In-Out Surface Modification of Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs) for Excellent Cure of Epoxy: Chemistry and Kinetics Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
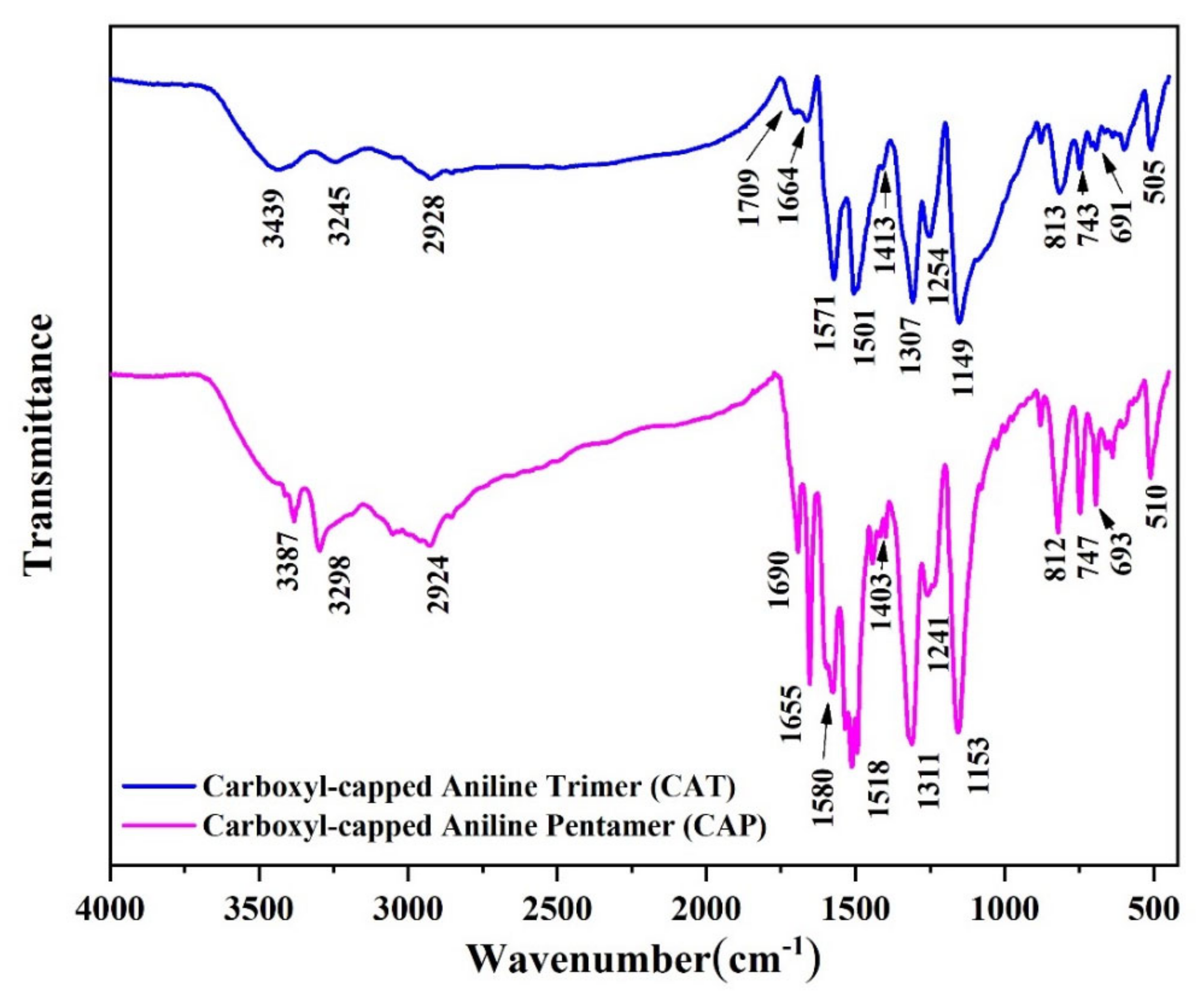
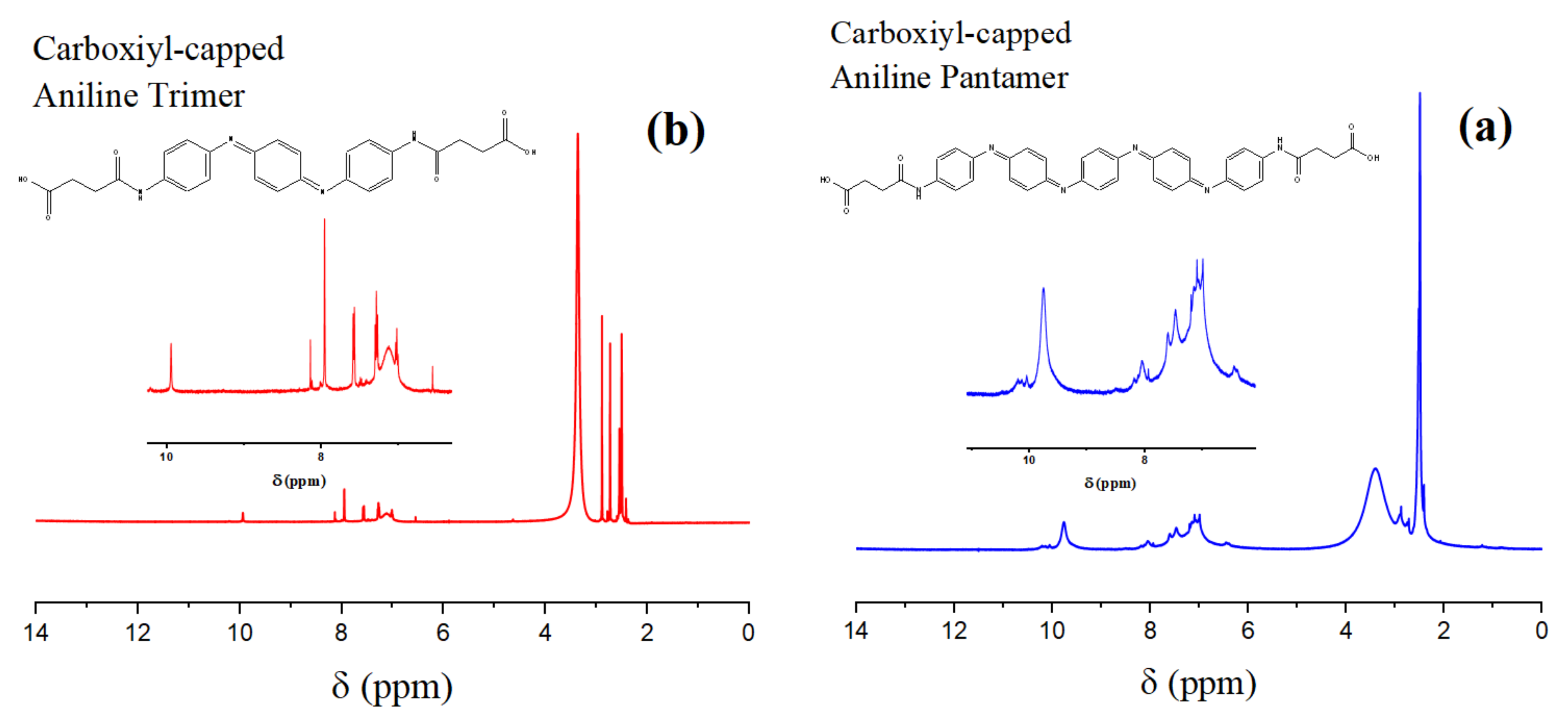
2.1. Characterization of the Synthesized Oligoanilines
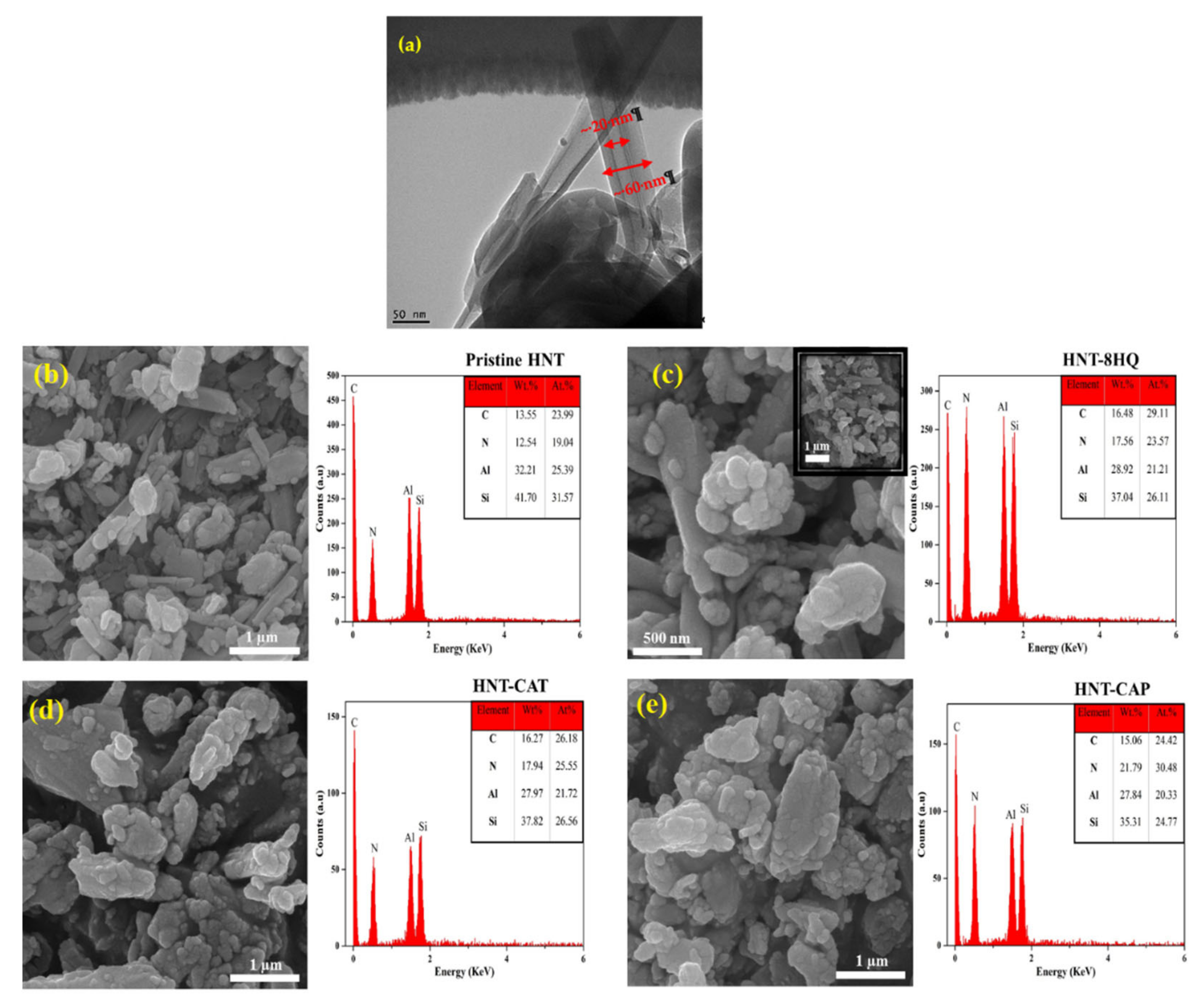
2.2. Characterization of HNT Nanotubes
2.3. Encapsulation Confirmation
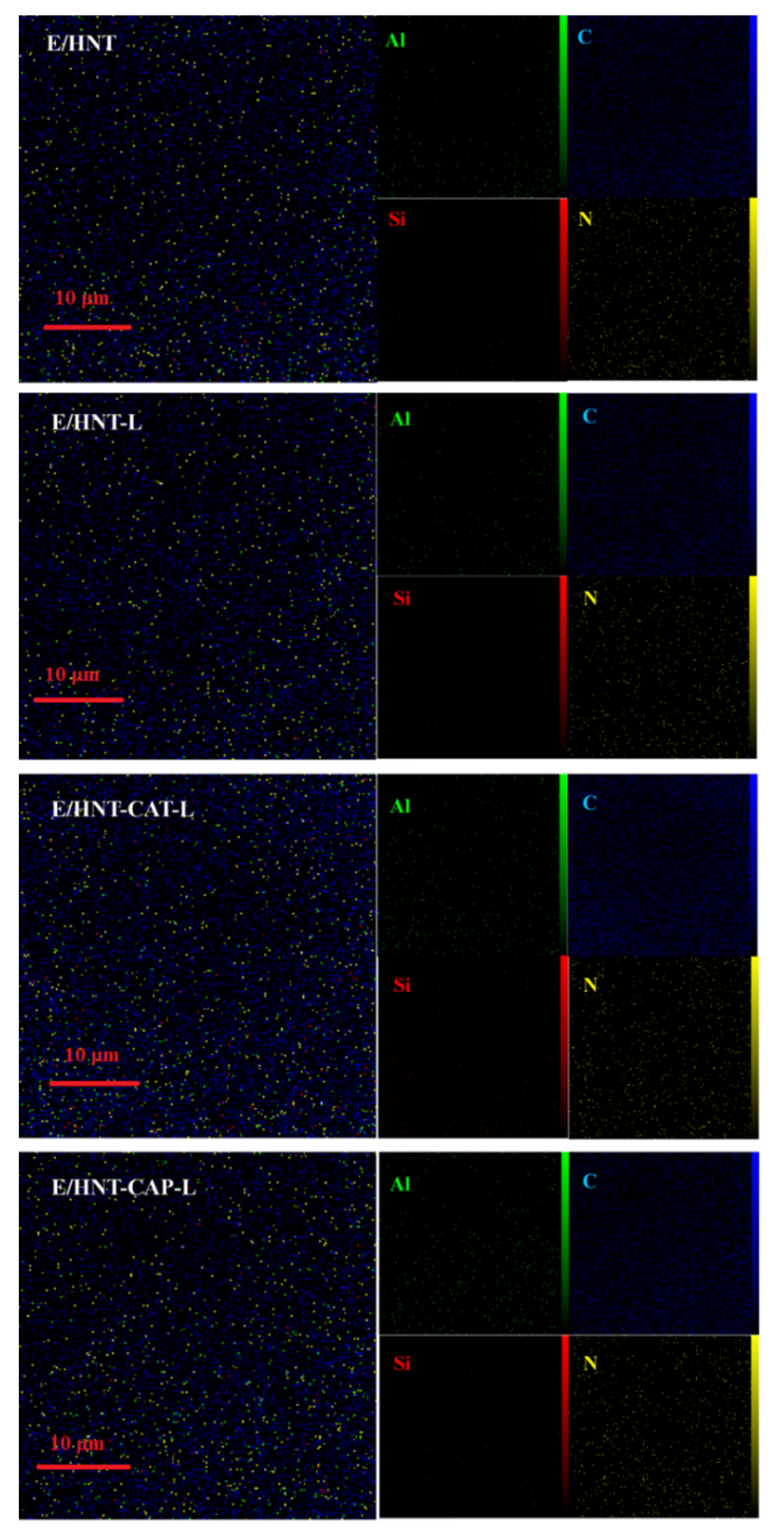
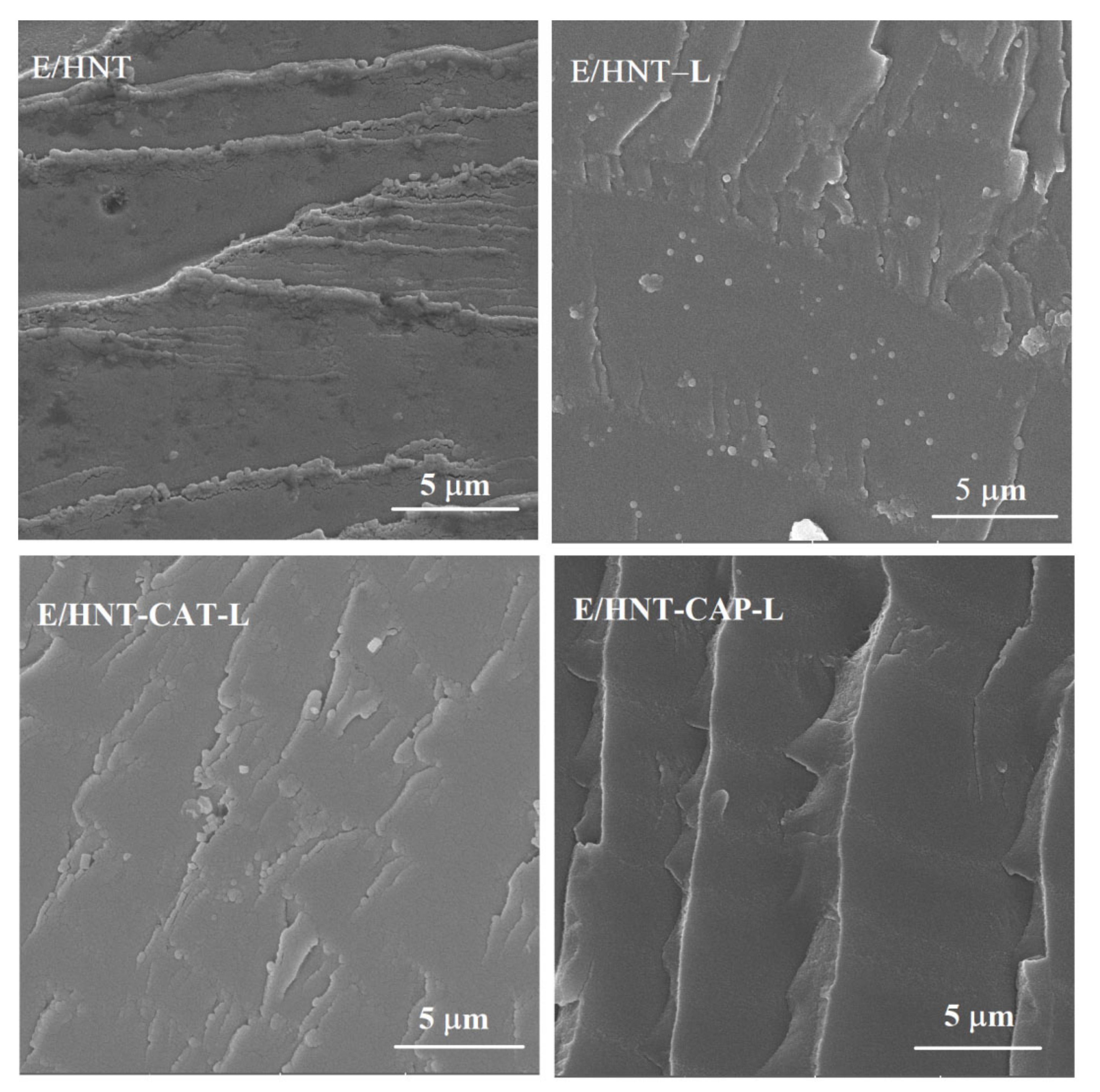
2.4. Microstructure of HNTs and Epoxy/HNT-Based Nanocomposites
2.5. Qualitative Cure Analysis
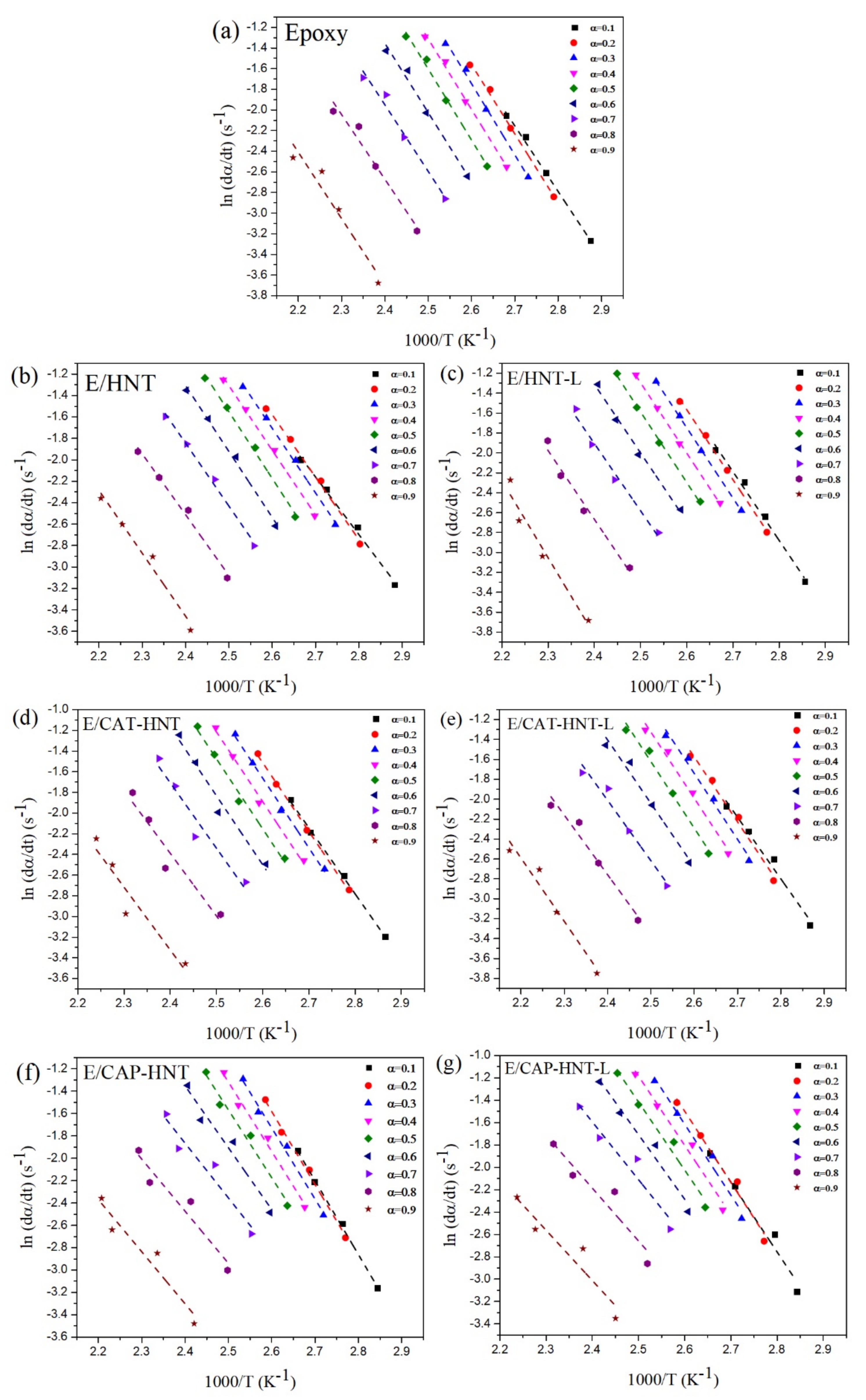
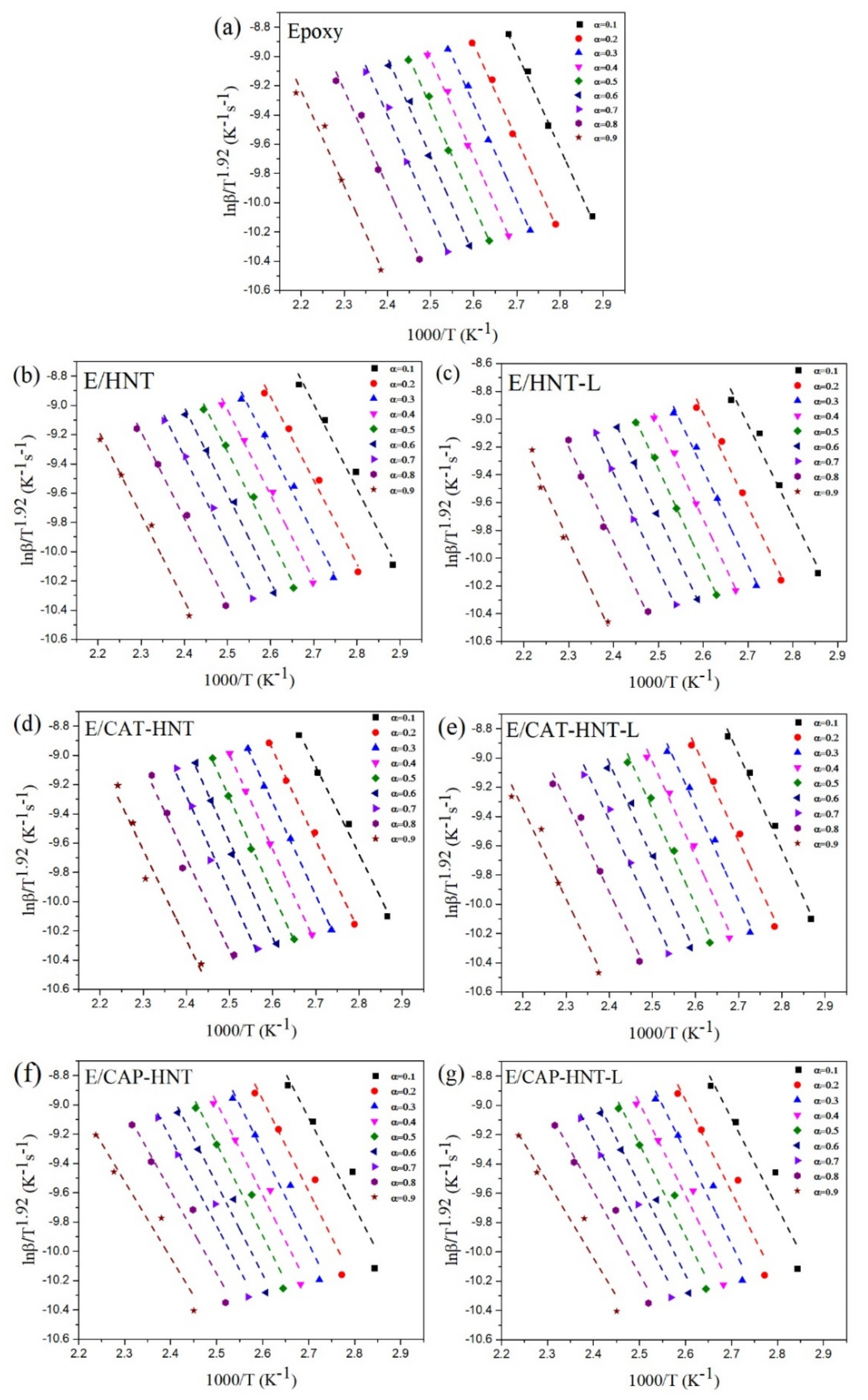
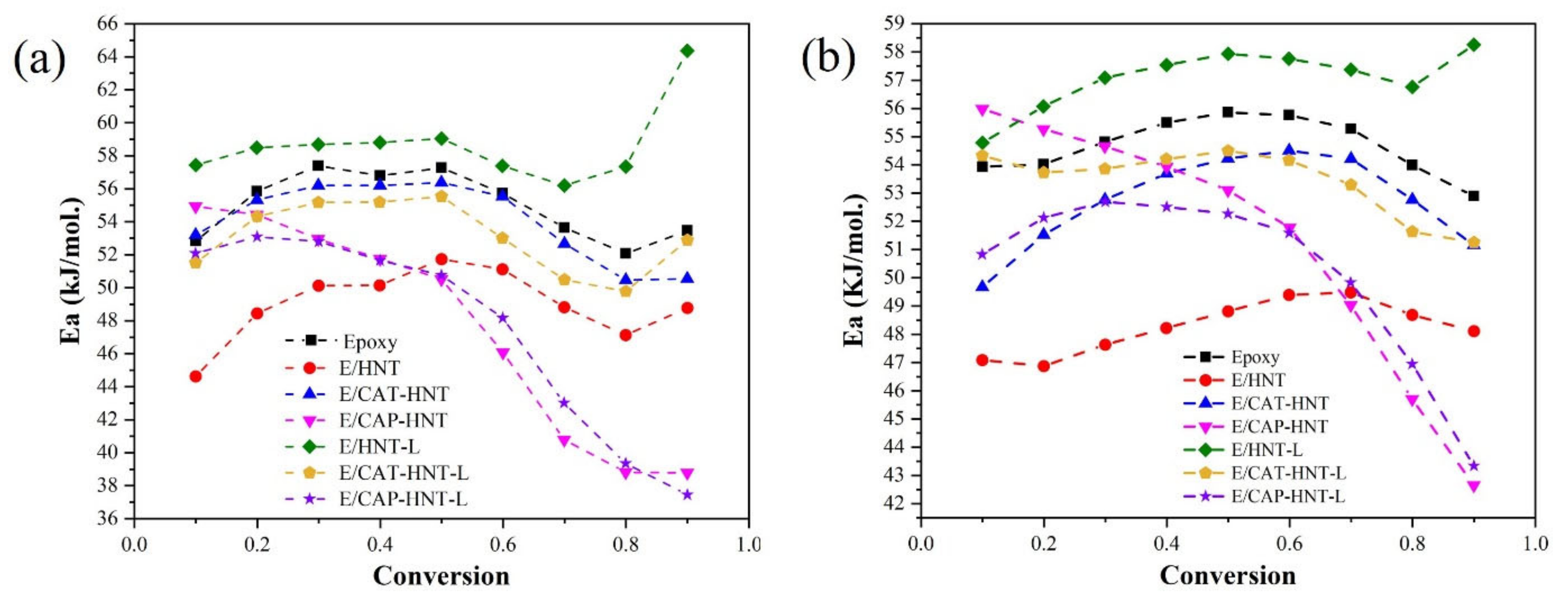
2.6. Quantitative Cure Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
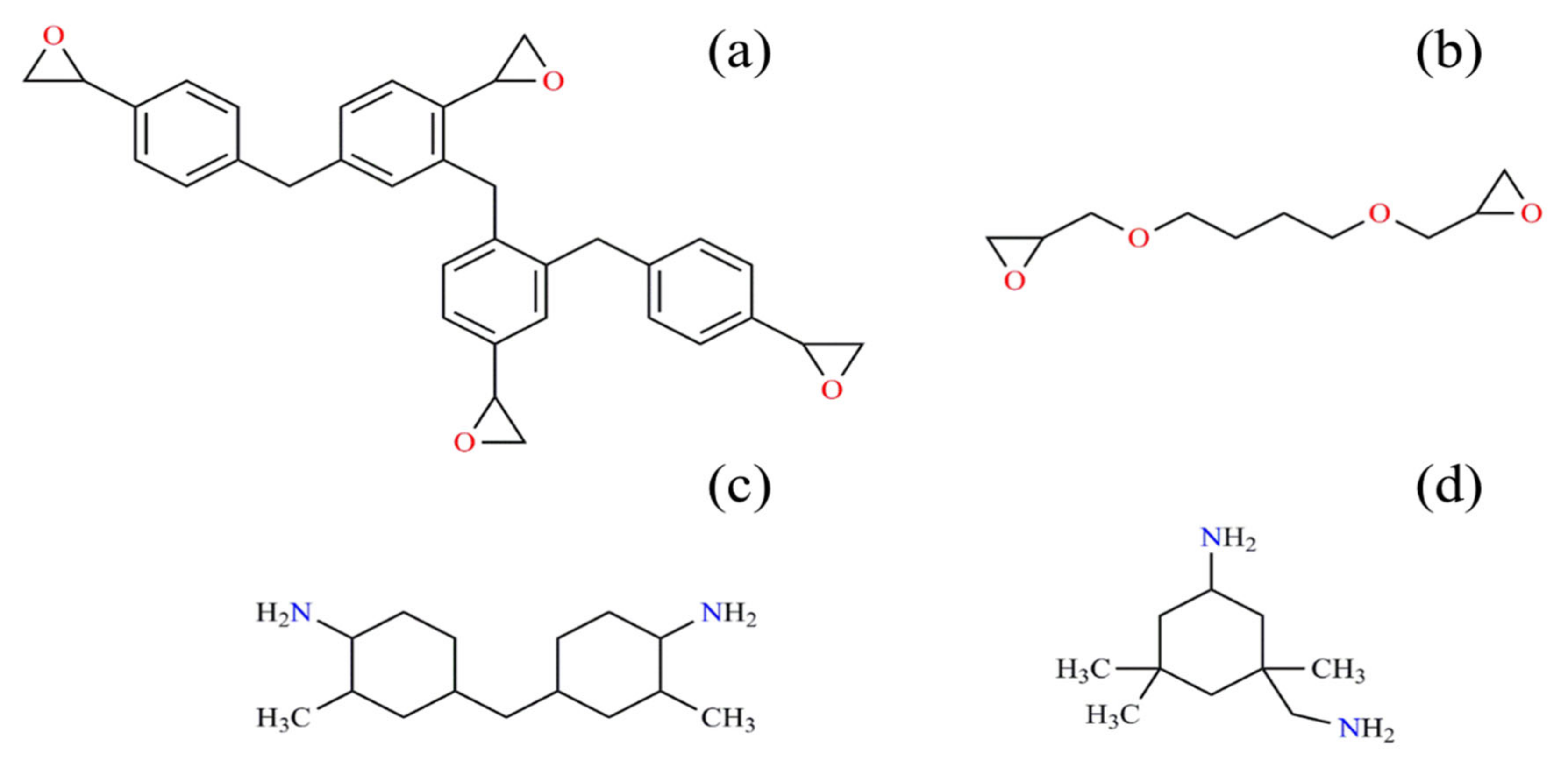
4.1. Materials
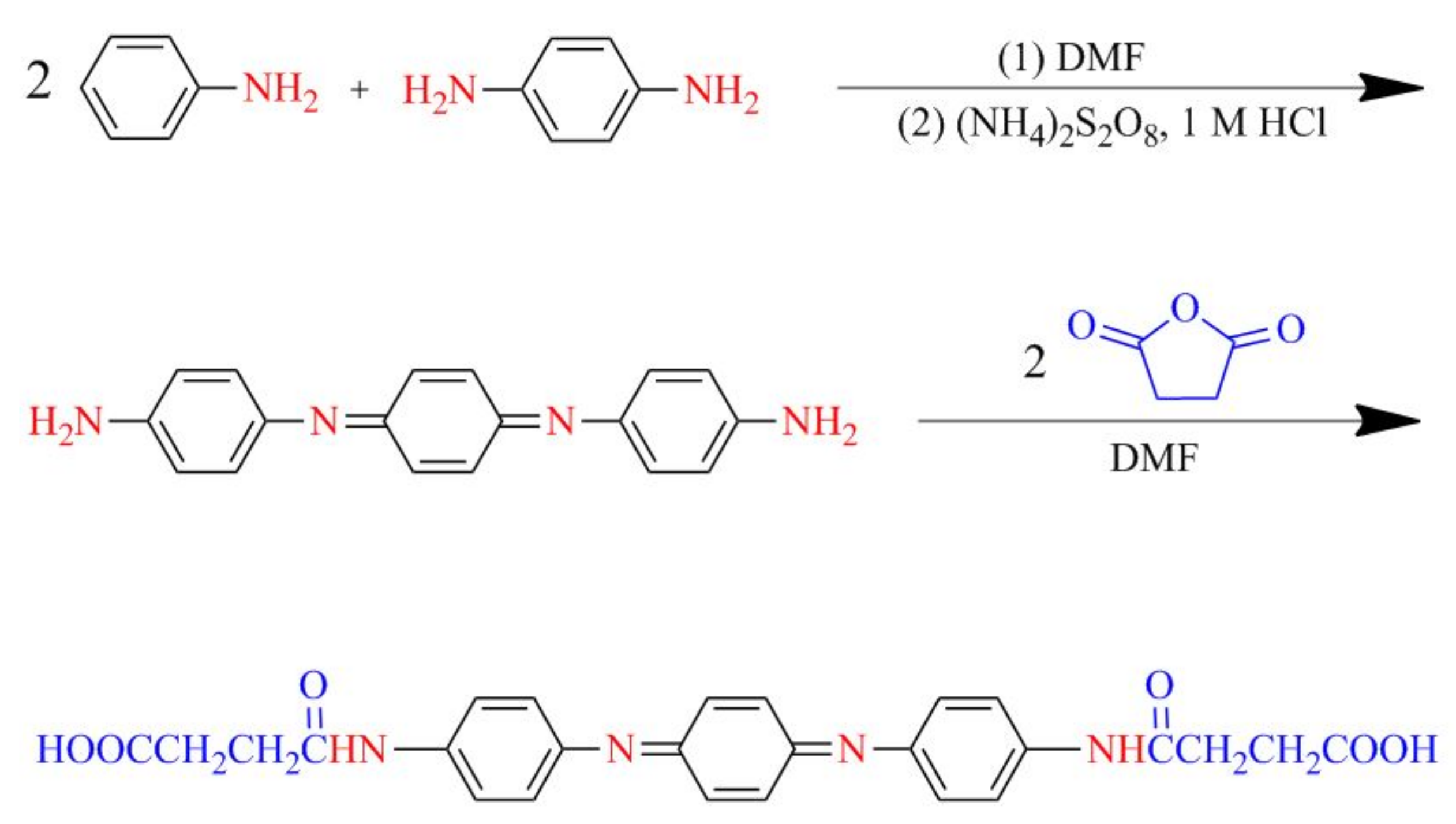
4.2. Synthesis of Aniline Oligomer
4.2.1. Carboxyl-Capped Aniline Trimer (CAT)
4.2.2. Carboxyl-Capped Aniline Pentamer (CAP)
4.3. Preparation of Surface Modified HNTs
4.3.1. Surface Functionalization of HNTs with APTES (A-HNT)
4.3.2. Surface Modification of A-HNTs with Aniline Oligomers (CAT-HNT and CAP-HNT)
4.4. Encapsulation of Corrosion Inhibitor in Oligoaniline-Modified HNTs
4.5. Preparation of Oligoaniline-Modified HNT/Epoxy Nanocomposites
4.6. Characterization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Mapping Analysis
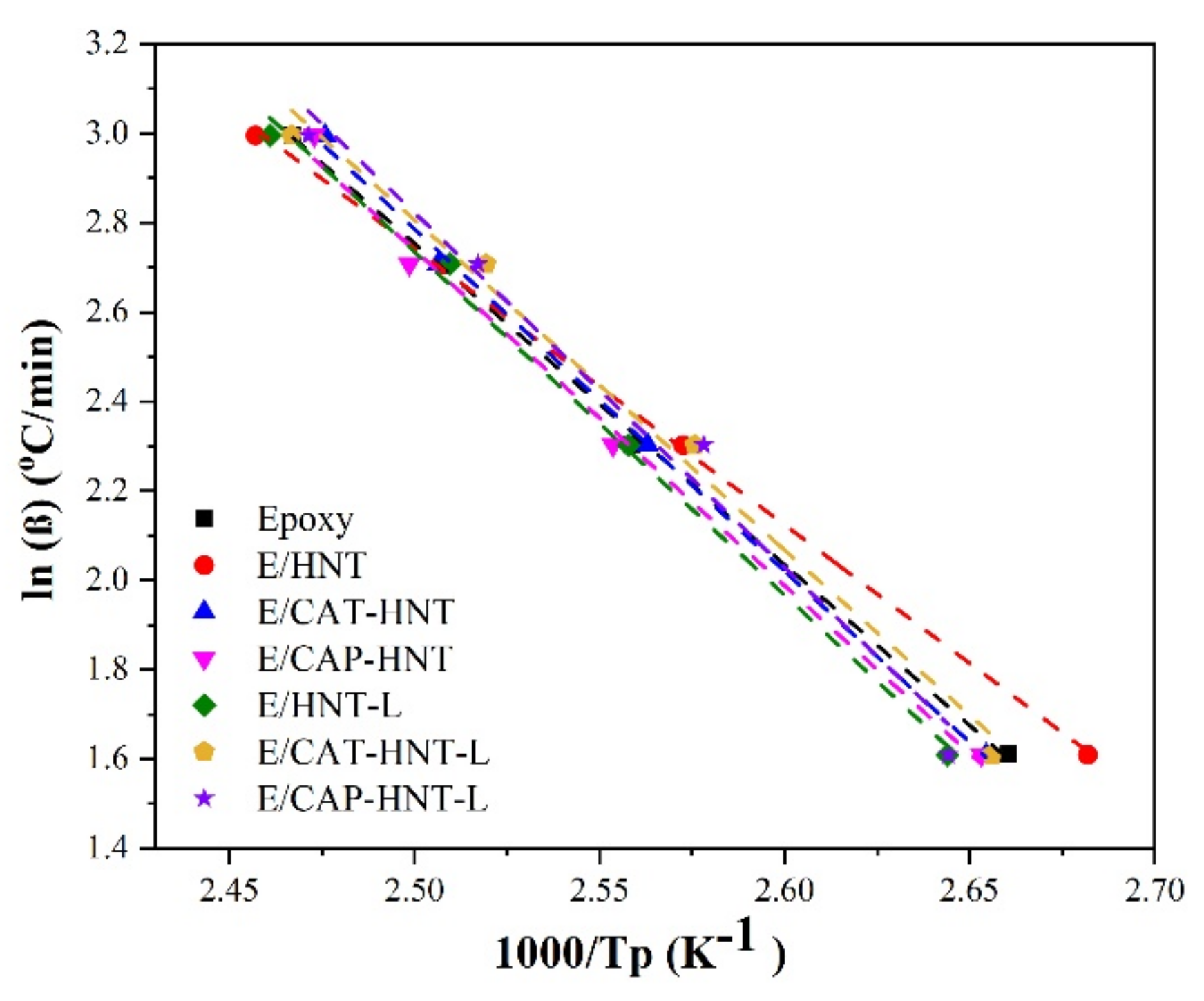
Appendix B. Isoconversional Kinetic Methods
Appendix B.1. Friedman Model
Appendix B.2. KAS Method
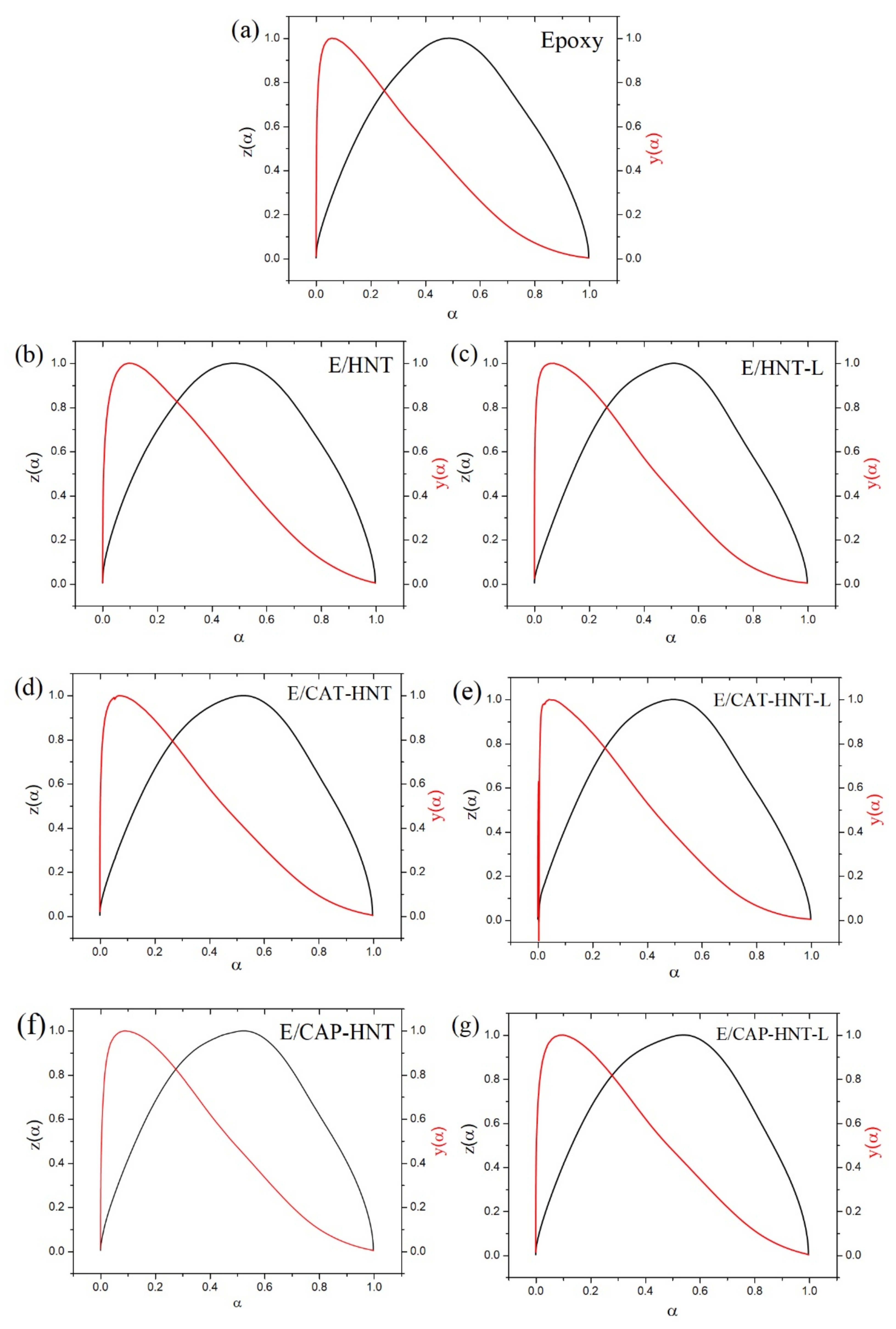
Appendix C. Determination of Curing Reaction Model
Appendix C.1. Friedman Model
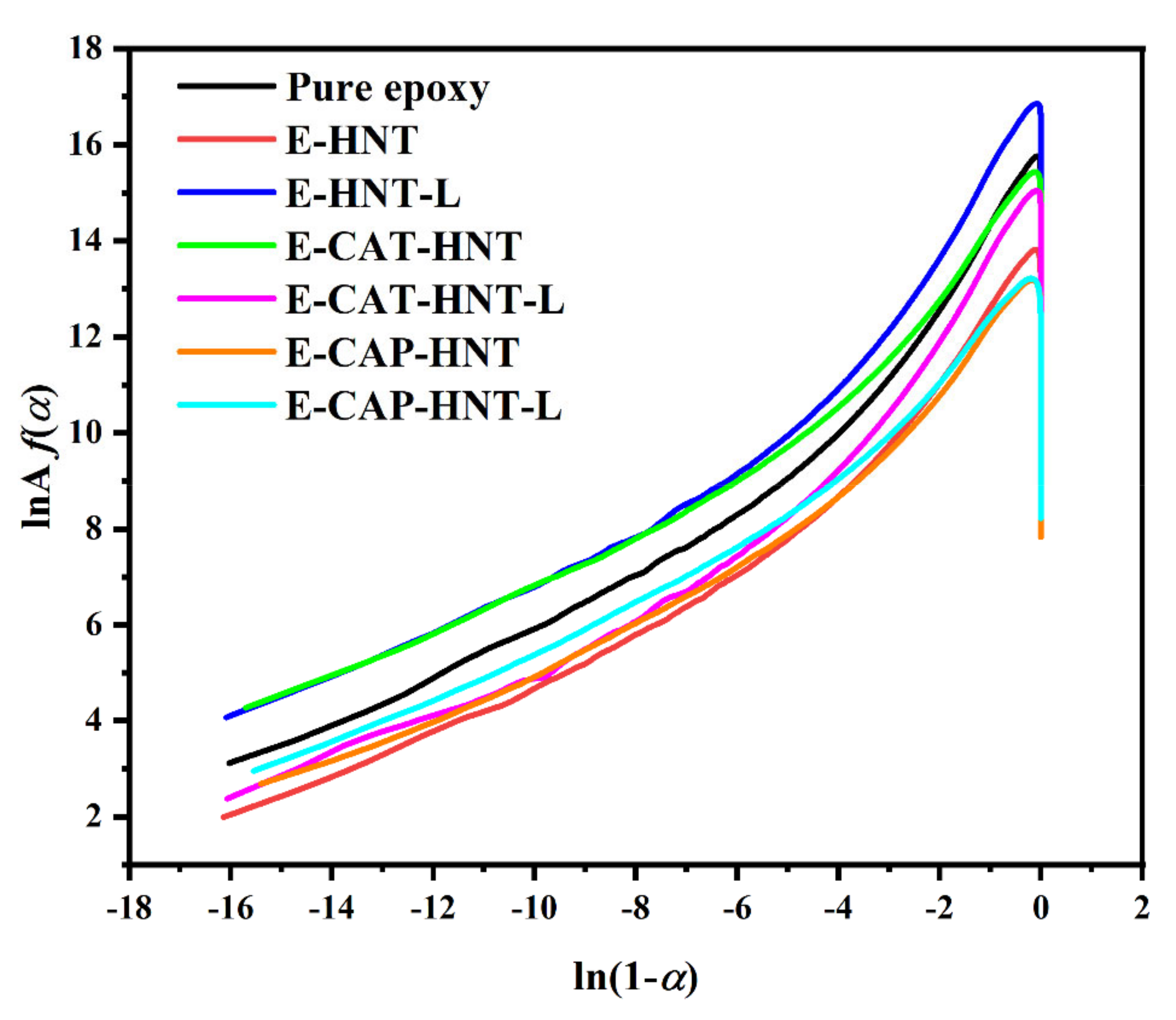
Appendix C.2. Malek Method
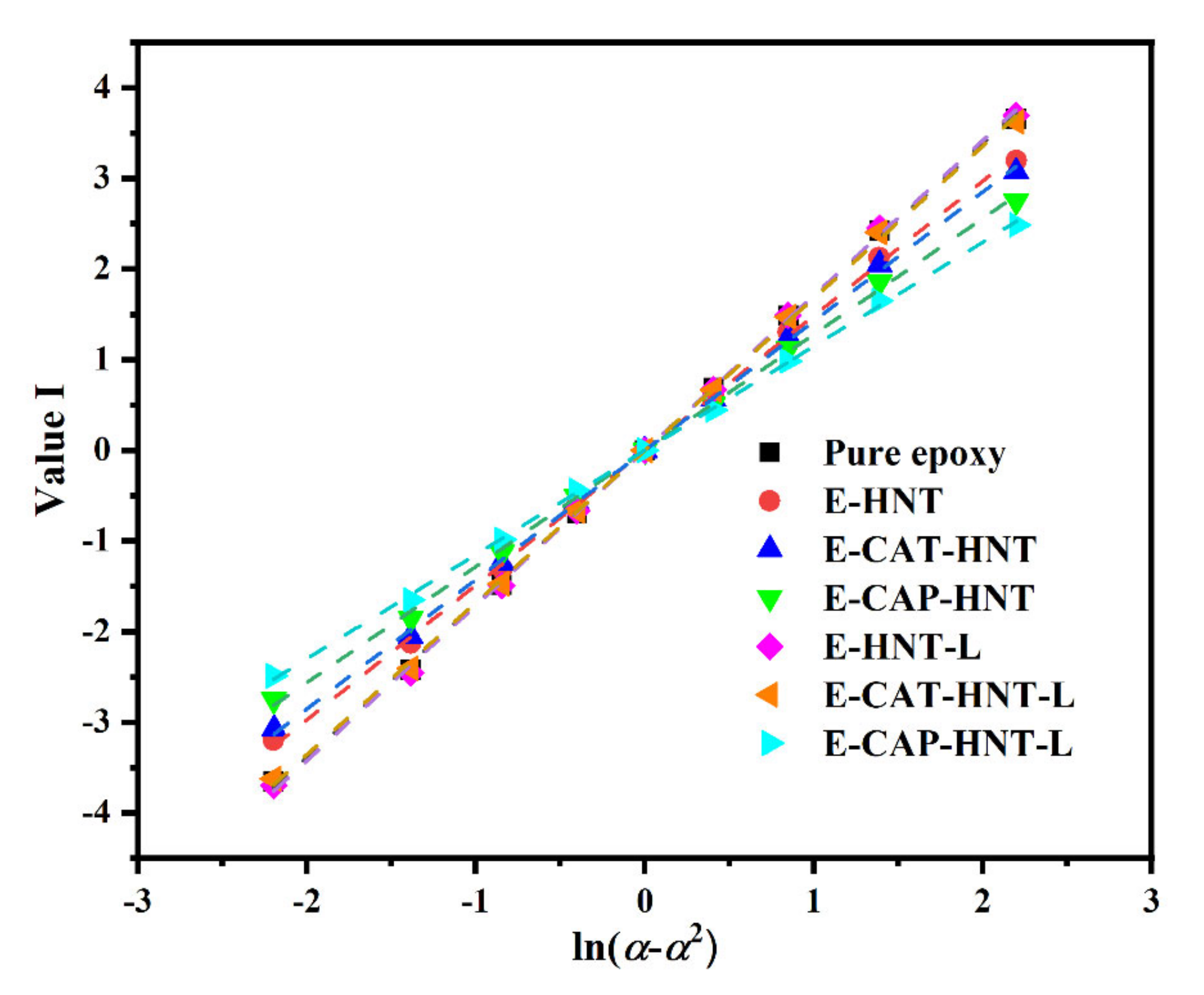
Appendix D. Determination of the Degree of Reaction

References
- Jouyandeh, M.; Tikhani, F.; Shabanian, M.; Movahedi, F.; Moghari, S.; Akbari, V.; Gabrion, X.; Laheurte, P.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R. Synthesis, characterization, and high potential of 3D metal–organic framework (MOF) nanoparticles for curing with epoxy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 829, 154547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, Z.; Jouyandeh, M.; Ali, J.A.; Ganjali, M.R.; Aghazadeh, M.; Maadani, M.; Rallini, M.; Luzi, F.; Torre, L.; Puglia, D.; et al. Cure Index for labeling curing potential of epoxy/LDH nanocomposites: A case study on nitrate anion intercalated Ni-Al-LDH. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, F.; Jouyandeh, M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Vahabi, H.; Habibzadeh, S.; Formela, K.; Saeb, M.R. Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)/Epoxy Coatings: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Paran, S.M.R.; Khadem, S.S.M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Akbari, V.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R. Nonisothermal cure kinetics of epoxy/MnxFe3-xO4 nanocomposites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Yarahmadi, E.; Didehban, K.; Ghiyasi, S.; Paran, S.M.R.; Puglia, D.; Ali, J.A.; Jannesari, A.; Saeb, M.R.; Ranjbar, Z.; et al. Cure kinetics of epoxy/graphene oxide (GO) nanocomposites: Effect of starch functionalization of GO nanosheets. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Ali, J.A.; Aghazadeh, M.; Paran, S.M.R.; Naderi, G.; Saeb, M.R.; Thomas, S. Curing epoxy with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) surface-functionalized ZnxFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, S.; Moini Jazani, O.; Molla-Abbasi, P.; Jouyandeh, M.; Saeb, M.R. Thin films of epoxy adhesives containing recycled polymers and graphene oxide nanoflakes for metal/polymer composite interface. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Moini Jazani, O.; Navarchian, A.; Saeb, M. Epoxy coatings physically cured with hydroxyl-contained silica nanospheres and halloysite nanotubes. Prog. Color Colorants Coat. 2018, 11, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Ali, J.A.; Aghazadeh, M.; Stadler, F.J.; Saeb, M.R. Curing epoxy with electrochemically synthesized NixFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Zarrintaj, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Ali, J.A.; Karimzadeh, I.; Aghazadeh, M.; Ghaffari, M.; Saeb, M.R. Curing epoxy with electrochemically synthesized GdxFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Rahmati, N.; Movahedifar, E.; Hadavand, B.S.; Karami, Z.; Ghaffari, M.; Taheri, P.; Bakhshandeh, E.; Vahabi, H.; Ganjali, M.R.; et al. Properties of nano-Fe3O4 incorporated epoxy coatings from Cure Index perspective. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 133, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzad, S.; Maryam, J.; Ali, T.; Mohsen, T.; Sajjad, H.; Yongcan, J.; Huining, X.; Payam, Z.; Reza, S.M. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane/epoxy coatings: A review. Surf. Innov. 2021, 9, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Karami, Z.; Ali, J.A.; Karimzadeh, I.; Aghazadeh, M.; Laoutid, F.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R.; Ganjali, M.R.; Dubois, P. Curing epoxy with polyethylene glycol (PEG) surface-functionalized NixFe3-xO4magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ali, J.A.; Aghazadeh, M.; Formela, K.; Saeb, M.R.; Ranjbar, Z.; Ganjali, M.R. Curing epoxy with electrochemically synthesized ZnxFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhani, F.; Moghari, S.; Jouyandeh, M.; Laoutid, F.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R.; Dubois, P. Curing Kinetics and Thermal Stability of Epoxy Composites Containing Newly Obtained Nano-Scale Aluminum Hypophosphite (AlPO2). Polymers 2020, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karami, Z.; Jouyandeh, M.; Hamad, S.M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Aghazadeh, M.; Torre, L.; Puglia, D.; Saeb, M.R. Curing epoxy with Mg-Al LDH nanoplatelets intercalated with carbonate ion. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaei, A.; Nasirpouri, F. Epoxy/polyaniline–ZnO nanorods hybrid nanocomposite coatings: Synthesis, characterization and corrosion protection performance of conducting paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour-Ali, S.; Dehghanian, C.; Kosari, A. Corrosion protection of the reinforcing steels in chloride-laden concrete environment through epoxy/polyaniline–camphorsulfonate nanocomposite coating. Corros. Sci. 2015, 90, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrintaj, P.; Yazdi, M.K.; Jouyandeh, M.; Saeb, M.R. Chapter 7—PANI-Based Nanostructures. In Fundamentals and Emerging Applications of Polyaniline; Mozafari, M., Chauhan, N.P.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Qiu, T.; Guo, L.; Ye, J.; He, L.; Li, X. Preparation of pH responsive smart nanocontainer via inclusion of inhibitor in graphene/halloysite nanotubes and its application in intelligent anticorrosion protection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, T.; Chen, B.; Ma, X.; Jiang, D.; Luo, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y. Epoxy composite coating with excellent anticorrosion and self-healing performances based on multifunctional zeolitic imidazolate framework derived nanocontainers. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahsepar, M.; Mohebbi, F.; Hayatdavoudi, H. Synthesis and characterization of inhibitor-loaded silica nanospheres for active corrosion protection of carbon steel substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 709, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahidah, K.A.; Kakooei, S.; CheIsmail, M.; Bothi Raja, P. Halloysite nanotubes as nanocontainer for smart coating application: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 111, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paran, S.M.R.; Vahabi, H.; Jouyandeh, M.; Ducos, F.; Formela, K.; Saeb, M.R. Thermal decomposition kinetics of dynamically vulcanized polyamide 6–acrylonitrile butadiene rubber–halloysite nanotube nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, V.; Jouyandeh, M.; Paran, S.M.R.; Ganjali, M.R.; Abdollahi, H.; Vahabi, H.; Ahmadi, Z.; Formela, K.; Esmaeili, A.; Mohaddespour, A.; et al. Effect of Surface Treatment of Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs) on the Kinetics of Epoxy Resin Cure with Amines. Polymers 2020, 12, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vahedi, V.; Pasbakhsh, P. Instrumented impact properties and fracture behaviour of epoxy/modified halloysite nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2014, 39, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, G.; Rathnakar, G.; Santhosh, N.; Chennakeshava, R.; Hashmi, M.A. Enhancement of mechanical properties of epoxy/halloysite nanotube (HNT) nanocomposites. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lvov, Y.; Panchal, A.; Fu, Y.; Fakhrullin, R.; Kryuchkova, M.; Batasheva, S.; Stavitskaya, A.; Glotov, A.; Vinokurov, V. Interfacial Self-Assembly in Halloysite Nanotube Composites. Langmuir 2019, 35, 8646–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodke, S.A.; Sonawane, S.H.; Bhanvase, B.A.; Mishra, S.; Joshi, K.S.; Potoroko, I. Functionalization, Uptake and Release Studies of Active Molecules Using Halloysite Nanocontainers. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. E 2019, 100, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.M.; Shchukin, D.G.; Möhwald, H.; Price, R.R. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Controlled Release of Protective Agents. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Danilushkina, A.A.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Rozhina, E.V.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Halloysite Nanotubes: Controlled Access and Release by Smart Gates. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y. Clay nanotubes for corrosion inhibitor encapsulation: Release control with end stoppers. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suner, S.S.; Demirci, S.; Yetiskin, B.; Fakhrullin, R.; Naumenko, E.; Okay, O.; Ayyala, R.S.; Sahiner, N. Cryogel composites based on hyaluronic acid and halloysite nanotubes as scaffold for tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Parisi, F.; Milioto, S.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lazzara, G. Core/Shell Gel Beads with Embedded Halloysite Nanotubes for Controlled Drug Release. Coatings 2019, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahidah, K.A.; Kakooei, S.; Kermanioryani, M.; Mohebbi, H.; Ismail, M.C.; Raja, P.B. Benzimidazole-loaded halloysite nanotube as a smart coating application. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Innov. 2017, 7, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, P.P.; Hany El-Gawady, Y.M.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.S.A. Halloysite Nanotube as Multifunctional Component in Epoxy Protective Coating. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 11186–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinzadeh, A.R.; Javadpour, S. Formulation of a smart nanocomposite coating with pH-responsive loaded halloysite and investigation of its anticorrosion behaviour. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2020, 43, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Song, H.; Feng, X.; Run, M.; Cui, H.; Wu, L.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z. Liquid Crystalline Phase Behavior and Sol–Gel Transition in Aqueous Halloysite Nanotube Dispersions. Langmuir 2013, 29, 12358–12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, V.; Naja, F.; Vahabi, H.; Jouyandeh, M.; Badawi, M. Surface chemistry of halloysite nanotubes controls the curability of low filled epoxy nanocomposites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 135, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Jazani, O.M.; Navarchian, A.H.; Shabanian, M.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R. Bushy-surface hybrid nanoparticles for developing epoxy superadhesives. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 479, 1148–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xu, W.; Tang, R.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q. pH-Responsive nanovalves based on encapsulated halloysite for the controlled release of a corrosion inhibitor in epoxy coating. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 90609–90620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, D.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Wang, L. POSS-tetraaniline modified graphene for active corrosion protection of epoxy-based organic coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Faul, C.F.J.J. Aniline oligomers—Architecture, function and new opportunities for nanostructured materials. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Xue, Z.; Guo, D. Spectroscopic and electrical characterization of some aniline oligomers and polyaniline. Synth. Met. 1986, 16, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taka, Z.I.; Mustafa, M.K.; Asman, S.; Sekak, K.A.; Muhammada, J. Preparation of Aniline Dimer-COOH Modified Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles by Ultrasonic Dispersion Method. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Jing, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, F. Infrared Spectra of Soluble Polyaniline. Synth. Met. 1988, 24, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulszewicz-Bajer, I.; Różalska, I.; Kuryłek, M. Synthesis and spectroscopic properties of aniline tetramers. Comparative studies. New J. Chem. 2004, 28, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Seidi, F.; Xiao, H.; Saeb, M.R. Nonisothermal Cure Kinetics of Epoxy/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Functionalized Superparamagnetic Nano-Fe3O4 Composites: Effect of Zn and Mn Doping. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossier, J.N.S.; Pavic, A.; Vojnovic, S.; Stringer, T.; Bättig, S.; Smith, G.S.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Zobi, F. Antiplasmodial Activity and In Vivo Bio-Distribution of Chloroquine Molecules Released with a 4-(4-Ethynylphenyl)-Triazole Moiety from Organometallo-Cobalamins. Molecules 2019, 24, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Tikhani, F.; Hampp, N.; Akbarzadeh Yazdi, D.; Zarrintaj, P.; Reza Ganjali, M.; Reza Saeb, M. Highly curable self-healing vitrimer-like cellulose-modified halloysite nanotube/epoxy nanocomposite coatings. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, Z.; Jia, Q.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Kou, K. Fabrication and characterization of surface modified HMX@ PANI core-shell composites with enhanced thermal properties and desensitization via in situ polymerization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 515, 146042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Das, S.; Ghosh, C.; Maity, A.; Pradhan, M. Halloysite nanotubes capturing isotope selective atmospheric CO2. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, E.M.; Humelnicu, I.V.; Ghirvu, C.I. Some aspects of 8-hydroxyquinoline in solvents. Acta Chem. Iasi 2009, 17, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.; Ma, R. Facile synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles grown on halloysite nanotubes for enhanced photocatalytic properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ali, J.A.; Akbari, V.; Aghazadeh, M.; Paran, S.M.R.; Naderi, G.; Saeb, M.R.; Ranjbar, Z.; Ganjali, M.R. Curing epoxy with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) surface-functionalized MnxFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, F.; Jouyandeh, M.; Akbari, V.; Paran, S.M.R.; Livi, S.; Ducos, F.; Vahabi, H.; Ganjali, M.R.; Saeb, M.R. Super-crosslinked ionic liquid-intercalated montmorillonite/epoxy nanocomposites: Cure kinetics, viscoelastic behavior and thermal degradation mechanism. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 1940–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonlert-Uthai, T.; Samthong, C.; Somwangthanaroj, A. Synthesis, Thermal Properties and Curing Kinetics of Hyperbranched BPA/PEG Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2019, 11, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tikhani, F.; Jouyandeh, M.; Jafari, S.H.; Chabokrow, S.; Ghahari, M.; Gharanjig, K.; Klein, F.; Hampp, N.; Ganjali, M.R.; Formela, K.; et al. Cure Index demonstrates curing of epoxy composites containing silica nanoparticles of variable morphology and porosity. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 135, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyranpourkhameneh, F.; Alahyarizadeh, G.; Minuchehr, H. The Thermo-Mechanical Properties estimation of Fullerene-Reinforced Resin Epoxy Composites by Molecular Dynamics Simulation- A Comparative Study. Polymer 2016, 88, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Ali, J.A.; Aghazadeh, M.; Stadler, F.J.; Saeb, M.R. Curing epoxy with electrochemically synthesized MnxFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Ali, J.A.; Akbari, V.; Karami, Z.; Aghazadeh, M.; Zarrintaj, P.; Saeb, M.R. Curing epoxy with polyethylene glycol (PEG) surface-functionalized GdxFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 137, 105283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, Z.; Paran, S.M.R.; Vijayan, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Jouyandeh, M.; Esmaeili, A.; Habibzadeh, S.; Stadler, F.J.; Saeb, M.R. A Comparative Study on Cure Kinetics of Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH)/Epoxy Nanocomposites. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Karami, Z.; Hamad, S.M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Akbari, V.; Vahabi, H.; Kim, S.-J.; Zarrintaj, P.; Saeb, M.R. Nonisothermal cure kinetics of epoxy/ZnxFe3-xO4 nanocomposites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Shabanian, M.; Khaleghi, M.; Paran, S.M.R.; Ghiyasi, S.; Vahabi, H.; Formela, K.; Puglia, D.; Saeb, M.R. Acid-aided epoxy-amine curing reaction as reflected in epoxy/Fe3O4 nanocomposites: Chemistry, mechanism, and fracture behavior. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 125, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, H.; Ismail, H.; Rashid, A.A. Effects of partial replacement of commercial fillers by recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate) powder on the properties of natural rubber composites. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2012, 18, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Finne-Wistrand, A.; Albertsson, A.-C. Molecular Architecture of Electroactive and Biodegradable Copolymers Composed of Polylactide and Carboxyl-Capped Aniline Trimer. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Huang, L.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y.; Jing, X. A new oxidation state of aniline pentamer observed in water-soluble electroactive oligoaniline-chitosan polymer. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchukin, D.G.; Lamaka, S.V.; Yasakau, K.A.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Mohwald, H. Active Anticorrosion Coatings with Halloysite Nanocontainers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Designation | β (°C/min) | Tonset (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tendset (°C) | ΔT (°C) | ΔH∞ (J/g) | ΔT* (°C) | ΔH*∞ (J/g) | CI | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 5 | 42.1 | 102.7 | 199.9 | 157.9 | 406.0 | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | 55.3 | 117.6 | 209.8 | 154.5 | 388.2 | - | - | - | - | |
| 15 | 57.3 | 125.6 | 218.5 | 161.3 | 402.9 | - | - | - | - | |
| 20 | 56.3 | 132.2 | 246.0 | 189.7 | 471.7 | - | - | - | - | |
| E/HNT | 5 | 46.1 | 99.7 | 190.8 | 144.8 | 348.3 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.79 | Poor |
| 10 | 50.4 | 115.6 | 199.9 | 149.5 | 365.5 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.91 | Poor | |
| 15 | 56.7 | 125.6 | 215.5 | 158.8 | 395.2 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.97 | Poor | |
| 20 | 59.2 | 133.8 | 231.5 | 172.4 | 376.6 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.73 | Poor | |
| E/CAT-HNT | 5 | 45.9 | 103.6 | 177.4 | 131.5 | 437.9 | 0.83 | 1.08 | 0.90 | Excellent |
| 10 | 54.3 | 117.0 | 208.7 | 154.4 | 425.5 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 1.10 | Excellent | |
| 15 | 59.2 | 125.8 | 207.9 | 148.8 | 400.4 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.92 | Poor | |
| 20 | 68.2 | 130.7 | 215.8 | 147.7 | 373.3 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.62 | Poor | |
| E/CAP-HNT | 5 | 47.7 | 103.8 | 179.9 | 132.3 | 476.6 | 0.84 | 1.17 | 0.98 | Excellent |
| 10 | 51.4 | 118.4 | 195.6 | 144.2 | 418.7 | 0.93 | 1.08 | 1.01 | Excellent | |
| 15 | 61.7 | 127.1 | 227.0 | 165.3 | 397.6 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 1.01 | Poor | |
| 20 | 65.5 | 131.2 | 230.9 | 165.4 | 415.8 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.77 | Poor | |
| E/HNT-L | 5 | 40.8 | 105.1 | 201.4 | 160.5 | 492.1 | 1.02 | 1.21 | 1.23 | Good |
| 10 | 52.1 | 117.8 | 217.7 | 165.6 | 500.2 | 1.07 | 1.29 | 1.38 | Good | |
| 15 | 53.2 | 125.3 | 231.2 | 178.0 | 448.5 | 1.10 | 1.11 | 1.23 | Good | |
| 20 | 59.8 | 133.2 | 222.8 | 163.0 | 379.3 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.69 | Poor | |
| E/CAT-HNT-L | 5 | 33.1 | 103.4 | 208.9 | 175.9 | 526.1 | 1.11 | 1.30 | 1.44 | Good |
| 10 | 39.44 | 115.1 | 233.3 | 193.9 | 454.6 | 1.26 | 1.17 | 1.47 | Good | |
| 15 | 41.5 | 123.8 | 244.6 | 203.0 | 578.2 | 1.26 | 1.44 | 1.81 | Good | |
| 20 | 50.5 | 132.2 | 273.9 | 223.4 | 426.5 | 1.18 | 0.90 | 1.07 | Poor | |
| E/CAP-HNT-L | 5 | 50.2 | 105.0 | 169.3 | 119.1 | 409.6 | 0.76 | 1.01 | 0.76 | Excellent |
| 10 | 54.3 | 114.7 | 186.8 | 132.5 | 395.2 | 0.86 | 1.02 | 0.88 | Excellent | |
| 15 | 61.4 | 124.1 | 214.7 | 153.3 | 451.3 | 0.95 | 1.12 | 1.07 | Excellent | |
| 20 | 69.2 | 131.5 | 219.6 | 150.4 | 396.6 | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.67 | Poor |
| Designation | β (°C/min) | αp∞ | αm | αp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 5 | 0.449 | 0.058 | 0.484 |
| 10 | 0.498 | 0.080 | 0.489 | |
| 15 | 0.546 | 0.080 | 0.501 | |
| 20 | 0.488 | 0.087 | 0.490 | |
| E/HNT | 5 | 0.440 | 0.096 | 0.480 |
| 10 | 0.586 | 0.108 | 0.504 | |
| 15 | 0.576 | 0.135 | 0.501 | |
| 20 | 0.581 | 0.152 | 0.502 | |
| E/CAT-HNT | 5 | 0.488 | 0.071 | 0.526 |
| 10 | 0.414 | 0.060 | 0.500 | |
| 15 | 0.510 | 0.104 | 0.518 | |
| 20 | 0.454 | 0.107 | 0.511 | |
| E/CAP-HNT | 5 | 0.460 | 0.091 | 0.525 |
| 10 | 0.554 | 0.102 | 0.534 | |
| 15 | 0.394 | 0.091 | 0.488 | |
| 20 | 0.398 | 0.101 | 0.493 | |
| E/HNT-L | 5 | 0.470 | 0.072 | 0.512 |
| 10 | 0.460 | 0.061 | 0.491 | |
| 15 | 0.483 | 0.056 | 0.492 | |
| 20 | 0.599 | 0.104 | 0.501 | |
| E/CAT-HNT-L | 5 | 0.452 | 0.041 | 0.497 |
| 10 | 0.425 | 0.065 | 0.484 | |
| 15 | 0.467 | 0.093 | 0.501 | |
| 20 | 0.358 | 0.089 | 0.483 | |
| E/CAP-HNT-L | 5 | 0.505 | 0.098 | 0.541 |
| 10 | 0.496 | 0.036 | 0.552 | |
| 15 | 0.392 | 0.081 | 0.519 | |
| 20 | 0.403 | 0.100 | 0.513 |
| Designation | β (°C/min) | Ēa (kJ/mol) | ln A (s−1) | Mean Value (s−1) | m | Mean Value | n | Mean Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 5 | 55.01 | 16.18 | 16.22 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 1.79 | 1.79 |
| 10 | 16.12 | 0.07 | 1.73 | |||||
| 15 | 16.27 | 0.12 | 1.74 | |||||
| 20 | 16.30 | 0.17 | 1.90 | |||||
| E/HNT | 5 | 48.99 | 14.30 | 14.40 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 1.61 | 1.64 |
| 10 | 14.36 | 0.14 | 1.57 | |||||
| 15 | 14.46 | 0.20 | 1.66 | |||||
| 20 | 14.48 | 0.24 | 1.70 | |||||
| E/CAT-HNT | 5 | 54.06 | 15.98 | 16.03 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 1.58 | 1.66 |
| 10 | 15.94 | 0.12 | 1.74 | |||||
| 15 | 16.07 | 0.21 | 1.67 | |||||
| 20 | 16.11 | 0.21 | 1.67 | |||||
| E/CAP-HNT | 5 | 47.67 | 13.94 | 14.03 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 1.54 | 1.62 |
| 10 | 14.09 | 0.28 | 1.55 | |||||
| 15 | 13.98 | 0.21 | 1.70 | |||||
| 20 | 14.12 | 0.25 | 1.69 | |||||
| E/HNT-L | 5 | 58.64 | 17.49 | 17.39 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 1.89 | 1.86 |
| 10 | 17.35 | 0.10 | 1.88 | |||||
| 15 | 17.37 | 0.09 | 1.89 | |||||
| 20 | 17.36 | 0.14 | 1.77 | |||||
| E/CAT-HNT-L | 5 | 53.10 | 15.67 | 15.74 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 1.86 | 1.89 |
| 10 | 15.71 | 0.13 | 1.88 | |||||
| 15 | 15.85 | 0.24 | 1.87 | |||||
| 20 | 15.72 | 0.20 | 1.93 | |||||
| E/CAP-HNT-L | 5 | 47.60 | 13.97 | 14.12 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 1.43 | 1.51 |
| 10 | 14.13 | 0.25 | 1.39 | |||||
| 15 | 14.18 | 0.28 | 1.62 | |||||
| 20 | 14.20 | 0.30 | 1.60 |
| Designation | β (°C/min) | Ēa (kJ/mol) | ln A (s−1) | Mean Values (s−1) | m | Mean Values | n | Mean Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 5 | 54.67 | 16.08 | 16.11 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 1.79 | 1.79 |
| 10 | 16.01 | 0.08 | 1.73 | |||||
| 15 | 16.16 | 0.13 | 1.74 | |||||
| 20 | 16.20 | 0.17 | 1.89 | |||||
| E/HNT | 5 | 48.26 | 14.06 | 14.17 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 1.60 | 1.63 |
| 10 | 14.14 | 0.15 | 1.56 | |||||
| 15 | 14.23 | 0.21 | 1.65 | |||||
| 20 | 14.26 | 0.25 | 1.69 | |||||
| E/CAT-HNT | 5 | 52.73 | 15.56 | 15.62 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 1.57 | 1.65 |
| 10 | 15.53 | 0.14 | 1.72 | |||||
| 15 | 15.67 | 0.22 | 1.65 | |||||
| 20 | 15.72 | 0.22 | 1.65 | |||||
| E/CAP-HNT | 5 | 51.35 | 15.10 | 15.16 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 1.59 | 1.67 |
| 10 | 15.22 | 0.24 | 1.60 | |||||
| 15 | 15.09 | 0.17 | 1.75 | |||||
| 20 | 15.21 | 0.21 | 1.74 | |||||
| E/HNT-L | 5 | 57.06 | 16.99 | 16.91 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 1.87 | 1.84 |
| 10 | 16.87 | 0.11 | 1.86 | |||||
| 15 | 16.89 | 0.11 | 1.87 | |||||
| 20 | 16.90 | 0.16 | 1.75 | |||||
| E/CAT-HNT-L | 5 | 53.44 | 15.78 | 15.84 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 1.87 | 1.89 |
| 10 | 15.82 | 0.13 | 1.89 | |||||
| 15 | 15.96 | 0.23 | 1.87 | |||||
| 20 | 15.82 | 0.19 | 1.94 | |||||
| E/CAP-HNT-L | 5 | 50.24 | 14.81 | 14.93 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1.46 | 1.54 |
| 10 | 14.94 | 0.22 | 1.42 | |||||
| 15 | 14.98 | 0.25 | 1.65 | |||||
| 20 | 14.98 | 0.27 | 1.63 |
| Sample | Tg (°C) |
|---|---|
| Neat epoxy | 97.5 |
| E/HNT | 97.3 |
| E/HNT-L | 98.1 |
| E/HNT-CAT | 99.2 |
| E/HNT-CAP | 99.8 |
| E/HNT-CAT-L | 100.3 |
| E/HNT-CAP-L | 101.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moghari, S.; Jafari, S.H.; Yazdi, M.K.; Jouyandeh, M.; Hejna, A.; Zarrintaj, P.; Saeb, M.R. In-Out Surface Modification of Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs) for Excellent Cure of Epoxy: Chemistry and Kinetics Modeling. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113078
Moghari S, Jafari SH, Yazdi MK, Jouyandeh M, Hejna A, Zarrintaj P, Saeb MR. In-Out Surface Modification of Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs) for Excellent Cure of Epoxy: Chemistry and Kinetics Modeling. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113078
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoghari, Shahab, Seyed Hassan Jafari, Mohsen Khodadadi Yazdi, Maryam Jouyandeh, Aleksander Hejna, Payam Zarrintaj, and Mohammad Reza Saeb. 2021. "In-Out Surface Modification of Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs) for Excellent Cure of Epoxy: Chemistry and Kinetics Modeling" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113078
APA StyleMoghari, S., Jafari, S. H., Yazdi, M. K., Jouyandeh, M., Hejna, A., Zarrintaj, P., & Saeb, M. R. (2021). In-Out Surface Modification of Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs) for Excellent Cure of Epoxy: Chemistry and Kinetics Modeling. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113078











