Thermal, Morphological, Electrical Properties and Touch-Sensor Application of Conductive Carbon Black-Filled Polyamide Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermogravimetric (TGA) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analyses
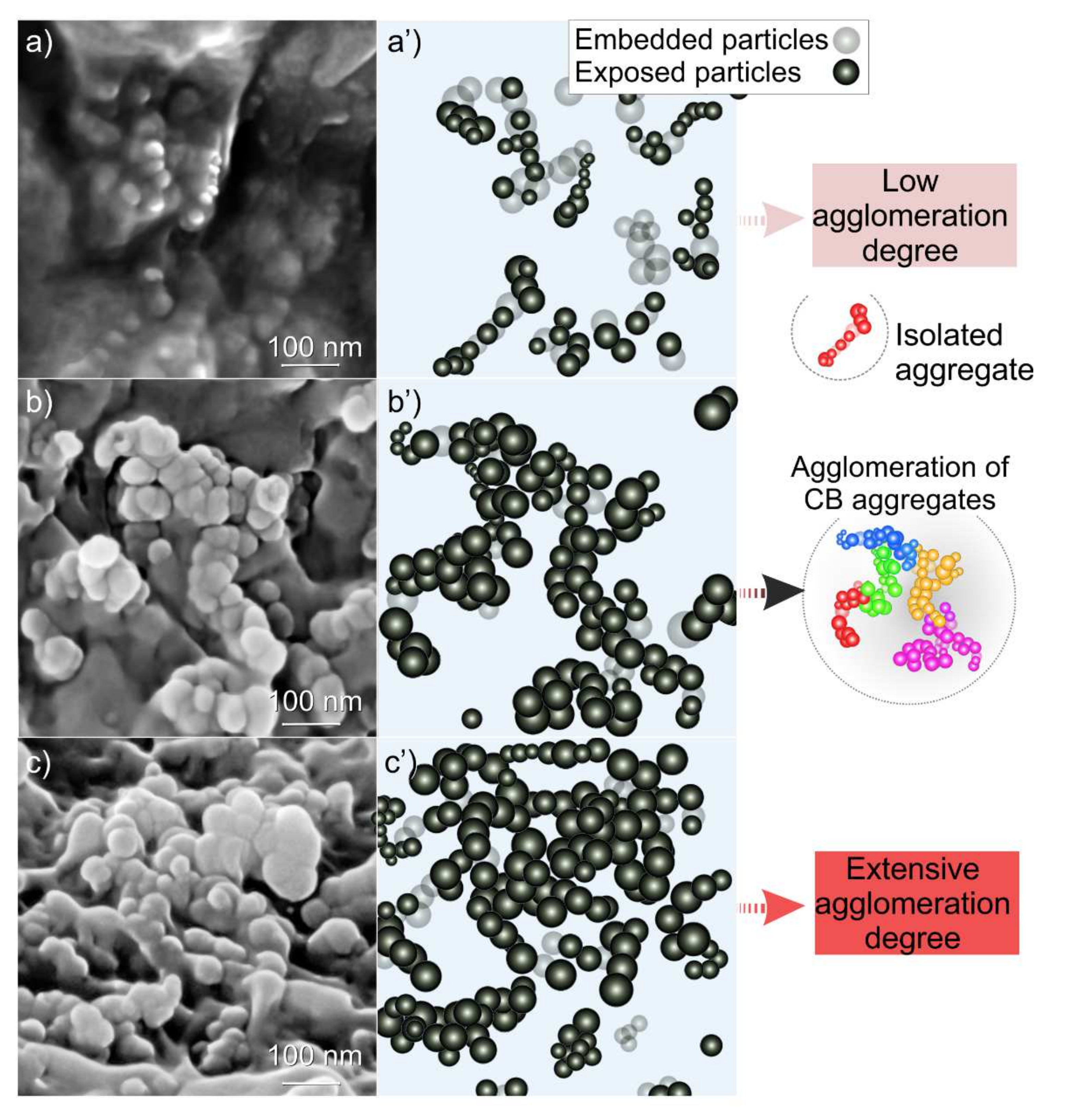
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
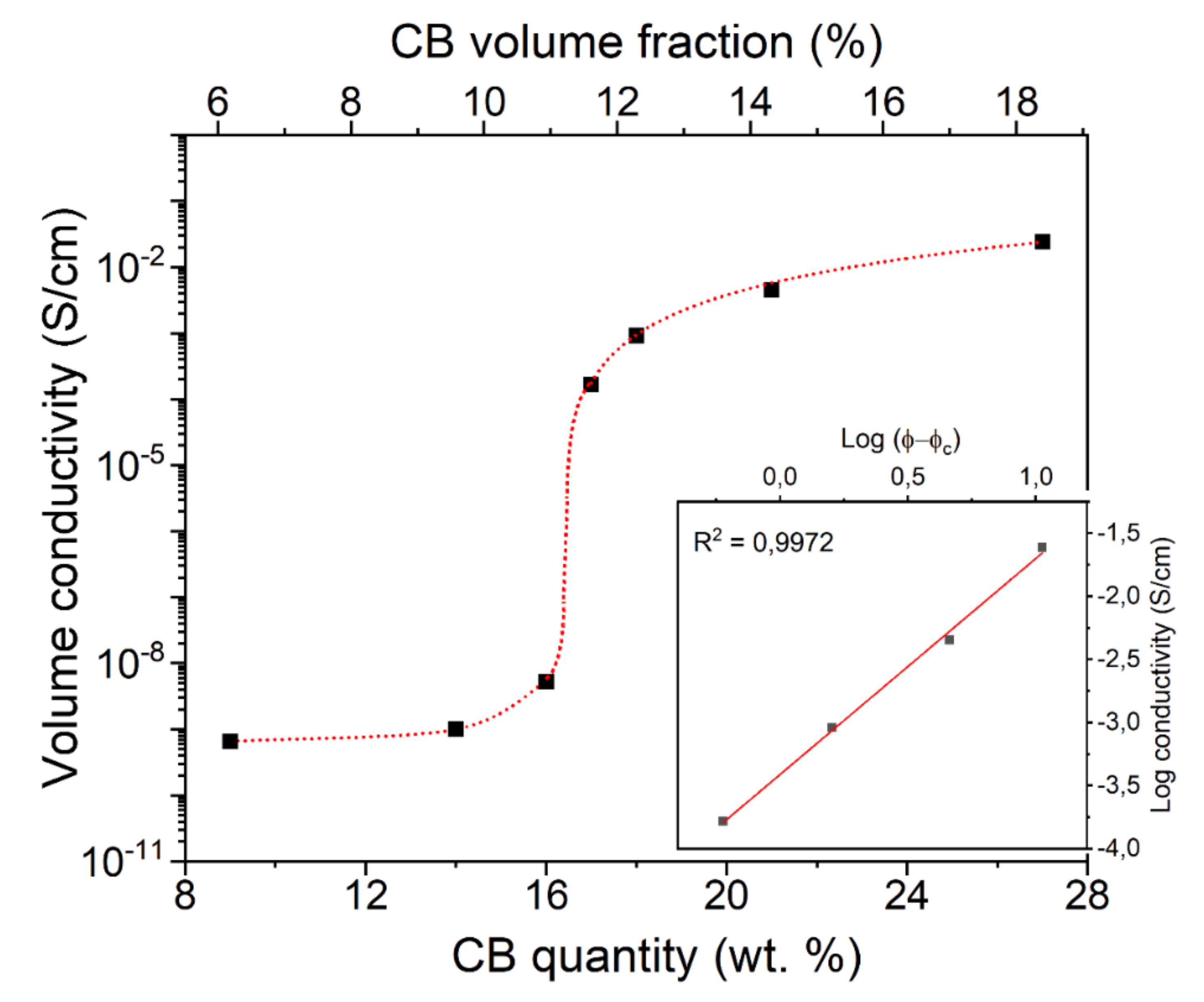
3.3. DC Electrical Properties at 25 °C
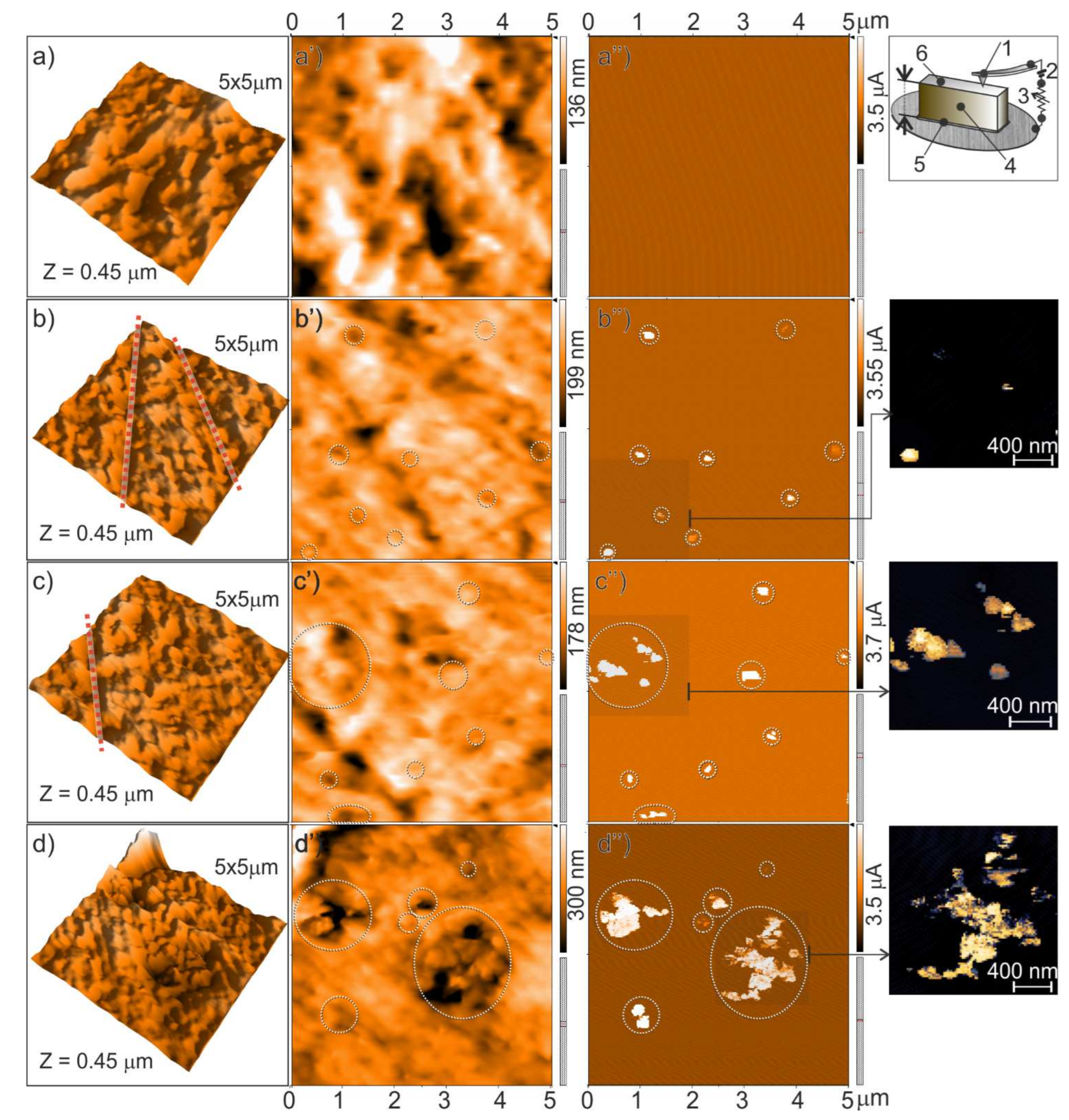
3.4. AFM Imaging of the Conductive Paths in the Composite Materials
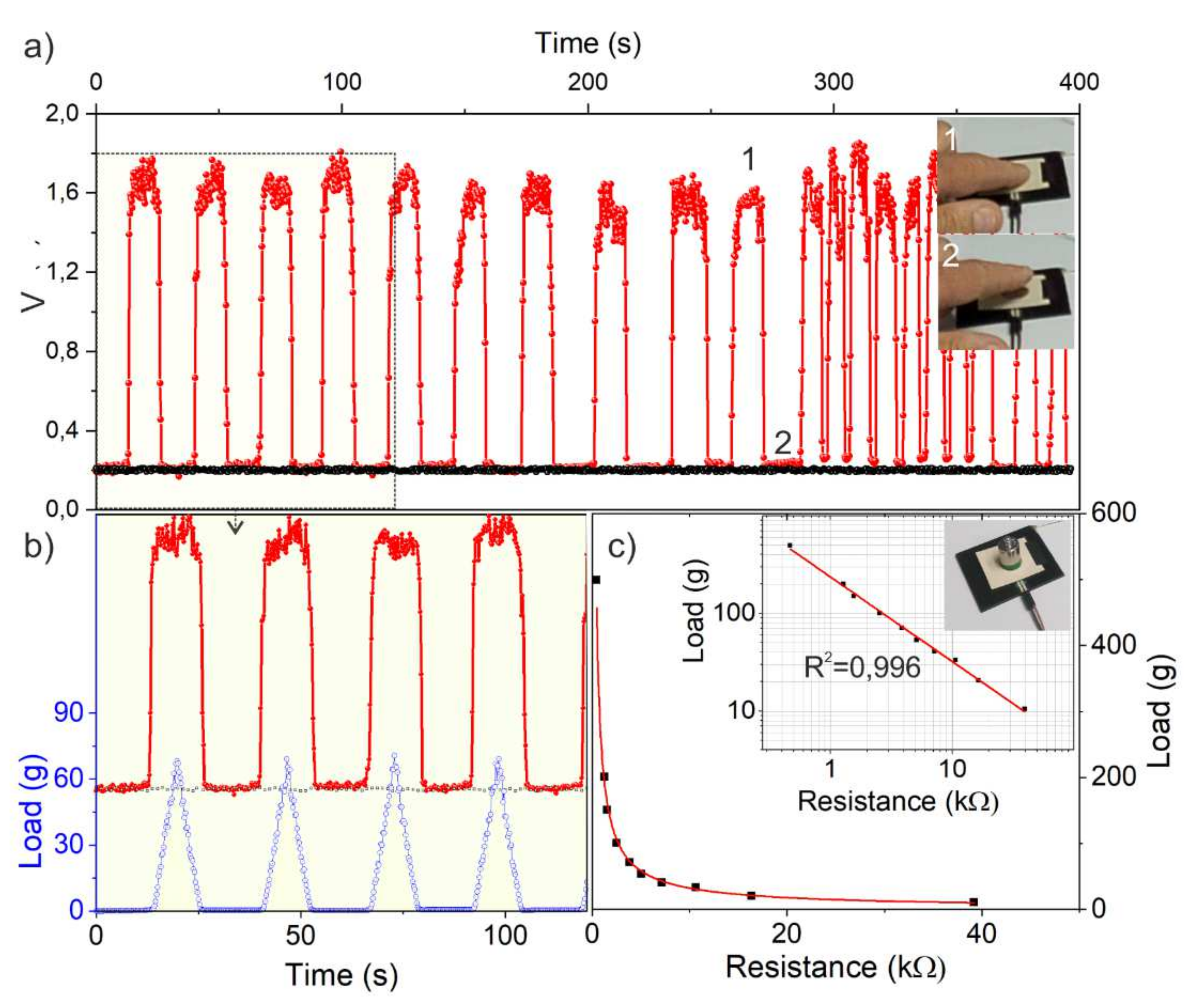
3.5. Touch-Sensor Prototype
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kunz, K.; Krause, B.; Kretzschmar, B.; Juhasz, L.; Kobsch, O.; Jenschke, W.; Ullrich, M.; Pötschke, P. Direction dependent electrical conductivity of polymer/carbon filler composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, G.; Rhee, K.Y.; Mišković-Stanković, V.; Hui, D. Reinforcements in multi-scale polymer composites: Processing, properties, and applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 138, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Etrick, N.R.; Frey, M.W.; Norris, E.J.; Coats, J.R. Structure and Properties of Polyamide Fabrics with Insect-Repellent Functionality by Electrospinning and Oxygen Plasma-Treated Surface Coating. Polymers 2020, 12, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyuftin, A.A.; Kerry, J.P. Review of surface treatment methods for polyamide films for potential application as smart packaging materials: Surface structure, antimicrobial and spectral properties. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.; Ishak, Z. Polyamide blend-based nanocomposites: A review. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troughton, M.J. Chapter 25—Polyamides. In Handbook of Plastics Joining, 2nd ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 25–281. [Google Scholar]
- Unal, H.; Mimaroglu, A. Influence of Filler Addition on the Mechanical Properties of Nylon-6 Polymer. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2004, 23, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N. Some basic aspects of polymer nanocomposites: A critical review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsona, E.O.; Codou, A.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. A critical review on the fabrication processes and performance of polyamide biocomposites from a biofiller perspective. Mater. Today Sustain. 2019, 5, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haznedar, G.; Cravanzola, S.; Zanetti, M.; Scarano, D.; Zecchina, A.; Cesano, F. Graphite nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes based polyethylene composites: Electrical conductivity and morphology. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 143, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Ghosh, P.; Das, N.C. Preparation, development, outcomes, and application versatility of carbon fiber-based polymer composites: A review. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2019, 2, 214–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, M.; Armentano, I.; Cesano, F.; Scarano, D.; Frache, A.; Torre, L.; Monti, M. Effect of Injection Molding Conditions on Crystalline Structure and Electrical Resistivity of PP/MWCNT Nanocomposites. Polymers 2020, 12, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesano, F.; Zaccone, M.; Armentano, I.; Cravanzola, S.; Muscuso, L.; Torre, L.; Kenny, J.M.; Monti, M.; Scarano, D. Relationship between morphology and electrical properties in PP/MWCNT composites: Processing-induced anisotropic percolation threshold. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 180, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.; Keinath, M.; Thomann, R.; Mülhaupt, R. Thermoplastic Carbon/Polyamide 12 Composites Containing Functionalized Graphene, Expanded Graphite, and Carbon Nanofillers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Jawaid, M.; Khan, A.A.P.; Asiri, A.M. Electrically Conductive Polymer and Polymer Composites. In Carbon Nanomaterial-Based Conducting Polymer Composites for Biosensing Applications; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cesano, F.; Uddin, M.J.; Lozano, K.; Zanetti, M.; Scarano, D. All-Carbon Conductors for Electronic and Electrical Wiring Applications. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleşa, I.; Noţingher, P.V.; Schlögl, S.; Sumereder, C.; Muhr, M. Properties of Polymer Composites Used in High-Voltage Applications. Polymers 2016, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesano, F.; Uddin, M.J.; Damin, A.; Scarano, D. Multifuctional Conductive Paths Obtained by Laser Processing of Non-Conductive Carbon Nanotube/Polypropylene Composites. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, G.; Morgan, J.J.; Murphy, C.; Torres Alonso, E.; Wade, J.; Ott, A.K.; Russo, S.; Alves, H.; Craciun, M.F.; Neves, A.I.S. Low Operating Voltage Carbon–Graphene Hybrid E-textile for Temperature Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 29861–29867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesano, F.; Rattalino, I.; Bardelli, F.; Sanginario, A.; Gianturco, A.; Veca, A.; Viazzi, C.; Castelli, P.; Scarano, D.; Zecchina, A. Structure and properties of metal-free conductive tracks on polyethylene/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites as obtained by laser stimulated percolation. Carbon 2013, 61, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meo, E.; Agnelli, S.; Veca, A.; Brunella, V.; Zanetti, M. Piezoresistive and mechanical Behavior of CNT based polyurethane foam. J. Comp. Sci. 2020, 4, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, L.; Sun, B.; Li, X.; Kang, S.H. Review—Recent Progress in Flexible and Stretchable Piezoresistive Sensors and Their Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravanzola, S.; Haznedar, G.; Scarano, D.; Zecchina, A.; Cesano, F. Carbon-based piezoresistive polymer composites: Structure and electrical properties. Carbon 2013, 62, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Sun, J. Electrical Conductivity and Percolation Behavior of Polymer Nanocomposites. In Polymer Nanocomposites; Huang, X., Zhi, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 51–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.; Tirumali, M.; Wang, X.; Naebe, M.; Kandasubramanian, B. Polymer composite for antistatic application in aerospace. Def. Technol. 2020, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, F.; Cinti, S.; Mazzaracchio, V.; Scognamiglio, V.; Amine, A.; Moscone, D. Carbon black as an outstanding and affordable nanomaterial for electrochemical (bio)sensor design. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.M.; Sim, C.U.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.C. Effects of the carbon fillers on the EMI shielding performance and physical properties of Nylon66 composites. Polymer 2017, 41, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clingerman, M.L.; Weber, E.H.; King, J.A.; Schulz, K.H. Synergistic effects of carbon fillers in electrically conductive nylon 6,6 and polycarbonate based resins. Polym. Compos. 2002, 23, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheeskumar, S.; Kanagaraj, G. Experimental investigation on tribological behaviours of PA6, PA6-reinforced Al2O3 and PA6-reinforced graphite polymer composites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 1467–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toghchi, J.M.; Campagne, C.; Cayla, A.; Bruniaux, P.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Burgnies, L.; Chen, Y. Electrical conductivity enhancement of hybrid PA6,6 composite containing multiwall carbon nanotube and carbon black for shielding effectiveness application in textiles. Synth. Met. 2019, 251, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espera, A.H., Jr.; Valino, A.D.; Palaganas, J.O.; Souza, L.; Chen, Q.; Advincula, R.C. 3D Printing of a Robust Polyamide-12-Carbon Black Composite via Selective Laser Sintering: Thermal and Electrical Conductivity. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Zhao, Z.; Leng, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. Two-step approach based on selective laser sintering for high performance carbon black/ polyamide 12 composite with 3D segregated conductive network. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahr, M.E.; Gilardi, R.; Bonacchi, D. Carbon Black for Electrically Conductive Polymer Applications, Ch. 19. In Fillers for Polymer Applications; Rothon, R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; p. 489. [Google Scholar]
- Billingham, N. Physical phenomena in the oxidation and stabilisation of polymers. In Oxidation Inhibition in Organic Materials; Klemchuk, P., Pospisil, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; Volume 2, pp. 249–298. [Google Scholar]
- Blaine, R.L. Thermal Application Notes: Polymer Heats of Fusion; TA Instruments: New Castle, DE, USA.
- Weidenfeller, B.; Rode, H.; Weidenfeller, L.; Weidenfeller, K. Crystallinity, thermal diffusivity, and electrical conductivity of carbon black filled polyamide 46. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Wu, C. Crystallization Behavior of Polypropylene Filled with Modified Carbon Black. Polym. J. 2007, 39, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Song, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, W. Mechanical properties, crystallization and melting behaviors of carbon fiber-reinforced PA6 composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, W.; Wu, C. The nucleation effect of modified carbon black on crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-C. Carbon black filled conducting polymers and polymer blends. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2002, 21, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahr, M.E.; Rothon, R. Carbon Black as a Polymer Filler. In Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series; Palsule, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Dai, K.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Shen, C. The strain-sensing behaviors of carbon black/polypropylene and carbon nanotubes/polypropylene conductive composites prepared by the vacuum-assisted hot compression. Coll. Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunella, V.; Rossatto, B.G.; Mastropasqua, C.; Cesano, F.; Scarano, D. Thermal/Electrical properties and texture of carbon black PC polymer composites near the electrical percolation threshold. J. Comp. Sci. 2021, 5, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-J.; Kim, M.S.; Ahn, D.; Yeo, S.Y.; Lee, S. Electrical percolation threshold of carbon black in a polymer matrix and its application to antistatic fibre. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Psarras, G.C. Charge transport properties in carbon black/polymer composites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2007, 45, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, J.; Ou, R.; Capozzi, C.J.; Gupta, S.; Parker, C.A.; Gerhardt, R.A.; Seal, K.; Kalinin, S.V.; Baddorf, A.P. Detection of percolating paths in polyhedral segregated network composites using electrostatic force microscopy and conductive atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 233122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, D.; Bertarione, S.; Cesano, F.; Spoto, G.; Zecchina, A. Imaging polycrystalline and smoke MgO surfaces with atomic force microscopy: A case study of high resolution image on a polycrystalline oxide. Surf. Sci. 2004, 570, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bârsan, O.A.; Hoffmann, G.G.; van der Ven, L.G.J.; de With, G. Quantitative Conductive Atomic Force Microscopy on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Polymer Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19701–19708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trionfi, A.; Scrymgeour, D.A.; Hsu, J.W.P.; Arlen, M.J.; Tomlin, D.; Jacobs, J.D.; Wang, D.H.; Tan, L.-S.; Vaia, R.A. Direct imaging of current paths in multiwalled carbon nanofiber polymer nanocomposites using conducting-tip atomic force microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 083708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu-Zanetti, C.; Mechler, A. Applications of Conductive AtomicForce Microscopy. Micr. Anal. 2005, 19, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cesano, F.; Agostini, G.; Scarano, D. Nanocrystalline TiO2 micropillar arrays grafted on conductive glass supports: Microscopic and spectroscopic studies. Thin Solid Film. 2015, 590, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravier, J.; Houzé, F.; Carmona, F.; Schneegans, O.; Saadaoui, H. Mesostructure of polymer/carbon black composites observed by conductive probe atomic force microscopy. Carbon 2001, 39, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Tony, A.; Yin, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W. Tactile and Thermal Sensors Built from Carbon–Polymer Nanocomposites—A Critical Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Marulanda, J.M.; Xu, Y.; Sharma, A. Carbon-Based Electronics: Transistors and Interconnects at the Nanoscale; Jenny Stanford Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, T.; Foti, G.; Scheurer, F.; Speisser, V.; Schull, G. Chemical control of electrical contact to sp2 carbon atoms. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
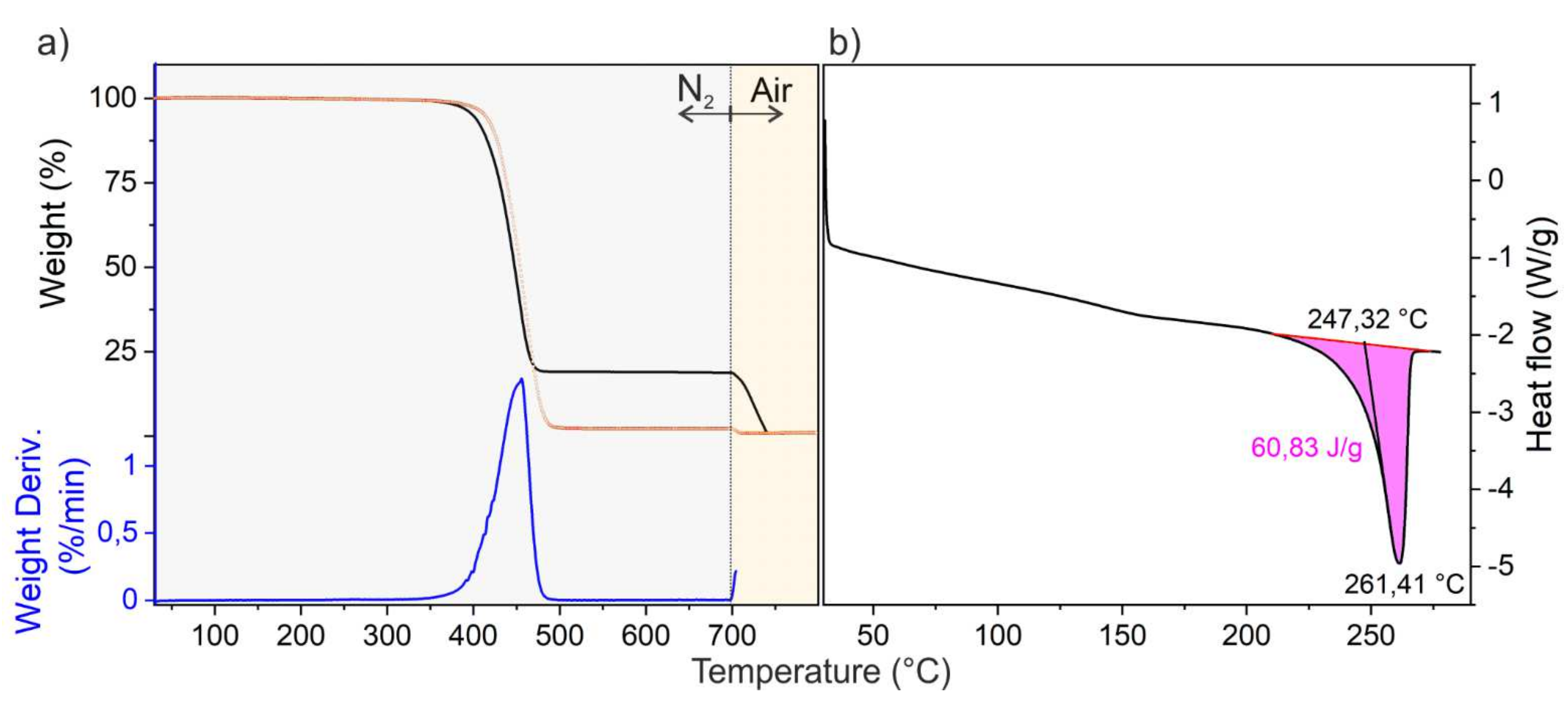


| Sample Name | Filler Content (wt. %)/Type 1 | Melting Point (°C) | Enthalpy of Fusion (ΔH) Measured (J/g) | Degree of Crystallinity (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA Technyl | - | 263.3 °C | 67.0 | 30 |
| PA-CB 9 | 9/CB | 262.1 °C | 66.6 | 29 |
| PA-CB 17 | 17/CB | 261.4 °C | 60.8 | 27 |
| PA-CB 21 | 21/CB | 261.7 °C | 57.4 | 25 |
| PA-CB 27 | 27/CB | 263.0 °C | 47.6 | 21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brunella, V.; Rossatto, B.G.; Scarano, D.; Cesano, F. Thermal, Morphological, Electrical Properties and Touch-Sensor Application of Conductive Carbon Black-Filled Polyamide Composites. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113103
Brunella V, Rossatto BG, Scarano D, Cesano F. Thermal, Morphological, Electrical Properties and Touch-Sensor Application of Conductive Carbon Black-Filled Polyamide Composites. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113103
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrunella, Valentina, Beatrice Gaia Rossatto, Domenica Scarano, and Federico Cesano. 2021. "Thermal, Morphological, Electrical Properties and Touch-Sensor Application of Conductive Carbon Black-Filled Polyamide Composites" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113103
APA StyleBrunella, V., Rossatto, B. G., Scarano, D., & Cesano, F. (2021). Thermal, Morphological, Electrical Properties and Touch-Sensor Application of Conductive Carbon Black-Filled Polyamide Composites. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113103








