Are Titania Photocatalysts and Titanium Implants Safe? Review on the Toxicity of Titanium Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Toxicity of Titanium and Its Alloys
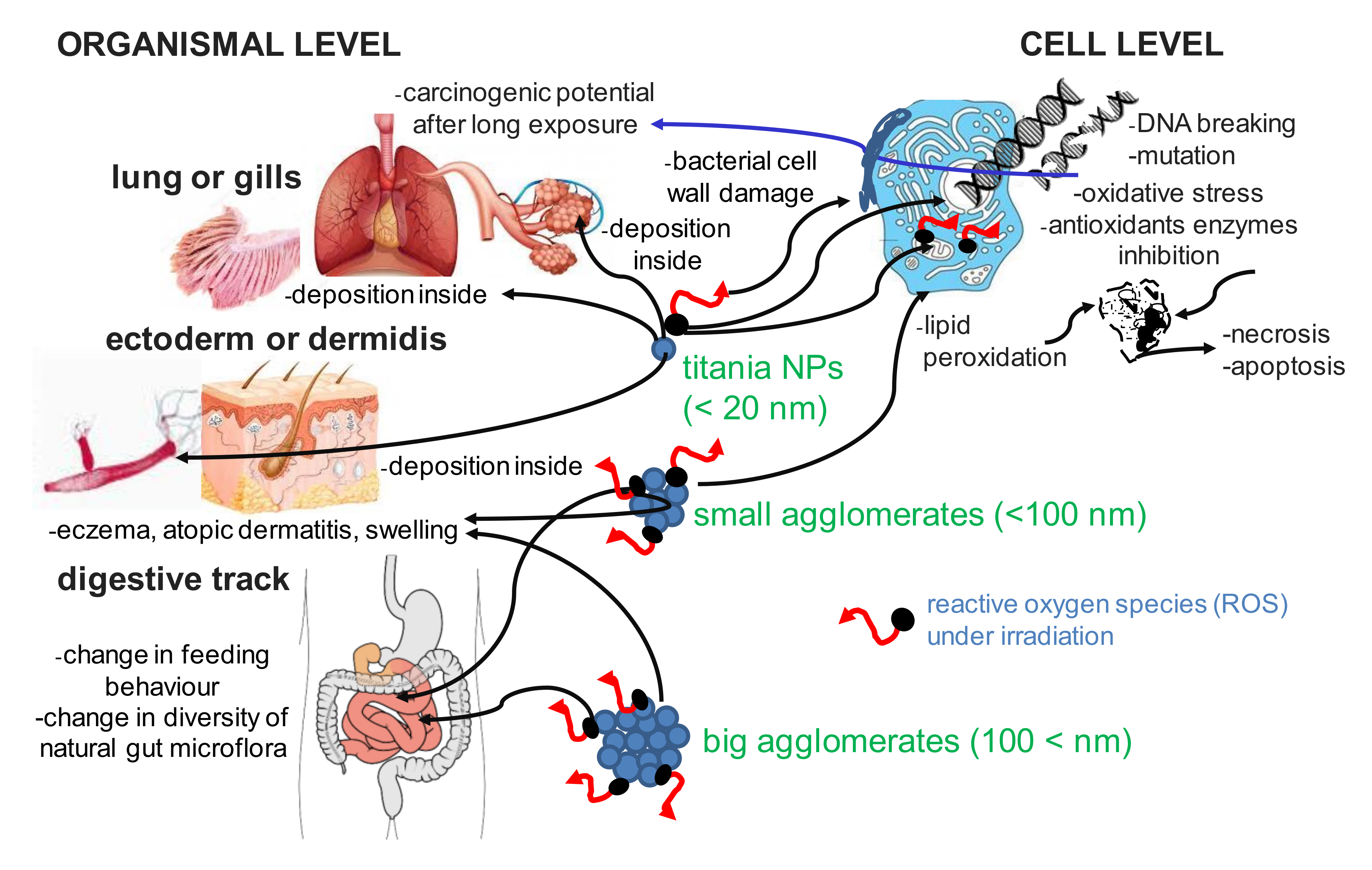
3. Toxicity of Titanium(IV) Oxide
3.1. Can Inhalation of Titania Cause Cancer?
3.2. Dermal and Oral Exposure to Titania

3.3. Titania Ecotoxicity
4. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ANSES | French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health and Safety |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| BBB | Brain Blood Barrier |
| BMSCs | Bone Marrow Stem Cells |
| BP-3 | Benzophenone-3 |
| CARS | Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Scattering and Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Scattering spectroscopy |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CLP | Classification, Labelling and Packaging |
| CMH2DCFDA | General Oxidative Stress Indicator, i.e., 5-(and-6)-chlomethyl-2′7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate acetyl ester |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EC | European Council |
| EC50 | Half maximal Effective Concentration |
| EU | European Union |
| ECHA | European Chemicals Agency |
| GP | Glutathione Peroxidase |
| GR | Glutathione Reductase |
| GST | Glutathione-S-Transferase |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IP | Intraperitoneal injection |
| LD50 | Median Lethal Dose |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| MAK | Maximum Concentration values in the Workplace |
| MCF7 | Breast cancer cells (Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 cell line) |
| MC3T3-E1 | Mouse osteoblastic cells |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NLM | National Library of Medicine |
| NIOSH | National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health |
| NOAEL | No-Observed-Adverse-Effect Level |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| OSHA | The Occupational Safety and Health Administration |
| P25 | Evonik (Degussa) titanium dioxide (type P25) |
| PEL | Permissible Exposure Limit |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PDL-hTERT | Periodontal Ligament human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase |
| PPCPs | Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products |
| PPE | Personal Protective Equipment |
| RAC | Risk Assessment Committee |
| RANK-RANKL | Receptor Activator of Nuclear factor Kappa-Β–Receptor Activator of Nuclear factor Kappa-Β Ligand |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances |
| TBT | Tributyltin |
| TDMA | Titanium Dioxide Manufacturers Association |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor α |
| TPS | Titanium Plasma-Sprayed |
| TWA | Time-Weighted Average |
| UV-A | Ultraviolet A |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| YAP | Yes-Associated Protein |
| YNS | Yellow Nail Syndrome |
References
- Schwartz, M. Encyclopedia and Handbook of Materials, Parts and Finishes, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hock, C.W. How TiCl3 Catalysts Control Texture of as-polymerized Polypropylene. Polym. Sci. 1966, 4, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. Mechanical Properties of Biomedical Titanium Alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 1998, 243, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Rapidly Solidified Powder Metallurgy Mg97Zn1Y2 Alloys with Excellent Tensile Yield Strength above 600 MPa. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, E.O. Key Improvements in the Machining of Difficult-to-cut Aerospace Superalloys. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manu. 2005, 45, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.H.; Huang, Q.L.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, Z.X.; Liang, L.X. Powder Metallurgical Ti-Mg Metal-metal Composites Facilitate Osteoconduction and Osseointegration for Orthopedic Application. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Tian, J.; Liu, Z.; Lu, X.; Hayat, M.D.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z.; Qu, X.; Wen, C. Novel porous Ti35Zr28Nb scaffolds fabricated by powder metallurgy with excellent osteointegration ability for bone-tissue engineering applications. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2019, 105, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharubin, S.; Hu, Y.; Sooriyaarachchi, D.; Cong, W.; Tan, G.Z. Laser Engineered Net Shaping of Antimicrobial and Biocompatible Titanium-silver Alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Xie, J.; Mao, L. One-pot assembly Tannic Acid-titanium Dual Network Coating for Low-pressure Nanofiltration Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 233, 116051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schkroeder, H.A.; Balassa, J.J.; Tipton, I.H. Abnormal Trace Metals in Man: Titanium. J. Chronic Dis. 1963, 16, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branemark, P. Osseointegration and Its Experimental Background. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 50, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouilleau, J.; Devilliers, D.; Garrido, F.; Durand-Vidal, S.; Mahé, E. Structure and Composition of Passive Titanium Oxide Films. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 1997, 47, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, T. Metal Ion Release from Metal Implants. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2004, 24, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, T. Surface Treatment and Modification of Metals to Add Biofunction. Dent. Mater. J. 2017, 36, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, T.P. An Overview of the Corrosion Aspect of Dental Implants (Titanium and its Alloys). Indian J. Dent. Res. 2009, 20, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fage, S.W.; Muris, J.; Jakobsen, S.S.; Thyssen, J.P. Titanium: A Review on Exposure, Release, Penetration, Allergy, Epidemiology, and Clinical Reactivity. Contact Dermat. 2016, 74, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabrzyński, J.; Jaworski, Ł. Myths and Facts about Combining Metals in Orthopedic surgery. Chir. Narz. Ruchu Ortop. Pol. 2017, 82, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Spriano, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Baino, F.; Ferraris, S. A Critical Review of Multifunctional Titanium Surfaces: New Frontiers for Improving Osseointegration and Host Response, Avoiding Bacteria Contamination. Acta Biomater. 2018, 79, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Eo, M.Y.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Kim, S.M. General Review of Titanium Toxicity. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2019, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strietzel, R.; Hösch, A.; Kalbfleisch, H.; Buch, D. In Vitro Corrosion of Titanium. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicilia, A.; Cuesta, S.; Coma, G.; Arregui, I.; Guisasola, C.; Ruiz, E.; Maestro, A. Titanium Allergy in Dental Implant Patients: A Clinical Study on 1500 Consecutive Patients. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhola, R.; Bhola, S.M.; Mishra, B.; Olson, D.L. Corrosion in Titanium Dental Implants/prostheses—A Review. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2011, 25, 34–46. [Google Scholar]
- Evrard, L. Titanium: A new allergen. In Implant Dentistry—A Rapidly Evolving Practice; Turkyilmaz, I., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, J.J.; Skipor, A.K.; Patterson, L.M.; Hallab, N.J.; Paprosky, W.G.; Black, J.; Galante, J.O. Metal Release in Patients Who Have Had a Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Prospective, Controlled, Longitudinal Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1998, 80, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, Y.; Iida, R.; Uchida, A. Metal Concentrations in the Serum and Hair of Patients with Titanium Alloy Spinal Implants. Spine 2003, 28, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Alvaredo, J.; Blanco, E.; Bettmer, J.; Hevia, D.; Sainz, R.M.; López Cháves, C.; Sánchez, C.; Llopis, J.; Sanz-Medel, A.; Montes-Bayón, M. Evaluation of the Biological Effect of Ti Generated Debris from Metal Implants: Ions and Nanoparticles. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G. Potential Causes of Titanium Particle and Ion Release in Implant Dentistry: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, N.; Grosgogeat, B.; Lissac, M.; Dalard, F. Influence of Fluoride Content and pH on the Corrosion Resistance of Titanium and its Alloys. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Addison, O.; Davenport, A.J. A Synergistic Effect of Albumin and H2O2 Accelerates Corrosion of Ti6Al4V. Acta Biomater. 2015, 26, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penarrieta-Juanito, G.; Sordi, M.B.; Henriques, B.; Dotto, M.E.R.; Teughels, W.; Silva, F.S.; Magini, R.S.; Souza, J.C.M. Surface Damage of Dental Implant Systems and Ions Release After Exposure to Fluoride and Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Periodontal. Res. 2019, 54, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, D.R.; Rogers, S.D.; Hay, S.; Pearcy, M.J.; Howie, D.W. The Differences in Toxicity and Release of Bone-resorbing Mediators Induced by Titanium and Cobalt-chromium-alloy Wear Particles. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1993, 75, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettlemore, M.G.; Bundy, K.J. Toxicity Measurement of Orthopedic Implant Alloy Degradation Products Using a Bioluminescent Bacterial Assay. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 45, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Thouas, G.A. Metallic Implant Biomaterials. Mat. Sci. Eng. R. 2015, 87, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadija, G.; Saleem, A.; Akhtara, Z.; Naqvi, Z.; Gull, M.; Masood, M.; Mukhtar, S.; Batool, M.; Saleem, N.; Rasheed, T.; et al. Short Exposure to Titanium, Aluminum and Vanadium (Ti 6Al 4V) Alloy Powder Drastically Affects Behavior and Antioxidant Metabolites in Vital Organs of Male Albino Mice. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovan, V.; Tugce, T.; Topal, E.S. The Effect of Molybdenum on Titanium’s Castability in Dental Prosthesis Applications: A Numerical Analysis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2019, L 233, 1966–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, R.E.; Ma, J.; Verkhoturov, S.V.; Munoz-Pinto, D.; Karaman, I.; Rubitschek, F.; Maier, H.J.; Hahn, M.S. A Comparative Study of the Cytotoxicity and Corrosion Nickel-Titanium and Titanium-niobium Shape Memory Alloys. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirmanidou, T.; Sidira, M.; Drosou, M.E.; Bennani, V.; Bakopoulou, A.; Tsouknidas, A.; Michailidis, N.; Michalakis, K. New Ti-Alloys and Surface Modifications to Improve the Mechanical Properties and the Biological Response to Orthopedic and Dental Implants: A Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikarashi, Y.; Toyoda, K.; Kobayashi, E.; Doi, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Hamanaka, H.; Tsuchiya, T. Improved Biocompatibility of Titanium-zirconium (Ti–Zr) Alloy: Tissue Reaction and Sensitization to Ti–Zr Alloy Compared with Pure Ti and Zr in Rat Implantation Study. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2260–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbock, C.; Jakobi, J.; Gamrad, L.; Van Der Meer, S.; Tiedemann, D.; Taylor, U.; Kues, W.; Rath, D.; Barcikowski, S. Current State of Laser Synthesis of Metal and Alloy Nanoparticles as Ligand-free Reference Materials for Nano-toxicological Assays. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1523–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Yun, Y.P.; Park, K.; Kim, S.E. Gentamicin and Bone Morphogenic Protein-2 (BMP-2)-delivering heparinized-titanium Implant with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity and Osteointegration. Bone 2012, 50, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grischke, J.; Eberhard, J.; Stiesch, M. Antimicrobial Dental Implant Functionalization Strategies—A Systematic Review. Dent. Mat. J. 2016, 35, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, J.B.; Deslouches, B.; Montelaro, R.C.; Shanks, R.M.Q.; Doi, Y.; Urish, K.L. Elimination of Antibiotic Resistant Surgical Implant Biofilms Using an Engineered Cationic Amphipathic Peptide WLBU2. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, T. The Toxicity of Metals Used in Orthopaedic Prostheses. An Experimental Study Using Cultured Human Synovial Fibroblasts. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1981, 63-B, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, D.G.; Tasat, D.; Guglielmotti, M.B.; Cabrini, R.L. Titanium Transport Through the Blood Stream. An Experimental Study on Rats. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 14, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Reichl, F.X.; Wang, Y.; Michalke, B.; Milz, S.; Yang, Y.; Stolper, P.; Lindemaier, G.; Graw, M.; Hickel, R.; et al. Analysis of Titanium and Other Metals in Human Jawbones with Dental Implants—A Case Series Study. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukina, E.; Laka, A.; Kollerov, M.; Sampiev, M.; Mason, P.; Wagstaff, P.; Noordeen, H.; Yoon, W.W.; Blunn, G. Metal Concentrations in the Blood and Tissues After Implantation of Titanium Growth Guidance Sliding Instrumentation. Spine J. 2016, 16, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliephake, H.; Reiss, G.; Urban, R.; Neukam, F.W.; Guckel, S. Metal Release from Titanium Fixtures During Placement in the Mandible: An Experimental Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1993, 8, 502–511. [Google Scholar]
- Ipach, I.; Schäfer, R.; Mittag, F.; Leichtle, C.; Wolf, P.; Kluba, T. The Development of Whole Blood Titanium Levels After Instrumented Spinal Fusion—Is There a Correlation Between the Number of Fused Segments and Titanium Levels? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord 2012, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temiz, M.; Dayi, E.; Saruhan, N. Evaluation of Blood Titanium Levels and Total Bone Contact Area of Dental Implants. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 4121639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warme, B.A.; Epstein, N.J.; Trindade, M.C.; Miyanishi, K.; Ma, T.; Saket, R.R.; Regula, D.; Goodman, S.B.; Smith, R.L. Proinflammatory Mediator Expression in a Novel Murine Model of Titanium-particle-induced Intramedullary Inflammation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 71, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, A.; Pawar, V.; McAllister, K.; Weaver, C.; Hallab, N.J. Orthopedic Implant Cobalt-alloy Particles Produce Greater Toxicity and Inflammatory Cytokines than Titanium Alloy and Zirconium Alloy-based Particles in vitro, in Human Osteoblasts, Fibroblasts, and Macrophages. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachi, T.; Shuto, T.; Shinohara, Y.; Matono, Y.; Makihira, S. Release of Titanium Ions from an Implant Surface and their Effect on Cytokine Production Related to Alveolar Bone Resorption. Toxicology 2015, 327, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safioti, L.M.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Pozhitkov, A.E.; Chung, W.O.; Daubert, D.M. Increased Levels of Dissolved Titanium are Associated with Peri-implantitis—A Cross-sectional Study. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, M.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Salehiarjomand, H. Nano-anatase TiO2 Modulates the Germination Behavior and Seedling Vigority of Some Commercially Important Medicinal and Aromatic Plants. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 8, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Penmetsa, S.L.D.; Shah, R.; Thomas, R.; Kumar, A.B.T.; Gayatri, P.S.D.; Mehta, D.S. Titanium particles in tissues from peri-implant mucositis: An exfoliative cytology-based pilot study. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2017, 21, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suárez-López del Amo, F.; Garaicoa-Pazmiño, C.; Fretwurst, T.; Castilho, R.M.; Squarize, C.H. Dental Implants—Associated release of Titanium Particles: A A systematic Review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goutam, M.; Giriyapura, C.; Mishra, S.K.; Gupta, S. Titanium Allergy: A Literature Review. Indian J. Dermatol. 2014, 59, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bircher, A.J.; Stern, W.B. Allergic Contact Dermatitis from “Titanium” Spectacle Frames. Contact Dermat. 2001, 45, 244–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egusa, H.; Ko, N.; Shimazu, T.; Yatani, H. Suspected Association of An Allergic Reaction with Titanium Dental Implants: A Clinical Report. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 100, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.; Bandl, W.D.; Maier, S.; Summer, B.; Przybilla, B. Hypersensitivity to Titanium Osteosynthesis with Impaired Fracture Healing, Eczema, and T-cell Hyperresponsiveness In Vitro: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Contact Dermat. 2006, 55, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W.; Vermilyea, S.G. A Review of Selected Dental Literature on Evidence-based Treatment Planning for Dental Implants: Reports of the Committee on Research in Fixed Prosthodontics of the Academy of Fixed Prosthodontics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, F. Titanium and Yellow Nail Syndrome. In Novel Strategies in Lymphedema; EPublishing; Vannelli, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Decker, A.; Daly, D.; Scher, R.K. Role of Titanium in the Development of Yellow Nail Syndrome. Skin Appendage Disord. 2015, 1, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataya, A.; Kline, K.P.; Cope, J.; Alnuaimat, H. Titanium Exposure and Yellow Nail Syndrome. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2015, 16, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, P.D.; Ducheyne, P.; Cuckler, J.M. Local Accumulation of Titanium Released from a Titanium Implant in the Absence of Wear. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 31, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Pettersson, J.; Thoren, M.M.; Johansson, A. Release of Titanium After Insertion of Dental Implants with Different Surface Characteristics—An ex vivo Animal Study. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Scand. 2018, 3, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, D.; Fini, M.; Franchi, M.; Pasquale, V.D.; Bacchelli, B.; Gamberini, M.; Tinti, A.; Taddei, P.; Giavaresi, G.; Ottani, V.; et al. Detachment of Titanium and Fluorohydroxyapatite Particles in Unloaded Endosseous Implants. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Chen, J.; Guo, D.; Ye, Q.; Liang, X. The Effect of Titanium Particles on Rat Bone Marrow Stem Cells In Vitro. Toxicol. Mech. Method. 2009, 19, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, C.C.; Moreira, L.M.; Santos, V.J.S.V.; Ramos, A.S.; Lyon, J.P.; Soares, C.P.; Santos, F.V. Assessment of the Genetic Risks of a Metallic Alloy Used in Medical Implants. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2011, 34, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassopoulou, J. Metal-DNA Interactions. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 651–653, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, M.H.; Kraatz, H.M. Interactions of Metal Ions with DNA and Some Applications. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2012, 23, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Toxicity of Metal Compounds: Knowledge and Myths. Organometallics 2017, 36, 4071–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hartlieb, E.; Rothmund, L.; Waschke, J.; Wu, X.; Van Landuyt, K.L.; Milz, S.; Michalke, B.; Hickel, R.; Reichl, F.X.; et al. Intracellular Uptake and Toxicity of Three Different Titanium Particle. Dental Mater. 2015, 31, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumazawa, R.; Watari, F.; Takashi, N.; Tanimura, Y.; Uo, M.; Totsuka, Y. Effects of Ti Ions and Particles on Neutrophil Function and Morphology. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3757–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.J. Cell Damage In Vitro Following Direct Contact with Fine Particles of Titanium, Titanium Alloy and Cobalt-chrome-molybdenum Alloy. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Takashi, N.; Kumazawa, R.; Watari, F.; Totsuka, Y. Effects of Particle Size on Cell Function and Morphology in Titanium and Nickel. Mater. Trans. 2012, 43, 3052–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Ming, P.; Qiu, J.; Shao, S.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, S.; Tang, C. Effect of Titanium Ions on the Hippo/YAP Signaling Pathway in Regulating Biological Behaviors of MC3T3-E1 Osteoblasts. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suska, F.; Gretzer, C.; Esposito, M.; Emanuelsson, L.; Wennerberg, A.; Tengvall, P.; Thomsen, P. In Vivo Cytokine Secretion and NF-κB Activation Around Titanium and Copper Implants. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obando-Pereda, G.A.; Fischer, L.; Stach-Machado, D.R. Titanium and Zirconia Particle-induced Pro-inflammatory Gene Expression in Cultured Macrophages and Osteolysis, Inflammatory Hyperalgesia and Edema In Vivo. Life Sci. 2014, 97, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.S.; Caughman, G.B. Alterations of Cell Lipids by Metal Salts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 70, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Jornet, P.; Perrez, F.P.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Lor-Ros, I.L.; Ramírez-Fernández, P. Metallic Ion Content and Damage to the DNA in Oral Mucosa Cells Patients Treated Dental Implants. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Wurtz, T.; Li, J. Influence of Titanium Ion on Mineral Formation and Properties of Osteoid Nodules in Rat Calvaria Cultures. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 47, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fretwurst, T.; Buzanich, G.; Nahles, S.; Woelber, J.P.; Riesemeier, H.; Nelson, K. Metal Elements in Tissue with Dental Peri-implantitis: A Pilot Study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fretwurst, T.; Nelson, K.; Tarnow, D.P.; Wang, H.L.; Giannobile, W.V. Is Metal Particle Release Associated with Peri-implant Bone Destruction? An Emerging Concept. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydoğan, Z.; Sisman, T.; Icekara, U.; Gurol, A. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Some Aquatic Insects (Coleoptera: Hydrophilidae) and Tissue of Chondrostoma regium (Heckel, 1843) Relevant to Their Concentration in Water and Sediments from Karasu River, Erzurum, Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9566–9574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rodríguez, G.; Galván, M.; González-Unzaga, M.; Ávila, J.H.; Pérez-Labra, M. Blood Toxic Metals and Hemoglobin Levels in Mexican Children. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elagli, K.; Neut, C.; Romond, C.; Hildebrand, H.F. In Vitro Effects of Titanium Powder on Oral Bacteria. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, A.; Dahlén, G. Effect of Titanium on Selected Oral Bacterial Species in Vitro. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1995, 103, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.W.; Moore, T.J.; Safar, J.A.; Henry, C.A.; Wagner, M.J. Antibacterial Activity of Dental Implant Metals. Implant Dent. 1992, 1, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzoff, M.; Burns, J.E.; Aslani, A.; Tobin, E.J.; Nguyen, C.; De La Torre, N.; Golshan, N.H.; Ziemer, K.S.; Webster, T.J. Decreased Bacterial Growth on Titanium Nanoscale Topographies Created by Ion Beam Assisted Evaporation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pichat, P. A Brief Survey of the Potential Health Risks of TiO2 Particles and TiO2-Containing Photocatalytic and Non-photocatalytic Materials. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2010, 13, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friehs, E.; Al Salka, Y.; Jonczyk, R.; Lavrentieva, A.; Jochums, A.; Walter, J.G.; Stahl, F.; Scheper, T.; Bahnemann, D. Toxicity, Phototoxicity and Biocidal Activity of Nanoparticles Employed in Photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2016, 29, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hex, P.M.; Tomenson, J.A.; Thompson, P. Titanium Dioxide: Inhalation Toxicology and Epidemiology. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2005, 49, 461–472. [Google Scholar]
- Bomgardner, M.M. Europe May Call TiO2 a Carcinogen. Inhalation Studies in Rats Spark Push for Classification. Chem. Eng. News 2017, 95, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, J. EU Moves Forward with TiO2 Carcinogen Classification; Food Packing Forum: Zurich, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://www.foodpackagingforum.org/news/eu-moves-forward-with-tio2-carcinogen-classification (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- EC, 2019 Commission Delegated Regulation (EU)…/…of XXX Amending, for the Purposes of its Adoption to Technical and Scientific Progress, Regulation (EC) 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Classification, Labelling and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures and Correcting that Regulation. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/transparency/regdoc/rep/3/2019/EN/C-2019-7227-1-EN-MAIN-PART-1.PDF (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Relier, C.; Dubreuil, M.; Lozano Garcia, O.; Cordelli, E.; Mejia, J.; Eleuteri, P.; Robidel, F.; Loret, T.; Pacchierotti, F.; Lucas, S.; et al. Study of TiO2 P25 Nanoparticles Genotoxicity on Lung, Blood, and Liver Cells in Lung Overload and Non-overload Conditions After Repeated Respiratory Exposure in Rats. Toxol. Sci. 2017, 156, 527–537. [Google Scholar]
- Skocaj, M.; Filipic, M.; Petkovic, J.; Novak, S. Titanium Dioxide in Our Everyday Life; Is It Safe? Radiol. Oncol. 2011, 45, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toxnet Toxicological Data Network. Available online: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/a?dbs+hsdb:@term+@DOCNO+869 (accessed on 7 December 2019).
- Yamadori, I.; Ohsumi, S.; Taguchi, K. Titanium Dioxide Deposition and Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. Acta Pathol. Jpn. 1986, 36, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans 1972–Present; Multivolume Work; World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, J.C. Systemic Granulomatous Disease, of the Sarcoid Type, Caused by Inhalation of Titanium Dioxide. Anatomo-clinical and Experimental Study. Acta Med. Port. 1992, 5, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moran, C.A.; Mullick, F.G.; Ishak, K.G.; Johnson, F.B.; Hummer, W.B. Identification of Titanium in Human Tissues: Probable Role in Pathologic Processes. Hum. Pathol. 1991, 22, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Fayerweather, W.E. Epidemiologic study of workers exposed to titanium dioxide. J. Occup. Med. 1988, 30, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffetta, P.; Soutar, A.; Cherrie, J.W.; Granath, F.; Andersen, A.; Anttila, A.; Blettner, M.; Gaborieau, V.; Klug, S.J.; Langard, S.; et al. Mortality Among Workers Employed in the Titanium Dioxide Production Industry in Europe. Cancer Causes Control 2004, 15, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryzek, J.P.; Chadda, B.; Marano, D.; White, K.; Schweitzer, S.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Blot, W.J. A Cohort Mortality Study Among Titanium Dioxide Manufacturing Workers in the United States. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 45, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, Y. Lung Injury Induced by TiO2 Nanoparticles Depends on Their Structural Features: Size, Shape, Crystal Phases, and Surface Coating. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22258–22278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, E. The Role of Surface Charge in Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Medical Nanoparticles. Int. J. Naomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Magaye, R.; Castranova, V.; Zhao, J. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: A Review of Current Toxicological Data. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennat, C.; Muller-Goymann, C.C. Skin Penetration and Stabilization of Formulations Containing Microfine Titanium Dioxide as Physical UV Filter. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2000, 22, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senzui, M.; Tamura, T.; Miura, K.; Ikarashi, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Fujii, M. Study on Penetration of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles into Intact and Damaged Skin in Vitro. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 35, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanedo-Cázares, J.P.; Martínez-Rosales, K.; Hernández-Blanco, D.; Valdés-Rodríguez, G.; Torres-Álvarez, B. In Vitro Assessment of Commercial Sunscreens Available in Latin America. Invest. Clin. 2014, 55, 142–154. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Penetration of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Through Slightly Damaged Skin in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2015, 13, e356–e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Wiench, K.; Landsiedel, R.; Schulte, S.; Inman, A.O.; Riviere, J.E. Safety Evaluation of Sunscreen Formulations Containing Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in UVB Sunburned Skin: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosera, M.; Prodi, A.; Mauro, M.; Pelin, M.; Florio, C.; Bellomo, F.; Adami, G.; Apostoli, P.; De Palma, G.; Bovenzi, M.; et al. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Penetration Into the Skin and Effects on HaCaT cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9282–9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, R.; Salinaro, A.; Cai, L.; Serpone, N.; Horikoshi, S.; Hidaka, H.; Knowland, J. Chemical Oxidation of DNA Damage Catalysed by Inorganic Sunscreen Ingredients. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, P.J.; Knowland, J. Characterization of DNA Damage Inflicted by Free Radicals from a Mutagenic Sunscreen Ingredient and its Location Using an in vitro Genetic Reversion Assay. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 66, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Koike, T.; Sato, T.; Serpone, N. DNA Damage Photoinduced by Cosmetic Pigments and Sunscreen Agents Under Solar Exposure and Artificial UV Illumination. J. Oleo Sci. 2006, 55, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buchalska, M.; Kras, G.; Oszajca, M.; Lasocha, W.; Macyk, W. Singlet Oxygen Generation in the Presence of Titanium Dioxide Materials Used as Sunscreens in Suntan Lotions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2010, 213, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borza, C.; Muntean, D.; Dehelean, C.; Săvoiu, G.; Şerban, C.; Simu, G.; Andoni, M.; Butur, M.; Drăgan, S. Oxidative Stress and Lipid Peroxidation—A Lipid Metabolism Dysfunction. In Lipid Metabolism; Baez, R.V., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Wei, Z.; Kowalska, E. The Influence of the Light-activated Titania P25 on Human Breast Cancer Cells. Catalysts 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Di Domenico, A.; Dusemund, B.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Lambre, C.; et al. Re-evaluation of Titanium Dioxide (E 171) as a Food Additive. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. J. 2016, 14, e04545. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y.; Jia, G.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Sun, J.; et al. Acute Toxicity and Biodistribution of Different Sized Titanium Dioxide Particles in Mice After Oral Administration. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraets, L.; Oomen, A.; Krystek, P.; Jacobsen, N.; Wallin, H.; Laurentie, M.; Verharen, H.; Brandon, E.; de Jong, W.H. Tissue Distribution and Elimination After Oral and Intravenous Administration of Different Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, R.; Raza, S.; Yadav, A.; Kushwaha, P.; Flora, S.J. Effects of Sub-acute Exposure to TiO2, ZnO and Al2O3 Nanoparticles on Oxidative Stress and Histological Changes in Mouse Liver and Brain. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 37, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warheit, D.B.; Brown, S.C.; Donner, E.M. Acute and Subchronic Oral Toxicity Studies in Rats with Nanoscale and Pigment Grade Titanium Dioxide Particles. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 84, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekanski, D.; Spremo-Potparević, B.; Bajić, V.; Živković, L.; Topalović, D.; Sredojević, D.N.; Lazić, V.; Nedeljković, J.M. Acute Toxicity Study in Mice of Orally Administrated TiO2 Nanoparticles Functionalized with Caffeic Acid. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 115, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadda, L.M.; Hagar, H.; Mohamed, A.M.; Ali, H.M. Quercetin and Idebenone Ameliorate Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, DNA Damage, and Apoptosis Induced by Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Rat Liver. Dose Response 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, M.; Jabeen, F.; Shabbir, S.; Asghar, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Chaudhry, A.S. Toxicity of Nano-Titanium Dioxide (TiO2-NP) Through Various Routes of Eexposure: A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 172, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, N.I.; Hamza, S.M.; Abou-Zeid, E.H. Toxic Impact of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) in Male Albino rats with Special Reference to Its Effect on Reproductive System. J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 865–872. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadipour, A.; Hosseini, M.; Fazel, A.; Haghir, H.; Rafatpanah, H.; Pourganji, M.; Bideskan, A.E. The Effects of Exposure to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles During Lactation Period on Learning and Memory of Rat Offspring. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 32, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bideskan, A.E.; Mohammadipour, A.; Fazel, A.; Haghir, H.; Rafatpanah, H.; Hosseini, M.; Rajabzadeh, A. Maternal Exposure to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles During Pregnancy and Lactation Alters Offspring Hippocampal mRNA BAX and Bcl-2 levels, Induces Apoptosis and Decreases Neurogenesis. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 69, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Szwajgier, D.; Oleszczuk, P.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A. Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Exposure on Human Health—A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1993, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, E. Materials for Food Storage with Antiseptic Properties. Global Grand Challenges: Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Grand Challenges Explorations Grant; GCE RB, OPP1060234). Available online: https://gcgh.grandchallenges.org/grant/materials-food-storage-antiseptic-properties (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Hong, F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sheng, L.; Wang, L. Maternal Exposure to Nanosized Titanium Dioxide Suppresses Embryonic Development in Mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6197–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannunah, A.M.; Vllasaliu, D.; Lord, J.; Stolnik, S. Mechanisms of Nanoparticle Internalization and Transport Across an Intestinal Epithelial Cell Model: Effect of Size and Surface Charge. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4363–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitrowski, C.; Al-Jubory, A.R.; Handy, R.D. Uptake of Different Crystal Structures of TiO2 Nanoparticles by Caco-2 Intestinal Cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 226, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, S.; Lei, R.; Gu, W.; Qin, Y.; Ma, S.; Chen, K.; Chang, Y.; Bai, X.; Xia, S.; et al. Oral Administration of Rutile and Anatase TiO2 Nanoparticles Shifts Mouse Gut Microbiota Structure. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 7736–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.M.; Mantaj, J.; Cheng, Y.; Vllasaliu, D. Delivery of Nanoparticles Across the Intestinal Epithelium via the Transferrin Transport Pathway. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinget, G.; Tan, J.; Janac, B.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Angelatos, A.S.; O’Sullivan, J.; Koay, Y.C.; Sierro, F.; Davis, J.; Divakarla, S.K.; et al. Impact of the Food Additive TiLitanium Dioxide (E171) on Gut Microbiota-host Interaction. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, J.; Ronde, E.; English, N.; Clark, S.K.; Hart, A.L.; Knight, S.C.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Al-Hassi, H.O. Tight Junctions in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Associated Colorectal Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettini, S.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Cartier, C.; Coméra, C.; Gaultier, E.; Dupuy, J.; Naud, N.; Taché, S.; Grysan, P.; Reguer, S.; et al. Food-grade TiO2 Impairs Intestinal and Systemic Immune Homeostasis, Initiates Preneoplastic Lesions and Promotes Aberrant Crypt Development in the Rat Colon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, R.; Wang, B.; Cai, C.; Zheng, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Ouyang, H.; Zhou, X.; Chi, Z.; et al. The Effects of Orally Administered Ag, TiO2 and SiO2 Nanoparticles on Gut Microbiota Composition and Colitis Induction in Mice. NanoImpact 2017, 8, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Setyawati, M.I.; Kai, T.J.; Ding, I.; Wang, J.; Nga, M.E.; Ho, H.K.; Leong, D.T. Nanoparticles Promote in Vivo Breast Cancer Cell Intravasation and Extravasation by Inducing Endothelial Leakiness. Nat. Nanotech. 2019, 14, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott, F.; Roller, M. Carcinogenicity Study with Nineteen Granular Dusts in Rats. Eur. J. Oncol. 2005, 10, 249–281. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, J.; Tang, G. In Vivo Acute Toxicity of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles to Mice After Intraperitioneal Injection. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2009, 29, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disdier, C.; Devoy, J.; Cosnefroy, A.; Chalansonnet, M.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Brun, E.; Lund, A.; Mabondzo, A. Tissue Biodistribution of Intravenously Administrated Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Revealed Blood-brain Barrier Clearance and Brain Inflammation in Rat. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, N.B.R.; Amara, S.; Mrad, I.; Ben-Slama, I.; Jeljeli, M.; Omri, K.; El Ghoul, K.; El Mir, L.; Rhouma, K.B.; Abdelmelek, H.; et al. Subacute Toxicity of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles in Male Rats: Emotional Behavior and Pathophysiological Examination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 8728–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreyling, W.G.; Holzwarth, U.; Haberl, N.; Kozempel, J.; Hirn, S.; Wenk, A.; Schleh, C.; Schäffler, M.; Lipka, J.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; et al. Quantitative Biokinetics of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles After Intravenous Injection in Rats: Part 1. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scown, T.M.; Van Aerle, R.; Johnston, B.D.; Cumberland, S.; Lead, J.R.; Owen, R.; Tyler, C.R. High Doses of Intravenously Administered Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Accumulate in the Kidneys of Rainbow Trout but with no Observable Impairment of Renal Function. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 109, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, A.; Drobne, D.; Jemec, A. Ecotoxicity of Nanosized TiO2. Review of in Vivo Data. Environ. Poll. 2011, 159, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amde, M.; Liu, J.; Tan, Z.Q.; Bekana, D. Transformation and Bioavailability of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Aquatic and Terrestrial Environments. A Review. Environ. Poll. 2017, 230, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, M.A.; Westerhoff, P.; Benn, T.; Wang, Y.; Pérez-Rivera, J.; Hristovski, K. Titanium Nanomaterial Removal and Release from Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6757–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bystrzejewska-Piotrowska, G.; Golimowski, J.; Urban, P.L. Nanoparticles: Their Potential Toxicity, Waste and Environmental Management. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brausch, J.M.; Rand, G.M. A Review of Personal Care Products in the Aquatic Environment: Environmental Concentrations and Toxicity. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labille, J.; Slomberg, D.; Catalano, R.; Robert, S.; Boudenne, J.L.; Apers-Tremelo, M.L.; Masion, A.; De Garidel, C. Evaluation of the Environmental Exposure to Nanoparticulate UV-filters Used in Sunscreens. In Proceedings of the Goldschmidt Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 12–17 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Cai, Z. TiO2 Nanoparticles in the Marine Environment: Impact on the Toxicity of Tributyltin to Abalone (Haliotis diversicolor supertexta) Embryos. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3753–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libralato, G.; Minetto, D.; Totaro, S.; Mičetić, S.; Pigozzo, A.; Sabbioni, E.; Marcomini, A.; Ghirardini, A.V. Embryotoxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles to Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lmk). Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 92, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agata, A.; Fasulo, S.; Dallas, L.J.; Fisher, A.S.; Maisano, M.; Readman, J.W.; Jha, A.N. Enhanced Toxicity of ’Bulk’ Titanium Dioxide Compared to ’Fresh’ and ’Aged’ nano-TiO2 in Marine Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canesi, L.; Ciacci, C.; Vallotto, D.; Gallo, G.; Marcomini, A.; Pojana, G. In Vitro Effects of Suspensions of Selected Nanoparticles (C60 fullerene, TiO2, SiO2) on Mytilus hemocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.J.; Bennett, S.; Keller, A.A.; Pease, S.; Lenihan, H.S. TiO2 Nanoparticles are Phototoxic to Marine Phytoplankton. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danovaro, R.; Corinaldesi, C. Sunscreen Products Increase Virus Production Through Prophage Induction in Marine Bacterioplankton. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 45, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danovaro, R.; Bongiorni, L.; Corinaldesi, C.; Giovannelli, D.; Damiani, E.; Astolfi, P.; Greci, L.; Pusceddu, A. Sunscreens Cause Coral Bleaching by Promoting Viral Infections. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giokas, D.L.; Salvador, A.; Chisvert, A. UV Filters: From Sunscreens to Human Body and the Environment. TRAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.; Lewis, C.; Dolciotti, I.; Johnston, B.D.; Moger, J.; Regoli, F. Sublethal Toxicity of Nano-titanium Dioxide and Carbon Nanotubes in a Sediment Dwelling Marine Polychaete. Environ. Poll. 2010, 158, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Cai, Z. The Toxicity and Oxidative Stress of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Marine Abalone (Haliotis diversicolor supertexta). Mar. Poll. Bull. 2011, 63, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmo, C.; Ciacci, C.; Canonico, B.; Fabbri, R.; Cortese, K.; Balbi, T.; Marcomini, A.; Pojana, G.; Gallo, G.; Canesi, L. In Vivo Effects of N-TiO2 on Digestive Gland and Immune Function of the Marine Bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 132–133, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, Z.; Castro, V.L.; Jonsson, C.M.; Fraceto, L.F. Minimal Levels of Ultraviolet Light Enhance the Toxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles to Two Representative Organisms of Aquatic Systems. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lao, Y.; Lv, X.; Tao, Y.; Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Cai, Z. TiO2 Nanoparticles in the Marine Environment: Physical Effects Responsible for the Toxicity on Algae Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, E.C. Toxicological Effects of Commercial Sunscreens on Coral Reef Ecosystems: New Protocols for Coral Restoration. HCNSO Student Capstones, Nova Southeastern University NSU Works. 2018. Available online: https://nsuworks.nova.edu/cnso_stucap/335 (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; González-Silva, N.; Yahia, E.M.; González-Vargas, O.A.; Montalvo-González, E.; Pérez-Larios, A. Effect of TiO2-ZnO-MgO Mixed Oxide on Microbial Growth and Toxicity Against Artemia salina. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobek, A.; Bejgarn, S.; Rudén, C.; Molander, L.; Breitholtz, M. In the Shadow of the Cosmetic Directive—Inconsistencies in EU Environmental Hazard Classification Requirements for UV-Filters. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prichard, E.; Granek, E.F. Effects of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products on Marine Organisms: From Single-species Studies to an Ecosystem-based Approach. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2016, 23, 22365–22384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B.; Grieger, K.; Kusk, K.O. Ecotoxicity of Engineered Nanoparticles to Aquatic Invertebrates: A Brief Review and Recommendations for Future Toxicity Testing. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, D.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.; Shen, S. Effects of ZnO, CuO, Au, and TiO2 Nanoparticles on Daphnia magna and Early Life Stages of Zebrafish Danio Rerio. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2014, 40, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Heinlaan, M.; Ivask, A.; Blinova, I.; Dubourguier, H.C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of Nanosized and Bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to Bacteria Vibrio fischeri and Crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Y. Toxicity and Bioaccumulation of TiO2 Nanoparticle Aggregates in Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Lee, D.K. Preparation of TiO2-coated Hollow Glass Beads and Their Application to the Control of Algal Growth in Eutrophic Water. Microchem. J. 2005, 80, 227–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, A.; Dubourguier, H.C. From Ecotoxicology to Nanoecotoxicology. Toxicology 2010, 269, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead, J.R.; Batley, G.E.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Croteau, M.N.; Handy, R.D.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Judy, J.D.; Schirmerh, K. Nanomaterials in the Environment: Behavior, Fate, Bioavailability, and Effects—An Updated Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2029–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.W.; Zhang, X.Z.; Niu, Q.; Chen, Y.S.; Crittenden, J.C. Enhanced Accumulation of Arsenate in Carp in the Presence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Water Air Soil Poll. 2007, 178, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.S.; Smith, T.J.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D. Dietary Exposure to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): No Effect on Growth, but Subtle Biochemical Disturbances in the Brain. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 939–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linhua, H.; Zhenyu, W.; Baoshan, X. Effect of Sub-acute Exposure to TiO2 Nanoparticles on Oxidative Stress and Histopathological Changes in Juvenile Carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Louis, K.M.; Pedersen, J.A.; Hamers, R.J.; Peterson, R.E.; Heideman, W. Using Citrate-functionalized TiO2 Nanoparticles to Study the Effect of Particle Size on Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity. Analyst 2014, 139, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asztemborska, M.; Jakubiak, M.; Stęborowski, R.; Chajduk, E.; Bystrzejewska-Piotrowska, G. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Circulation in an Aquatic Ecosystem. Water Air Soil Poll. 2018, 229, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vevers, W.F.; Jha, A.N. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Potential of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles on Fish Cells in Vitro. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, J.F.; Davies, S.J.; Dodd, N.J.; Jha, A.N. Hydroxyl Radicals (OH) are Associated with Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticle-induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative DNA Damage in Fish Cells. Mut. Res. 2008, 640, 113122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Sun, H.W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Niu, Q.; Chen, Y.S.; Crittenden, J.C. Enhanced Bioaccumulation of Cadmium in Carp in the Presence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larue, C.C.; Baratange, C.; Vantelon, D.; Khodja, H.; Surblé, S.; Elger, A.; Carrière, M. Influence of Soil Type on TiO2 Nanoparticle Fate in an Agro-ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, M.; Richaume, A.; Guyonnet, J.P.; Dubost, A.; Martins, J.F.M.; Pommier, T. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Strongly Impact Soil Microbial Function by Affecting Archaeal Nitrifiers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobne, D.; Jemec, A.; Tkalec, Z.P. In Vivo Screening to Determine Hazards of Nanoparticles: Nanosized TiO2. Environ. Poll. 2009, 157, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.Y.; Park, Y.K.; Park, K.; Choi, J. Ecotoxicological Investigation of CeO2 and TiO2 Nanoparticles on the Soil Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans Using Gene Expression, Growth, Fertility, and Survival as Endpoints. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 29, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.W.; Li, M.; Cui, Y.B.; Li, D.S.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.Y. Toxicological Effects of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles in Soil on Earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.; Venkatachalam, P.; Sahi, S.; Sharma, N. Silver and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Toxicity in Plants: A Review of Current Research. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 107, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.P.; King, G.; Plocher, M.; Storm, M.; Pokhrel, L.R.; Johnson, M.G.; Rygiewicz, P.T. Germination and Early Plant Development of Ten Plant Species Exposed to Titanium Dioxide and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Interaction of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles with Soil Components and Plants: Current Knowledge and Future Research Needs—A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, U.; Shin, M.; Lee, G.; Roh, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, E.J. Functional Analysis of TiO2 Nanoparticle Toxicity in Three Plant Species. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 155, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Z.; Chen, J.; Dou, R.Z.; Gao, X.; Mao, C.B.; Wang, L. Assessment of the Phytotoxicity of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles on Two Crop Plants, Maize (Zea mays L.) and Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15100–15109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Mingyu, S.; Chao, L.; Liang, C.; Hao, H.; Xiao, W.; Xiaoqing, L.; Fan, Y.; Fengqing, G.; Fashui, H. Effects of Nanoanatase TiO2 on Photosynthesis of Spinach Chloroplasts Under Different Light Iillumination. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2007, 119, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klancnik, K.; Drobne, D.; Valant, J.; Koce, J.D. Use of a Modified Allium Test with NanoTiO2. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumy, D.; Rincon, A.G.; Hajdu, R.; Pulgarin, C. Solar Photocatalysis for Detoxification and Disinfection of Water: Different Types of Suspended and Fixed TiO2 Catalysts Study. Sol. Energy 2006, 80, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malato, S.; Blanco, J.; Alarcón, D.C.; Maldonado, M.I.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Gernjak, W. Photocatalytic Decontamination and Disinfection of Water with Solar Collectors. Catal. Today 2007, 122, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, H.A.; Ditta, I.B.; Varghese, S.; Steele, A. Photocatalytic Disinfection Using Titanium Dioxide: Spectrum and Mechanism of Antimicrobial Activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1847–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Ulfig, K.; Morawski, A.W. The Application of Titanium Dioxide for Deactivation of Bioparticulates: An Overview. Catal. Today 2011, 169, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigeot-Rémy, S.; Simonet, F.; Errazuriz-Cerda, E.; Lazzaroni, J.C.; Atlan, D.; Guillard, C. Photocatalysis and Disinfection of Water: Identification of Potential Bacterial Targets. Appl. Cat. B 2011, 104, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial Activity of Metals: Mechanisms, Molecular Targets and Applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Li, Q. Applications of Nanotechnology in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3931–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, F.; Perales-Perez, O.J.; Hwang, S.; Román, F. Antimicrobial Nanomaterials as Water Disinfectant: Applications, Limitations and Future Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The Antimicrobial Activity of Nanoparticles: Present Situation and Prospects for the Future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Zeid, Y.; Williams, G.R. The Potential Anti-infective Applications of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: A Systematic Review. Wiley Interdiscp. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogniat, G.; Dukan, S. TiO2 Photocatalysis Causes DNA Damage via Fenton Reaction-Generated Hydroxyl Radicals During the Recovery Period. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7740–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Grieken, R.; Marugan, J.; Pablos, C.; Lopez, A. Comparison Between the Photocatalytic Inactivation of Gram-positive E. faecalis and Gram-negative E. coli Faecal Contamination Indicator Microorganisms. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 100, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Wang, K.; Rokicka, P.; Endo, M.; Wei, Z.; Ohtani, B.; Morawski, A.W.; Kowalska, E. The Effect of Anatase and Rutile Crystallites Isolated from Titania P25 Photocatalyst on Growth of Selected Mould fungi. J. Photch. Photobiol. B 2015, 151, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, J.W.; Chang, H.H. Bactericidal Effects and Mechanisms of Visible Light-responsive Titanium Dioxide Photocatalysts on Pathogenic Bacteria. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Ex. 2012, 60, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Liu, G.; Yang, K.; Tong, M.; Lin, D. Toxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles to Escherichia coli: Effects of Particle Size, Crystal Phase and Water Chemistry. PLoS ONE 2014, 10, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, E.; Wei, Z.; Karabiyik, B.; Herissan, A.; Janczarek, M.; Endo, M.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Remita, H.; Ohtani, B. Silver-modified Titania with Enhanced Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Properties under UV and Visible Light Irradiation. Catal. Today 2015, 252, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.H.; Xu, X.; Ma, A.P.; Liu, F.; Ng, A.M.; Shen, Z.; Gethings, L.A.; Guo, M.Y.; Djurišić, A.B.; Lee, P.K.; et al. Toxicity of ZnO and TiO2 to Escherichia coli Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Endo, M.; Wang, K.; Charbit, E.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Ohtani, B.; Kowalska, E. Noble Metal-modified Octahedral Anatase Titania Particles with Enhanced activity for Decomposition of Chemical and Microbiological Pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 318, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanag, A.; Rokicka, P.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Kapica-Kozar, J.; Wróbel, R.J.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Morawski, A.W. Antibacterial Properties of TiO2 Modified with Reduced Graphene Oxide. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchon, M.; Ferrari, R.; Guyot, F.; Gélabert, A.; Menguy, N.; Chanéac, C.; Thill, A.; Benedetti, M.F.; Spalla, O. Interaction Between Escherichia coli and TiO2 Nanoparticles in Natural and Artificial Waters. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 102, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marugan, J.; Van Grieken, R.; Sordo, C.; Cruz, C. Kinetics of the Photocatalytic Disinfection of Escherichia coli Suspensions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 82, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabbou, A.K.; Derriche, Z.; Felix, C.; Lejeune, P.; Guillard, C. Photocatalytic Inactivation of Escherischia coli: Effect of Concentration of TiO2 and Microorganism, Nature, and Intensity of UV Irradiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 76, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Chung, H.; Choi, W.; Yoon, J. Linear Correlation Between Inactivation of E. coli and OH Radical Concentration in TiO2 Photocatalytic Disinfection. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiwi, J.; Nadtochenko, V. New Evidence for TiO2 Photocatalysis During Bilayer Lipid Peroxidation. J. Chem. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17675–17684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, O.K.; Stefanakos, E.; Trotz, M.A.; Goswami, D.Y. A Review of the Mechanisms and Modeling of Photocatalytic Disinfection. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 98, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ghafoor, K.; Lee, J.; Feng, M.; Hong, J.; Lee, D.U.; Park, J. Bacterial Inactivation in Water, DNA Strand Breaking, and Membrane Damage Induced by Ultraviolet-assisted Titanium Dioxide Photocatalysis. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4403–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Janczarek, M.; Wei, Z.; Wang, K.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Ohtani, B.; Kowalska, E. Bactericidal Properties of Plasmonic Photocatalysts Composed of Noble-metal Nanoparticles on Faceted Anatase Titania. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 9, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Wei, Z.; Wang, K.; Karabiyik, B.; Kenta, Y.; Rokicka, P.; Ohtani, O.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Kowalska, E. Noble Metal-modified Titania with Visible-Light Activity for the Decomposition of Microorganisms. Beilstein J. Nanotech. 2018, 9, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, A.; Saygin, H.; Ustabasi, G.S. Physicochemical Transformation of ZnO and TiO2 Nanoparticles in Sea Water and its Impact on Bacterial Toxicity. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. 2019, 6, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Toxicity and Mechanisms of Action of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Living Organisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, K.; Qian, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, B.; Tian, X.; Jin, W.; He, X. Differential Toxicity of Anatase and Rutile TiO2 Nanoparticles to the Antioxidant Enzyme System and Metabolic Activities of Freshwater Biofilms Based on Microelectrodes and Fluorescence in situ Hybridization. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2626–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



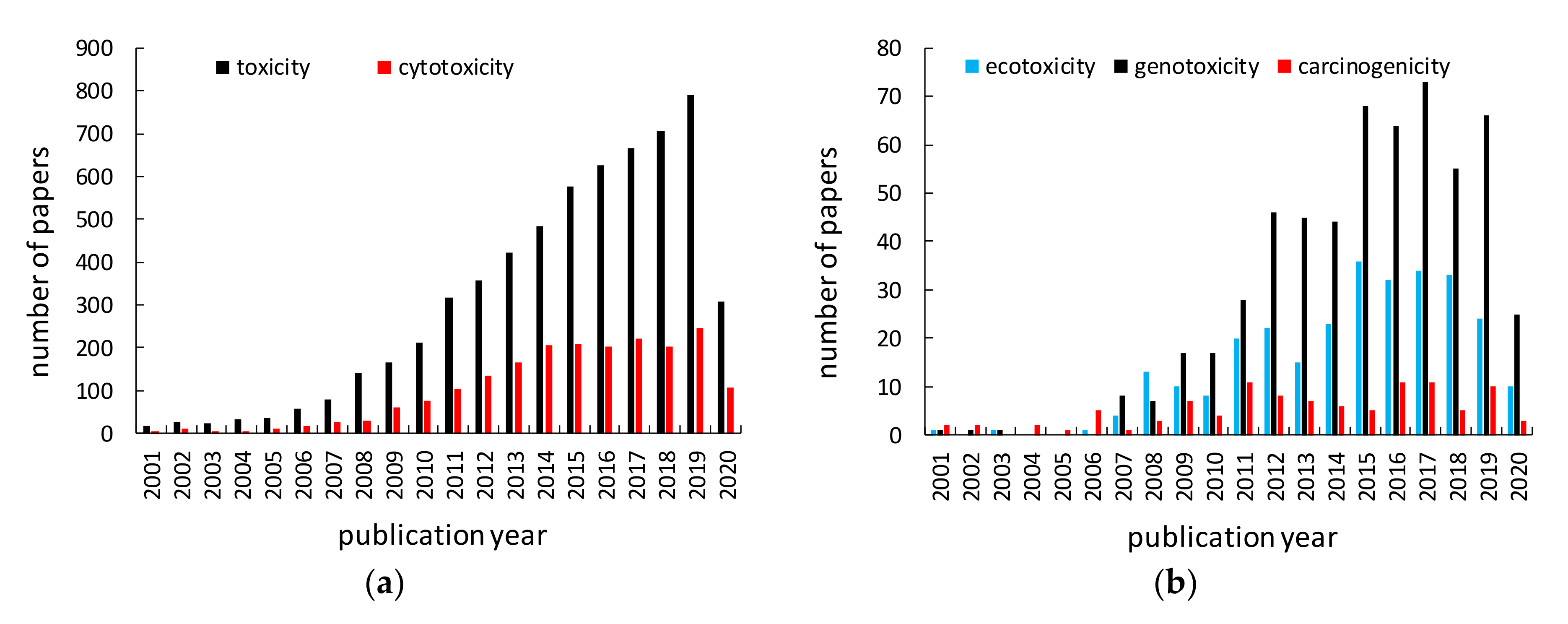






| Case | Contact | Exposed Persons | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13 years | 53-year old man employed to pack titania | pneumoconiosis accompanied by right lung cancer | [100] |
| 2 | 9 years | Man employed to pack titania into cans | slight fibrosis of interstitial lung tissue surrounding bronchioles and alveolar spaces after 5 years | [101] |
| 3 | - | 55-year old man, heavily exposed to titania dust (rutile) | extensive pulmonary deposition of white pigment and absence of inflammatory and fibrotic changes | [101] |
| 4 | - | Four workers exposed to the inhalation of titania dust (not pure) | epithelioid granuloma, confirmed the inflammatory route of exposure | [102] |
| 5 | - | Four men and two women, between the ages of 22 and 65 years, unknown source of exposure | fibrosis and numerous macrophages with abundant deposition of a black pigment, confirmed presence of large quantity of titania in the pigment granule | [103] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Endo-Kimura, M.; Paszkiewicz, O.; Kowalska, E. Are Titania Photocatalysts and Titanium Implants Safe? Review on the Toxicity of Titanium Compounds. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102065
Markowska-Szczupak A, Endo-Kimura M, Paszkiewicz O, Kowalska E. Are Titania Photocatalysts and Titanium Implants Safe? Review on the Toxicity of Titanium Compounds. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(10):2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102065
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkowska-Szczupak, Agata, Maya Endo-Kimura, Oliwia Paszkiewicz, and Ewa Kowalska. 2020. "Are Titania Photocatalysts and Titanium Implants Safe? Review on the Toxicity of Titanium Compounds" Nanomaterials 10, no. 10: 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102065
APA StyleMarkowska-Szczupak, A., Endo-Kimura, M., Paszkiewicz, O., & Kowalska, E. (2020). Are Titania Photocatalysts and Titanium Implants Safe? Review on the Toxicity of Titanium Compounds. Nanomaterials, 10(10), 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102065








