Microfluidic Study of the Effect of Nanosuspensions on Enhanced Oil Recovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microfluidic Chip
2.2. Crude Oil and Displacing Fluids
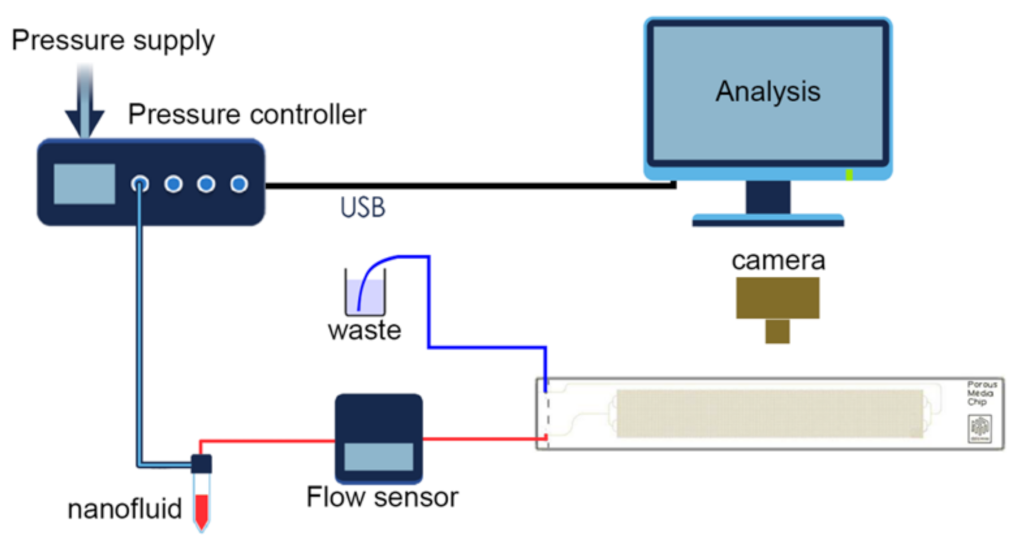
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Experimental Procedure
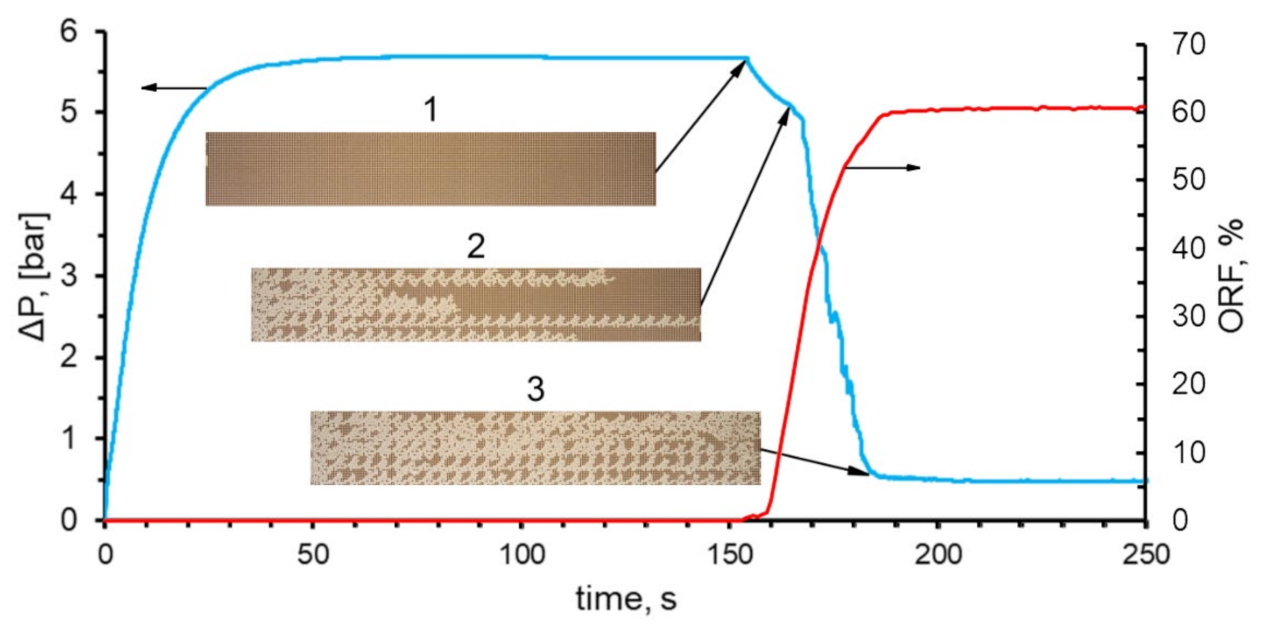
2.5. Estimation of the Oil Recovery Factor
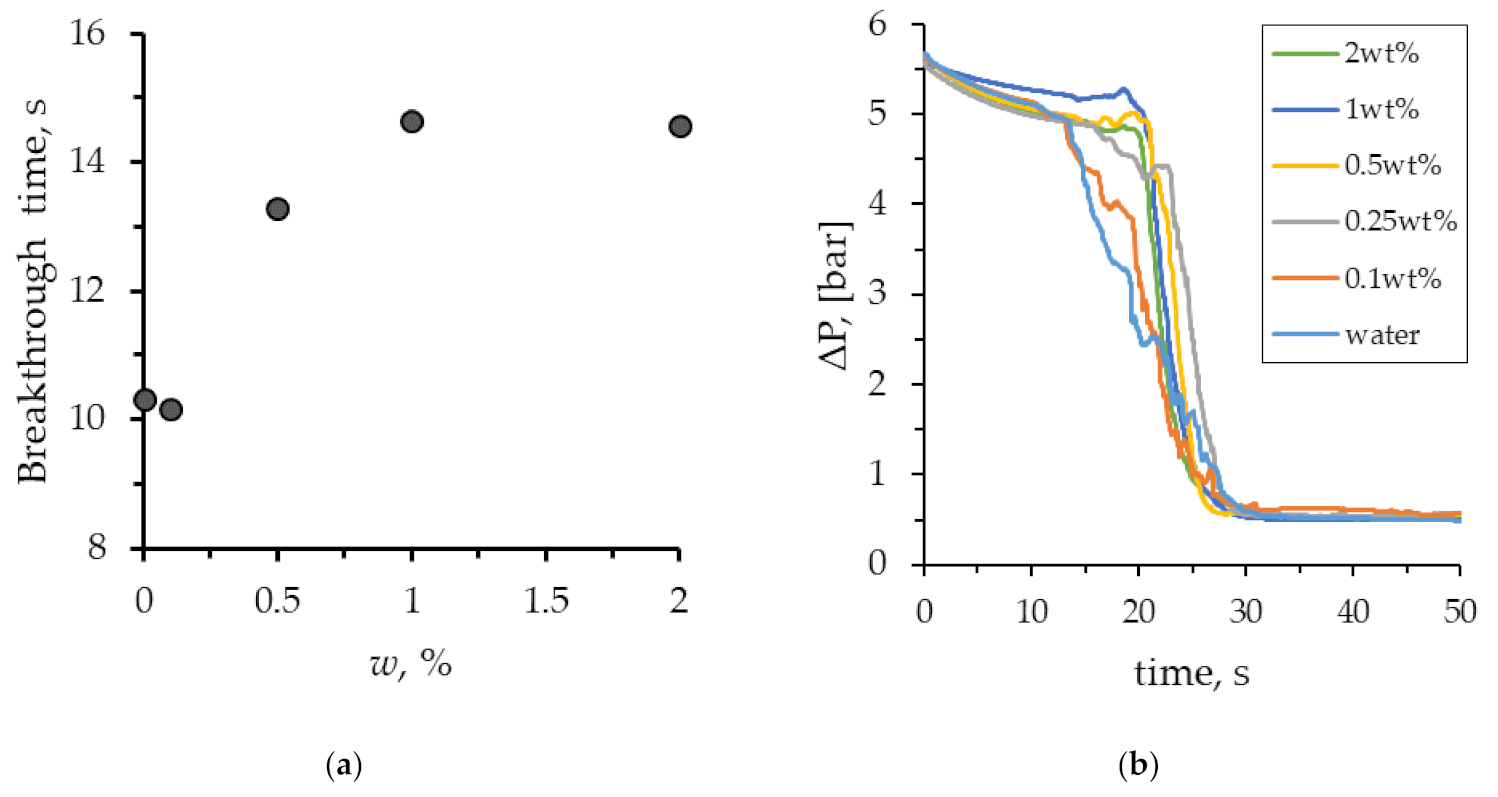
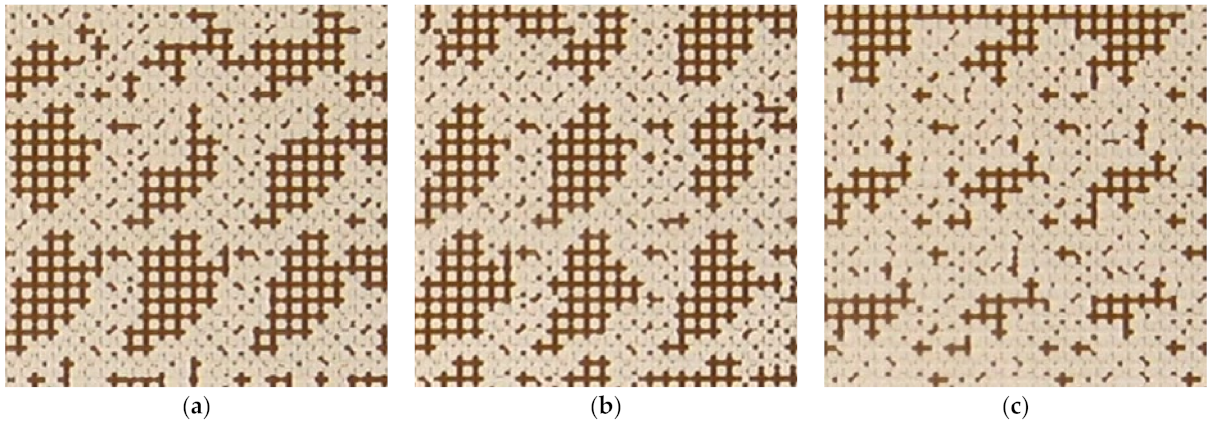
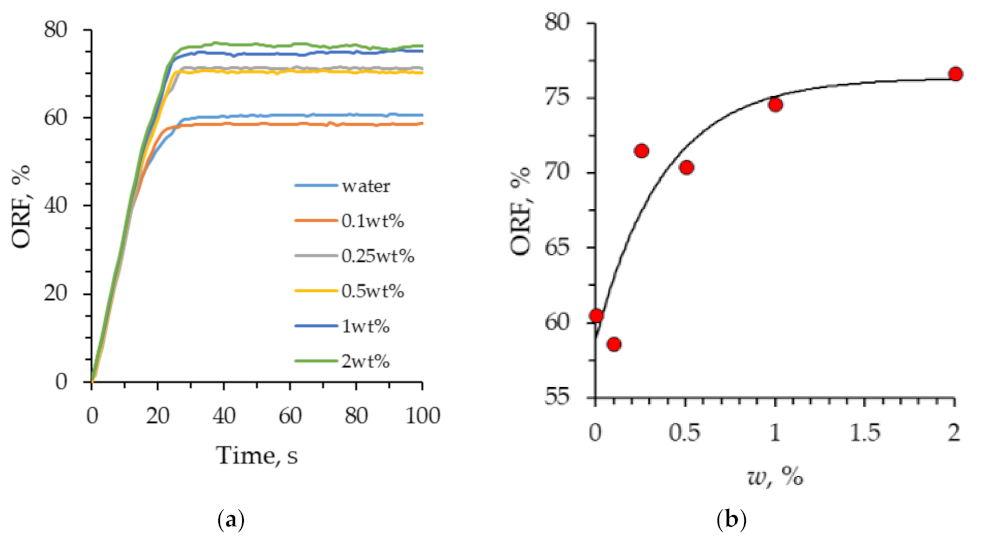
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, S. Enhanced oil recovery—An overview. Rev. IFP Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2008, 63, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarado, V.; Manrique, E. Enhanced Oil Recovery: An Update Review. Energies 2010, 3, 1529–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Nguyen, N.; Nguyen, Q.P. Low tension gas flooding for secondary oil recovery in low-permeability, high-salinity reservoirs. Fuel 2020, 264, 116601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhicajee, P.; Romero-Zerón, L. Effect of different low salinity flooding schemes and the addition of alkali on the performance of low-salinity waterflooding during the recovery of heavy oil from unconsolidated sandstone. Fuel 2021, 289, 119981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FouadSnosy, M.; El Ela, M.A.; El-Banbi, A.; Sayyouh, H. Impact of the injected water salinity on oil recovery from sandstone formations: Application in an Egyptian oil reservoir. Petroleum 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Atta, D.Y.; Negash, B.M.; Yekeen, N.; Habte, A.D. A state-of-the-art review on the application of natural surfactants in enhanced oil recovery. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Vardhan, K.H.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.B.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Vellaichamy, P. A review on a systematic approach for microbial enhanced oil recovery technologies: Opportunities and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarweh, O.; Abushaikha, A.S. A review of recent developments in CO2 mobility control in enhanced oil recovery. Petroleum 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Cao, B.; Xie, K.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Enhanced oil recovery mechanisms of polymer flooding in a heterogeneous oil reservoir. Petrol. Explor. Develop. 2021, 48, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakasai, F.; Jaafar, M.Z.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Agi, A. Current developments and future outlook in nanofluid flooding: A comprehensive review of various parameters influencing oil recovery mechanisms. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 93, 138–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bila, A.; Stensen, J.Å.; Torsæter, O. Experimental investigation of polymer-coated silica nanoparticles for enhanced oil recovery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salaudeen, I.; Hashmet, M.R.; Pourafshary, P. Catalytic effects of temperature and silicon dioxide nanoparticles on the acceleration of production from carbonate rocks. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Lee, J. Impact of design parameters on oil recovery performance in polymer flooding with low-salinity water-flooding. Geosyst. Eng. 2020, 23, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Bonsu, K.; Grassia, P.; Shokri, N. Investigation of foam flow in a 3D printed porous medium in the presence of oil. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadat, M.; Tsai, P.A.; Ho, T.H.; Øye, G.; Dudek, M. Development of a microfluidic method to study enhanced oil recovery by low salinity water flooding. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17521–17530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadat, M.; Yang, J.; Dudek, M.; Øye, G.; Tsai, P.A. Microfluidic investigation of enhanced oil recovery: The effect of aqueous floods and network wettability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadland, R.C.; Akarri, S.; Heggset, E.B.; Syverud, K.; Torsæter, O. A core flood and microfluidics investigation of nanocellulose as a chemical additive to water flooding for EOR. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, Y.; Liao, G.; Liu, W. Visualizing in-situ emulsification in porous media during surfactant flooding: A microfluidic study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 578, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; William Carey, J.; Viswanathan, H.S.; Porter, M. Effectiveness of supercritical-CO2 and N2 huff-and-puff methods of enhanced oil recovery in shale fracture networks using microfluidic experiments. Appl. Energy 2018, 230, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavra, E.D.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, S.; Hirasaki, G.J.; Biswal, S.L. Microfluidic devices for characterizing pore-scale event processes in porous media for oil recovery applications. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, e56592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, M.A.; Kulkarni, R.; Gerberich, L.; Hammond, R.; Singh, R.; Baumhoff, E.; Rothstein, J.P. Effect of fluid rheology on enhanced oil recovery in a microfluidic sandstone device. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2013, 202, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Jiang, H.; Xu, F.; Fan, Z.; Su, H.; Li, J. New insights into flow physics in the EOR process based on 2.5D reservoir, micromodels. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 181, 106214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, S.; Olmos, C.M.; Pérez, M.; Lerner, B.; Franco, C.A.; Riazi, M.; Gallego, J.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Cortés, F.B. A microfluidic study to investigate the effect of magnetic iron core-carbon shell nanoparticles on displacement mechanisms of crude oil for chemical enhanced oil recovery. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 184, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, J.T.; Cudjoe, S.E.; Aryana, S.A.; Ghahfarokhi, R.B. Investigation into fluid-fluid interaction phenomena during low salinity waterflooding using a reservoir-on-a-chip microfluidic model. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 108074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, H.S.; Orb, D.; Liu, Y.; Lai, C.Y.; Lu, N.B.; Datta, S.S.; Stone, H.A.; Shokri, N. Suppressing viscous fingering in structured porous media. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4833–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, W.; Chang, S.; Cogswell, D.A.; Eichmann, S.L.; Gizzatov, A.; Thomas, G.; Al-Hazza, N.; Abdel-Fattah, A.; Wang, W. Toward reservoir-on-a-chip: Rapid performance evaluation of enhanced oil recovery surfactants for carbonate reservoirs using a calcite-coated micromodel. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangirala, S.; Sheng, J. Effects of invasion of water with and without surfactant on the oil production and flowback through an oil-wet matrix—A microfluidic chip-based study. Open J. Yangtze Gas Oil 2018, 3, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaol, C.L.; Wegner, J.; Ganzer, L. Real structure micromodels based on reservoir rocks for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) applications. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, S.; Gogoi, S.B. Review on microfluidic studies for EOR application. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2019, 9, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaol, C.L.; Ganzer, L.; Mukherjee, S.; Alkan, H. Parameters govern microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR) performance in real-structure micromodels. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, E.; Akarri, S.; Torsæter, O.; Moreno, R.B.Z.L. Experimental investigation of the effect of adding nanoparticles to polymer flooding in water-wet micromodels. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, A.; Abdollahi, H.; Derikvand, Z.; Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A.; Mosavi, A.; Nabipour, N. Insights into the effects of pore size distribution on the flowing behavior of carbonate rocks: Linking a nano-based enhanced oil recovery method to rock typing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yu, H.; Niu, L.; Ni, D.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Utilization of Janus-silica/surfactant nanofluid without ultra-low interfacial tension for improving oil recovery. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 228, 115964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakov, A.V.; Guzei, D.V.; Filimonov, S.A.; Voronenkova, Y.O. 3D pore-scale modeling of nanofluids-enhanced oil recovery. Petrol. Explor. Develop. 2021, 48, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcorn, Z.P.; Føyen, T.; Gauteplass, J.; Benali, B.; Soyke, A.; Fernø, M. Pore- and core-scale insights of nanoparticle-stabilized foam for CO2-Enhanced oil recovery. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryazhnikov, M.I.; Minakov, A.V. Bulk viscosity of a suspension of silicon oxide nanoparticles. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2020, 46, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, B.C.; Cho, Y.I. Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp. Heat Transf. 1998, 11, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargozarfard, Z.; Riazi, M.; Ayatollahi, S. Viscous fingering and its effect on areal sweep efficiency during waterflooding: An experimental study. Petrol. Sci. 2018, 16, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minakov, A.V.; Pryazhnikov, M.I.; Zhigarev, V.A.; Rudyak, V.Y.; Filimonov, S.A. Numerical study of the mechanisms of enhanced oil recovery using nanosuspensions. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2021, 35, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakov, A.V.; Pryazhnikov, M.I.; Suleymana, Y.N.; Meshkova, V.D.; Guzei, D.V. Experimental study of nanoparticle size and material effect on the oil wettability characteristics of various rock types. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 327, 114906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
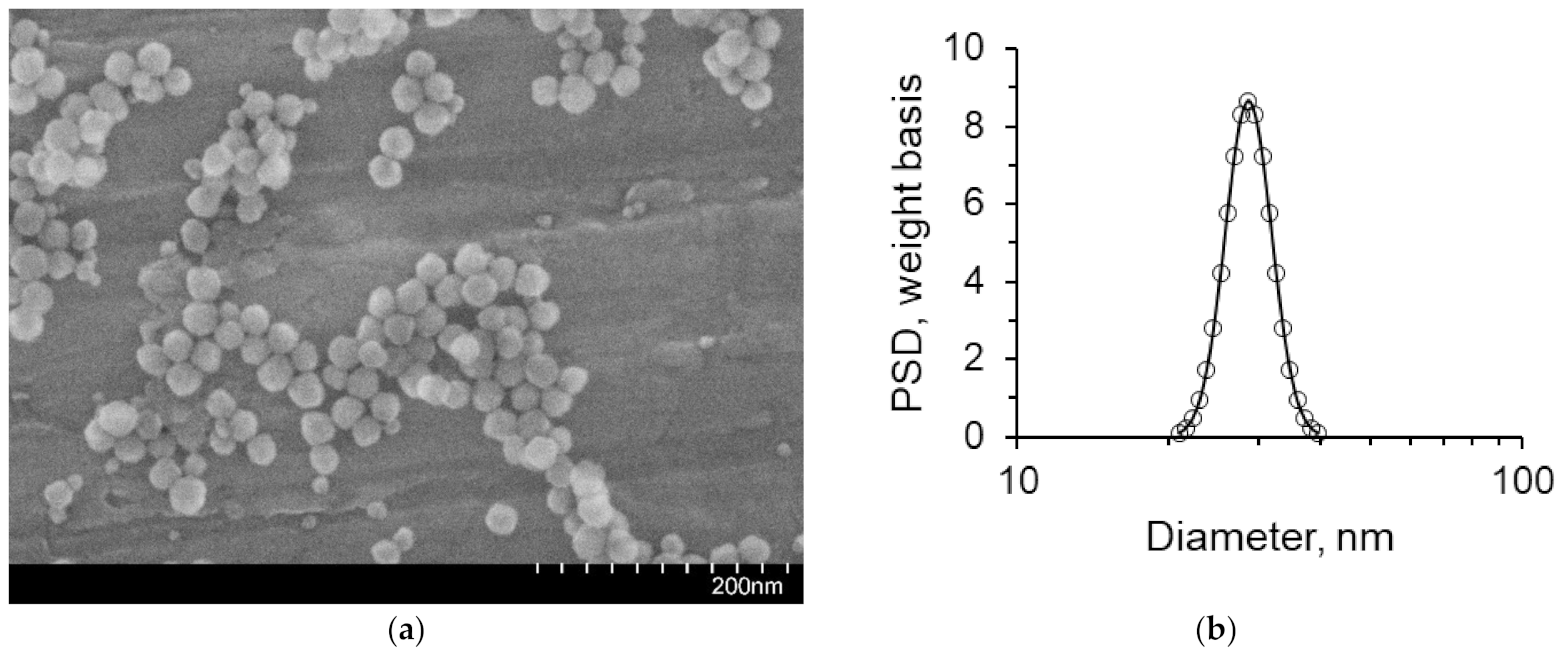
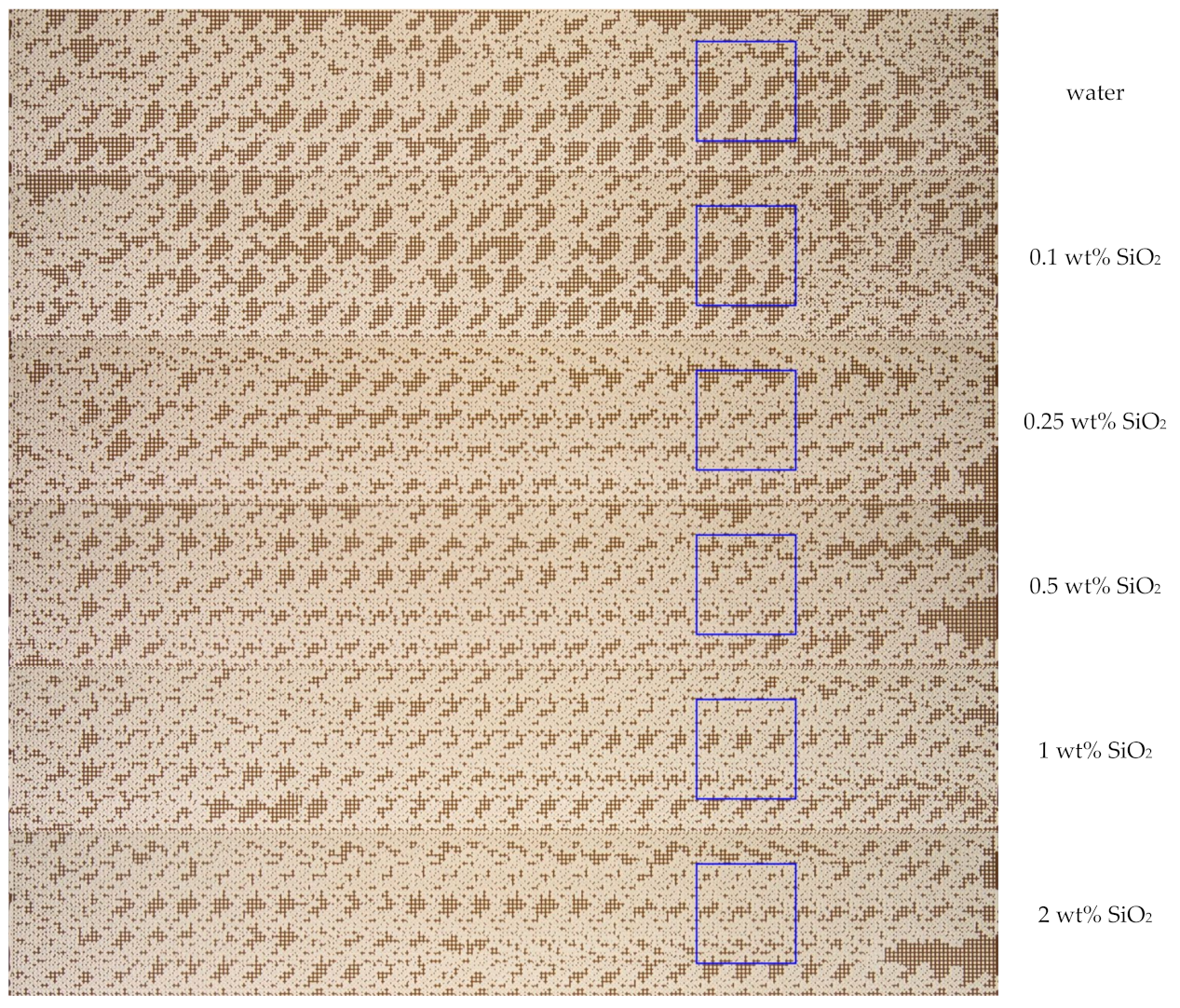






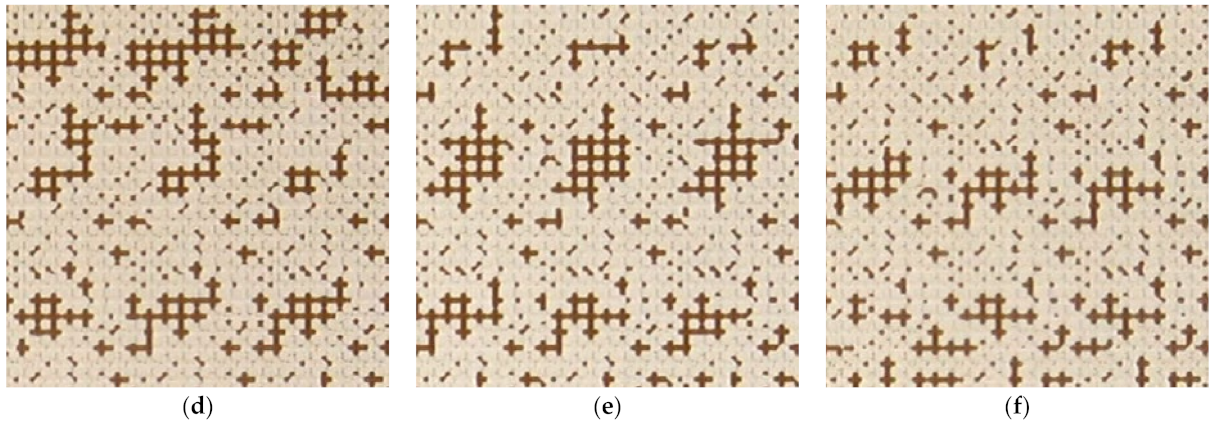
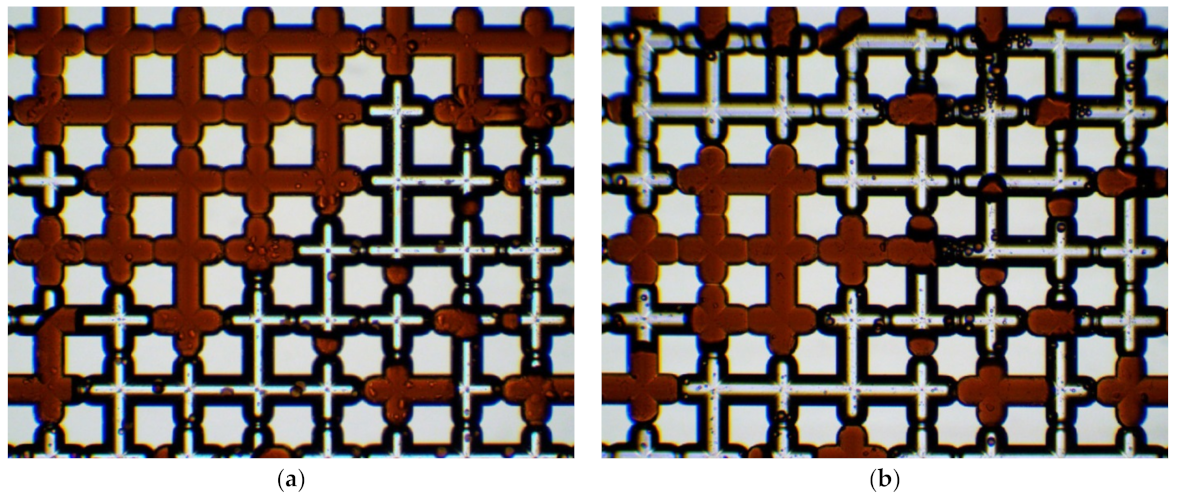
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| microchannel cross-section | 100 × 110 µm |
| pore cross-section | Ø85 µm and Ø63 µm |
| input channel length, including bifurcations | 27.7 mm |
| output channel length, including bifurcations | 99.2 mm |
| the total length of the porous channel | 4800 mm |
| inlet channel volume | 0.9 µL |
| outlet channel volume | 3.2 µL |
| porous space volume | 38 µL |
| surface roughness of channels | 5 nm |
| channel coating | hydrophilic |
| Fluid | Density, g cm−3 | Viscosity, mPa s |
|---|---|---|
| oil | 0.8510 | 24.6 |
| distilled water | 0.9970 | 0.890 |
| 0.1 wt% SiO2 | 0.9975 | 0.892 |
| 0.25 wt% SiO2 | 0.9984 | 0.896 |
| 0.5 wt% SiO2 | 0.9997 | 0.902 |
| 1 wt% SiO2 | 1.003 | 0.914 |
| 2 wt% SiO2 | 1.008 | 0.939 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pryazhnikov, M.I.; Minakov, A.V.; Pryazhnikov, A.I.; Denisov, I.A.; Yakimov, A.S. Microfluidic Study of the Effect of Nanosuspensions on Enhanced Oil Recovery. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030520
Pryazhnikov MI, Minakov AV, Pryazhnikov AI, Denisov IA, Yakimov AS. Microfluidic Study of the Effect of Nanosuspensions on Enhanced Oil Recovery. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030520
Chicago/Turabian StylePryazhnikov, Maxim I., Andrey V. Minakov, Andrey I. Pryazhnikov, Ivan A. Denisov, and Anton S. Yakimov. 2022. "Microfluidic Study of the Effect of Nanosuspensions on Enhanced Oil Recovery" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030520
APA StylePryazhnikov, M. I., Minakov, A. V., Pryazhnikov, A. I., Denisov, I. A., & Yakimov, A. S. (2022). Microfluidic Study of the Effect of Nanosuspensions on Enhanced Oil Recovery. Nanomaterials, 12(3), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030520








