Silver Nanoparticles Stable to Oxidation and Silver Ion Release Show Size-Dependent Toxicity In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Hybrid Lipid Shielded Silver Nanoparticles (Ag–SOA–PC–1HT)
2.3. UV–Visible Spectroscopy (UV–Vis) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.4. Inductively Coupled Plasma—Mass Spectroscopy (ICP-MS)
2.5. Stability Studies of Hybrid Lipid-Coated AgNPs in the Presence of CN and FW Media
2.6. Zebrafish Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Zebrafish Ag Uptake Quantification
2.9. Sample Digestion
2.10. Sample Dilutions
3. Results and Discussion
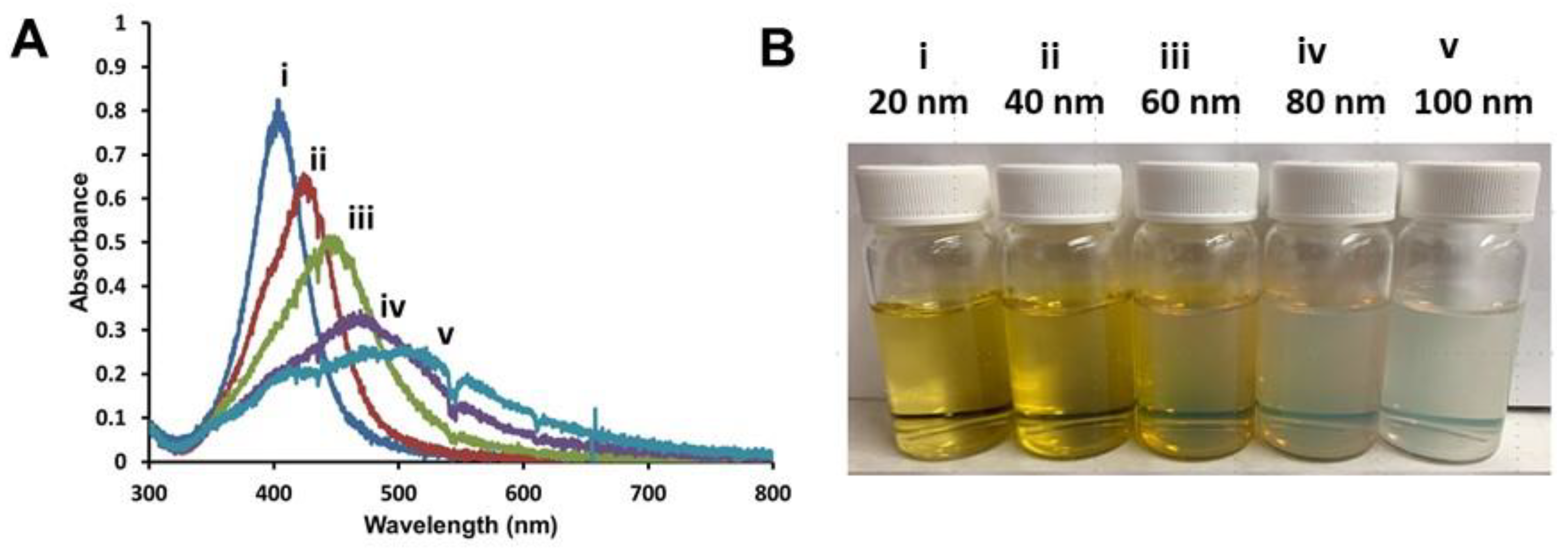
3.1. Preparation of Hybrid Lipid-Coated AgNPs of Varying Sizes
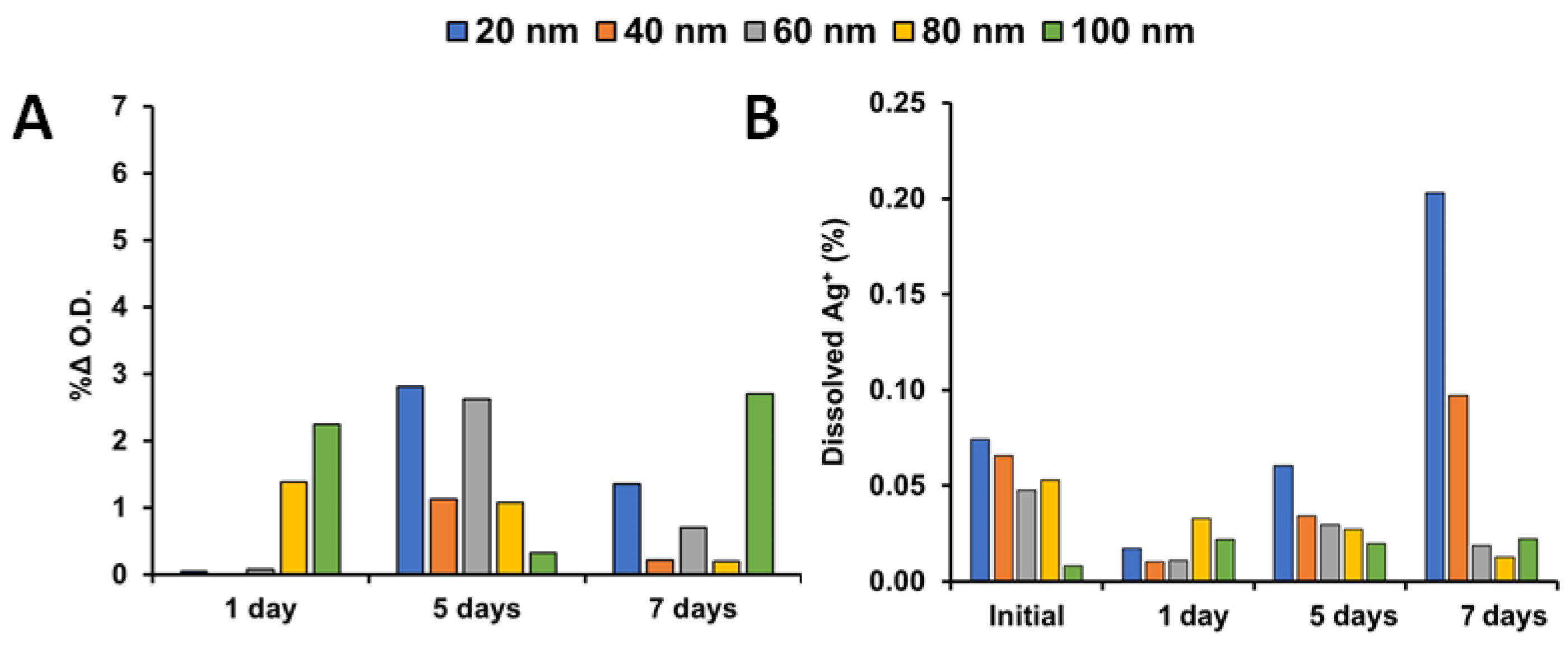
3.2. Stability Studies of Shielded AgNPs
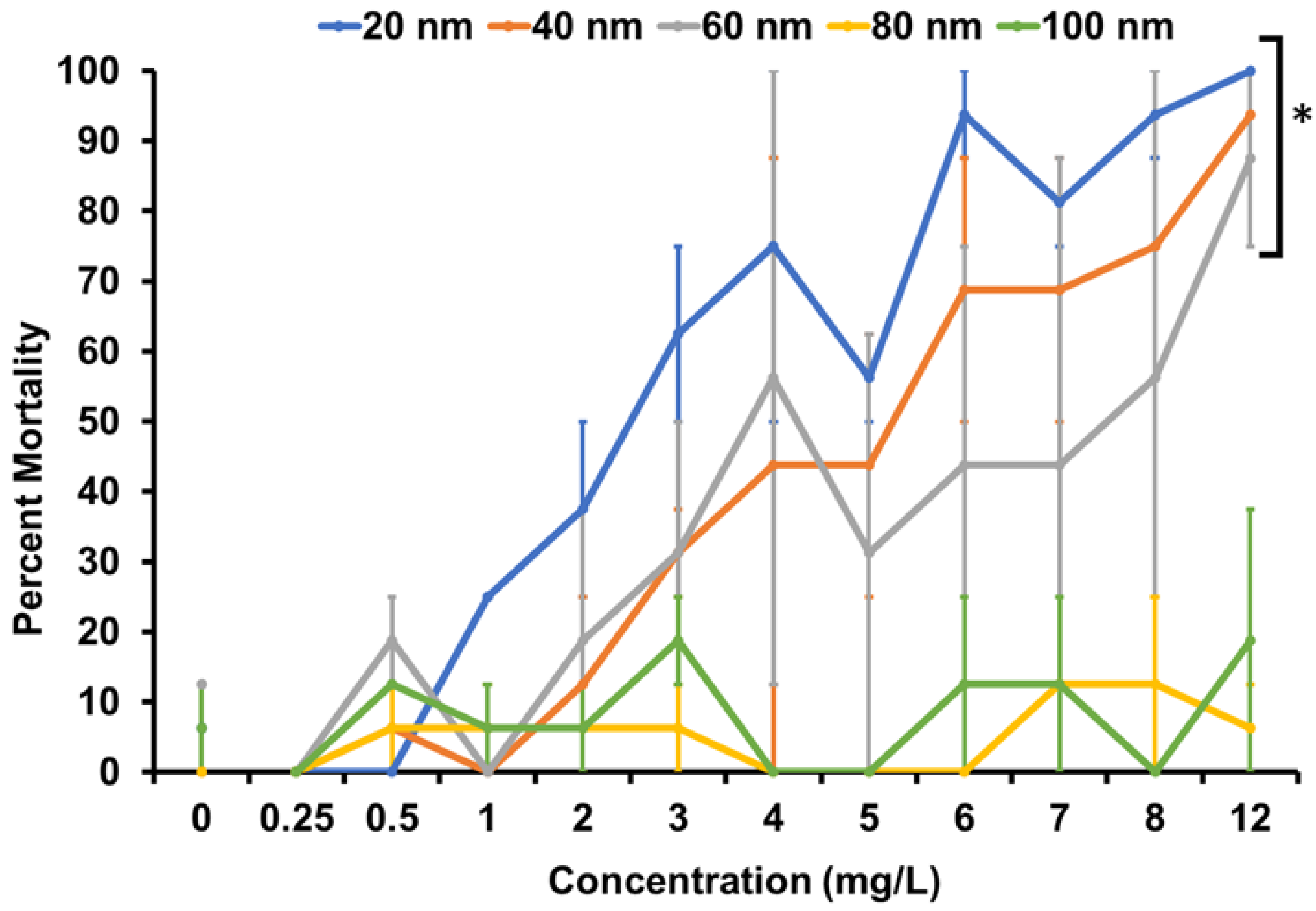
3.3. Toxicity Testing
3.4. Quantifying Ag Uptake in Zebrafish
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Y.; Li, H.; Fei, X.; Peng, L. Carboxymethyl cellulose/cellulose nanocrystals immobilized silver nanoparticles as an effective coating to improve barrier and antibacterial properties of paper for food packaging applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istiqola, A.; Syafiuddin, A. A review of silver nanoparticles in food packaging technologies: Regulation, methods, properties, migration, and future challenges. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 1942–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsalya, E.; MosaChristas, K.; Balashanmugam, P.; Manivasagan, V.; Devasena, T.; Jaquline, C.R.I. Sustainable use of biowaste for synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its incorporation into gelatin-based nanocomposite films for antimicrobial food packaging applications. J. Food Process. Eng. 2021, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.G.; Torres, J.G.T.; Vidal, H.P.; Rocha, M.A.L.; Pérez, J.C.A.; López, I.C.; Romero, D.D.L.C.; Reyna, A.E.; Sosa, J.G.P.; Pavón, A.A.S.; et al. Application of silver nanoparticles for water treatment. In Silver Nanoparticles—Fabrication, Characterization and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, K.; Dutta, S.D.; Patel, D.K.; Lim, K.-T. Aquananotechnology; Kamel, A., Abd-Elsalam, K.A., Khan, M.Z., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 385–401. [Google Scholar]
- Wasef, L.G.; Shaheen, H.M.; El-Sayed, Y.S.; Shalaby, T.I.; Samak, D.H.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Al-Owaimer, A.; Saadeldin, I.M.; El-Mleeh, A.; Ba-Awadh, H.; et al. Effects of silver nanoparticles on burn wound healing in a mouse model. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 193, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Nthumba, P.M.; Gu, G.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, J. Engineering an adhesive based on photosensitive polymer hydrogels and silver nanoparticles for wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5756–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Aassar, M.R.; Ibrahim, O.M.; Fouda, M.M.G.; El-Beheri, N.G.; Agwa, M.M. Wound healing of nanofiber comprising polygalacturonic/hyaluronic acid embedded silver nanoparticles: In-vitro and in-vivo studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, F.R.; Maia, R.C.A.; Rannier, L.; Andrade, L.N.; Chaud, M.V.; da Silva, C.F.; Corrêa, C.B.; de Albuquerque Junior, R.L.C.; da Costa, L.P.; Shin, S.R.; et al. Silver nanoparticles-composing alginate/gelatine hydrogel improves wound healing in vivo. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sun, R.W.; Chen, R.; Hui, C.K.; Ho, C.M.; Luk, J.M.; Lau, G.K.; Che, C.M. Silver nanoparticles inhibit hepatitis B virus replication. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemzadeh-Narbat, M.; Cheng, H.; Chabok, R.; Alvarez, M.M.; De La Fuente-Nunez, C.; Phillips, K.S.; Khademhosseini, A. Strategies for antimicrobial peptide coatings on medical devices: A review and regulatory science perspective. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 94–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Kim, K.Y.; Kang, J.M.; Ryu, D.S.; Kim, D.H.; Song, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.O.; Park, J.H. metallic stent mesh coated with silver nanoparticles suppresses stent-induced tissue hyperplasia and biliary sludge in the rabbit extrahepatic bile duct. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, A.B. Silver in health care: Antimicrobial effects and safety in use. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lem, K.W.; Choudhury, A.; Lakhani, A.A.; Kuyate, P.; Haw, J.R.; Lee, D.D.; Iqbal, Z.; Brumlik, C.J. Use of nanosilver in consumer products. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 6, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulit-Prociak, J.; Banach, M. Silver nanoparticles–a material of the future…? Open Chem. 2016, 14, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivask, A.; ElBadawy, A.; Kaweeteerawat, C.; Boren, D.; Fischer, H.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Liu, R.; Tolaymat, T.; Telesca, D.; et al. Toxicity mechanisms in Escherichia coli vary for silver nanoparticles and differ from ionic silver. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, B.V.; Ramirez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panáček, A.; Kvitek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolar, M.; Vecerova, R.; Pizurova, N.; Sharma, V.K. Silver colloid nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, C.M.; Mocan, T.; Manolea, M.; Lasca, L.I.; Tăbăran, F.A.; Mocan, L. Review on silver nanoparticles as a novel class of antibacterial solutions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, H.H.; Ayala-Nuñez, N.V.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C. Mode of antiviral action of silver nanoparticles against HIV-1. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; Alves, O.L.; De Souza, G.I.; Esposito, E. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with HIV-1. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2005, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, A.A. A review of affective chemistry education research and its implications for future research. Chem. Educ. Res. Pr. 2020, 21, 698–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, S.; Sarkar, S.; Kharrazi, S.; Amini, S.M.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A.; Ay, M.R.; Ghadiri, H. Evaluation of size, morphology, concentration, and surface effect of gold nanoparticles on X-ray attenuation in computed tomography. Phys. Med. 2018, 45, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullan, B.F.; Madsen, M.T.; Messerle, L.; Kolesnichenko, V.; Kruger, J. X-ray attenuation coefficients of high-atomic-number, hexanuclear transition metal cluster compounds: A new paradigm for radiographic contrast agents. Acad. Radiol. 2000, 7, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, P.C.; Lau, K.C.; Hsu, J.C.; Hajfathalian, M.; Mian, S.; Chhour, P.; Uppuluri, L.; McDonald, E.S.; Maidment, A.D.; Cormode, D.P. Gold silver alloy nanoparticles (GSAN): An imaging probe for breast cancer screening with dual-energy mammography or computed tomography. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 13740–13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambiar, S.; Osei, E.K.; Yeow, J.T.W.; Osei, E.K. Effects of particle size on X-ray transmission characteristics of PDMS/Ag nano-and microcomposites. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 15th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Rome, Italy, 27–30 July 2015; pp. 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, R.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. A tumor-targeting near-infrared laser-triggered drug delivery system based on GO@Ag nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal therapy and X-ray imaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5847–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Hannula, M.; Misra, S.; Feng, H.; Labrador, R.H.; Aula, A.S.; Hyttinen, J.; Pyykkö, I. Micro CT visualization of silver nanoparticles in the middle and inner ear of rat and transportation pathway after transtympanic injection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Park, J.H.; Han, J.W.; Kim, J.H. Comparative assessment of the apoptotic potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Bacillus tequilensis and Calocybe indica in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells: Targeting p53 for anticancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4203–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.R.; Shaheen, F.; Rafique, R.; Bal, J.; Waseem, S.; Park, T.J. Grass-mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their drug delivery evaluation: A biocompatible anti-cancer therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shan, K.; Shao, X.; Shi, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jacob, J.A.; Deng, L. Nanotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles on normal HEK-293 cells in comparison to cancerous HeLa cell line. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W. Targeted silver nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy via macrophage apoptosis and Re-polarization. Biomaterials 2021, 264, 120390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Das, A.; Hu, Z. Bacterial response to a shock load of nanosilver in an activated sludge treatment system. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5432–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Park, C.-S.; Murayama, M.; Hochella, M.F., Jr. Discovery and characterization of silver sulfide nanoparticles in final sewage sludge products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7509–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reidy, B.; Haase, A.; Luch, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Lynch, I. Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle release, transformation and toxicity: A critical review of current knowledge and recommendations for future studies and applications. Materials 2013, 36, 2295–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luoma, S.N.; Ho, Y.; Bryan, G. Fate, bioavailability and toxicity of silver in estuarine environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratte, H.T. Bioaccumulation and toxicity of silver compounds: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.K.; Jin, T.; Behari, J. Dose-dependent in-vivo toxicity assessment of silver nanoparticle in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.V.; Neigh, A.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; de la Fonteyne, L.J.; Verharen, H.W.; Briedé, J.J.; van Loveren, H.; de Jong, W.H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9810–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Hess, K.; Gearhart, J.; Geiss, K.; Schlager, J. In vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2005, 19, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braydich-Stolle, L.; Hussain, S.; Schlager, J.J.; Hofmann, M.-C. In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 88, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorka, D.E.; Osterberg, J.S.; Gwin, C.A.; Colman, B.P.; Meyer, J.N.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Gunsch, C.K.; DiGulio, R.T.; Liu, J. Reducing environmental toxicity of silver nanoparticles through shape control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10093–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kroger, M.; Liu, W.K. Shape effect in cellular uptake of PEGylated nanoparticles: Comparison between sphere, rod, cube and disk. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16631–16646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tree-Udom, T.; Seemork, J.; Shigyou, K.; Hamada, T.; Sangphech, N.; Palaga, T.; Insin, N.; Pan-In, P.; Wanichwecharungruang, S. Shape effect on particle-lipid bilayer membrane association, cellular uptake, and cytotoxicity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23993–24000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Lin, S.; Ji, Z.; Thomas, C.R.; Li, L.; Mecklenburg, M.; Meng, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xia, T.; et al. Surface defects on plate-shaped silver nanoparticles contribute to its hazard potential in a fish gill cell line and zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3745–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramenko, N.B.; Demidova, T.B.; Abkhalimov, E.V.; Ershov, B.G.; Krysanov, E.Y.; Kustov, L.M. Ecotoxicity of different-shaped silver nanoparticles: Case of zebrafish embryos. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 347, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.; Kwak, J.I.; An, Y.-J. The effects of silver nanomaterial shape and size on toxicity to Caenorhabditis elegans in soil media. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Truong, L.; Wehmas, L.; Tanguay, R.L. Silver nanoparticle toxicity in the embryonic zebrafish is governed by particle dispersion and ionic environment. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 957–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Ilan, O.; Albrecht, R.M.; Fako, V.E.; Furgeson, D.Y. Toxicity assessments of multisized gold and silver nanoparticles in zebrafish embryos. Small 2009, 5, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, N.; Wang, X. Toxicity responses of different organs of zebrafish (Danio rerio) to silver nanoparticles with different particle sizes and surface coatings. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Rotchell, J.M.; Cheng, J.; Yi, J.; Zhang, Q. Silver nanoparticles affect the neural development of zebrafish embryos. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.M.; Mizuta, Y.; Akagi, J.I.; Toyoda, T.; Sone, M.; Ogawa, K. Size-dependent acute toxicity of silver nanoparticles in mice. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018, 31, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Browning, L.M.; Nallathamby, P.D.; Desai, T.; Cherukuri, P.K.; Xu, X.H.N. In vivo quantitative study of sized-dependent transport and toxicity of single silver nanoparticles using zebrafish embryos. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Gondikas, A.P.; Marinakos, S.M.; Auffan, M.; Liu, J.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Meyer, J.N. Mechanism of silver nanoparticle toxicity is dependent on dissolved silver and surface coating in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A Study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, C.M.; Slotkin, T.A.; Seidler, F.J.; Badireddy, A.R.; Padilla, S. Silver nanoparticles alter zebrafish development and larval behavior: Distinct roles for particle size, coating and composition. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aerle, R.; Lange, A.; Moorhouse, A.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Ball, K.; Johnston, B.D.; de-Bastos, E.; Booth, T.; Tyler, C.R.; Santos, E.M. Molecular mechanisms of toxicity of silver nanoparticles in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8005–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laban, G.; Nies, L.F.; Turco, R.F.; Bickham, J.W.; Sepúlveda, M.S. The effects of silver nanoparticles on fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) embryos. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.C.; Naha, P.C.; Lau, K.C.; Chhour, P.; Hastings, R.; Moon, B.F.; Stein, J.M.; Witschey, W.R.; McDonald, E.S.; Maidment, A.D.; et al. An all-in-one nanoparticle (AION) contrast agent for breast cancer screening with DEM-CT-MRI-NIRF imaging. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 17236–17248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, A.P.; Bea, D.B.; Civit, S.; Contera, S.A.; Cerveto, A.I.; Trigueros, S. Three strategies to stabilise nearly monodispersed silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Leng, W.; Vikesland, P.J. Controlled evaluation of the impacts of surface coatings on silver nanoparticle dissolution rates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanedrin, R.G.; Huang, L.; Jang, J.W.; Kakkassery, J.; Mirkin, C.A. Polyethylene glycol as a novel resist and sacrificial material for generating positive and negative nanostructures. Small 2008, 4, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y. The role of poly(ethylene glycol) in the formation of silver nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 288, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkilnyy, A.; Soucé, M.; Dubois, P.; Warmont, F.; Saboungi, M.L.; Chourpa, I. Poly(ethylene glycol)-stabilized silver nanoparticles for bioanalytical applications of SERS spectroscopy. Analyst 2009, 134, 1868–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Guadagnini, A.; Agnoli, S.; Badocco, D.; Pastore, P.; Fracasso, G.; Gerosa, M.; Vurro, F.; Busato, A.; Marzola, P. Polymer-coated silver-iron nanoparticles as efficient and biodegradable MRI contrast agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 596, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J.A.; Pryor, J.B.; Harper, B.J.; Harper, S.L. The impact of aminated surface ligands and silica shells on the stability, uptake, and toxicity of engineered silver nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunamuni, R.; Naha, P.C.; Lau, K.C.; Al-Zaki, A.; Popov, A.V.; Delikatny, E.J.; Tsourkas, A.; Cormode, D.P.; Maidment, A.D. Development of silica-encapsulated silver nanoparticles as contrast agents intended for dual-energy mammography. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3301–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miesen, T.J.; Engstrom, A.M.; Frost, D.C.; Ajjarapu, R.; Ajjarapu, R.; Lira, C.N.; Mackiewicz, M.R. A hybrid lipid membrane coating “shape-locks” silver nanoparticles to prevent surface oxidation and silver ion dissolution. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15677–15693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, A.M.; Wu, H.; Mackiewicz, M.R.; Harper, S.L. Controlling silver ion release of silver nanoparticles with hybrid lipid membranes with long-chain hydrophobic thiol anchors decreases in vivo toxicity. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2020, 10, 12–28. [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom, A.M.; Faase, R.A.; Marquart, G.W.; Baio, J.E.; Mackiewicz, M.R.; Harper, S.L. Size-dependent interactions of lipid-coated gold nanoparticles: Developing a better mechanistic understanding through model cell membranes and in vivo toxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4091–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.J.; Teraoka, H.; Heideman, W.; Peterson, R.E. Zebrafish as a model vertebrate for investigating chemical toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropepe, V.; Sive, H.L. Can zebrafish be used as a model to study the neurodevelopmental causes of autism? Genes Brain Behav. 2003, 2, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zon, L.I.; Peterson, R.T. In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asharani, P.; Wu, Y.L.; Gong, Z.; Valiyaveettil, S. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in zebrafish models. Nanotechnology 2008, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, V.; Capelle, M.; Fent, K. Silver nanoparticles induce endoplasmatic reticulum stress response in zebrafish. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 272, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, B.; Thomas, D.; Chikkagoudar, S.; Baker, N.; Tang, K.; Heredia-Langner, A.; Lins, R.; Harper, S. Comparative hazard analysis and toxicological modeling of diverse nanomaterials using the embryonic zebrafish (EZ) metric of toxicity. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, S.; Usenko, C.; Hutchison, J.; Maddux, B.; Tanguay, R. In vivo biodistribution and toxicity depends on nanomaterial composition, size, surface functionalisation and route of exposure. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2008, 3, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, S.L.; Carriere, J.L.; Miller, J.M.; Hutchison, J.E.; Maddux, B.L.; Tanguay, R.L. Systematic evaluation of nanomaterial toxicity: Utility of standardized materials and rapid assays. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4688–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, S.L.; Dahl, J.A.; Maddux, B.L.; Tanguay, R.L.; Hutchison, J.E. Proactively designing nanomaterials to enhance performance and minimise hazard. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2008, 5, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Ear, J.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Low-Kam, C.; Yamada, K.; Meng, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Zebrafish high-throughput screening to study the impact of dissolvable metal oxide nanoparticles on the hatching enzyme, ZHE1. Small 2013, 9, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Nel, A.E.; Lin, S. Zebrafish: An in vivo model for nano EHS studies. Small 2013, 9, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Nallathamby, P.D.; Browning, L.M.; Osgood, C.J.; Xu, X.-H.N. In vivo imaging of transport and biocompatibility of single silver nanoparticles in early development of zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajizadeh, S.; Farhadi, K.; Forough, M.; Sabzi, R.E. Silver nanoparticles as a cyanide colorimetric sensor in aqueous media. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz, M.R.; Hodges, H.L.; Reed, S.M. C-reactive protein induced rearrangement of phosphatidylcholine on nanoparticle mimics of lipoprotein particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 5556–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaula, S.; Mackiewicz, M.R.; Reed, S.M. Gold nanoparticles become stable to cyanide etch when coated with hybrid lipid bilayers. Chem. Commun. 2008, 26, 3013–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringe, E.; Zhang, J.; Mark, R.L.; Sohn, K.; Cobley, C.; Au, L.; Xia, Y.; Chad, A.M.; Huang, J.; Laurence, D.M.; et al. Effect of size, shape, composition, and support film on localized surface plasmon resonance frequency: A single particle approach applied to silver bipyramids and gold and silver nanocubes. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2009, 1208, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Xu, X.-H.N. Synthesis and characterization of tunable rainbow colored colloidal silver nanoparticles using single-nanoparticle plasmonic microscopy and spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9867–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.S.; Messersmith, R.E.; Reed, S.M. Membrane curvature recognition by C-reactive protein using lipoprotein mimics. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7909–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orendorff, C.J.; Murphy, C.J. Quantitation of metal content in the silver-assisted growth of gold nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3990–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molleman, B.; Hiemstra, T. Time, pH, and size dependency of silver nanoparticle dissolution: The road to equilibrium. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lowest Observable Adverse Effect Level (mg/L) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 hpf | 120 hpf | |||||||||||||||
| AgNP Size | DP | SM | YSE | Axis | Eye | Snout | Jaw | Otic | PE | Brain | Somite | Pectoral Fin | Caudal Fin | Circulation | Trunk | TR |
| 20 nm | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | - |
| 40 nm | - | 8 | 7 | - | 6 | 6 | 7 | - | 7 | - | - | 7 | 7 | - | - | 7 |
| 60 nm | - | 12 | 12 | - | 8 | 8 | 8 | - | 7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 80 nm | - | - | 8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 100 nm | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sample | Ag | LOAEL |
|---|---|---|
| Fishwater | 0.18 ng per ml | NA |
| Control Fish | 0.078 ng per fish | NA |
| 20 nm AgNP | 1.478 ng per fish | 3 mg/L |
| 40 nm AgNP | 1.972 ng per fish | 3 mg/L |
| 60 nm AgNP | 0.62 ng per fish | 4 mg/L |
| 80 nm AgNP | 1.244 ng per fish | 8 mg/L |
| 100 nm AgNP | 0.356 ng per fish | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cunningham, B.; Engstrom, A.M.; Harper, B.J.; Harper, S.L.; Mackiewicz, M.R. Silver Nanoparticles Stable to Oxidation and Silver Ion Release Show Size-Dependent Toxicity In Vivo. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061516
Cunningham B, Engstrom AM, Harper BJ, Harper SL, Mackiewicz MR. Silver Nanoparticles Stable to Oxidation and Silver Ion Release Show Size-Dependent Toxicity In Vivo. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(6):1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061516
Chicago/Turabian StyleCunningham, Brittany, Arek M. Engstrom, Bryan J. Harper, Stacey L. Harper, and Marilyn R. Mackiewicz. 2021. "Silver Nanoparticles Stable to Oxidation and Silver Ion Release Show Size-Dependent Toxicity In Vivo" Nanomaterials 11, no. 6: 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061516
APA StyleCunningham, B., Engstrom, A. M., Harper, B. J., Harper, S. L., & Mackiewicz, M. R. (2021). Silver Nanoparticles Stable to Oxidation and Silver Ion Release Show Size-Dependent Toxicity In Vivo. Nanomaterials, 11(6), 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061516