Security-Enhanced 3D Data Encryption Using a Degradable pH-Responsive Hydrogel
Abstract
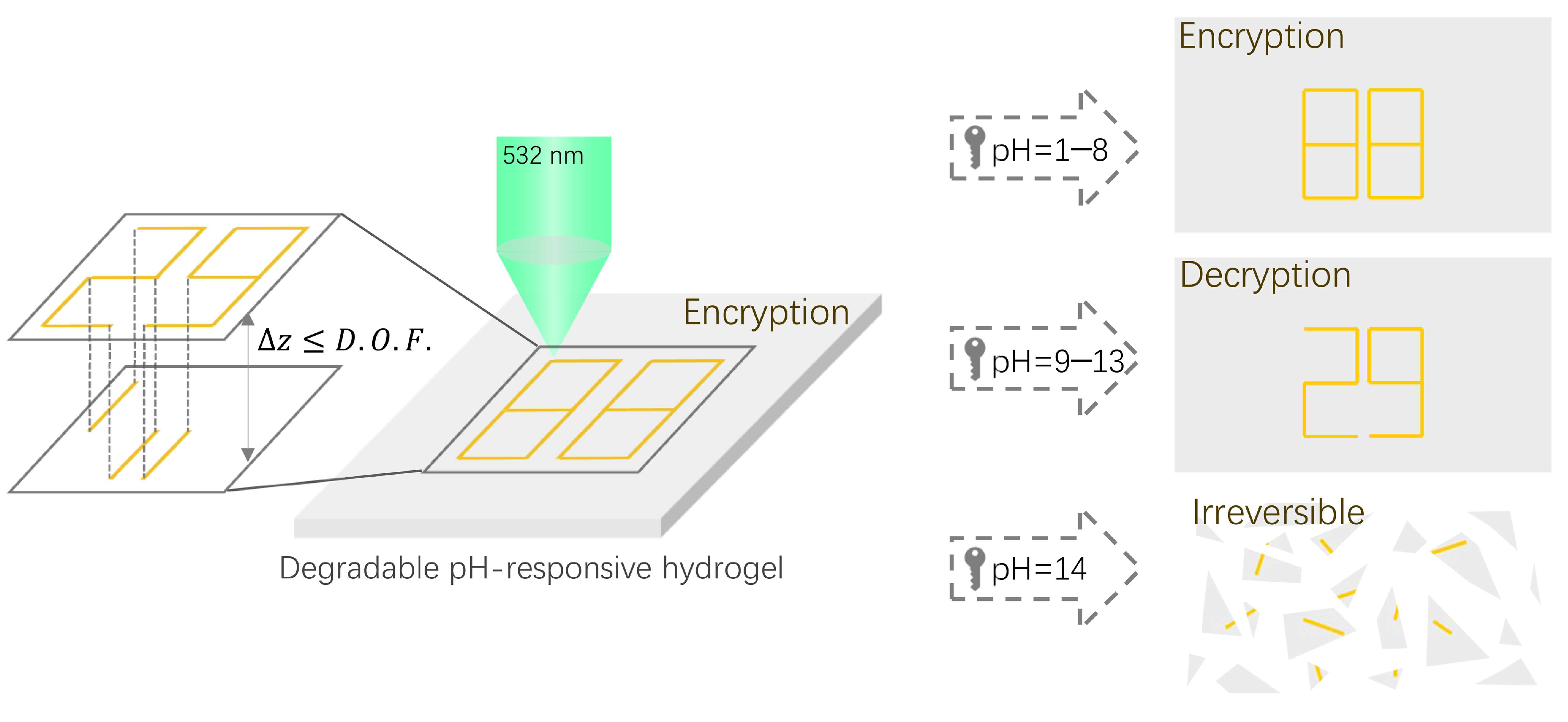
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
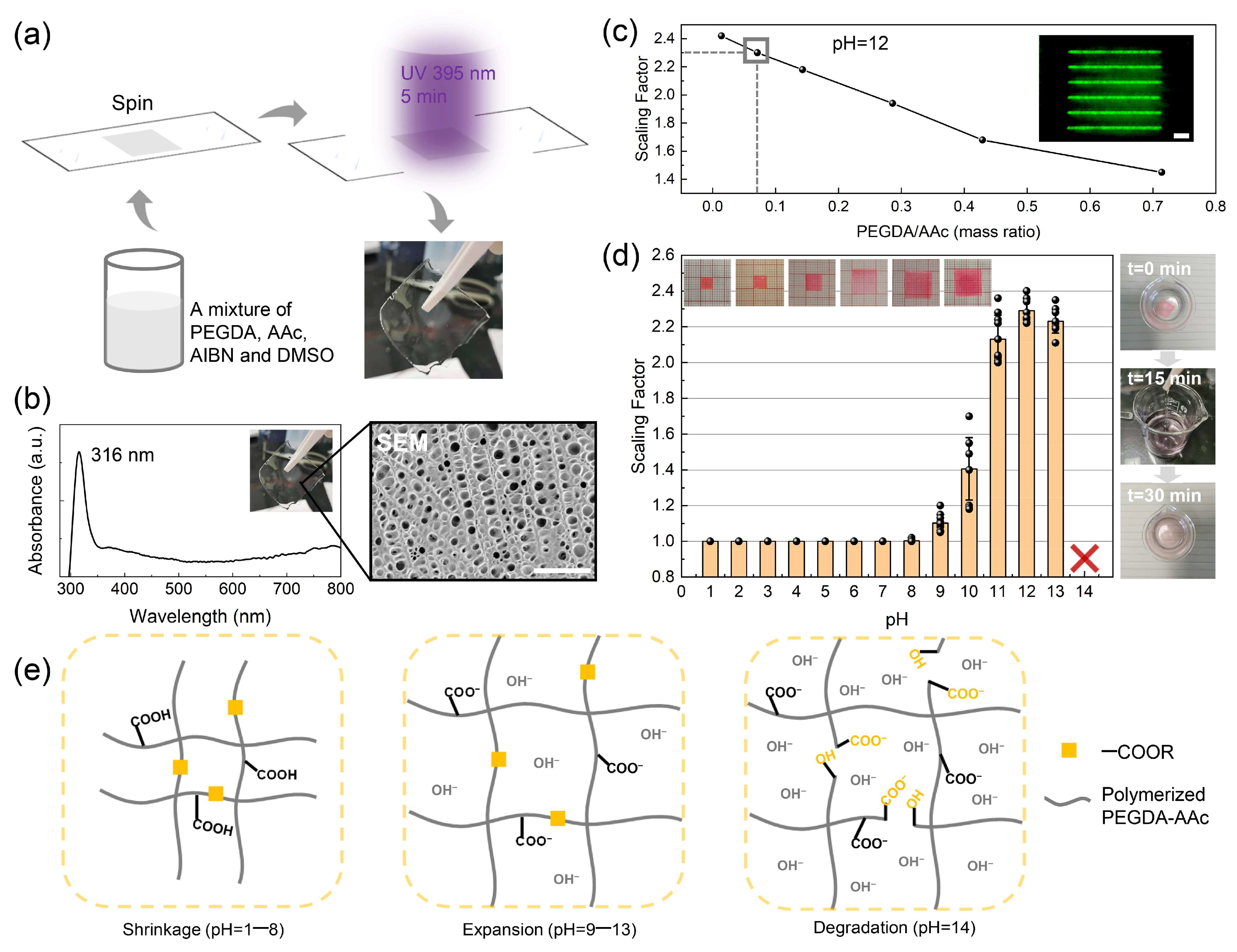
2.2. Preparation of the PEGDA/AAc Composite Hydrogel
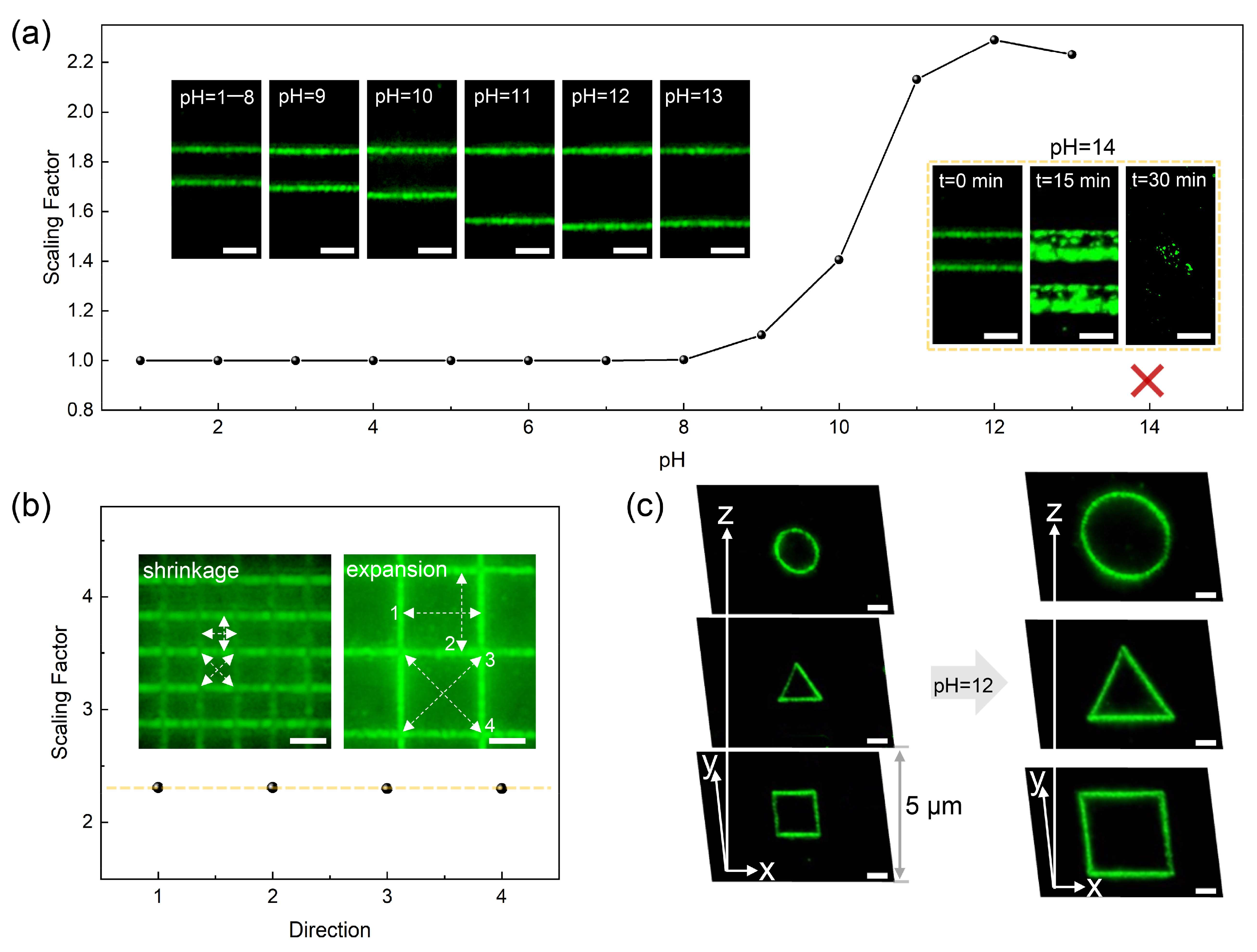
2.3. Acid/Alkali Treatments
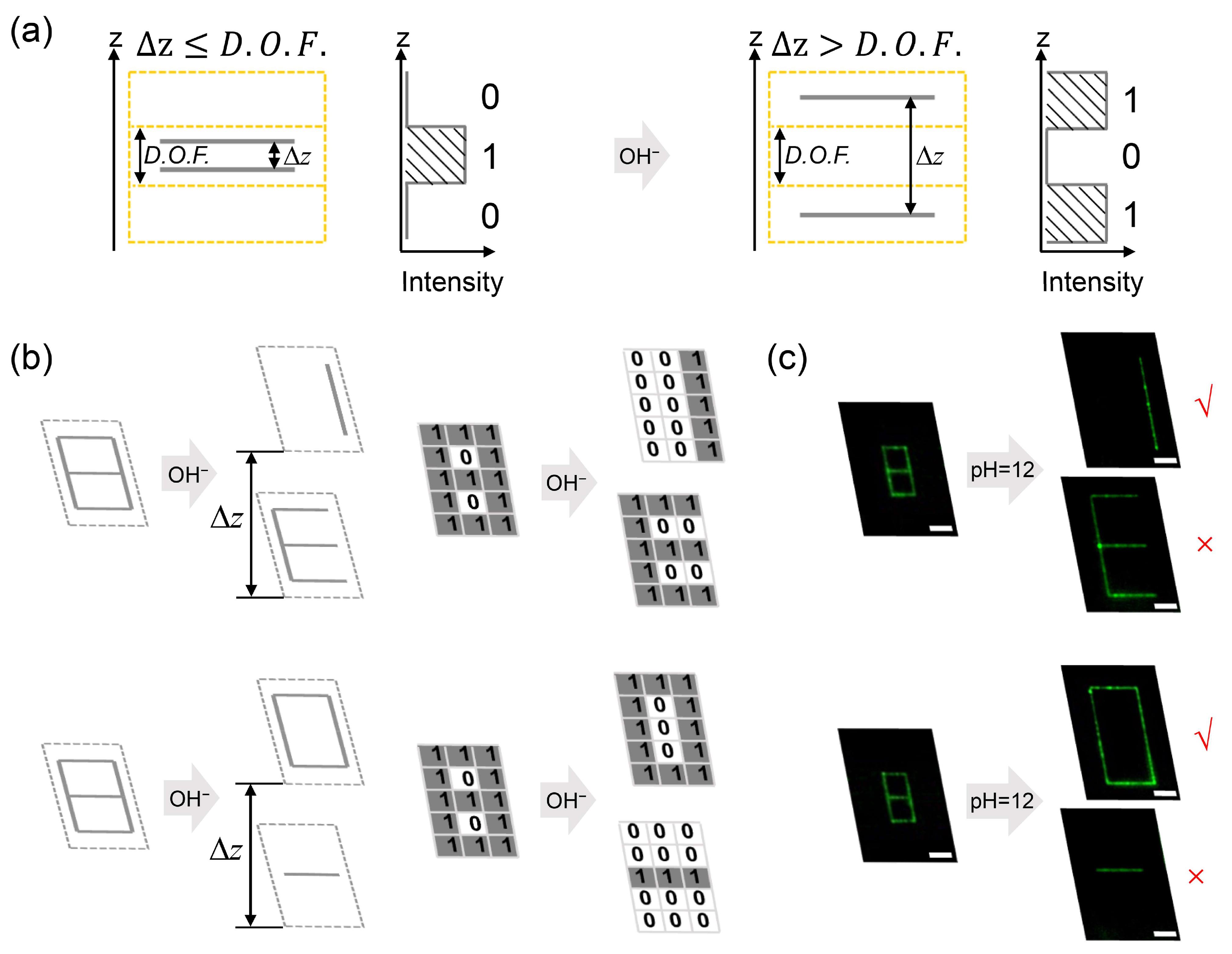
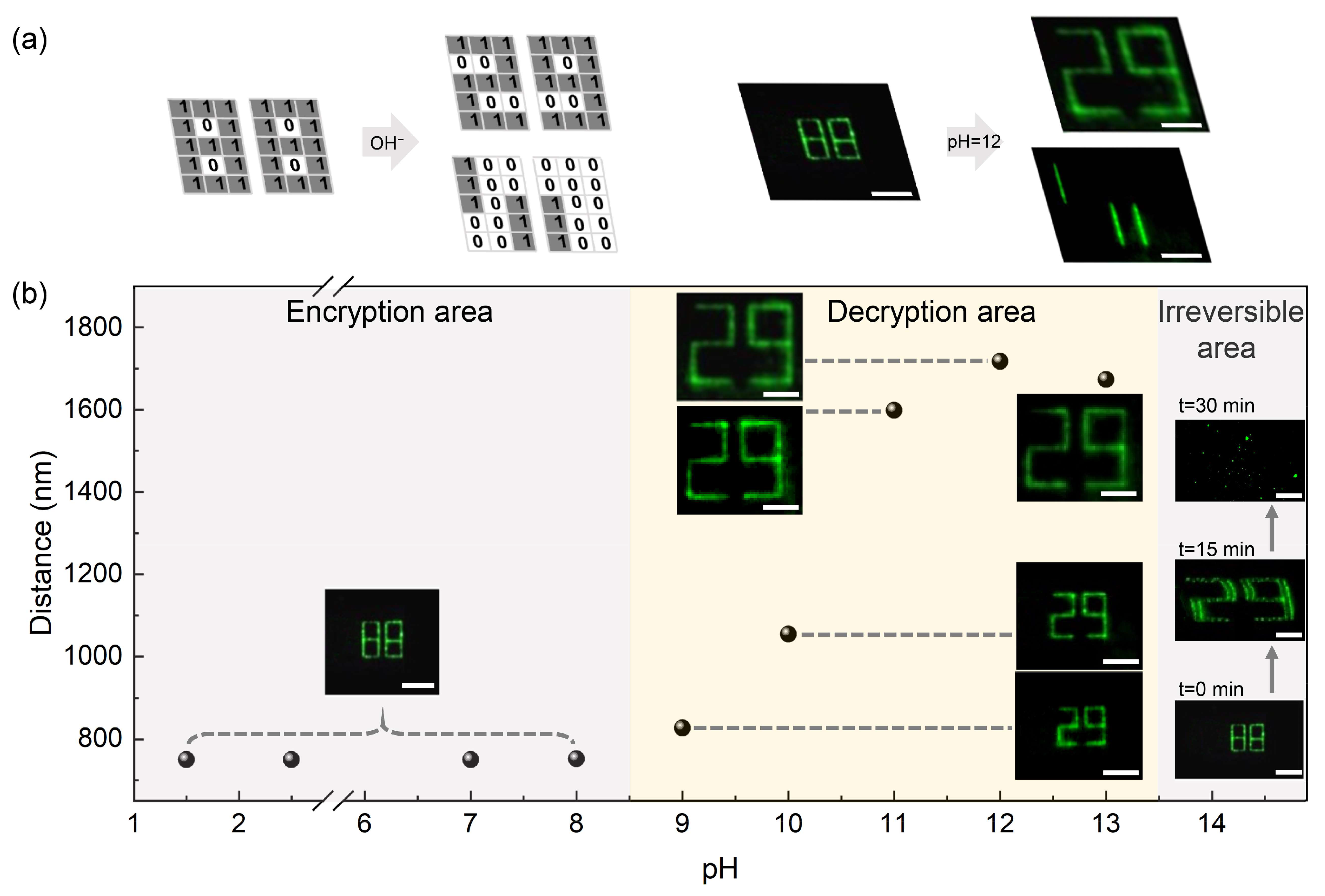
2.4. Data Inscription
2.5. Measurements and Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, M.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. Optical storage arrays: A perspective for future big data storage. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matoba, O.; Nomura, T.; Perez-Cabre, E.; Millan, M.S.; Javidi, B. Optical techniques for information security. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1128–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Xu, L.; Ahmad, M.A.; Liu, S. Double image encryption by using iterative random binary encoding in gyrator domains. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 12033–12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.H.; Gourevich, I.; Oh, J.K.; Jonkman, J.E.; Kumacheva, E. A multidye nanostructured material for optical data storage and security data encryption. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Gao, J. 3D Janus plasmonic helical nanoapertures for polarization-encrypted data storage. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.; Neebe, M.; Juchem, T.; Hampp, N.A. Biomolecular optical data storage and data encryption. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2003, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, J.; Wu, H.; Xu, X.; Yu, X.; Zhou, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q. No-interference reading for optical information storage and ultra-multiple anti-counterfeiting applications by designing targeted recombination in charge carrier trapping phosphors. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1900006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, P.; Ma, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xie, M.; Li, F.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Q. Dynamic luminescence manipulation for rewritable and multi-level security printing. Matter 2019, 1, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tebaldi, M.; Furlan, W.D.; Torroba, R.; Bolognini, N. Optical-data storage-readout technique based on fractal encrypting masks. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, J.F.; Henao, R.; Tebaldi, M.; Torroba, R.; Bolognini, N. Multiplexing encrypted data by using polarized light. Opt. Commun. 2006, 260, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Image encryption algorithm by using fractional Fourier transform and pixel scrambling operation based on double random phase encoding. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heanue, J.; Bashaw, M.; Hesselink, L. Encrypted holographic data storage based on orthogonal-phase-code multiplexing. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 6012–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Shang, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Lu, G.; Xue, Q.; Chen, T. A urease-containing fluorescent hydrogel for transient information storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3640–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Lim, K.H.; Gonuguntla, S.; Lim, K.W.; Pranantyo, D.; Yong, W.P.; Yam, W.J.T.; Low, Z.; Teo, W.J. The pathway to intelligence: Using stimuli-responsive materials as building blocks for constructing smart and functional systems. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1804540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazi, M.I.; Jeong, W.; Kim, J.M. Functional materials and systems for rewritable paper. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Han, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Duan, Y.; Li, Z.; Han, T. Strategy for optical data encryption and decryption using a DA type stimuli-responsive AIE material. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2020, 239, 118486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Li, D.; Ushakova, E.V.; Maslov, V.G.; Zhou, D.; Jing, P.; Shen, D.; Qu, S.; Rogach, A.L. Multilevel data encryption using thermal-treatment controlled room temperature phosphorescence of carbon dot/polyvinylalcohol composites. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Song, B.; Zhang, H.L.; Chen, H.; Cai, H.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y. A stimuli-responsive smart lanthanide nanocomposite for multidimensional optical recording and encryption. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2689–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Yan, F. Imidazolium-type ionic liquid-based carbon quantum dot doped gels for information encryption. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 20965–20972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Lu, C.; Yang, X. Efficient room temperature phosphorescence carbon dots: Information encryption and dual-channel pH sensing. Carbon 2019, 152, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, A.; Tang, B.Z. Simultaneously achieving high capacity storage and multilevel anti-counterfeiting using electrochromic and electrofluorochromic dual-functional aie polymers. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 7058–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Phua, S.Z.F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Jana, D.; Liu, G.; Lim, W.Q.; Ong, W.K.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y. Ultralong room temperature phosphorescence from amorphous organic materials toward confidential information encryption and decryption. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdollahi, A.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Salami-Kalajahi, M.; Razavi, B. Encryption and authentication of security patterns by ecofriendly multi-color photoluminescent inks containing oxazolidine-functionalized nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 580, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.; Xu, Y.; Gao, H.; Han, G.; Cao, R.; Guo, P.; Feng, W.; Chen, L. Tetraphenylethylene@ graphene oxide with switchable fluorescence triggered by mixed solvents for the application of repeated information encryption and decryption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 35255–35263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Le, X.; Jian, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T. 3D fluorescent hydrogel origami for multistage data security protection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Liao, L. Multi-responsive hydrogel actuator with photo-switchable color changing behaviors. Dyes Pigment. 2020, 174, 108042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Van Vliet, K.; Holten-Andersen, N.; Miserez, A. A double-layer mechanochromic hydrogel with multidirectional force sensing and encryption capability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Xie, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y. Photoresponsive luminescent polymeric hydrogels for reversible information encryption and decryption. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Tong, Z. pH responsive strong polyion complex shape memory hydrogel with spontaneous shape changing and information encryption. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2000747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Itzhaki, E.; Hadad, E.; Gedanken, A.; Margel, S. Microwave-synthesized polysaccharide-derived carbon dots as therapeutic cargoes and toughening agents for elastomeric gels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 51940–51951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Sun, X.-C.; Xia, H.; Yu, Y.-H.; Wang, G.; Cao, X.-W.; Li, S.-X.; Wang, Y.-S.; Chen, Q.-D.; Yu, Y.-D. Humidity-responsive actuation of programmable hydrogel microstructures based on 3D printing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Mondal, S.; Das, P.; Bhawal, P.; Maity, P.P.; Ghosh, S.; Dhara, S.; Das, N.C. Design of psyllium-g-poly (acrylic acid-co-sodium acrylate)/cloisite 10A semi-IPN nanocomposite hydrogel and its mechanical, rheological and controlled drug release behaviour. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 983–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Li, W.; Xie, F.; Xiong, Z.; Song, S.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. Reversible data encryption–decryption using a pH stimuli-responsive hydrogel. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Cho, C.-S. Drug release from pH-sensitive interpenetrating polymer networks hydrogel based on poly (ethylene glycol) macromer and poly (acrylic acid) prepared by UV cured method. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 1996, 19, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Song, S.; Xie, F.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Feng, Z.; Wu, S.; Han, J.; Guan, B.-O.; Xu, X. Great chiral fluorescence from the optical duality of silver nanostructures enabled by 3D laser printing. Mate. Horiz. 2020, 7, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, S.; Feng, Z.; Hu, D.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. Bidirectional plasmonic coloration with gold nanoparticles by wavelength-switched photoredox reaction. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21910–21917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.Y.; Takeyasu, N.; Tanaka, T.; Duan, X.M.; Kawata, S. 3D metallic nanostructure fabrication by surfactant-assisted multiphoton-induced reduction. Small 2009, 5, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.W.; Cheng, W.; Martini, I.B.; Dunn, B.; Schwartz, B.J.; Yablonovitch, E. Two-photon photographic production of three-dimensional metallic structures within a dielectric matrix. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1438–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Yu, J.; Huang, Y.; Ke, H.; Liu, H. Development of an autofocusing system using an electrically tunable lens in large area holographic lithography. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 2521–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browe, D.P.; Wood, C.; Sze, M.T.; White, K.A.; Scott, T.; Olabisi, R.M.; Freeman, J.W. Characterization and optimization of actuating poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate/acrylic acid hydrogels as artificial muscles. Polymer 2017, 117, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokufuta, E.; Wang, B.; Yoshida, R.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Hirata, M. Volume phase transition of polyelectrolyte gels with different charge distributions. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 6878–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, H.; Wang, B.; Zhu, H.; Wu, S.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. Security-Enhanced 3D Data Encryption Using a Degradable pH-Responsive Hydrogel. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071744
Wen H, Wang B, Zhu H, Wu S, Xu X, Li X, Cao Y. Security-Enhanced 3D Data Encryption Using a Degradable pH-Responsive Hydrogel. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(7):1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071744
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Hongjing, Bin Wang, Hongbo Zhu, Shiyu Wu, Xiaoxuan Xu, Xiangping Li, and Yaoyu Cao. 2021. "Security-Enhanced 3D Data Encryption Using a Degradable pH-Responsive Hydrogel" Nanomaterials 11, no. 7: 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071744
APA StyleWen, H., Wang, B., Zhu, H., Wu, S., Xu, X., Li, X., & Cao, Y. (2021). Security-Enhanced 3D Data Encryption Using a Degradable pH-Responsive Hydrogel. Nanomaterials, 11(7), 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071744






