Recent Developments and Advancements in Graphene-Based Technologies for Oil Spill Cleanup and Oil–Water Separation Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Oil–Water Separation Techniques
3. Graphene-Based Membranes in Oil/Water Separation
3.1. Graphene-Based Sponges for Oil/Water Separation
3.2. Graphene-Based Hydrogels for Oil/Water Separation
3.3. Graphene-Based Aerogels for Oil/Water Separation
3.4. Graphene Foam
3.5. Graphene Decorated Meshes for Oil–Water Separation
3.6. Graphene-Coated Cotton for Oil/Water Separation
4. Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohal, M.; Ainsworth, C.; Lupher, B.; Montagna, P.A.; Paris, C.B.; Perlin, N.; Suprenand, P.M.; Yoskowitz, D. The effect of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on two ecosystem services in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 133, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; O’Reilly, S.E.; Zhao, D. Study of residual oil in Bay Jimmy sediment 5 years after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill: Persistence of sediment retained oil hydrocarbons and effect of dispersants on desorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.R.; Moye, J.K.; Cacela, D.; Dean, K.M.; Pritsos, C.A. Low level exposure to crude oil impacts avian flight performance: The Deepwater Horizon oil spill effect on migratory birds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 146, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.; Oh, J.H.; Hong, J.-S.; Kim, D. Effect of the Hebei Spirit oil spill on intertidal meiofaunal communities in Taean, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Bu, S. Trajectory and weathering of oil spill in Daya bay, the South China sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Hong, S.H.; Won, J.; Yim, U.H.; Jung, J.-H.; Ha, S.Y.; An, J.G.; Joo, C.; Kim, E.; Han, G.M.; et al. Petroleum hydrocarbon contaminations in the intertidal seawater after the Hebei Spirit oil spill—Effect of tidal cycle on the TPH concentrations and the chromatographic characterization of seawater extracts. Water Res. 2013, 47, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oribayo, O.; Feng, X.; Rempel, G.L.; Pan, Q. Synthesis of lignin-based polyurethane/graphene oxide foam and its application as an absorbent for oil spill clean-ups and recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, Z.; Samadi, M.T.; Kazemi, A.; Rashidi, A.M.; Rahmani, A.R. Nanoporous graphene and graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge as a highly efficient, superhydrophobic, and reusable oil spill absorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5025–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teas, C.; Kalligeros, S.; Zanikos, F.; Stournas, S.; Lois, E.; Anastopoulos, G. Investigation of the effectiveness of absorbent materials in oil spills clean up. Desalination 2001, 140, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar-Mohajer, N.; Lam, A.; Dora, L.; Katz, J.; Rule, A.M.; Koehler, K. Impact of dispersant on crude oil content of airborne fine particulate matter emitted from seawater after an oil spill. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharuddin, S.H.; Mustahil, N.A.; Reddy, A.V.B.; Abdullah, A.A.; Mutalib, M.I.A.; Moniruzzaman, M. Development, formulation and optimization of a novel biocompatible ionic liquids dispersant for the effective oil spill remediation. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Callies, U. A probabilistic model of decision making regarding the use of chemical dispersants to combat oil spills in the German Bight. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Lewis, A.; Beegle-Krause, C.J. A critical review of marine snow in the context of oil spills and oil spill dispersant treatment with focus on the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Callies, U. Implications of using chemical dispersants to combat oil spills in the German Bight—Depiction by means of a Bayesian network. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.U.H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Sivapragasam, M.; Talukder, M.M.R.; Yusup, S.B.; Goto, M. A binary mixture of a biosurfactant and an ionic liquid surfactant as a green dispersant for oil spill remediation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 280, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunswick, P.; MacInnis, C.Y.; Kim, M.; Yan, J.; Fieldhouse, B.; Brown, C.E.; van Aggelen, G.; Shang, D. Improved oil spill dispersant monitoring in seawater using dual tracers: Dioctyl and monoctyl sulfosuccinates sourced from corexit EC9500A. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1598, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wang, H.; Jing, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Bao, M. An efficient and environmental-friendly dispersant based on the synergy of amphiphilic surfactants for oil spill remediation. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Ribicic, D.; Winkler, A.; Netzer, R. Biodegradation of dispersed oil in seawater is not inhibited by a commercial oil spill dispersant. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guodong, Q.; Yupeng, Z.; Xuhe, R.; Jie, C. Research on Development and Effectiveness Evaluation Technology of New Environment-friendly Oil Spill Dispersant. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 3, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinier, V.; Le Goué, E.; Rondón-Gonzáles, M.; Passade-Boupat, N.; Bourrel, M. Optimization of chemical dispersants effectiveness in case of subsurface oil spill. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 541, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, F.L.; Stoyanov, S.R.; Soares, J.B.P. Development and application of an amylopectin-graft-poly(methyl acrylate) solidifier for rapid and efficient containment and recovery of heavy oil spills in aqueous environments. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, F.L.; Stoyanov, S.R.; Soares, J.B.P. Application of solidifiers for oil spill containment: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaravadivelu, D.; Suidan, M.T.; Venosa, A.D.; Rosales, P.I. Characterization of solidifiers used for oil spill remediation. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneddon, J.; Hardaway, C.; Bobbadi, K.K.; Beck, J.N. A study of a crude oil spill site for selected metal concentrations remediated by a controlled burning in Southwest Louisiana. Microchem. J. 2006, 82, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Pricop, L.; Samoila, P.; Rotaru, R.; Harabagiu, V. Surface hydrophobization of polyester fibers with poly(methylhydro-dimethyl)siloxane copolymers: Experimental design for testing of modified nonwoven materials as oil spill sorbents. Polym. Test. 2017, 59, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A. Oil spill cleanup by raw flax fiber: Modification effect, sorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5553–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.T.M.; Oliveira, L.F.A.M.; Sonsin, A.F.; Duarte, J.L.S.; Soletti, J.I.; Fonseca, E.J.S.; Ribeiro, L.M.O.; Meili, L. Ultrafast diesel oil spill removal by fibers from silk-cotton tree: Characterization and sorption potential evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Dorneanu, P.P.; Airinei, A.; Olaru, N.; Samoila, P.; Rotaru, A. Design and evaluation of electrospun polysulfone fibers and polysulfone/NiFe2O4 nanostructured composite as sorbents for oil spill cleanup. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 70, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorneanu, P.P.; Cojocaru, C.; Olaru, N.; Samoila, P.; Airinei, A.; Sacarescu, L. Electrospun PVDF fibers and a novel PVDF/CoFe2O4 fibrous composite as nanostructured sorbent materials for oil spill cleanup. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 424, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Herrero, C.; Romero, A.; Esteban-Arranz, A.; de la Osa, A.R.; Sánchez-Silva, L. Utilization and reusability of hydroxyethyl cellulose alumina based aerogels for the removal of spilled oil. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.A.; Cortés, F.B.; Nassar, N.N. Adsorptive removal of oil spill from oil-in-fresh water emulsions by hydrophobic alumina nanoparticles functionalized with petroleum vacuum residue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 425, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmodi, G.; Dangwal, S.; Zarrintaj, P.; Zhu, M.; Mao, Y.; McLlroy, D.N.; Reza Saeb, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Ramsey, J.D.; Kim, S.-J. NaA zeolite-coated meshes with tunable hydrophilicity for oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajenifuja, E.; Alayande, S.O.; Aromolaran, O.A.; Ajao, J.A.; Dare, E.O.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Ajayi, E.O.B. Equilibrium kinetics study of electrospun polystyrene and polystyrene-zeolite fibres for crude oil-water separation. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 19, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, L.; Franus, M.; Józefaciuk, G.; Franus, W. Synthetic zeolites from fly ash as effective mineral sorbents for land-based petroleum spills cleanup. Fuel 2015, 147, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqa, A.; Shahid, A.; Gill, R. Silica decorated CNTs sponge for selective removal of toxic contaminants and oil spills from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassod, A.; Gibril, M.; Islam, S.R.; Huang, W.; Xu, G. Polypropylene/lignin blend monoliths used as sorbent in oil spill cleanup. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.F.; Mather, R.R.; Fotheringham, A.F.; Yang, R.D. Evaluation of nonwoven polypropylene oil sorbents in marine oil-spill recovery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Hong, Y.-J.; Hu, A.H. Using a composite material containing waste tire powder and polypropylene fiber cut end to recover spilled oil. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhen, Q.; Cui, J.-Q.; Liu, R.-T.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Qian, X.-M.; Liu, Y. Groove-shaped polypropylene/polyester micro/nanofibrous nonwoven with enhanced oil wetting capability for high oil/water separation. Polymer 2020, 193, 122356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasvand, S.; Rahmani, A.; Samadi, M.; Asgari, G.; Azizian, S.; Poormohammadi, A. Application of polystyrene nanofibers filled with sawdust as separator pads for separation of oil spills. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 146, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Shang, Y.; Ding, B.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Nanoporous polystyrene fibers for oil spill cleanup. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Cao, J.; Hong, M.; Zhou, C.; Xu, Q. Fabrication of polystyrene fibers with tunable co-axial hollow tubing structure for oil spill cleanup. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 367, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghunaimi, F.I.; Alsaeed, D.J.; Harith, A.M.; Saleh, T.A. Synthesis of 9-octadecenoic acid grafted graphene modified with polystyrene for efficient light oil removal from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Sha, S.; Yang, S.; Wu, J.; Ma, J.; Hou, C.; Sheng, Z. The coating and reduction of graphene oxide on meshes with inverse wettability for continuous water/oil separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 538, 147948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Su, Y.; Fan, Q.; Li, Z.; Cui, W.; Yu, M.; Ning, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y. Robust Graphene@ PPS Fibrous Membrane for Harsh Environmental Oil/Water Separation and All-Weather Cleanup of Crude Oil Spill by Joule Heat and Photothermal Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19377–19386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothi Prakash, C.; Prasanth, R. Approaches to design a surface with tunable wettability: A review on surface properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 108–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; He, Z.; Gong, H.; He, L. Recent advances in oil-water separation materials with special wettability modified by graphene and its derivatives: A review. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2021, 170, 108678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Ma, P.; Lai, D.; Lai, X.; Zeng, X.; Li, H. Superhydrophobic reduced graphene oxide@ poly (lactic acid) foam with electrothermal effect for fast separation of viscous crude oil. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 11266–11277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddon, R.C. Graphene—The Mother of Two-Dimensional (2-D) Materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2191–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Xu, C.; Gao, Y. Open-air combustion synthesis of three-dimensional graphene for oil absorption and energy storage. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 238–239, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Cui, Y.; Qin, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. A novel robust adsorbent for efficient oil/water separation: Magnetic carbon nanospheres/graphene composite aerogel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Tang, S.; Chang, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, D.; Liu, T.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, Y. A bifunctional melamine sponge decorated with silver-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for oil-water separation and antibacterial applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Mubarak, N.M.; Abdullah, E.C.; Nizamuddin, S.; Khalid, M.; Inamuddin. Recent trends in the synthesis of graphene and graphene oxide based nanomaterials for removal of heavy metals—A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 66, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Dai, B.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xu, F.; Peng, Q.; Yang, Z.; Bai, J.; et al. Multifunctional three-dimensional graphene nanoribbons composite sponge. Carbon 2016, 104, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, G.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; Lin, S. Reduced graphene oxide composites and its real-life application potential for in-situ crude oil removal. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, K.; Li, X. Facile preparation of nitrogen-doped graphene sponge as a highly efficient oil absorption material. Mater. Lett. 2016, 178, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotin, K.I.; Sikes, K.J.; Jiang, Z.; Klima, M.; Fudenberg, G.; Hone, J.; Kim, P.; Stormer, H.L. Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene. Solid State Commun. 2008, 146, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Superior Thermal Conductivity of Single-Layer Graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-M.; Shenai, P.; Zhao, Y. Tight binding description on the band gap opening of pyrene-dispersed graphene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2011, 13, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Shim, B. Graphene: An emerging material for biological tissue engineering. Carbon Lett. 2013, 14, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheehy, D.E.; Schmalian, J. Optical transparency of graphene as determined by the fine-structure constant. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 193411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papageorgiou, D.G.; Kinloch, I.A.; Young, R.J. Mechanical properties of graphene and graphene-based nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 90, 75–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-U.; Yoon, D.; Cheong, H. Estimation of Young’s Modulus of Graphene by Raman Spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4444–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.-A.; Jin, Z.; Ma, P.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Shi, J.-Y.; Niu, J.-B.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, S.-Q.; Li, M.; Liu, X.-Y.; et al. The sheet resistance of graphene under contact and its effect on the derived specific contact resistivity. Carbon 2015, 82, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Rout, G.C. Band gap opening in graphene: A short theoretical study. Int. Nano Lett. 2017, 7, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Weng, D.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, S.; Wang, J. Separation Mechanism and Construction of Surfaces with Special Wettability for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11006–11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junaidi, N.F.D.; Othman, N.H.; Fuzil, N.S.; Mat Shayuti, M.S.; Alias, N.H.; Shahruddin, M.Z.; Marpani, F.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Aba, N.D. Recent development of graphene oxide-based membranes for oil–water separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.-Y.; Choi, Y.-S.; Shin, H.; Kim, K.; Shin, D.M.; Lee, J.-C. Cross-Linked Graphene Oxide Membrane Functionalized with Self-Cross-Linkable and Bactericidal Cardanol for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 2600–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z. Free-Standing Graphene Oxide-Palygorskite Nanohybrid Membrane for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8247–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, D.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. TiO2/sulfonated graphene oxide/Ag nanoparticle membrane: In situ separation and photodegradation of oil/water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Sol–gel fabrication of a non-laminated graphene oxide membrane for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19517–19524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, W.; Su, D.; Sang, Z.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; Liang, J.; Dou, S.X. A multifunctional hierarchical porous SiO2/GO membrane for high efficiency oil/water separation and dye removal. Carbon 2020, 160, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, E.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, W. Covalently intercalated graphene oxide for oil–water separation. Carbon 2015, 82, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.V.; George, R.; Sharma, A.K.; Malwal, D.; Lahiri, I. Development of superhydrophillic tannic acid-crosslinked graphene oxide membranes for efficient treatment of oil contaminated water with enhanced stability. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, O.; Wahab, M.A.; Abdala, A. Mixed matrix membranes containing aspartic acid functionalized graphene oxide for enhanced oil-water emulsion separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alammar, A.; Park, S.-H.; Williams, C.J.; Derby, B.; Szekely, G. Oil-in-water separation with graphene-based nanocomposite membranes for produced water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Ji, D.; Zhang, H. One-step facile fabrication of PVDF/graphene composite nanofibrous membrane with enhanced oil affinity for highly efficient gravity-driven emulsified oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Barras, A.; Lu, S.; Xu, W.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Fabrication of superhydrophobic/superoleophilic functionalized reduced graphene oxide/polydopamine/PFDT membrane for efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y. One-step preparation of sepiolite/graphene oxide membrane for multifunctional oil-in-water emulsions separation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 181, 105208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Qin, C.; Meng, M.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Peng, J. A mussel inspired highly stable graphene oxide membrane for efficient oil-in-water emulsions separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, F.; Chen, Q.; Yin, D.; Min, X. A novel reduced graphene oxide-based composite membrane prepared via a facile deposition method for multifunctional applications: Oil/water separation and cationic dyes removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, J.A.; Bhuvana, S.; Anbharasi, V.; Ayyanar, N.; Boodhoo, K.V.K.; Singh, G. Ultra-wetting graphene-based PES ultrafiltration membrane—A novel approach for successful oil-water separation. Water Res. 2016, 103, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Pan, X.; Xue, Q.; He, D.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Q. Antifouling hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile/graphene oxide membrane with spindle-knotted structure for highly effective separation of oil-water emulsion. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 532, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Q.; Song, L. The improved oil/water separation performance of graphene oxide modified Al2O3 microfiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.Y.; Chua, H.S.; Ng, C.Y. Incorporation of graphene oxide-based nanocomposite in the polymeric membrane for water and wastewater treatment: A review on recent development. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, A.P.; Wu, W.-P.; Ravindranath, R.; Roy, P.; Lin, G.-L.; Chang, H.-T. Polymer/reduced graphene oxide functionalized sponges as superabsorbents for oil removal and recovery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y.; Yin, L.; Tang, H.; Li, C. Versatile fabrication of the magnetic polymer-based graphene foam and applications for oil–water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 468, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Lee, C.-L.; Hsieh, P.-Y.; Chen, C.-S.; Kang, Y.-Y.; Chin, W.-C.; Tai, N.-H. Superhydrophobic graphene-based sponge as a novel sorbent for crude oil removal under various environmental conditions. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pethsangave, D.A.; Wadekar, P.H.; Khose, R.V.; Some, S. Super-hydrophobic carrageenan cross-linked graphene sponge for recovery of oil and organic solvent from their water mixtures. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridis, L.V.; Kokkinos, N.C.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Chapter 8—Graphene aerogels for oil absorption. In Interface Science and Technology; Kyzas, G.Z., Mitropoulos, A.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 30, pp. 173–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, M.; Xia, M.; Cao, W.; Du, M.; Dou, J.; Zhao, D. Novel high-capacity and reusable carbonaceous sponges for efficient absorption and recovery of oil from water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 487, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.M.G.; Anis, B.; Khalil, A.S.G. Facile surface treatment and decoration of graphene-based 3D polymeric sponges for high performance separation of heavy oil-in-water emulsions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Tai, N.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Kuo, W.-S. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties of graphene-based sponges fabricated using a facile dip coating method. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7908–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Cui, Z.; Wei, W.; Xie, J.; Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, J. Constructing polyurethane sponge modified with silica/graphene oxide nanohybrids as a ternary sorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. How to reduce household carbon emissions: A review of experience and policy design considerations. Energy Policy 2017, 102, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, L. In situ fastening graphene sheets into a polyurethane sponge for the highly efficient continuous cleanup of oil spills. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, C.; Li, B. Highly reusable and superhydrophobic spongy graphene aerogels for efficient oil/water separation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Su, X.; Liang, T.; Zeng, X. Thiolated graphene-based superhydrophobic sponges for oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Li, Y.; Fei, T.; Gong, W. Facile one-pot synthesis of superhydrophobic reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge at the presence of ethanol for oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamsaz, A.; Goharshadi, E.K. Flame retardant, superhydrophobic, and superoleophilic reduced graphene oxide/orthoaminophenol polyurethane sponge for efficient oil/water separation. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 112979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yu, B.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Ming, Z.; Yang, S.-T. One-pot hydrothermal preparation of graphene sponge for the removal of oils and organic solvents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 362, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, F.; Hu, L.-L.; Gong, L.-X.; Zhao, L.; Li, S.-N.; Tang, L.-C. Facile synthesis of super-hydrophobic, electrically conductive and mechanically flexible functionalized graphene nanoribbon/polyurethane sponge for efficient oil/water separation at static and dynamic states. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2154–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilifard, M.; Javadian, S. Magnetic superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge loaded with Fe3O4@oleic acid@graphene oxide as high performance adsorbent oil from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 408, 127369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Pan, F.; Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Yin, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Mechanically robust polybenzoxazine/reduced graphene oxide wrapped-cellulose sponge towards highly efficient oil/water separation, and solar-driven for cleaning up crude oil. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 197, 108254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Xu, H.; Guo, K.-Y.; Zhang, J.-W.; Xia, Q.-Q.; Zhang, G.-D.; Zhao, L.; Gao, J.-F.; Tang, L.-C. Mechanically flexible, super-hydrophobic and flame-retardant hybrid nano-silica/graphene oxide wide ribbon decorated sponges for efficient oil/water separation and fire warning response. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Qiao, W. Reduced graphene-based superhydrophobic sponges modified by hexadecyltrimethoxysilane for oil adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 589, 124433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, G.; Zhang, L. Silk fibroin-graphene oxide functionalized melamine sponge for efficient oil absorption and oil/water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497, 143762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Ning, X.; Yuan, Y. Solar-heated graphene sponge for high-efficiency clean-up of viscous crude oil spill. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ji, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Lu, H. Air-dried graphene-based sponge for Water/oil separation and strain sensing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 555, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Chen, G.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.; He, K.; Huang, Z.; Hu, L.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Yuan, L.; et al. Superhydrophobic kaolinite modified graphene oxide-melamine sponge with excellent properties for oil-water separation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 163, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Yan, T.; Yu, J.; Jiao, F. Super-hydrophobic and super-lipophilic functionalized graphene oxide/polyurethane sponge applied for oil/water separation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Hao, G.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Yu, L. One-pot synthesis of robust superhydrophobic, functionalized graphene/polyurethane sponge for effective continuous oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Chen, Y. Recycle and reusable melamine sponge coated by graphene for highly efficient oil-absorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 488, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Yan, B.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Gong, L.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Zhu, L.; et al. An amphiphobic graphene-based hydrogel as oil-water separator and oil fence material. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.K.; Tan, I.S.; Foo, H.C.Y.; Lam, M.K.; Tiong, A.C.Y.; Lim, S. Optimization and evaluation of reduced graphene oxide hydrogel composite as a demulsifier for heavy crude oil-in-water emulsion. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 33, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Bian, F.; Zou, M.; Zhao, Y. Graphene oxide hydrogel particles from microfluidics for oil decontamination. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 528, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Ding, C. Graphene aerogel prepared through double hydrothermal reduction as high-performance oil adsorbent. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 226, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Yue, Q.; Xu, X.; Kong, W.; Gao, B.; Cai, Z.; Chen, Y. A tunable amphiphilic Enteromorpha-modified graphene aerogel for oil/water separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 763, 142958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ke, W.-T.; Liao, Y.-C. Elastic nanocellulose/graphene aerogel with excellent shape retention and oil absorption selectivity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 111, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Jana, S.C. Shrinkage reduced polyimide-graphene oxide composite aerogel for oil absorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 307, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, T.; Yu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, H. A lignin-based carbon aerogel enhanced by graphene oxide and application in oil/water separation. Fuel 2020, 278, 118376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.V.; Pinna, A.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Malfatti, L.; Guardia, P.; Cabot, A.; Casula, M.F. Performance of oil sorbents based on reduced graphene oxide–silica composite aerogels. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, T.; Qin, L.; Yu, Z.-Z. Photothermal hierarchical carbon nanotube/reduced graphene oxide microspherical aerogels with radially orientated microchannels for efficient cleanup of crude oil spills. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 570, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhu, J.; Ge, S.; Jiang, C.; Guo, T.; Peng, T.; Huang, T.; Xie, L. Biocompatible, hydrophobic and resilience graphene/chitosan composite aerogel for efficient oil−water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 385, 125361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Hou, X.; Hu, X. Super-performance photothermal conversion of 3D macrostructure graphene-CuFeSe2 aerogel contributes to durable and fast clean-up of highly viscous crude oil in seawater. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Xu, X.; Kong, W.; Li, N.; Jiang, W. A facile approach to ultralight and recyclable 3D self-assembled copolymer/graphene aerogels for efficient oil/water separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, Z. Ultralight, highly compressible, hydrophobic and anisotropic lamellar carbon aerogels from graphene/polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanofiber aerogel as oil removing absorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Kong, W.; Zang, Y.; Jiang, W. Grass-modified graphene aerogel for effective oil-water separation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 129, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Fan, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, R. Compressive, ultralight and fire-resistant lignin-modified graphene aerogels as recyclable absorbents for oil and organic solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Politowicz, A.L.; Chen, E.; Huang, H.-X.; Turng, L.-S. Highly compressible ultra-light anisotropic cellulose/graphene aerogel fabricated by bidirectional freeze drying for selective oil absorption. Carbon 2018, 132, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Lyu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Facile synthesis of fluorinated polydopamine/chitosan/reduced graphene oxide composite aerogel for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, P.-w.; Liu, Y.-c.; Wang, L.; Feng, L.-j.; Li, C.-h. Dopamine and L-arginine tailored fabrication of ultralight nitrogen-doped graphene aerogels for oil spill treatment. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2017, 45, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, P.; Zeng, W.; Ling, C.; Zhao, S.; Liao, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, A. Highly hydrophobic and ultralight graphene aerogel as high efficiency oil absorbent material. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1957–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, S.; Tran, D.N.H.; Altalhi, T.; Losic, D. Outstanding adsorption performance of graphene–carbon nanotube aerogels for continuous oil removal. Carbon 2014, 80, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-Y.; Sohn, E.-H.; Park, S.; Park, H.S. Highly-efficient and recyclable oil absorbing performance of functionalized graphene aerogel. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Lv, C.; Miao, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, S. Gold nanoparticles modified graphene foam with superhydrophobicity and superoleophilicity for oil-water separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 758, 143660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebsz, M.; Pasinszki, T.; Tung, T.T.; Nine, M.J.; Losic, D. Multiple applications of bio-graphene foam for efficient chromate ion removal and oil-water separation. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, J.; Abraham, J.; Sunny, J.; Mathew, J.; George, S.C. Hydrophobic, superabsorbing materials from reduced graphene oxide/MoS2 polyurethane foam as a promising sorbent for oil and organic solvents. Polym. Test. 2020, 87, 106429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tai, T.; He, Y. Solar heated graphene-melamine foam for absorbing oil and organic solvents. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Tian, D.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, G. Superhydrophobic magnetic reduced graphene oxide-decorated foam for efficient and repeatable oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Mu, L.; Ma, P.-C. Magnetic graphene foam for efficient adsorption of oil and organic solvents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yang, H.; Su, C.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, Z. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted synthesis of stable reduced graphene oxide modified melamine foam with superhydrophobicity and high oil adsorption capacities. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, B. Graphene oxide coated meshes with stable underwater superoleophobicity and anti-oil-fouling property for highly efficient oil/water separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Guo, T.; Li, X.; Xing, W.; Xue, Q. A durable mesh decorated with polydopamine/graphene oxide for highly efficient oil/water mixture separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 479, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sha, S.; Lu, H.; Wu, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, D.; Hou, C.; Sheng, Z. Graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide coated cotton fabrics with opposite wettability for continuous oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Men, X.; Zhou, X.; Xue, Q. A graphene coated cotton for oil/water separation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 102, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoai, N.T.; Sang, N.N.; Hoang, T.D. Thermal reduction of graphene-oxide-coated cotton for oil and organic solvent removal. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 216, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
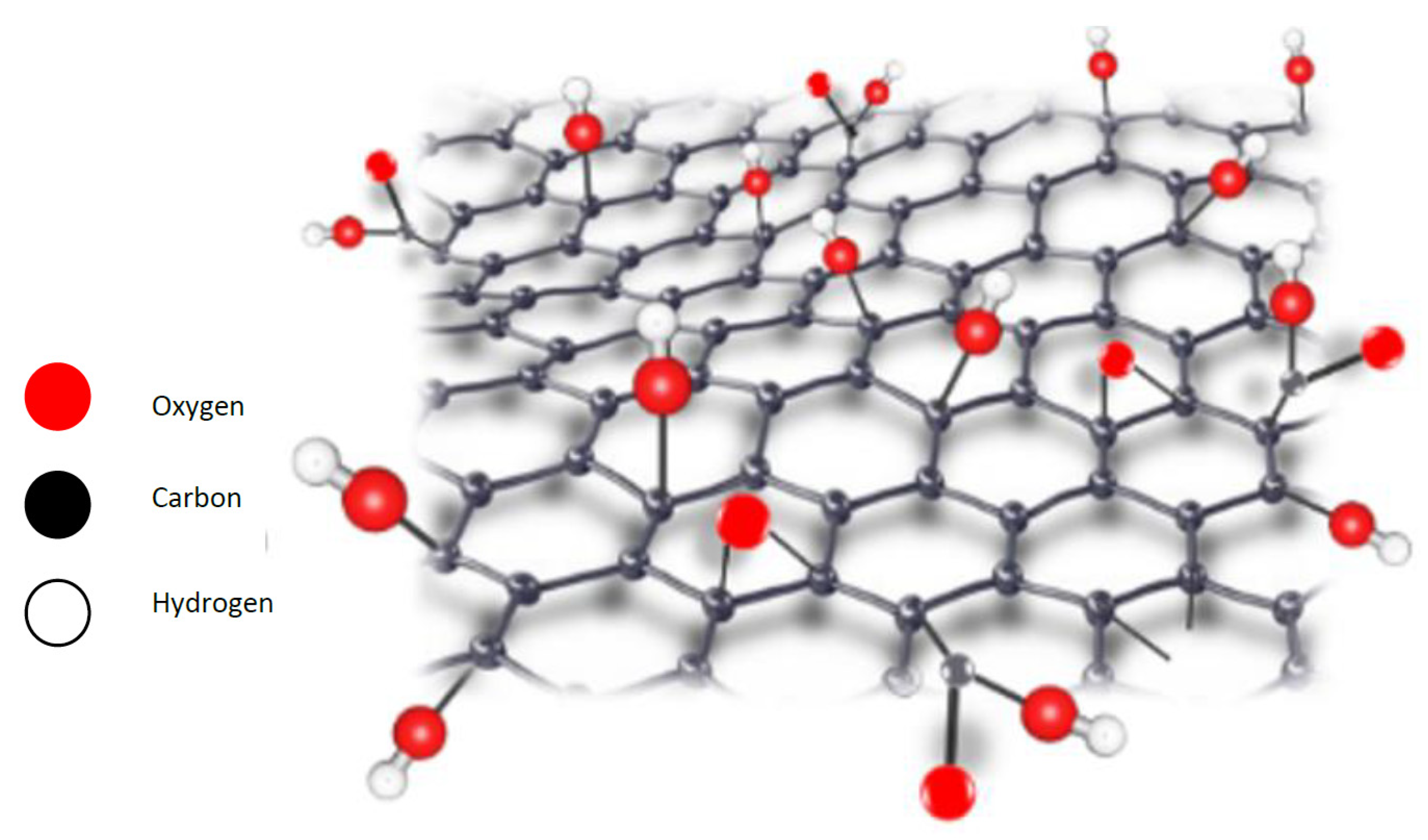
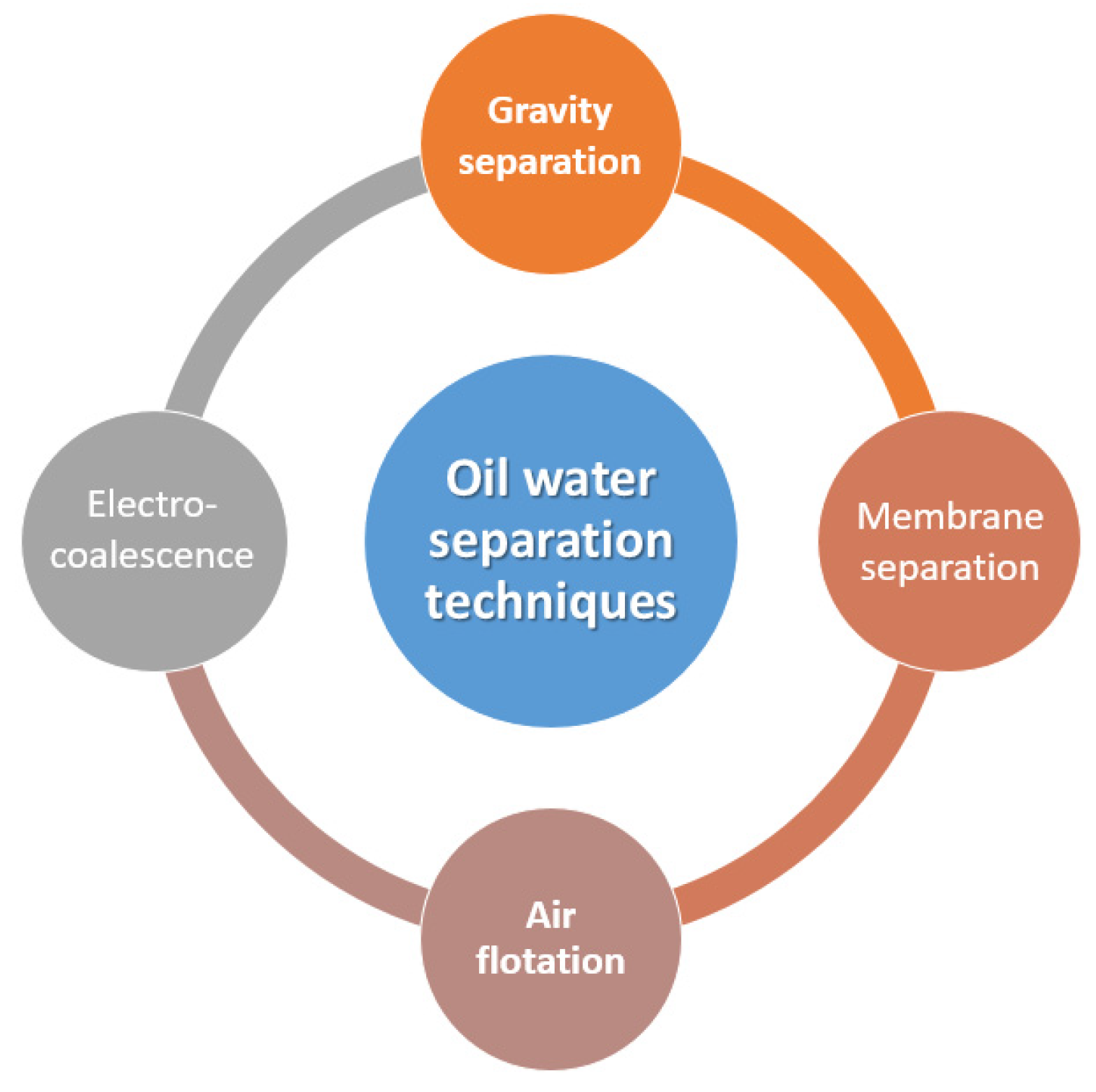
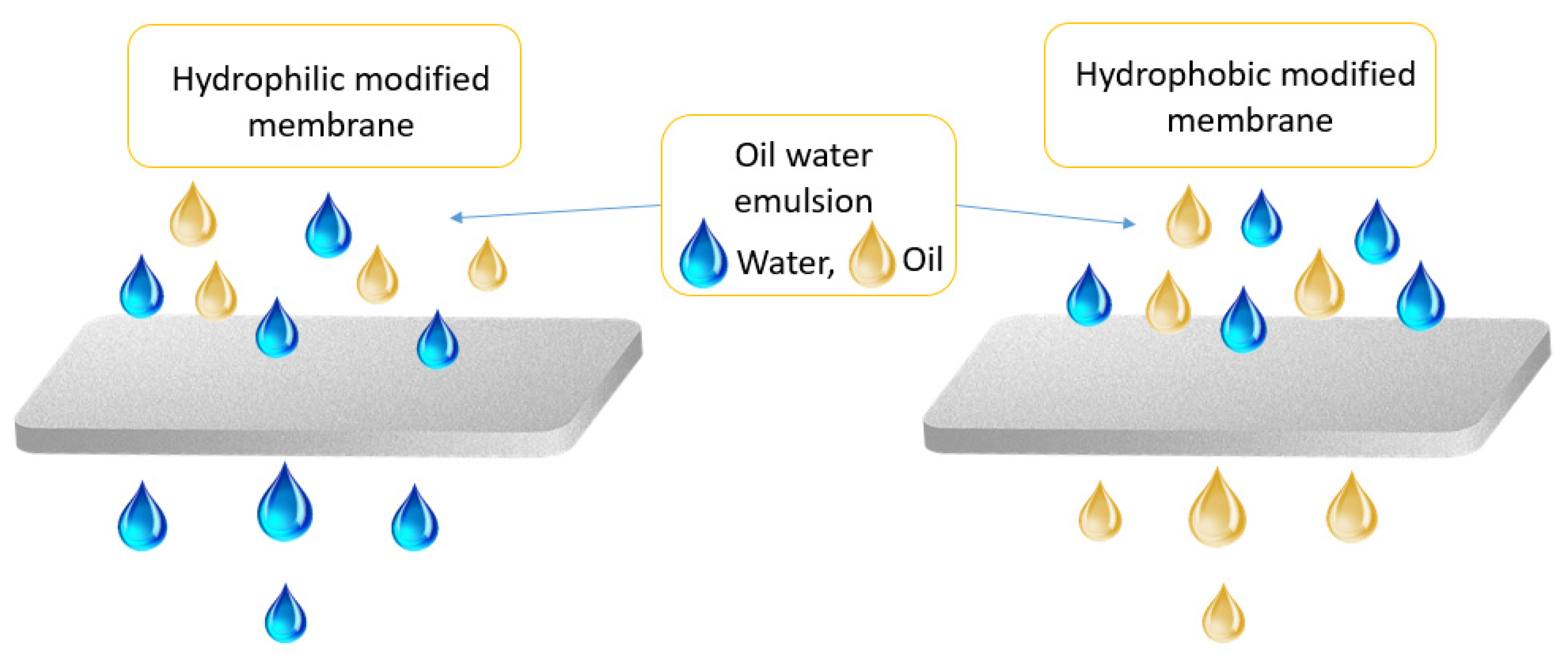
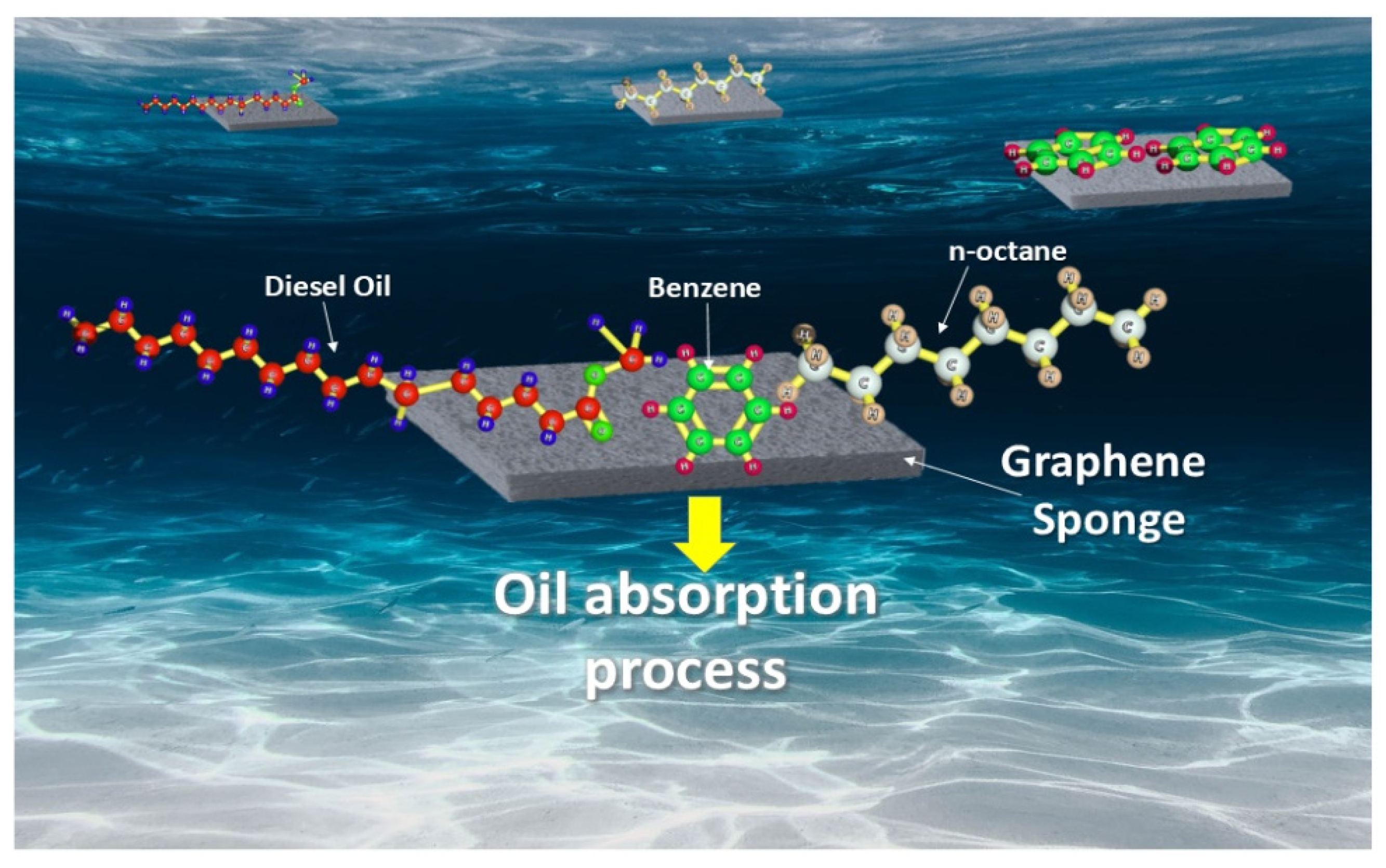

| Physical Property | Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Charge carrier mobility | 200,000 cm2/V·s | [57] |
| Thermal conductivity | 5000 W/m·K | [58] |
| C–C bond length | 1.4 2 Å | [59] |
| Specific surface area | 2630 m2/g | [60] |
| Optical transparency | 97.7% | [61] |
| Tensile strength | 1100 GPa | [62] |
| Young’s modulus | 2.4 ± 0.4 TPa | [63] |
| Resistivity | 10−6 Ω cm2 | [64] |
| Band gap | Zero | [65] |
| Membrane | Feed Components | Operating Pressure (MPa) | Oil Rejection (%) | Oil/Water Flux (L·m−2·h−1·bar) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardanol-GO | Petroleum ether/water containing CuSO4 | Gravity driven | 99% | N/A | [68] |
| PGS/GO | pump oil, hexadecane, soybean oil/ultrapure water | 0–0.15 | >99.9% | 3734 | [69] |
| TiO2/SGO/Ag | Gasoline, toluene, n-heptane, chloroform/water | Gravity driven under UV | 99.6% | 53–175 | [70] |
| PEI-g-GO | Water/hexane | Gravity driven | 99% | 688 | [71] |
| SiO2/GO | Soybean, gas, diesel, pump oil/DI water | Vacuum (~0.1) | 99.4% | 470 | [72] |
| GO-ePOSS | CH2Cl2, petroleum/H2O | Gravity driven | 99% | N/A | [73] |
| Sorbent Material | Type of Oil | Sorption Capacity (g/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| rGO@MF modified sponge | Crude oil-in-water | 2.1–5.6 | [92] |
| Graphene-based sponge | Oil and organic solvents | 50–165 | [93] |
| SiO2/GO-PU sponge | Oil and organic solvents | 80.0–180.0 | [94] |
| Graphene-coated PU sponge | lubricate oil | 31.0 | [95] |
| NMP/graphene PU sponge | Oil and organic solvents | 40.0–80.0 | [96] |
| GO/PU sponge | Oil and organic solvents | 30.0–55.0 | [97] |
| Thiolated graphene/PU sponge | crude oil | 29.5–90.0 | [98] |
| RGO/PU sponge | Oil and organic solvents | 24.2–37.6 | [99] |
| RGO/OAP/PU sponge | Oil and organic solvents | 24.7–80.3 | [100] |
| G sponge | Machine oil | 35.5 | [101] |
| Polyethylenimine/RGO decorated PU sponge | Bicycle chain oil | 8.8 | [86] |
| RGO and octadecylamine decorated PU sponge | Silicon oil | 29.7 | [7] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elhenawy, S.; Khraisheh, M.; AlMomani, F.; Hassan, M.K.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Selvaraj, R. Recent Developments and Advancements in Graphene-Based Technologies for Oil Spill Cleanup and Oil–Water Separation Processes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010087
Elhenawy S, Khraisheh M, AlMomani F, Hassan MK, Al-Ghouti MA, Selvaraj R. Recent Developments and Advancements in Graphene-Based Technologies for Oil Spill Cleanup and Oil–Water Separation Processes. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleElhenawy, Salma, Majeda Khraisheh, Fares AlMomani, Mohammad K. Hassan, Mohammad A. Al-Ghouti, and Rengaraj Selvaraj. 2022. "Recent Developments and Advancements in Graphene-Based Technologies for Oil Spill Cleanup and Oil–Water Separation Processes" Nanomaterials 12, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010087
APA StyleElhenawy, S., Khraisheh, M., AlMomani, F., Hassan, M. K., Al-Ghouti, M. A., & Selvaraj, R. (2022). Recent Developments and Advancements in Graphene-Based Technologies for Oil Spill Cleanup and Oil–Water Separation Processes. Nanomaterials, 12(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010087











