Construction of a Nano-Controlled Release Methotrexate Delivery System for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Local Percutaneous Administration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Animals
2.2. Materials
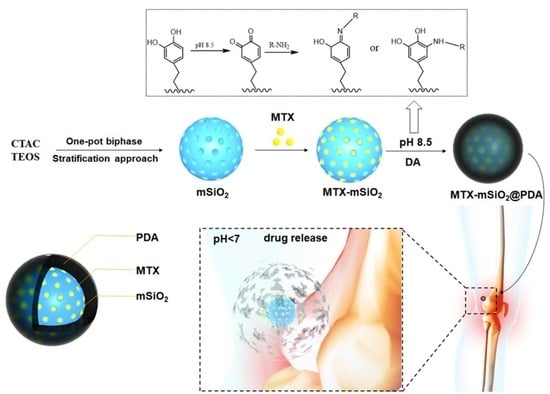
2.3. Synthesis of MTX-mSiO2@PDA
2.3.1. Loading of MTX into mSiO2
2.3.2. Construction of MTX-mSiO2@PDA
2.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Analysis of Cellular Uptake
2.5. In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity
2.6. Release Behaviors of MTX-mSiO2 and MTX-mSiO2@PDA
2.7. In Vitro Percutaneous Experiment
2.8. In Vivo Pharmacodynamics Study
2.8.1. Establishment of the CIA Model
2.8.2. In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Nanoparticles
3.2. Analysis of Cellular Uptake
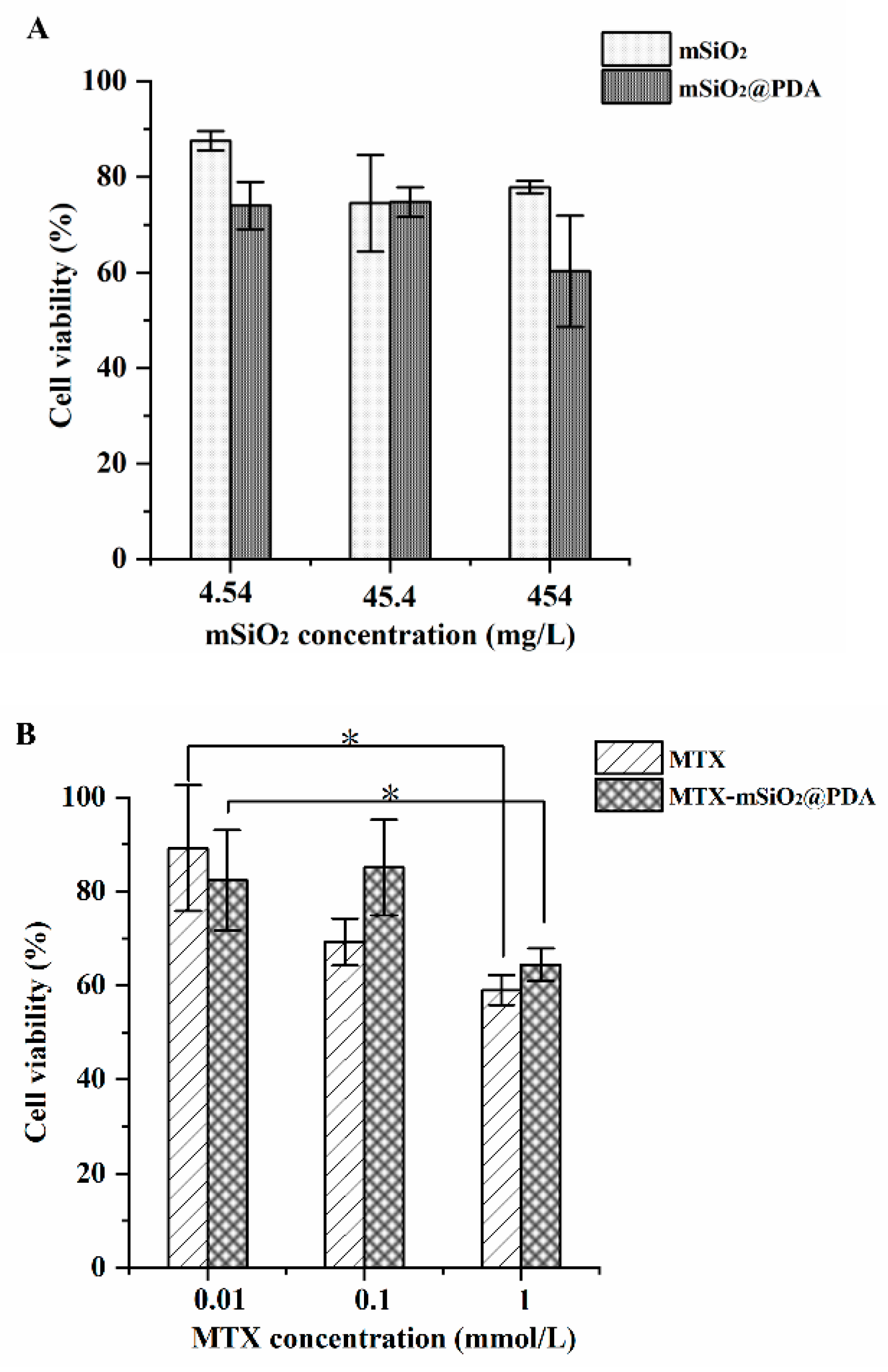
3.3. In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity
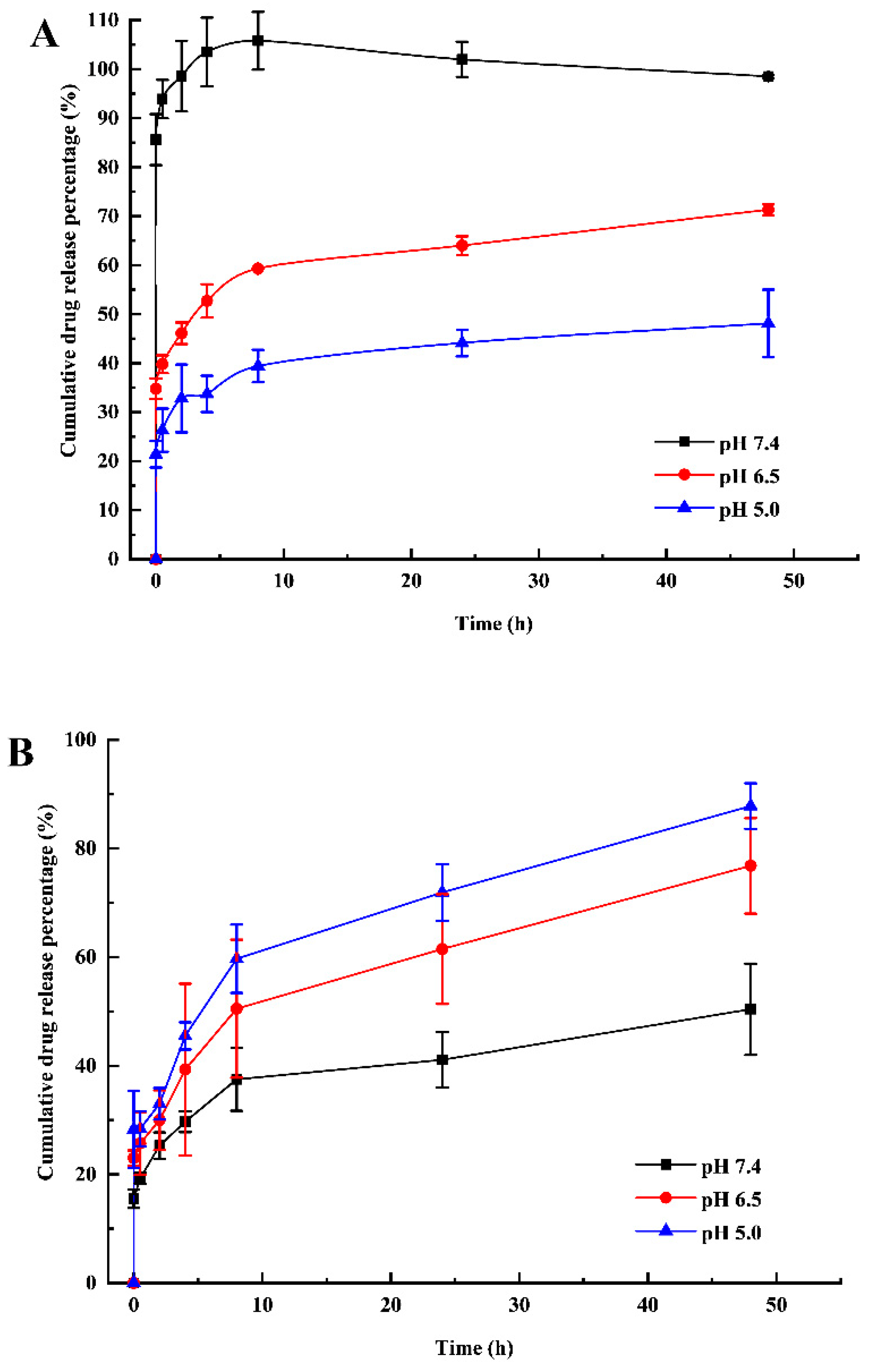
3.4. pH-Sensitive Drug Release
3.5. Local Percutaneous Administration
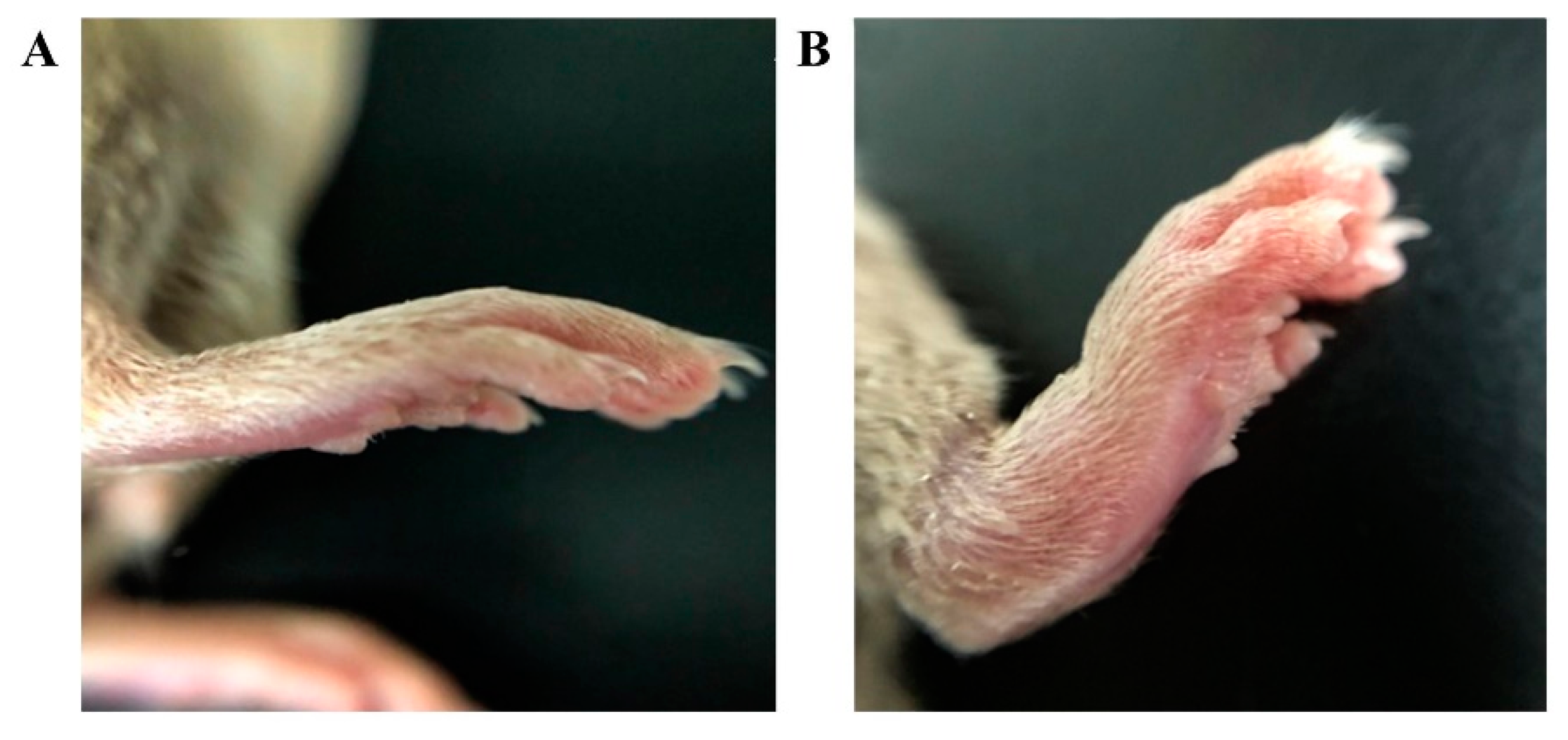
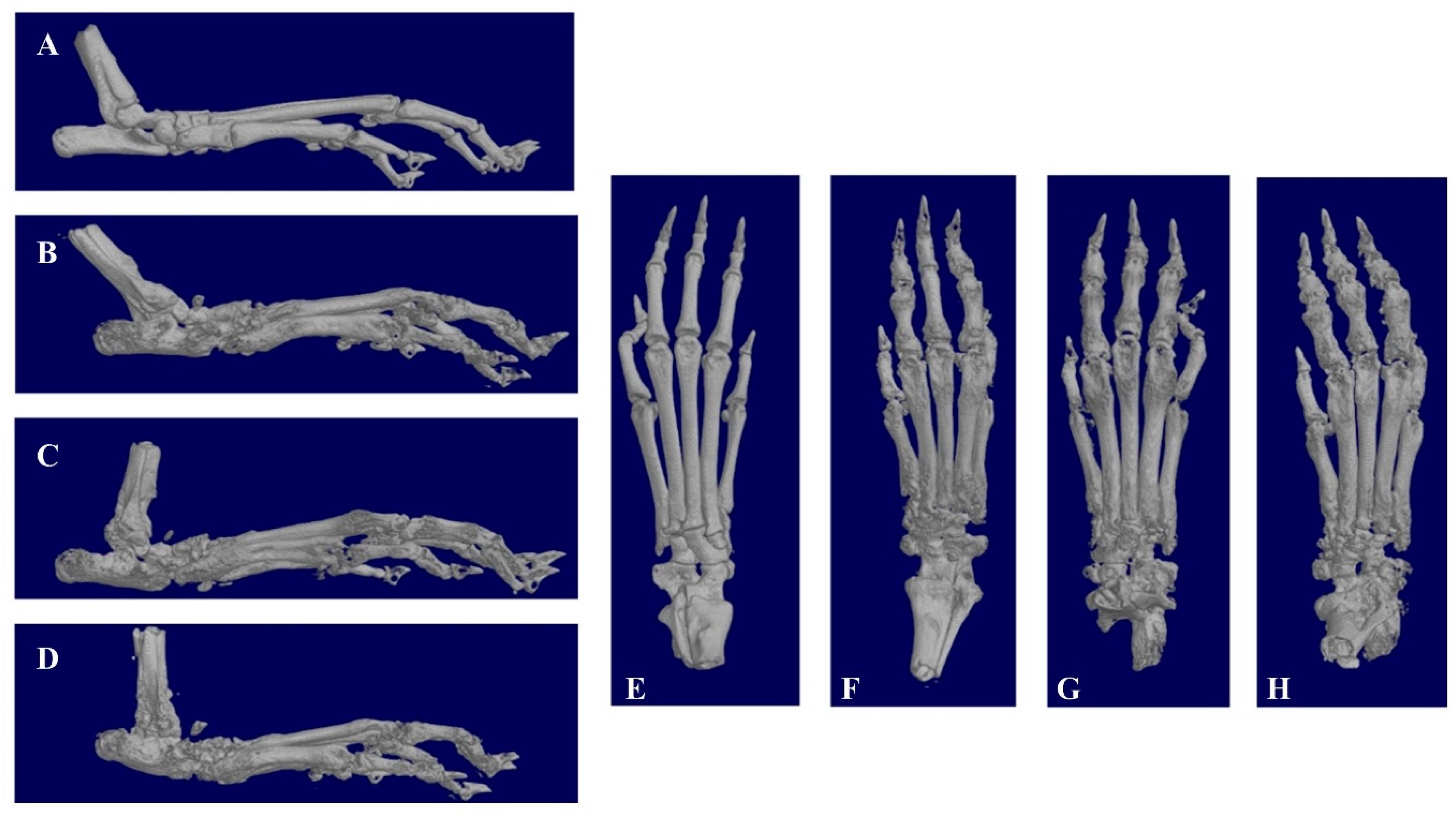
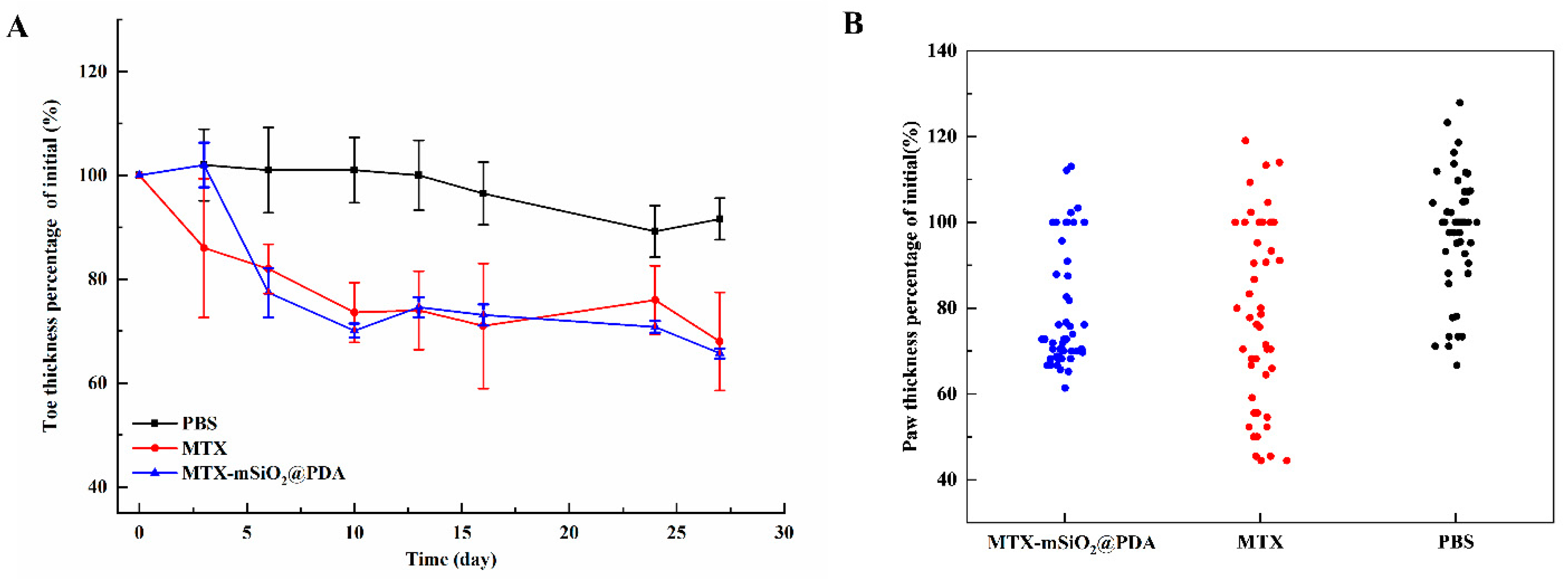
3.6. In Vivo Pharmacodynamics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cush, J.J. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 105, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, B.; Basyal, B.; Sarao, M.S.; Nookala, V.; Thein, Y. Prevalence of Cancer in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Epidemiological Study Based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Cureus 2020, 12, e7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, B.; Cronstein, B. Methotrexate mechanism in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2019, 86, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, G.; Caporali, R.; Todoerti, M.; Mattana, P. Methotrexate and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Evidence Regarding Subcutaneous Versus Oral Routes of Administration. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinblatt, M.E. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis: A quarter century of development. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2013, 124, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L. Side effects of methotrexate therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, M.A.; Abdelwhab, S.M.; Elgawish, M.H. Intra-articular methotrexate versus corticosteroid injections in medium-sized joints of rheumatoid arthritis patients-an intervention study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Christopoulos, C.; Kukreja, N.; Gorog, D.A. Local drug delivery for percutaneous coronary intervention. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 129, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauvais-Javis, P.; Baudot, N.; Castaigne, D.; Banzet, P.; Kuttenn, F. trans-4-Hydroxytamoxifen concentration and metabolism after local percutaneous administration to human breast. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choonara, I. Percutaneous drug absorption and administration. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1994, 71, F73–F74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qindeel, M.; Ullah, M.H.; Fakhar ud, D.; Ahmed, N.; Rehman, A.U. Recent trends, challenges and future outlook of transdermal drug delivery systems for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, J.; Shende, P. Potential of Sonophoresis as a Skin Penetration Technique in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Transdermal Patch. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mukherjee, B.; Chaudhuri, S.; Roy, T.; Mukherjee, A.; Sengupta, S. Methotrexate Aspasomes Against Rheumatoid Arthritis: Optimized Hydrogel Loaded Liposomal Formulation with In Vivo Evaluation in Wistar Rats. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1320–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Gui, S. Polyvinylpyrrolidone microneedles for localized delivery of sinomenine hydrochloride: Preparation, release behavior of in vitro & in vivo, and penetration mechanism. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekko, I.A.; Chen, G.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Hamdan, I.M.N.; Vora, L.; Larrañeta, E.; McElnay, J.C.; McCarthy, H.O.; Rooney, M.; et al. Development and characterisation of novel poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)-based hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays for enhanced and sustained transdermal delivery of methotrexate. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.K.; Singh, B.; Tyagi, R.K.; Sharma, G.; Katare, O.P. Effective transdermal delivery of methotrexate through nanostructured lipid carriers in an experimentally induced arthritis model. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Tang, X.; Yang, M.; Yang, D.; Liu, J. Transdermal drug delivery of triptolide-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: Preparation, pharmacokinetic, and evaluation for rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Su, J.; Cai, W.; Liu, J.X. Nanomaterials Manipulate Macrophages for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 699245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidlářová, L.; Romero, G.B.; Hanuš, J.; Štěpánek, F.; Müller, R.H. Nanocrystals for dermal penetration enhancement—Effect of concentration and underlying mechanisms using curcumin as model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 104, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.P.; Hul, J.; Sui, H.; Zhao, Y.S.; Feng, J.; Liu, C. Glabridin nanosuspension for enhanced skin penetration: Formulation optimization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Die Pharm. 2016, 71, 252–257. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, A.; Planinšek, O. Application of commercially available mesoporous silica for drug dissolution enhancement in oral drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 167, 106015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinavel, S.; Korrapati, P.S.; Kalaiselvi, P.; Dharmalingam, S. Mesoporous silica incorporated PCL/Curcumin nanofiber for wound healing application. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 167, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Wiraja, C.; Qi, L.W.; Ting, S.C.W.; Jana, D.; Zheng, M.; Hu, X.; Xu, C. One-step synthesis of amine-coated ultra-small mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Garnes, M.; Morales, V.; Sanz, R.; García-Muñoz, R.A. Cytostatic and Cytotoxic Effects of Hollow-Shell Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Containing Magnetic Iron Oxide. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watermann, A.; Brieger, J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cancer. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Quan, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, B.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Biphase Stratification Approach to Three-Dimensional Dendritic Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-Inspired Surface Chemistry for Multifunctional Coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Hu, M.; Peng, D.; Peng, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Acidity and Glutathione Dual-Responsive Polydopamine-Coated Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Delivery. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 1940–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Wei, E.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, L.; Ge, B. Polydopamine and peptide decorated doxorubicin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery system for bladder cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, T.; Kang, X.; Ren, S.; Ouyang, X.; Chang, M. Construction of a Nano-Controlled Release Methotrexate Delivery System for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Local Percutaneous Administration. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112812
Guo T, Kang X, Ren S, Ouyang X, Chang M. Construction of a Nano-Controlled Release Methotrexate Delivery System for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Local Percutaneous Administration. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112812
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Tingting, Xu Kang, Sifan Ren, Xianjin Ouyang, and Mingming Chang. 2021. "Construction of a Nano-Controlled Release Methotrexate Delivery System for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Local Percutaneous Administration" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112812
APA StyleGuo, T., Kang, X., Ren, S., Ouyang, X., & Chang, M. (2021). Construction of a Nano-Controlled Release Methotrexate Delivery System for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Local Percutaneous Administration. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112812