Graphene-Modified Co-B-P Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of GO
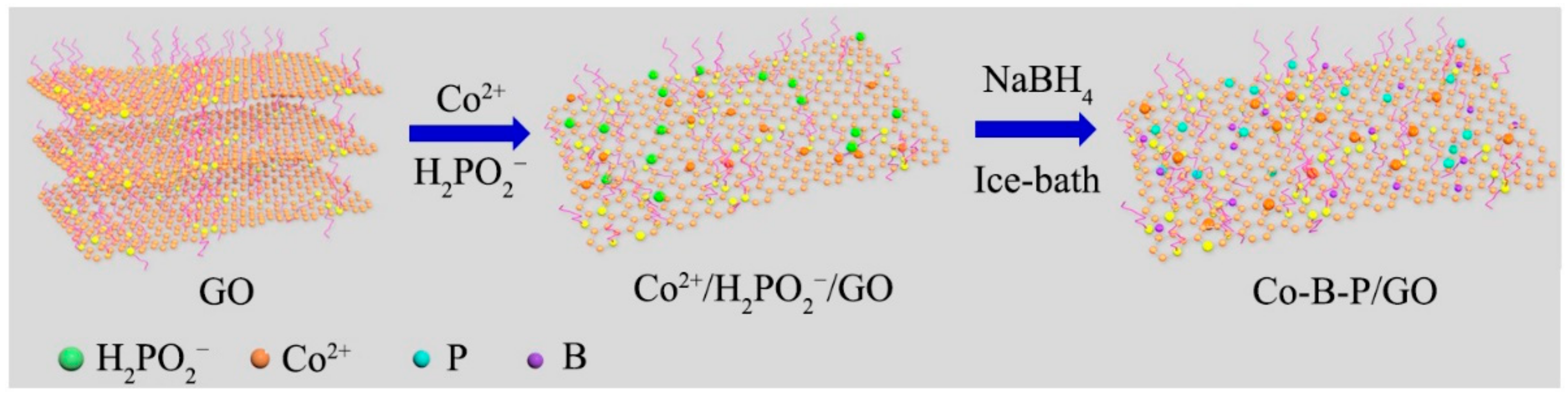
2.3. Catalyst Preparation
2.4. Catalyst Characterization
2.5. Hydrogen Generation Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
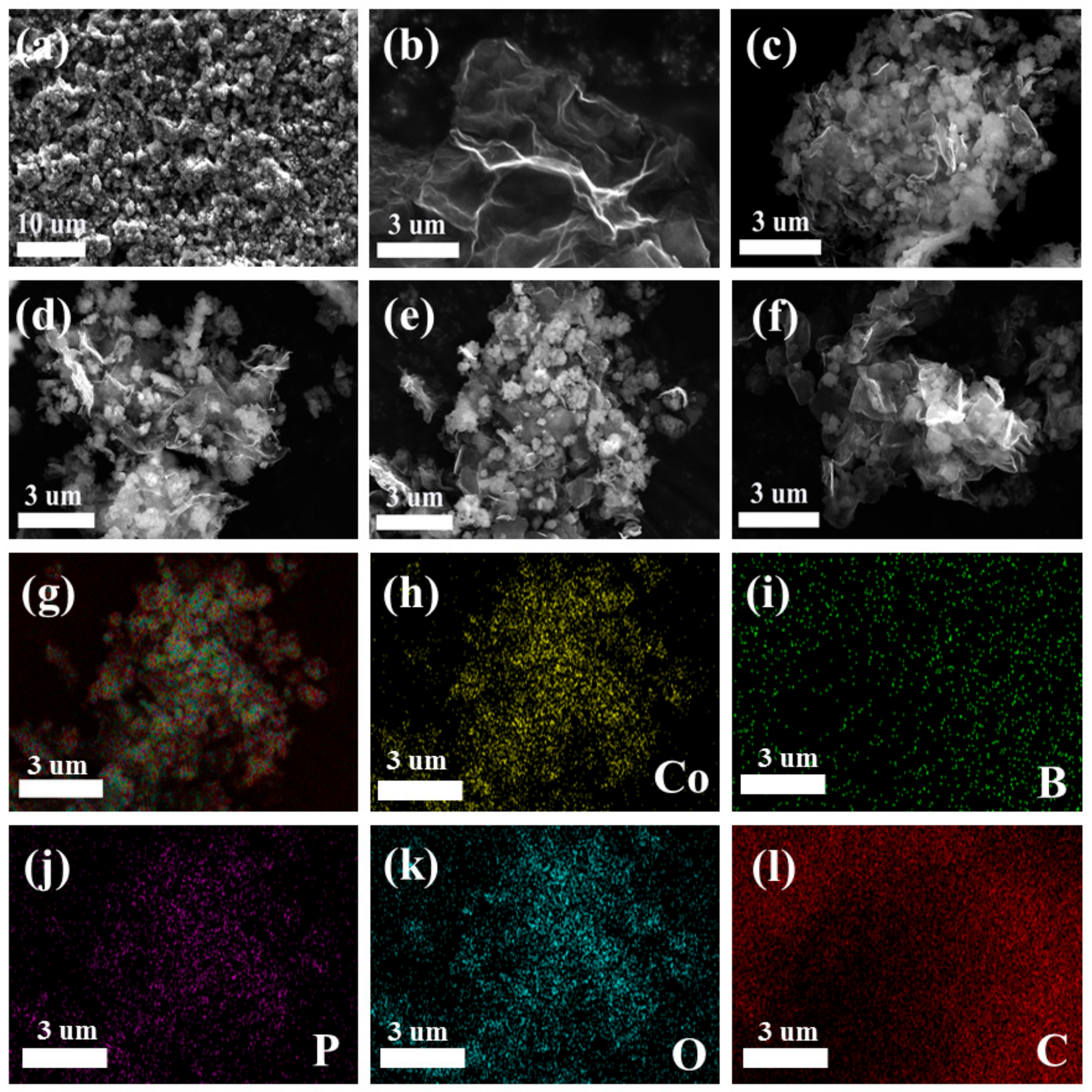
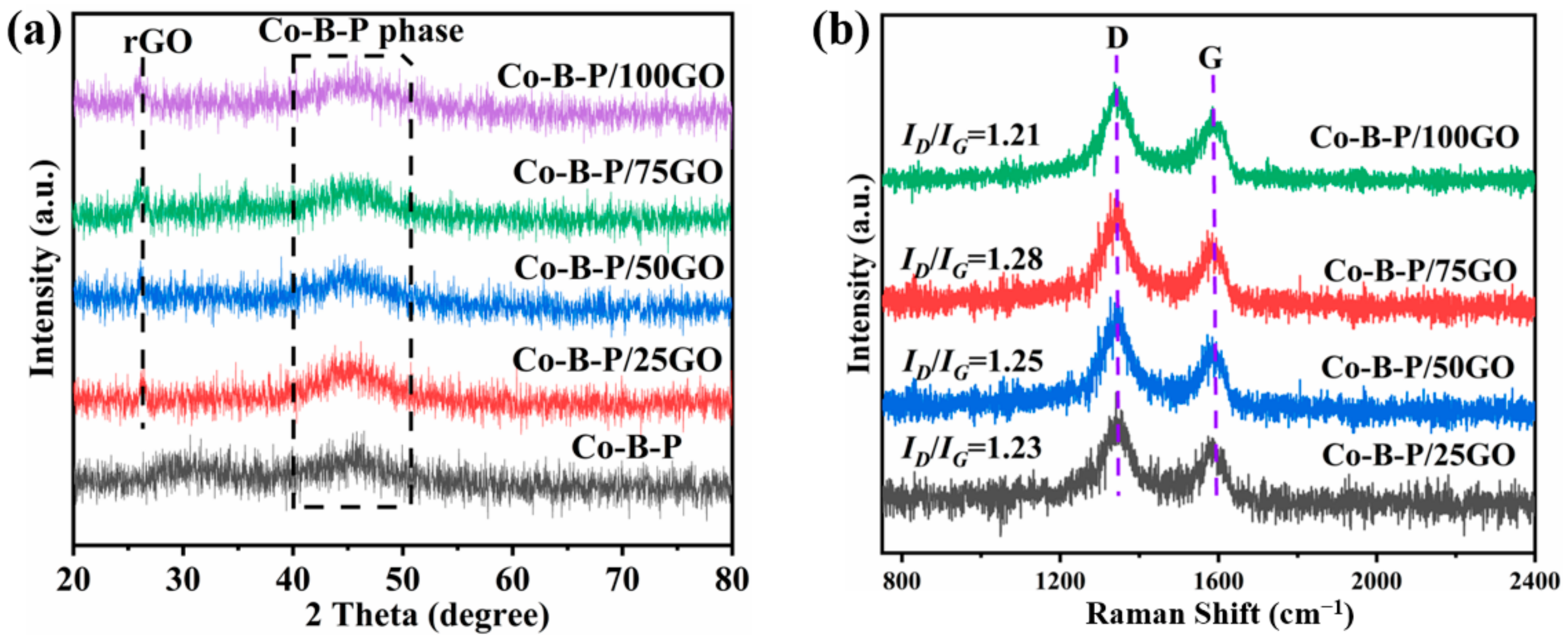
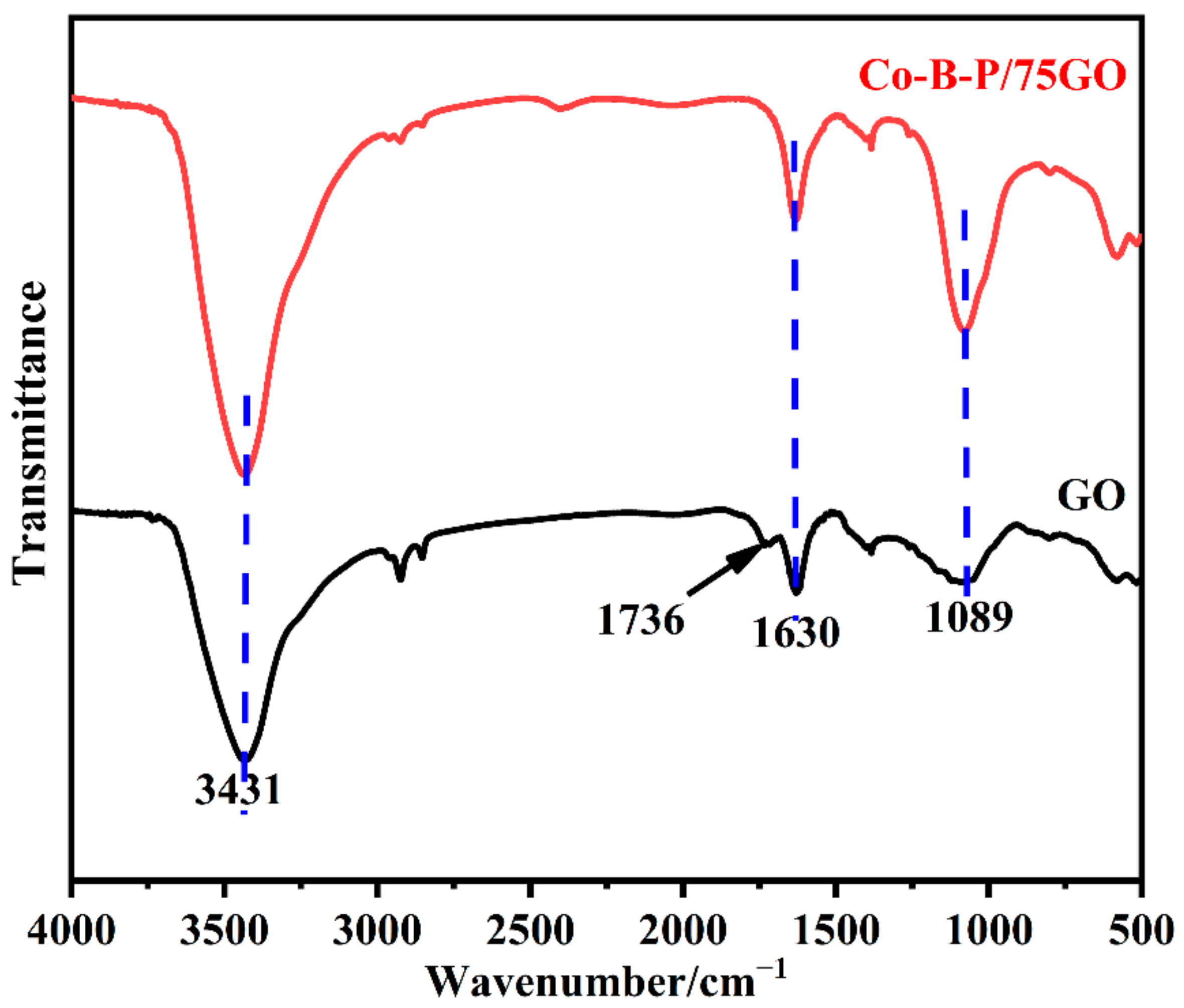
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
3.2. Effect of Different Types of Catalysts
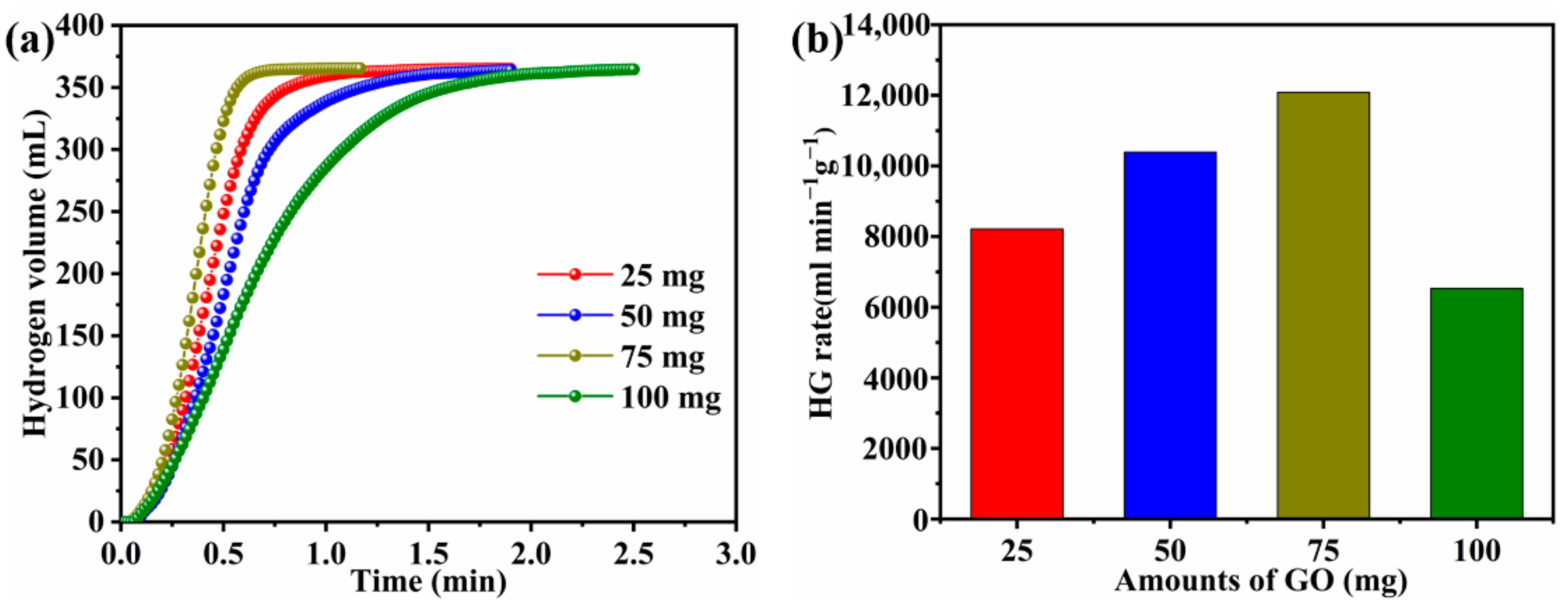
3.3. Effect of GO Amount
3.4. Effect of Catalyst Amount
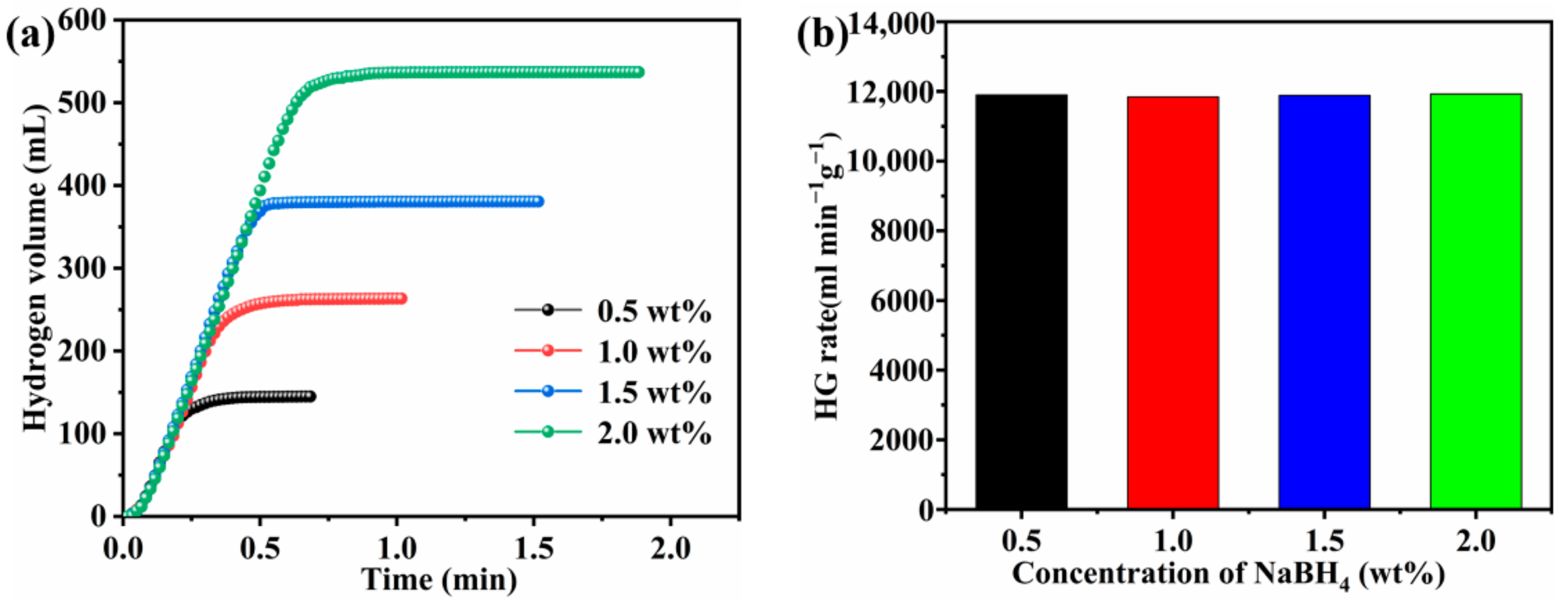
3.5. Effect of NaBH4 Concentration
3.6. Kinetic Studies at Different Temperatures
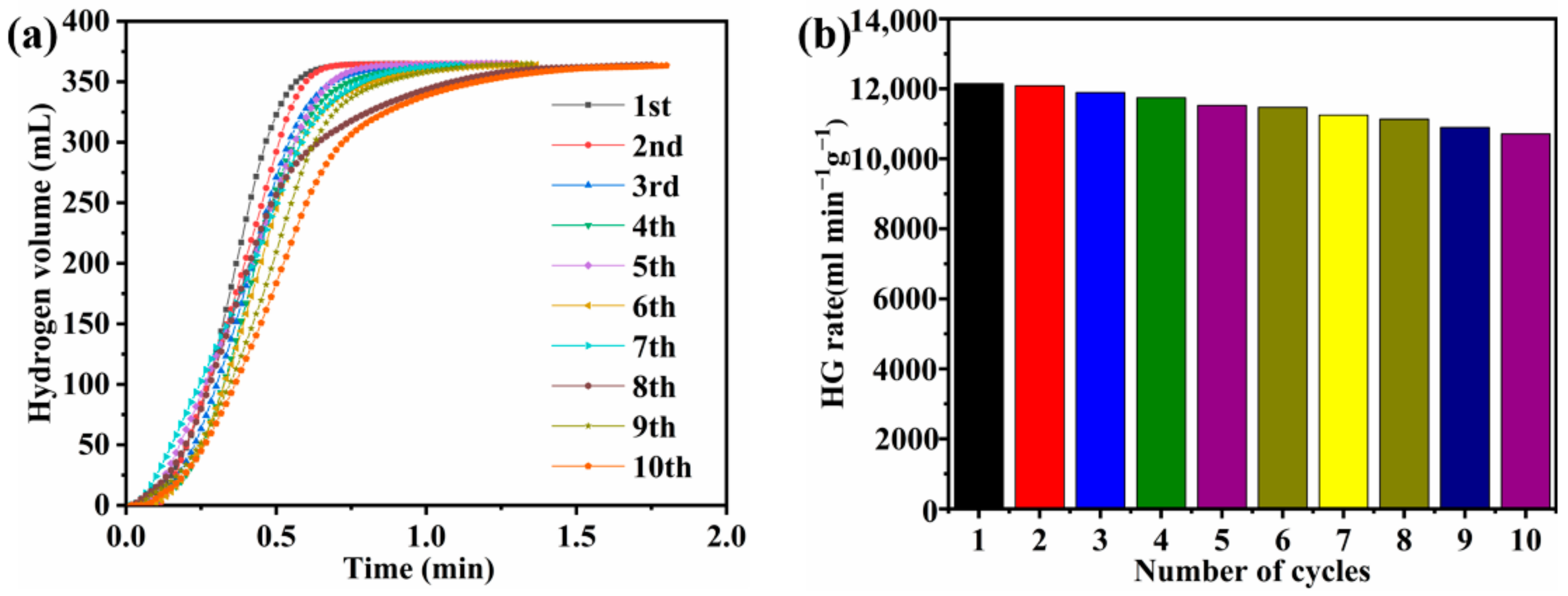
3.7. Reusability Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, Z.Q.; Yao, Z.D.; Li, R.H.; Xiao, X.Z.; Ye, Z.C.; Wang, X.C.; Qi, J.C.; Bi, J.P.; Fan, X.L.; Kou, H.Q.; et al. Regulating local chemistry in ZrCo-based orthorhombic hydrides via increasing atomic interference for ultra-stable hydrogen isotopes storage. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 69, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.T.; Yang, Y.Z.; Tao, P.J.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Wang, H. Correlation between structural stability of LiBH4 and cation electronegativity in metal borides: An experimental insight for catalyst design. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 4987–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 2001, 414, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Zhong, H.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, H.; Shao, H.Y.; Huang, Z.G.; Zhu, M. Closing the loop for hydrogen storage: Facile regeneration of NaBH4 from its hydrolytic product. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 8701–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimi, A.S.; Nohan, M.A.N.M.; Chin, S.X.; Zakaria, S.; Chia, C.H. Copper Nanowires as Highly Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst for Rapid Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride. Nanomaterials 2020, 9, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, K.L.; Wang, D.; Meng, W.; Qi, N.; Cao, Z.Q.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.H.; Li, G.D. Highly efficient hydrogen evolution from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane solution with the Co-Mo-B/NF nanocatalyst. Renew. Energy 2020, 154, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Ye, J.S.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.D.; Zhu, M. An one-step approach towards hydrogen production and storage through regeneration of NaBH4. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 7, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kong, K.Y.; Jung, C.R.; Cho, E.; Yoon, S.P.; Han, J.; Lee, T.G.; Nam, S.W. A structured Co–B catalyst for hydrogen extraction from NaBH4 solution. Catal. Today 2007, 120, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.K.; An, C.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zang, L.; Shao, H.X.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.T.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.J. Cost-effective mechanochemical synthesis of highly dispersed supported transition metal catalysts for hydrogen storage. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, L.; Rodriguez-Perez, I.A.; Miao, W.K.; Chen, K.L.; Wang, W.F.; Li, Y.; Han, S.M. Carbon nanospheres supported bimetallic Pt-Co as an efficient catalyst for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 540, 148296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Ning, H.L.; Peng, S.G.; Yu, Y.H.; Ran, C.; Chen, Y.M.; Ma, J.Y.; Xie, J.P. Surface tailored Ru catalyst on magadiite for efficient hydrogen generation. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 631, 127627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.C.; Nie, M.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Liu, H.L. Kinetics of NaBH4 hydrolysis on carbon-supported ruthenium catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 12343–12351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Ning, Z.; Tian, J.N.; Wang, H.W.; Liang, X.Y.; Nie, S.L.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.X. Hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of alkaline NaBH4 solution on Co–Mo–Pd–B amorphous catalyst with efficient catalytic properties. J. Power Sources 2012, 207, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.P.; Xia, G.L.; Sun, D.L.; Fang, F.; Yu, X.B. Magnesium hydride nanoparticles self-assembled on graphene as anode material for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3816–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Ji, W.Q.; Zhao, J.Z.; Liang, J.; Chen, J. Preparation, characterization and catalytic NaBH4 hydrolysis of Co-B hollow spheres. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 474, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, K.M.; Fan, A.Y.; Jiang, W.D. Efficient Hydrogen Generation from the NaBH4 Hydrolysis by Cobalt-Based Catalysts: Positive Roles of Sulfur-Containing Salts. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 9376–9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.J.; Xu, C.; Gao, M.; Ma, Z.L.; Meng, Y.Y.; Li, L.Q.; Hu, X.H.; Zhu, Y.F.; Pan, S.P.; Li, W. Hydrogenation properties of five-component Mg60Ce10Ni20Cu5 × 5 (X=Co, Zn) metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2019, 108, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didehban, A.; Zabihi, M.; Shahrouzi, J.R. Experimental studies on the catalytic behavior of alloy and core-shell supported Co-Ni bimetallic nano-catalysts for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20645–20660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.S.; Cho, K.W.; Kwon, H.S. Effects of electroless deposition conditions on microstructures of cobalt-phosphorous catalysts and their hydrogen generation properties in alkaline sodium borohydride solution. J. Power Sources 2008, 180, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, P.F.; Chu, D.S.; Li, H.X. Selective maltose hydrogenation to maltitol on a ternary Co-P-B amorphous catalyst and the synergistic effects of alloying B and P. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2007, 325, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Fernandes, R.; Miotello, A. Hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of NaBH4 with efficient Co-P-B catalyst: A kinetic study. J. Power Sources 2009, 188, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Zhao, J.Z.; Cheng, F.Y.; Liang, J.; Tao, Z.L.; Chen, J. Electroless-deposited Co–P catalysts for hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 8363–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, A.; Cengiz, E.; Kuncan, M.; Sahin, Ö. Hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solutions both in the presence of Ni-B catalyst and in the case of microwave application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 34749–34760. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.M.; Meng, J.; Jiao, L.F.; Cheng, F.Y.; Chen, J. A review of transition-metal boride/phosphide-based materials for catalytic hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of boron-hydrides. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.P.; Ren, Q.L.; Jiao, L.F.; Yuan, H.T. Effect of Ni Content in Co1-xNixB Catalysts on Hydrogen Generation during Hydrolysis. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2010, 26, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ö.; Karakaş, D.E.; Kaya, M.; Saka, C. The effects of plasma treatment on electrochemical activity of Co-B-P catalyst for hydrogen production by hydrolysis of NaBH4. J. Energy Inst. 2017, 90, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, X.W.; Xu, D.Y.; Tao, X.M.; Dai, P.; Guo, Q.J.; Liu, X. Synthesis of MOF-derived Co@C composites and application for efficient hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 469, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.F.; Chen, N.Q.; Chen, D.; Yang, S.Z.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, L.; Wu, P.W.; Phillip, N.; Yang, J.; Dai, S. Ultra-Stable and High-Cobalt-Loaded Cobalt@Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Catalysts: All-in-One Deoxygenation of Ketone into Alkylbenzene. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 3299–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.M.; Chen, Z.; Jian, Z.Y.; Guo, F.H.; Gao, C.L. Carbon nanotubes-promoted Co-B catalysts for rapid hydrogen generation via NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 19868–19877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Chen, M.S.; Chen, Y.W. Hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride on CoB/SiO2 catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D.; Ma, L.; Yi, B.L. Hydrogen generation utilizing alkaline sodium borohydride solution and supported cobalt catalyst. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Z.; Zheng, J.L.; Chen, T.W.; Ma, G.S.; Zhou, W. RGO-wrapped Ni-P hollow octahedrons as noble-metal-free catalysts to boost the hydrolysis of ammonia borane toward hydrogen generation. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Lu, Z.H.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.S.; Zhu, J. Highly Pt-like activity of Ni-Mo/graphene catalyst for hydrogen evolution from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 8579–8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 208, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.; Patel, N.; Miotello, A. Efficient catalytic properties of Co-Ni-P-B catalyst powders for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of alkaline solution of NaBH4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, D.Y.; Liu, K.; Dai, P.; Gao, J. Remarkable enhancement of PdAg/rGO catalyst activity for formic acid dehydrogenation by facile boron-doping through NaBH4 reduction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 512, 145746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Liu, P.L.; Wu, K.; Tan, S.; Li, W.S.; Yang, Y.Q. Preparation of hydrophobic reduced graphene oxide supported Ni-B-P-O and Co-B-P-O catalysts and their high hydrodeoxygenation activities. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.M.; Xie, W.; Jian, Z.Y.; Liao, X.M.; Wang, Y.J. Graphene modified Co-B catalysts for rapid hydrogen production from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 17954–17962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, K.Z.; Wu, S.W.; Cao, Z.Q.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Y.S.; Liu, H.X. Preparation, characterization and catalytic sodium borohydride hydrolysis of nanostructured cobalt-phosphorous catalysts. J. Power Sources 2015, 284, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.B.; Liang, Y.; Wang, P. Effect of trapped hydrogen on the induction period of cobalt-tungsten-boron/nickel foam catalyst in catalytic hydrolysis reaction of sodium borohydride. Catal. Today 2011, 170, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, G.; Anwer, S.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Alhseinat, E.; Banat, F.; Ponpandian, N. Sunlight-Induced photochemical synthesis of Au nanodots on α-Fe2O3@Reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite and their enhanced heterogeneous catalytic properties. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riahi, K.Z.; Sdiri, N.; Ennigrou, D.J.; Horchani-Naifer, K. Investigations on electrical conductivity and dielectric properties of graphene oxide nanosheets synthetized from modified Hummer’s method. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1216, 128304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, L.; Xu, H.T.; Wang, Y. Tunable and Specific Formation of C@NiCoP Peapods with Enhanced HER Activity and Lithium Storage Performance. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.J.; Yin, Y.; Gao, Y.B.; Xiang, C.L.; Chu, H.L.; Qiu, S.J.; Yan, E.H.; Xu, F.; Sun, L.X. Chitosan-mediated Co-Ce-B nanoparticles for catalyzing the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 4912–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Huang, W.; Wang, C. In situ synthesis of Ru/RGO nanocomposites as a highly efficient catalyst for selective hydrogenation of halonitroaromatics. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6819–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moddeman, W.E.; Burke, A.R.; Bowling, W.C.; Foose, D.S. Surface oxides of boron and B12O2 as determined by XPS. Surf. Interface Anal. 1989, 14, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, H.L.; Zhu, S.L.; Liang, Y.Q.; Wu, S.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Luo, S.Y.; Cui, Z.D.; Inoue, A. Highly efficient nanoporous CoBP electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Rare Metals 2021, 40, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.M.; Zhang, G. Improved Low-Temperature Activity of CuO-CeO2-ZrO2 Catalysts for Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2-Rich Streams. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.G.; Han, X.; Chu, W.; Chen, H.; Ji, X.Y. Preparation of mesoporous Co-B catalyst via self-assembled triblock copolymer templates. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4679–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ke, D.D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Wang, C.X.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y.J.; Han, S.M. Efficient hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride catalyzed by cobalt nanoparticles supported on three-dimensional graphene oxide. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 95, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Feng, X.L.; Cheng, L.; Hou, X.W.; Li, Y.; Han, S.M. Non-noble Co anchored on nanoporous graphene oxide, as an efficient and long-life catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Colloid Surf. A 2019, 563, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Shi, Q.Y.; Yang, Y.M.; Yu, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.S.; Wei, L.; Lu, Y.H. CoO-Co2P composite nanosheets as highly active catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis to generate hydrogen. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2020, 13, 2051025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Hong, X.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Luo, Y.M.; Huang, P.R.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.X.; Zou, Y.J.; Sun, L.X.; Xu, F.; et al. Encapsulated cobalt nanoparticles as a recoverable catalyst for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 27, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.N.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, G.W. Properties of Cu-Co-P/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for efficient hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of alkaline NaBH4 solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 5749–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.N.; Luo, Y.M.; Chen, Y.N.; Zhu, H. Co-P nanoparticles supported on dandelion-like CNTs-Ni foam composite carrier as a novel catalyst for hydrogen generation from NaBH4 methanolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 8805–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Dong, X.L.; Yang, Y.M.; Shi, Q.Y.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Yu, Y.N.; Zhang, M.H.; Qi, M.; Wang, Q. Co-O-P composite nanocatalysts for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 10745–10753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ma, J. In situ synthesis of graphene supported Co-Sn-B alloy as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.P.; Wang, G.X.; Xie, G.W. Hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution using Co-Ni-Mo-P/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.L.; Wang, L.N.; Liu, T.Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, G.X.; Xie, G.W. Hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solution using supported amorphous alloy catalysts (Ni-Co-P/γ-Al2O3). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14935–14941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

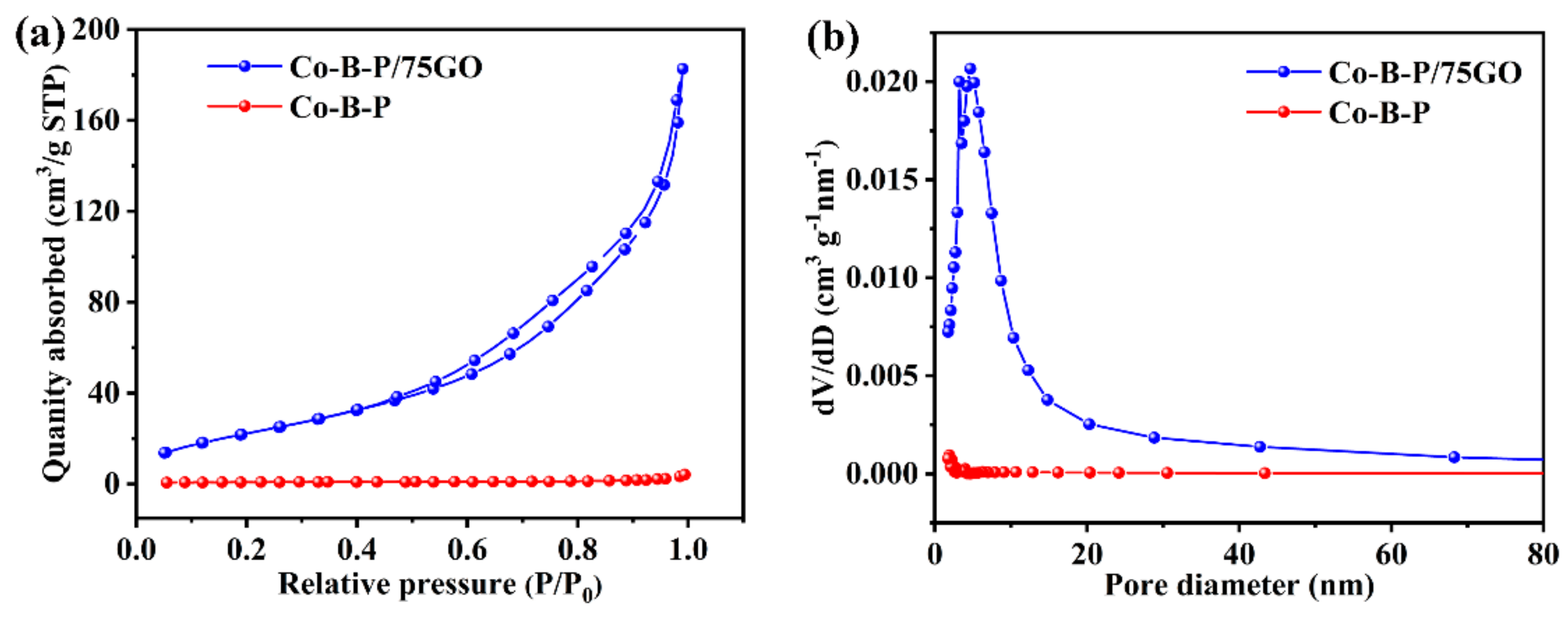



| Catalyst | Specific Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co-B-P | 3 | 0.01 | 12.0 |
| Co-B-P/75rGO | 89 | 0.28 | 9.0 |
| Sample | Maximum HG Rate (mL min−1 g−1) | Ea (kJ mol–1) | Number of Cycles | Cyclic Stability | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co@3DGO | 4394 | 37.42 | 5 | 54.0% | [50] |
| Co@GO | 5955 | 64.87 | 5 | 73.0% | [51] |
| Co-P | 1647.9 | 47.0 | 5 | 31.0% | [39] |
| CoO-Co2P | 3940 | 27.4 | 4 | 60.0% | [52] |
| Co@N MGC-500 | 3575 | 35.2 | 20 | 82.5% | [53] |
| Cu-Co-P/γ-Al2O3 | 1115 | 47.8 | 6 | 66.0% | [54] |
| Co-P/CNTs-Ni foam | 2430 | 49.94 | 8 | 74.0% | [55] |
| Co-B-10CNTs | 12,000 | 23.5 | 5 | 64.0% | [29] |
| Co-O-P | 4850 | 63 | 5 | 78.0% | [56] |
| Co-B-50GO | 14,430 | 26.2 | 5 | 81.5% | [40] |
| Co-B-P/75rGO | 12,087.8 | 28.64 | 10 | 88.9% | This work |
| Catalyst | Amount of Co (wt%) | Amount of B (wt%) | Amount of P (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co-B-P/25GO | 35.80 | 0.04 | 16.48 |
| Co-B-P/50GO | 40.2 | 1.02 | 12.62 |
| Co-B-P/75GO | 61.79 | 2.51 | 5.50 |
| Co-B-P/100GO | 34.65 | 0.72 | 14.34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, X.; Sang, Z.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Pan, H.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, R.; Yu, Y.; Hu, H.; Kang, L.; et al. Graphene-Modified Co-B-P Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162732
Jia X, Sang Z, Sun L, Xu F, Pan H, Zhang C, Cheng R, Yu Y, Hu H, Kang L, et al. Graphene-Modified Co-B-P Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(16):2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162732
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Xinlei, Zhen Sang, Lixian Sun, Fen Xu, Hongge Pan, Chenchen Zhang, Riguang Cheng, Yuqian Yu, Haopan Hu, Li Kang, and et al. 2022. "Graphene-Modified Co-B-P Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis" Nanomaterials 12, no. 16: 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162732
APA StyleJia, X., Sang, Z., Sun, L., Xu, F., Pan, H., Zhang, C., Cheng, R., Yu, Y., Hu, H., Kang, L., & Bu, Y. (2022). Graphene-Modified Co-B-P Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis. Nanomaterials, 12(16), 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162732






