Abstract
During the last two decades several nanoscale materials were engineered for industrial and medical applications. Among them carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are the most exploited nanomaterials with global production of around 1000 tons/year. Besides several commercial benefits of CNTs, the fiber-like structures and their bio-persistency in lung tissues raise serious concerns about the possible adverse human health effects resembling those of asbestos fibers. In this review, we present a comparative analysis between CNTs and asbestos fibers using the following four parameters: (1) fibrous needle-like shape, (2) bio-persistent nature, (3) high surface to volume ratio and (4) capacity to adsorb toxicants/pollutants on the surface. We also compare mechanisms underlying the toxicity caused by certain diameters and lengths of CNTs and asbestos fibers using downstream pathways associated with altered gene expression data from both asbestos and CNT exposure. Our results suggest that indeed certain types of CNTs are emulating asbestos fiber as far as associated toxicity is concerned.
1. Introduction
The last few decades have seen an explosion of thousands of engineered nanomaterials synthesized with precise size, shape and structural specifications. These nano-structured materials are composed of different base materials (mainly carbon, silicon and metals, such as gold, silver, titanium, cadmium and selenium) and have numerous novel and useful properties as they have substantially more reactive atoms on their surfaces compared to similar materials in the micro size range. Among the newly designed materials, carbon nanomaterials are the most used engineered nanomaterials in the form of nanoparticles, nanowires or nanotubes. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are hollow nanofibers of single (single wall carbon nanotube—SWCNT) or multiple (multi-wall carbon nanotube—MWCNT) layers of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb-like structure with two dimensions sized in nanoscale, i.e., 1–100 nm while the third dimension is very long (sometimes up to several millimeters in lengths), comparable to fibrous materials [1]. Due to their unique electrochemical properties, effectiveness in heat conductivity, unusual strength (10-fold stronger than steel and 1.2-fold harder than diamond) and very light weight [2], CNTs have emerged as highly exploitable materials for a wide spectrum of industrial and medical applications [3,4,5,6,7]. The global market of CNT, which was around $50.9 million in 2006 [8] had increased to $4.47 billion by 2018 and is expected to reach around $15 billion by 2026 [9]. The properties responsible for the exponential growth in the application and production of CNTs also raise potential concerns about potential adverse health effects. In particular, the fiber-like structure, high aspect ratios (high length: width ratio), physiochemical durability and presumed bio-persistency in lung tissues are linked to past experience with hazardous asbestos fibers, have brought these materials under scrutiny [10,11,12,13,14,15,16].
Various epidemiological and animal studies have shown that other non-asbestos fibers, e.g., erionite, fluoro-edenite, organic fibers from plant origin and manmade vitreous fibers that are more than 5µm in length and narrow enough to reach the distal lung upon inhalation might conform to the ‘fibre pathogenicity paradigm’ and might be associated with development of malignant mesothelioma [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. These studies indicate that fiber morphology is one of the main decisive factors responsible for malignant mesothelioma in the exposed population. Several groups have pointed out the potential of CNTs to induce malignant mesothelioma in a way similar to asbestos fibers [11,24,26,27,28,29,30,31,32].
Earlier studies revealed a high level of genetic damage in the lymphocytes of workers exposed in an asbestos factory, particularly among workers who also smoked [33]. In one study on male Fischer rats, Sakamoto and colleagues assessed the carcinogenic hazard of MWCNTs (1 mg/kg body weight) compared to crocidolite (blue asbestos) (2 mg/kg body weight) exposure. They found that after 37–40 weeks, 6 of the 7 MWCNT-treated animals (85.7%) died or became moribund due to intraperitoneally disseminated mesothelioma associated with bloody ascites, while all crocidolite-treated rats survived for 52 weeks without any changes except deposition of asbestos. Their results suggest that MWCNTs are capable of inducing mesothelioma at a high rate in normal male rats compared to asbestos [24]. Similarly, Takagi and colleagues have demonstrated that MWCNTs form fibrous or rod-shaped particles of length around 10–20 µm and induce mesothelioma in a similar way to crocidolite [34].
Generally, the harmful effects of CNTs arise from the combination of various parameters that are known to be associated with fiber pathogenicity, and the following four are of great concern: (a) high surface to volume ratio, (b) fibrous needle-like shape that resembles asbestos, (c) bio-persistent nature of nanotubes and (d) capacity to adsorb toxicants/pollutants on the surface. The first two parameters are invariably the same for any type of fibrous structures capable of inducing acute pleural inflammation while the last two depend on the chemical nature of fibers. The pathogenicity paradigm of long, thin and bio-persistent fibers is shown in Figure 1.
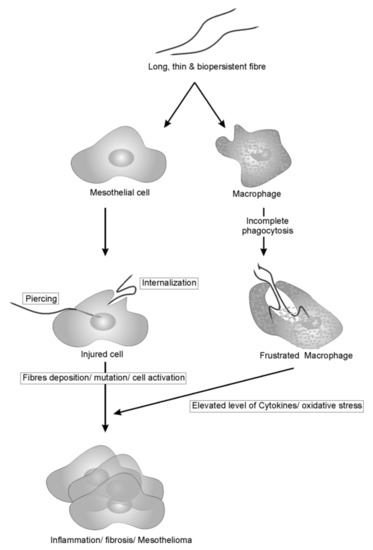
Figure 1.
Pathogenicity paradigm of long, thin, bio-persistent fibers on mesothelial cells and macrophage. Fibers, once inhaled, induces cell injury either by piercing or internalization in mesothelial cells, resulting in mutation and cell activation. On the other hands, foreign fibers recognized by macrophages resulted in the incomplete phagocytosis due to length and bio-persistent nature. This incomplete phagocytosis frustrates macrophages that result in elevated level of cytokines and ROS which indirectly associated with the activation of cancer signaling pathways.
CNTs have been listed by the International Chemical Secretariat (ChemSec) as so-called SIN (‘Substitute It Now’) chemicals to be restricted or banned in the EU in November 2019 [35], www.sinlist.chemsec.org accessed on 15 January 2022). However, there are numerous types of CNTs and they differ substantially in physico-chemical properties, and so cannot be evaluated only on the basis of chemical composition [36]. MWCNT-7 has been already classified as possibly carcinogenic to humans by IARC (Group 2B) [37]. CNTs have a high aspect ratio which resembles that of asbestos and other fibers causing lung cancer and mesothelioma.
High aspect ratio nanomaterials (HARN) are defined as nanofibers with two similar external dimensions and a significantly larger third dimension (aspect ratio of 3:1 or greater) and substantially parallel sides’ [38]. Not all HARNs are associated with mesothelioma [39], and aspect ratio is not the only factor responsible for potential pathogenicity.
2. Do Asbestos and CNTs Have the Same Mechanism of Pathogenicity?
To identify the commonality between asbestos and CNT pathogenicity, it is important to understand the mechanism by which asbestos induces asbestosis, bronchogenic carcinoma and mesothelioma in humans. Bernstein and colleagues proposed that the mechanisms of lung disease caused by certain fibers are numerous and include mainly oxidative stress, inflammation and direct or indirect genotoxicity [40]. As reviewed by Nagai and Toyokuni, there are four main hypotheses (highlighted in Figure 2), regarding the mechanisms of asbestos-induced pathogenicity [41]. (a) oxidative stress, (b) chromosome tangling, (c) adsorption and (d) chronic inflammation. Various studies were conducted in the past to support these hypotheses. Interestingly, several studies on CNTs have reported similar mechanisms of action as discussed in the following text.
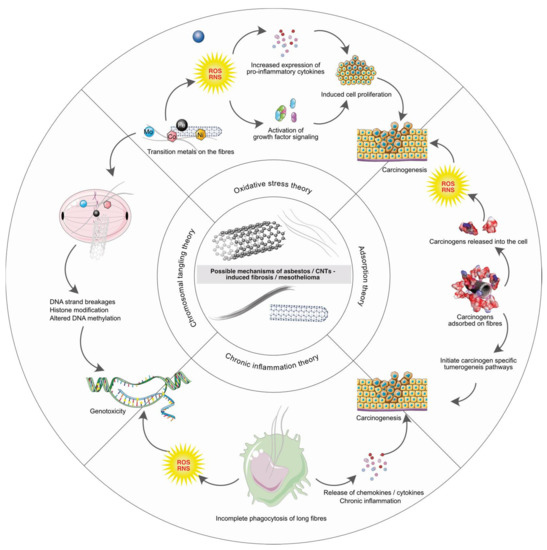
Figure 2.
The four possible mechanisms of asbestos/CNTs induced pathogenicity i.e., oxidative stress theory, chromosomal tangling theory, adsorption theory and chronic inflammation theory are highlighted.
2.1. Oxidative Stress Theory
The first theory postulates the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) as a consequence of injury to pleural mesothelioma cells injury due to exposure to asbestos fibers [42,43,44,45,46,47]. Several studies also showed the formation of free radicals, accumulation of peroxidative products and depletion of cell antioxidants in the keratinocytes and bronchial epithelial cells exposed in vitro to SWCNTs [48,49,50] and MWCNTs [51,52,53,54,55]. Like asbestos, SWCNTs/MWCNTs contain high levels of Fe, Ni, Co, Mo and other transition metal impurities which are known to induce ROS/RNS formation. These metals or metal mixtures are common components used in CNT synthesis, and all of these have demonstrated toxicity [56,57]. In general, each CNT sample invariably contains three classes of residual impurities from the synthesis process: metals, organics, and growth support material. It is worth mentioning that even purified grade CNTs still contain 1–5% residual metal by mass [58]. The residual organics include various forms of bulk carbon (amorphous soot particles or micro-structured graphite sheets) and other residual organic molecules. Aluminate and silicate residues are shown to be present on CNTs as they are used as materials to support the catalyst or growth region [59]. Furthermore, functionalization of CNTs by the addition of certain surface molecule groups can modify their specific toxicity [60,61]. Mainly the metals, organics and growth support materials present on CNTs, when they come into the contact with cells, result in oxidative stress [57,62,63,64] and damage cellular macromolecules.
Oxidative stress induced by asbestos activates several signaling cascades that are necessary for cell proliferation, such as, MAPK, NF-ĸB, AP-1 and ERK 1/2 [65,66,67,68,69] in dose- and time-dependent manner. AP-1 and NF-ĸB (redox-sensitive transcription factors), which are activated by asbestos/CNT exposure, regulate expression of several genes involved in inflammation, proliferation, apoptosis and the carcinogenesis process. Several studies report the mitochondria-mediated production of ROS, their localization and the resulting damage in response to asbestos/CNT exposures [70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78].
In their study on male CD-ICR mice, Yang and colleagues showed accumulation of SWCNTs in the liver, spleen and lung 90 days after a single tail vein injection with 40 µg, 200 µg or 1.0 mg of SWCNTs per mouse (10–30 nm diameter and 2–3 µm length, containing impurities (wt%): Fe 0.4, Ni 3.0 and Y 1.3) [79]. Although no abnormal symptoms were observed, reduced glutathione (GSH) levels were found in the liver and lungs of all exposed groups along with increases in malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in the liver and lung indicating that SWCNTs induce oxidative damage. In another study, Murray and colleagues measured the dermal toxicity of purified/unpurified SWCNT both in vitro and in vivo using EpiDerm FT engineered skin, murine epidermal cells (JB6 P+) and immune-competent nude SKH-1 mice. Upon SWCNT exposure, the EpiDerm FT engineered skin, showed enhanced epidermal thickness due to accumulation and activation of dermal fibroblasts. The unpurified SWCNTs (with 30% Fe) exposure to JB6 P+ cells resulted in an increase in hydroxyl radical concentration. Although no significant changes were observed in the AP-1 activation with the partially purified SWCNTs (with 0.23% Fe), NF-ĸB was activated in a dose-dependent manner by exposure to both unpurified and partially purified SWCNTs. Reduction in glutathione concentration and oxidation of protein thiols/carbonyls were observed in SKH-1 mice due to oxidative stress when they were exposed to unpurified SWCNTs (5 days, with daily doses of 40 µg/mouse, 80 µg/mouse or 160 µg/mouse) [80]. These data highlight the role of SWCNT-mediated oxidative stress in causing dermal toxicity.
In another study with industrial MWCNTs (6–24 nm in diameter and 2–5 µm in length, containing 0.4 wt% Fe impurity), Thurnherr and colleagues exposed A549 human lung epithelial cells and T lymphocytes for 2 h. They observed concentration-dependent levels of ROS and decreased mitochondrial activities; however, no morphological changes in the cells were noticed [81]. Fenoglio and co-workers exposed murine alveolar macrophages (MH-S) with two distinct sets of MWCNTs with similar length (<5 µm) but different diameters (9.4 and 70 nm). Both samples were internalized in the MH-S cells; however, the MWCNTs with thin diameter generated a high level of ROS as measured by DCF-DA fluorescence in comparison to those of larger diameter on a mass-dose basis, confirming that thin MWCNTs are more toxic [82].
In a study on rat epithelial cells exposed to MWCNTs, researchers found induction of mitochondrial apoptotic factors responsible for the reduced cellular ATP contents due to the collapse of mitochondrial membrane integrity [83]. Zhou and co-workers have reported changes in the mitochondrial transmembrane potential caused by localization of PL-PEG functionalized SWCNTs in mitochondria of both tumor as well as normal cells [73], ultimately leading to exaggerated ROS production due to collapse of mitochondrial membrane potential. A dose- and time-dependent decrease in the mitochondrial membrane potential due to generation of intracellular oxygen species was observed in rat macrophages and A549 cells exposed to commercially available SWCNTs and MWCNTs with metal impurities whereas no effect was detected with the CNTs treated with acid to remove residual transitional metal traces [84]. These findings suggest that cells exposed to CNTs will have dysfunctional mitochondrial activities. However, a study in A549 cells, in which the ROS formation induced by MWCNTs was independent of mitochondrial activity as measured by MTT assay, suggests that there are also other factors that generate ROS after CNT exposure [85]. The ROS generated on exposure to fibers were shown to cause lipid peroxidation as indicated by the synthesis of mutagenic compounds such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxynenal. MDA formation was observed after exposure of HUVEC cells [86] and A549 cells [85] to MWCNTs. High levels of MDA were also observed in rat blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid after CNT exposure through intraperitoneal/intravenous injections or via intratracheal instillation [86,87,88].
Several studies have shown that exposure to fibers causes depletion of intracellular antioxidant defense by the generation of free radicals. The A549 cells when exposed with crocidolite-like silicate fibers inhibited the pentose phosphate pathway (a key antioxidant intracellular system) by the inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase [89]. The same cell lines when exposed to MWCNTs were also found to have reduced catalase and glutathione activity [85]. SWCNTs also elicit the same effect in rat lung epithelial cells [90].
All these studies clearly indicate that both asbestos and CNT fibers share common mechanisms of oxidative stress upon exposure.
2.2. Chromosome Tangling
Several studies have demonstrated the disruption of chromosomal structure, due to asbestos fiber exposure at the time of mitosis, resulting in the inheritance of abnormal chromosome by the daughter cells including mesothelial cells [91,92,93,94,95,96]. Trisomy of chromosome 11 was found in six out of eight Syrian hamster embryo cell lines derived immediately after asbestos exposure [97]. Jiang and colleagues have demonstrated the direct interaction of asbestos fibers with the chromosomes [98]. Exposure of cultured cells with chrysotile have been shown to cause double strand breaks in DNA [99,100] along with intrachromosomal deletion and DNA mutations [101]. Cortez and co-workers have identified aneuploid cell formation, increased number of cells in G2/M phase and cells with multipolar mitosis in an in vitro study of chrysotile-exposed lung cancer cells [102]. Various types of chromosomal damage may be observed in cells presented with asbestos fibers, including chromosomal breaks and fragments (micronuclei), exchange of chromosomal, lagging chromosomes, segments between two chromosomes and chromosomal mis-segregation [103]. Some of the asbestos fibers genotoxicity studies are highlighted in Table 1.

Table 1.
Selected studies related to the asbestos induced genotoxicity.
Similar to the asbestos fibers, several carbon-based nanomaterials exhibit genotoxicity [52,108,109]. MWCNTs were found to be genotoxic to human lung cells in vitro at occupationally relevant dose [110,111,112]. Sasaki and colleagues analyzed MWCNTs with different shape and size and found that straight MWCNTs induce more polyploidy followed by curved and tangled fibers in Chinese hamster lung cell line (CHL/IU) [112]. Siegrist and colleagues showed cell cycle disruption, mitotic spindle disruption and aneuploidy in human lung epithelial cell lines (BEAR-2B and SAEC) exposed to MWCNT-7, designed by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, and two physiochemically-altered MWCNTs [111]. SWCNTs/MWCNTs (~1–25 nm diameter and ~500–1000 nm in length) have been shown to disrupt chromosomal distribution during mitosis resulting in aneuploidy in the daughter cells [113,114,115,116,117]. Li et al. observed that SWCNTs preferentially bind to the major groove of DNA with GC preference [118]. The inhibition of DNA duplex association and formation of telomeric i-motif was also observed due to the binding of SWCNTs at the 5′-end major groove of DNA [119]. Mangum and co-workers showed the joining of daughter cells of alveolar macrophages by the formation of carbon bridges composed of CNTs [120]. CNT exposure significantly increased micronuclei in human primary small airway epithelial cells (SAEC) indicating aneugenic events triggered by CNTs [121]. Sargent and co-workers have shown mitotic spindle aberrations in SAEC exposed to 24, 48 and 96 µg/cm2 SWCNTs [114]. Moreover, fragmented centrosomes, disrupted mitotic spindles and aneuploidy were observed in the SAEC exposed to SWCNTs for 24–72 h at doses equivalent to 20 weeks of exposure at the permissible exposure limit for particulates [113]. In a study by Zhu and colleagues on mouse embryonic stem cells, MWCNTs were shown to increase the mutation frequency by 2-fold compared to the spontaneous mutation frequency. The increased expression of the key base excision repair pathway enzyme 8-oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1) and double strand break repair proteins (Rad51 and XRCC4) was also observed with MWCNT exposure [122].
These studies clearly suggest that both asbestos and CNTs induce genotoxicity due to disruption of chromosomal structure, mutations and double-strand DNA breakage. Table 2 shows some of the important genotoxicity studies after the exposure of SWNCTs/MWCNTs in both in vitro and in vivo settings.

Table 2.
Selected genotoxicity studies related to the exposure of carbon nanotubes.
2.3. Adsorption Theory
The adsorption theory postulates the surface reactivity of fibers for certain proteins and molecules. Due to the surface reactivity, many carcinogenic molecules may get adsorbed on fiber surfaces from various environmental matrices. These molecules, once released into the cell after fiber internalization, cause the pathogenicity. MacCorkle and co-workers demonstrated that internalized asbestos fibers have high affinity to bind with proteins involved in the regulation of cell cycle, cytoskeleton and mitotic process to induce aneuploidy and genotoxicity. However, pre-coated asbestos fibers with protein complexes did not induce aneuploidy without affecting fiber uptake by the cells [128]. Various known mutagens such as benzo(a)pyrene from cigarette smoke have high affinity for asbestos [129,130,131,132]. Jiang et al. also showed that chrysotile fibers accumulate iron from surrounding tissue, probably via a hemolysis process and that this catalytic iron plays an important role in asbestos-induced carcinogenesis [98].
Like asbestos, toxicity of CNTs not only comes from their own structure but also from the various toxic substances adsorbed on their surfaces. Highly hydrophobic surfaces of CNTs have already been reported as strong adsorbents for various organic compounds such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons [133,134,135,136,137], phenolic compounds [138,139,140], chlorobenzenes [141,142,143,144], dioxin [145,146] and other natural organic materials [147,148,149,150]. Moreover, several studies highlight the adsorption potential of CNTs for heavy metals [151,152]. Although many of these absorption studies underline a potential role for CNTs in cleaning polluted water and other environmental matrixes, many of the adsorbed compounds have also been responsible for inducing carcinogenesis and thus, the fate of these compounds on the CNTs is still a matter of concern, as it is for asbestos fibers.
2.4. Chronic Inflammation
The last established theory of asbestos-induced carcinogenesis suggests the role of persistent macrophage activation resulting in chronic inflammation as one of the major events associated with the disease progression. Several studies have drawn similarities between asbestos and CNTs for inducing inflammatory reactions in human lung epithelial cells [10,153,154,155,156,157]. Rydman and co-workers explored the variation between two different CNTs and asbestos in inducing pro-inflammatory reactions in C57BL/6 mice subsequent to single pharyngeal aspiration exposure [158]. In their experiment, they used long tangled, and long rod-like CNT as well as crocidolite asbestos at a dose of 10 or 40 µg/mouse and mice were sacrificed 4 and 16 hours or 7, 14 and 28 days after the exposure. The study clearly indicates that long rod-like CNT is considerably more potent to induce lung inflammation than asbestos and long tangled fibers, with the involvement of IL-1β in mediating the inflammatory processes [158].
The long fibrous foreign materials are generally captured by macrophages and entrapped within lysosomes. However, these materials are not fully phagocytosed which ultimately results in frustrated macrophages and further inducing of chronic inflammation. In many clinical studies, these immune responses with chronic inflammatory conditions were directly linked with the progression of malignant diseases. Glass fibers of length ~17 µm were found to play a major role in incomplete phagocytosis and to induce the production of the pro-inflammatory mediators NF-κB and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in mouse macrophages, However, short (~7 µm) fibers showed both complete phagocytosis and less expression of inflammatory mediators [159]. Hsieh and co-worker showed airway hyperactivity and air flow obstruction due to granulomatous changes in the lung parenchyma up to six months after a single instillation of SWCNTs to the intratracheal region of mice. They also identified up-regulation of cathepsin K, MMP12, chemokines C-C motif ligands (CCL2 and CCL3) and macrophage receptors (Toll-like receptor 2, macrophage scavenger receptor 1) [160]. Several previous studies also demonstrated the activation of NF-kB and AP-1transcriptional machinery that stimulates many proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and the expression of genes involved in the inflammation and cell proliferation processes due to exposure to long fibers such as CNTs and asbestos [161,162,163,164]. Among the highly expressed genes, COX-2 is mainly associated with cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis [165,166,167]. Many other inflammatory genes such as TNF-α, IL-8 and IL-1β are also regulated after exposure to CNTs and other long fibers [168,169]. In a comprehensive study on the effects of pulmonary exposure to 10 commercial MWCNTs, Poulsen and co-workers found that inflammation and genotoxicity were related to dose, time and physicochemical properties [170]. More specifically, they found that MWCNTs with larger diameter and small BET surface area are associated with increased genotoxicity and inflammation.
All these studies suggest that both asbestos and certain carbon nanofibers share mechanisms underlying chronic inflammation which can mainly be attributed to their fibrous structure.
3. Toxicogenomics Analysis of Altered Gene Expression Due to Asbestos and CNT Exposure
Toxicogenomics is a field of science which helps in formulating hypotheses about underlying mechanisms of toxicity by merging conventional toxicology and functional genomics. Using genomics approaches, information regarding specific mechanisms at a molecular level about nanomaterial distribution or toxicity towards multiple cellular functions becomes clearer. Conventional toxicity assays are quick in predicting the impact of exposure at the phenotypic level, but fail to formulate hypotheses about how such changes affect human beings [171].
Various studies have been performed to investigate the toxic effect of asbestos and CNT’s in different organisms using toxicogenomics studies; however, the results were always controversial due to various factors such as length, diameter, surface area, purity and tendency for agglomeration and dispersion in media [172,173,174,175]. As mentioned earlier, many studies confirmed that CNTs of various size and shape induce ROS generation, immune suppression and pulmonary fibrosis that is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. This is mainly due to the change in the gene expression profiles related to oxidative stress response, cellular transport, metabolism and cell cycle regulation in both in vivo and in vitro systems [176,177,178,179,180,181,182].
In a 104-week long carcinogenicity study, Kasai et al. found that lung carcinomas were significantly increased in a concentration- and dose-dependent manner in both male and female rats exposed to MWCNT-7 [183]. Signaling pathways in the lung induced by asbestos cause changes in gene expression, release of cytokines, blocking of mitochondrial activities and apoptosis, ultimately leading to cancer [184]. In other studies, it has been shown that when asbestos or CNTs come into the contact with macrophages, they start inducing tumor necrosis factor (TNF), an inflammatory cytokine, and cause interleukin (IL) up-regulation. The above-mentioned studies clearly show that TNF and interleukins (IL6, IL8 and IL10) are up regulated by asbestos and MWCNT treatments.
Kim and his co-workers studied toxicogenomic effects of MWCNTs and asbestos (crocidolite) on 31,647 genes at the 50% growth inhibition (GI 50) concentration on normal human bronchial epithelia (NHBE) cells [185]. These cells were exposed to asbestos and MWCNTs for 6 and 24 h. In total 1201 and 1252 genes were up-regulated, while 1977 and 1542 genes were down-regulated by both asbestos and MWCNTs, after 6 and 24 h of exposure, respectively. Interestingly, 12 mesothelioma and 22 lung cancer-related genes were differentially regulated over two-fold by both asbestos and MWCNTs exposure in comparison to the negative control, indicating the similarity between asbestos- and CNT-mediated toxicity mechanisms.
Asbestos and CNTs can also affect signaling pathway networks which regulate the expression of genes associated with inflammatory response, apoptosis and oxidative stress. Using single-cell RNAseq, Joshi and colleagues found that macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling is essential in monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages and fibroblasts during asbestos-induced fibrosis [186]. Different studies revealed that nanoparticles interact with cell membrane elements responsible for the regulation of receptor-mediated signaling pathways [187,188]. Mukherjee and colleagues proposed that SWCNTs interact with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in the absence of a protein corona through hydrophobic interactions and attract cytokine and chemokine cascades [189]. Many recent studies focus on global mRNA and ncRNA expression profiles in the blood of workers exposed to CNTs; they have found many differentially regulated genes involved in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis and proliferation similar to those affected by asbestos fibers [178,180,190].
Nymark and colleagues exposed human bronchial epithelial BEAS 2B cells to MWCNTs and asbestos and found decreased mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) for MWCNTs at a biologically relevant dose (0.25 μg/cm2) and for asbestos at 2 μg/cm2. They also identified 330 gene signatures related to MWCNT- and asbestos-induced MMP, of which 26 were already known for mitochondrial function [190]. In another study by Poulsen and colleagues, both in vitro and in vivo experiments were performed and compared using DNA array followed by gene-specific RT-qPCR assay after the exposure of lung epithelial cells (FE1) and mouse models. In both models, oxidative stress, fibrosis and inflammation related processes were altered with different sets of associated genes [191]. In a recent study by Jiang and colleagues, effects of length, functional group and electronic structures of various types of SWCNTs were observed in a toxicogenomic assay involving A549 cells. Their toxicogenomic analyses suggest that short SWCNTs (0.5–2 μm) had a higher toxicity level than the long ones (5–30 μm) while carboxylated SWCNTs induced greater genotoxicity, chemical stress and protein damage compared with hydroxylated ones [192].
All the above studies suggest that toxicogenomic analysis is very helpful in analyzing similarities and differences between the asbestos- and CNT-associated genes and biological pathways. Together with adverse outcome pathway (AOP) analysis, describing mechanistic information on toxicology response and toxicity initiation events, toxicogenomic studies can be a useful tool for safety assessment of emerging nanomaterials [193]. We see a clear picture of CNTs following in the footprints of asbestos in terms of toxicological outcomes through similar cellular processes, cellular transport, metabolism, cell cycle regulation, stress response, immune response, inflammatory response, genotoxicity and apoptosis in both in vitro and in vivo settings [194].
4. Conclusions
Several possible mechanisms have been proposed to define the toxicity and carcinogenicity of fibrous materials including certain types of CNTs and asbestos fibers. These include oxidative stress, chromosomal damage, adsorption of toxicants and pollutant and chronic inflammation. These pathogenic theories include a variety of intrinsic and extrinsic factors that modulate the biological responses. Among these, we have focused on how asbestos fibers and CNTs enter non-phagocytic cells, which is important in mesothelial/epithelial cell injury. Based on current evidence, all four theories hint towards the carcinogenic outcomes and could extensively contribute to the explanation of the toxicity of asbestos and certain nanomaterials. The profiles of gene expression upon exposure to asbestos and CNTs provide important information on the pathways that are commonly shared or unique to each fibrous type. Based on this discussion, it is evident that asbestos and certain diameters and lengths of CNTs share common mechanisms for pathogenicity and thus indicate an immediate need for the designing of a protocol to regulate the industrial use of some CNTs to avoid a hazardous situation such as was witnessed with asbestos fibers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.R., M.D. and S.G.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.G., K.P.S. and S.G.; writing—review and editing, M.D., Q.R. and S.G.; supervision, Q.R.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
QR acknowledge the support by Amity University Lucknow Campus. MD acknowledges European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program projects RiskGONE (grant agreement 814425, 2019). SSG acknowledge support from Helmholtz Virtual Institute HICE – Aerosol and Health, Germany.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Simeonova, P.P. Update on Carbon Nanotube Toxicity. Nanomedicine 2009, 4, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, T.W.; Lezec, H.J.; Hiura, H.; Bennett, J.W.; Ghaemi, H.F.; Thio, T. Electrical Conductivity of Individual Carbon Nanotubes. Nature 1996, 382, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.H.; Zakhidov, A.A.; De Heer, W.A. Carbon Nanotubes—The Route toward Applications. Science 2002, 297, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.N. Carbon Nanotubes: Properties and Application. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 43, 61–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Taylor, S.; Li, H.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Qu, L.; Wang, W.; Gu, L.; Zhou, B.; Sun, Y.P. Advances toward Bioapplications of Carbon Nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, A.M. Carbon Nanotubes by the Metric Ton. Chem. Eng. News 2007, 85, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Murthy, C.N.; Prabha, C.R. Recent Advances in Carbon Nanotube Based Electrochemical Biosensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivet, J. Carbon Nanotubes: Technology and Commercial Prospective. Available online: www.bcc.research.comlre-Dort (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Garside, M. Carbon Nanotube Market Value. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/714463/global-market-value-of-carbon-nanotubes/ (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Donaldson, K.; Poland, C.A.; Murphy, F.A.; MacFarlane, M.; Chernova, T.; Schinwald, A. Pulmonary Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes and Asbestos—Similarities and Differences. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsi, M.; Al Hatem, C.; Leinardi, R.; Huaux, F. Carbon Nanotubes under Scrutiny: Their Toxicity and Utility in Mesothelioma Research. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.W.; James, J.T.; McCluskey, R.; Hunter, R.L. Pulmonary Toxicity of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes in Mice 7 and 90 Days after Intractracheal Instillation. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 77, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic Potential of Materials at the Nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Poland, C.A. Nanotoxicology: New Insights into Nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Aitken, R.; Tran, L.; Stone, V.; Duffin, R.; Forrest, G.; Alexander, A. Carbon Nanotubes: A Review of Their Properties in Relation to Pulmonary Toxicology and Workplace Safety. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H.; Gao, H. The Asbestos-Carbon Nanotube Analogy: An Update. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 361, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanoos, R.L.; Churg, A.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Gibbs, A.R.; Roggli, V.L. Malignant Mesothelioma and Its Non-Asbestos Causes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikensoy, O. Mesothelioma Due to Environmental Exposure to Erionite in Turkey. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2008, 14, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comba, P.; Gianfagna, A.; Paoletti, L. Pleural Mesothelioma Cases in Biancavilla Are Related to a New Fluoro-Edenite Fibrous Amphibole. Arch. Environ. Health 2003, 58, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baris, I.; Artvinli, M.; Saracci, R.; Simonato, L.; Pooley, F.; Skidmore, J.; Wagner, C. Epidemiological and Environmental Evidence of the Health Effects of Exposure to Erionite Fibres: A Four-year Study in the Cappadocian Region of Turkey. Int. J. Cancer 1987, 39, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Man-Made Vitreous Fibres; IARC: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 81. [Google Scholar]
- Kliment, C.R.; Clemens, K.; Oury, T.D. North American Erionite-Associated Mesothelioma with Pleural Plaques and Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Case Report. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2009, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, A.; Hirose, A.; Futakuchi, M.; Tsuda, H.; Kanno, J. Dose-Dependent Mesothelioma Induction by Intraperitoneal Administration of Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes in P53 Heterozygous Mice. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Nakae, D.; Fukumori, N.; Tayama, K.; Maekawa, A.; Imai, K.; Hirose, A.; Nishimura, T.; Ohashi, N.; Ogata, A. Induction of Mesothelioma by a Single Intrascrotal Administration of Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotube in Intact Male Fischer 344 Rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 34, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasani, B.; Gibbs, A. Mesothelioma Not Associated with Asbestos Exposure. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2012, 136, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. Integration of Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cancer Induced by Carbon Nanotubes. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1244–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, D.; Wang, Q.; He, J.; Alexander, D.B.; Abdelgied, M.; El-Gazzar, A.M.; Futakuchi, M.; Suzui, M.; Kanno, J.; Hirose, A.; et al. Persistent Pleural Lesions and Inflammation by Pulmonary Exposure of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huaux, F.; d’Ursel de Bousies, V.; Parent, M.A.; Orsi, M.; Uwambayinema, F.; Devosse, R.; Ibouraadaten, S.; Yakoub, Y.; Panin, N.; Palmai-Pallag, M.; et al. Mesothelioma Response to Carbon Nanotubes Is Associated with an Early and Selective Accumulation of Immunosuppressive Monocytic Cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zandwijk, N.; Frank, A.L. Potential Toxicities of Carbon Nanotubes: Time for a Reminder. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, C.A.; Duffin, R.; Kinloch, I.; Maynard, A.; Wallace, W.A.H.; Seaton, A.; Stone, V.; Brown, S.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K. Carbon Nanotubes Introduced into the Abdominal Cavity of Mice Show Asbestos-like Pathogenicity in a Pilot Study. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.A.; Poland, C.A.; Duffin, R.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; Ali-Boucetta, H.; Nunes, A.; Byrne, F.; Prina-Mello, A.; Volkov, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Length-Dependent Retention of Carbon Nanotubes in the Pleural Space of Mice Initiates Sustained Inflammation and Progressive Fibrosis on the Parietal Pleura. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2587–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Futakuchi, M.; Shimizu, H.; Alexander, D.B.; Yanagihara, K.; Fukamachi, K.; Suzui, M.; Kanno, J.; Hirose, A.; Ogata, A.; et al. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Translocate into the Pleural Cavity and Induce Visceral Mesothelial Proliferation in Rats. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušinská, M.; Collins, A.; Kažimírová, A.; Barančoková, M.; Harrington, V.; Volkovová, K.; Staruchová, M.; Horská, A.; Wsólová, L.; Kočan, A.; et al. Genotoxic Effects of Asbestos in Humans. Mutat. Res.—Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2004, 553, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, A.; Hirose, A.; Nishimura, T.; Fukumori, N.; Ogata, A.; Ohashi, N.; Kitajima, S.; Kanno, J. Induction of Mesothelioma in P53+/- Mouse by Intraperitoneal Application of Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotube. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 33, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.F.; Lennquist, A. Carbon Nanotubes Added to the SIN List as a Nanomaterial of Very High Concern. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadeel, B.; Kostarelos, K. Grouping All Carbon Nanotubes into a Single Substance Category Is Scientifically Unjustified. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Some Nanomaterials and Some Fibres; IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017; ISBN 978-92-832-0149-6. [Google Scholar]
- European Chemicals Agency (EU body or agency). Appendix for Nanoforms to the Guidance on Registration and the Guidance on Substance Identification; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019; ISBN 978-92-9481-357-2.
- Murphy, F.; Dekkers, S.; Braakhuis, H.; Ma-Hock, L.; Johnston, H.; Janer, G.; di Cristo, L.; Sabella, S.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Oomen, A.G.; et al. An Integrated Approach to Testing and Assessment of High Aspect Ratio Nanomaterials and Its Application for Grouping Based on a Common Mesothelioma Hazard. NanoImpact 2021, 22, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, B.; Schwerdtle, T.; Poser, I.; Hoffmann, E.; Hartwig, A.; Müller, W.U.; Rettenmeier, A.W.; Seemayer, N.H.; Dopp, E. Effects of Asbestos on Initiation of DNA Damage, Induction of DNA-Strand Breaks, P53-Expression and Apoptosis in Primary, SV40-Transformed and Malignant Human Mesothelial Cells. Mutat. Res.—Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2004, 558, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Toyokuni, S. Biopersistent Fiber-Induced Inflammation and Carcinogenesis: Lessons Learned from Asbestos toward Safety of Fibrous Nanomaterials. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 502, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallyathan, V.; Mega, J.F.; Shi, X.; Dalal, N.S. Enhanced Generation of Free Radicals from Phagocytes Induced by Mineral Dusts. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1992, 6, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, D.W.; Graceffa, P.; Pryor, W.A.; Weitzman, S.A. The Role of Free Radicals in Asbestos-Induced Diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1992, 12, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broaddus, V.C.; Yang, L.; Scavo, L.M.; Ernst, J.D.; Boylan, A.M. Asbestos Induces Apoptosis of Human and Rabbit Pleural Mesothelial Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, D.W.; Weitzman, S.A. The Molecular Basis of Asbestos Induced Lung Injury. Thorax 1999, 54, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacurari, M.; Castranova, V.; Vallyathan, V. Single- and Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes versus Asbestos: Are the Carbon Nanotubes a New Health Risk to Humans? J. Toxicol. Environ. Health—Part Curr. Issues 2010, 73, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Lee, S.; Kumagai-Takei, N.; Min, Y.; Sada, N.; Yoshitome, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Maeda, M.; Otsuki, T. Cytotoxicity Caused by Asbestos Fibers and Acquisition of Resistance by Continuous Exposure in Human T Cells. In Cytotoxicity; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.S.; Wu, R.; Jafvert, C.T. Light-Independent Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Formation through Electron Transfer from Carboxylated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11330–11336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangarpour, A.; Alboghobeish, S.; Oroojan, A.A.; Dehghani, M.A. Mice Pancreatic Islets Protection from Oxidative Stress Induced by Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes through Naringin. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Humes, S.T.; Robinson, S.E.; Loeb, J.C.; Sabaraya, I.V.; Saleh, N.B.; Khattri, R.B.; Merritt, M.E.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Lednicky, J.A.; et al. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Repress Viral-Induced Defense Pathways through Oxidative Stress. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1176–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghini, A.; Roursgaard, M.; Andreassi, M.G.; Kermanizadeh, A.; Møller, P. Repair Activity of Oxidatively Damaged DNA and Telomere Length in Human Lung Epithelial Cells after Exposure to Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.; Pereira, J.F.S.; Matos, P.; Marques, B.; Jordan, P.; Sousa-Uva, A.; Silva, M.J. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of MWCNT-7 and Crocidolite: Assessment in Alveolar Epithelial Cells versus Their Coculture with Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Aziz, S.A.; Wu, D.; Williams, A.; Yauk, C.L.; White, P.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U.; Halappanavar, S. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Induced Genotoxic, Inflammatory and pro-Fibrotic Responses in Mice: Investigating the Mechanisms of Pulmonary Carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res.—Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2017, 823, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.J.; Verhein, K.C.; Vellers, H.L.; Burkholder, A.B.; Garantziotis, S.; Kleeberger, S.R. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Upregulate Mitochondrial Gene Expression and Trigger Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Primary Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1344–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzui, M.; Futakuchi, M.; Fukamachi, K.; Numano, T.; Abdelgied, M.; Takahashi, S.; Ohnishi, M.; Omori, T.; Tsuruoka, S.; Hirose, A.; et al. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Intratracheally Instilled into the Rat Lung Induce Development of Pleural Malignant Mesothelioma and Lung Tumors. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C. The Contributions of Metal Impurities and Tube Structure to the Toxicity of Carbon Nanotube Materials. NPG Asia Mater. 2012, 4, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, A.; Wada, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kataura, H. Oxidative Stress of Carbon Nanotubes on Proteins Is Mediated by Metals Originating from the Catalyst Remains. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiciński, W.; Dyjak, S. Transition Metal Impurities in Carbon-Based Materials: Pitfalls, Artifacts and Deleterious Effects. Carbon 2020, 168, 748–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.J. Carbon Nanotube Structures and Compositions: Implications for Toxicological Studies. In Nanotoxicology: Characterization, Dosing and Health Effects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 7–18. ISBN 9781420045154. [Google Scholar]
- Pendyala, V.R.R.; Jacobs, G.; Graham, U.M.; Shafer, W.D.; Martinelli, M.; Kong, L.; Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Influence of Acid Treatment and Preparation Method on Carbon Nanotube Supported Ruthenium Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 6408–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Baweja, L.; Wolkenhauer, O.; Rahman, Q.; Gupta, S.K. Impact of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials (GBNMs) on the Structural and Functional Conformations of Hepcidin Peptide. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2018, 32, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, V.E.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Konduru, N.V.; Potapovich, A.I.; Osipov, A.N.; Kisin, E.R.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Mercer, R.; Castranova, V.; et al. Direct and Indirect Effects of Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes on RAW 264.7 Macrophages: Role of Iron. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 165, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, A.S.; Zhang, T.D.; Burkert, S.C.; Adiguzel, Z.; Acilan, C.; Star, A.; Saunders, W.S. Characterizing the Cellular Response to Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanocups. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Xiao, R.; Shao, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Zeng, G.; et al. Effects of Carbon Nanotubes on Biodegradation of Pollutants: Positive or Negative? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M. The Regulation of AP-1 Activity by Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1996, 351, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J.L.; Zanella, C.L.; Janssen, Y.M.W.; Timblin, C.R.; Jimenez, L.A.; Vacek, P.; Taatjes, D.J.; Mossman, B.T. Novel Cell Imaging Techniques Show Induction of Apoptosis and Proliferation in Mesothelial Cells by Asbestos. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 17, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pache, J.C.; Janssen, Y.M.W.; Walsh, E.S.; Quinlan, T.R.; Zanella, C.L.; Low, R.B.; Taatjes, D.J.; Mossman, B.T. Increased Epidermal Growth Factor-Receptor Protein in a Human Mesothelial Cell Line in Response to Long Asbestos Fibers. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.; Gulumian, M.; Hei, T.K.; Kamp, D.; Rahman, Q.; Mossman, B.T. Multiple Roles of Oxidants in the Pathogenesis of Asbestos-Induced Diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapoli, L.; Ramos-Nino, M.E.; Martinelli, M.; Mossman, B.T. Src-Dependent ERK5 and Src/EGFR-Dependent ERK1/2 Activation Is Required for Cell Proliferation by Asbestos. Oncogene 2004, 23, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panduri, V.; Weitzman, S.A.; Chandel, N.S.; Kamp, D.W. Mitochondrial-Derived Free Radicals Mediate Asbestos-Induced Alveolar Epithelial Cell Apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol.—Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L1220–L1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panduri, V.; Weitzman, S.A.; Chandel, N.; Kamp, D.W. The Mitochondria-Regulated Death Pathway Mediates Asbestos-Induced Alveolar Epithelial Cell Apoptosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, D.W.; Panduri, V.; Weitzman, S.A.; Chandel, N. Asbestos-Induced Alveolar Epithelial Cell Apoptosis: Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Caused by Iron-Derived Free Radicals. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 234–235, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xing, D.; Wu, B.; Wu, S.; Ou, Z.; Chen, W.R. New Insights of Transmembranal Mechanism and Subcellular Localization of Noncovalently Modified Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manke, A.; Wand, L.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 942916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Peng, D. Hydroxylation of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Reduces Their Cytotoxicity by Limiting the Activation of Mitochondrial Mediated Apoptotic Pathway. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasras, S.; Kalantari, H.; Rezaei, M.; Dehghani, M.A.; Zeidooni, L.; Alikarami, K.; Dehghani, F.; Alboghobeish, S. Single-Walled and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Induce Oxidative Stress in Isolated Rat Brain Mitochondria. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2019, 35, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehcheh, M.; Alboghobeish, S.; Dehghani, M.A.; Zeidooni, L. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Induce Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Dysfunction in Isolated Rat Heart Mitochondria: Protective Effect of Naringin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13447–13456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Nasarzadeh, P.; Seydi, E.; Ghasemi, A.; Taghi Joghataei, M.; Ashtari, K.; Akbari, M. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Dysfunction Induced by Single- and Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes: A Comparative Study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.—Part A 2017, 105, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.T.; Wang, X.; Jia, G.; Gu, Y.; Wang, T.; Nie, H.; Ge, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Long-Term Accumulation and Low Toxicity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Intravenously Exposed Mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 181, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.R.; Kisin, E.; Leonard, S.S.; Young, S.H.; Kommineni, C.; Kagan, V.E.; Castranova, V.; Shvedova, A.A. Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Dermal Toxicity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Toxicology 2009, 257, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurnherr, T.; Brandenberger, C.; Fischer, K.; Diener, L.; Manser, P.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Kaiser, J.P.; Krug, H.F.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Wick, P. A Comparison of Acute and Long-Term Effects of Industrial Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes on Human Lung and Immune Cells in Vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 200, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoglio, I.; Aldieri, E.; Gazzano, E.; Cesano, F.; Colonna, M.; Scarano, D.; Mazzucco, G.; Attanasio, A.; Yakoub, Y.; Lison, D.; et al. Thickness of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Affects Their Lung Toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, P.; Baluchamy, S.; Sadanandan, B.; Gopikrishnan, R.; Biradar, S.; Ramesh, V.; Hall, J.C.; Ramesh, G.T. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Activate NF-ΚB and AP-1 Signaling Pathways to Induce Apoptosis in Rat Lung Epithelial Cells. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulskamp, K.; Diabaté, S.; Krug, H.F. Carbon Nanotubes Show No Sign of Acute Toxicity but Induce Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species in Dependence on Contaminants. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Pant, A.B.; Kashyap, M.P.; Kumar, V.; Lohani, M.; Jonas, L.; Rahman, Q. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Induce Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer Cell Line-A549. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.Q. Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells in Vitro. Mutat. Res.—Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2011, 721, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clichici, S.; Mocan, T.; Filip, A.; Biris, A.; Simon, S.; Daicoviciu, D.; Decea, N.; Parvu, A.; Moldovan, R.; Muresan, A. Blood Oxidative Stress Generation after Intraperitoneal Administration of Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Rats. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2011, 98, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.R.N.; Rao, M.V.; Krishna, D.R.; Himabindu, V.; Reddy, Y.N. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress and Anti-Oxidant Status in Rat Serum Following Exposure of Carbon Nanotubes. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 59, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzano, E.; Riganti, C.; Tomatis, M.; Turci, F.; Bosia, A.; Fubini, B.; Ghigo, D. Potential Toxicity of Nonregulated Asbestiform Minerals: Balangeroite from the Western Alps. Part 3: Depletion of Antioxidant Defenses. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health—Part A 2005, 68, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.S.; Sarkar, S.; Periyakaruppan, A.; Barr, J.; Wise, K.; Thomas, R.; Wilson, B.L.; Ramesh, G.T. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Induces Oxidative Stress in Rat Lung Epithelial Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshimura, M.; Hesterberg, T.W.; Barrett, J.C.; Tsutsui, T. Correlation of Asbestos-Induced Cytogenetic Effects with Cell Transformation of Syrian Hamster Embryo Cells in Culture. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 5017–5022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lechner, J.F.; Tokiwa, T.; LaVeck, M.; Benedict, W.F.; Banks-Schlegel, S.; Yeager, H.; Banerjee, A.; Harris, C.C. Asbestos-Associated Chromosomal Changes in Human Mesothelial Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 3884–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ault, J.G.; Cole, R.W.; Jensen, C.G.; Bachert, L.A.; Rieder, C.L.; Rieder, C.L. Behavior of Crocidolite Asbestos during Mitosis in Living Vertebrate Lung Epithelial Cells. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dopp, E.; Schiffmann, D. Analysis of Chromosomal Alterations Induced by Asbestos and Ceramic Fibers. Toxicol. Lett. 1998, 96–97, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poser, I.; Rahman, Q.; Lohani, M.; Yadav, S.; Becker, H.H.; Weiss, D.G.; Schiffmann, D.; Dopp, E. Modulation of Genotoxic Effects in Asbestos-Exposed Primary Human Mesothelial Cells by Radical Scavengers, Metal Chelators and a Glutathione Precursor. Mutat. Res.—Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2004, 559, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina, D.; Villegas, V.E.; Rodríguez-Leguizamón, G.; Rondón-Lagos, M. Analyzing Biological and Molecular Characteristics and Genomic Damage Induced by Exposure to Asbestos. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 4997–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshimura, M.; Hesterberg, T.W.; Barrett, J.C. An Early, Nonrandom Karyotypic Change in Immortal Syrian Hamster Cell Lines Transformed by Asbestos: Trisomy of Chromosome 11. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1986, 22, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Nagai, H.; Ohara, H.; Hara, S.; Tachibana, M.; Hirano, S.; Shinohara, Y.; Kohyama, N.; Akatsuka, S.; Toyokuni, S. Characteristics and Modifying Factors of Asbestos-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamvakas, S.; Vock, E.H.; Lutz, W.K. On the Role of DNA Souble-Strand Breaks in Toxicity and Carcinogenesis. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1997, 27, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msiska, Z.; Pacurari, M.; Mishra, A.; Leonard, S.S.; Castranova, V.; Vallyathan, V. DNA Double-Strand Breaks by Asbestos, Silica, and Titanium Dioxide: Possible Biomarker of Carcinogenic Potential? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Smilenov, L.B.; He, P.; Masumura, K.I.; Nohmi, T.; Yu, Z.; Hei, T.K. New Insight into Intrachromosomal Deletions Induced by Chrysotile in the Gpt Delta Transgenic Mutation Assay. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo Cortez, B.; Quassollo, G.; Caceres, A.; Machado-Santelli, G.M. The Fate of Chrysotile-Induced Multipolar Mitosis and Aneuploid Population in Cultured Lung Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, G.; Andujar, P.; Pairon, J.C.; Billon-Galland, M.A.; Dion, C.; Dumortier, P.; Brochard, P.; Sobaszek, A.; Bartsch, P.; Paris, C.; et al. Quantification of Short and Long Asbestos Fibers to Assess Asbestos Exposure: A Review of Fiber Size Toxicity. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2014, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unfried, K.; Schürkes, C.; Abel, J. Distinct Spectrum of Mutations Induced by Crocidolite Asbestos: Clue for 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine-Dependent Mutagenesis in Vivo. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.; Huang, X.; Lien, Y.C.; Bao, L.; Yu, Z.; Hei, T.K. Genotoxic Mechanisms of Asbestos Fibers: Role of Extranuclear Targets. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihn, B.; Coulais, C.; Kauffer, E.; Bottin, M.C.; Martin, P.; Yvon, F.; Vigneron, J.C.; Binet, S.; Monhoven, N.; Steiblen, G.; et al. Inhaled Crocidolite Mutagenicity in Lung DNA. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.X.L.; Partridge, M.A.; Ghandhi, S.A.; Davidson, M.M.; Amundson, S.A.; Hei, T.K. Mitochondria-Derived Reactive Intermediate Species Mediate Asbestos-Induced Genotoxicity and Oxidative Stress-Responsive Signaling Pathways. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadian, H.; Salami, M.S.; Jaymand, M.; Azarnezhad, A.; Najafi, M.; Barabadi, H.; Ahmadi, A. Genotoxicity Assessment of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials; Have Their Unique Physicochemical Properties Made Them Double-Edged Swords? Mutat. Res.—Rev. Mutat. Res. 2020, 783, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozesk, M.; Franqui, L.S.; Pinheiro, F.C.; Nóbrega, J.A.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Fernandes, M.N. Effects of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Co-Exposure with Cadmium on Zebrafish Cell Line: Metal Uptake and Accumulation, Oxidative Stress, Genotoxicity and Cell Cycle. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 202, 110892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegrist, K.J.; Reynolds, S.H.; Kashon, M.L.; Lowry, D.T.; Dong, C.; Hubbs, A.F.; Young, S.H.; Salisbury, J.L.; Porter, D.W.; Benkovic, S.A.; et al. Genotoxicity of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes at Occupationally Relevant Doses. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegrist, K.J.; Reynolds, S.H.; Porter, D.W.; Mercer, R.R.; Bauer, A.K.; Lowry, D.; Cena, L.; Stueckle, T.A.; Kashon, M.L.; Wiley, J.; et al. Mitsui-7, Heat-Treated, and Nitrogen-Doped Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Elicit Genotoxicity in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Asakura, M.; Ishioka, C.; Kasai, T.; Katagiri, T.; Fukushima, S. In Vitro Chromosomal Aberrations Induced by Various Shapes of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs). J. Occup. Health 2016, 58, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, L.M.; Hubbs, A.F.; Young, S.H.; Kashon, M.L.; Dinu, C.Z.; Salisbury, J.L.; Benkovic, S.A.; Lowry, D.T.; Murray, A.R.; Kisin, E.R.; et al. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Induced Mitotic Disruption. Mutat. Res.—Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2012, 745, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, L.M.; Shvedova, A.A.; Hubbs, A.F.; Salisbury, J.L.; Benkovic, S.A.; Kashon, M.L.; Lowry, D.T.; Murray, A.R.; Kisin, E.R.; Friend, S.; et al. Induction of Aneuploidy by Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2009, 50, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, L.M.; Reynolds, S.H.; Castranova, V. Potential Pulmonary Effects of Engineered Carbon Nanotubes: In Vitro Genotoxic Effects. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.; Decordier, I.; Kirsch-Volders, M. Induction of Chromosome Malsegregation by Nanomaterials. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schins, R.P.F.; Albrecht, C.; Gerloff, K.; Van Berlo, D. Genotoxicity of Carbon Nanotubes. In The Toxicology of Carbon Nanotubes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; Volume 9781107008, pp. 150–173. ISBN 9780511919893. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Qu, X. Carbon Nanotubes Selective Destabilization of Duplex and Triplex DNA and Inducing B-A Transition in Solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3670–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Carboxyl-Modified Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Selectively Induce Human Telomeric i-Motif Formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19658–19663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangum, J.B.; Turpin, E.A.; Antao-Menezes, A.; Cesta, M.F.; Bermudez, E.; Bonner, J.C. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube (SWCNT)-Induced Interstitial Fibrosis in the Lungs of Rats Is Associated with Increased Levels of PDGF MRNA and the Formation of Unique Intercellular Carbon Structures That Bridge Alveolar Macrophages In Situ. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2006, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisin, E.R.; Murray, A.R.; Sargent, L.; Lowry, D.; Chirila, M.; Siegrist, K.J.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Leonard, S.; Castranova, V.; Fadeel, B.; et al. Genotoxicity of Carbon Nanofibers: Are They Potentially More or Less Dangerous than Carbon Nanotubes or Asbestos? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 252, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Chang, D.W.; Dai, L.; Hong, Y. DNA Damage Induced by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3592–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szendi, K.; Varga, C. Lack of Genotoxicity of Carbon Nanotubes in a Pilot Study. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Erdely, A.; Hulderman, T.; Salmen, R.; Liston, A.; Zeidler-Erdely, P.C.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Castranova, V.; Koyama, S.; Kim, Y.A.; Endo, M.; et al. Cross-Talk between Lung and Systemic Circulation during Carbon Nanotube Respiratory Exposure. Potential Biomarkers. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Endoh, S.; Maru, J.; Honda, K.; Ema, M.; Tanaka, J.; Fukumuro, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakajima, M.; et al. In Vivo Genotoxicity Study of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes Using Comet Assay Following Intratracheal Instillation in Rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giorgio, M.L.; Di Bucchianico, S.; Ragnelli, A.M.; Aimola, P.; Santucci, S.; Poma, A. Effects of Single and Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes on Macrophages: Cyto and Genotoxicity and Electron Microscopy. Mutat. Res.—Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2011, 722, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Sung, J.H.; Song, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, G.H.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, J.H.; Park, J.D.; et al. Persistent DNA Damage Measured by Comet Assay of Sprague Dawley Rat Lung Cells after Five Days of Inhalation Exposure and 1 Month Post-Exposure to Dispersed Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTS) Generated by New MWCNT Aerosol Generation System. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 128, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCorkle, R.A.; Slattery, S.D.; Nash, D.R.; Brinkley, B.R. Intracellular Protein Binding to Asbestos Induces Aneuploidy in Human Lung Fibroblasts. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 2006, 63, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPaolo, J.A.; DeMarinis, A.J.; Doniger, J. Asbestos and Benzo(a)Pyrene Synergism in the Transformation of Syrian Hamster Embryo Cells. Pharmacology 1983, 27, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossman, B.T.; Eastman, A.; Bresnick, E. Asbestos and Benzo[a]Pyrene Act Synergistically to Induce Squamous Metaplasia and Incorporation of [3H]Thymidine in Hamster Tracheal Epithelium. Carcinogenesis 1984, 5, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Ishihara, T.; Lee, W.H.; Ohara, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Okawa, K.; Toyokuni, S. Asbestos Surface Provides a Niche for Oxidative Modification. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamwong, Y.; Tangamornsuksan, W.; Lohitnavy, O.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Scholfield, C.N.; Reisfeld, B.; Lohitnavy, M. Additive Synergism between Asbestos and Smoking in Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Carbon Nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jialong, L.U.; Xing, B. Sorption of Organic Contaminants by Carbon Nanotubes: Influence of Adsorbed Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Zhu, D. Adsorption of Nonionic Aromatic Compounds to Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Effects of Aqueous Solution Chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7225–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E.J.; Pinto, R.A.; Landrum, P.F.; Weber, W.J. Influence of Carbon Nanotubes on Pyrene Bioaccumulation from Contaminated Soils by Earthworms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4181–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Anderson, T.A.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Payton, P.; Cañas-Carrell, J.E. The Influence of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Bioavailability and Toxicity to Soil Microbial Communities in Alfalfa Rhizosphere. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 116, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Phenolic Compounds by Carbon Nanotubes: Role of Aromaticity and Substitution of Hydroxyl Groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7254–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah; Asmaly, H.A.; Saleh, T.A.; Laoui, T.; Gupta, V.K.; Atieh, M.A. Enhanced Adsorption of Phenols from Liquids by Aluminum Oxide/Carbon Nanotubes: Comprehensive Study from Synthesis to Surface Properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 206, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Mostofi, M.; Alimohammadi, M.; McKay, G.; Yetilmezsoy, K.; Albadarin, A.B.; Heibati, B.; AlGhouti, M.; Mubarak, N.M.; Sahu, J.N. High-Performance Removal of Toxic Phenol by Single-Walled and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Kinetics, Adsorption, Mechanism and Optimization Studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Duan, L.; Zhu, D. Adsorption of Polar and Nonpolar Organic Chemicals to Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8295–8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Li, Y.; Luan, Z.; Di, Z.; Wang, H.; Tian, B.; Jia, Z. Adsorption of 1,2-Dichlorobenzene from Water to Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 376, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.M.; Hu, W.B.; Ahmad, I.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Peng, X.J.; Luan, Z.K. Carbon Nanotubes—The Promising Adsorbent in Wastewater Treatment. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 61, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragulj, M.; Tričković, J.; Kukovecz, Á.; Jović, B.; Molnar, J.; Rončević, S.; Kónya, Z.; Dalmacija, B. Adsorption of Chlorinated Phenols on Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24920–24929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.Q.; Yang, R.T. Carbon Nanotubes as Superior Sorbent for Dioxin Removal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2058–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, I.; Tulaphol, S.; Shengyong, L.; Pan, D.; Zhang, P.; Khan, M.S.; Yan, M.; Stevens, W.R. Online Measurement of 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene as Dioxin Indicator on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyung, H.; Kim, J.H. Natural Organic Matter (NOM) Adsorption to Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Effect of NOM Characteristics and Water Quality Parameters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4416–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Fulvic Acid by Carbon Nanotubes from Water. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Lu, C. Adsorption Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Desorption of Natural Dissolved Organic Matter by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Environ. Sci. Health—Part A 2007, 42, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verneuil, L.; Silvestre, J.; Mouchet, F.; Flahaut, E.; Boutonnet, J.C.; Bourdiol, F.; Bortolamiol, T.; Baqué, D.; Gauthier, L.; Pinelli, E. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Natural Organic Matter, and the Benthic Diatom Nitzschia Palea: “A Sticky Story”. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qu, R.; Liu, J.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z. Effect of Different Carbon Nanotubes on Cadmium Toxicity to Daphnia Magna: The Role of Catalyst Impurities and Adsorption Capacity. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihsanullah; Abbas, A.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Laoui, T.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Nasser, M.S.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.A. Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Solution by Advanced Carbon Nanotubes: Critical Review of Adsorption Applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, J.; Murphy, D.J. Mesothelioma: Identical Routes to Malignancy from Asbestos and Carbon Nanotubes. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1173–R1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Jeon, S.; Han, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.; Yu, I.J.; Song, K.S.; Kang, A.; Yun, W.S.; Kang, S.M.; et al. Threshold Rigidity Values for the Asbestos-like Pathogenicity of High-Aspect-Ratio Carbon Nanotubes in a Mouse Pleural Inflammation Model. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10867–10879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernova, T.; Murphy, F.A.; Galavotti, S.; Sun, X.M.; Powley, I.R.; Grosso, S.; Schinwald, A.; Zacarias-Cabeza, J.; Dudek, K.M.; Dinsdale, D.; et al. Long-Fiber Carbon Nanotubes Replicate Asbestos-Induced Mesothelioma with Disruption of the Tumor Suppressor Gene Cdkn2a (Ink4a/Arf). Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 3302–3314.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohcharoenkal, W.; Wang, L.; Stueckle, T.A.; Dinu, C.Z.; Castranova, V.; Liu, Y.; Rojanasakul, Y. Chronic Exposure to Carbon Nanotubes Induces Invasion of Human Mesothelial Cells through Matrix Metalloproteinase-2. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7711–7723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerce, E.; Ghosh, M.; Öner, D.; Duca, R.C.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Bekaert, B.; Hoet, P.H.M.; Godderis, L. Carbon Nanotube- and Asbestos-Induced DNA and RNA Methylation Changes in Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydman, E.M.; Ilves, M.; Vanhala, E.; Vippola, M.; Lehto, M.; Kinaret, P.A.S.; Pylkkänen, L.; Happo, M.; Hirvonen, M.R.; Greco, D.; et al. A Single Aspiration of Rod-like Carbon Nanotubes Induces Asbestos-like Pulmonary Inflammation Mediated in Part by the IL-1 Receptor. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zeidler, P.; Young, S.H.; Martinez, A.; Robinson, V.A.; Jones, W.; Baron, P.; Shi, X.; Castranova, V. Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase P38 and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Is Involved in Glass Fiber-Induced Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Production in Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 5360–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, W.Y.; Chou, C.C.; Ho, C.C.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Chou, H.Y.E.; Chen, J.J.W.; Chen, H.W.; Yang, P.C. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Induce Airway Hyperreactivity and Parenchymal Injury in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacurari, M.; Yin, X.J.; Zhao, J.; Ding, M.; Leonard, S.S.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Ducatman, B.S.; Sbarra, D.; Hoover, M.D.; Castranova, V.; et al. Raw Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes Induce Oxidative Stress and Activate MAPKs, AP-1, NF-ΚB, and Akt in Normal and Malignant Human Mesothelial Cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. In Vivo Activation and Pro-Fibrotic Function of NF-ΚB in Fibroblastic Cells during Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis Induced by Carbon Nanotubes. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Roh, J.; Kim, S.N.; Kang, M.S.; Han, Y.A.; Kim, Y.; Hong, J.T.; Choi, K. A Single Intratracheal Instillation of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Induced Early Lung Fibrosis and Subchronic Tissue Damage in Mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabolli, V.; Lison, D.; Huaux, F. The Complex Cascade of Cellular Events Governing Inflammasome Activation and IL- 1β Processing in Response to Inhaled Particles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, B.C.; Taylor, A.J.; Glista-Baker, E.E.; Shipley-Phillips, J.K.; Dackor, R.T.; Edin, M.L.; Lih, F.B.; Tomer, K.B.; Zeldin, D.C.; Langenbach, R.; et al. Role of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Exacerbation of Allergen-Induced Airway Remodeling by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Sayers, B.C.; Chun, K.S.; Lao, H.C.; Shipley-Phillips, J.K.; Bonner, J.C.; Langenbach, R. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Induce COX-2 and INOS Expression via MAP Kinase-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms in Mouse RAW264.7 Macrophages. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. Type 2 Immune Mechanisms in Carbon Nanotube-Induced Lung Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinis, S.I.; Hatzoglou, C.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Zarogiannis, S.G. Carbon Nanotubes and Other Engineered Nanoparticles Induced Pathophysiology on Mesothelial Cells and Mesothelial Membranes. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinaret, P.A.S.; Scala, G.; Federico, A.; Sund, J.; Greco, D. Carbon Nanomaterials Promote M1/M2 Macrophage Activation. Small 2020, 16, 1907609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, S.S.; Jackson, P.; Kling, K.; Knudsen, K.B.; Skaug, V.; Kyjovska, Z.O.; Thomsen, B.L.; Clausen, P.A.; Atluri, R.; Berthing, T.; et al. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Physicochemical Properties Predict Pulmonary Inflammation and Genotoxicity. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatzidou, E.T.; Zira, A.N.; Theocharis, S.E. Toxicogenomics: A Pivotal Piece in the Puzzle of Toxicological Research. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2007, 27, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, B.; Chen, C. Understanding the Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, H.J.; Hutchison, G.R.; Christensen, F.M.; Peters, S.; Hankin, S.; Aschberger, K.; Stone, V. A Critical Review of the Biological Mechanisms Underlying the in Vivo and in Vitro Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes: The Contribution of Physico-Chemical Characteristics. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 207–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhanova, A.; Bozrova, S.; Sokolov, P.; Berestovoy, M.; Karaulov, A.; Nabiev, I. Dependence of Nanoparticle Toxicity on Their Physical and Chemical Properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, C.; Zhernovkov, V.; Cassidy, H.; Kholodenko, B.; Matallanas, D.; Cosnier, F.; Gaté, L. Inhaled Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Differently Modulate Global Gene and Protein Expression in Rat Lungs. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, P.X.; Wan, B.; Guo, L.H. In Vitro Toxicity of Acid-Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Effects on Murine Macrophages and Gene Expression Profiling. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacurari, M.; Qian, Y.; Porter, D.W.; Wolfarth, M.; Wan, Y.; Luo, D.; Ding, M.; Castranova, V.; Guo, N.L. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Induced Gene Expression in the Mouse Lung: Association with Lung Pathology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 255, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvedova, A.A.; Yanamala, N.; Kisin, E.R.; Khailulli, T.O.; Birch, M.E.; Fatkhutdinova, L.M. Integrated Analysis of Dysregulated NcRNA and MRNA Expression Profiles in Humans Exposed to Carbon Nanotubes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaanderen, J.; Pronk, A.; Rothman, N.; Hildesheim, A.; Silverman, D.; Hosgood, H.D.; Spaan, S.; Kuijpers, E.; Godderis, L.; Hoet, P.; et al. A Cross-Sectional Study of Changes in Markers of Immunological Effects and Lung Health Due to Exposure to Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaliullin, T.O.; Yanamala, N.; Newman, M.S.; Kisin, E.R.; Fatkhutdinova, L.M.; Shvedova, A.A. Comparative Analysis of Lung and Blood Transcriptomes in Mice Exposed to Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 390, 114898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahle, S.; Cassidy, H.; Leroux, M.M.; Mercier, R.; Ghanbaja, J.; Doumandji, Z.; Matallanas, D.; Rihn, B.H.; Joubert, O.; Ferrari, L. Genes Expression Profiling of Alveolar Macrophages Exposed to Non-Functionalized, Anionic and Cationic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Shows Three Different Mechanisms of Toxicity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder-Talkington, B.N.; Dong, C.; Singh, S.; Raese, R.; Qian, Y.; Porter, D.W.; Wolfarth, M.G.; Guo, N.L. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Induced Gene Expression Biomarkers for Medical and Occupational Surveillance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, T.; Umeda, Y.; Ohnishi, M.; Mine, T.; Kondo, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Fukushima, S. Lung Carcinogenicity of Inhaled Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube in Rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nymark, P.; Guled, M.; Borze, I.; Faisal, A.; Lahti, L.; Salmenkivi, K.; Kettunen, E.; Anttila, S.; Knuutila, S. Integrative Analysis of MicroRNA, MRNA and ACGH Data Reveals Asbestos- and Histology-Related Changes in Lung Cancer. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2011, 50, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Choi, Y.C.; Yu, I.J.; Song, K.S.; Bang, I.S.; Lee, J.K.; Kang, C.S. Toxicogenomic Comparison of Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) and Asbestos. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Watanabe, S.; Verma, R.; Jablonski, R.P.; Chen, C.I.; Cheresh, P.; Markov, N.S.; Reyfman, P.A.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Sichizya, L.; et al. A Spatially Restricted Fibrotic Niche in Pulmonary Fibrosis Is Sustained by M-CSF/M-CSFR Signalling in Monocyte-Derived Alveolar Macrophages. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, E.Y.; Speck, M.; Shimoda, L.M.N.; Kahue, K.; Sung, C.; Stokes, A.J.; Turner, H. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Exposure Induces Membrane Rearrangement and Suppression of Receptor-Mediated Signalling Pathways in Model Mast Cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraku, Y.; Guo, F.; Ma, N.; Yamada, T.; Wang, S.; Kawanishi, S.; Murata, M. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Induces Nitrative DNA Damage in Human Lung Epithelial Cells via HMGB1-RAGE Interaction and Toll-like Receptor 9 Activation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.P.; Bondarenko, O.; Kohonen, P.; Andón, F.T.; Brzicová, T.; Gessner, I.; Mathur, S.; Bottini, M.; Calligari, P.; Stella, L.; et al. Macrophage Sensing of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes via Toll-like Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nymark, P.; Wijshoff, P.; Cavill, R.; Van Herwijnen, M.; Coonen, M.L.J.; Claessen, S.; Catalán, J.; Norppa, H.; Kleinjans, J.C.S.; Briedé, J.J. Extensive Temporal Transcriptome and MicroRNA Analyses Identify Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Human Lung Cells. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, S.S.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Labib, S.; Wu, D.; Husain, M.; Williams, A.; Bøgelund, J.P.; Andersen, O.; Kbøler, C.; Mløhave, K.; et al. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Novel Mechanistic Insight into Murine Biological Responses to Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Lungs and Cultured Lung Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Amadei, C.A.; Gou, N.; Lin, Y.; Lan, J.; Vecitis, C.D.; Gu, A.Z. Toxicity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs): Effect of Lengths, Functional Groups and Electronic Structures Revealed by a Quantitative Toxicogenomics Assay. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 1348–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halappanavar, S.; Van Den Brule, S.; Nymark, P.; Gaté, L.; Seidel, C.; Valentino, S.; Zhernovkov, V.; Høgh Danielsen, P.; De Vizcaya, A.; Wolff, H.; et al. Adverse Outcome Pathways as a Tool for the Design of Testing Strategies to Support the Safety Assessment of Emerging Advanced Materials at the Nanoscale. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokuni, S. Genotoxicity and Carcinogenicity Risk of Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 2098–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).