Evaluating a Human Ear-Inspired Sound Pressure Amplification Structure with Fabry–Perot Acoustic Sensor Using Graphene Diaphragm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
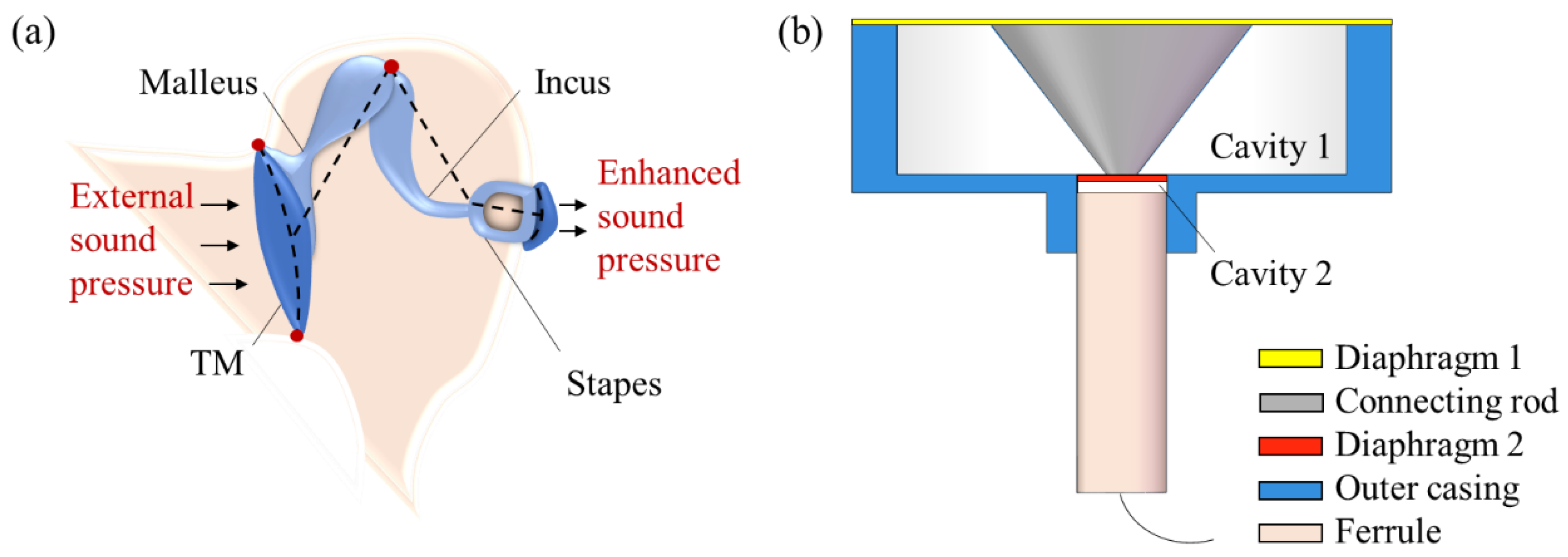
2. The Model Adapted to SPAS
3. Simulation on Acoustic Amplification Effect
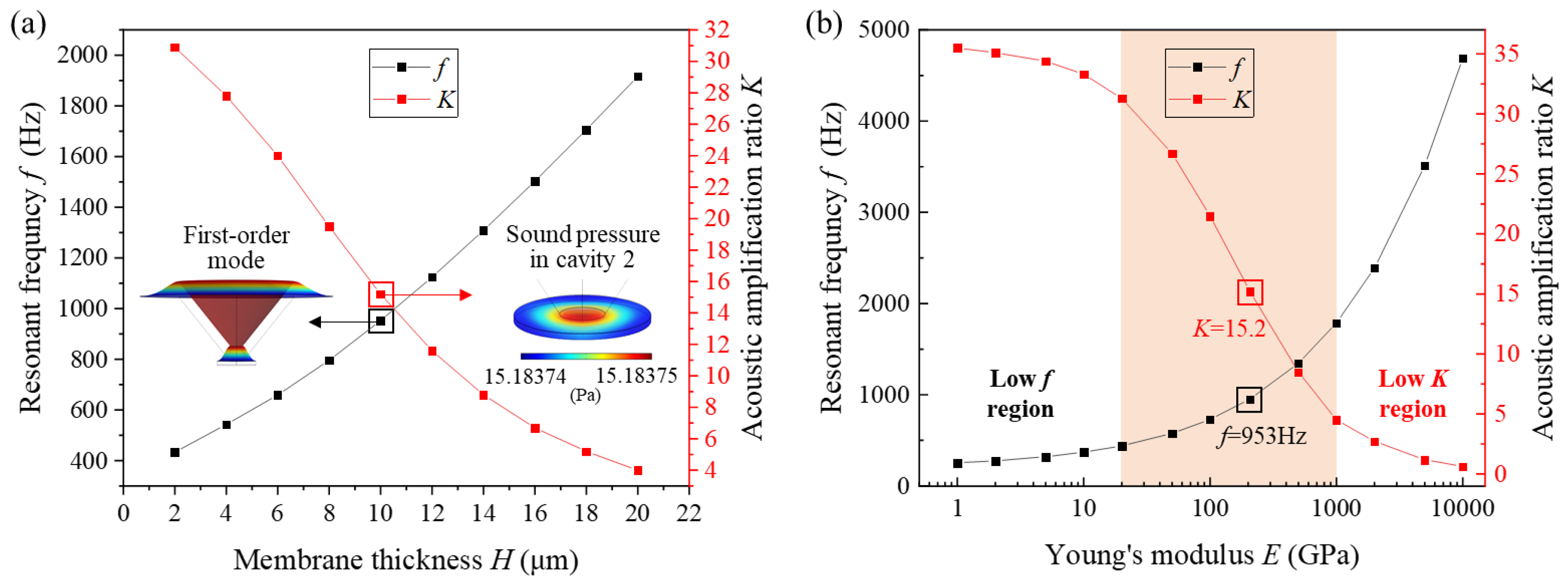
3.1. Effect of SPAS Structural Parameters on Amplification Ratio
3.2. Effect of Diaphragm Parameters on Acoustic Amplification
4. Experiment and Result Analysis
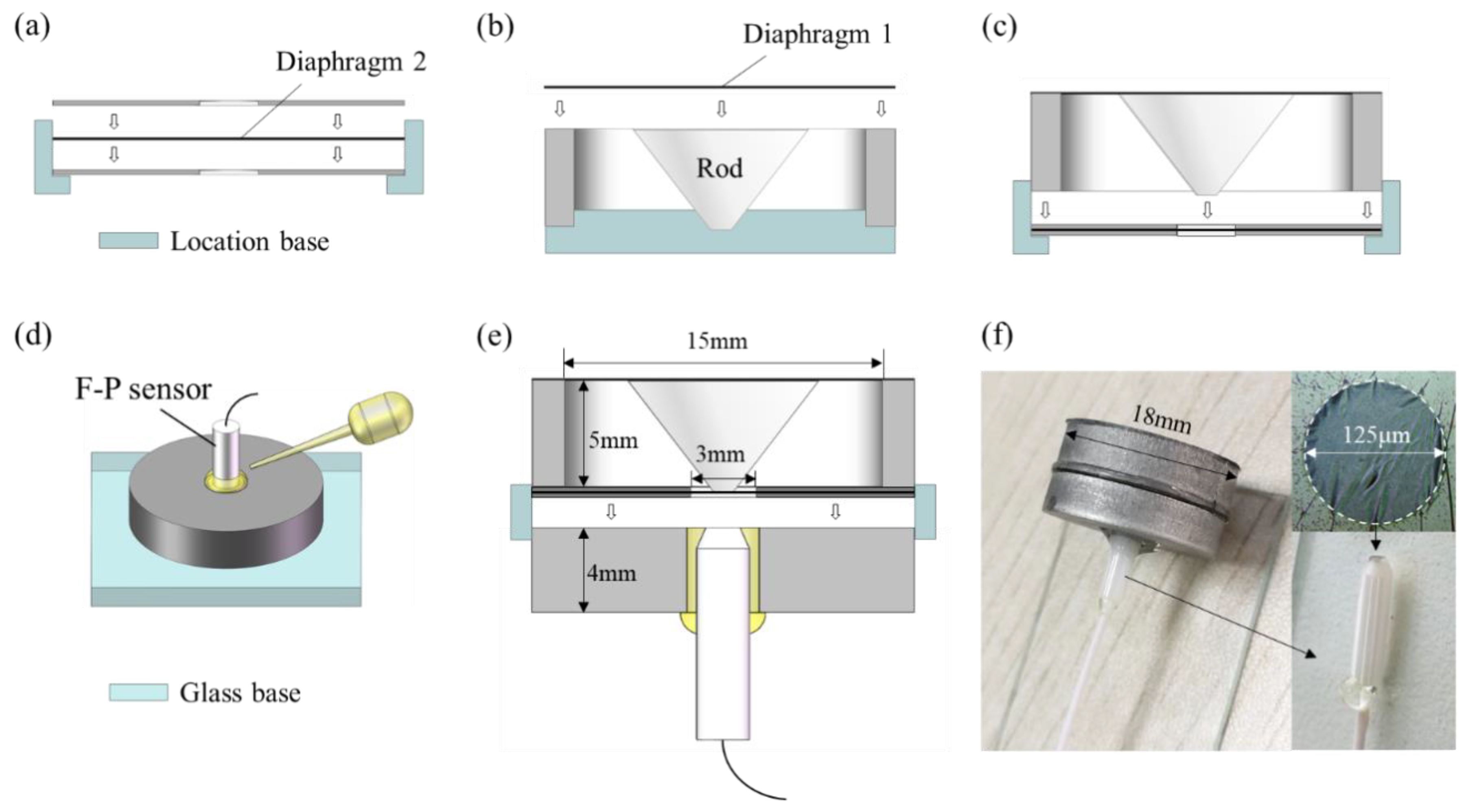
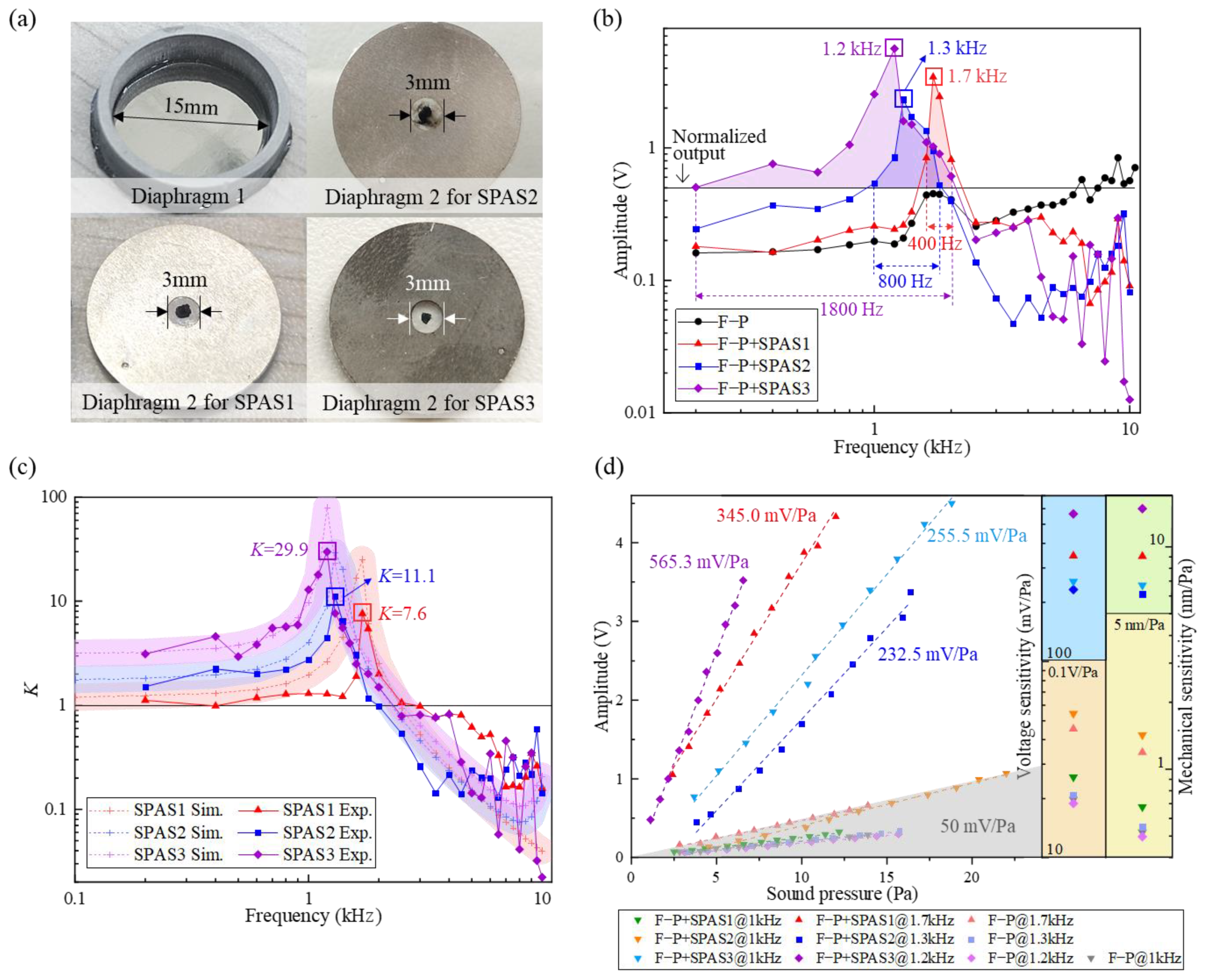
4.1. SPSA Fabrication
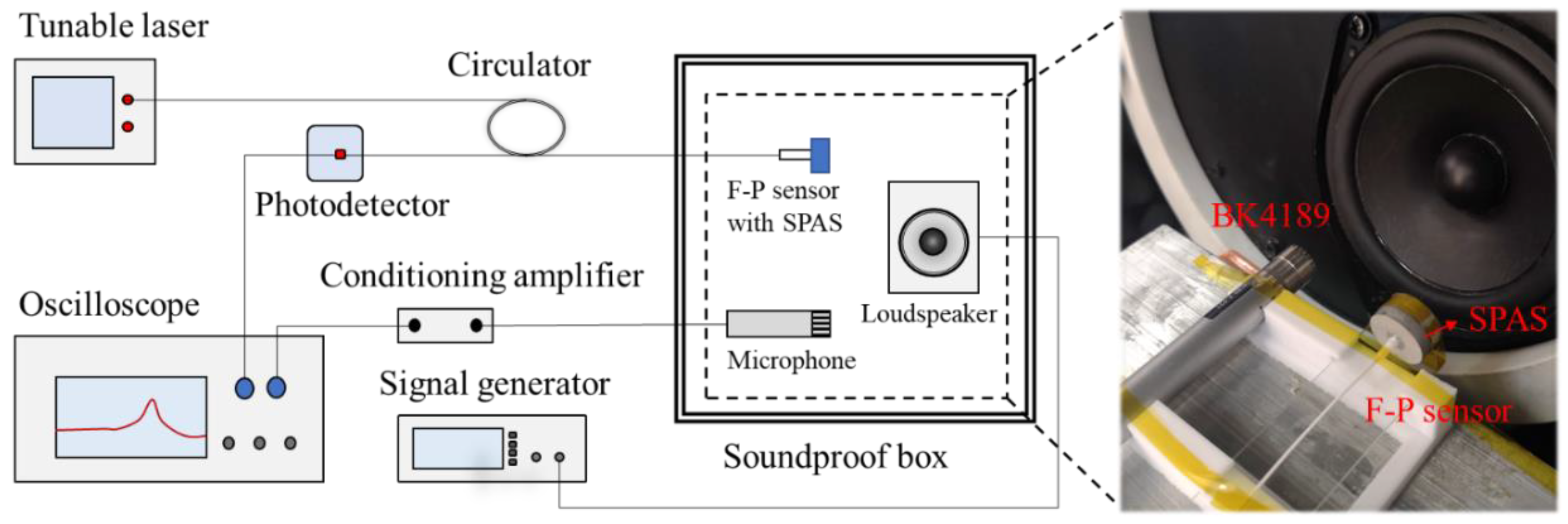
4.2. Acoustic Measurement Setup
4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanjo, E. Noisespy: A real-time mobile phone platform for urban noise monitoring and mapping. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2010, 15, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Jin, W.; Ho, H.L.; Ma, J. Miniature fiber-tip photoacoustic spectrometer for trace gas detection. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhbari, S.; Sammoura, F.; Eovino, B.; Yang, C.; Lin, L. Bimorph piezoelectric micromachined ultrasonic transducers. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2016, 25, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.G.; Marques, C. Diaphragm-embedded optical fiber sensors: A review and tutorial. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 12719–12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lin, J.; Liu, H.; Jin, A.; Jin, P. Extrinsic Fabry-Perot fiber acoustic pressure sensor based on large-area silver diaphragm. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 166, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Shi, J.; Gong, K.; Li, H.; Hui, R.; Yu, B. Fiber-optic acoustic pressure sensor based on large-area nanolayer silver di-aghragm. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2838–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, Z.; Chen, K.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zou, H.; Yu, Q. High-sensitivity Fabry-Perot interferometric acoustic sensor for low-frequency acoustic pressure detections. J. Light. Technol. 2017, 35, 5276–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Yan, W.; Lu, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Fu, X.; Zhang, J. High sensitivity fiber-optic Michelson interferometric low-frequency acoustic sensor based on a gold diaphragm. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 25238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xiong, L.; Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Cai, C.; Qi, Z.-M. Development of highly sensitive fiber-optic acoustic sensor and its preliminary application for sound source localization. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 164504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, R.; Kek, H.; Miao, J.; Zou, B. Sensitivity-improved silicon condenser microphone with a novel single deeply corru-gated diaphragm. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 92, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jin, L.; Liang, Y.; Ma, J.; Guan, B. Corrugated-diaphragm based fiber laser hydrophone with Sub-100 μPa/Hz1/2 resolution. Sensors 2017, 17, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Ni, X.; Ni, H. An optical fiber Fabry–Perot pressure sensor using corrugated diaphragm and angle polished fiber. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2017, 34, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Shan, M.; Jin, P.; Zhong, Z. An optical fiber Fabry-Perot microphone based on corrugated silver diaphragm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 1994–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, G.; Wang, A.; Gui, C.; Yu, H.; Shan, M.; Jin, P.; Zhong, Z. Optical fiber Fabry–Perot acoustic sensors based on corrugated silver diaphragms. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 3874–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, V.; Fonsen, J.; Roth, K.; Kauppinen, J. Cantilever enhanced photoacoustic detection of carbon dioxide using a tunable diode laser source. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 86, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, L.; Lei, J.; Zhu, W.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Chen, C.; Xiao, H. Micro-cantilever-based fiber optic hy-drophone fabricated by a femtosecond laser. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2459–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yang, B.; Deng, H.; Guo, M.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, W.; Yu, Q. Simultaneous measurement of acoustic pressure and temperature using a Fabry-Perot interferometric fiber-optic cantilever sensor. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 15050–15061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Feng, C.; Li, Q.; Yu, H. High sensitivity all-optical acoustic pressure sensor based on resonant micro-opto-mechanical cantilever with integrated rib waveguide. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 285, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, P.; Li, R.; Liu, T. Flywheel-like diaphragm-based fiber-optic Fabry–Perot frequency tailored acoustic sensor. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 415102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.S.; Seong, K.W.; Lim, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, J.H. Implantable microphone with acoustic tube for fully implantable hearing devices. IEICE Electron. Express 2011, 8, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, P.; Tong, X.; Zhao, M.; Deng, C.; Guo, Q.; Mao, Y.; Wang, K. Study on high temperature Fabry–Perot fiber acoustic sensor with temperature self-compensation. Opt. Eng. 2015, 54, 097104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, H.; Zhu, D.; Fan, G.; Jiao, W.; Liang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; He, X.; et al. Sensitivity enhancement of optical fiber vibration sensor through encapsulation of acoustic Helmholtz resonator. Optik 2018, 169, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Kwak, J.-H.; Joe, D.J.; Hong, S.K.; Wang, H.S.; Park, J.H.; Hur, S.; Lee, K.J. Basilar membrane-inspired self-powered acoustic sensor enabled by highly sensitive multi tunable frequency band. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Lee, J.; Jang, H.; Choi, H. A triboelectric-based artificial basilar membrane to mimic cochlear tonotopy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2481–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, H.; Goode, R.L. Sound pressure gain produced by the human middle ear. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibara, R.; Welsh, J.T.; Puria, S.; Goode, R.L. Human middle-ear sound transfer function and cochlear input impedance. Hear. Res. 2001, 152, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, P.; Prendergast, P. Middle-ear dynamics before and after ossicular replacement. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Thakur, P.; Rablau, C.; Avrutsky, I.; Cheng, M.M.-C. Miniature optical fiber pressure sensor with exfoliated graphene diaphragm. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5621–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, W. A large-area and nanoscale graphene oxide diaphragm-based extrinsic fiber-optic Fabry–Perot acoustic sensor applied for partial discharge detection in air. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Gan, R.Z.; Chang, K.-H.; Dormer, K.J. Computer-integrated finite element modeling of human middle ear. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2002, 1, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshenko, S. Theory of Plates and Shells; Hill Book Limited: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Borgnakke, C.; Sonntag, R. Fundamentals of Thermodynamics, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xiao, J.; Guo, T.; Fan, S.; Jin, W. Interference characteristics in a Fabry–Perot cavity with graphene membrane for optical fiber pressure sensors. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 21, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Guo, T.; Xiao, J.; Fan, S.; Jin, W. Analyzing the applicability of miniature ultra-high sensitivity Fabry–Perot acoustic sensor using a nanothick graphene diaphragm. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 085101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xuan, H.; Ho, H.L.; Jin, W.; Yang, Y.; Fan, S. Fiber-optic Fabry–Pérot acoustic sensor with multilayer graphene dia-phragm. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2013, 25, 932–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
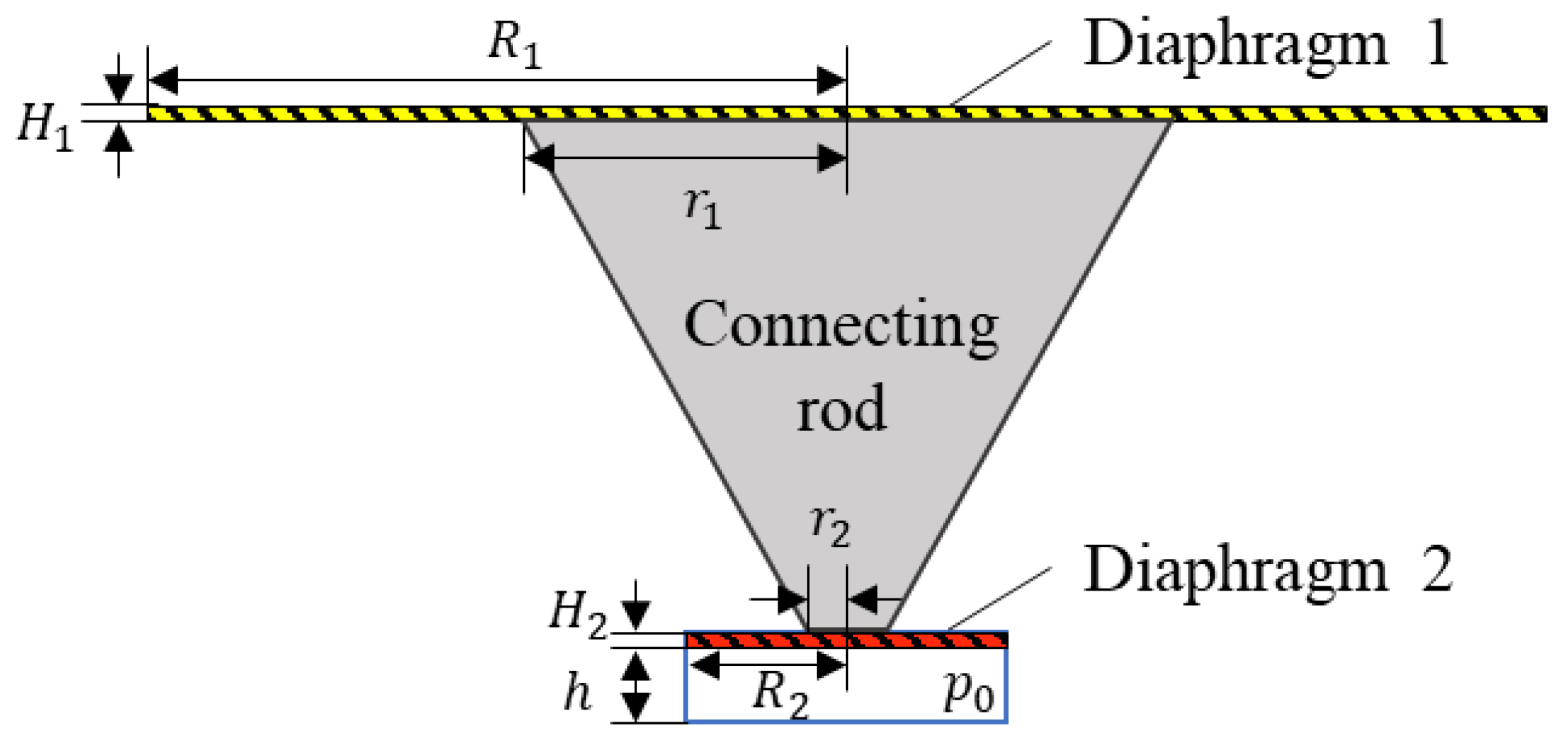

| Structural Parameter | Value/mm | Material Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1, R2 | 7.5, 1.5 | E | 2.07 × 1011 Pa |
| r1, r2 | 4.5, 0.5 | μ | 0.29 |
| 0.01 | Pressure in cavity 2 | Value | |
| h | 0.1 | p0 | 1.01 × 105 Pa |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Xiao, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, X. Evaluating a Human Ear-Inspired Sound Pressure Amplification Structure with Fabry–Perot Acoustic Sensor Using Graphene Diaphragm. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092284
Li C, Xiao X, Liu Y, Song X. Evaluating a Human Ear-Inspired Sound Pressure Amplification Structure with Fabry–Perot Acoustic Sensor Using Graphene Diaphragm. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(9):2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Cheng, Xi Xiao, Yang Liu, and Xuefeng Song. 2021. "Evaluating a Human Ear-Inspired Sound Pressure Amplification Structure with Fabry–Perot Acoustic Sensor Using Graphene Diaphragm" Nanomaterials 11, no. 9: 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092284
APA StyleLi, C., Xiao, X., Liu, Y., & Song, X. (2021). Evaluating a Human Ear-Inspired Sound Pressure Amplification Structure with Fabry–Perot Acoustic Sensor Using Graphene Diaphragm. Nanomaterials, 11(9), 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092284







