Towards Rapid Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Multi-Beam Nanostructuring with 40,401 Beams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
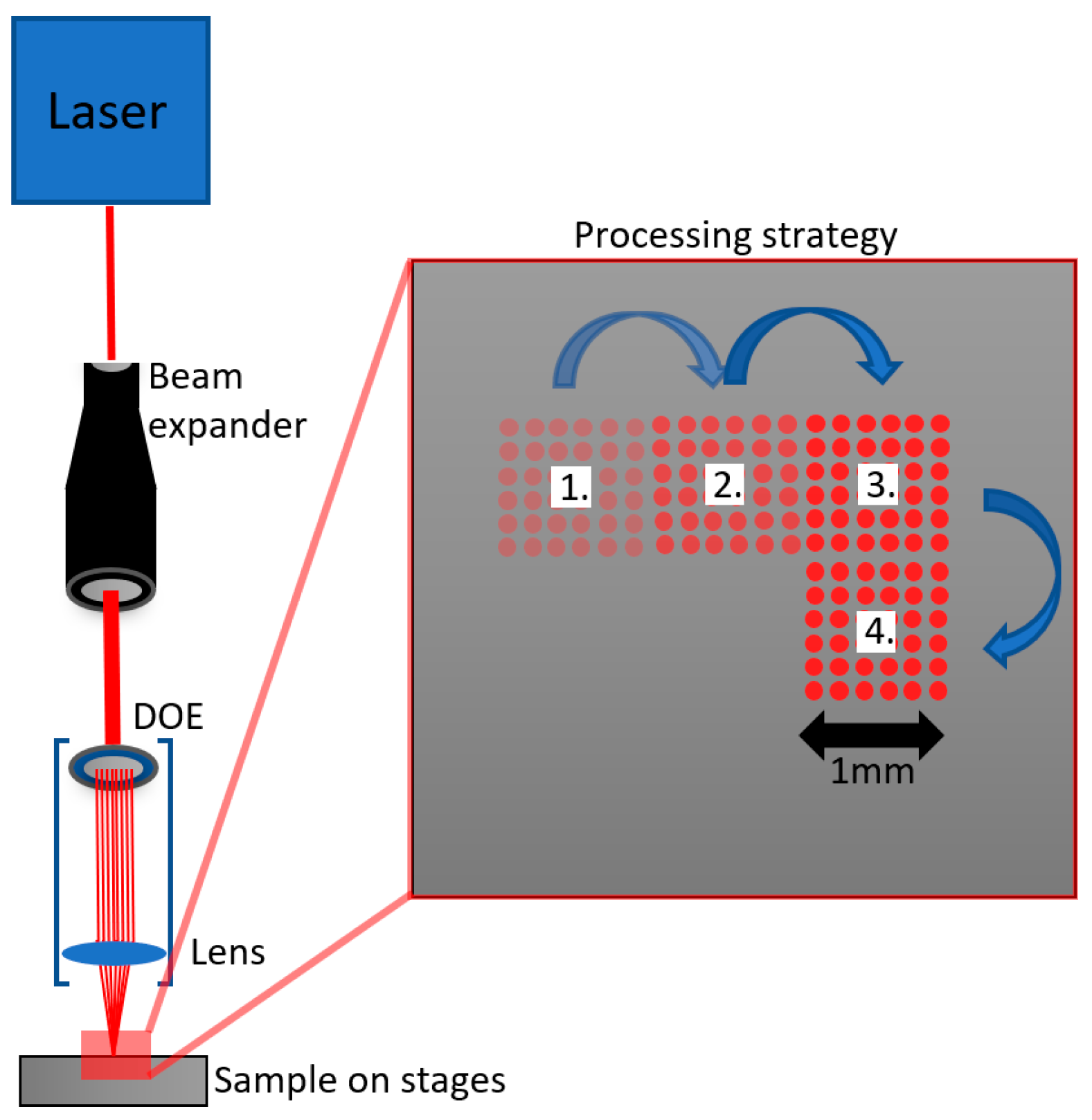
2. Materials and Methods
Beam Splitting with Diffractive Laser-Induced Texturing (DLITe) Elements
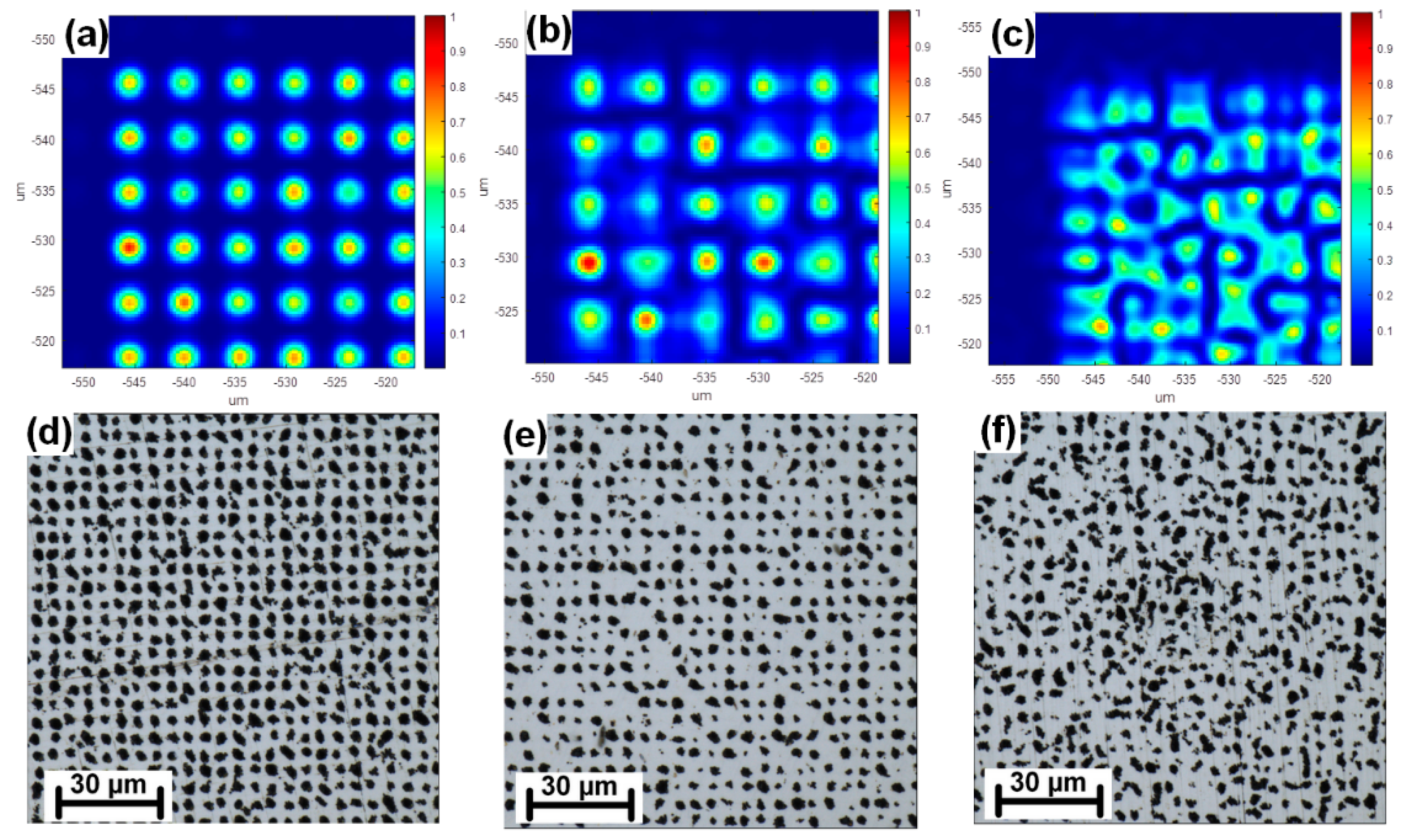
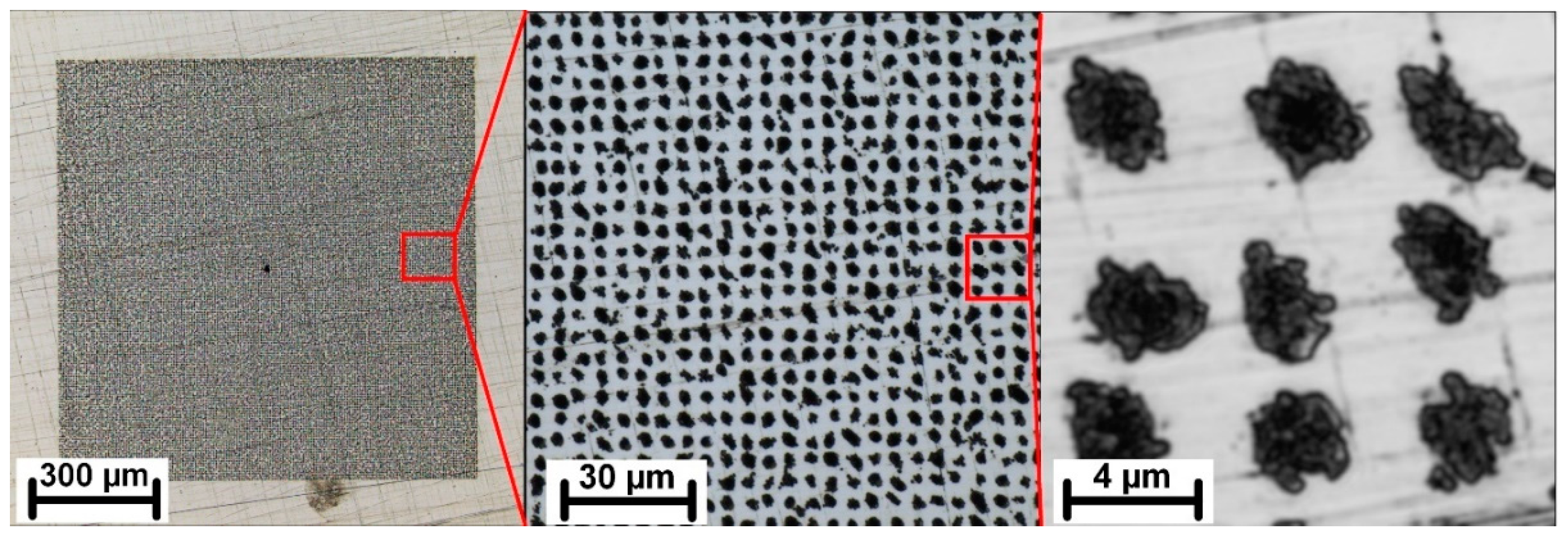
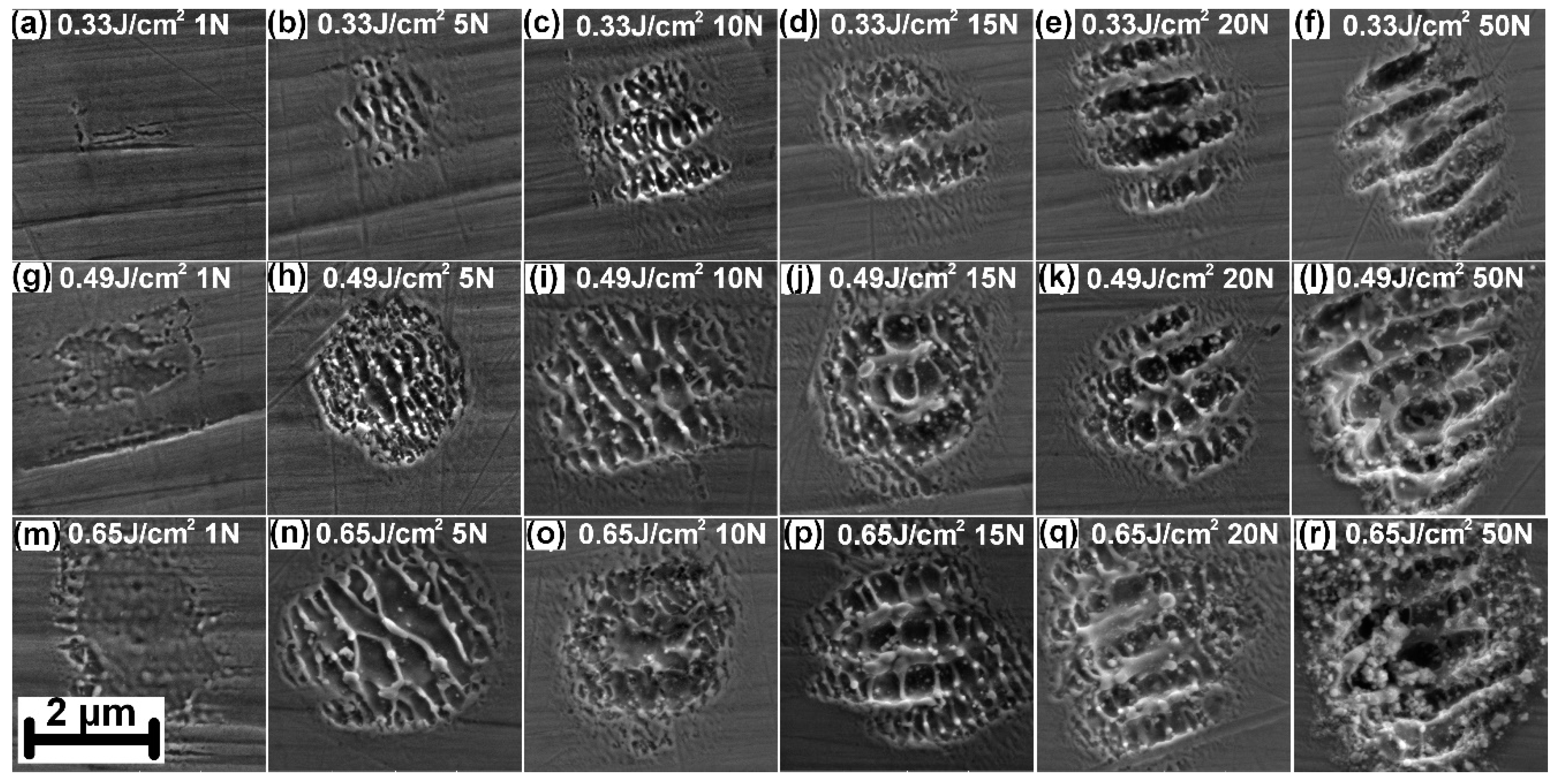
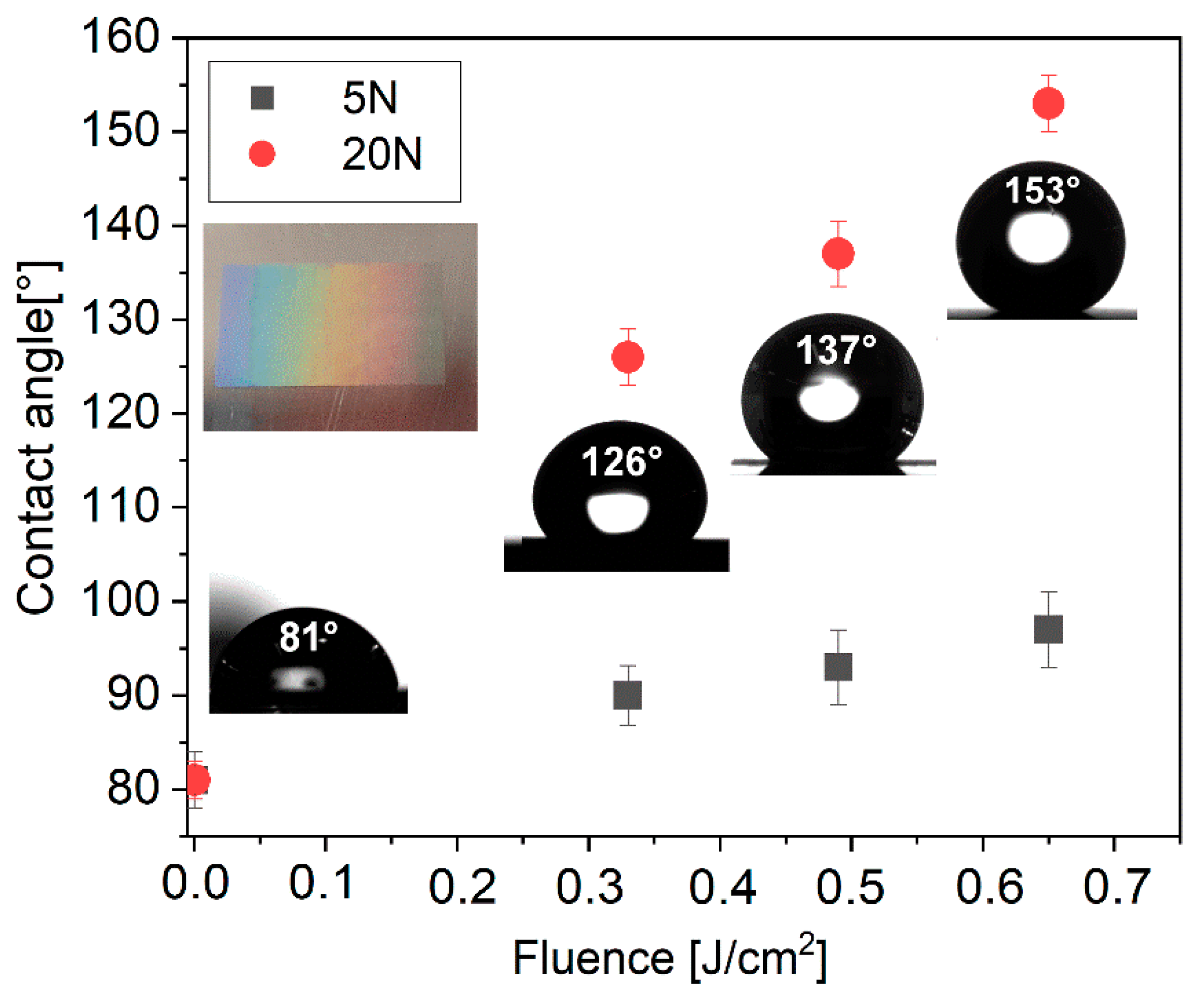
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, K.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Recent developments in bio-inspired special wettability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3240–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Bio-inspired design of multiscale structures for function integration. Nano Today 2011, 6, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevahan, J.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Joseph, G.B.; Durairaj, R.; Mageshwaran, G. Superhydrophobic surfaces: A review on fundamentals, applications, and challenges. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenjimbayashi, M.; Higashi, M.; Yamazaki, T.; Takenaka, I.; Matsubayashi, T.; Moriya, T.; Komine, M.; Yoshikawa, R.; Manabe, K.; Shiratori, S. Droplet motion control on dynamically hydrophobic patterned surfaces as multifunctional liquid manipulators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10371–10377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falde, E.J.; Yohe, S.T.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Superhydrophobic materials for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliver, J.; Huh, C.; Mason, S. Resistance to spreading of liquids by sharp edges. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1977, 59, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quéré, D. Wetting and roughness. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, S.; Aguilar-Morales, A.I.; Lasagni, A.F. Controlling the wettability of polycarbonate substrates by producing hierarchical structures using direct laser interference patterning. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.A.A.; Ritikos, R.; Rahman, S.A. Wetting behaviour of carbon nitride nanostructures grown by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 328, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, J.-Y.; Kuo, C.-W.; Chen, P.; MOU, C.-Y. Fabrication of tunable superhydrophobic surfaces by nanosphere lithography. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremaldi, J.; Bhushan, B. Fabrication of bioinspired, self-cleaning superliquiphilic/phobic stainless steel using different pathways. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 518, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, K.; Meyer-Plath, A.; Keller, D.; Besch, W.; Babucke, G.; Ohl, A. Plasma-induced surface functionalization of polymeric biomaterials in ammonia plasma. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2001, 41, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Höhm, S.; Kirner, S.V.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Laser-induced periodic surface structures—A scientific evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 9000615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Krüger, J.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J. Quo vadis LIPSS?—Recent and future trends on laser-induced periodic surface structures. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschwitz, P.; Stoklasa, B.; Kuchařík, J.; Turčičová, H.; Písařík, M.; Brajer, J.; Rostohar, D.; Mocek, T.; Duda, M.; Lucianetti, A. Micromachining of Invar with 784 Beams Using 1.3 ps Laser Source at 515 nm. Materials 2020, 13, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, V.; Madelung, A.; Alamri, S.; Steege, T.; Krupop, B.; Aguilar, A.I.; Kunze, T.; Lasagni, A.F. High-throughput direct laser interference patterning: New configurations and applications. In Laser-Based Micro-and Nanoprocessing XIV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 11268, p. 112680T. [Google Scholar]
- Lasagni, A.F.; Gachot, C.; Trinh, K.E.; Hans, M.; Rosenkranz, A.; Roch, T.; Eckhardt, S.; Kunze, T.; Bieda, M.; Günther, D.; et al. Direct laser interference patterning, 20 years of development: From the basics to industrial applications. In Laser-Based Micro-and Nanoprocessing XI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 10092, p. 1009211. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, S.; Kaplan, N.; Grossinger, I. Using Diffractive Optical Elements: DOEs for beam shaping–fundamentals and applications. Opt. Photonik 2018, 13, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuang, Z.; Perrie, W.; Leach, J.; Sharp, M.; Edwardson, S.P.; Padgett, M.; Dearden, G.; Watkins, K.G. High throughput diffractive multi-beam femtosecond laser processing using a spatial light modulator. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2284–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, V.; Roch, T.; Lasagni, A.F. High-Speed Surface Structuring of Polycarbonate Using Direct Laser Interference Patterning: Toward 1 m2 min− 1 Fabrication Speed Barrier. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschwitz, P.; Jochcová, D.; Jagdheesh, R.; Rostohar, D.; Brajer, J.; Kopeček, J.; Cimrman, M.; Smrž, M.; Mocek, T.; Lucianetti, A. Towards rapid large-scale LIPSS fabrication by 4-beam ps DLIP. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 133, 106532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, S.; Lasagni, A.F. Development of a general model for direct laser interference patterning of polymers. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 9603–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Liu, D.; Perrie, W.; Edwardson, S.; Sharp, M.; Fearon, E.; Dearden, G.; Watkins, K. Fast parallel diffractive multi-beam femtosecond laser surface micro-structuring. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 6582–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillner, A.; Finger, J.; Gretzki, P.; Niessen, M.; Bartels, T.; Reininghaus, M. High power laser processing with ultrafast and multi-parallel beams. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2019, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Smrž, M.; Mužík, J.; Štěpánková, D.; Turčičová, H.; Novák, O.; Chyla, M.; Hauschwitz, P.; Brajer, J.; Kubát, J.; Todorov, F.; et al. Picosecond thin-disk laser platform PERLA for multi-beam micromachining. OSA Contin. 2021, 4, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschwitz, P.; Jagdheesh, R.; Rostohar, D.; Brajer, J.; Kopeček, J.; Jiřícek, P.; Houdková, J.; Mocek, T. Hydrophilic to ultrahydrophobic transition of Al 7075 by affordable ns fiber laser and vacuum processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 505, 144523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, A.; Kaplan, N. Laser surface texturing using a single diffractive optical element as an alternative for direct laser interference patterning. J. Laser Appl. 2020, 32, 032011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Ma, C.; Feng, J.; Hong, W.; Zhang, Z. Formation of laser induced periodic structures on stainless steel using multi-burst picosecond pulses. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 6325–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraggelakis, F.; Mincuzzi, G.; Lopez, J.; Manek-Hönninger, I.; Kling, R. Texturing metal surface with MHz ultra-short laser pulses. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 18131–18139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsibidis, G.D.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. From ripples to spikes: A hydrodynamical mechanism to interpret femtosecond laser-induced self-assembled structures. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 041405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, J.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, H.; Fan, P. Superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity transition of picosecond laser microstructured aluminum in ambient air. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 441, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizi-Bandoki, P.; Valette, S.; Audouard, E.; Benayoun, S. Time dependency of the hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of metallic alloys subjected to femtosecond laser irradiations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschwitz, P.; Jagdheesh, R.; Rostohar, D.; Brajer, J.; Kopeček, J.; Jiříček, P.; Houdková, J.; Mocek, T. Nanostructure fabrication on the top of laser-made micropillars for enhancement of water repellence of aluminium alloy. Mater. Lett. 2019, 256, 126601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hauschwitz, P.; Bičštová, R.; Brodsky, A.; Kaplan, N.; Cimrman, M.; Huynh, J.; Brajer, J.; Rostohar, D.; Kopeček, J.; Smrž, M.; et al. Towards Rapid Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Multi-Beam Nanostructuring with 40,401 Beams. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081987
Hauschwitz P, Bičštová R, Brodsky A, Kaplan N, Cimrman M, Huynh J, Brajer J, Rostohar D, Kopeček J, Smrž M, et al. Towards Rapid Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Multi-Beam Nanostructuring with 40,401 Beams. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(8):1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081987
Chicago/Turabian StyleHauschwitz, Petr, Radka Bičštová, Alexander Brodsky, Natan Kaplan, Martin Cimrman, Jaroslav Huynh, Jan Brajer, Danijela Rostohar, Jaromír Kopeček, Martin Smrž, and et al. 2021. "Towards Rapid Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Multi-Beam Nanostructuring with 40,401 Beams" Nanomaterials 11, no. 8: 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081987
APA StyleHauschwitz, P., Bičštová, R., Brodsky, A., Kaplan, N., Cimrman, M., Huynh, J., Brajer, J., Rostohar, D., Kopeček, J., Smrž, M., & Mocek, T. (2021). Towards Rapid Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Multi-Beam Nanostructuring with 40,401 Beams. Nanomaterials, 11(8), 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081987







