Biosynthesis of Bonelike Apatite 2D Nanoplate Structures Using Fenugreek Seed Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biosynthesis Process
2.2. In Vitro Cell Culture
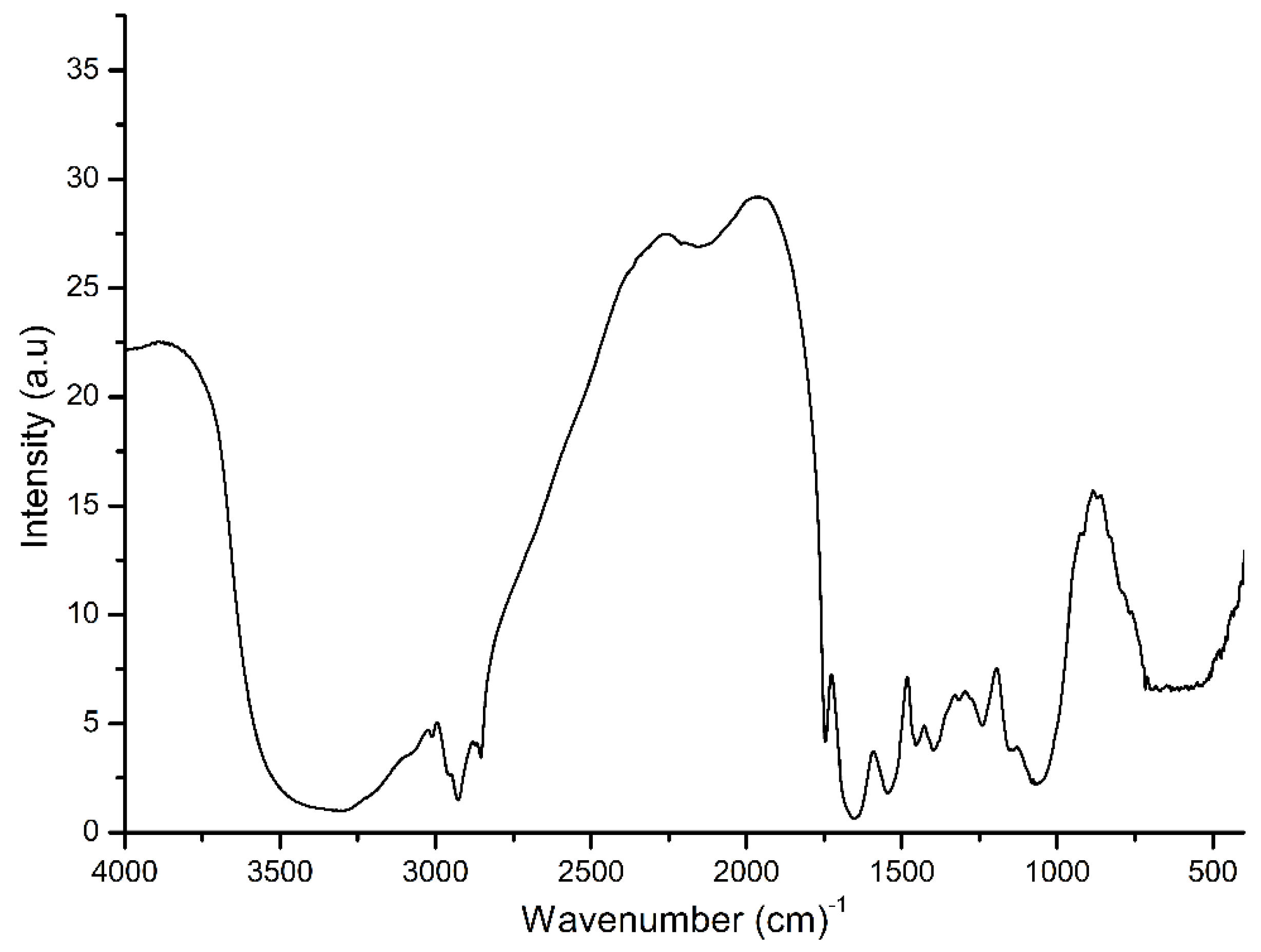
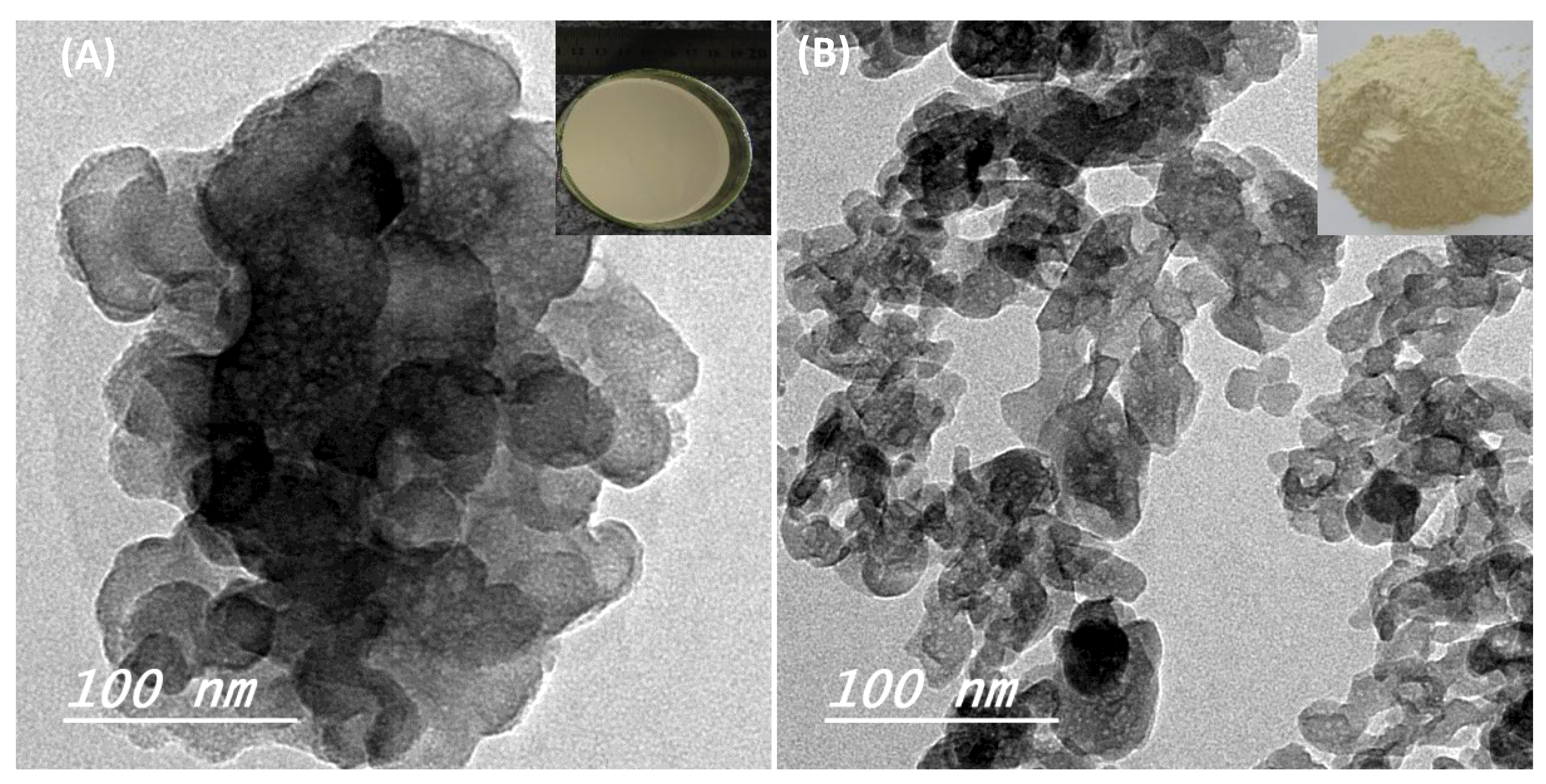
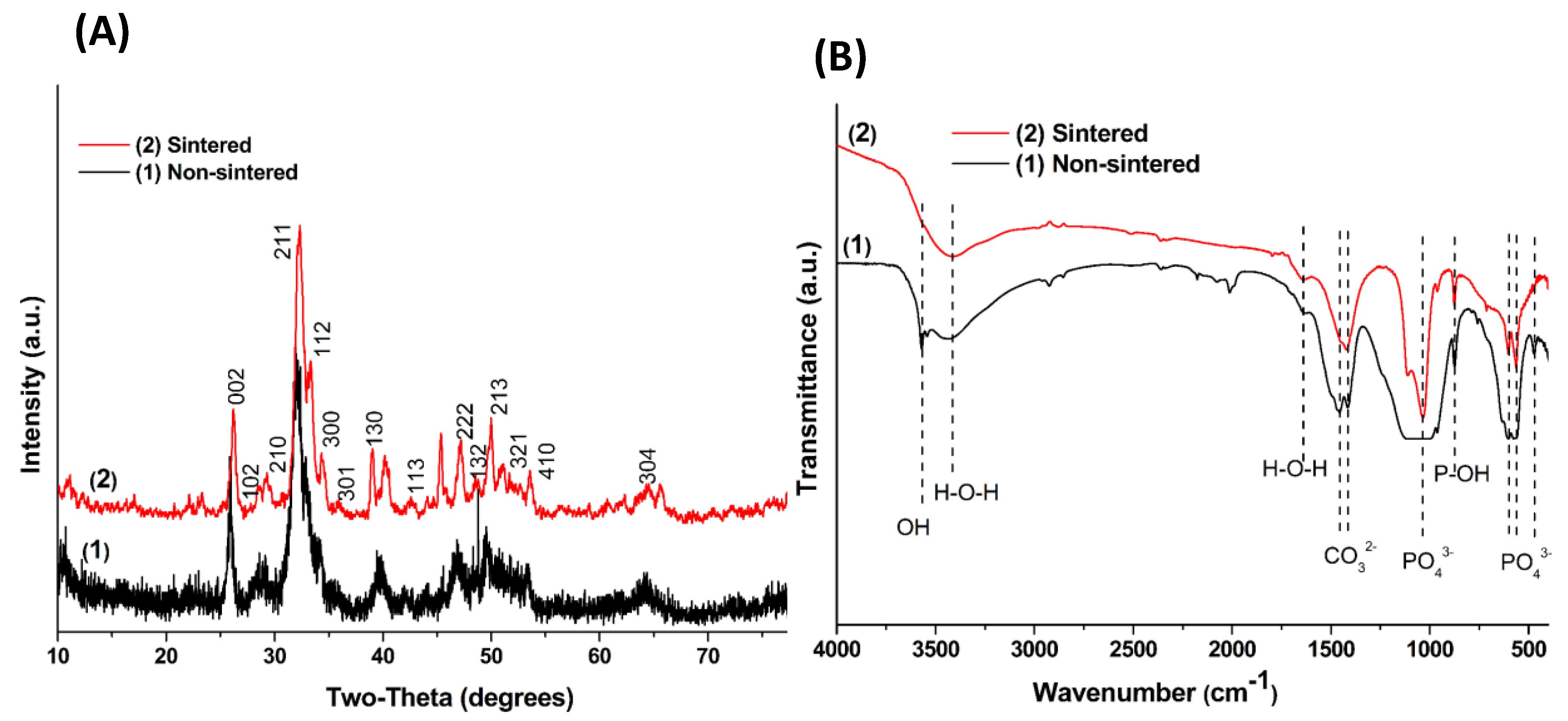
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, H.; Lee, J. Nanoscale hydroxyapatite particles for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2769–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Biomimetic porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 80, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predoi, D.; Iconaru, S.L.; Predoi, M.V.; Stan, G.E.; Buton, N. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Activity of Magnesium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Suspensions. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal-hay, A.; Barakat, N.A.; Lim, J.K. Hydroxyapatite-doped poly (lactic acid) porous film coating for enhanced bioactivity and corrosion behavior of AZ31 Mg alloy for orthopedic applications. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Gong, C.; Hu, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Biomimetic Hydroxyapatite on Graphene Supports for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopi, D.; Kanimozhi, K.; Bhuvaneshwari, N.; Indira, J.; Kavitha, L. Novel banana peel pectin mediated green route for the synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and their spectral characterization. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szałaj, U.; Świderska-Środa, A.; Chodara, A.; Gierlotka, S.; Łojkowski, W. Nanoparticle Size Effect on Water Vapour Adsorption by Hydroxyapatite. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, A.C. Synthesis of biomimetic Ca-hydroxyapatite powders at 37 °C in synthetic body fluids. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Mondal, S.; Jang, B.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Oh, J. Biomimetic synthesis of metal–hydroxyapatite (Au-HAp, Ag-HAp, Au-Ag-HAp): Structural analysis, spectroscopic characterization and biomedical application. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 20490–20500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Sakthivel, N. Green synthesis of biogenic metal nanoparticles by terrestrial and aquatic phototrophic and heterotrophic eukaryotes and biocompatible agents. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: Structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; McLean, J.E.; Latta, D.E.; Manangón, E.; Britt, D.W.; Johnson, W.P.; Boyanov, M.I.; Anderson, A.J. CuO and ZnO nanoparticles: Phytotoxicity, metal speciation, and induction of oxidative stress in sand-grown wheat. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, K.; Sathish, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Ramachandran, T. Fast kinetics and high adsorption capacity of green extract capped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the adsorption of Ni(II) ions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 59, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundrarajan, M.; Ambika, S.; Bharathi, K. Plant-extract mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pongamia pinnata and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Turkdemir, H.; Kilic, M.A.; Bayram, E.; Cicek, A.; Mete, A.; Ulug, B. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves of Stevia rebaudiana. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Yunus, R.M.; Alara, O.R.; Abayomi, O.O. Extraction, characterization and antioxidant activity of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seed oil. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aromal, S.A.; Philip, D. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum and its size-dependent catalytic activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 97, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanger, M.I.; Bukhari, S.B.; Memon, S. Chemistry, Antioxidative activity of extracts from a Fenugreek seeds (Trigonella foenum-graecum). Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2008, 9, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Kozłowska, M.; Gruczyńska, E.; Ścibisz, I.; Rudzińska, M. Fatty acids and sterols composition, and antioxidant activity of oils extracted from plant seeds. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chu, B.; Hsiao, B.S. Mineralization of hydroxyapatite in electrospun nanofibrous poly(L-lactic acid) scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 79, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezwan, K.; Chen, Q.Z.; Blaker, J.J.; Boccaccini, A.R. Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3413–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Mak, A.F.; Li, J. Formation of bone-like apatite on poly(L-lactic acid) fibers by a biomimetic process. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 57, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Nabey, A.; Damir, A. Changes in some nutrients of fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum graecum L.) seeds during water boiling. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1990, 40, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Chin, T.S.; Lai, L.S.; Chiu, S.Y.; Chung, K.H.; Chang, C.S.; Lui, M.T. Hydroxyapatite synthesized by a simplified hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 1997, 23, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzi, G.; Celotti, G.; Landi, E.; La Torretta, T.M.G.; Sopyan, I.; Tampieri, A. A novel sol–gel technique for hydroxyapatite preparation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 78, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, A.N.; Zlotnikov, E.; Khinast, J.G.; Riman, R.E. Chemisorption of silane compounds on hydroxyapatites of various morphologies. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. Potassium Intake and Blood Pressure; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. Beneficial effects of potassium. BMJ 2001, 323, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, K.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, J.; Zang, Y.; Wu, J.; Kong, L.; Liu, S. A novel injectable calcium phosphate cement-bioactive glass composite for bone regeneration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal-hay, A.; Oh, Y.S.; Yousef, A.; Pant, H.R.; Vanegas, P.; Lim, J.K. In Vitro Deposition of Ca-P Nanoparticles on Air Jet Spinning Nylon 6 Nanofibers Scaffold For Bone Tissue Engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zberg, B.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Loffler, J.F. MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, S.; McBain, S.; Dobson, J.; El Haj, A.J. Selective activation of mechanosensitive ion channels using magnetic particles. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H. Preparation of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles by reverse microemulsion. Ceram. Int. 2005, 31, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, G.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H. Synthesis of single-crystal HAP nanorods. Ceram. Int. 2006, 32, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legroux-Gerot, I.; Vignau, J.; Collier, F.; Cortet, B. Bone loss associated with anorexia nervosa. Jt. Bone Spine 2005, 72, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.L.; Wong, T.L.; Wong, M.C.; Lang, N.P. A systematic review of post-extractional alveolar hard and soft tissue dimensional changes in humans. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Ca | Fe | K | Mg | Na | P | Zn | SO4 | Cl | CO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FG seeds extracts | 17 | 0.39 | 751 | 20 | 32.2 | 35 | 0.14 | 32 | 83.7 | 56 |
| BAp minerals | 2978 | 0.45 | 822 | 32 | 39.7 | 1014 | 0.24 | 38 | 78.5 | 169 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdal-hay, A.; Fouad, H.; A. ALshammari, B.; Khalil, K.A. Biosynthesis of Bonelike Apatite 2D Nanoplate Structures Using Fenugreek Seed Extract. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050919
Abdal-hay A, Fouad H, A. ALshammari B, Khalil KA. Biosynthesis of Bonelike Apatite 2D Nanoplate Structures Using Fenugreek Seed Extract. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(5):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050919
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdal-hay, Abdalla, H. Fouad, Basheer A. ALshammari, and Khalil Abdelrazek Khalil. 2020. "Biosynthesis of Bonelike Apatite 2D Nanoplate Structures Using Fenugreek Seed Extract" Nanomaterials 10, no. 5: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050919
APA StyleAbdal-hay, A., Fouad, H., A. ALshammari, B., & Khalil, K. A. (2020). Biosynthesis of Bonelike Apatite 2D Nanoplate Structures Using Fenugreek Seed Extract. Nanomaterials, 10(5), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050919








