Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles Synthesized by In Situ Solid-Phase Method for Removal of Methylene Blue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles
2.3. Experimental Procedure for Decolorization of MB
2.4. Adsorption Kinetic and Interparticle Diffusion Study
2.5. Adsorption Isotherm Study
2.6. Characteristic Methods
3. Results
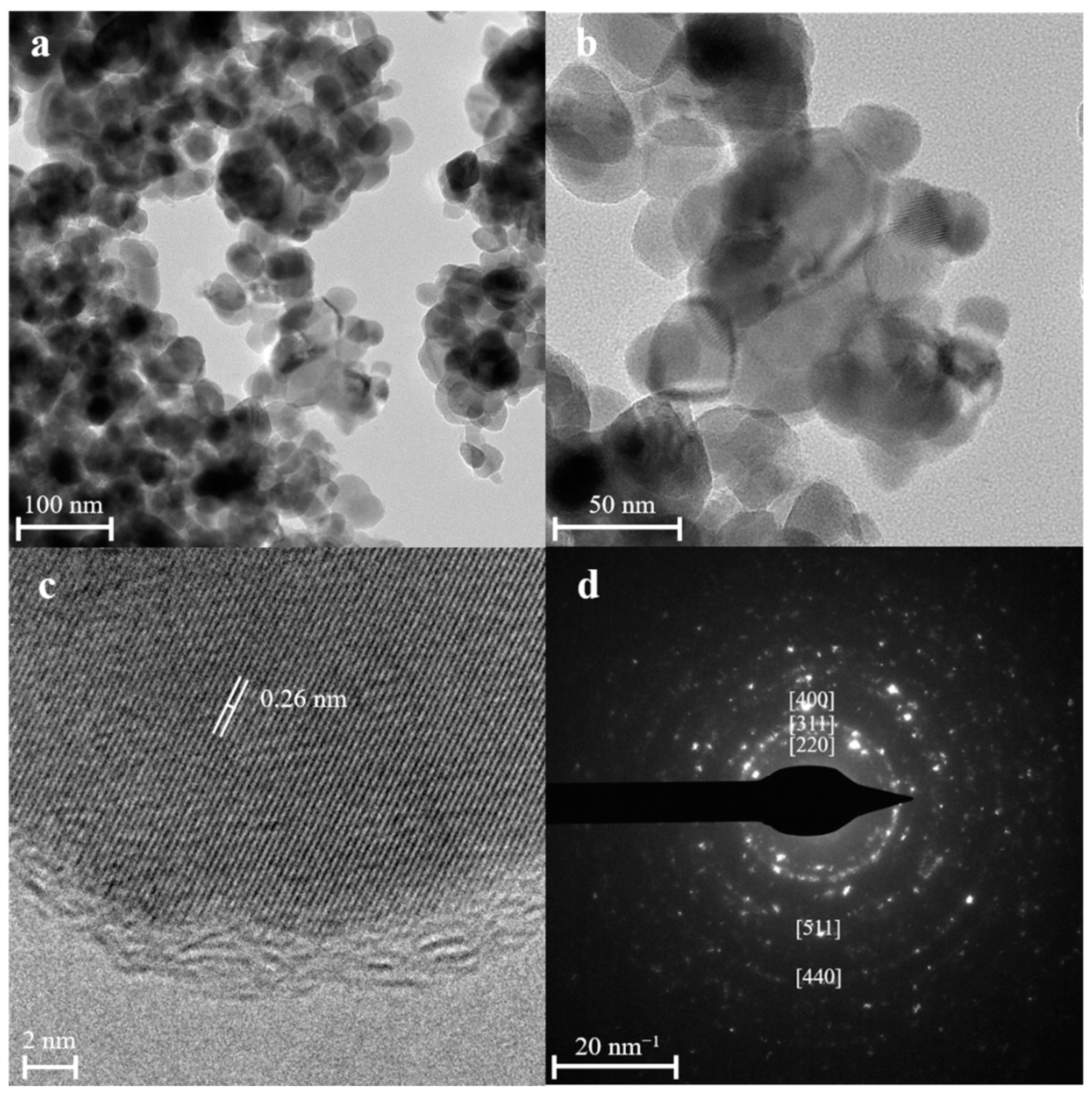
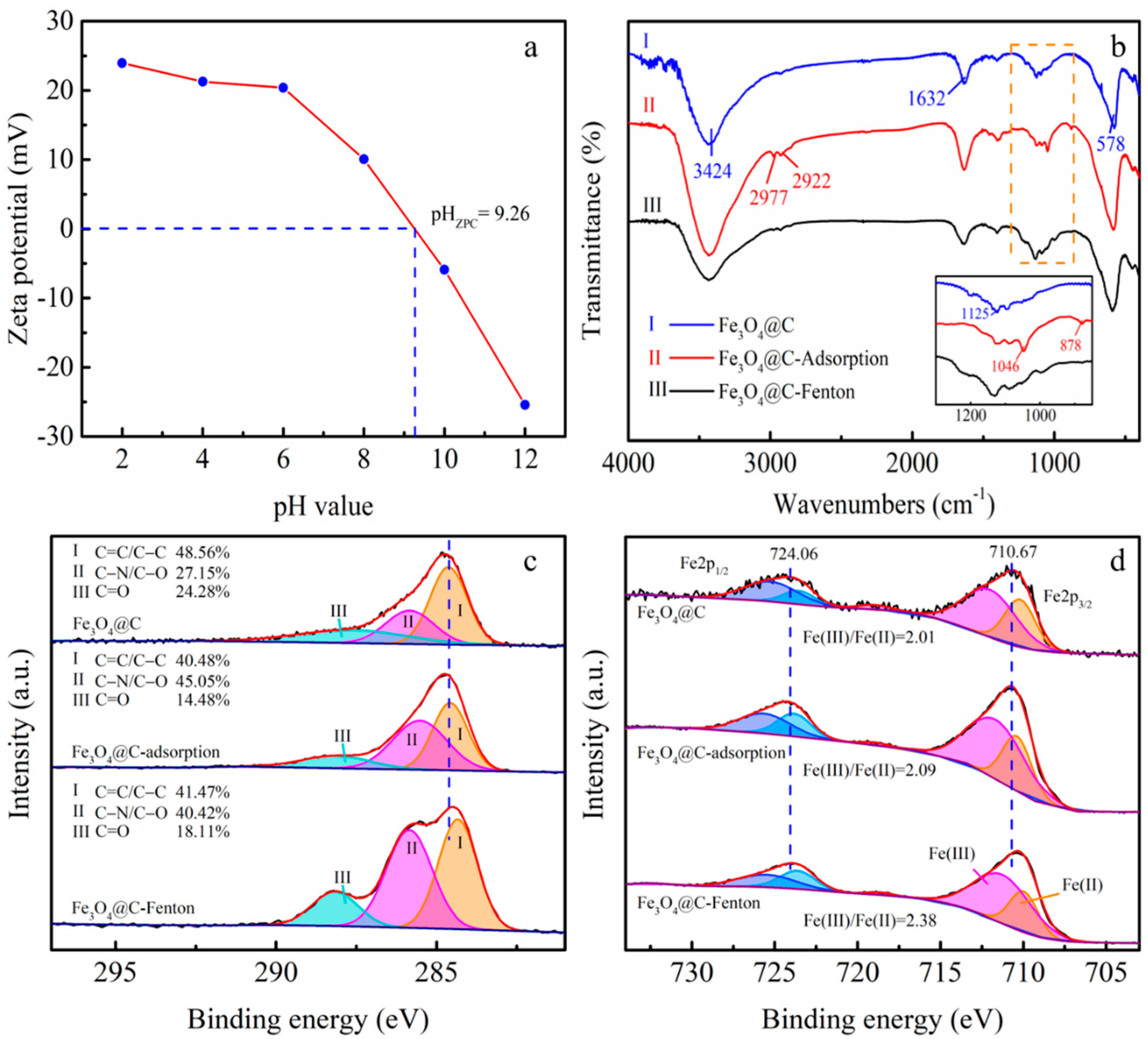
3.1. Characterization of the Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles
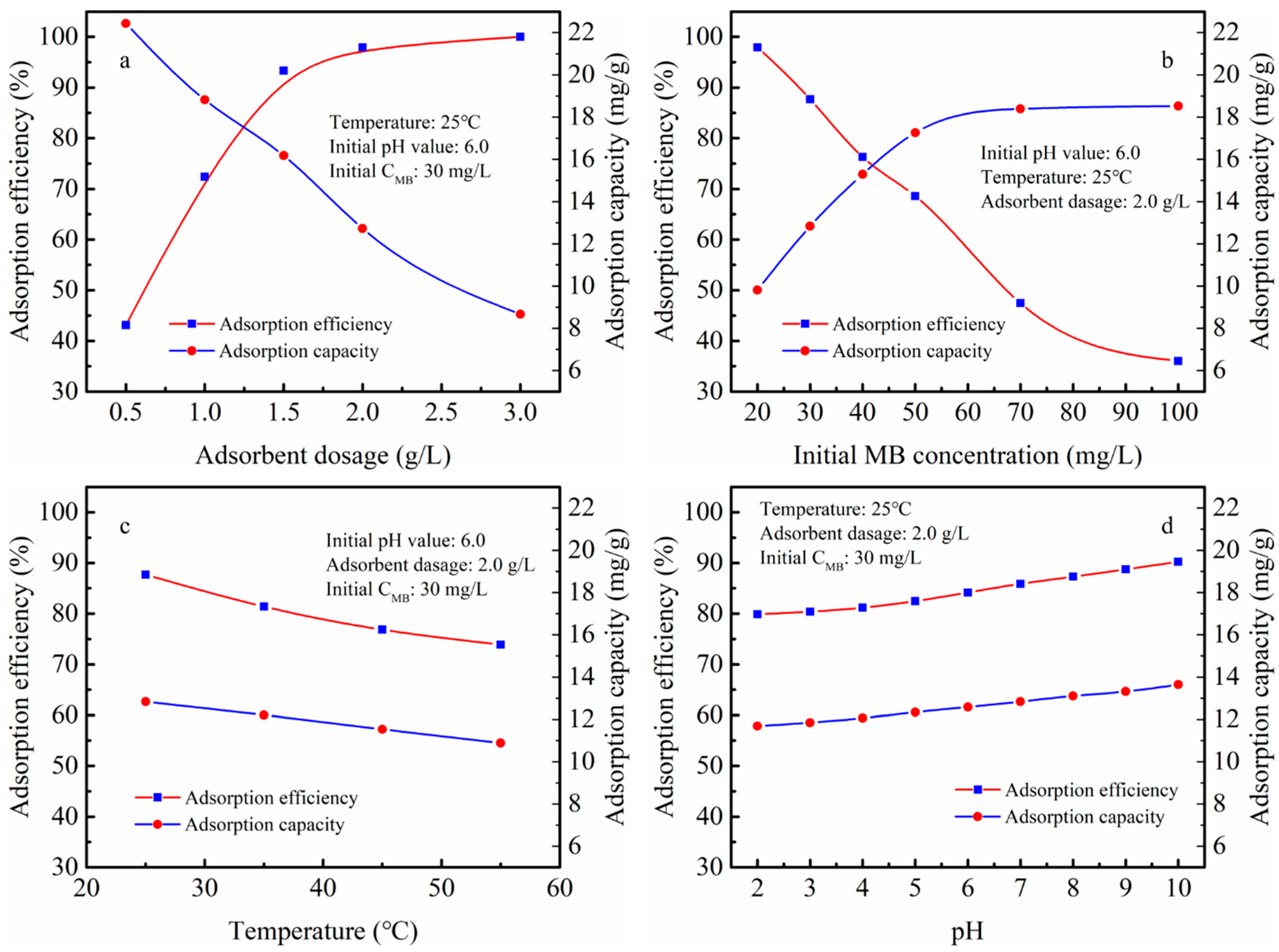
3.2. Adsorption Studies
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics and Interparticle Diffusion Analysis
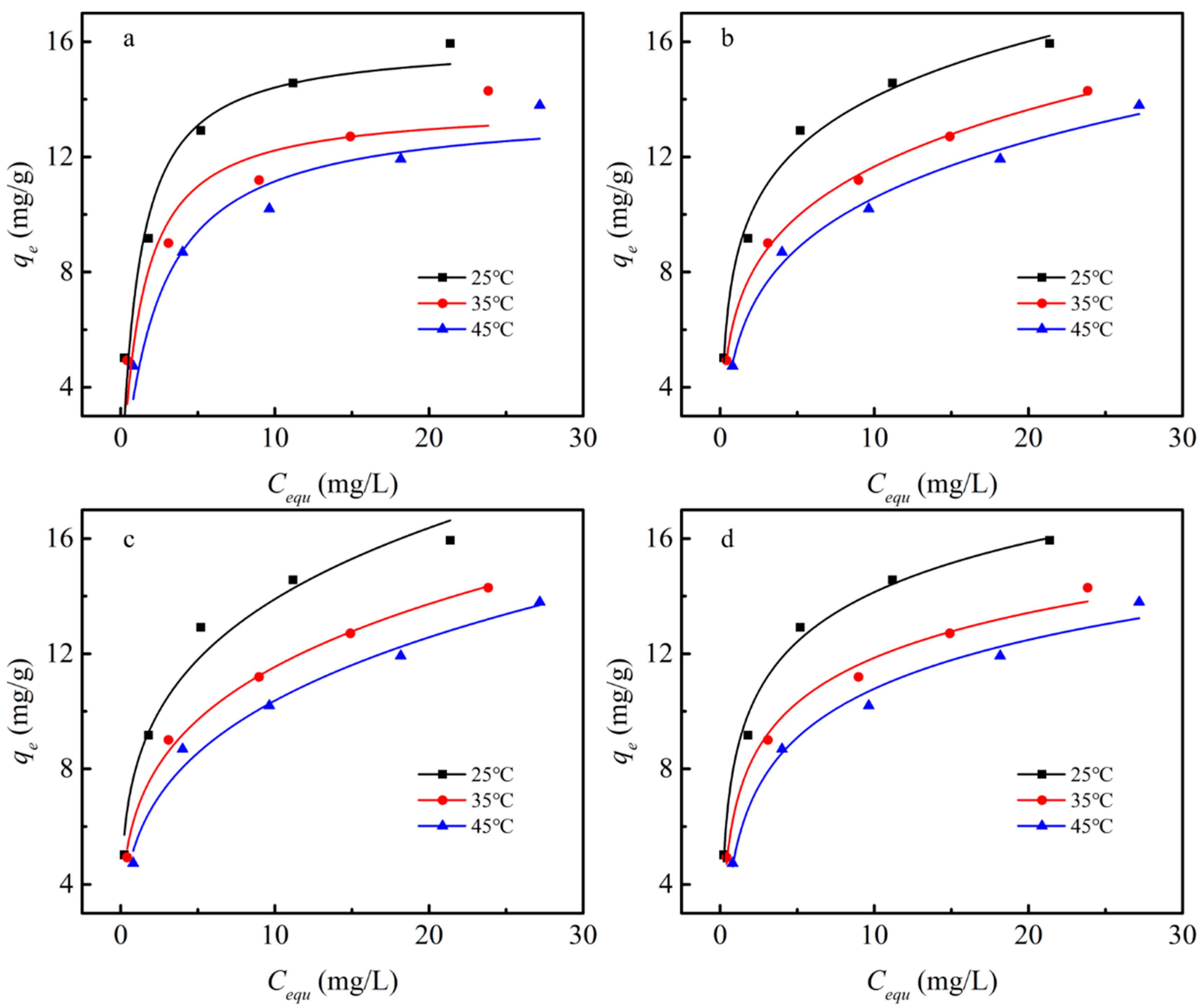
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm Study
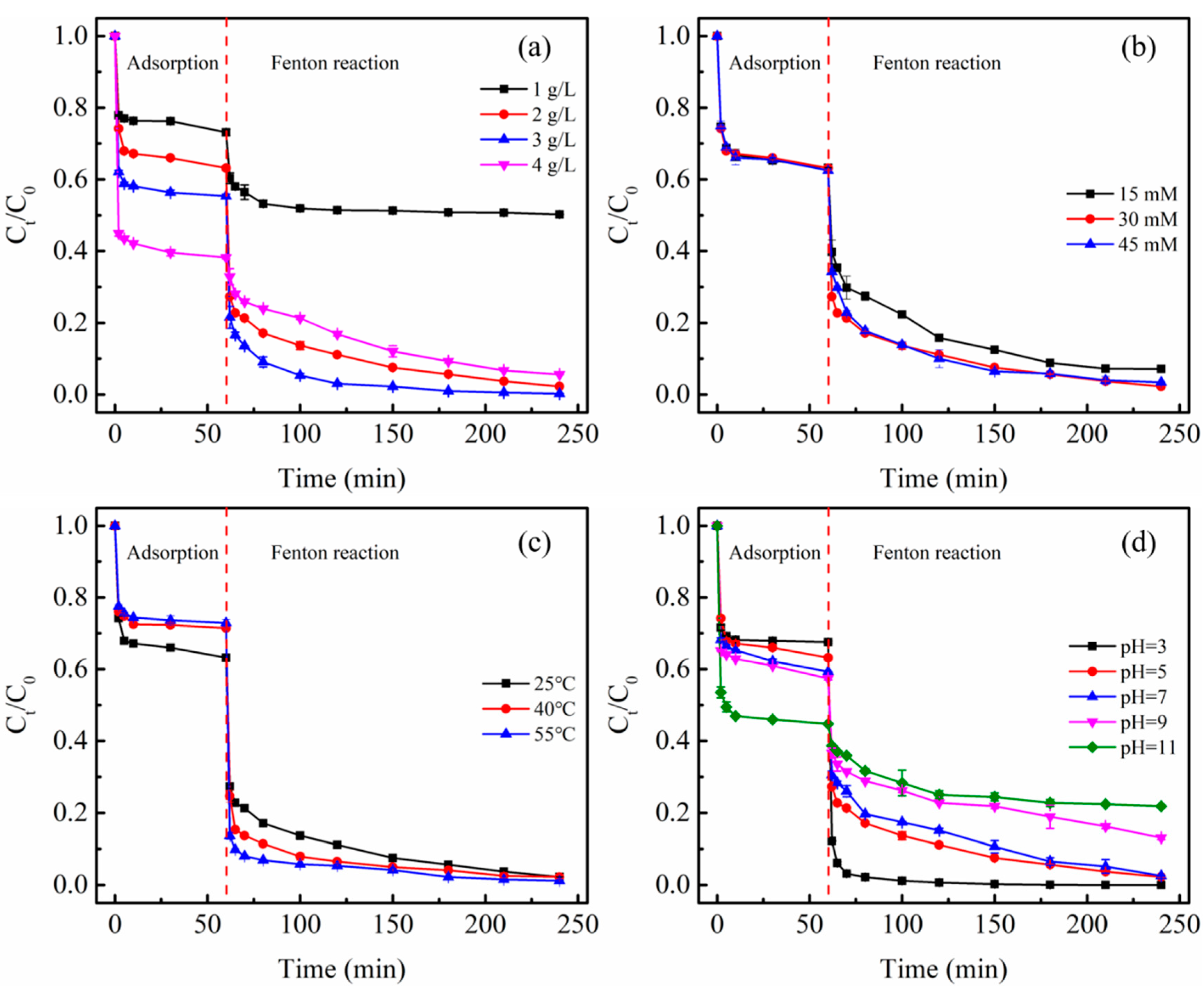
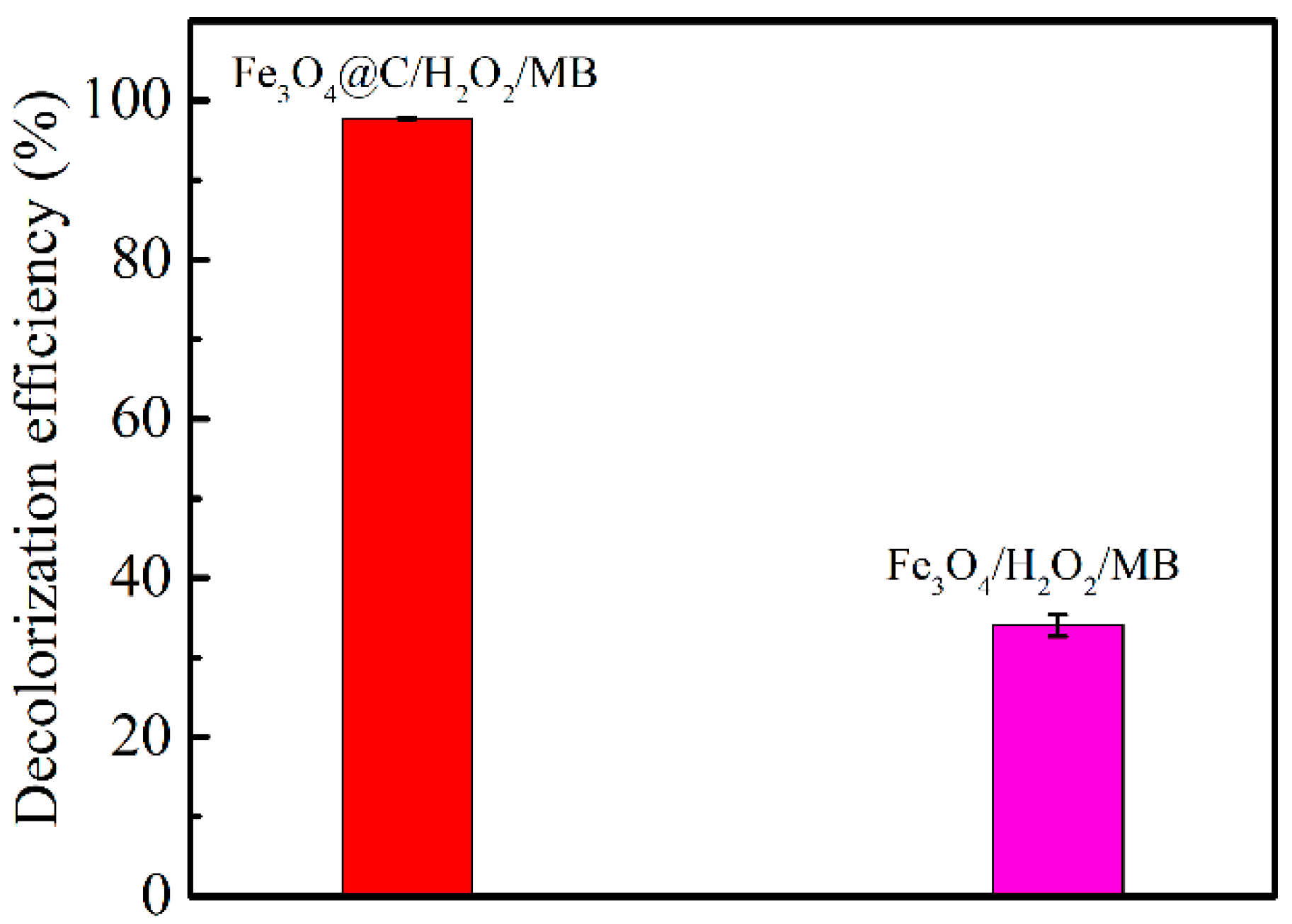
3.5. Fenton-Like Reaction
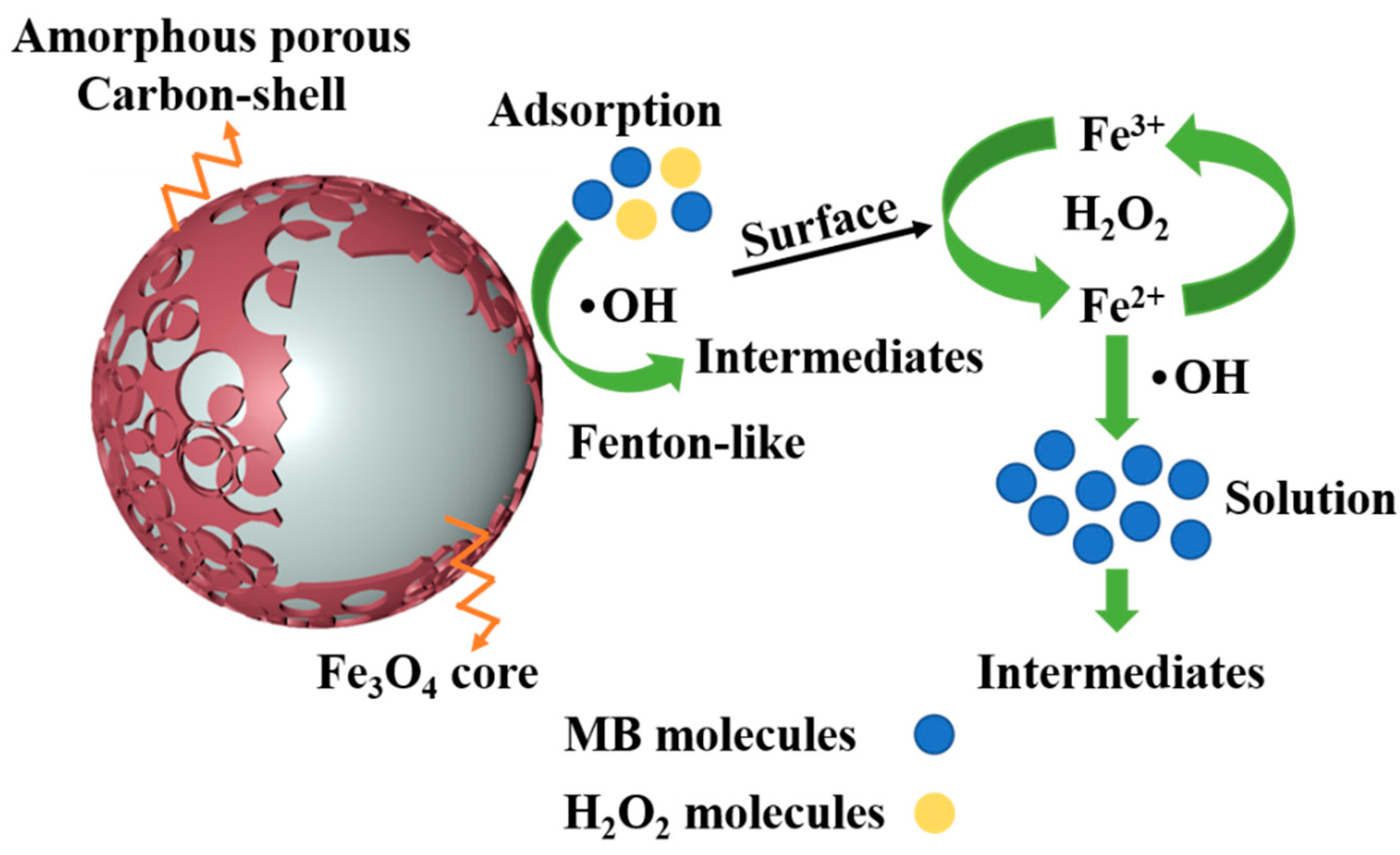
3.6. The Mechanism of the Decolorization of MB
3.7. Possible Degradation Pathways of MB
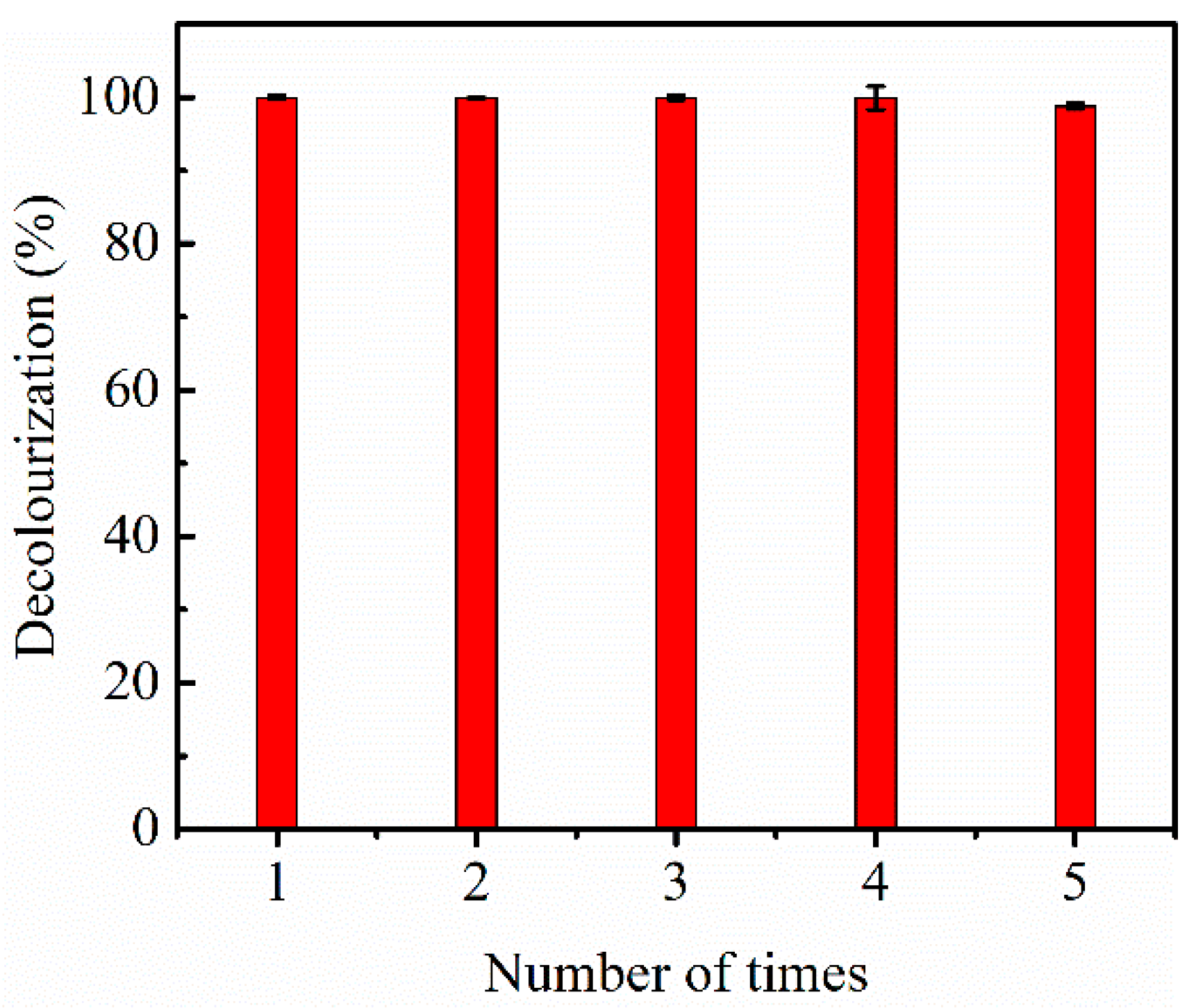
3.8. The Recyclability Tests of the Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qadri, S.; Ganoe, A.; Haik, Y. Removal and recovery of acridine orange from solutions by use of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karri, R.R.; Tanzifi, M.; Tavakkoli Yaraki, M.; Sahu, J.N. Optimization and modeling of methyl orange adsorption onto polyaniline nano-adsorbent through response surface methodology and differential evolution embedded neural network. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, Y.J.; Karri, R.R.; Mubarak, N.M.; Lau, S.Y.; Chua, H.B.; Khalid, M.; Jagadish, P.; Abdullah, E.C. Removal of dye using peroxidase-immobilized Buckypaper/polyvinyl alcohol membrane in a multi-stage filtration column via RSM and ANFIS. Environ. Sci Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 40121–40134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, G.K.; Mubarak, N.M.; Nizamuddin, S.; Al-Salim, H.S.; Sahu, J.N. Column performance of carbon nanotube packed bed for methylene blue and orange red dye removal from waste water. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 206, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Zhang, H.; He, R.; Zhao, M. The Comparative Study on the Rapid Decolorization of Azo, Anthraquinone and Triphenylmethane Dyes by Anaerobic Sludge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Han, T.; Luo, Z.; Liu, C.; Mei, Y.; Zhu, T. One-step fabricated Fe3O4@C core–shell composites for dye removal: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2015, 78, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Luo, X.; He, D.; Ao, M.; Peng, Q. Sulfidation modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an efficient Fenton-like catalyst for azo dyes degradation at wide pH range. Powder Technol. 2020, 376, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, N.M.; Fo, Y.T.; Al-Salim, H.S.; Sahu, J.N.; Abdullah, E.C.; Nizamuddin, S.; Jayakumar, N.S.; Ganesan, P. Removal of Methylene Blue and Orange-G from Waste Water Using Magnetic Biochar. Int. J. Nanosci. 2015, 14, 1550009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G. Controllable Preparation and Catalytic Performance of Heterogeneous Fenton-like α-Fe2O3/Crystalline Glass Microsphere Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 13751–13759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Guang, C.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Gong, S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y. Adsorption behavior of dyes from an aqueous solution onto composite magnetic lignin adsorbent. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.T.; Teng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X. Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by carbon nanofiber supported Fe3O4@carbon composites for efficient ibuprofen degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 401, 123428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Wan, C.; Bao, W.; Gao, H.; Liang, D.; Li, J. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@cellulose aerogel nanocomposite and its application in Fenton-like degradation of Rhodamine B. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Z.; Cai, Y. Humic acid coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as highly efficient Fenton-like catalyst for complete mineralization of sulfathiazole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Qian, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Jiang, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y. In situ synthesis of hierarchical mesoporous Fe3O4@C nanowires derived from coordination polymers for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 51960–51965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liu, J.-H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Xie, J.; Yu, B.; Ma, X.; Yang, S.-T.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Hydrothermal preparation of magnetic Fe3O4@C nanoparticles for dye adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, S.; Caratto, V.; Locardi, F.; Alberti, S.; Canepa, F.; Ferretti, M.; Sturini, M.; Speltini, A.; Maraschi, F. Enhancement of TiO2 NPs Activity by Fe3O4 Nano-Seeds for Removal of Organic Pollutants in Water. Materials 2016, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.-D.; Wang, H.-L.; Wei, X.-N.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yang, Y.-F.; Jiang, W.-F. Preparation and photocatalytic performance of magnetic Fe3O4@TiO2 core-shell microspheres supported by silica aerogels from industrial fly ash. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 659, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.S.; Kakavandi, B.; Noorisepehr, M.; Isari, A.A.; Zabih, S.; Bashardoust, P. Photocatalytic oxidation of tetracycline by magnetic carbon-supported TiO2 nanoparticles catalyzed peroxydisulfate: Performance, synergy and reaction mechanism studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 117936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Shen, N.; Zhao, J.; Su, Y.; Ren, H. Glutathione-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with enhanced Fenton-like activity at neutral pH for degrading 2,4-dichlorophenol. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wu, R.; Huo, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, X. Novel magnetic g-C3N4/α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 composite for the very effective visible-light-Fenton degradation of Orange II. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5180–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; He, M.; Liu, J.-H.; Liao, R.; Zhao, L.; Xie, J.; Wang, R.; Yang, S.-T.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Fe3O4@C nanoparticles as high-performance Fenton-like catalyst for dye decoloration. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3406–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, M.; Dashtian, K.; Mowla, D.; Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Ghaedi, M. Robust charge carrier by Fe3O4 in Fe3O4/WO3 core-shell photocatalyst loaded on UiO-66(Ti) for urea photo-oxidation. Chemosphere 2020, 267, 129206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, V.T.; Tran, V.A.; Tran, D.L.; Nguyen, T.L.H.; Doan, V.-D. Fabrication of Fe3O4/CuO@C composite from MOF-based materials as an efficient and magnetically separable photocatalyst for degradation of ciprofloxacin antibiotic. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Wang, Q.; Lyu, J.; Bai, P.; Guo, X. Boron removal and reclamation by magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticle: An adsorption and isotopic separation study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 231, 115930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Qian, J.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Song, H.-J. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of carbon@Fe3O4 nanoparticles with high adsorption capacity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chi, W.; Huang, Q.; Yu, C. Facile preparation and dye removal properties of Fe3O4@carbon nanocomposite. Micro Nano Lett. 2018, 13, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Yang, Z.; Su, B. Application of multi-functional chestnut shell in one-step preparing Fe3O4@C magnetic nanocomposite with high adsorption performance. Full. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2018, 26, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, I.; Kurniawan, E.; Gusti, D.R.; Yusnelti. Magnetite Fe3O4-activated carbon composite as adsorbent of rhodamine B dye. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 483, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Song, Y.; Shi, S.; Jiang, B.; Yang, J.; Xiao, S. Preparation and characterization of a novel Fe3O4-graphene-biochar composite for crystal violet adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamipour, A.; Khadiv Parsi, P.; Zahedi, P.; Moosavian, S.M.A. Using Fe3O4-coated nanofibers based on cellulose acetate/chitosan for adsorption of Cr(VI), Ni(II) and phenol from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhou, Z. Citrus pectin derived ultrasmall Fe3O4@C nanoparticles as a high-performance adsorbent toward removal of methylene blue. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 222, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gao, M.; Pan, H.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y. A facile synthesis of Fe3O4/C composite with high cycle stability as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wan, G.; Wang, G.; He, Z.; Shi, S.; Wu, L.; Wang, G. The construction of carbon-coated Fe3O4 yolk-shell nanocomposites based on volume shrinkage from the release of oxygen anions for wide-band electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 511, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Yao, Y. Facile synthesis of porous carbon/Fe3O4 composites derived from waste cellulose acetate by one-step carbothermal method as a recyclable adsorbent for dyes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3384–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, J.; Gu, H. Preparation of porous and hollow Fe3O4@C spheres as an efficient anode material for a high-performance Li-ion battery. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6430–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G. Structural evolution from mesoporous α-Fe2O3 to Fe3O4@C and γ-Fe2O3 nanospheres and their lithium storage performances. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 4709–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. A new green synthesis of porous magnetite nanoparticles from waste ferrous sulfate by solid-phase reduction reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 710, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Luz-Asunción, M.; Pérez-Ramírez, E.E.; Martínez-Hernández, A.L.; García-Casillas, P.E.; Luna-Bárcenas, J.G.; Velasco-Santos, C. Adsorption and kinetic study of Reactive Red 2 dye onto graphene oxides and graphene quantum dots. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2020, 109, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Ballweg, T.; Groß, L.; Gellermann, C.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A.; Mandel, K. Magnetic Carbon Composite Particles for Dye Adsorption from Water and their Electrochemical Regeneration. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2019, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of Ammonia Synthesis on Promoted Iron Catalyst. Acta Physicochim. URSS 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Redlich, O.; Peterson, D.L. A Useful Adsorption Isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1024–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, B.; Yang, L.; Yang, X. Characterization and synthesis of nanometer magnetite black pigment from titanium slag by microwave-assisted reduction method. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 147, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Qiang, Z.; Chang, J.-H.; Ben, W.; Qu, J. Synthesis of carbon-coated magnetic nanocomposite (Fe3O4@C) and its application for sulfonamide antibiotics removal from water. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtada, A.; Shahrouzianfar, A.; Ashiri, R. Facile synthesis of NiTiO3 yellow nano-pigments with enhanced solar radiation reflection efficiency by an innovative one-step method at low temperature. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 139, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodko, Y.; Habas, S.E.; Koebel, M.; Yang, P.; Frei, H.; Somorjai, G.A. Probing the Interaction of Poly(vinylpyrrolidone)with Platinum Nanocrystals by UV- Raman and FTIR. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 23052–23059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppiah, D.D.; Hamid, S.B.A. One step facile synthesis of ferromagnetic magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 414, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.S.; Piao, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Fabrication of spherical Fe3O4 particles with a solvothermal method and their magnetorheological characteristics. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Yuan, J.; Kang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T. One-pot synthesis of carbon-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with tunable size for production of gasoline fuels. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10861–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivakov, A.A.; Lin, C.-R.; Jhang, C.-J.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Tseng, Y.-T. Synthesis and characterization of carbon-coated wustite nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2019, 249, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadezky, A.; Muckenhuber, H.; Grothe, H.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: Spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon 2005, 43, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebanova, O.N.; Lazor, P. Raman spectroscopic study of magnetite (FeFe2O4): A new assignment for the vibrational spectrum. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 174, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Camacho, C.; Villalobos, M.; Rivas-Sánchez, M.d.l.L.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.; Alcaraz-Cienfuegos, J.; Gutiérrez-Ruiz, M.E. Characterization and surface reactivity of natural and synthetic magnetites. Chem. Geol. 2013, 347, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mohan, D. Magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticle synthesis and applications for lead (Pb2+) and chromium (Cr6+) removal from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xing, J.; Meng, A. Fast Removal of Methylene Blue by Fe(3)O(4) Magnetic Nanoparticles and Their Cycling Property. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karri, R.R.; Sahu, J.N.; Jayakumar, N.S. Optimal isotherm parameters for phenol adsorption from aqueous solutions onto coconut shell based activated carbon: Error analysis of linear and non-linear methods. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Wang, X.; Huang, P.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Yang, X. Chromium (VI) adsorption from wastewater using porous magnetite nanoparticles prepared from titanium residue by a novel solid-phase reduction method. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607-608, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Ren, G.; Yang, X.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. A low-cost solvent-free method to synthesize α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with applications to degrade methyl orange in photo-fenton system. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Suib, S.L.; Yang, H. Degradation of Congo Red dye by a Fe2O3@CeO2-ZrO2/Palygorskite composite catalyst: Synergetic effects of Fe2O3. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.G.L.; Mendes, H.M.; Bastos, S.L.; D’Agostino, L.C.; Tronto, J.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V.; Neto, J.L. Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue using Mg/Fe and MnMg/Fe layered double hydroxides as reusable catalysts. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 187, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, H.; Aghabarari, B.; Alizadeh, M.; Khanlarkhani, A.; Abu-Zahra, N. High efficiency decolorization of wastewater by Fenton catalyst: Magnetic iron-copper hybrid oxides. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 37, 101540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Jia, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Magnetic Porous Carbon Microspheres for Removal of Methylene Blue by a Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7275–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qian, J.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Jiang, D.; Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, H. Magnetically Separable Fe3O4 Nanoparticles-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Catalytic Wet Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2013, 23, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Magnetic porous Fe3O4/carbon octahedra derived from iron-based metal-organic framework as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xue, X.; Huang, X.; Yang, H. Adsorption and heterogeneous Fenton catalytic performance for magnetic Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide aerogel. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 15695–15708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, M.; Song, D.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Lu, X.; Rosso, K.M. Facet-Dependent Photodegradation of Methylene Blue by Hematite Nanoplates in Visible Light. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Cao, X.; Wei, H.; Huo, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, K. Strong enhancement effect of bisulfite on MIL-68(Fe)-catalyzed Fenton-like reaction for organic pollutants degradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 542, 148631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, K.; Panda, A.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Mandal, D.; Hossain, A.; Bera, P.; Seikh, M.M.; Gayen, A. Facile synthesis of CuCr2O4/CeO2 nanocomposite: A new Fenton like catalyst with domestic LED light assisted improved photocatalytic activity for the degradation of RhB, MB and MO dyes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 536, 147604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Shao, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, Q. Preparation of copper doped magnetic porous carbon for removal of methylene blue by a heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72423–72432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimin, D.; Jiaqi, Z.; Danyang, L.; Lanli, N.; Liling, Z.; Yi, Z.; Xiaohong, Z. Preparation of Congo red functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticle and its application for the removal of methylene blue. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 550, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, X.; Tan, L.; Ma, H.; Guo, D.; Pang, H.; Wang, X. Fabrication of double-shell hollow NiO@N-C nanotubes for a high-performance supercapacitor. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 13457–13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, X.; Li, H.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous removal of methylene blue and total dissolved copper in zero-valent iron/H2O2 Fenton system: Kinetics, mechanism and degradation pathway. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 555, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Dong, W.; Cui, G.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Xia, X.; Tang, B.; Wang, W. Highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by P2ABSA-modified TiO2 nanocomposite due to the photosensitization synergetic effect of TiO2 and P2ABSA. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 23699–23708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, S.; Chen, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, Z.; Crittenden, J.C.; Huang, M. Integration of a Photo-Fenton Reaction and a Membrane Filtration using CS/PAN@FeOOH/g-C3N4Electrospun Nanofibers: Synthesis, Characterization, Self-cleaning Performance and Mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 281, 119519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolski, L.; Ziolek, M. Insight into pathways of methylene blue degradation with H2O2 over mono and bimetallic Nb, Zn oxides. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 224, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, S.; Ning, P. Degradation Mechanism of Methylene Blue in a Heterogeneous Fenton-like Reaction Catalyzed by Ferrocene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 53, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cini g·L−1 | qe(expe) mg/g | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 min−1 | qe(calc) mg/g | k2 g/mg∙min | qe(calc) mg/g | h mg/mg∙min | ||||
| 20 | 9.809 | 0.1018 | 0.9962 | 0.9704 | 0.3924 | 9.827 | 0.9992 | 37.89 |
| 30 | 12.84 | 0.1133 | 2.445 | 0.9795 | 0.1464 | 12.93 | 0.9997 | 24.47 |
| 40 | 15.29 | 0.1262 | 4.333 | 0.9862 | 0.0794 | 15.51 | 0.9990 | 19.10 |
| 50 | 17.26 | 0.1369 | 4.718 | 0.9784 | 0.0775 | 17.48 | 0.9991 | 23.68 |
| Cint mg/L−1 | Kdif, 1 mg/g·min0.5 | ɛdif, 1 mg/g | Kdif, 2 mg/g·min0.5 | ɛdif, 2 mg/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.3964 | 8.336 | 0.8735 | 0.0610 | 9.369 | 0.8126 |
| 30 | 0.9254 | 9.336 | 0.9735 | 0.1353 | 11.86 | 0.8196 |
| 40 | 0.8963 | 10.98 | 0.9699 | 0.3039 | 13.17 | 0.6355 |
| 50 | 1.0562 | 12.60 | 0.9671 | 0.2554 | 15.45 | 0.7411 |
| Temp. °C | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
| qmax mg/g | kLC L/mg | KFC g/mg∙min | 1/n | |||
| 25 | 16.00 | 0.8955 | 0.8954 | 8.060 | 0.2365 | 0.9643 |
| 35 | 14.19 | 0.7804 | 0.8711 | 6.486 | 0.2503 | 0.9939 |
| 45 | 13.69 | 0.4383 | 0.9021 | 5.468 | 0.2779 | 0.9800 |
| Temp. °C | Redlich-Peterson | Temkin | ||||
| aR (L/mg)α | KR L/mg | B | A L/mg | |||
| 25 | 5.963 | 58.11 | 0.9830 | 2.488 | 29.36 | 0.9873 |
| 35 | 5.496 | 43.11 | 0.9971 | 2.450 | 19.26 | 0.9874 |
| 45 | 3.762 | 25.03 | 0.9878 | 2.254 | 8.159 | 0.9804 |
| Catalysts | [Catalysts] (g/L) | [H2O2] (mM) | [MB] (mg/L) | Removal Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnMg/Fe LDH | 1.0 | 10 | 20 | 93% in 300 min | [59] |
| Fe3O4/CuO | 1.6 | 32 | 10 | 95% in 120 min | [60] |
| MPCMSs | 2.0 | 16 | 40 | ~100% in 25 min | [61] |
| Fe3O4/rGO | 0.3 | 60 | 10 | ~99% in 120 min | [62] |
| Fe3O4/C | 0.5 | 90 | 10 | ~100% in 60 min | [63] |
| Fe3O4/rGO aerogel | 0.3 | 20 | 50 | ~100% in 360 min | [64] |
| Fe2O3 | 0.5 | 30 | 10 | ~70% in 420 min | [65] |
| MIL-68(Fe) | 0.2 | 50 | 20 | ~100% in 40 min | [66] |
| CuCr2O4/CeO2 | 1.0 | 4 | 10 | ~80% in 20 min | [67] |
| CuFe2O4/Cu@C | 0.5 | 16 | 20 | ~100% in 30 min | [68] |
| Fe3O4@C | 2.0 | 30 | 100 | ~99% in 180 min | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, H.; Ren, G.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles Synthesized by In Situ Solid-Phase Method for Removal of Methylene Blue. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020330
Xiang H, Ren G, Zhong Y, Xu D, Zhang Z, Wang X, Yang X. Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles Synthesized by In Situ Solid-Phase Method for Removal of Methylene Blue. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(2):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020330
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Hengli, Genkuan Ren, Yanjun Zhong, Dehua Xu, Zhiye Zhang, Xinlong Wang, and Xiushan Yang. 2021. "Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles Synthesized by In Situ Solid-Phase Method for Removal of Methylene Blue" Nanomaterials 11, no. 2: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020330
APA StyleXiang, H., Ren, G., Zhong, Y., Xu, D., Zhang, Z., Wang, X., & Yang, X. (2021). Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles Synthesized by In Situ Solid-Phase Method for Removal of Methylene Blue. Nanomaterials, 11(2), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020330




