Assessing the Toxicological Relevance of Nanomaterial Agglomerates and Aggregates Using Realistic Exposure In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Dispersions and Size Characterization
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. In Vitro Exposure Conditions
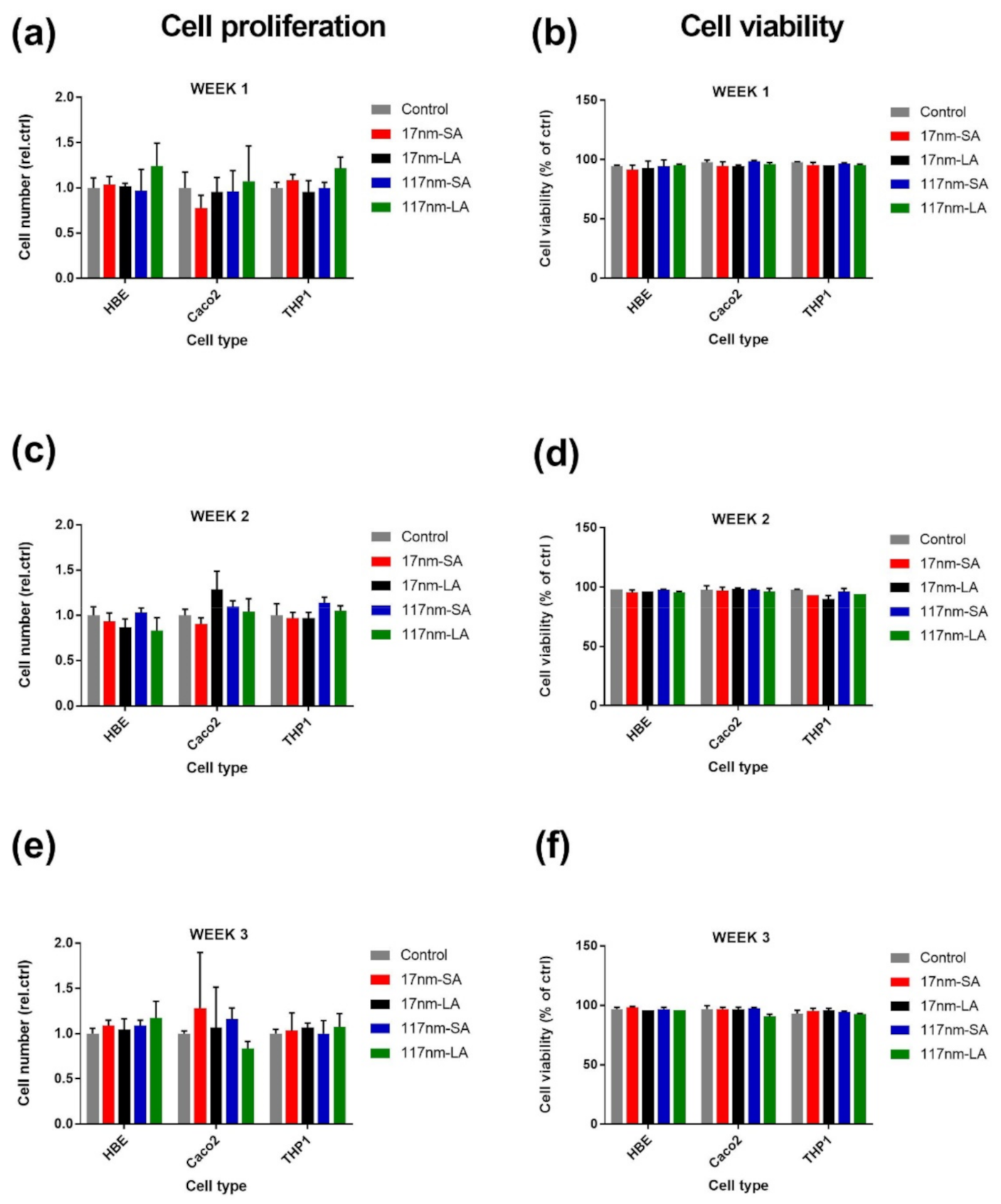
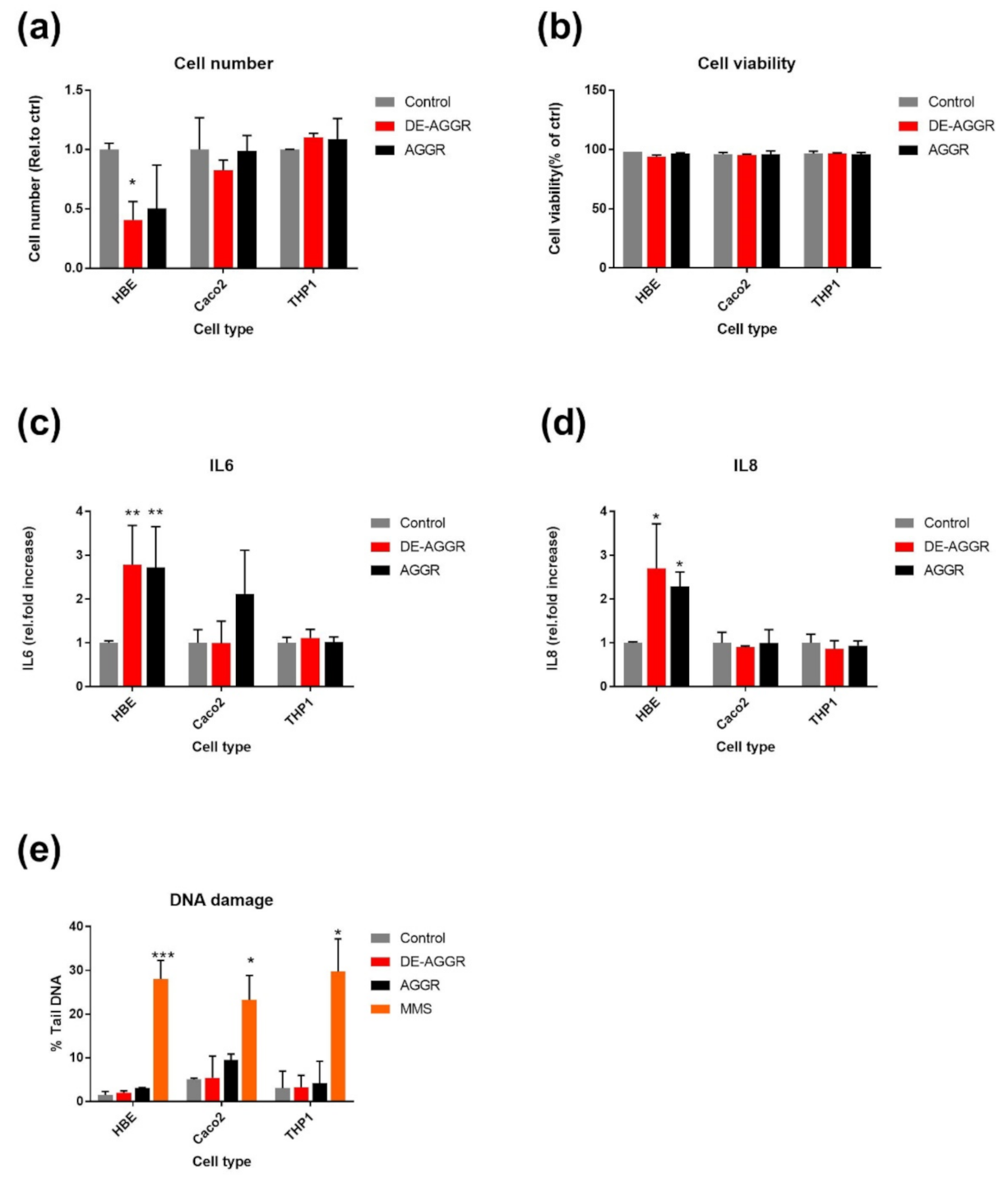
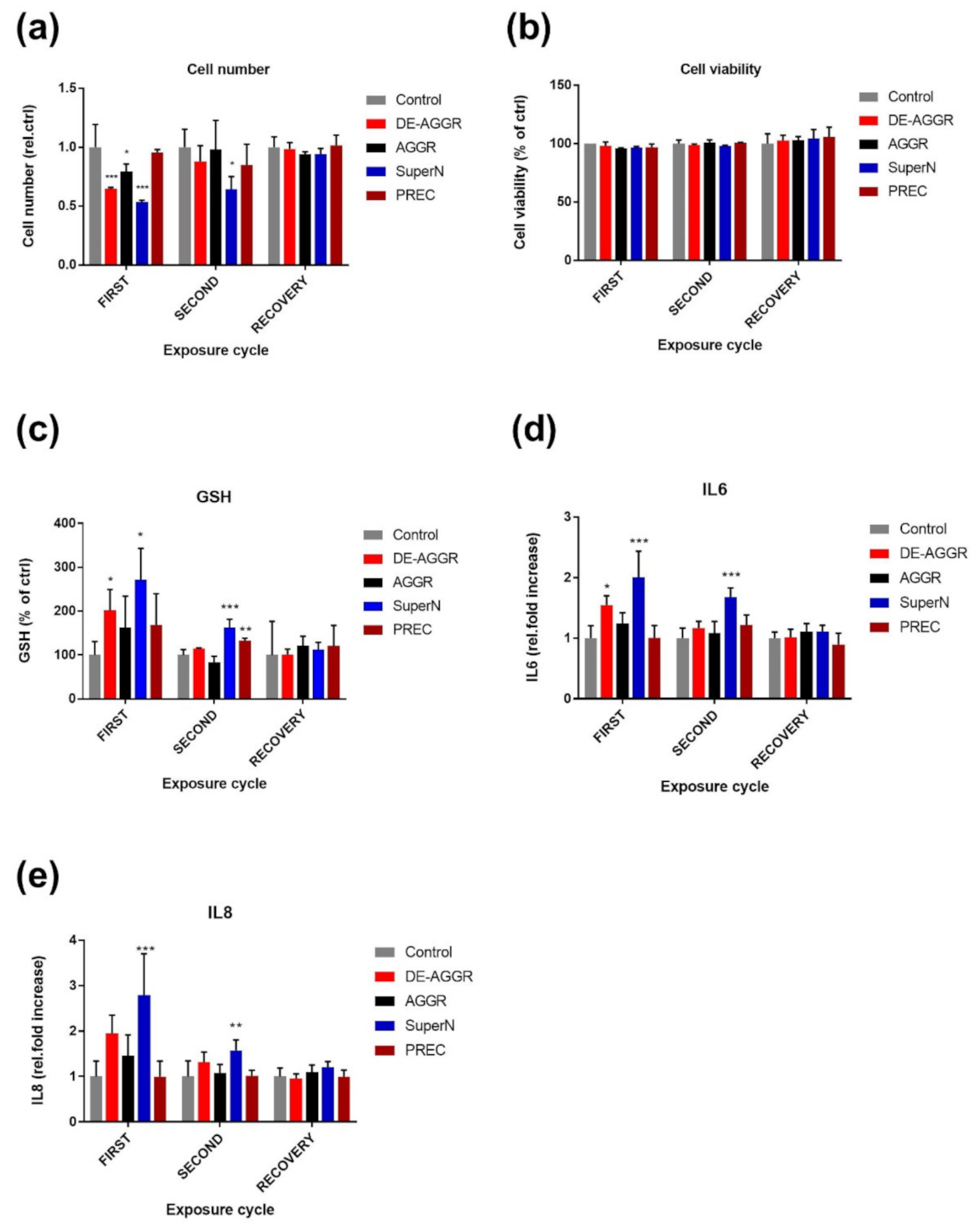
2.4. Cell Viability and Number Determination
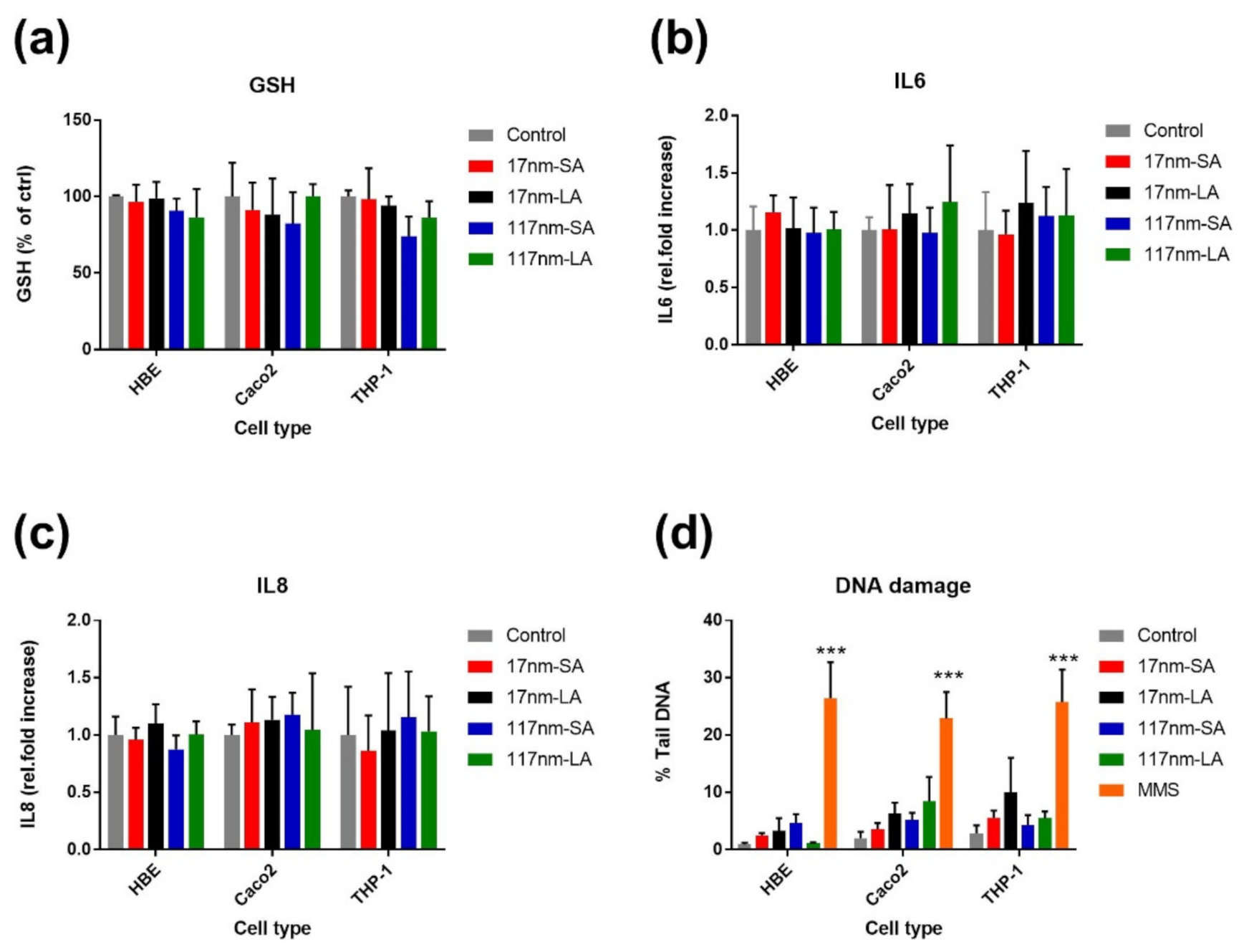
2.5. Total Glutathione Measurements
2.6. Cytokine Quantification
2.7. Comet Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dispersion and Size Characterization
3.1.1. TiO2 Suspensions
3.1.2. SAS Suspensions
3.2. Comparison of Biological Responses
3.2.1. TiO2 Suspensions
3.2.2. SAS Suspensions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vance, M.E.; Kuiken, T.; Vejerano, E.P.; McGinnis, S.P.; Hochella, M.F.; Hull, D.R. Nanotechnology in the real world: Redeveloping the nanomaterial consumer products inventory. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musial, J.; Krakowiak, R.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Goslinski, T.; Stanisz, B.J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products—What do we know about their safety? Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L.C.; Lison, D.; Martens, J.A.; Hoet, P.H. The nanosilica hazard: Another variable entity. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fruijtier-Pölloth, C. The safety of nanostructured synthetic amorphous silica (SAS) as a food additive (E 551). Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 2885–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Efsa. Titanium Dioxide: E171 No Longer Considered Safe When Used as a Food Additive. European Food Safety Authority. 2021. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/titanium-dioxide-e171-no-longer-considered-safe-when-used-food-additive (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- Mihalache, R.; Verbeek, J.; Graczyk, H.; Murashov, V.; Van Broekhuizen, P. Occupational exposure limits for manufactured nanomaterials, a systematic review. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlbusch, T.A.; Asbach, C.; Fissan, H.; Göhler, D.; Stintz, M. Nanoparticle exposure at nanotechnology workplaces: A review. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debia, M.; Bakhiyi, B.; Ostiguy, C.; Verbeek, J.H.; Brouwer, D.H.; Murashov, V. A Systematic Review of Reported Exposure to Engineered Nanomaterials. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2016, 60, 916–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, D. Primary Particles–Agglomerates–Aggregates. Nanomaterials 2013, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potočnik, J. Commission recommendation of 18 October 2011 on the definition of nanomaterial (2011/696/EU). Off. J. Eur. Union. 2011, L275, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Murugadoss, S.; Brassinne, F.; Sebaihi, N.; Petry, J.; Cokic, S.M.; Van Landuyt, K.L.; Godderis, L.; Mast, J.; Lison, D.; Hoet, P.H.; et al. Agglomeration of titanium dioxide nanoparticles increases toxicological responses in vitro and in vivo. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murugadoss, S.; Brule, S.V.D.; Brassinne, F.; Sebaihi, N.; Mejia, J.; Lucas, S.; Petry, J.; Godderis, L.; Mast, J.; Lison, D.; et al. Is aggregated synthetic amorphous silica toxicologically relevant? Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Magaye, R.; Castranova, V.; Zhao, J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: A review of current toxicological data. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fruijtier-Pölloth, C. The toxicological mode of action and the safety of synthetic amorphous silica—A nanostructured material. Toxicology 2012, 294, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugadoss, S.; Lison, D.; Godderis, L.; Brule, S.V.D.; Mast, J.; Brassinne, F.; Sebaihi, N.; Hoet, P.H. Toxicology of silica nanoparticles: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2967–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.A.; Hossain, K.F.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandebriel, R.J.; De Jong, W.H. A review of mammalian toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annangi, B.; Rubio, L.; Alaraby, M.; Bach, J.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Acute and long-term in vitro effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 90, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, W.-S.; Song, Z.-M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, N.; Yan, G.-H.; Gao, Y.; Cao, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Short-term and long-term toxicological effects of vanadium dioxide nanoparticles on A549 cells. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Song, Z.-M.; Tang, H.; Xi, W.-S.; Cao, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Toxicological Effects of Caco-2 Cells Following Short-Term and Long-Term Exposure to Ag Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC-NIOSH. Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards—Titanium Dioxide. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0617.html (accessed on 11 June 2021).
- CDC-NIOSH. Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards—Silica, Amorphous. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0552.html (accessed on 11 June 2021).
- De Temmerman, P.-J.; Verleysen, E.; Lammertyn, J.; Mast, J. Semi-automatic size measurement of primary particles in aggregated nanomaterials by transmission electron microscopy. Powder Technol. 2014, 261, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Technau, A.; Froelich, K.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Functional responses of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells to metal oxide nanoparticles in vitro. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocbek, P.; Teskač, K.; Kreft, M.E.; Kristl, J. Toxicological aspects of long-term treatment of keratinocytes with ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 1908–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vales, G.; Rubio, L.; Marcos, R. Long-term exposures to low doses of titaniumx dioxide nanoparticles induce cell transformation, but not genotoxic damage in BEAS-2B cells. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, A.R.; Skoglund, S.; Wallinder, I.O.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H.L. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: The role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, Q.; Lohani, M.; Dopp, E.; Pemsel, H.; Jonas, L.; Weiss, D.G.; Schiffmann, D. Evidence that ultrafine titanium dioxide induces micronuclei and apoptosis in Syrian hamster embryo fibroblasts. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L.C.J.; Rabolli, V.; Lison, D.; Gonzalez, L.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Martens, J.; Hoet, P.H. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of monodisperse silica nanoparticles in human endothelial cells. Small 2009, 5, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.S.; Gordon, T.; Price, O.; Asgharian, B. Thoracic and respirable particle definitions for human health risk assessment. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, A.; Torres-Hernandez, J.A.; Ault, J.G.; Pedersen-Lane, J.H.; Gao, D.; Lawrence, D.A. Silica nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and inflammation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell Stress Chaperon 2014, 19, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Jin, C.; Tang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, C.; Yang, Y. Cytotoxicity of silica nanoparticles on HaCaT cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 34, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Xia, Y.; Niu, P.; Jiang, L.; Duan, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z. Silica nanoparticles induce oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in vitro via activation of the MAPK/Nrf2 pathway and nuclear factor-κB signaling. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1463–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, C.J.; Driscoll, K.E.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Baggs, R.; O’Reilly, M.A.; Carter, J.; Gelein, R.; Oberdörster, G. Pulmonary chemokine and mutagenic responses in rats after subchronic inhalation of amorphous and crystalline silica. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 56, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arts, J.H.; Muijser, H.; Duistermaat, E.; Junker, K.; Kuper, C.F. Five-day inhalation toxicity study of three types of synthetic amorphous silicas in Wistar rats and post-exposure evaluations for up to 3months. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murugadoss, S.; Godderis, L.; Ghosh, M.; Hoet, P.H. Assessing the Toxicological Relevance of Nanomaterial Agglomerates and Aggregates Using Realistic Exposure In Vitro. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071793
Murugadoss S, Godderis L, Ghosh M, Hoet PH. Assessing the Toxicological Relevance of Nanomaterial Agglomerates and Aggregates Using Realistic Exposure In Vitro. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(7):1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071793
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurugadoss, Sivakumar, Lode Godderis, Manosij Ghosh, and Peter H. Hoet. 2021. "Assessing the Toxicological Relevance of Nanomaterial Agglomerates and Aggregates Using Realistic Exposure In Vitro" Nanomaterials 11, no. 7: 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071793
APA StyleMurugadoss, S., Godderis, L., Ghosh, M., & Hoet, P. H. (2021). Assessing the Toxicological Relevance of Nanomaterial Agglomerates and Aggregates Using Realistic Exposure In Vitro. Nanomaterials, 11(7), 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071793






