2008, 147, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkian, S.; Ghasemi, A.; Razavi, R.S. Cation distribution and magnetic analysis of wideband microwave absorptive CoxNi1-xFe2O4 ferrites. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6987–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, D.S.; Jadhav, S.V.; Khot, V.M.; Bohara, R.; Hong, C.K.; Mali, S.S.; Pawar, S. Cation distribution, structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Co1-xZnxFe2O4 (x = 0–1) nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 2338–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.; Banerjee, P.; Franco, A. Hydrothermal synthesis of nickel doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Optical and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 14657–14667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, Y.; Geng, B.; Sun, X.; Wang, M. The remanence ratio in CoFe2O4 nanoparticles with approximate single-domain sizes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zeng, D.; Liu, Z. The law of approach to saturation in ferromagnets originating from the magnetocrystalline anisotropy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 2375–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R. Magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.; Ceylan, A. Synthesis and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles prepared by wet chemical route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raut, A.; Barkule, R.; Shengule, D.; Jadhav, K. Synthesis, structural investigation and magnetic properties of Zn2+ substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the sol–gel auto-combustion technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 358, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, E.; Dupuis, V. Spin glasses: Experimental signatures and salient outcomes. In Frustrated Materials and Ferroic Glasses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]

| x | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Co | 0.5 | |||
| Fe | 0.5 | ||||
| Fe | 1 | ||||
| O | 1 | ||||
| 0.25 | Ni | 0.125 | |||
| Co | 0.375 | ||||
| Fe | 0.5 | ||||
| Fe | 1 | ||||
| O | 1 | ||||
| 0.5 | Ni | 0.25 | |||
| Co | 0.25 | ||||
| Fe | 0.5 | ||||
| Fe | 1 | ||||
| O | 1 | ||||
| 0.75 | Ni | 0.375 | |||
| Co | 0.125 | ||||
| Fe | 0.5 | ||||
| Fe | 1 | ||||
| O | 1 | ||||
| 1 | Ni | 0.5 | |||
| Fe | 0.5 | ||||
| Fe | 1 | ||||
| O | 1 |
| x | 0 | 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (nm) | 17.4 | 21.1 | 26.1 | 31.7 | 41.7 |
| 5.31 | 5.34 | 5.36 | 5.38 | 5.39 | |
| R-factors (%) | |||||
| 1.261 | 1.378 | 1.402 | 1.454 | 1.414 | |
| 1.303 | 1.444 | 1.439 | 1.528 | 1.788 | |
| () | 1.07 | 1.1 | 1.05 | 1.1 | 1.6 |
| Cell parameters (Å) | |||||
| 8.3706 | 8.3539 | 8.3458 | 8.3345 | 8.3303 | |
| u | 0.2564 | 0.2667 | 0.2691 | 0.2698 | 0.2565 |
| 1.9051 | 2.0807 | 2.0266 | 1.9214 | 1.8986 | |
| 2.0405 | 1.9441 | 1.9678 | 2.0184 | 2.0298 |
| x | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24.1 | 0.35 | |||
| 0.25 | 27.7 | 0.44 | |||
| 0.5 | 27.4 | 0.47 | |||
| 0.75 | 21.7 | 0.46 | |||
| 1 | 4.6 | 0.12 |
| x | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 68.1 | 2.86 | ||
| 0.25 | 63.6 | 2.67 | ||
| 0.5 | 57.7 | 2.42 | ||
| 0.75 | 46.8 | 1.96 | ||
| 1 | 36.9 | 1.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzoubi, G.M. Observation of Spin-Glass-like Behavior over a Wide Temperature Range in Single-Domain Nickel-Substituted Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071113
Alzoubi GM. Observation of Spin-Glass-like Behavior over a Wide Temperature Range in Single-Domain Nickel-Substituted Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(7):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071113
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzoubi, Gassem M. 2022. "Observation of Spin-Glass-like Behavior over a Wide Temperature Range in Single-Domain Nickel-Substituted Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 12, no. 7: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071113
APA StyleAlzoubi, G. M. (2022). Observation of Spin-Glass-like Behavior over a Wide Temperature Range in Single-Domain Nickel-Substituted Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 12(7), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071113






