Multifunctional Zn-Doped ITO Sol–Gel Films Deposited on Different Substrates: Application as CO2-Sensing Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
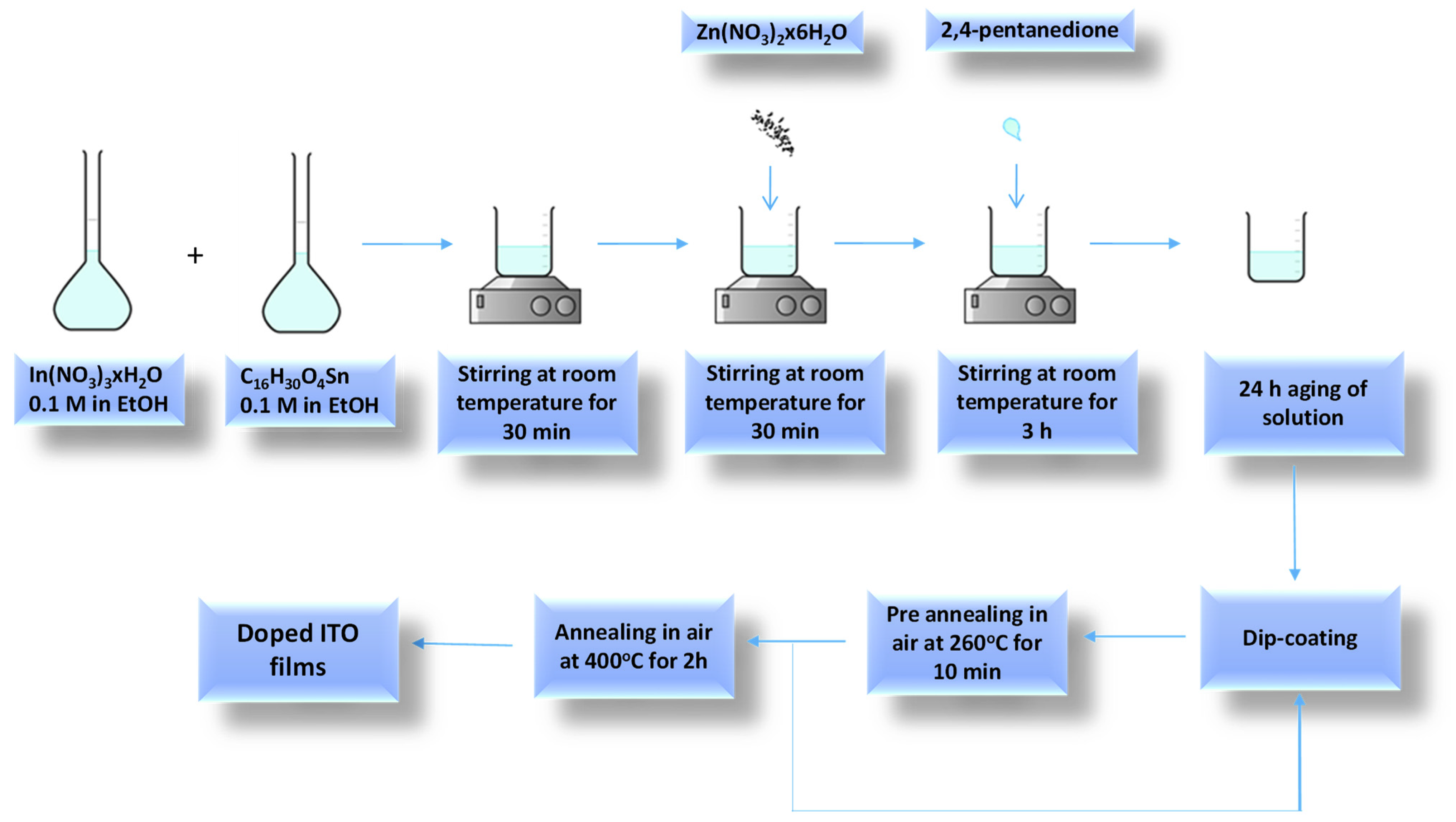
2.1. Film Preparation
2.2. Film Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
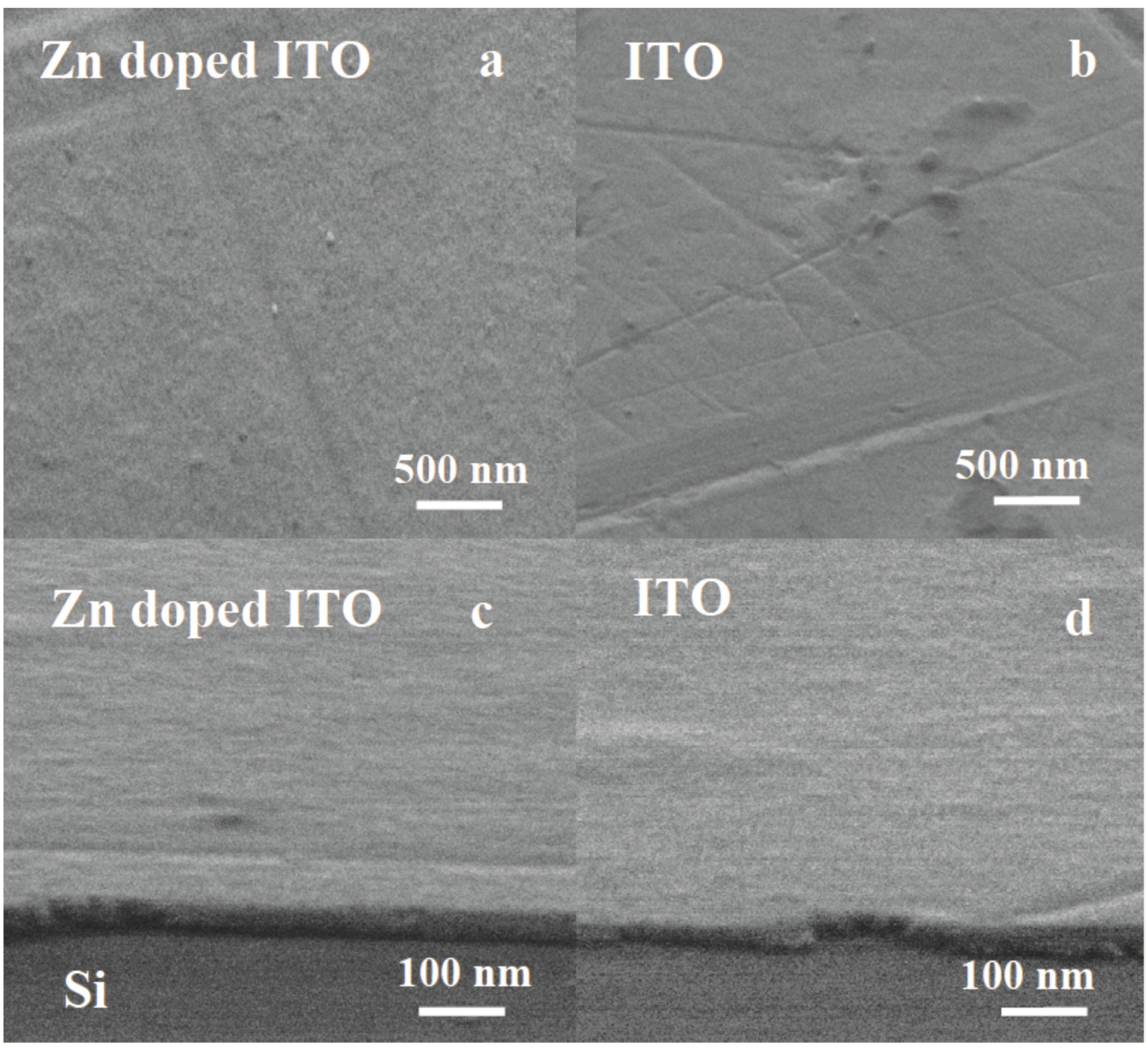
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
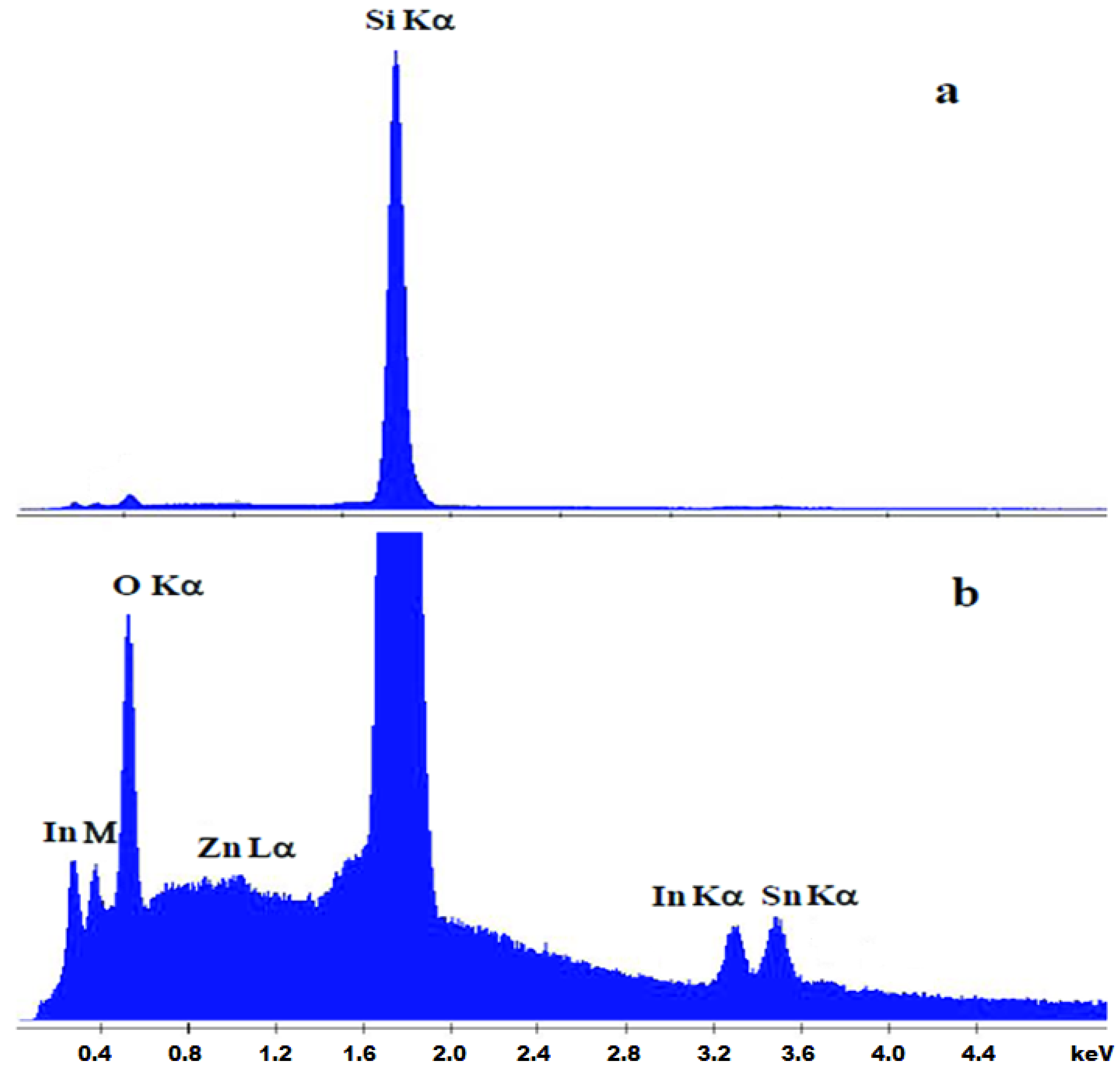
3.2. Chemical Characterization (EDX)
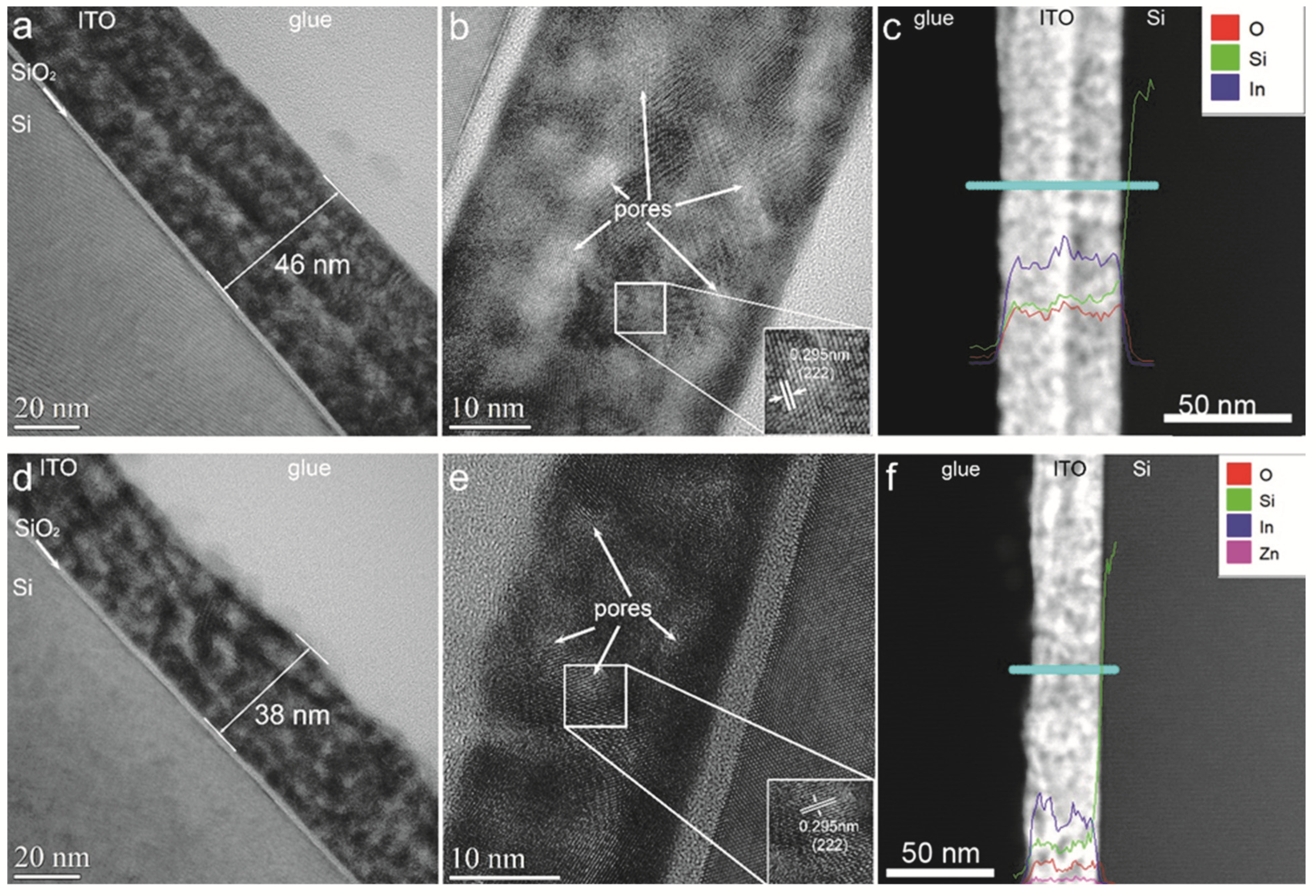
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray (EDX)
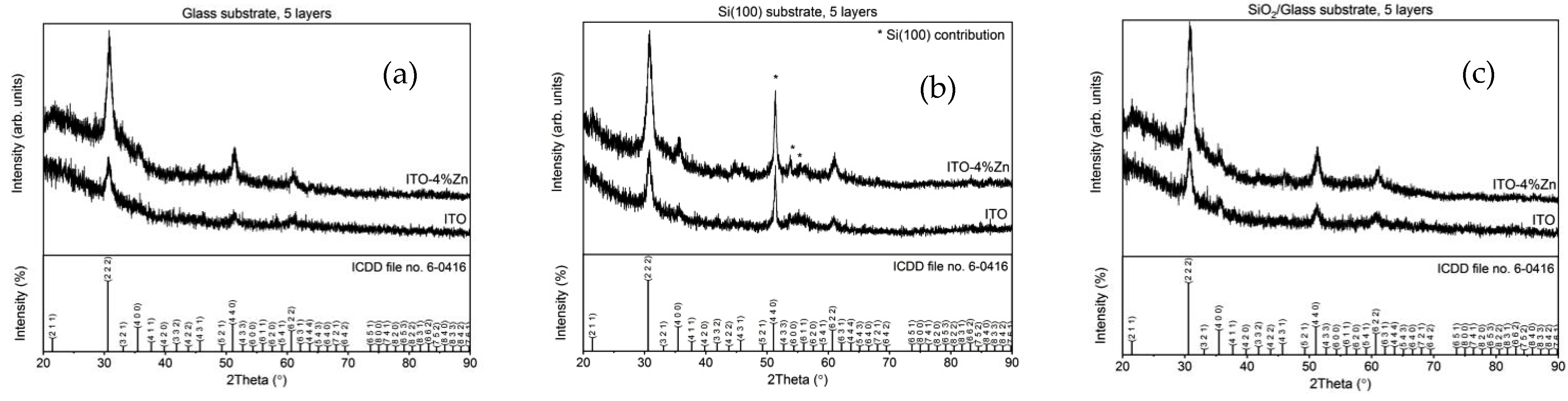
3.4. Structural Characterization (XRD)
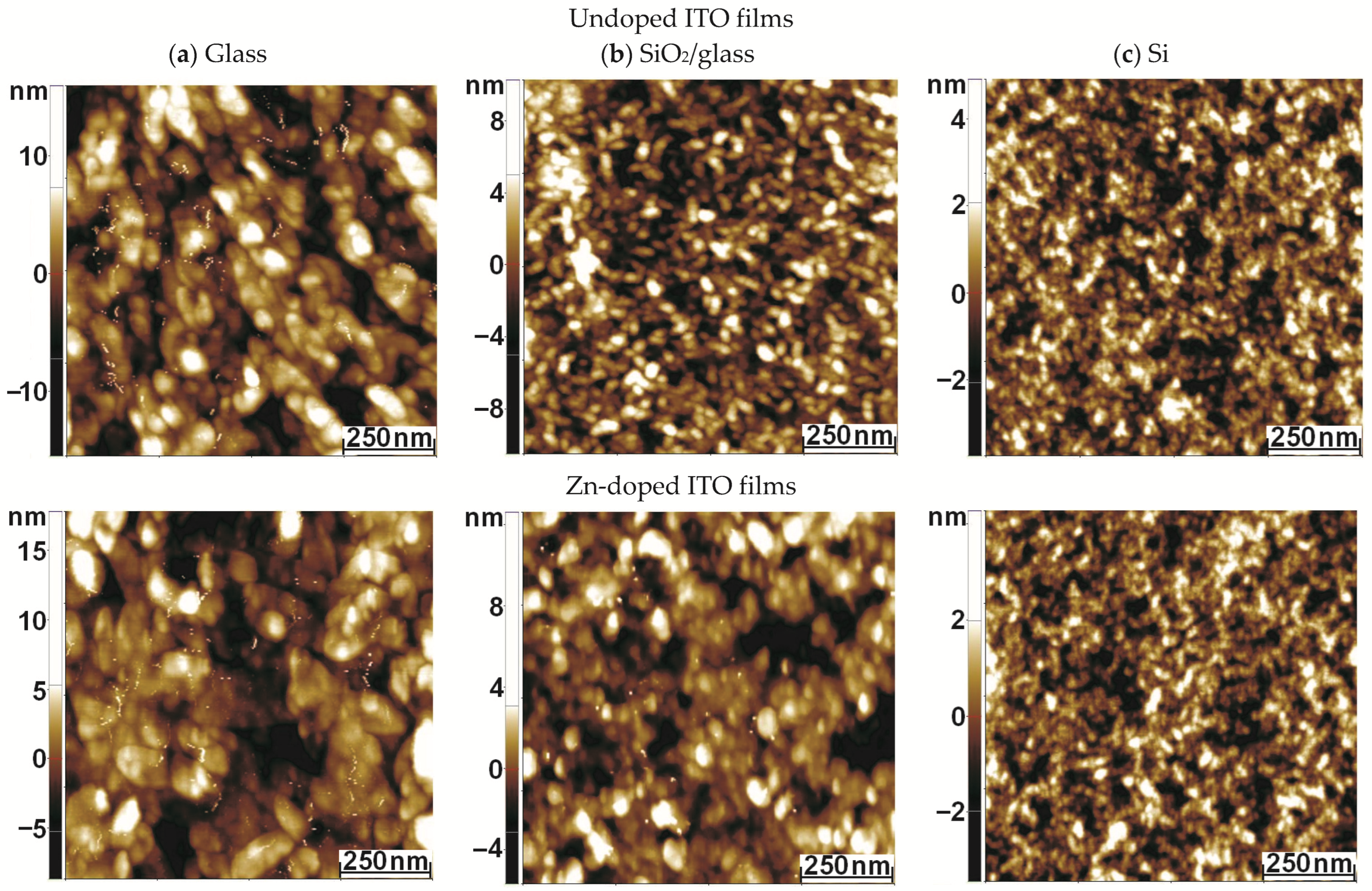
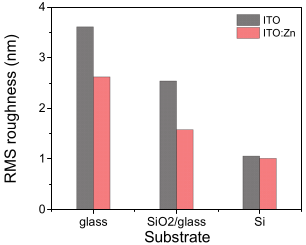
3.5. Morphological Characterization (AFM)
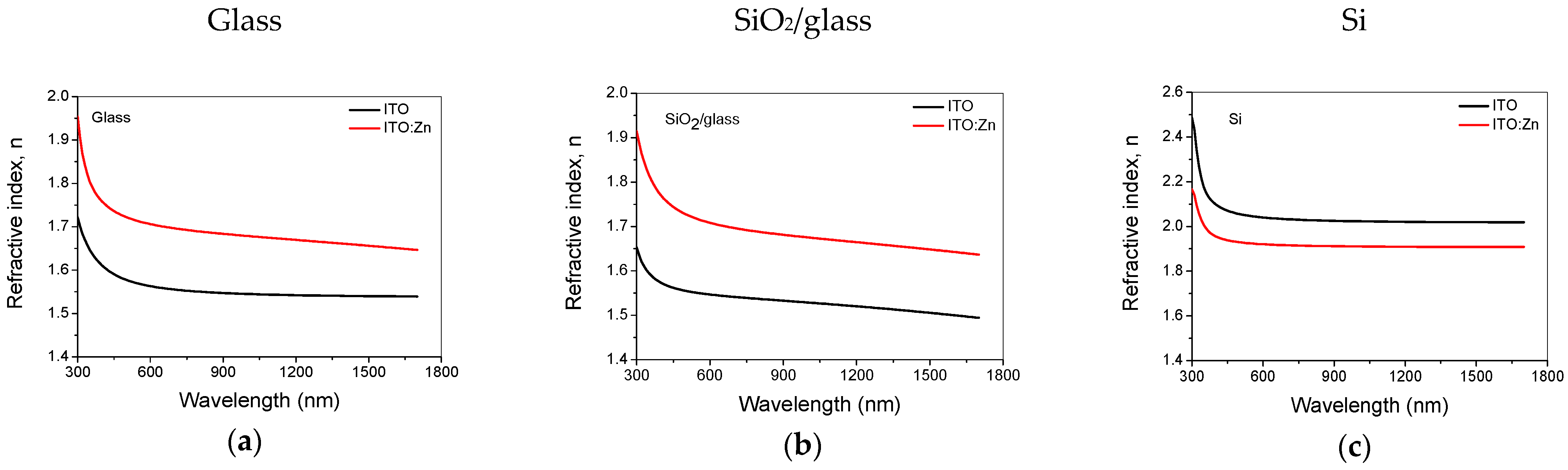
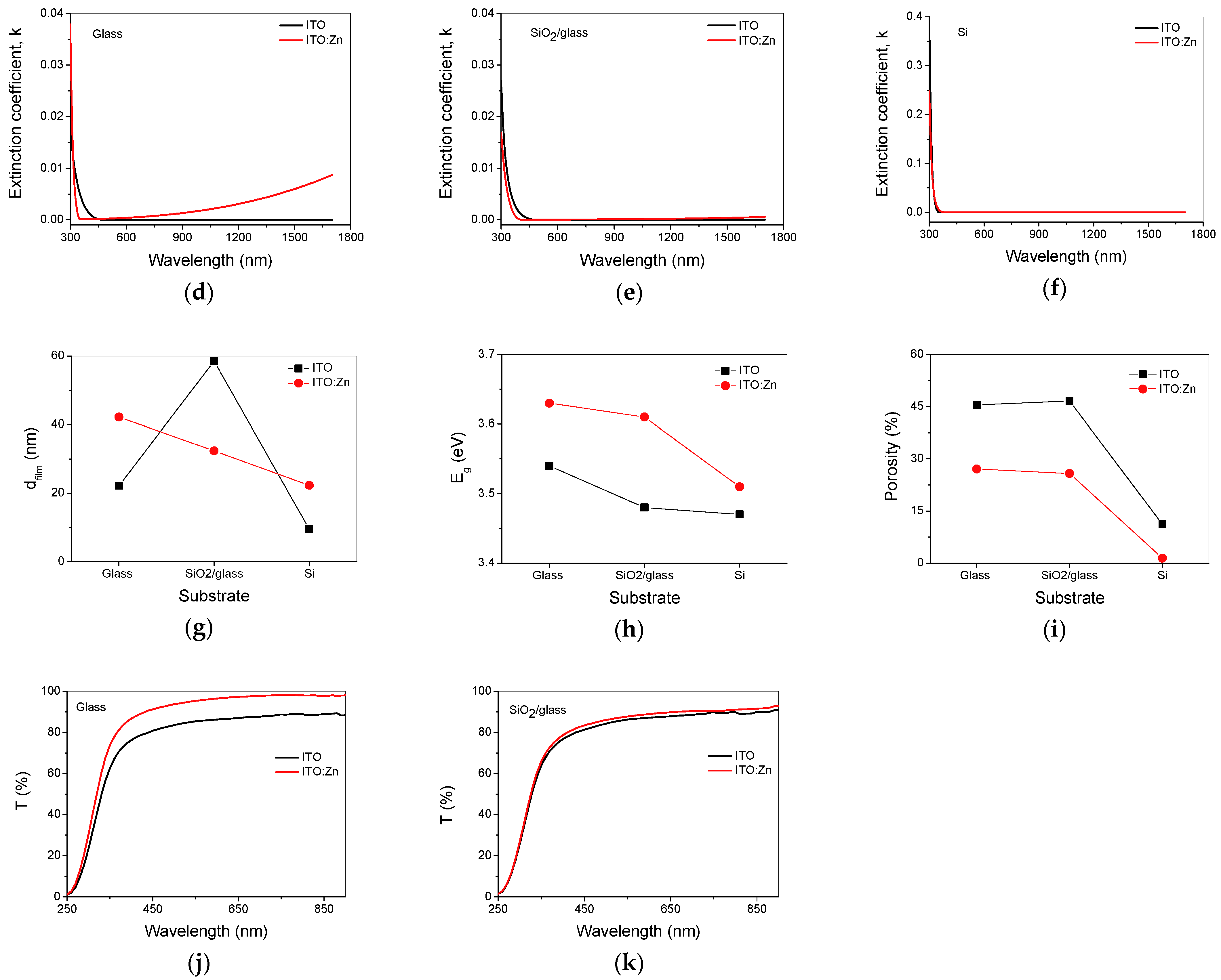
3.6. Optical Characterization
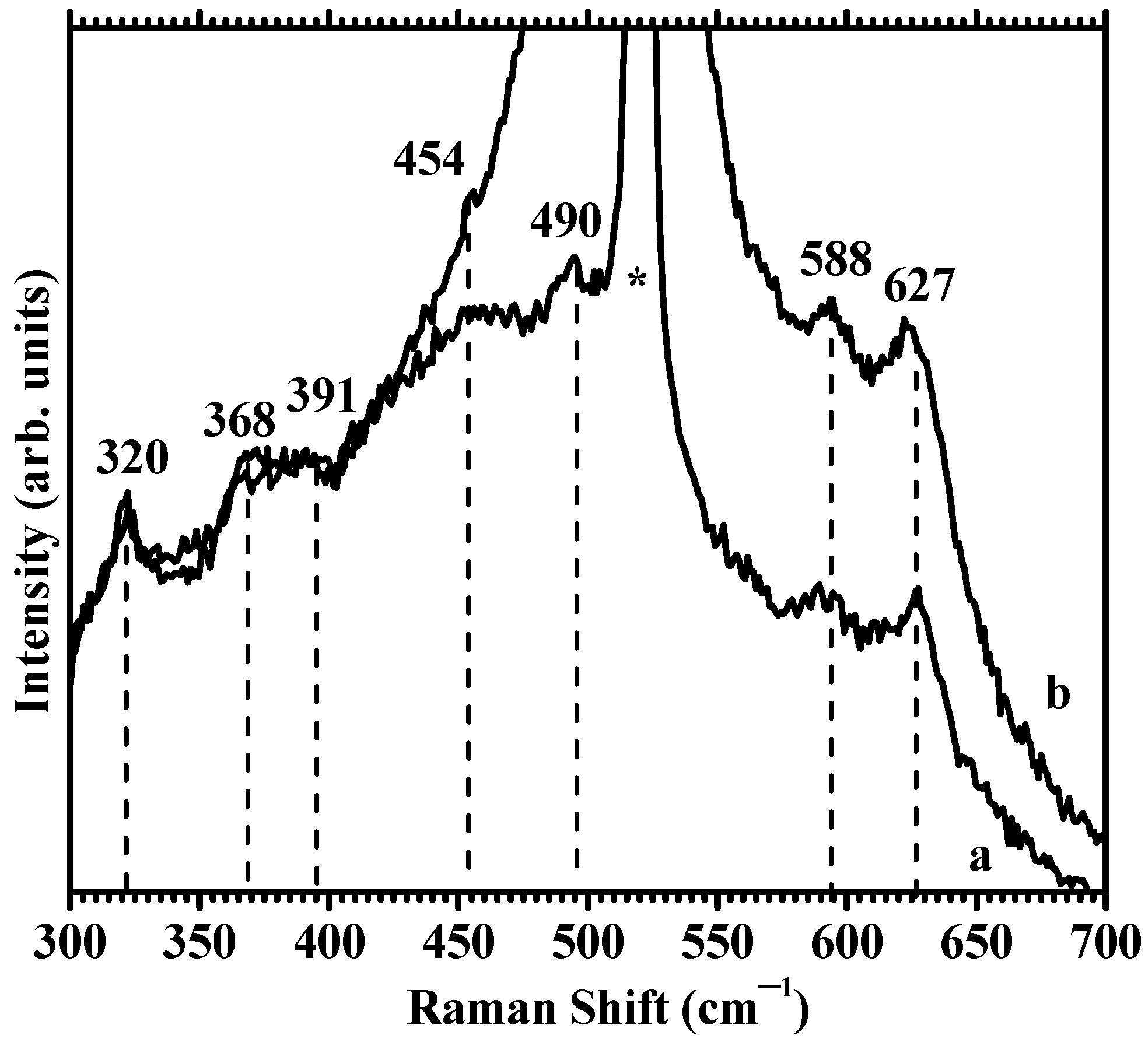
3.7. Raman Spectroscopy
3.8. Electrical Characterization (HE Measurements)
3.9. Impedance Spectroscopy Measurements
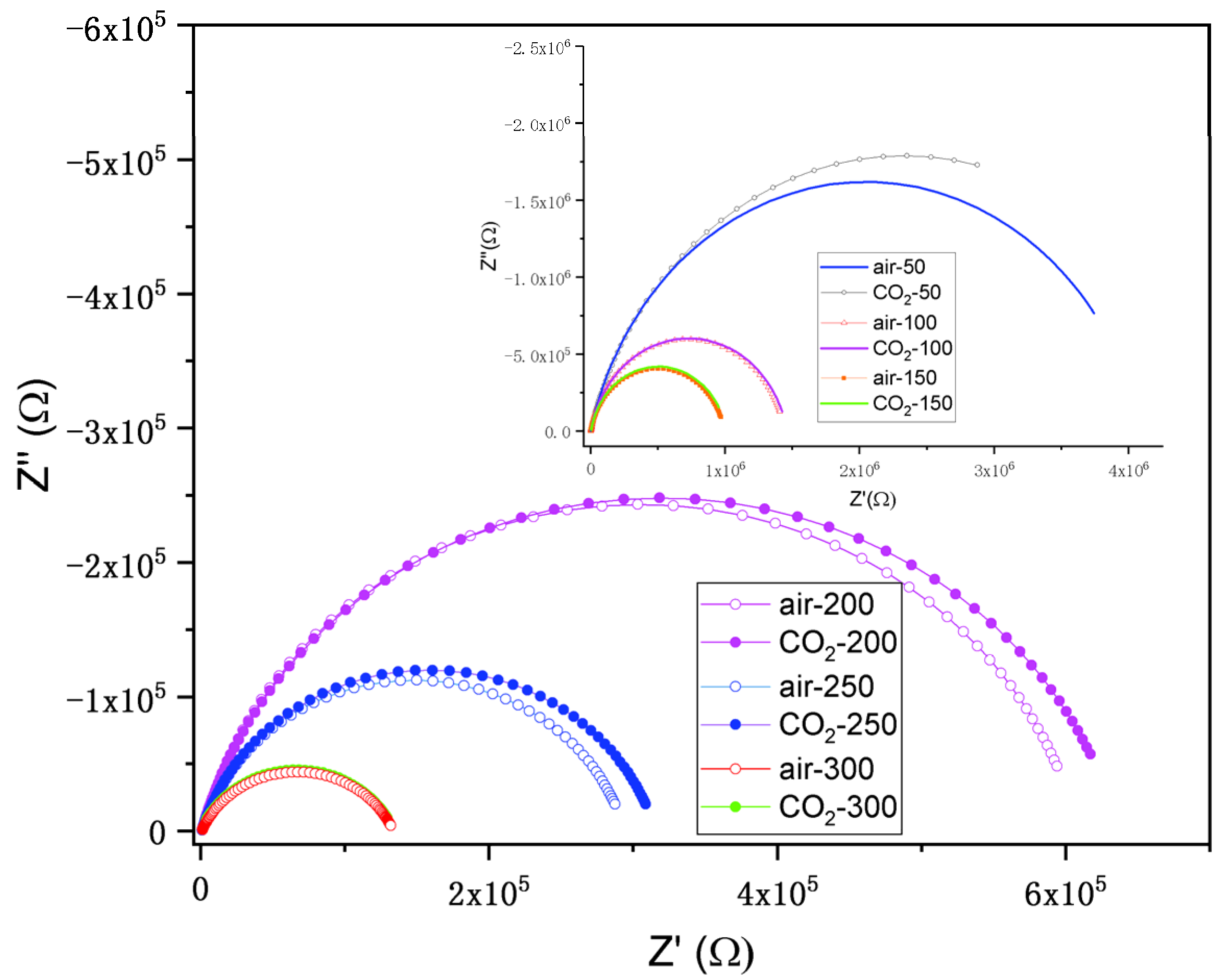
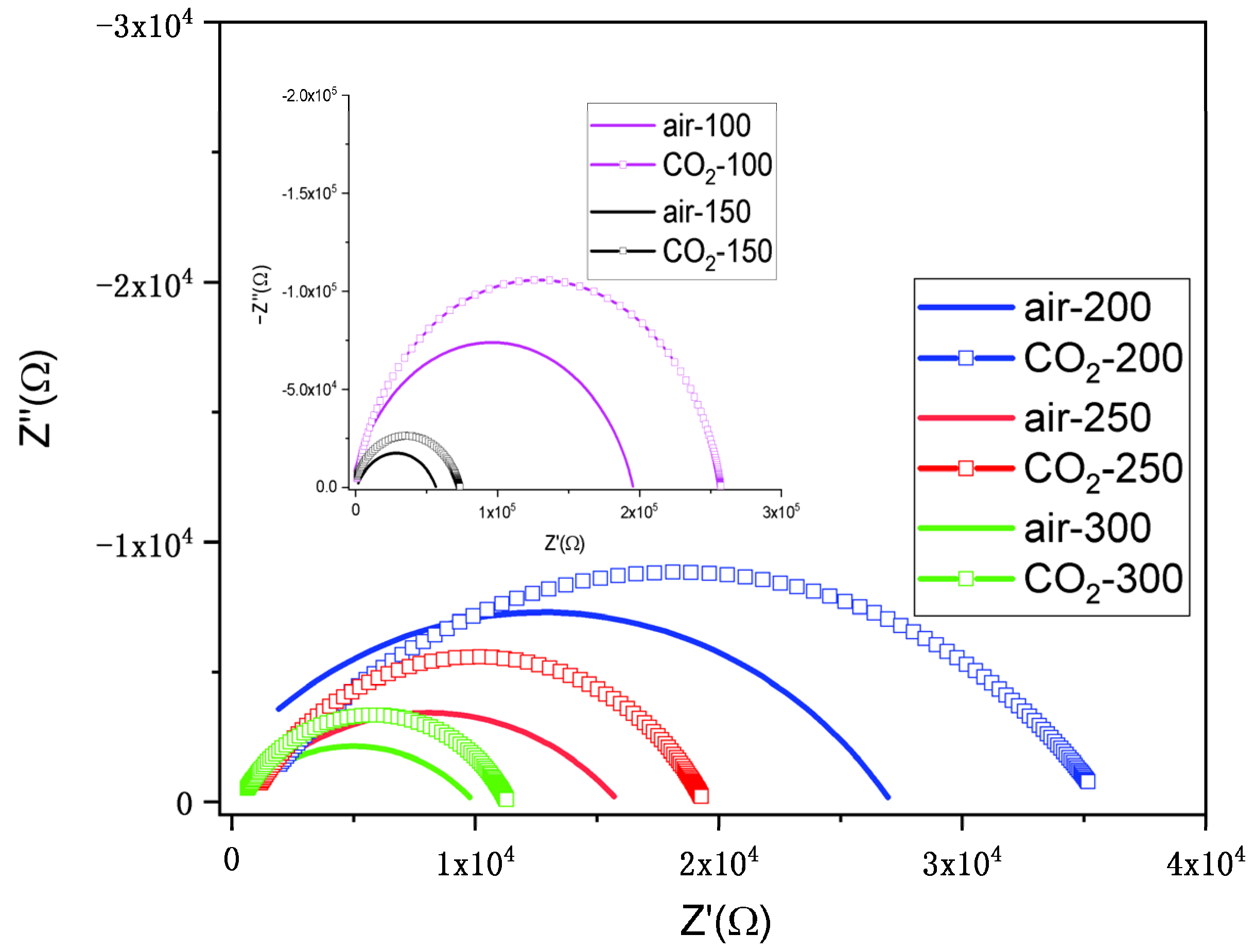
3.9.1. Nyquist Plots and Equivalent Circuit
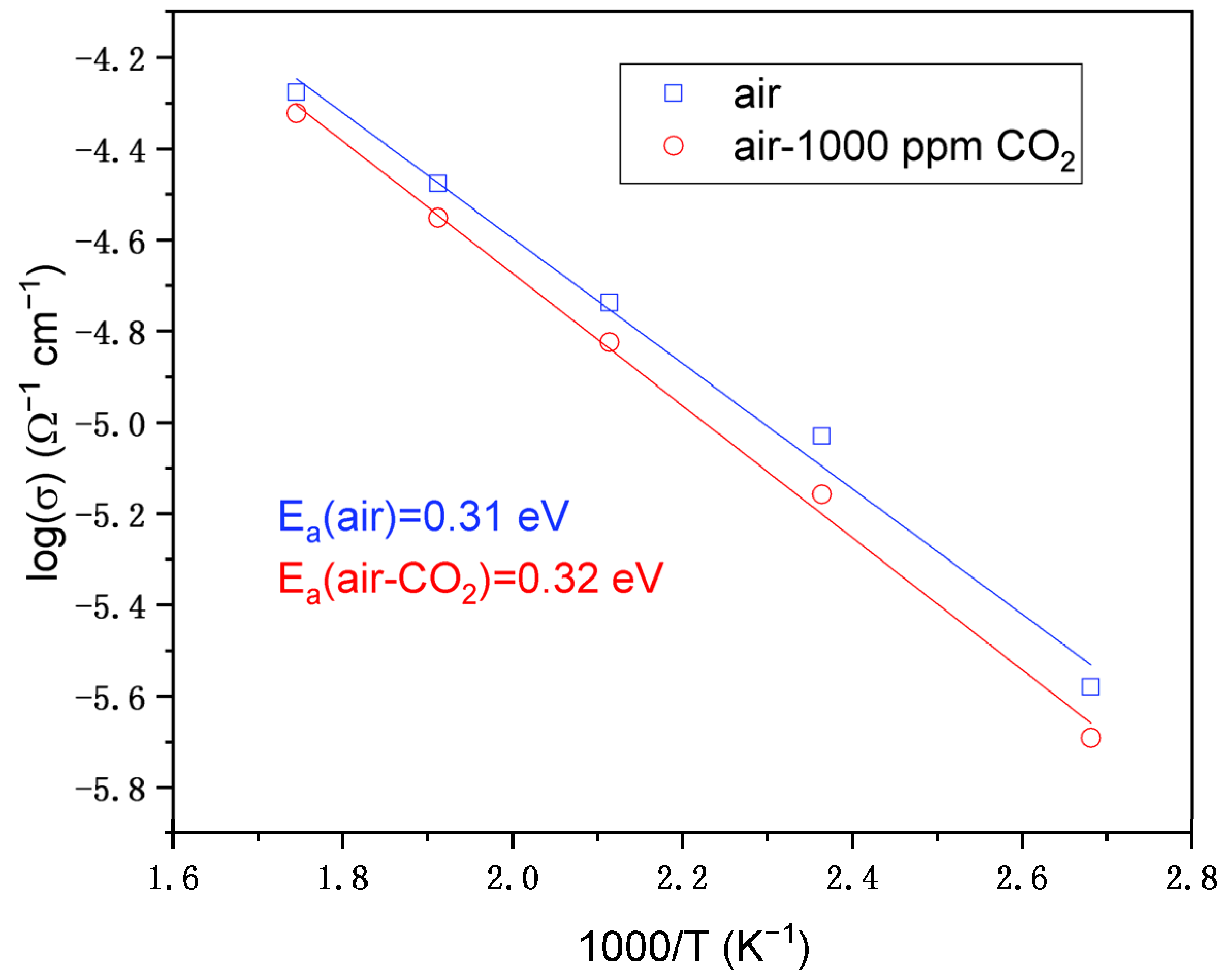
3.9.2. Activation Energy
3.9.3. Electrical Response to the CO2 Sensing Gas
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lunt, R.R.; Bulovic, V. Transparent, near-infrared organic photovoltaic solar cells for window and energy-scavenging applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 113305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, W.; Chu, A. ITO distributed Bragg reflectors fabricated at low temperature for light-trapping in thin-film solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 120, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H.; Ibrahim, K.; Rahman, M.M.; Henry, D.J.; Yin, C.Y.; Veder, J.P.; Amri, A.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z.T. Sol-gel derived ITO-based bi-layer and tri-layer thin film coatings for organic solar cells applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 530, 147164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Cho, E.S.; Kwon, S.J. Laser direct patterning of the T-shaped ITO electrode for high-efficiency alternative current plasma display panels. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaufrey, D.; Ben Khalifa, M.; Besland, M.P.; Tardy, J.; Sandu, C.; Blanchin, M.G.; Roger, J.A. Electrical and optical characteristics of indium tin oxide thin films deposited by cathodic sputtering for top emitting organic electroluminescent devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 21, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Chon, B.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jeoung, S.C.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.I.; Chu, H.Y.; Kim, H.R. Ultrafast laser ablation of indium tin oxide thin films for organic light-emitting diode application. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2006, 44, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.P.; Park, W.H.; Song, J.K.; Kim, S.S. High-performance ITO thin films for on-cell touch sensor of foldable OLED displays. J. Inf. Disp. 2021, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; Tu, W.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Pei, Y.; Wang, G. High mobility indium tin oxide thin film and its application at infrared wavelengths: Model and experiment. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 22123–22134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, F. Solution assisted roll-coating of transparent conducting oxide thin films for organic photovoltaic applications. Thin Solid Films 2019, 677, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, I.; Bouzid, B.; Saadoun, M.; Bessaïs, B. Synthesis and characterization of ITO–ZnO nanocomposite and its application as NO2 gas sensor. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 6552–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matatagui, D.; Fernandez, M.; Fontecha, J.; Santos, J.; Sayago, I.; Horrillo, C.; Gracia, I.; Lozano, J. Love wave toluene sensor based on multi-guiding layers. In Proceedings of the 2017 Spanish Conference on Electron Devices (CDE), Barcelona, Spain, 8–10 February 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslik, J.; Kuritka, I.; Urbanek, P.; Krcmar, P.; Suly, P.; Masar, M.; Machovsky, M. Water-Based Indium Tin Oxide Nanoparticle Ink for Printed Toluene Vapours Sensor Operating at Room Temperature. Sensors 2018, 18, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VasanthiPillay, V.; Vijayalakshmi, K. Effect of rf power on the structural properties of indium tin oxide thin film prepared for application in hydrogen gas sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2012, 24, 1895–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Usha, S.P.; Gupta, B.D. A lossy mode resonance-based fiber optic hydrogen gas sensor for room temperature using coatings of ITO thin film and nanoparticles. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 045103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, S.; Çoban, O.; Shafai, C.; Tüzemen, S.; Gur, E. Growth conditions effects on the H2 and CO2 gas sensing properties of Indium Tin Oxide. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2016, 707, 12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, A.; Sohn, H.Y. Plasma-assisted chemical vapor synthesis of indium tin oxide (ITO) nanopowder and hydrogen-sensing property of ITO thin film. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 065045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarek, H.; Saadoun, M.; Bessaïs, B. Screen-printed Tin-doped indium oxide (ITO) films for NH3 gas sensing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Chen, H.I.; Chen, T.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Hsu, C.S.; Liu, R.C.; Liu, W.C. On an indium–tin-oxide thin film based ammonia gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Chen, H.I.; Chen, T.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Hsu, C.S.; Liu, W.C. Ammonia Sensing Characteristics of Sputtered Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Thin Films on Quartz and Sapphire Substrates. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2011, 58, 4407–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Kumari, D.; Gupta, B.D. Surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic ammonia gas sensor using ITO and polyaniline. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Kumar, A. Low concentration ammonia sensing performance of Pd incorporated indium tin oxide. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 780, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Gupta, B.D. Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based Fiber Optic Chlorine Gas Sensor Utilizing Indium-Oxide-Doped Tin Oxide Film. J. Light. Technol. 2015, 33, 2770–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdikas, A.; Martūnas, Z.; Šetkus, A. SnInO-based chlorine gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1992, 7, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Lee, K. Development of SAW-based multi-gas sensor for simultaneous detection of CO2 and NO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 154, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Motohi, S.; Matsushima, S. NO2 and CO2 Sensing Properties of LISICON-Based Sensor Operative at Room Temperature. Sens. Mater. 2012, 24, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Madhi, I.; Saadoun, M.; Bessais, B. Impedance Spectroscopy Study of Porous ITO Based Gas Sensor. Procedia Eng. 2012, 47, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, M.; Salehi, A.; Miripour, Z.S. Comparing different ITO-metal thin film structures for ethanol and carbon dioxide sensing application. Sens. Rev. 2018, 38, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrushin, A.S.; Fisenko, N.A.; Gorobtsov, P.Y.; Simonenko, T.L.; Glumov, O.V.; Melnikova, N.A.; Simonenko, N.P.; Bukunov, K.A.; Simonenko, E.P.; Sevastyanov, V.G.; et al. Pen plotter printing of ITO thin film as a highly CO sensitive component of a resistive gas sensor. Talanta 2020, 221, 121455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, B.M.; Vadivel, S. High performance humidity sensing properties of indium tin oxide (ITO) thin films by sol–gel spin coating method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 28, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.C.; Agrahari, K.; Singh, S.; Yadav, T.P. Fabrication and characterization of nanostructured indium tin oxide film and its application as humidity and gas Sensors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 4172–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.M.; Su, Y.K.; Chu, C.J.; Yang, R.Y.; Huang, R.M. Effects of Annealing Temperature of Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films Prepared onto Glass by Sol-Gel Spin Coating Method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 343–344, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzüak, G.D.; Coşkun, D. The effect of annealing on the structural, electrical, optical and electrochromic properties of indium-tin-oxide films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering technique. Optik 2017, 142, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachatryan, H.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.K. Roll-to-Roll fabrication of ITO thin film for flexible optoelectronics applications: The role of post-annealing. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 88, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Yang, C.; Zhang, D.; Jin, D.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, H. Effects of ambient high-temperature annealing on microstructure, elemental composition, optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 276, 115534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, S.Y.; Nautiyal, A.; Lee, S.J. Optoelectronic Properties of Indium–Tin Oxide Films Deposited on Flexible and Transparent Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Substrate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 115801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Jung, S.K.; Lee, S.Y. Properties of ITO films deposited on paper sheets using a low-frequency (60 Hz) DC-pulsed magnetron sputtering method. Vacuum 2021, 187, 110056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isiyaku, A.K.; Ali, A.H.; Abdu, S.G.; Tahan, M.; Raship, N.A.; Bakri, A.S.; Nayan, N. Improvement of transparent conductive indium tin oxide based multilayer films on p-silicon through the inclusion of thin copper-aluminium metals interlayer. Thin Solid Films 2021, 738, 138959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchenka, A.; Agdad, A.; Vall, M.C.S.; Hnawi, S.K.; Narjis, A.; Nkhaili, L.; Ibnouelghazi, E.; Ech-Chamikh, E. Effect of RF Sputtering Power and Deposition Time on Optical and Electrical Properties of Indium Tin Oxide Thin Film. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5556305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Gerhardt, A.R. Fabrication and characterization of highly transparent and conductive indium tin oxide films made with different solution-based methods. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 116408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamari, F.; Raoufi, D.; Arjomandi, J. Influence of thickness on crystallographic, stereometric, optoelectronic, and electrochemical characteristics of electron-beam deposited indium tin oxide thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 260, 124051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, T.H.; Yu, S.J.; Guo, P.C.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, Z.S. Effect of sputtering pressure on the optical and electrical properties of ITO film on fluorphlogopite substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 559, 149968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, D.; Bhattacharjee, S. Optical, structural, and electrical properties of modified indium-tin-oxide (ITO) films on glass surface by low energy ion implantation. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanauskas, R.; Iljinas, A.; Marcinauskas, L.; Milieška, M.; Kavaliauskas, Ž.; Gecevičius, G.; Čapas, V. Deposition and Application of Indium-Tin-Oxide Films for Defrosting Windscreens. Coatings 2022, 12, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Shiro, T.; Yatabe, T. Optimization and Properties of Zn Doped Indium Oxide Films on Plastic Substrate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, N.W.; Liu, W.S.; Cheng, H.M.; Hu, H.C.; Hsieh, W.T.; Yu, H.W.; Liang, S.C. Investigation of the Optoelectronic Properties of Ti-doped Indium Tin Oxide Thin Film. Materials 2015, 8, 6471–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H.; Jiang, Z.T.; Henry, D.J.; Amri, A.; Yin, C.Y.; Alias, A.B.; Zhao, X. Improved mechanical properties of sol-gel derived ITO thin films via Ag doping. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 14, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Liang, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Liu, C. Solution-processed ITO thin-film transistors with doping of gallium oxide show high on-off ratios and work at 1 mV drain voltage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 141604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.L.; Jo, J.H.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, S.H. Electrically Tunable Solution-Processed Transparent Conductive Thin Films Based on Colloidally Dispersed ITO@Ag Composite Ink. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.; Butt, M.; Muneer, I.; Bashir, F.; Saleem, M. Correlation between structural and optoelectronic properties of tin doped indium oxide thin films. Optik 2016, 128, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghemid, M.; Gueddaoui, H.; Hemissi, M.; Khelladi, M.; Bourzami, R. Thickness effect on structural, optoelectronic properties and photocatalytic activity of low-cost spin-coated In2O3 films. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 784, 139089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Kanatzidis, M.G.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J. Low-temperature fabrication of high-performance metal oxide thin-film electronics via combustion processing. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, G.S.; Kim, E. Dependence of the Structural and Electrical Properties of Co-Sputtered Zn-Doped ITO Thin Films on the Composition and Oxygen Partial Pressure. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2013, 50, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.J.; Heo, G.S.; Park, J.C.; Woo, J.J. Effect of zinc content on the refractive index of Co-sputtered Zn-doped ITO films. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 7277–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, G.S.; Gim, I.G.; Lee, H.K.; Song, J.H.; Kim, T.W. Investigation of Bending Stability of Amorphous Zn–In–Sn-O Thin Films on Flexible Poly(ether sulfone) Substrates. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 031104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Yang, I.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Jin, S.H.; Kim, S.; Song, P.K. Thermoelectric Properties of Zinc-Doped Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films Prepared Using the Magnetron Co-Sputtering Method. Coatings 2019, 9, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Kim, H.S.; Ha, Y.G.; He, J.; Kanatzidis, M.G.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J. High-Performance Solution-Processed Amorphous Zinc−Indium−Tin Oxide Thin-Film Transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10352–10364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghemid, M.; Gueddaoui, H.; Brahimi, R.; Trari, M. Simple and effective synthesis via sol–gel of Zn-doped ITO films and their microstructural, optical, and photoelectrochemical properties. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolescu, M.; Anastasescu, M.; Calderon-Moreno, J.; Maraloiu, A.; Teodorescu, V.; Preda, S.; Predoana, L.; Zaharescu, M.; Gartner, M. Optical, microstructural and vibrational properties of sol–gel ITO films. Opt. Mater. 2021, 114, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predoana, L.; Preda, S.; Nicolescu, M.; Anastasescu, M.; Calderon-Moreno, J.M.; Duta, M.; Gartner, M.; Zaharescu, M. Influence of the substrate type on the microstructural, optical and electrical properties of sol–gel ITO films. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 71, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, M.; Stroescu, H.; Marin, A.H.; Osiceanu, P.; Anastasescu, M.; Stoica, M.; Nicolescu, M.; Duta, M.; Preda, S.; Aperathitis, E.; et al. Effect of nitrogen incorporation on the structural, optical and dielectric properties of reactive sputter grown ITO films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 313, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duta, M.; Anastasescu, M.; Calderon-Moreno, J.M.; Predoana, L.; Preda, S.; Nicolescu, M.; Stroescu, H.; Bratan, V.; Dascalu, I.; Aperathitis, E.; et al. Sol–gel versus sputtering indium tin oxide films as transparent conducting oxide materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 4913–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroescu, H.; Anastasescu, M.; Preda, S.; Nicolescu, M.; Stoica, M.; Stefan, N.; Kampylafka, V.; Aperathitis, E.; Modreanu, M.; Zaharescu, M.; et al. Influence of thermal treatment in N2 atmosphere on chemical, microstructural and optical properties of indium tin oxide and nitrogen doped indium tin oxide rf-sputtered thin films. Thin Solid Films 2013, 541, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duta, M.; Predoana, L.; Calderon-Moreno, J.; Preda, S.; Anastasescu, M.; Marin, A.H.; Dascalu, I.; Chesler, P.; Hornoiu, O.C.; Zaharescu, M.; et al. Nb-doped TiO 2 sol–gel films for CO sensing applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 42, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://meersens.com/qualite-de-lair-interieur-limpact-du-co2-sur-la-sante-et-le-bien-etre-au-travail/ (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- González, G.B. Investigating the Defect Structures in Transparent Conducting Oxides Using X-ray and Neutron Scattering Techniques. Materials 2012, 5, 818–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, H.G. WVASE32® Software Manual; J.A. Woollam Co. Inc.: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bruggeman, D.A.G. Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Substanzen. III. Die elastischen Konstanten der quasiisotropen Mischkörper aus isotropen Substanzen. Ann. Phys. 1937, 421, 160–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi B 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajihara, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Tanaka, K.; Hirao, K.; Soga, N. Preparation of Macroporous Titania Films by a Sol-Gel Dip-Coating Method from the System Containing Poly(ethylene glycol). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 81, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Keramidas, V.G. Vibrational spectra of oxides with the C-type rare earth oxide structure. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Spectrosc. 1972, 28, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.P.; Sunder, W.A.; Griffiths, J.E. The In-P-O Phase Diagram: Construction and Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1982, 129, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Dai, Y.; Pezoldt, J.; Lu, B.; Kups, T.; Cimalla, V.; Ambacher, O. Phase Stabilization and Phonon Properties of Single Crystalline Rhombohedral Indium Oxide. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, A.H.; Shah, M.A.; Asokan, K. Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of ITO Thin Films. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 47, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berengue, O.M.; Rodrigues, A.D.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Lanfredi, A.J.C.; Leite, E.R.; Chiquito, A.J. Structural characterization of indium oxide nanostructures: A Raman analysis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 045401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, J.M.; Cardona, M. Resonant Raman scattering in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 1977, 16, 3753–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonoberov, V.A.; Balandin, A.A. Interface and confined optical phonons in wurtzite nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 233205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demangeot, F.; Paillard, V.; Chassaing, P.M.; Pagès, C.; Kahn, M.L.; Maisonnat, A.; Chaudret, B. Experimental study of LO phonons and excitons in ZnO nanoparticles produced by room-temperature organometallic synthesis. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 071921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkoc, H.; Özgür, Ü. Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., Ltd. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Buchholz, D.B.; Ma, Q.; Alducin, D.; Ponce, A.; Jose-Yacaman, M.; Khanal, R.; Medvedeva, J.E.; Chang, R.P.H. The Structure and Properties of Amorphous Indium Oxide. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5401–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Kondo, M. Effects of carrier concentration on the dielectric function of ZnO:Ga and In2O3:Sn studied by spectroscopic ellipsometry: Analysis of free-carrier and band-edge absorption. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 075109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, M.; Dolati, A. Effects of tin valence on microstructure, optical, and electrical properties of ITO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 75, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhu, G.S.; Xu, H.R.; Jiang, X.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yan, D.L.; Yuan, L.; Yu, A.B. Preparation of indium tin oxide (ITO) thin film with (400) preferred orientation by sol–gel spin coating method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 8047–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-del-Solar, M.; Blanco, E. Porous Thin Films from Sol-Gel. In Submicron Porous Materials; Bettotti, P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 157–188. ISBN 978-3-319-53035-2. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, C.; Hurd, A.; Schunk, P.; Frye, G.; Ashley, C. Review of sol-gel thin film formation. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 1992, 147–148, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dislich, H. New Routes to Multicomponent Oxide Glasses. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1971, 10, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguerá, M.; Calzada, M.L.; Pardo, L.; Snoeck, E. Combined effect of grain size and tensile stresses on the ferroelectric properties of sol-gel (Pb,La)TiO3 thin films. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 4570–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretos, I.; Jiménez, R.; Ricote, J.; Calzada, M.L. Photochemistry in the Low-Temperature Processing of Metal Oxide Thin Films by Solution Methods. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 9277–9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Cheng, H. Fabrication of Highly Transparent and Conductive Indium–Tin Oxide Thin Films with a High Figure of Merit via Solution Processing. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13836–13842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, M.; Hwang, D.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Myoung, J.M.; Lee, T.I. Eco-friendly method of fabricating indium-tin-oxide thin films using pure aqueous sol-gel. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 2927–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| In (%) | Sn (%) | Zn (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITO | 84 | 16 | 0 |
| ITO:Zn | 81 | 15 | 4 |
| Sample Name | 2θ (°) | d (Å) | FWHM (°) | D (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2/Glass | ||||
| ITO | 30.68 (5) | 2.912 (4) | 0.77 (5) | 112 (7) |
| ITO:Zn | 30.84 (2) | 2.897 (2) | 0.94 (2) | 91 (2) |
| Si (100) | ||||
| ITO | 30.70 (5) | 2.910 (4) | 0.82 (5) | 104 (6) |
| ITO:Zn | 30.82 (3) | 2.899 (2) | 0.94 (2) | 92 (2) |
| Glass | ||||
| ITO | 30.73 (7) | 2.907 (6) | 0.90 (7) | 95 (7) |
| ITO:Zn | 30.83 (3) | 2.898 (3) | 0.95 (3) | 91 (3) |
| Sample | Substrate | ρ (×10−2 Ω·cm) | µ (cm2/V·s) | N (×1019 cm−3) | σ (1/Ω·cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE | SE | HE | SE | HE | SE | HE | SE | ||
| ITO:Zn | Glass | 1.32 | 1.46 | 9.49 | 14.63 | 3.53 | 2.91 | 75.75 | 68.49 |
| SiO2/glass | 1.77 | 5.42 | 16.67 | 9.06 | 3.9 | 1.26 | 56.49 | 18.45 | |
| Si | 2.31 | 2.56 | 9.50 | 10.56 | 3.83 | 2.30 | 43.29 | 39.06 | |
| ITO | Glass | 2.83 | 2.31 | 11.2 | 7.26 | 1.18 | 3.18 | 35.33 | 43.29 |
| SiO2/glass | 2.91 | 2.51 | 15.6 | 8.72 | 5.38 | 3.02 | 34.36 | 39.84 | |
| Si | 4.36 | 2.17 | 12.2 | 9.55 | 7.17 | 3.01 | 22.93 | 46.08 | |
| Sample | Substrate | Average Transmittance (%) | Resistivity (10−2 Ω·cm) | Mobility (cm2/V·s) | Carrier Concentration (1019 cm−3) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITO | Glass | >85 | 70 | 7.6 | 0.61 | [81] |
| ITO | Glass | 74 | 9.24 | * | * | [49] |
| ITO | Glass | >85 | 0.41 | 14.8 | 10.2 | [82] |
| ITO | Glass | 77 | * | 1.99 | 3.6 | [57] |
| Zn-doped ITO | Glass | >80 | * | 1.01 | 4.3 | [57] |
| ITO | Glass | 80 | 2.83 | 11.2 | 3.01 | This work |
| Zn-doped ITO | Glass | 90 | 1.32 | 9.49 | 2.91 |
| Gaseous Atmosphere/Temperature | Rp | CPE-T | CPE-P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air/100 °C | 199,180 | 9.02 × 10−11 | 0.81381 |
| Air/150 °C | 56,072 | 1.83 × 10−9 | 0.7087 |
| Air/200 °C | 28,605 | 5.58 × 10−9 | 0.60087 |
| Air/250 °C | 15,693 | 3.97 × 10−8 | 0.52506 |
| Air/300 °C | 9886 | 9.50 × 10−8 | 0.5201 |
| Air–1000 ppm CO2/100 °C | 257,480 | 5.50 × 10−11 | 0.87624 |
| Air–1000 ppm CO2/150 °C | 75,274 | 2.12 × 10−10 | 0.77648 |
| Air–1000 ppm CO2/200 °C | 34,974 | 1.77 × 10−8 | 0.59574 |
| Air–1000 ppm CO2/250 °C | 18,648 | 8.24 × 10−9 | 0.68611 |
| Air–1000 ppm CO2/300 °C | 10,988 | 9.64 × 10−9 | 0.69566 |
| Temperature (°C) | Response (RCO2/Rair) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 1.29 |
| 150 | 1.34 |
| 200 | 1.22 |
| 250 | 1.19 |
| 300 | 1.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gartner, M.; Anastasescu, M.; Calderon-Moreno, J.M.; Nicolescu, M.; Stroescu, H.; Hornoiu, C.; Preda, S.; Predoana, L.; Mitrea, D.; Covei, M.; et al. Multifunctional Zn-Doped ITO Sol–Gel Films Deposited on Different Substrates: Application as CO2-Sensing Material. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183244
Gartner M, Anastasescu M, Calderon-Moreno JM, Nicolescu M, Stroescu H, Hornoiu C, Preda S, Predoana L, Mitrea D, Covei M, et al. Multifunctional Zn-Doped ITO Sol–Gel Films Deposited on Different Substrates: Application as CO2-Sensing Material. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(18):3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183244
Chicago/Turabian StyleGartner, Mariuca, Mihai Anastasescu, Jose Maria Calderon-Moreno, Madalina Nicolescu, Hermine Stroescu, Cristian Hornoiu, Silviu Preda, Luminita Predoana, Daiana Mitrea, Maria Covei, and et al. 2022. "Multifunctional Zn-Doped ITO Sol–Gel Films Deposited on Different Substrates: Application as CO2-Sensing Material" Nanomaterials 12, no. 18: 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183244
APA StyleGartner, M., Anastasescu, M., Calderon-Moreno, J. M., Nicolescu, M., Stroescu, H., Hornoiu, C., Preda, S., Predoana, L., Mitrea, D., Covei, M., Maraloiu, V.-A., Teodorescu, V. S., Moldovan, C., Petrik, P., & Zaharescu, M. (2022). Multifunctional Zn-Doped ITO Sol–Gel Films Deposited on Different Substrates: Application as CO2-Sensing Material. Nanomaterials, 12(18), 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183244










