The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
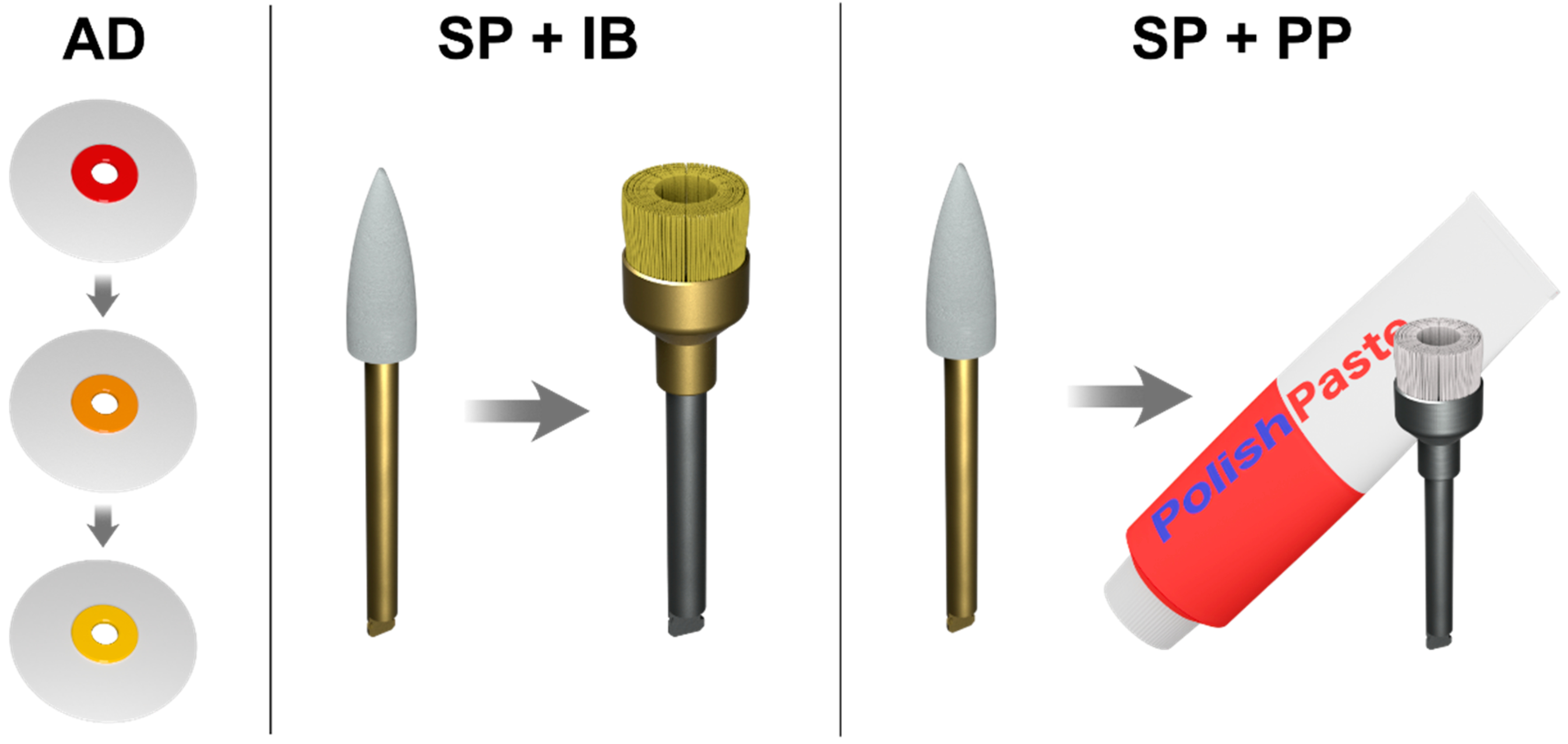
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Surface Roughness Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
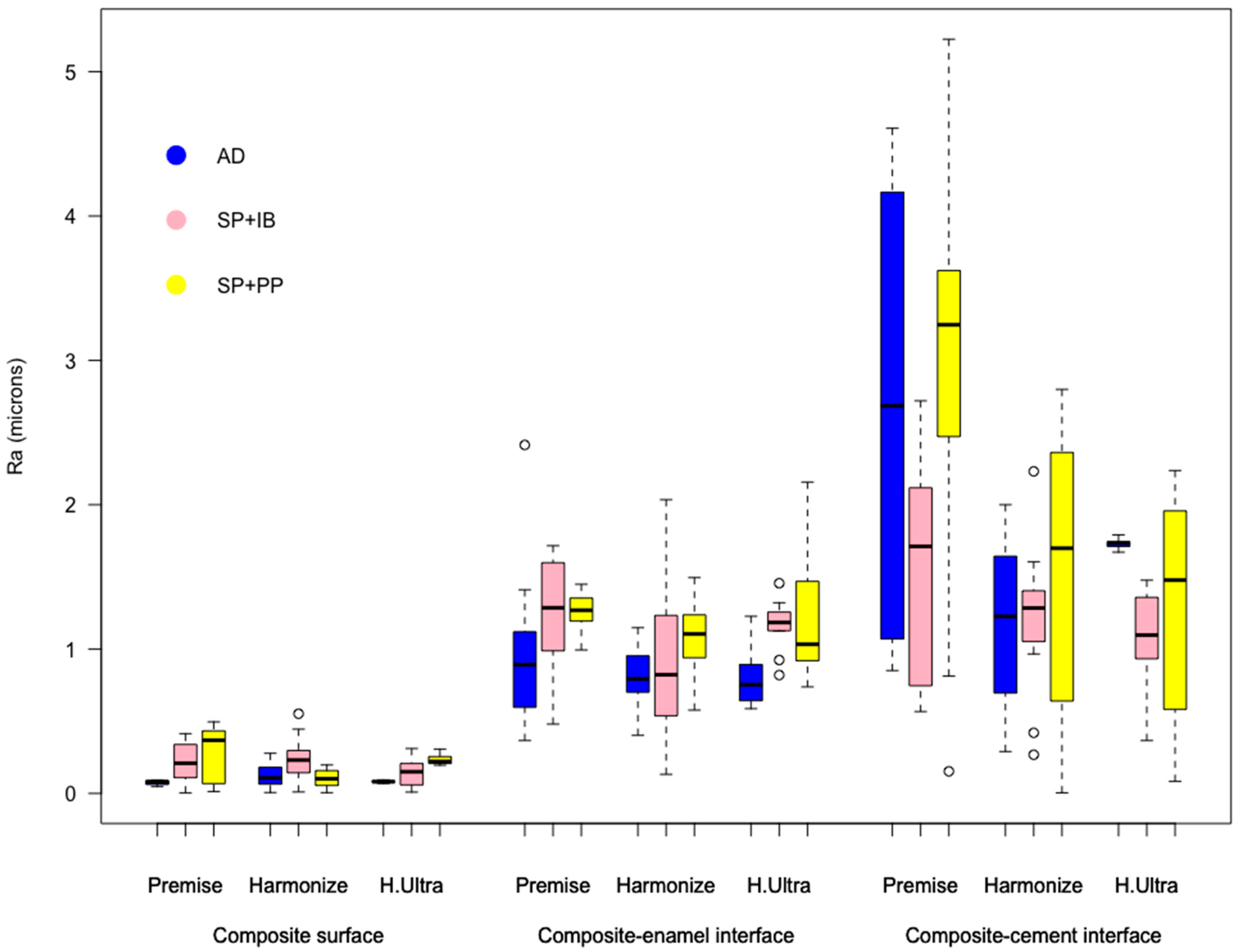
3. Results
4. Discussion
- Premise, pre-polymerized (30–50 µm) + irregular (0.4 µm) + nano size (20 nm) filler;
- Herculite Ultra, pre-polymerized (1 µm) + irregular (0.4 µm) + nano size (50 nm) filler;
- Harmonize, pre-polymerized + irregular (0.4 µm) + nanometric spherical conglomerate (30 nm) filler.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Scribante, A.; Massironi, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Vallittu, P.; Lassila, L.; Sfondrini, M.F.; Gandini, P. Effects of nanofillers on mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced composites polymerized with light-curing and additional postcuring. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2015, 13, e296–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, D.A.; Rodrigues, N.S.; Souza, L.C.; Lomonaco, D.; Rodrigues, F.P.; Degrazia, F.W.; Collares, F.M.; Sauro, S.; Saboia, V.P.A. Physicochemical and microbiological assessment of an experimental composite doped with triclosan-loaded halloysite nanotubes. Materials (Basel) 2018, 11, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scribante, A.; Bollardi, M.; Chiesa, M.; Poggio, C.; Colombo, M. Flexural properties and elastic modulus of different esthetic restorative materials: Evaluation after exposure to acidic drink. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.J.; Leitune, V.C.B.; Balbinot, G.D.S.; Degrazia, F.W.; Arakelyan, M.; Sauro, S.; Collares, F.M. Antibacterial and remineralizing fillers in experimental orthodontic adhesives. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdy, N.M.; Kola, M.Z.; Hussain Alqahtani, H.; Alqahtani, M.D.; Alghmlas, A.S. Evaluation of surface roughness of different direct resin-based composites. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2017, 7, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, E.; Medioni, E.; Brulat-Bouchard, N. Finishing and polishing effects of multiblade burs on the surface texture of 5 resin composites: Microhardness and roughness testing. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2019, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaagaoglu, H.; Aslan, T.; Gürbulak, A.; Albayrak, H.; Taşdemir, Z.; Gumus, H. Efficacy of polishing kits on the surface roughness and color stability of different composite resins. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2017, 20, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhananjaya, K.M.; Vadavadagi, S.V.; Almalki, S.A.; Verma, T.; Arora, S.; Kumar, N.N. In Vitro Analysis of Different Polishing Systems on the Color Stability and Surface Roughness of Nanocomposite Resins. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2019, 20, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, K.; Gupta, S.; Nikhil, V.; Jaiswal, S.; Jain, A.; Aggarwal, N. Effect of Different Finishing and Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness of Resin Composite and Enamel: An In vitro Profilometric and Scanning Electron Microscopy Study. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2019, 9, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, R.; Ceci, M.; De Pani, G.; Vialba, L.; Federico, R.; Poggio, C.; Colombo, M. Effect of different surface finishing/polishing procedures on color stability of esthetic restorative materials: A spectrophotometric evaluation. Eur. J. Dent. 2018, 12, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettini, F.; Corsalini, M.; Savino, M.G.; Stefanachi, G.; Di Venere, D.; Pappalettere, C.; Monno, G.; Boccaccio, A. Roughness Analysis on Composite Materials (Microfilled, Nanofilled and Silorane) After Different Finishing and Polishing Procedures. Open Dent. J. 2015, 9, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Madhyastha, P.S.; Hegde, S.; Srikant, N.; Kotian, R.; Iyer, S.S. Effect of finishing/polishing techniques and time on surface roughness of esthetic restorative materials. Dent. Res. J. (Isfahan) 2017, 14, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.A.; Teixeira, V.C.F.; Rodrigues, S.S.M.F.G.; de Oliveira, R.S.M.F.; Salvio, L.A. Evaluation of the roughness of composite resins submitted to different surface treatments. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2012, 25, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sturz, C.R.C.; Faber, F.-J.; Scheer, M.; Rothamel, D.; Neugebauer, J. Effects of various chair-side surface treatment methods on dental restorative materials with respect to contact angles and surface roughness. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 796–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhairy, F.I. The effects of irradiance and exposure time on the surface roughness of bulk-fill composite resin restorative materials. Saudi Med. J. 2018, 39, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Sainudeen, S.; Padmanabhan, P.; Vijayashankar, L.; Sujathan, U.; Pillai, R. Three-dimensional evaluation of surface roughness of resin composites after finishing and polishing. J. Conserv. Dent. 2016, 19, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, G.F.; Taxt-Lamolle, S.F.; Haugen, H.J. Wear model simulating clinical abrasion on composite filling materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Endo, T.; Finger, W.J.; Kanehira, M.; Utterodt, A.; Komatsu, M. Surface texture and roughness of polished nanofill and nanohybrid resin composites. Dent. Mater. J. 2010, 29, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumari, C.M.; Bhat, K.M.; Bansal, R. Evaluation of surface roughness of different restorative composites after polishing using atomic force microscopy. J. Conserv. Dent. 2016, 19, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, K.; Tekçe, N.; Tuncer, S.; Serim, M.E.; Demirci, M. Evaluation of the surface hardness, roughness, gloss and color of composites after different finishing/polishing treatments and thermocycling using a multitechnique approach. Dent. Mater. J. 2016, 35, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.D.; Raisingani, D.; Jindal, D.; Mathur, R. A Comparative Analysis of Different Finishing and Polishing Devices on Nanofilled, Microfilled, and Hybrid Composite: A Scanning Electron Microscopy and Profilometric Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 9, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, E.S.; Rosen, M.; Cleaton-Jones, P.E.; Volchansky, A. Scientific surface roughness values for resin based materials. SADJ 2004, 59, 59. [Google Scholar]
- St-Pierre, L.; Martel, C.; Crépeau, H.; Vargas, M.A. Influence of polishing systems on surface roughness of composite resins: Polishability of composite resins. Oper. Dent. 2019, 44, E122–E132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, F.; Conti, A. Superficial roughness on composite surface, composite enamel and composite dentin junctions after different finishing and polishing procedures. Part I: Roughness after treatments with tungsten carbide vs diamond burs. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2014, 9, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishii, R.; Takamizawa, T.; Tsujimoto, A.; Suzuki, S.; Imai, A.; Barkmeier, W.; Latta, M.; Miyazaki, M. Effects of Finishing and Polishing Methods on the Surface Roughness and Surface Free Energy of Bulk-fill Resin Composites. Oper. Dent. 2019, 45, E91–E104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosco, V.; Monterubbianesi, R.; Orilisi, G.; Procaccini, M.; Grandini, S.; Putignano, A.; Orsini, G. Effect of four different finishing and polishing systems on resin composites: Roughness surface and gloss retention evaluations. Minerva Stomatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, A.; Gray, G.; Lynch, C.D.; Wilson, N.H.F.; Blum, I.R. A randomised controlled study on the use of finishing and polishing systems on different resin composites using 3D contact optical profilometry and scanning electron microscopy. J. Dent. 2018, 71, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, B.; Pamir, T.; Baltaci, A.; Orman, M.N.; Turk, T. Effect of storage solutions on microhardness of crown enamel and dentin. Eur. J. Dent. 2015, 9, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, A.R.; Da Aznar, F.D.C.; Da Silva, A.L.; Sales-Peres, A.; De Sales-Peres, S.H.C. Assessment of the effects of decontamination and storage methods on the structural integrity of human enamel. Rev. Odontol. Da UNESP 2016, 45, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humel, M.M.C.; Oliveira, M.T.; Cavalli, V.; Giannini, M. Effect of storage and disinfection methods of extracted bovine teeth on bond strength to dentin. Brazilian J. Oral Sci. 2007, 6, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.S.; Ahmed, N. The effects of acid etching time on surface mechanical properties of dental hard tissues. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopperud, H.M.; Johnsen, G.F.; Lamolle, S.; Kleven, I.S.; Wellendorf, H.; Haugen, H.J. Effect of short LED lamp exposure on wear resistance, residual monomer and degree of conversion for Filtek Z250 and Tetric EvoCeram composites. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avsar, A.; Yuzbasioglu, E.; Sarac, D. The effect of finishing and polishing techniques on the surface roughness and the color of nanocomposite resin restorative materials. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Takamizawa, T.; Kurokawa, H.; Rikuta, A.; Ando, S. Influence of polishing duration on surface roughness of resin composites. J. Oral Sci. 2005, 47, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasoohi, N.; Hoorizad, M.; Tabatabaei, S.F. Effects of Wet and Dry Finishing and Polishing on Surface Roughness and Microhardness of Composite Resins. J. Dent. (Tehran) 2017, 14, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, F.C.R.; Ferreira, R.C.; Silveira, R.R.; Pereira, C.N.B.; Moreira, A.N.; Magalhães, C.S. Surface Roughness, Microhardness, and Microleakage of a Silorane-Based Composite Resin after Immediate or Delayed Finishing/Polishing. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, C.M.; Lambrechts, P.; Quirynen, M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: A review of the literature. Dent. Mater. 1997, 13, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, F.; Liang, X.; Li, D. Effects of surface properties of polymer-based restorative materials on early adhesion of Streptococcus mutans in vitro. J. Dent. 2016, 54, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitman, R.T.; Eames, W.B. Plaque accumulation on composite surfaces after various finising procedures. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1975, 91, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; An, J.S.; Lim, W.H.; Lim, B.S.; Ahn, S.J. Microbial changes in biofilms on composite resins with different surface roughness: An in vitro study with a multispecies biofilm model. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 493.e1–493.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.S.; Billington, R.W.; Pearson, G.J. The in vivo perception of roughness of restorations. Br. Dent. J. 2004, 196, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.-H. Effects of finishing and polishing procedures on the surface texture of resin composites. Dent. Mater. 1994, 10, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gönülol, N.; Yilmaz, F. The effects of finishing and polishing techniques on surface roughness and color stability of nanocomposites. J. Dent. 2012, 40, e64–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De da Costa, G.F.A.; de Fernandes, A.C.B.C.J.; de Carvalho, L.A.O.; de Andrade, A.C.; de Assunção, I.V.; Borges, B.C.D. Effect of additional polishing methods on the physical surface properties of different nanocomposites: SEM and AFM study. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heintze, S.D.; Forjanic, M.; Rousson, V. Surface roughness and gloss of dental materials as a function of force and polishing time in vitro. Dent. Mater. 2006, 22, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Sehr, K.; Klimek, J. Surface texture of four nanofilled and one hybrid composite after finishing. Oper. Dent. 2007, 32, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-C.; Lai, E.H.-H.; Kunzelmann, K.-H. Polishing mechanism of light-initiated dental composite: Geometric optics approach. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2016, 115, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paravina, R.D.; Roeder, L.; Lu, H.; Vogel, K.; Powers, J.M. Effect of finishing and polishing procedures on surface roughness, gloss and color of resin-based composites. Am. J. Dent. 2004, 17, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy, V.; Rodrigues, S. Iatrogenic dentistry and the periodontium. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2007, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Molina, R.; Kaplan, A.E. Influence of polishing protocol on flexural properties of several dental composite resins. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2015, 28, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Resin Composite | Manufacturer | Organic Resin | Filler Type | Filler Loading, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premise | Kerr, Scafati, Italy | BisGMA TEGDMA EBPADMA | Barium-aluminum-borosilicate glass (mean particle size 0.4 μm); fumed silica nanofiller (20 nm); prepolymerized filler (≈30–50 μm). | 84 (by weight) |
| Herculite Ultra | Kerr, Scafati, Italy | BisGMA TEGDMA EBPADMA | Barium-aluminum-borosilicate glass (mean particle size 0.4 μm); fumed silica nanofiller (50 nm); prepolymerized filler (≈1 μm). | 78 (by weight) |
| Harmonize | Kerr, Scafati, Italy | BisGMA TEGDM EBPADMA | Barium-aluminum-borosilicate glass (mean particle size 0.4 μm); aggregated zirconia/silica cluster filler (2–3 μm) comprised of 20 nm spherical fumed silica and 5 nm zirconia particles; prepolymerized filler. | 81.5 (by weight) |
| Composite/Polishing Method | Premise | Harmonize | Herculite Ultra | All Composites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | |
| AD | 0.08 ± 0.02a | 0.07–0.08 | 0.12 ± 0.08ac | 0.08–0.15 | 0.08 ± 0.01a | 0.08–0.09 | 0.09 ± 0.05A | 0.07–0.12 |
| SP + IB | 0.22 ± 0.13b | 0.15–0.29 | 0.23 ± 0.15bc | 0.15–0.31 | 0.15 ± 0.09ab | 0.10–0.20 | 0.2 ± 0.13B | 0.13–0.27 |
| SP + PP | 0.29 ± 0.18b | 0.19–0.38 | 0.10 ± 0.06a | 0.07–0.14 | 0.23 ± 0.04b | 0.22–0.25 | 0.21 ± 0.16B | 0.14–0.28 |
| Average | 0.20 ± 0.16A | 0.11–0.28 | 0.15 ± 0.12A | 0.09–0.21 | 0.15 ± 0.08A | 0.10–0.20 | 0.17 ± 0.12 | 0.10–0.23 |
| Composite/Polishing Method | Premise | Harmonize | Herculite Ultra | All Composites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | |
| AD | 0.96 ± 0.50a | 0.69–1.22 | 0.80 ± 0.21a | 0.69–0.91 | 0.80 ± 0.19a | 0.69–0.90 | 0.86 ± 0.34A | 0.68–1.03 |
| SP + IB | 1.26 ± 0.36a | 1.07–1.45 | 0.92 ± 0.51a | 0.65–1.19 | 1.18 ± 0.16a | 1.10–1.26 | 1.12 ± 0.39B | 0.91–1.33 |
| SP + PP | 1.25 ± 0.14a | 1.18–1.32 | 1.06 ± 0.28a | 0.91–1.21 | 1.18 ± 0.39a | 0.97–1.39 | 1.16 ± 0.30B | 1.01–1.32 |
| Average | 1.16 ± 0.38A | 0.95–1.36 | 0.93 ± 0.34B | 0.74–1.12 | 1.05 ± 0.32AB | 0.08–1.22 | 1.05 ± 0.34 | 0.85–1.24 |
| Composite/Polishing Method | Premise | Harmonize | Herculite Ultra | All Composites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | |
| AD | 2.64 ± 1.42a | 1.90–3.38 | 1.19 ± 0.53b | 0.90–1.46 | 1.73 ± 0.03ab | 1.71–1.75 | 1.85 ± 1.05A | 1.30–2.40 |
| SP + IB | 1.55 ± 0.72b | 1.17–1.93 | 1.21 ± 0.47b | 0.96–1.46 | 1.08 ± 0.29b | 0.93–1.24 | 1.28 ± 0.55B | 0.99–1.57 |
| SP + PP | 3.00 ± 1.41a | 2.26–3.74 | 1.57 ± 0.92b | 1.09–2.05 | 1.27 ± 0.77b | 0.86–1.68 | 1.95 ± 1.29A | 1.27–2.62 |
| Average | 2.39 ± 1.35A | 1.69–3.10 | 1.32 ± 0.68B | 0.97–1.68 | 1.36 ± 0.54B | 1.08–1.64 | 1.69 ± 1.05 | 1.15–2.24 |
| Composite/Polishing Method | Premise | Harmonize | Herculite Ultra | All Composites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | M ± σ | CI 95% | |
| AD | 150 ± 14a | 143–158 | 157 ± 05a | 155–159 | 165 ± 20a | 155–175 | 157 ± 15A | 149–165 |
| SP + IB | 152 ± 14ac | 145–159 | 117 ± 22b | 105–129 | 145 ± 08c | 141–149 | 138 ± 22B | 127–149 |
| SP + PP | 129 ± 01b | 128–130 | 91 ± 02c | 89–92 | 128 ± 03b | 126–130 | 116 ± 18C | 107–125 |
| Average | 144 ± 15A | 136–152 | 122 ± 30B | 106–138 | 146 ± 20A | 136–156 | 137 ± 25 | 124–150 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babina, K.; Polyakova, M.; Sokhova, I.; Doroshina, V.; Arakelyan, M.; Novozhilova, N. The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071339
Babina K, Polyakova M, Sokhova I, Doroshina V, Arakelyan M, Novozhilova N. The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(7):1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071339
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabina, Ksenia, Maria Polyakova, Inna Sokhova, Vladlena Doroshina, Marianna Arakelyan, and Nina Novozhilova. 2020. "The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces" Nanomaterials 10, no. 7: 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071339
APA StyleBabina, K., Polyakova, M., Sokhova, I., Doroshina, V., Arakelyan, M., & Novozhilova, N. (2020). The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces. Nanomaterials, 10(7), 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071339






