Polymer Binders of Ceramic Nanoparticles for Precision Casting of Nickel-Based Superalloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- preparation of a wax pattern,
- (b)
- fabrication of a multilayer ceramic shell mould on the readymade wax pattern,
- (c)
- dewaxing/stripping,
- (d)
- burn off of a ceramic shell mould,
- (e)
- casting, in which ceramic shell moulds are filled with metal alloys (e.g., IN713C, IN100, Mar 247, CMXS 6, M509),
- (f)
- hardening and hammering shell moulds,
- (g)
- finishing and assessing the properties of the readymade shell moulds.
2. Synthetic Resins
3. Alcoholic Binders
- ethyl silicate (ES) and hydrolysed ethyl silicate (HES);
- silicic acid sol (SAS, e.g., Sizol 30);
- ES and HES mixtures (copolymer binders, e.g., Sikop);
- binders containing nano-silica, in which water is the diluent [19].
3.1. Ethyl Silicate
3.2. Hydrolysed Ethyl Silicate
3.3. Silicic Acid Sol
3.4. ES and HES Mixtures
- long storage life and parameter stability;
- good surface wettability of the wax model;
- longer drying process of individual layers of a ceramic mould (up to 4 h), which is about 1.5 times longer than the moulding systems based on ES;
- sufficient strength of a casting mould obtained with a binder which is a mixture of ES and HES;
- ease of binder preparation during precision casting [41].
4. Water Binders
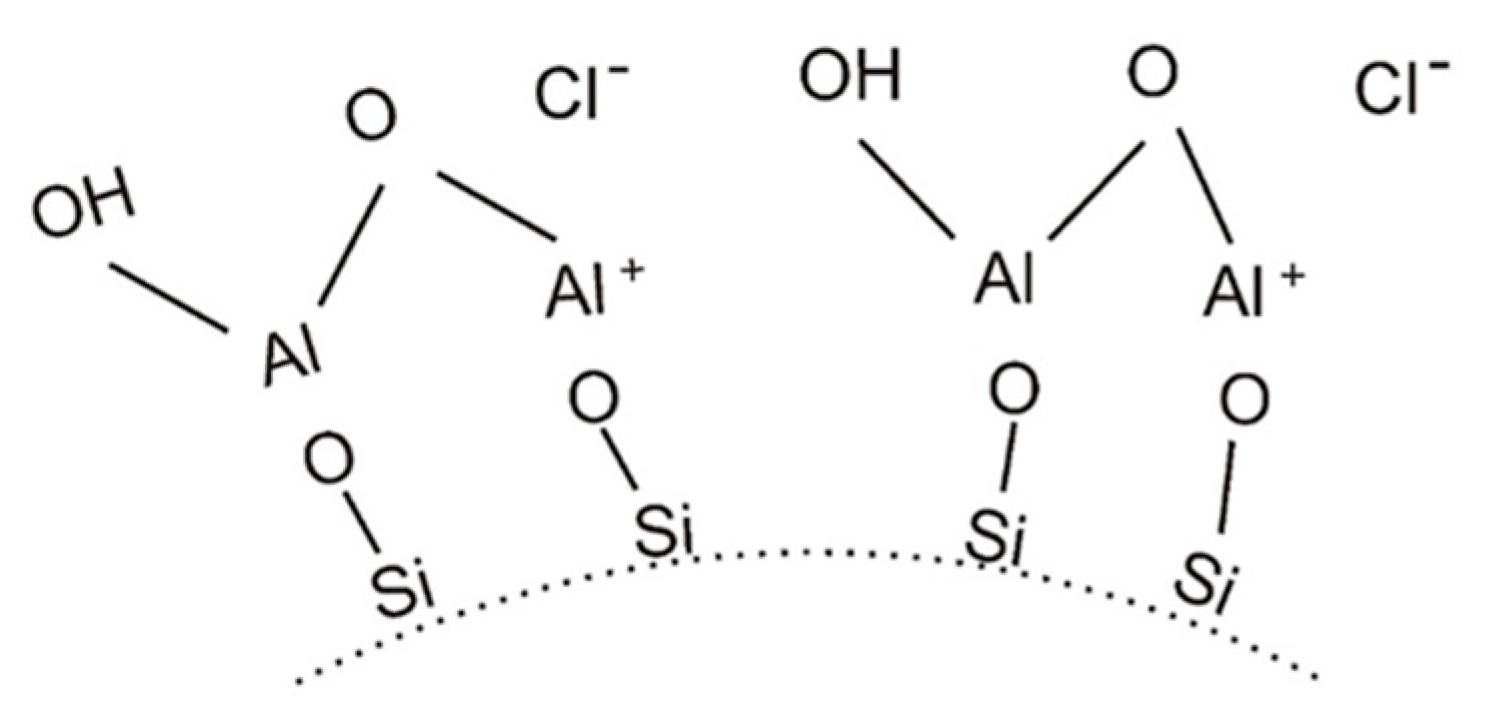
4.1. Water-Soluble Binder Containing Nano-Al2O3
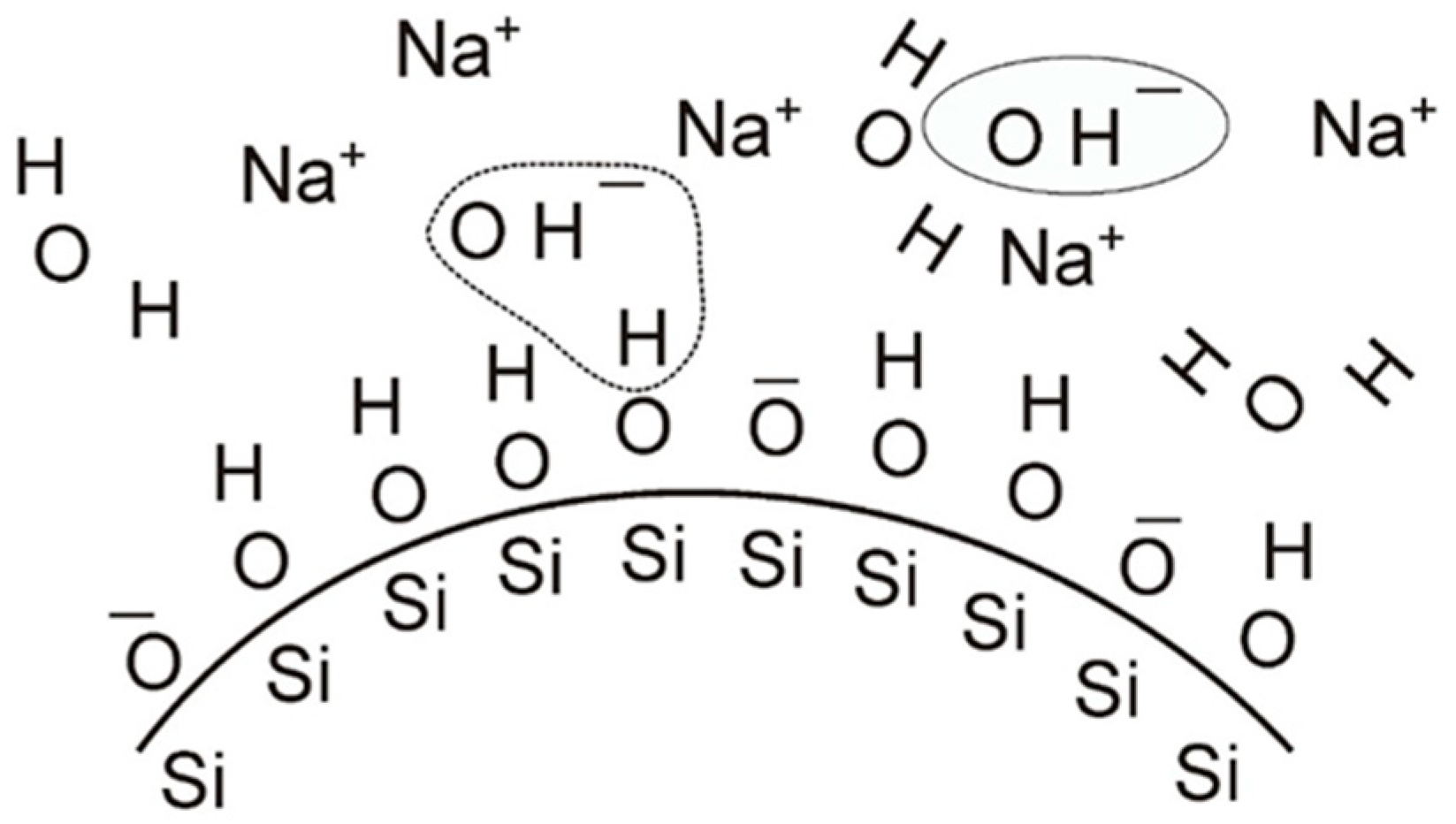
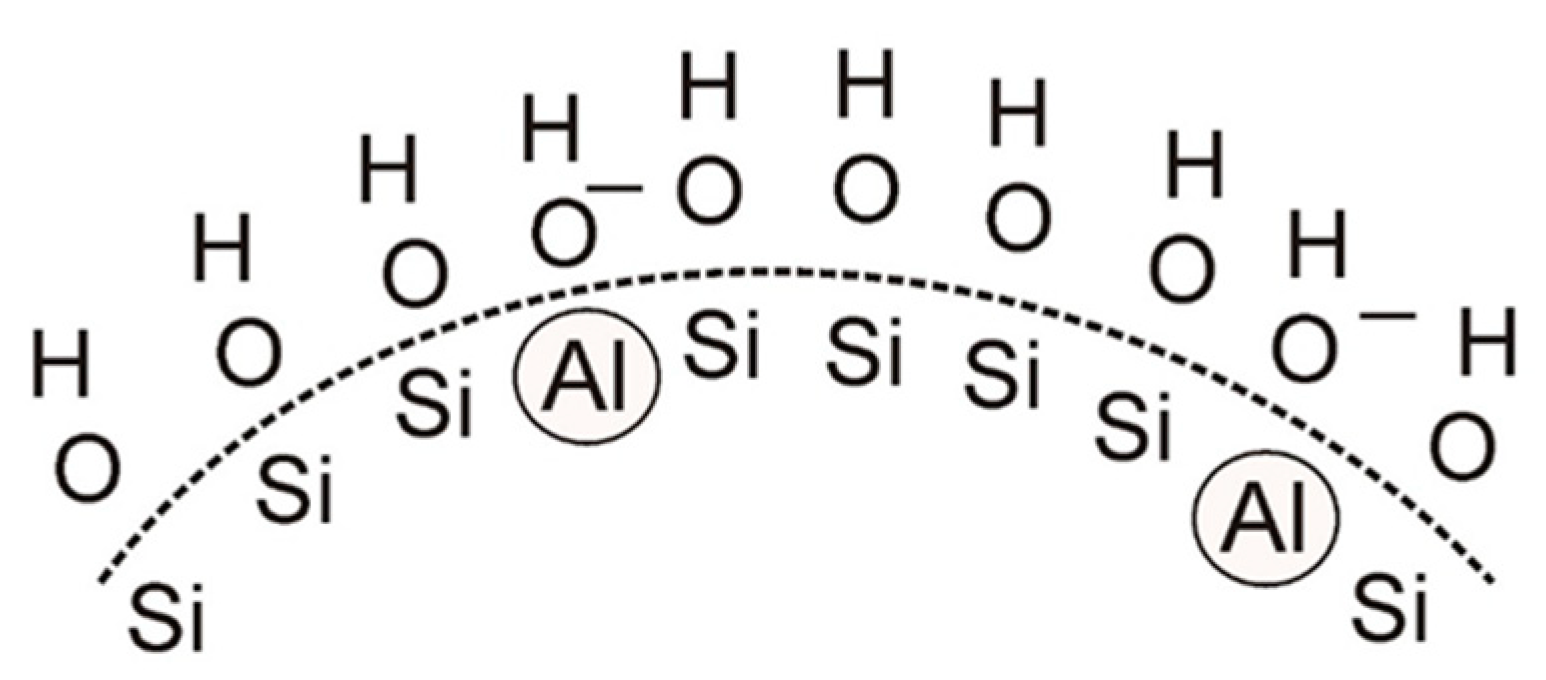
4.2. Water-Soluble Binders Containing Nano-SiO2
- (a)
- long lifetime (period of technological usefulness),
- (b)
- good surface wettability of the wax model,
- (c)
- sufficient strength of the mould throughout the whole technological process,
- (d)
- ease of binder preparation in facility conditions.
4.3. Properties of Selected Binders Based on Colloidal Silica
- content of solid phase in binders,
- wettability of binders,
- viscosity and density of binders,
- bonding capacity of binders.
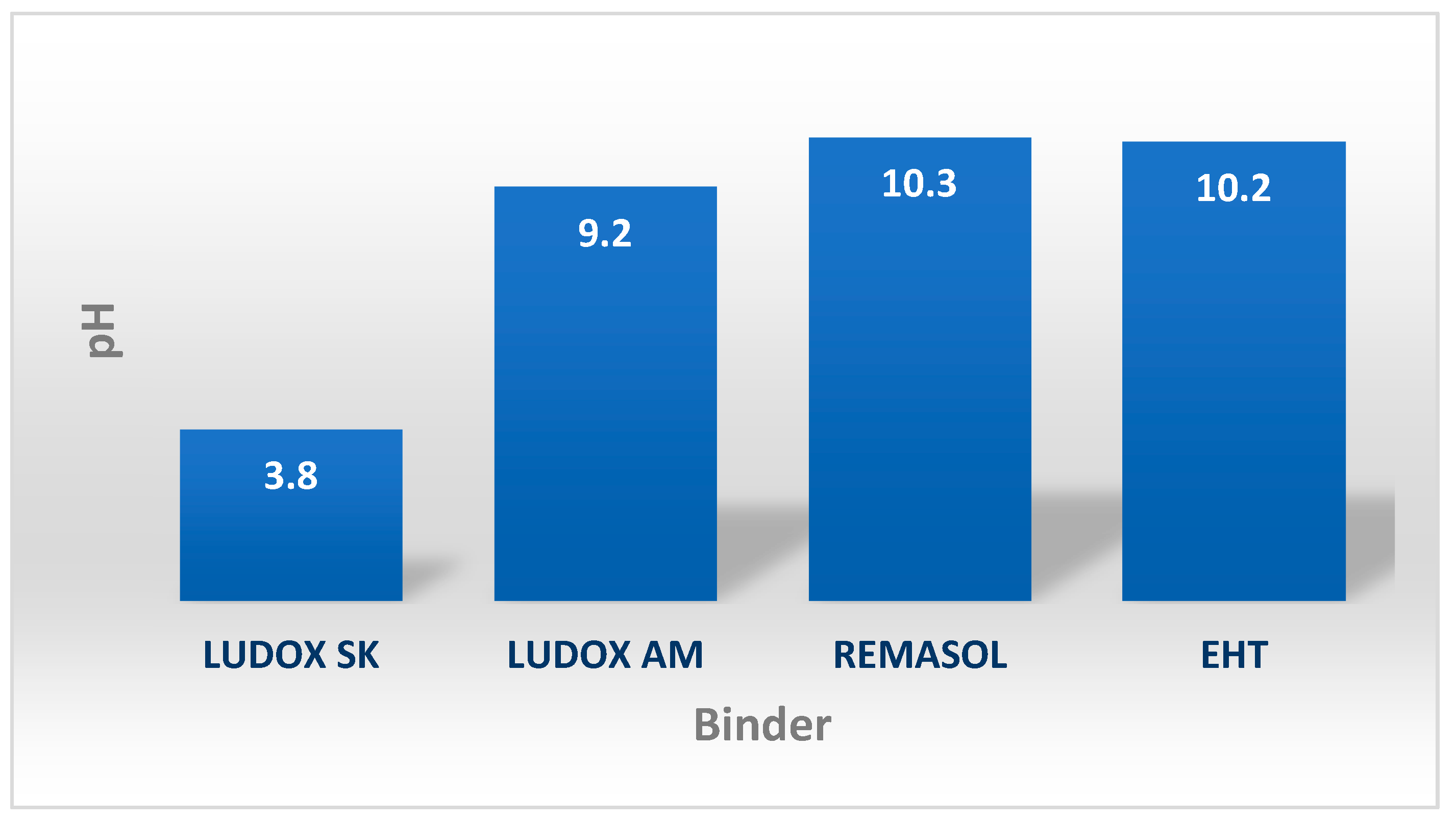
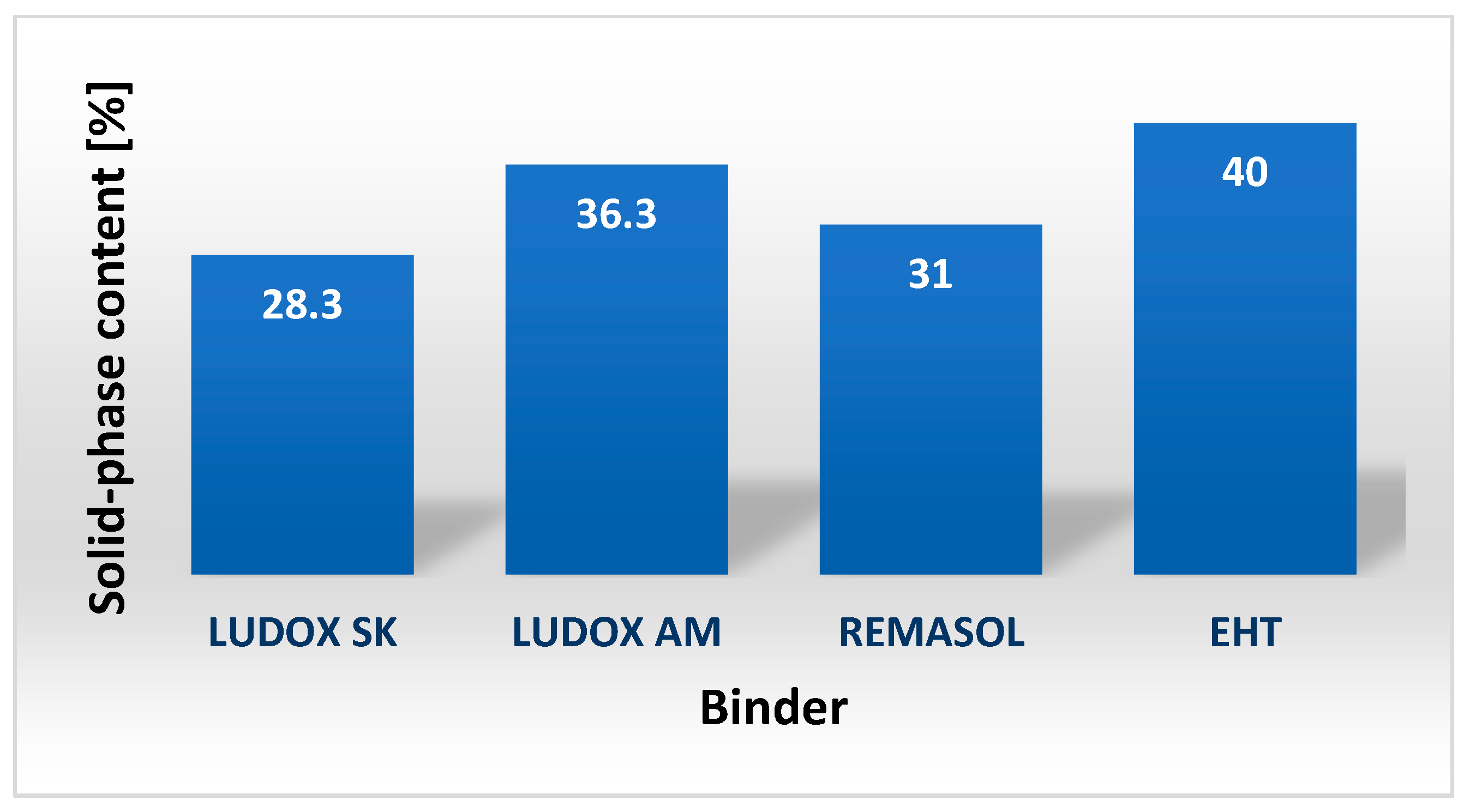
4.3.1. External Appearance, pH, and Solid-Phase Content of Selected Binders Based on Colloidal Silica
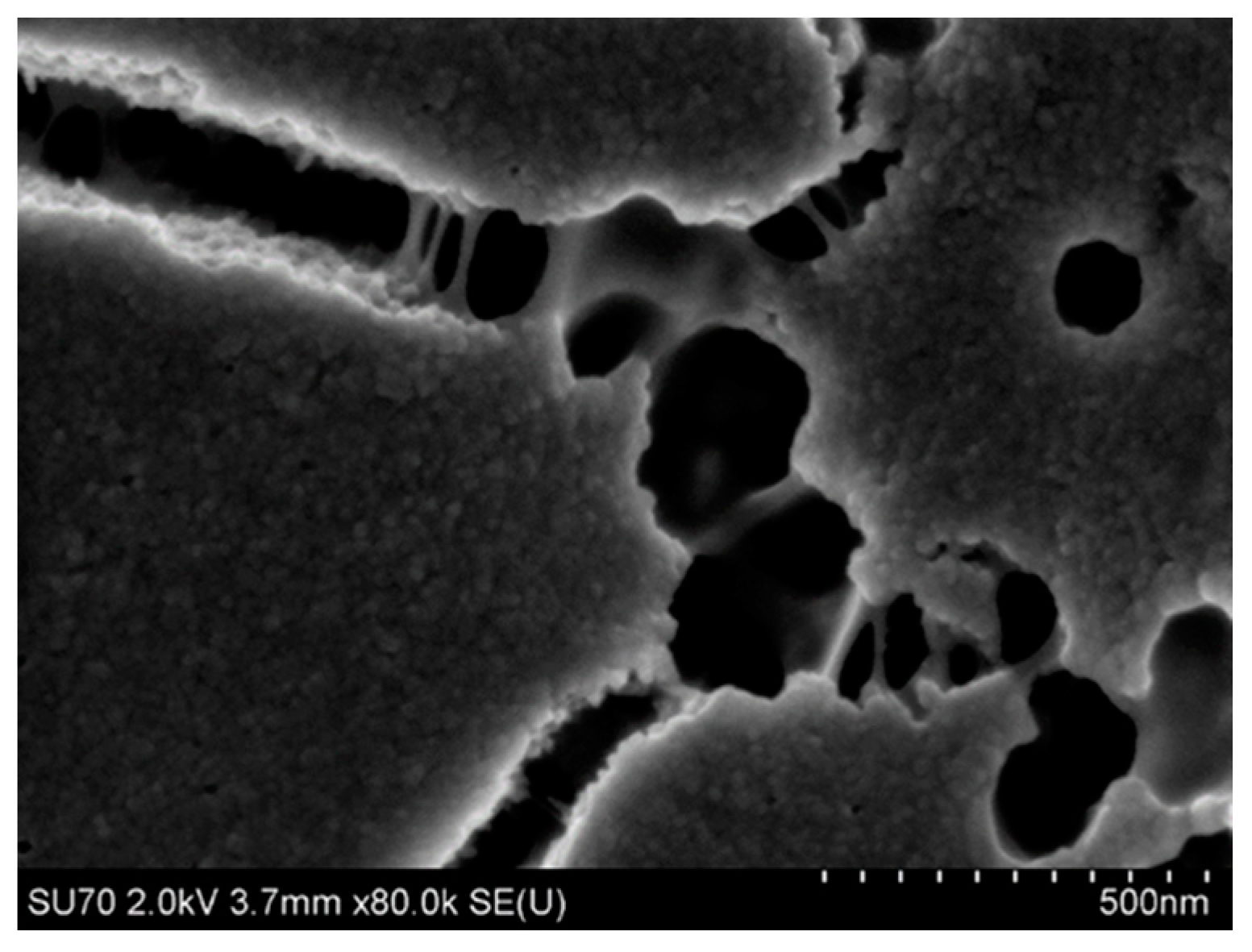
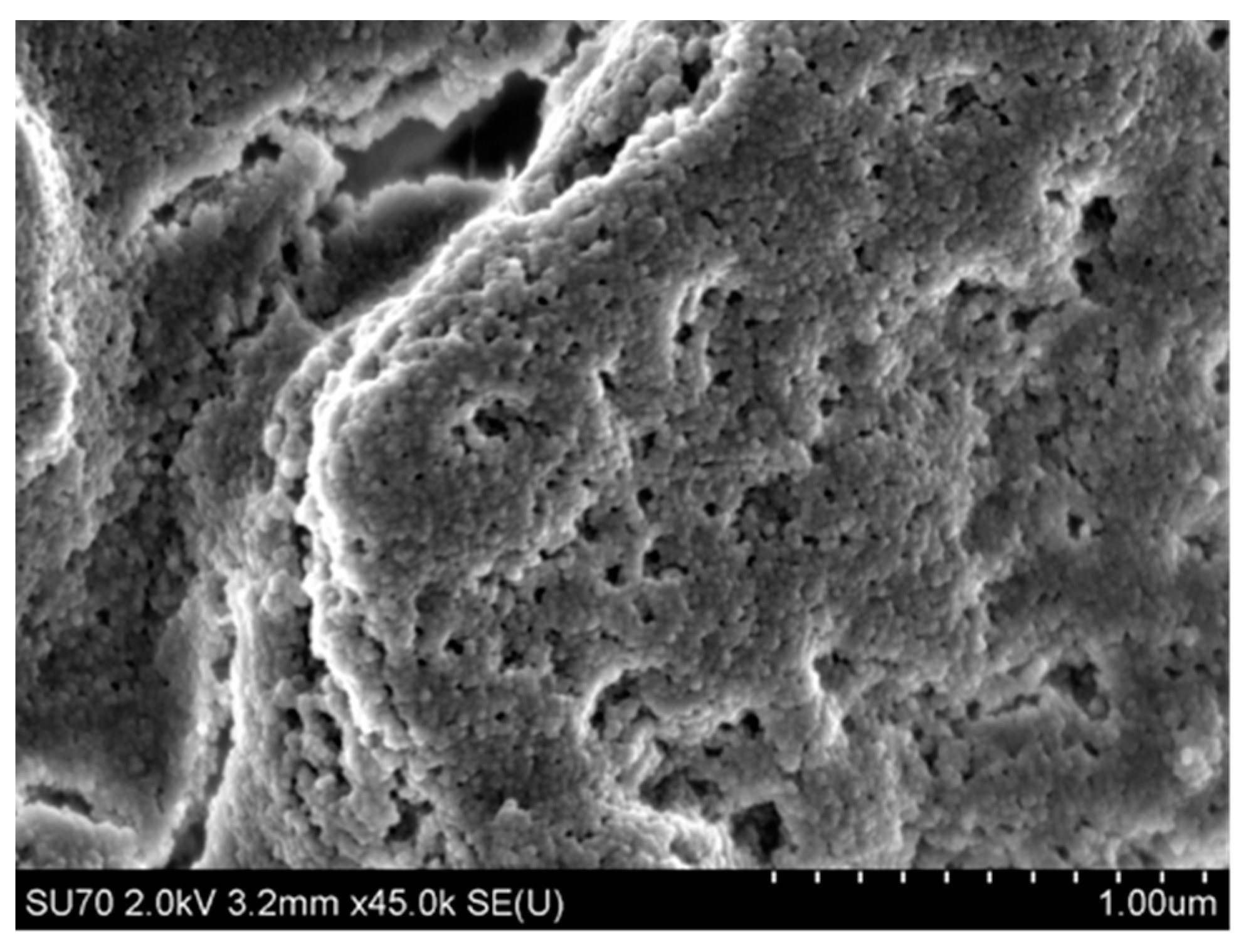
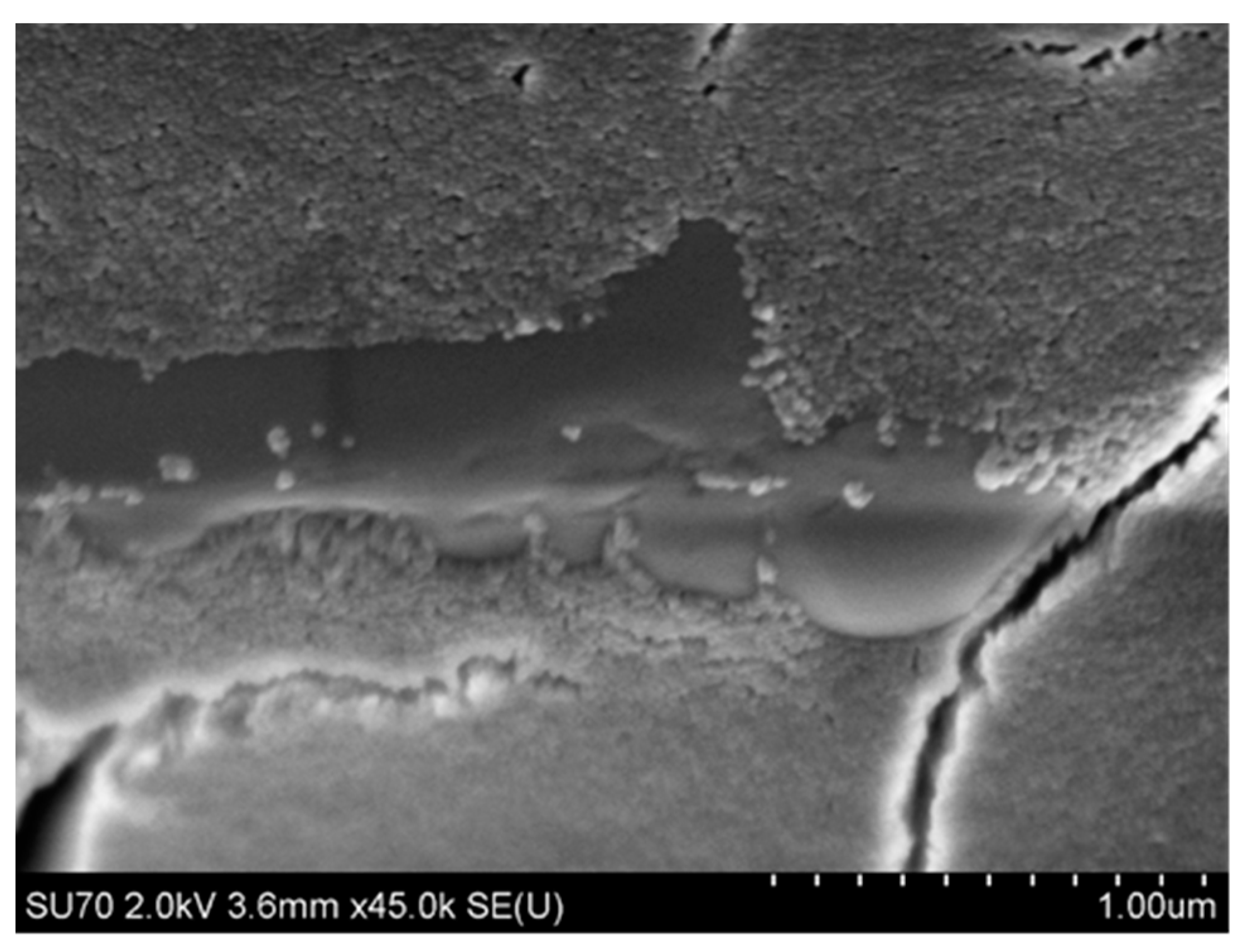
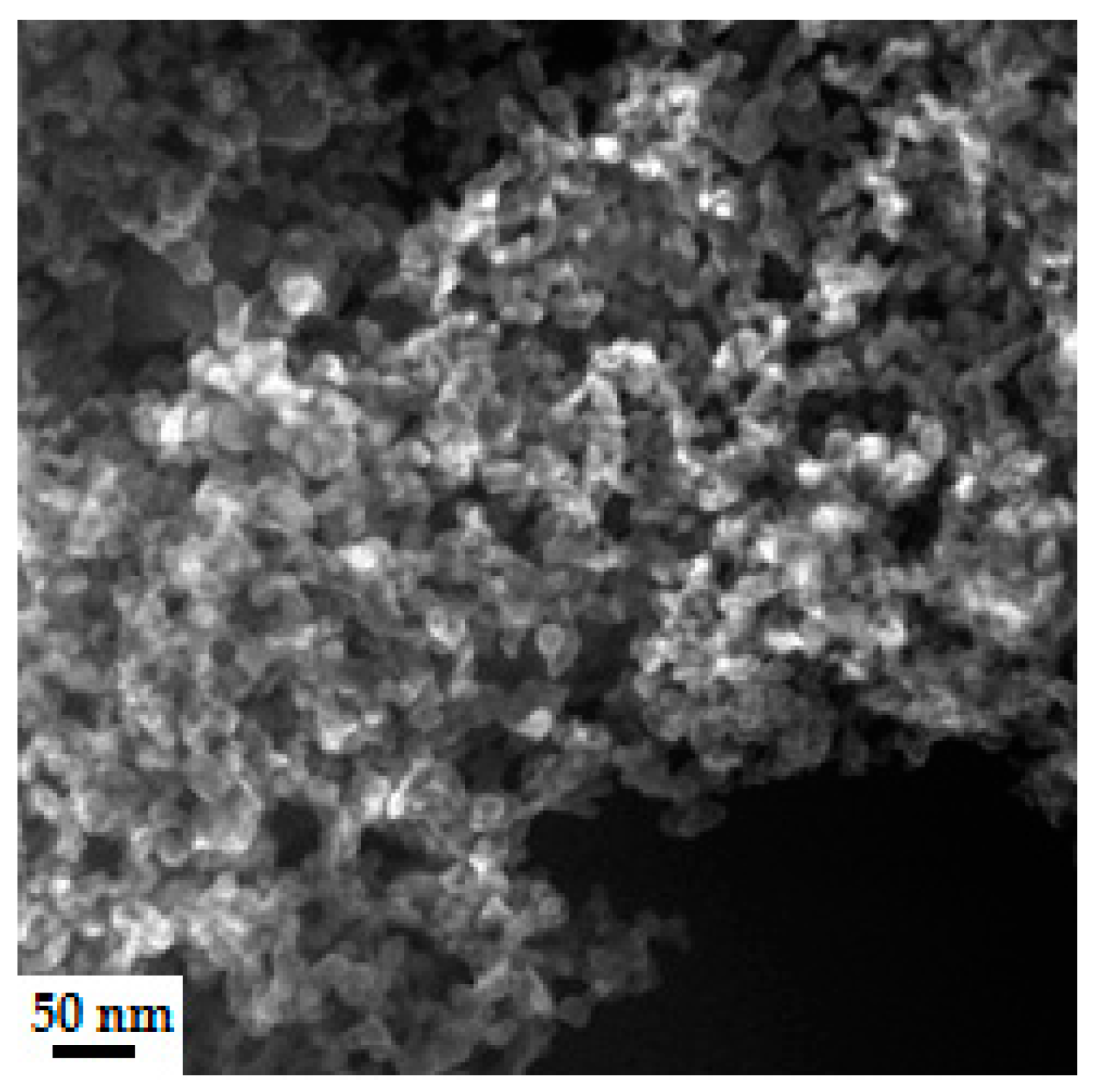
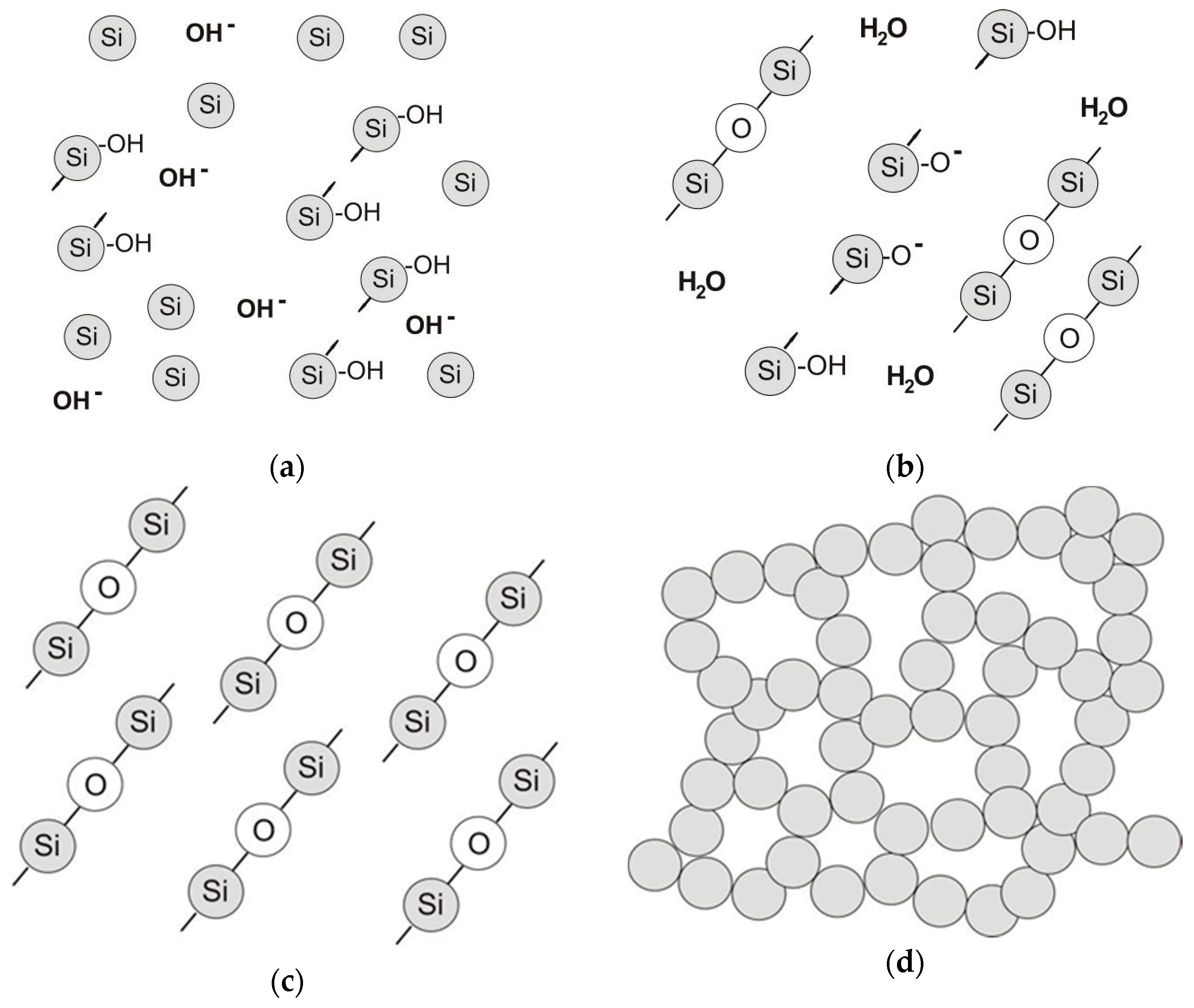
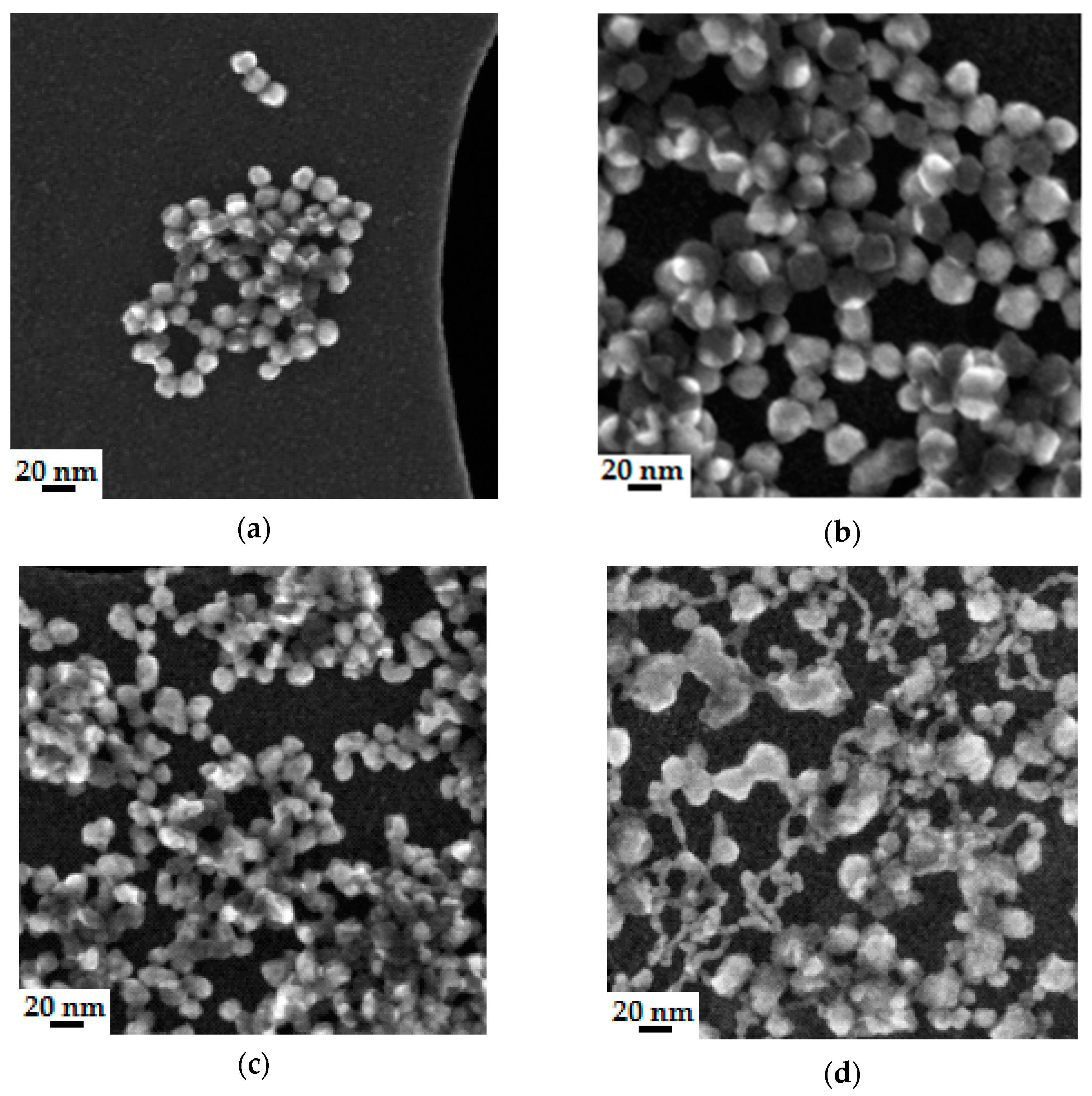
4.3.2. Microstructure of Polymeric Binders Based on Colloidal Silica
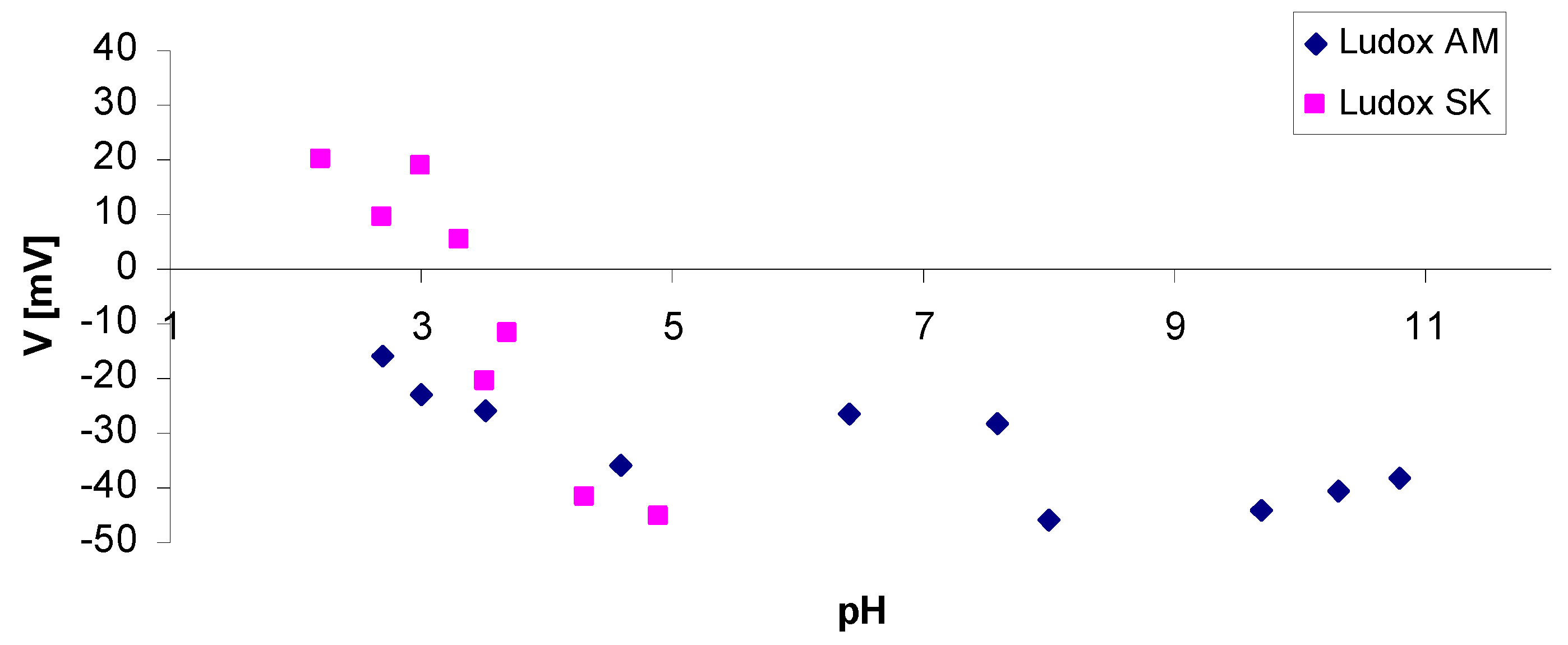
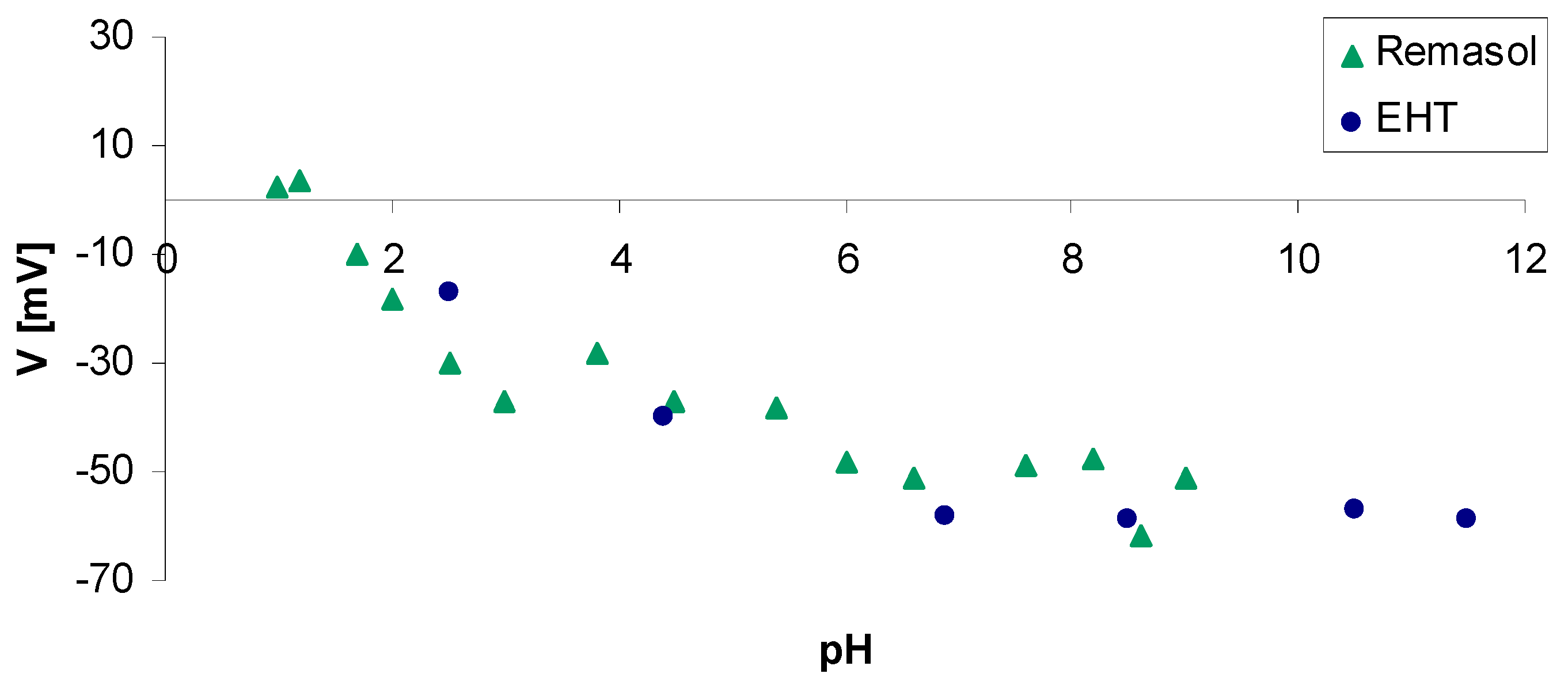
4.3.3. Zeta Potential of Selected Binders Based on Colloidal Silica
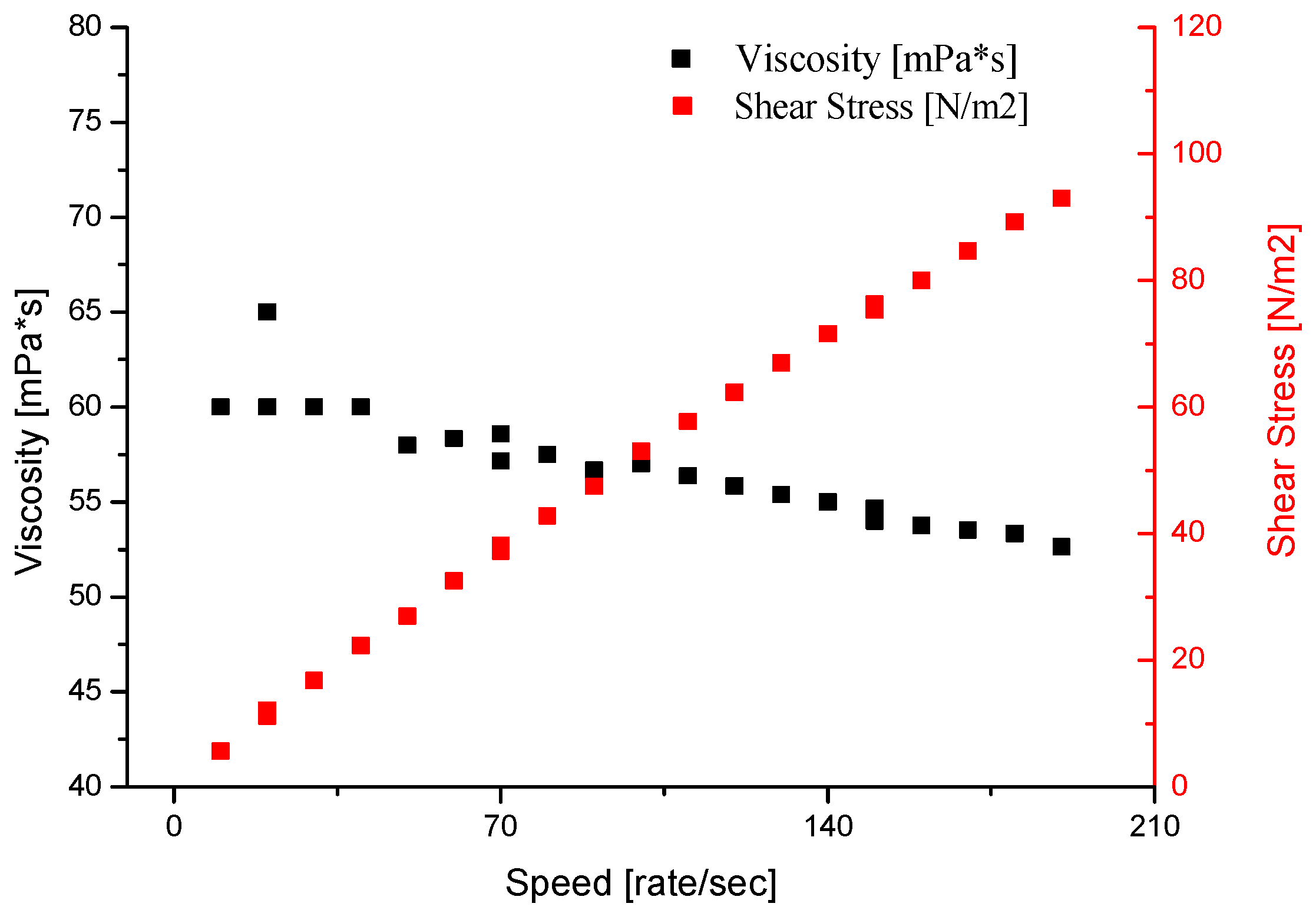
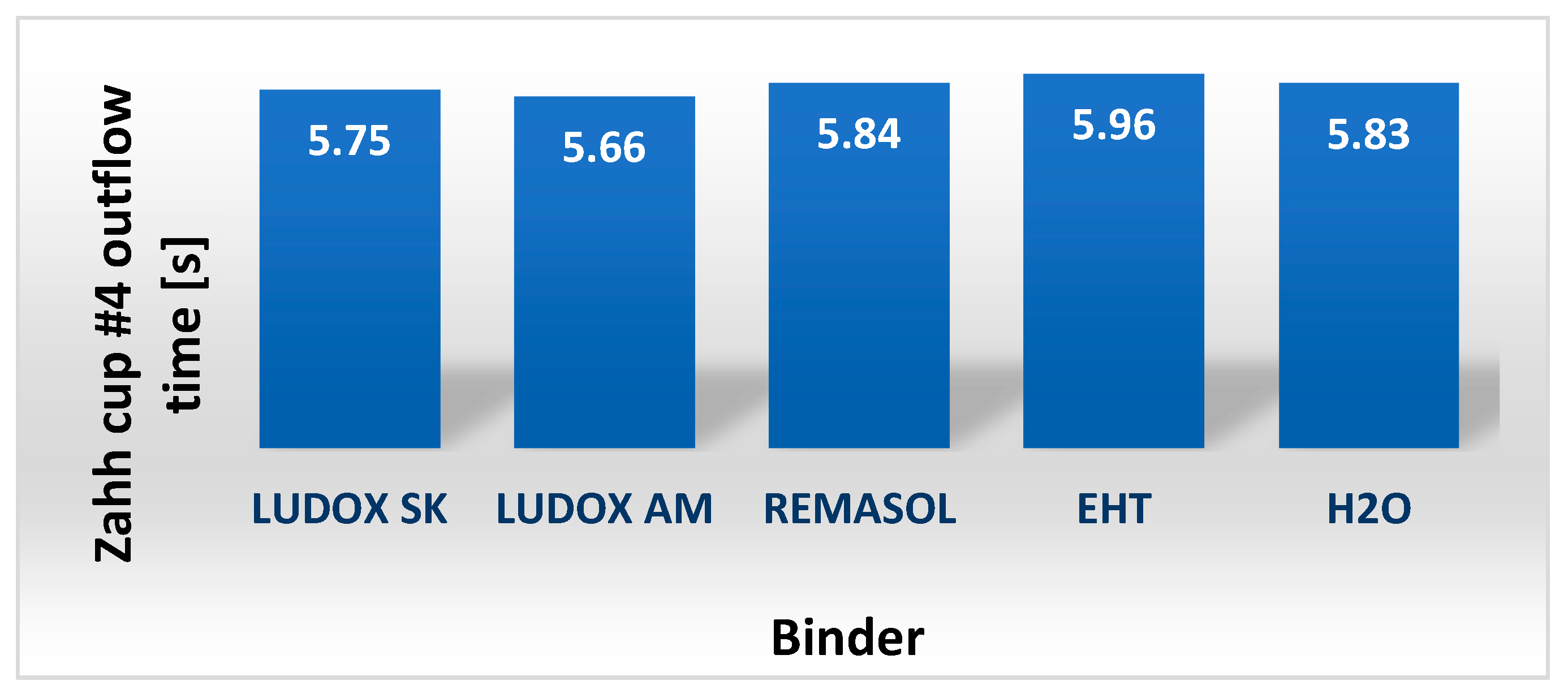
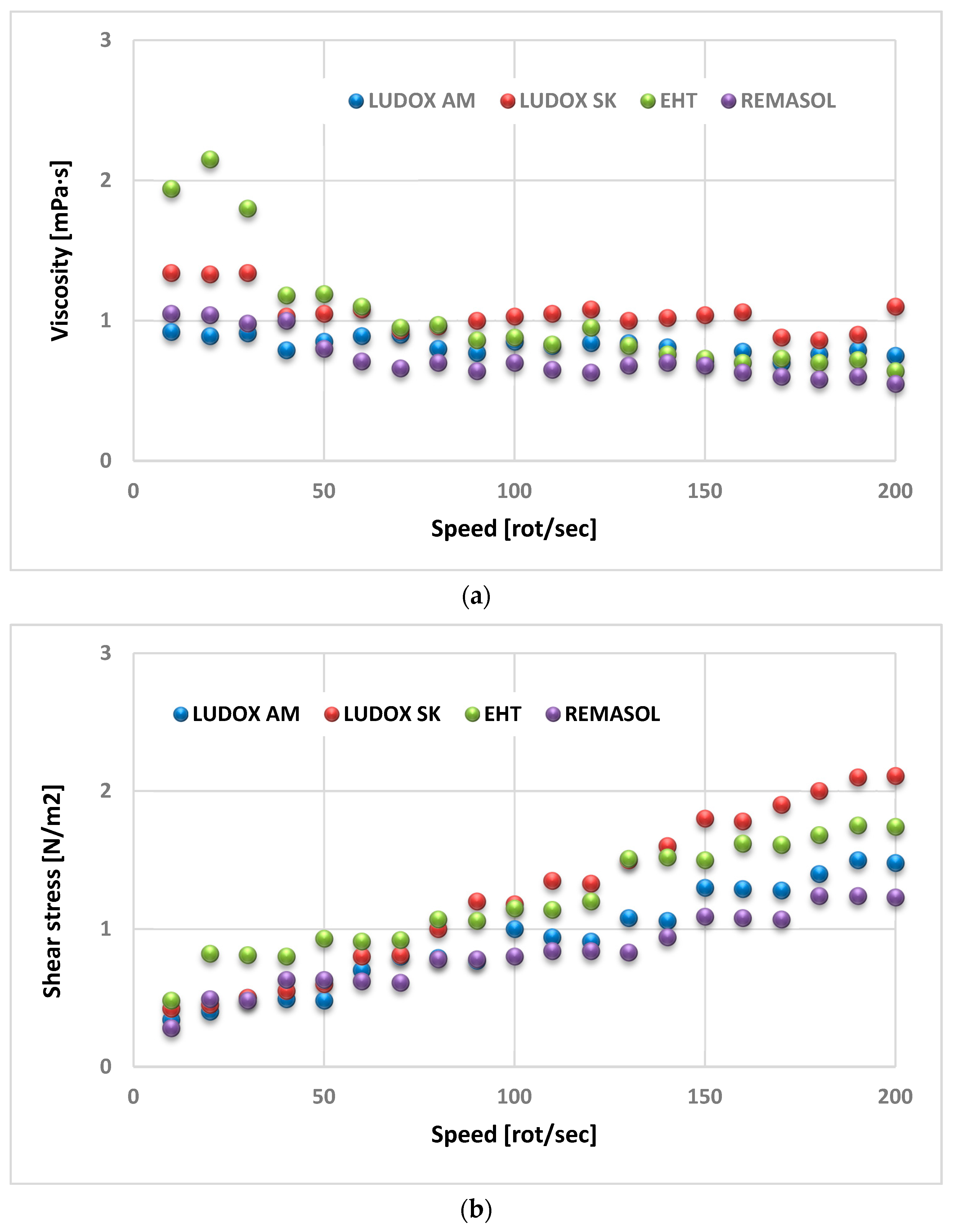
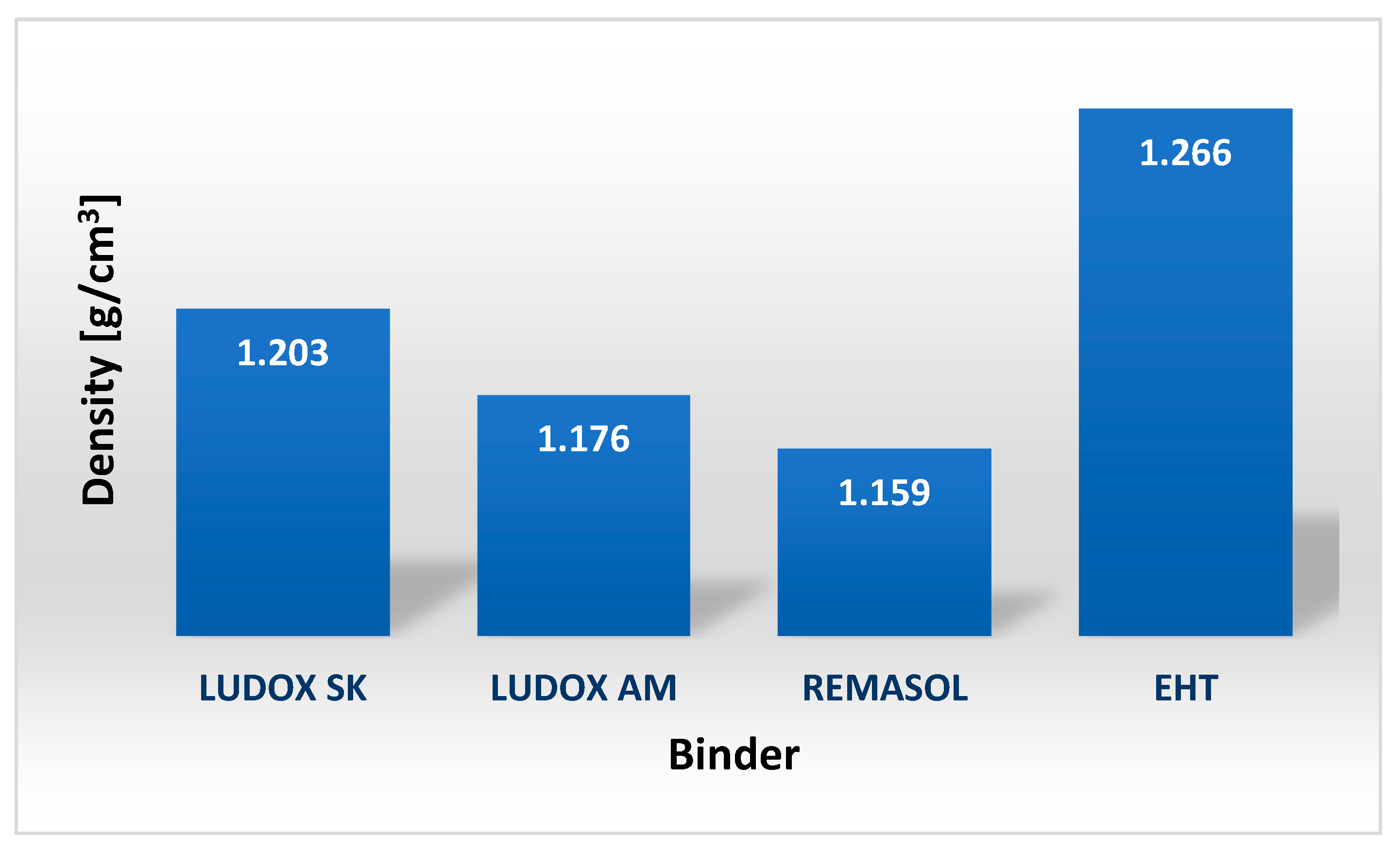
4.3.4. Viscosity and Density of Selected Binders Based on Colloidal Silica
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewandowski, J.L. Tworzywa na Formy Odlewnicze; Wydawnictwo Naukowe Akapit: Kraków, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, R.C. The Superalloys, Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; Yuan, C. Advances in shell moulding for investment casting. J. Mat. Proc. Technol. 2003, 135, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, C.-A.; Rappaz, M.; Tintillier, R. Three-Dimensional Probabilistic Simulation of Solidification Grain Structures: Application to Superalloy Precision Castings. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perzyk, M. Odlewnictwo; Wydawnictwo Naukowo-Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Ma, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Sun, B.; Dong, A.; Li, F.; Bührig-Polaczek, A. Freckle Defect Formation near the Casting Interfaces of Directionally Solidified Superalloys. Materials 2016, 9, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewski, P.; Małek, M.; Mizera, J.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Effect of adding water-based binders on the technological properties of ceramic slurries based on silicon carbide. Mater. Technol. 2017, 51, 225–227. [Google Scholar]
- Kanyo, J.E.; Schafföner, S.; Uwanyuze, S.R.; Leary, K.S. An overview of ceramic molds for investment casting of nickel superalloys. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 4955–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, S.; Karunakar, D.B.; Jha, P.K. Developments in investment casting process—A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 2332–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.W.; Li, X.L.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, J.; Dao, M. Modeling of shrinkage during investment casting of thin-walled hollow turbine blades. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 244, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winardi, L.; Littleton, H.E.; Bates, C.E. New technique for measuring permeability of cores made from various sands, binders, additives and coatings. AFS Trans. 2005, 113, 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Kolczyk, J.; Zych, J. Rheological properties of ceramic slurries with colloidal binders used in the investment casting technology. Metalurgija 2013, 52, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjay, K.; Karunakar, D.B. Enhancing the permeability and properties of ceramic shell in investment casting process using ABS powder and needle coke. Int. J. Metalcast. 2019, 13, 588–596. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Karunakar, D.B. Characterization and Properties of Ceramic Shells in Investment Casting Process. Int. J. Metalcast. 2020, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jin, S.; Lai, X.; He, B.; Li, F. Influence of complex structure on the shrinkage of part in investment casting process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrecki, M.; Kamińska, J.; Jakubski, J.; Wieliczko, P. Strength properties of ceramic moulds containing spent moulding sand after initial reclamation. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2019, 19, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski, P.; Sitek, R.; Towarek, A.; Choińska, E.; Moszczyńska, D.; Mizera, J. Molding Binder Influence on the Porosity and Gas Permeability of Ceramic Casting Molds. Materials 2020, 13, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Lu, G.; Yan, Q.; Mao, P. Effect of Ceramic and Nylon Fiber Content on Composite Silica Sol Slurry Properties and Bending Strength of Investment Casting Shell. Materials 2019, 12, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratym, R.; Biernacki, R.; Myszka, D. Ekologiczne Wytwarzanie Dokładnych Odlewów w Formach Ceramicznych; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Warszawskiej: Warszawa, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Żymankowska-Kumon, S.; Bobrowski, A.; Grabowska, B. Comparison of the Emission of Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Moulding Sands with Furfural Resin with the Low Content of Furfuryl Alcohol and Different Activators. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2016, 16, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grabowska, B.; Grabowski, G.; Olejnik, E.; Kaczmarska, K. Studies of the Thermal Degradation of the BioCo3 Polymer Binder. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2013, 11, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Major-Gabryś, K.; Dobosz, S.M.; Jakubski, J. Thermal deformation of moulding sands with biopolymer binders. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2010, 10, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Faber, J.; Perszewska, K.; Żmudzińska, M. Aromatic compounds in waste gases formed during thermal decomposition of foundry binders. Trans. Foundry Res. Inst. 2015, 55, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Major-Gabryś, K.; Hosadyna-Kondracka, K.; Grabarczyk, A.; Kamińska, J. Selection of hardening technology of moulding sand with hydrated sodium silicate binder devoted to aluminum alloys ablation casting. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2019, 64, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, J.; Tipton, A. Synthetic biodegradable polymers as medical devices. Med. Plast. Biomater. 1998, 3, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J. Protein—Based binder update: Performance put to the Test. Mod. Cast. 2000, 10, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, E.J.; Park, J.K. Study on biodegradability of PCL/SAN blend using composting method. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1996, 52, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G. Green polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, D.M.; Scott, G. Polyolefins with controlled environmental degradability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, A.; Tokiwa, Y. Enzymatic degradation of plastics containing polycaprolactone. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1994, 45, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastmond, G.C. Poly(ε-caprolactone) Blends. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2000, 149, 59–222. [Google Scholar]
- Sposób Otrzymywania Krzemionki Koloidalnej w Roztworze Wodnym. Polish Patent P-116013, 31 May 1978.
- Wojnowski, W.; Przyjemska, K.; Konieczny, S.; Karwiński, A.; Stachańczyk, J.; Luśniak, L.; Piech, K. Spoiwo Kopolimerowe Sikop. Polish Patent PAT.135579, 30 November 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Piłkowski, Z.; Nadolski, M. Niektóre Problemy Wytrzymałości Cienkościennych Form Odlewniczych. Arch. Foundry 2004, 4, 413–419. [Google Scholar]
- Doles, R.S. Method of Increasing the Strength and Solids Level of Investment Casting Shells. U.S. Patent 6540013, 1 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra, M. Fast Processing Water Based Binder System. U.S. Patent 5629369, 13 May 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Jin, S.; Lai, X.; Wang, F.; Li, F. Permafrost Analysis Methodology (Pam) For Ceramic Shell Deformation in the Firing Process. Int. J. Metalcast. 2019, 13, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwiński, A.; Haratym, R.; Biernacki, R. Accuracy of Ceramic Mould Filling with Liquid AlSi9 Aluminium Alloy in the Process Using Back-pressure. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2013, 13, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwiński, A.; Adamczyk, Z.; Stachańczyk, J. Spoiwo Krzemianowe Nieorganiczne w Wodnym Roztworze EKOSIL. Polish Patent Pat.182949, 2 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Parashar, G.; Srivastava, D.; Kumar, P. Review: Ethyl silicate binders for high performance coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2001, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospennikova, O.G.; Pikulina, L.V.; Antipin, L.M. Application of a Hydrolyzed Ethyl Silicate in Investment Casting. Inorg. Mater. 2010, 46, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, M.R.; Anjos, R.D.D.; Salomao, R.; Pandolfelli, V.C. Colloidal silica as a nostructured binder for refractory castables. Refract. Appl. News 2006, 11, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski, P. Evaluating Silicon Carbide-Based Slurries and Molds for the Manufacture of Aircraft Turbine Components by the Investment Casting. Crystals 2020, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechstedt, F.; Kackell, P.; Zywietz, A.; Karch, K.; Adolph, B.; Tenelsen, K.; Furthmuller, J. Polytypism and Properties of Silicon Carbide. Phys. Stat. Sol. B 1997, 202, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Miyano, K.; Sameshima, S.; Kamino, Y. Reaction between SiC surface and aqueous solutions containing Al Ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 133, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenc, J.; Matysiak, H.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Organic Viscosity Modifiers for Controlling Rheology of Ceramic Slurries Used in the Investment Casting. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małek, M.; Wiśniewski, P.; Matysiak, H.; Zagórska, M.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Technological properties of SiC-based ceramic slurries for manufacturing investment casting shell moulds. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2014, 59, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małek, M.; Wiśniewski, P.; Szymańska, J.; Mizera, J.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Technological Properties of Ceramic Slurries Based on Silicon Carbide with Poly (vinyl alcohol) Addition for Shell Moulds Fabrication in Precision Casting Process. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2016, 129, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysiak, H.; Wiśniewski, P.; Ferenc-Dominik, J.; Michalski, J.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Badania właściwości reologicznych ceramicznych mas lejnych do odlewania precyzyjnego części turbin lotniczych. Szkło Ceram. 2011, 62, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Książek, M.; Tchórz, A.; Krzak, I.; Żaba, K.; Kurdziel, P.; Dydak, A.; Sitek, R.; Mizera, J. An investigation on microstructural and mechanical properties of ceramic moulds applied in the investment casting of critical parts of aircraft engines. In Proceedings of the 73rd World Foundry Congress, Kraków, Poland, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 107–108. [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki, J. Badanie Właściwości Mas Lejnych Oraz Form Ceramicznych na Bazie SiC. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Materials Science and Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Budzik, G.; Ferenc, J.; Jakubowicz, G.; Kurzydłowski, K.J.; Lipiński, Z.; Matysiak, H.; Michalski, J.; Wawulska, P.; Zych, J. Formy ceramiczne do odlewania precyzyjnego techniką wytapianych modeli. unpublished.
- Malesa, M. Nanonapełniacze kompozytów polierowych Nanonapełniacze kompozytów polimerowych. Część II. Krzemionka, Elastomery 2006, 10, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bergna, H.E.; Roberts, W.O. Colloidal Silica Fundamentals and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Volume 131. [Google Scholar]
- Beeley, P.R.; Smart, R.F. Investment Casting; The University Press Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Matysiak, H.; Ferenc, J.; Lipinski, Z.; Grabarz, K.; Michalski, J.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Charakterystyka i kontrola właściwości technologicznych mieszanek ceramicznych do wytworzenia form odlewniczych do odlewania precyzyjnego części turbin lotniczych metodą Bridgmana. Inż. Mater. 2009, 30, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmulski, M. Surface charge and zeta potential of silica In mixtures of organic solvents and water. Surf. Sci. Ser. 2000, 90, 343–367. [Google Scholar]
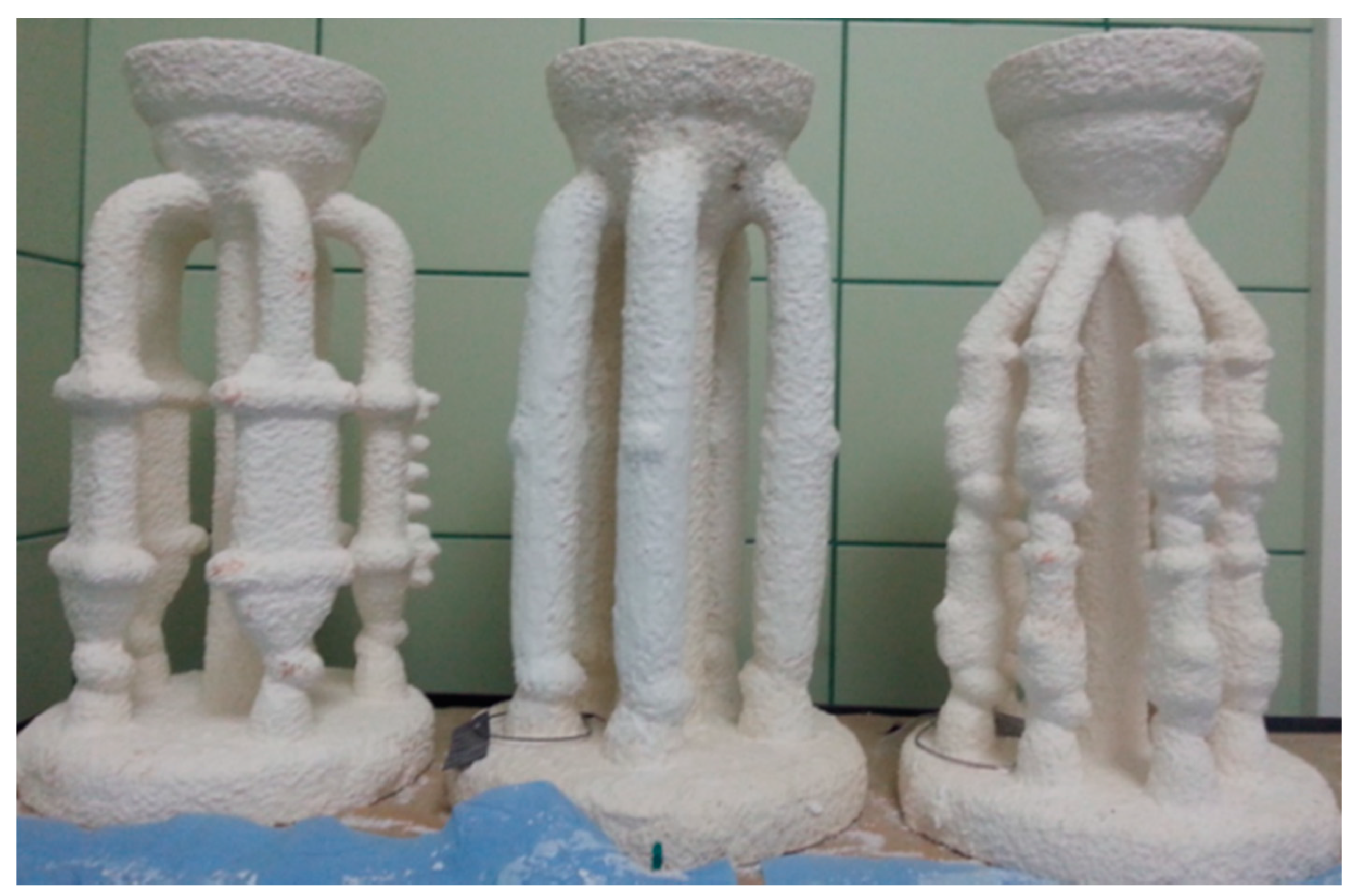
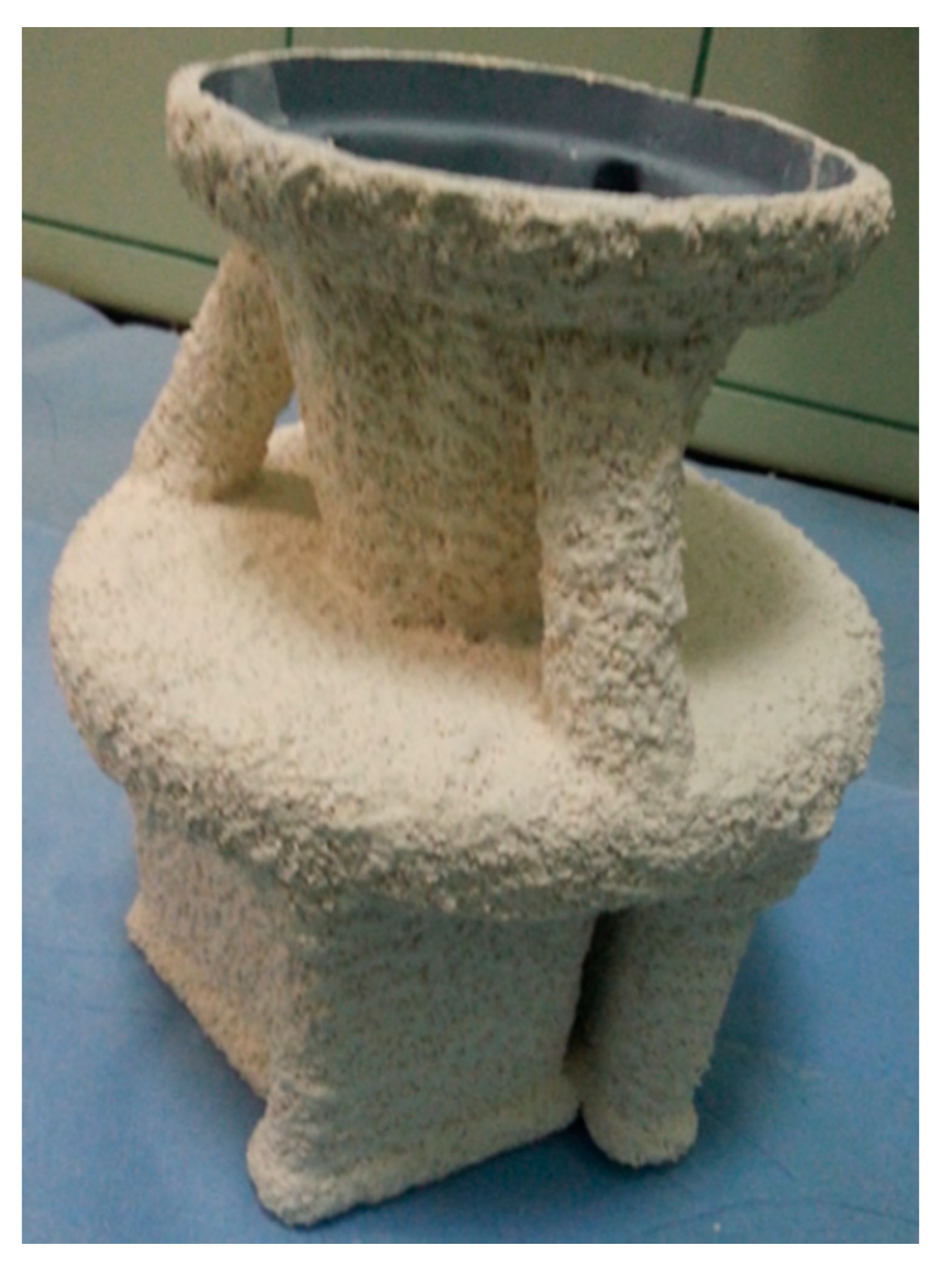






| Binder | Solid-Phase Content [%] | Density [g/cm3] | pH | Time out of Zahn’s Cup #4 [s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imerys W440 | 44.00 | 1.28 | 7.67 | 6.8 |
| Zeta Potential ξ [mV] | Suspension Properties |
|---|---|
| approx. 0–5 | Fast coagulation |
| approx. 5–10 | Slow coagulation |
| approx. 10–30 | Instability |
| approx. 30–40 | Variable stability |
| approx. 40–60 | Good stability |
| >60 | Very good stability |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiśniewski, P. Polymer Binders of Ceramic Nanoparticles for Precision Casting of Nickel-Based Superalloys. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071714
Wiśniewski P. Polymer Binders of Ceramic Nanoparticles for Precision Casting of Nickel-Based Superalloys. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(7):1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071714
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiśniewski, Paweł. 2021. "Polymer Binders of Ceramic Nanoparticles for Precision Casting of Nickel-Based Superalloys" Nanomaterials 11, no. 7: 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071714
APA StyleWiśniewski, P. (2021). Polymer Binders of Ceramic Nanoparticles for Precision Casting of Nickel-Based Superalloys. Nanomaterials, 11(7), 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071714






