Development of ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Hybrid Nanostructures Used for PVOH/ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Active Packaging Films Preparation via a Melt-Extrusion Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation
2.2.1. Preparation of ZnO/NaMt Hybrid Nanostructures
2.2.2. Preparation of PVOH/ZnO/NaMt Nanocomposite Films
2.3. XRD Analysis
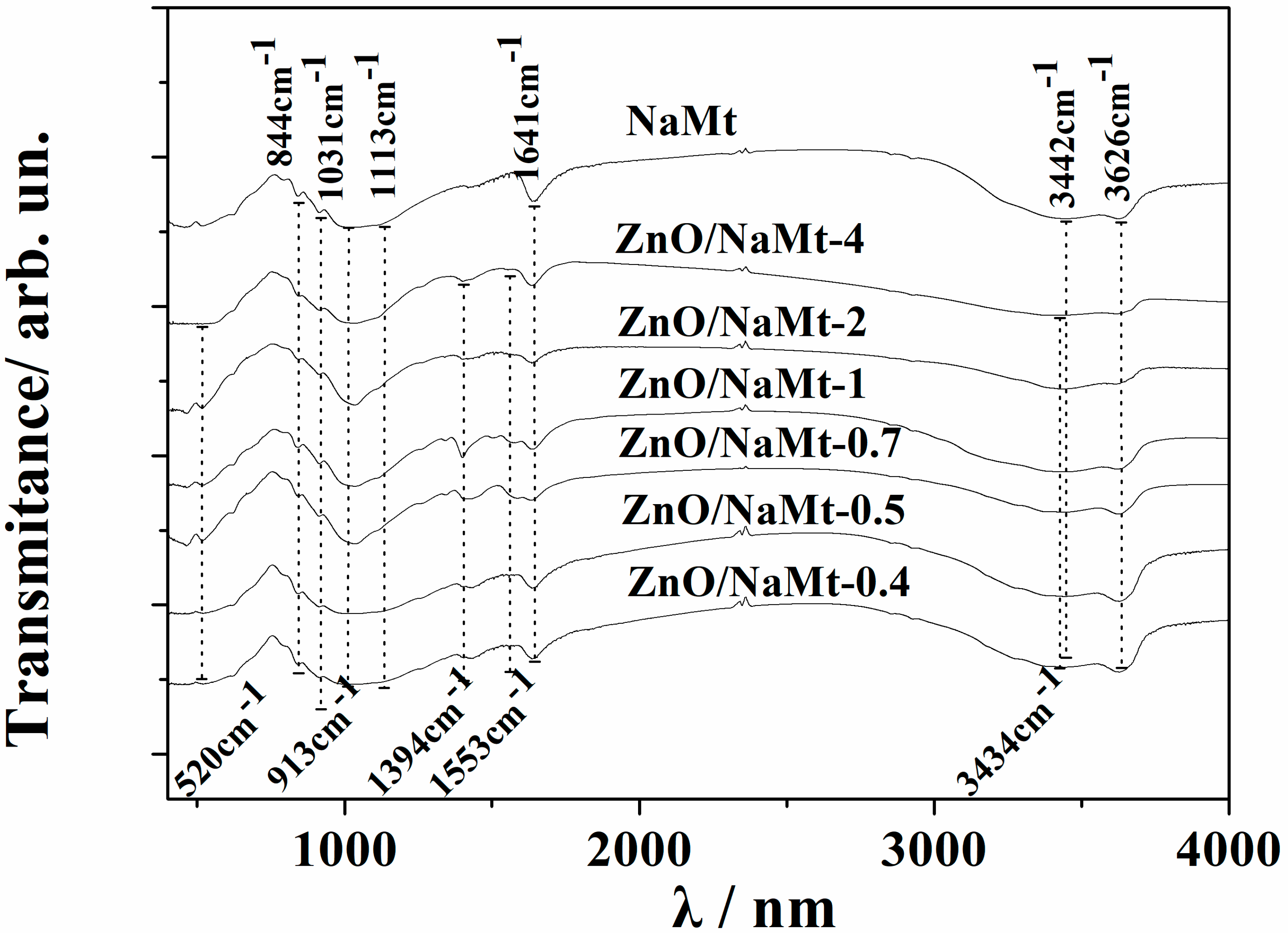
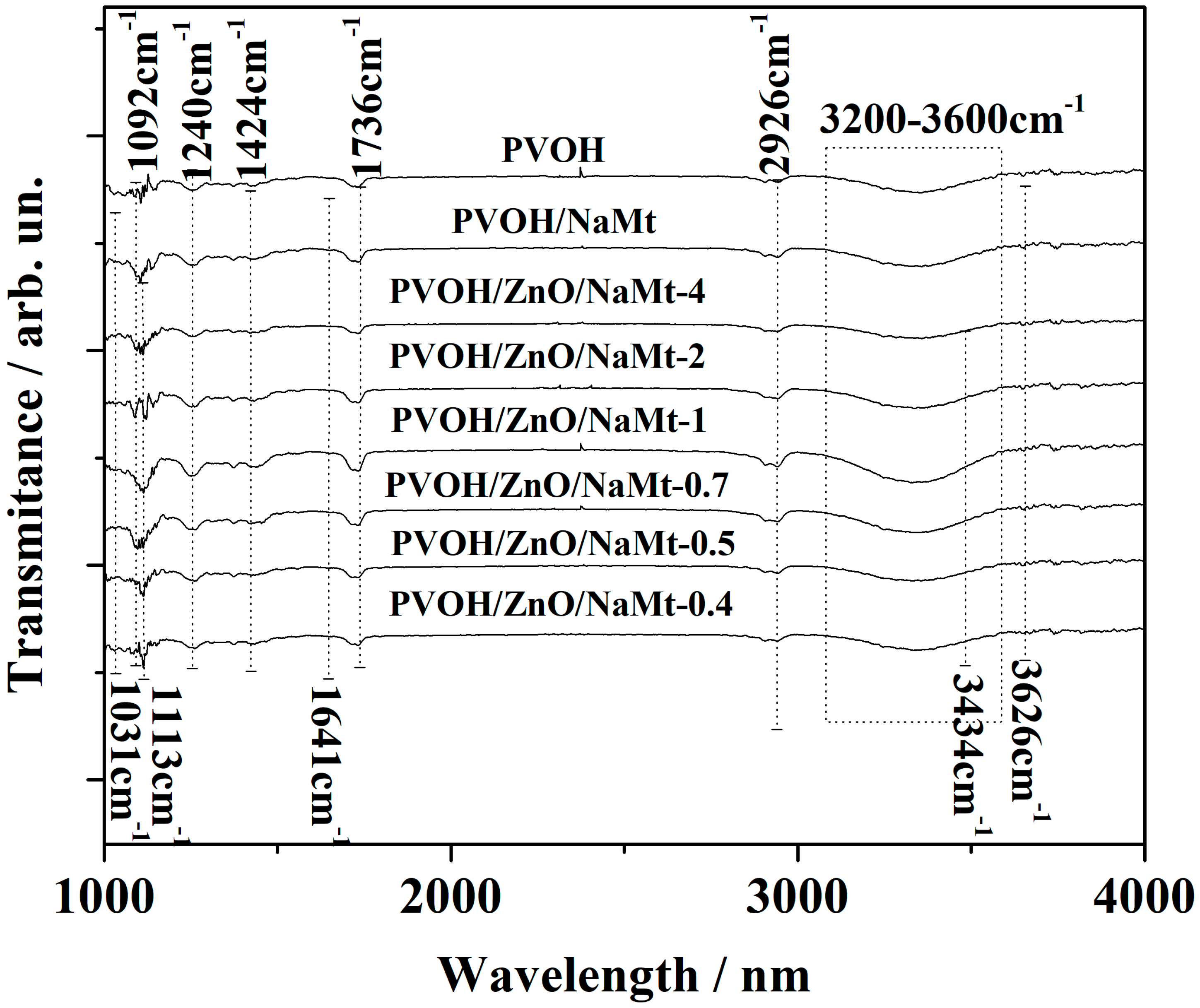
2.4. FTIR Spectrometry
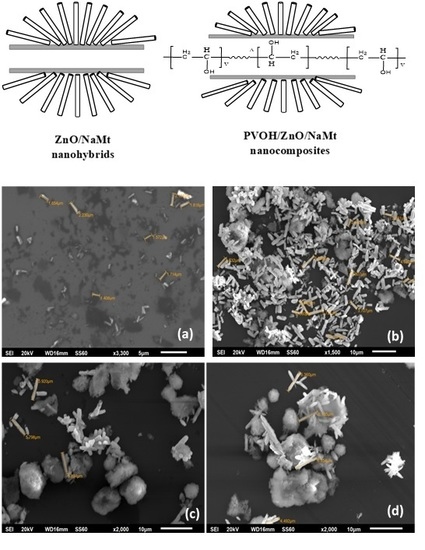
2.5. SEM Images
2.6. Tensile Properties
2.7. Water Sorption
2.8. Water Vapor Permeability (WVTR)
2.9. Oxygen Permeability
2.10. UV–Vis Absorbance Analysis of Films
2.11. Antimicrobial Activity Tests
3. Results
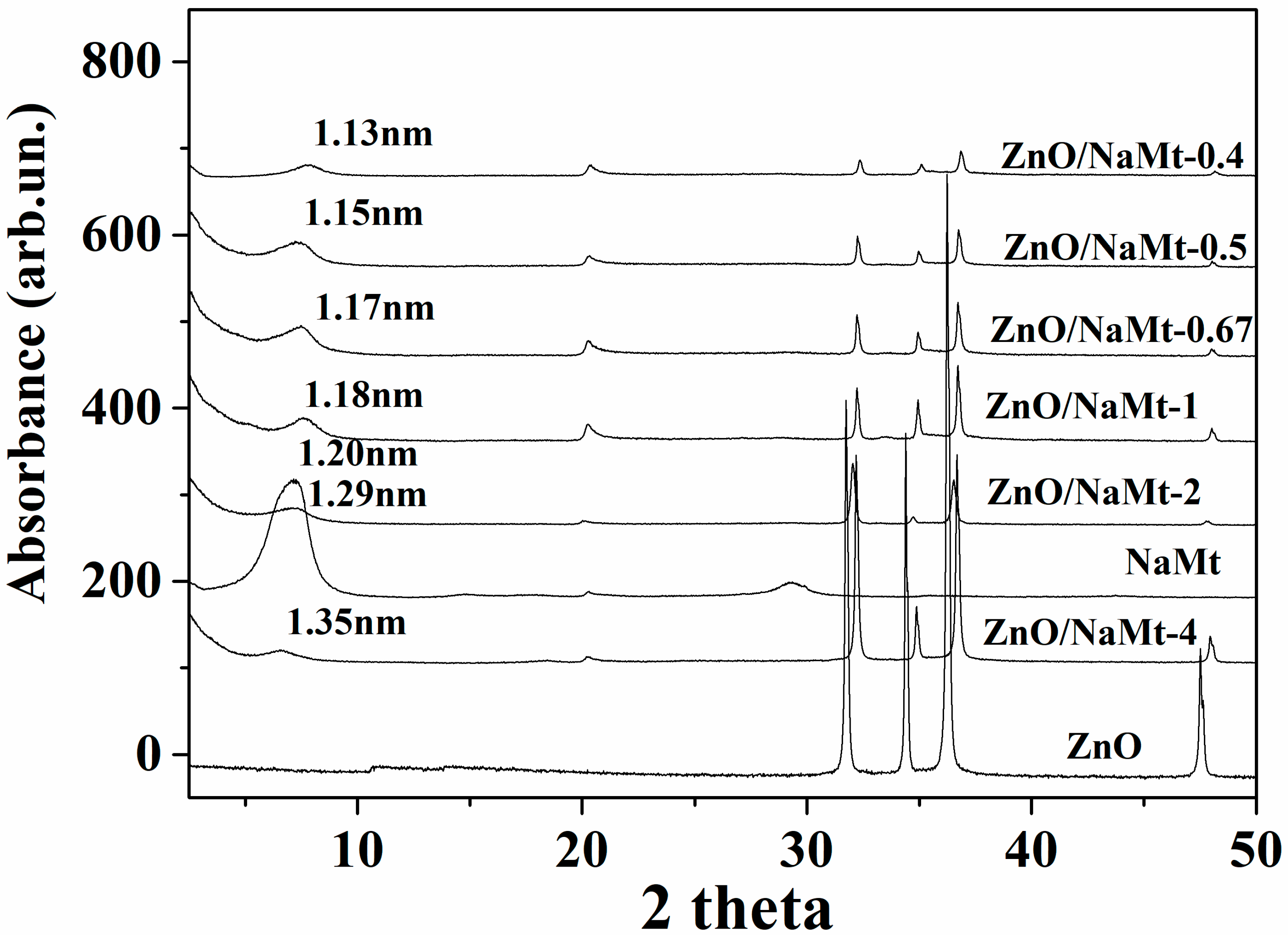
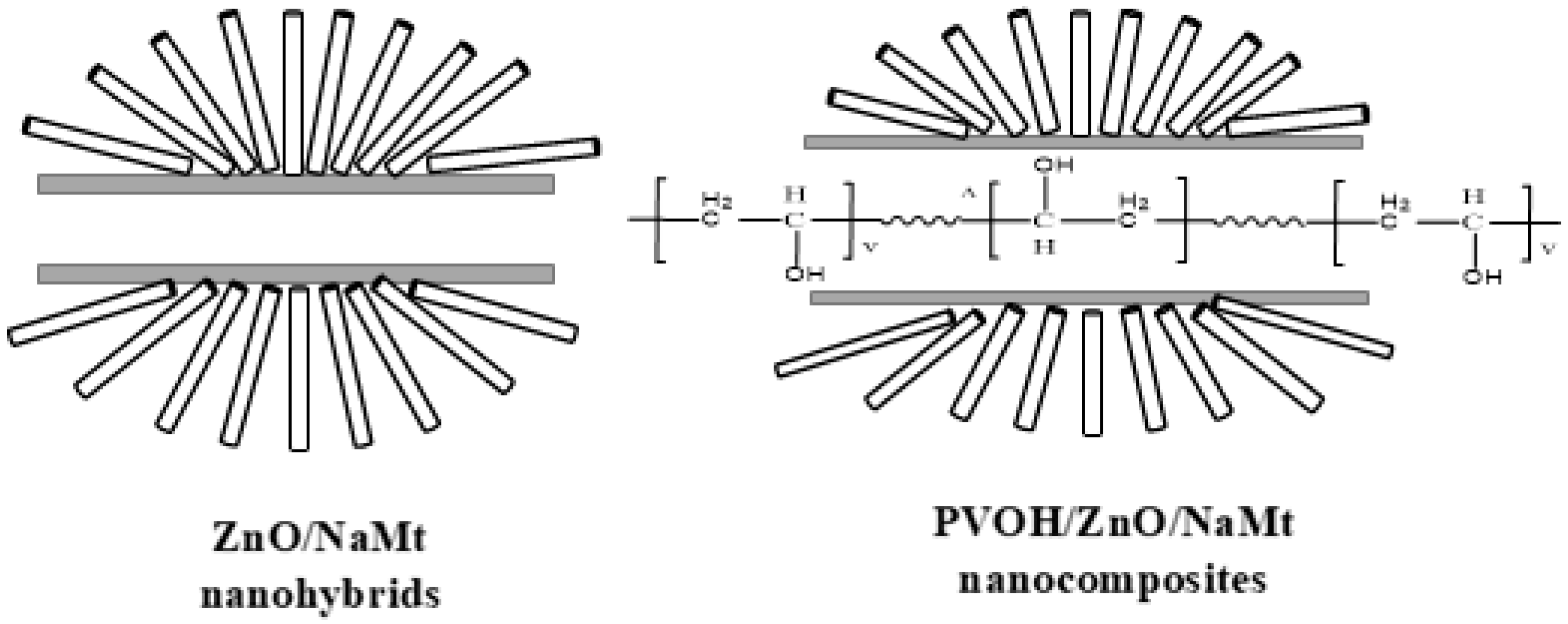
3.1. Characterization of ZnO/NaMt Hybrid Nanostructures
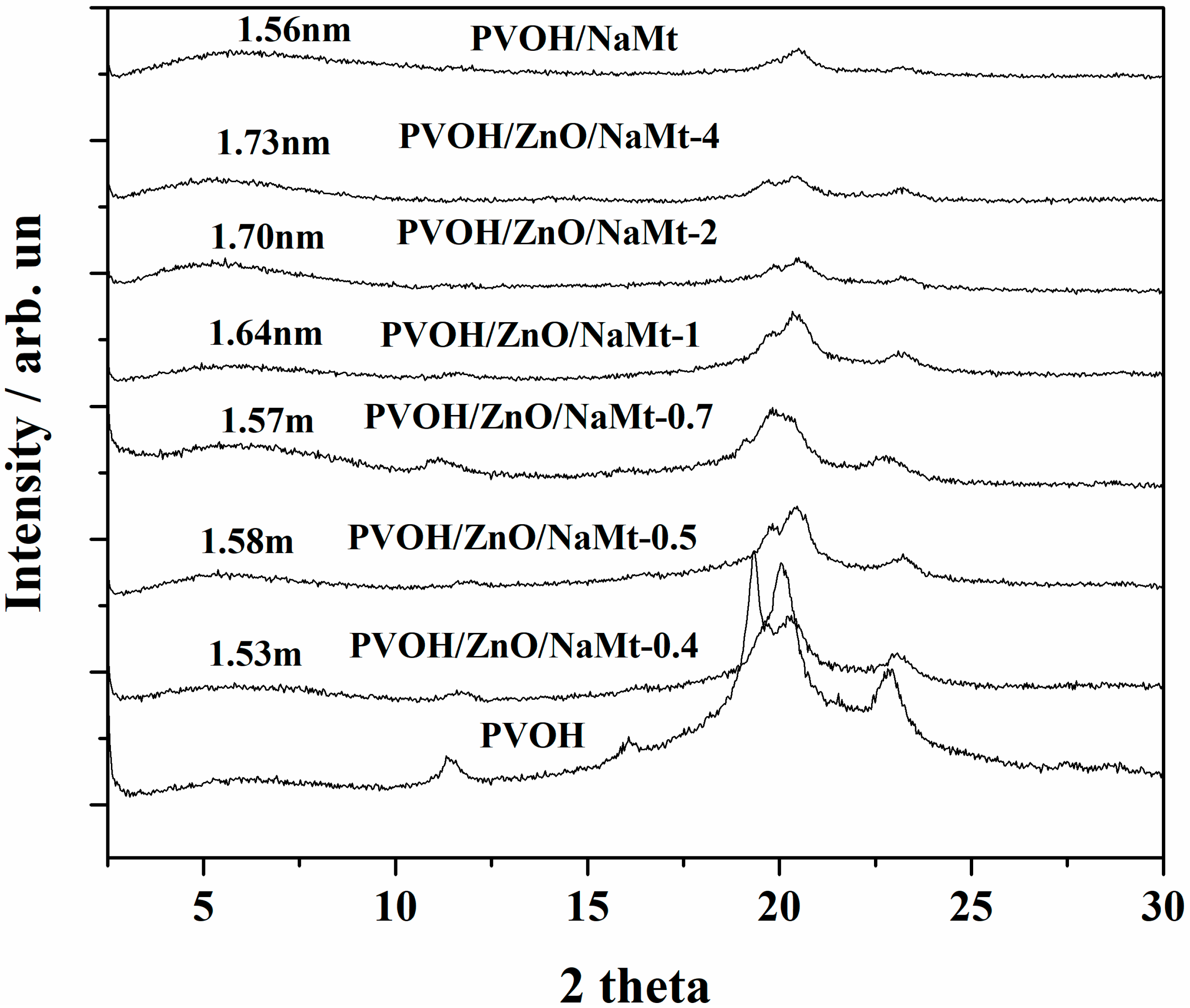
3.2. Characterization of PVOH/ZnO/NaMt Nanocomposite Films
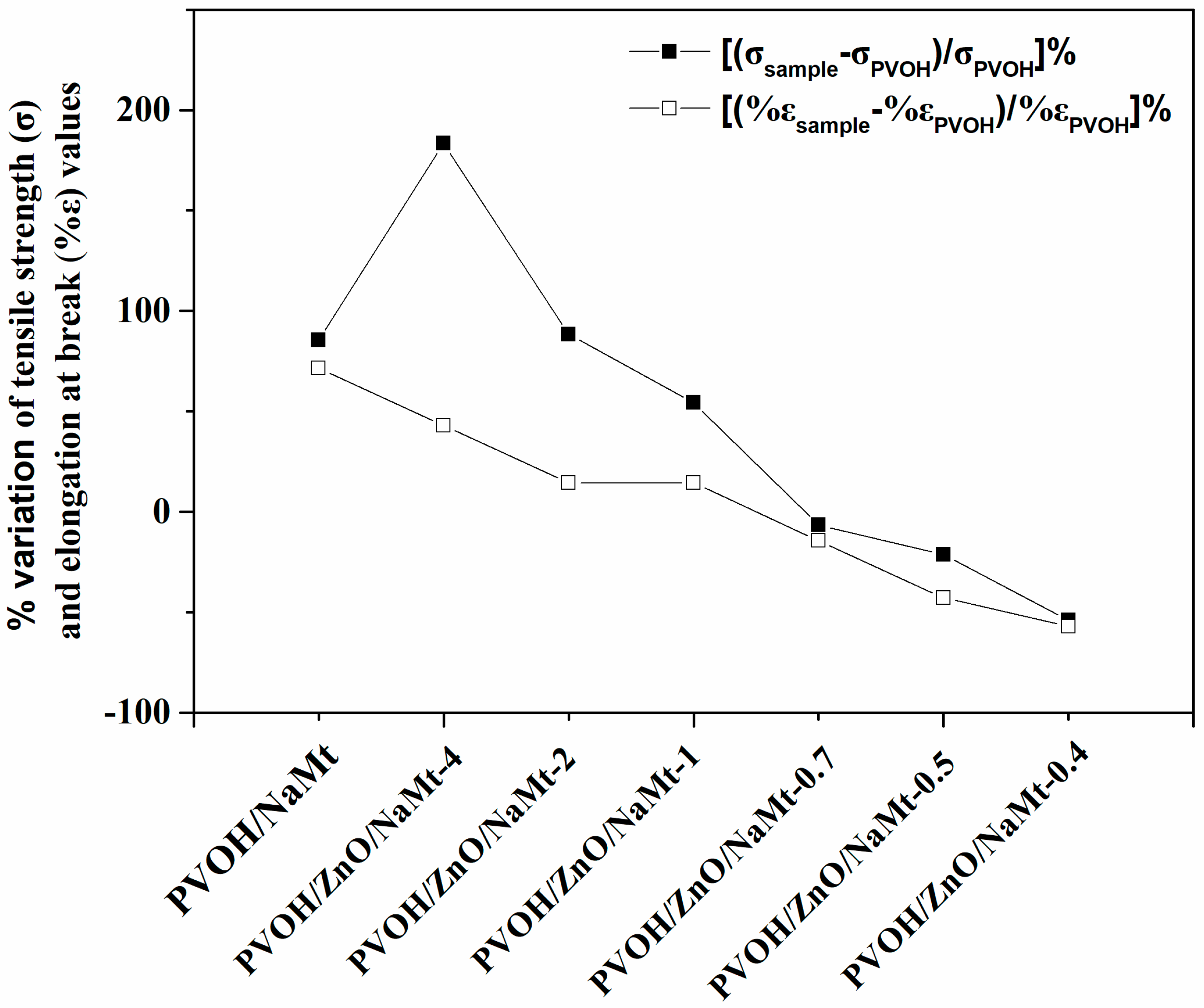
3.3. Tensile Properties of PVOH/ZnO/NaMt Nanocomposite Films
3.4. Water Sorption
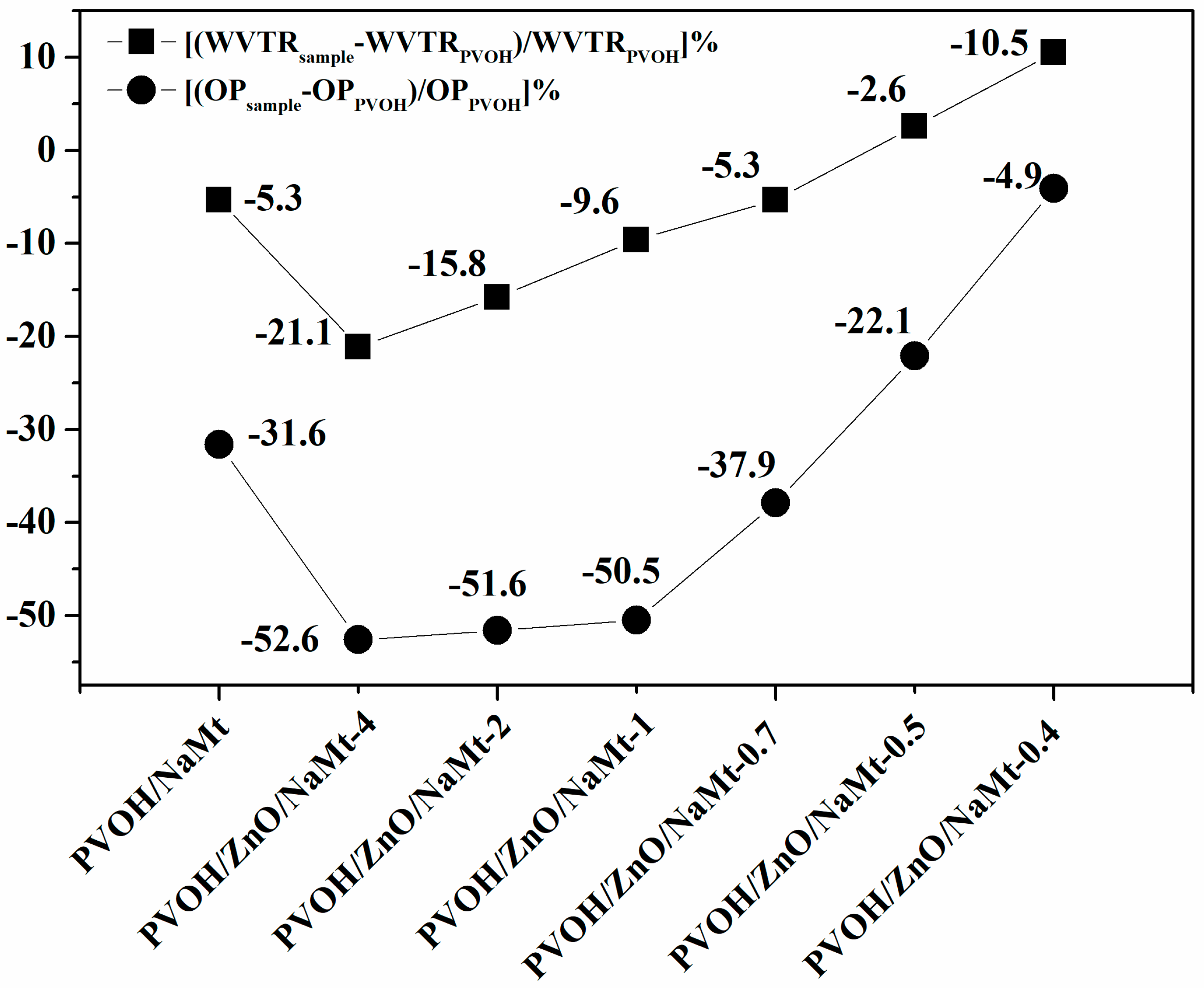
3.5. Water and Oxygen Barrier Properties
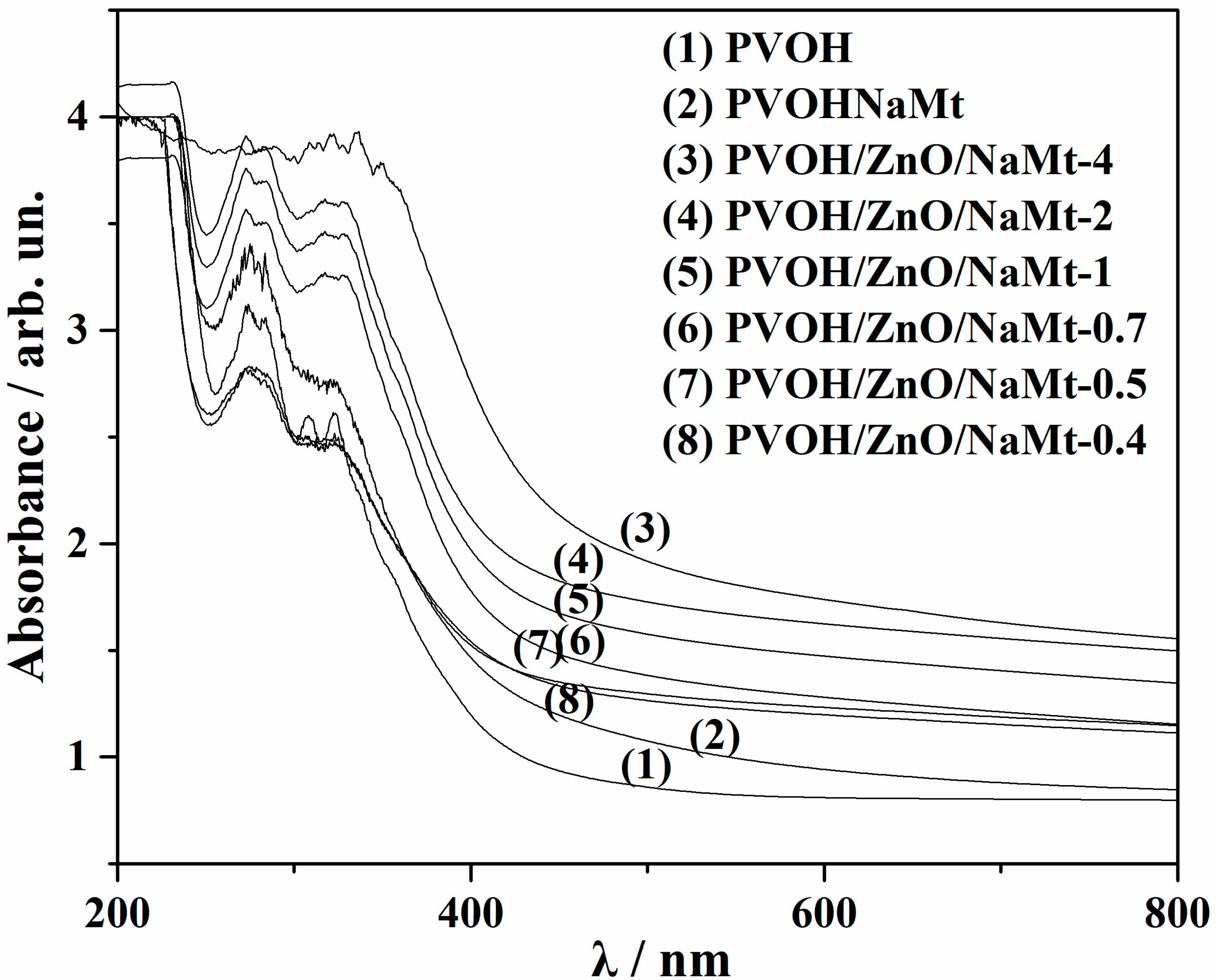
3.6. UV–Vis Films Absorbance
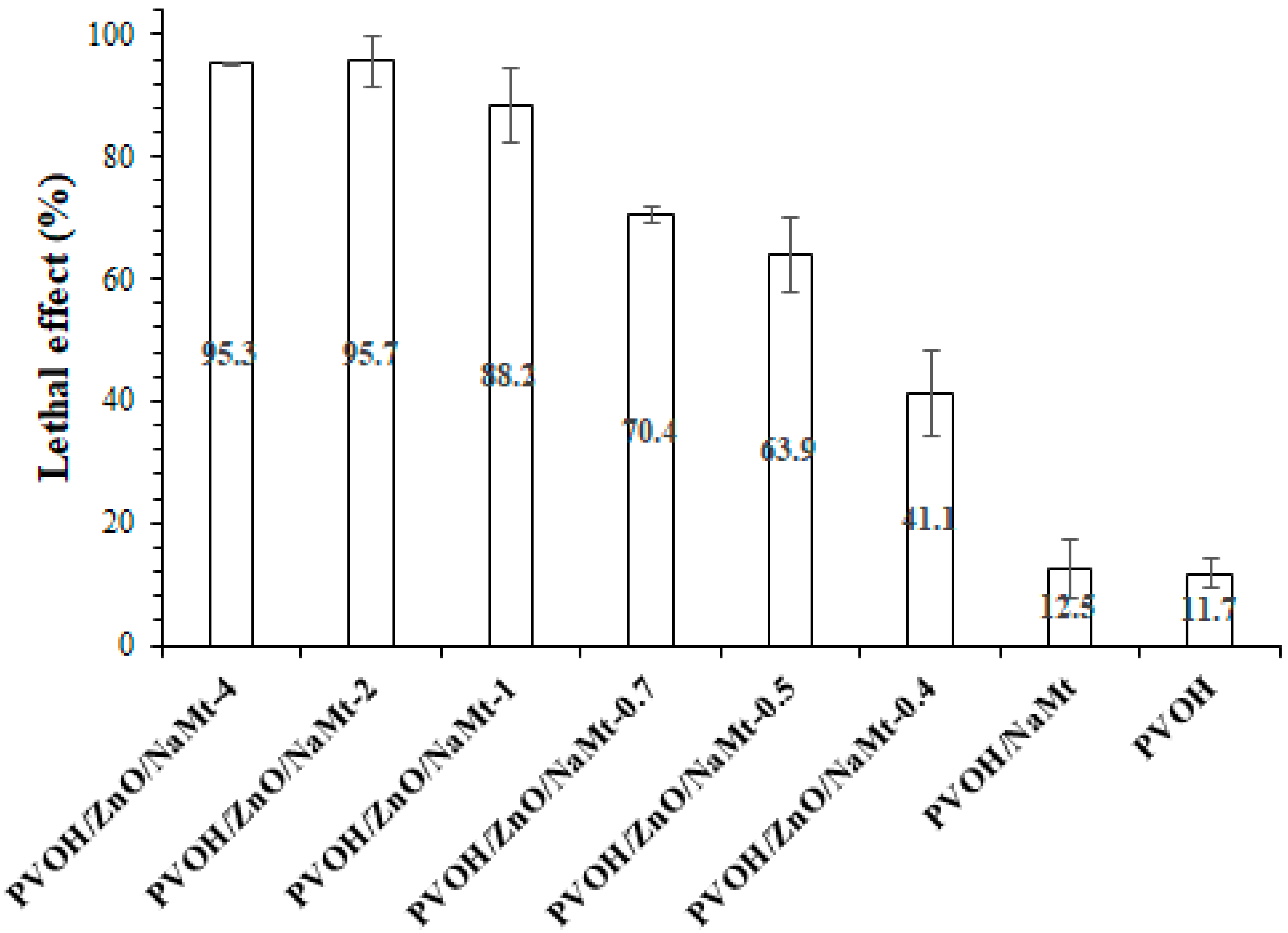
3.7. Antimicrobial Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajpai, V.K.; Kamle, M.; Shukla, S.; Mahato, D.K.; Chandra, P.; Hwang, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K. Prospects of using nanotechnology for food preservation, safety, and security. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakas, A.E.; Leontiou, A.A. Montmorillonite composite materials and food packaging. In Composites Materials for Food Packaging; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–71. ISBN 978-1-119-16024-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, F.; Swain, S.K. Bionanocomposites for food packaging applications. Nanotechnol. Appl. Food FlavorStab. Nutr. Saf. 2017, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi-Lalabadi, M.; Ehsani, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Divband, B. Polyvinyl alcohol/gelatin nanocomposite containing ZnO, TiO2 or ZnO/TiO2 nanoparticles doped on 4A zeolite: Microbial and sensory qualities of packaged white shrimp during refrigeration. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Ren, J.; Chang, M.; He, B.; Zhang, C. Effects of nano-ZnO and nano-SiO2 particles on properties of PVA/xylan composite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Madani, M. Transparent and thermally stable improved poly (vinyl alcohol)/Cloisite Na+/ZnO hybrid nanocomposite films: Fabrication, morphology and surface properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 74, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Fu, K.; Yang, F.; Xie, J. Properties, vapour-phase antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of active poly(vinyl alcohol) packaging films incorporated with clove oil. Food Control. 2018, 88, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Heera, K.V.; Sumi, T.S.; Joseph, M.; Mathew, S.; Praveen, G.; Nair, I.C.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Starch-PVA composite films with zinc-oxide nanoparticles and phytochemicals as intelligent pH sensing wraps for food packaging application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbudsanpharoke, N.; Ko, S. Nanoclays in food and beverage packaging. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Otoni, C.G.; Soares, N.F.F. Chapter 34—Zinc oxide nanoparticles for food packaging applications. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Barros-Velázquez, J., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 425–431. ISBN 978-0-12-800723-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Dang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. Evidence of the formation mechanism of ZnO in aqueous solution. Mater. Lett. 2012, 82, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Patsaoura, A.; Barkoula, N.-M.; Ladavos, A. A novel solution blending method for using olive oil and corn oil as plasticizers in chitosan based organoclay nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Salmas, C.; Leontiou, A.; Tsimogiannis, D.; Oreopoulou, A.; Braouhli, J. Novel LDPE/chitosan rosemary and melissa extract nanostructured active packaging films. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakas, A.; Xidas, P.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Katsoulidis, A.; Ladavos, A. Preparation and characterization of polymer/organosilicate nanocomposites based on unmodified LDPE. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriadi, K.; Giannakas, A.; Ladavos, A.K.; Barkoula, N.-M. Interplay between processing and performance in chitosan-based clay nanocomposite films. Polym. Bull. 2015, 72, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Giannakas, A.; Ladavos, A. Preparation and characterization of polystyrene/organolaponite nanocomposites. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 1411–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Grigoriadi, K.; Leontiou, A.; Barkoula, N.-M.; Ladavos, A. Preparation, characterization, mechanical and barrier properties investigation of chitosan–clay nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Vlacha, M.; Salmas, C.; Leontiou, A.; Katapodis, P.; Stamatis, H.; Barkoula, N.-M.; Ladavos, A. Preparation, characterization, mechanical, barrier and antimicrobial properties of chitosan/PVOH/clay nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgou, D.; Thomou, E.; Vourvou, N.T.; Lyra, K.-M.; Chalmpes, N.; Enotiadis, A.; Spyrou, K.; Katapodis, P.; Gournis, D.; Stamatis, H. Antibacterial and algicidal effects of porous carbon cuboid nanoparticles. Acs Omega 2019, 4, 4991–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Du, G.-H.; Ren, T.-Z.; Bouvy, C.; Halasa, M.; Su, B.-L. Simple approach to highly oriented ZnO nanowire arrays: Large-scale growth, photoluminescence and photocatalytic properties. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Cheng, C.-S.; Chang, C.-C.; Yang, S.; Chang, C.-S.; Hsieh, W.-F. Orientation-enhanced growth and optical properties of ZnO nanowires grown on porous silicon substrates. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaorapapong, N.; Khumchoo, N.; Ogawa, M. Preparation of zinc oxide–montmorillonite hybrids. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.; Ma, R. Facile synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles grown on halloysite nanotubes for enhanced photocatalytic properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarona, E.; Koutzagioti, C.; Salmas, C.; Ntalos, G.; Skoulikidou, M.-C.; Tsamis, C. Enhancing wood resistance to humidity with nanostructured ZnO coatings. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2017, 10, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.L.; Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Boyd, I.W. Pulsed-laser deposited ZnO for device applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1996, 96, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Alkhtaby, L.A.; Giorgetti, E.; Zoppi, A.; Muniz Miranda, M. Effect of Mn doping on structural and optical properties of sol gel derived ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 2014, 145, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, M.; Aranda, P.; Ben Rhaiem, H.; Ben Haj Amara, A.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. ZnO/clay nanoarchitectures: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation as photocatalysts. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 131, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, T.; Liu, J. Photo-degradation of Acid Yellow 11 in aqueous on nano-ZnO/Bentonite under ultraviolet and visible light irradiation. Mater. Lett. 2014, 117, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.M.; Tong, D.S.; Zhao, L.Z.; Yu, W.H.; Zhou, C.H.; Wang, H. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis for hydrothermal transformation of microcrystalline cellulose on montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djomgoue, P.; Njopwouo, D. FT-IR spectroscopy applied for surface clays characterization. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2013, 3, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Tsagkalias, I.; Achilias, D.S.; Ladavos, A. A novel method for the preparation of inorganic and organo-modified montmorillonite essential oil hybrids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anžlovar, A.; Orel, Z.C.; Kogej, K.; Zigon, M. Polyol-mediated synthesis of Zinc Oxide nanorods and nanocomposites with Poly(methyl methacrylate). J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, B.H.; Deshpande, M.P.; Bhatt, S.V.; Garg, N.; Chaki, S.H. Studies on ZnO nanorods synthesized by hydrothermal method and their characterization. J. Nano Electron. Phys. 2013, 5, 04077. [Google Scholar]
- Kandhol, G.; Wadhwa, H.; Chand, S.; Mahendia, S.; Kumar, S. Study of dielectric relaxation behavior of composites of Poly (vinyl alchohol) (PVA) and Reduced graphene oxide (RGO). Vacuum 2019, 160, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceran, Ö.B.; Şimşek, B.; Şara, O.N. Preparation and characterization novel dioctyl terephthalate blended polyvinyl alcohol-composite films incorporated with the graphene oxide and silver nanoparticles. Polym. Test. 2020, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, S.; Pratihar, S.K.; Behera, S.K. Strong and ductile graphene oxide reinforced PVA nanocomposites. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 684, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, F.; Di Michele, A.; Torre, L.; Puglia, D. Active Role of ZnO Nanorods in thermomechanical and barrier performance of Poly(vinyl alcohol-co-ethylene) formulations for flexible packaging. Polymer 2019, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abutalib, M.M. Effect of zinc oxide nanorods on the structural, thermal, dielectric and electrical properties of polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyle cellulose composites. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2019, 557, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaceri, H.; Wang, L.; Erfurt, D.; Riedel, W.; Mangalgiri, G.; Khaldoun, A.; El Kenz, A.; Benyoussef, A.; Ennaoui, A. Water-resistant surfaces using zinc oxide structured nanorod arrays with switchable wetting property. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 299, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.; Kwon, H.; Kim, D.; Seo, J.; Han, H.; Khan, S.B. Highly-enhanced water resistant and oxygen barrier properties of cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) hybrid films for packaging applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 85, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawhecker, K.E.; Manias, E. Structure and properties of Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Na+ montmorillonite nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasimi, A.; Stavropoulou, A.; Papadokostaki, K.G.; Sanopoulou, M. Transport of water in polyvinyl alcohol films: Effect of thermal treatment and chemical crosslinking. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 4098–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.J.; García-Gutiérrez, M.C.; Nogales, A.; Rueda, D.R.; Kwiatkowska, M.; Szymczyk, A.; Roslaniec, Z.; Concheso, A.; Guinea, I.; Ezquerra, T.A. Influence of preparation procedure on the conductivity and transparency of SWCNT-polymer nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1867–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Loganathan, S.; Valapa, R.B.; Thomas, S.; Varghese, T.O. UV protective poly(lactic acid)/rosin films for sustainable packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei-Ghazvini, A.; Shahabi-Ghahfarrokhi, I.; Goudarzi, V. Preparation of UV-protective starch/kefiran/ZnO nanocomposite as a packaging film: Characterization. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 16, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.M.; Partila, A.M.; El-Rehim, H.A.A.; Deghiedy, N.M. Antimicrobial ZnO nanoparticle–doped polyvinyl alcohol/pluronic blends as active food packaging films. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, M.; Firouzabadi, F.B. Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticle suspensions on food-borne pathogens. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2012, 66, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Habib, S.S.; Memic, A. Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: A comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 6003–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| A/A | Code Name | Zn(CH3COO)2×2H2O (g) | ZnO (g) | NaMt | Batch Total Volume (Water-mL) | Reflux (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ZnO | 4.525 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 50 | 1 |
| 2 | ZnO/NaMt-4 | 4.525 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 50 | 1 |
| 3 | ZnO/NaMt-2 | 4.525 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 50 | 1 |
| 4 | ZnO/NaMt-1 | 4.525 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 50 | 1 |
| 5 | ZnO/NaMt-0.7 | 4.525 | 20 | 3.0 | 50 | 1 |
| 6 | ZnO/NaMt-0.5 | 4.525 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 50 | 1 |
| 7 | ZnO/NaMt-0.4 | 4.525 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 50 | 1 |
| Samples Code Names | PVOH (g) | ZnO/NaMt*(g) | %ZnO Content | %NaMt Content | Extrusion Process | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | Speed (rpm) | Time (min) | |||||
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-4 | 4.85 | 0.15 | 2.4 | 0.6 | 190 | 100 | 10 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-2 | 4.85 | 0.15 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 190 | 100 | 10 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-1 | 4.85 | 0.15 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 190 | 100 | 10 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.7 | 4.85 | 0.15 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 190 | 100 | 10 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.5 | 4.85 | 0.15 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 190 | 100 | 10 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.4 | 4.85 | 0.15 | 0.86 | 2.14 | 190 | 100 | 10 |
| PVOH/NaMt | 4.85 | 0.15 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 190 | 100 | 10 |
| Samples Code Names | Young’s Modulus-(E) | Tensile Strength-(σuts) | % Elongation at Break (%ε) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVOH | 2066.6 ± 146.5 | 6.7 ± 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
| PVOH/NaMt | 2602.2 ± 158.8 | 12.5 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.2 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-4 | 3154.3 ± 167.3 | 19.1 ± 0.7 | 1.0 ± 0.2 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-2 | 2546.6 ± 158.5 | 12.7 ± 0.7 | 0.8 ± 0.2 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-1 | 2328.8 ± 145.2 | 10.4 ± 0.6 | 0.8 ± 0.3 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.7 | 2168.3 ± 163.2 | 6.3 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.5 | 1978.2 ± 125.8 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.4 | 936.5 ± 98.5 | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| Samples Code Names | % Water Sorption | WVTR (g/m2/d) | OP (cm3.mm/m2/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVOH | 633.3 ± 5.5 | 30.1 ± 0.3 | 9.5 ± 0.4 |
| PVOH/NaMt | 626.3 ± 4.4 | 28.5 ± 0.4 | 6.5 ± 0.3 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-4 | 66.5 ± 2.3 | 23.7 ± 0.3 | 4.5 ± 0.2 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-2 | 155.9 ± 3.2 | 25.3 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 0.3 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-1 | 165.2 ± 3.1 | 27.2 ± 0.2 | 4.7 ± 0.2 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.7 | 220.2 ± 3.6 | 28.5 ± 0.2 | 5.9 ± 0.2 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.5 | 290.5 ± 3.5 | 30.9 ± 0.3 | 7.4 ± 0.2 |
| PVOH/ZnO/NaMt-0.4 | 310.3 ± 3.8 | 33.3 ± 0.3 | 9.1 ± 0.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salmas, C.; Giannakas, A.; Katapodis, P.; Leontiou, A.; Moschovas, D.; Karydis-Messinis, A. Development of ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Hybrid Nanostructures Used for PVOH/ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Active Packaging Films Preparation via a Melt-Extrusion Process. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061079
Salmas C, Giannakas A, Katapodis P, Leontiou A, Moschovas D, Karydis-Messinis A. Development of ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Hybrid Nanostructures Used for PVOH/ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Active Packaging Films Preparation via a Melt-Extrusion Process. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061079
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalmas, Constantinos, Aris Giannakas, Petros Katapodis, Areti Leontiou, Dimitrios Moschovas, and Andreas Karydis-Messinis. 2020. "Development of ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Hybrid Nanostructures Used for PVOH/ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Active Packaging Films Preparation via a Melt-Extrusion Process" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061079
APA StyleSalmas, C., Giannakas, A., Katapodis, P., Leontiou, A., Moschovas, D., & Karydis-Messinis, A. (2020). Development of ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Hybrid Nanostructures Used for PVOH/ZnO/Na-Montmorillonite Active Packaging Films Preparation via a Melt-Extrusion Process. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061079