Biomechanical Effects of a New Macrogeometry Design of Dental Implants: An In Vitro Experimental Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
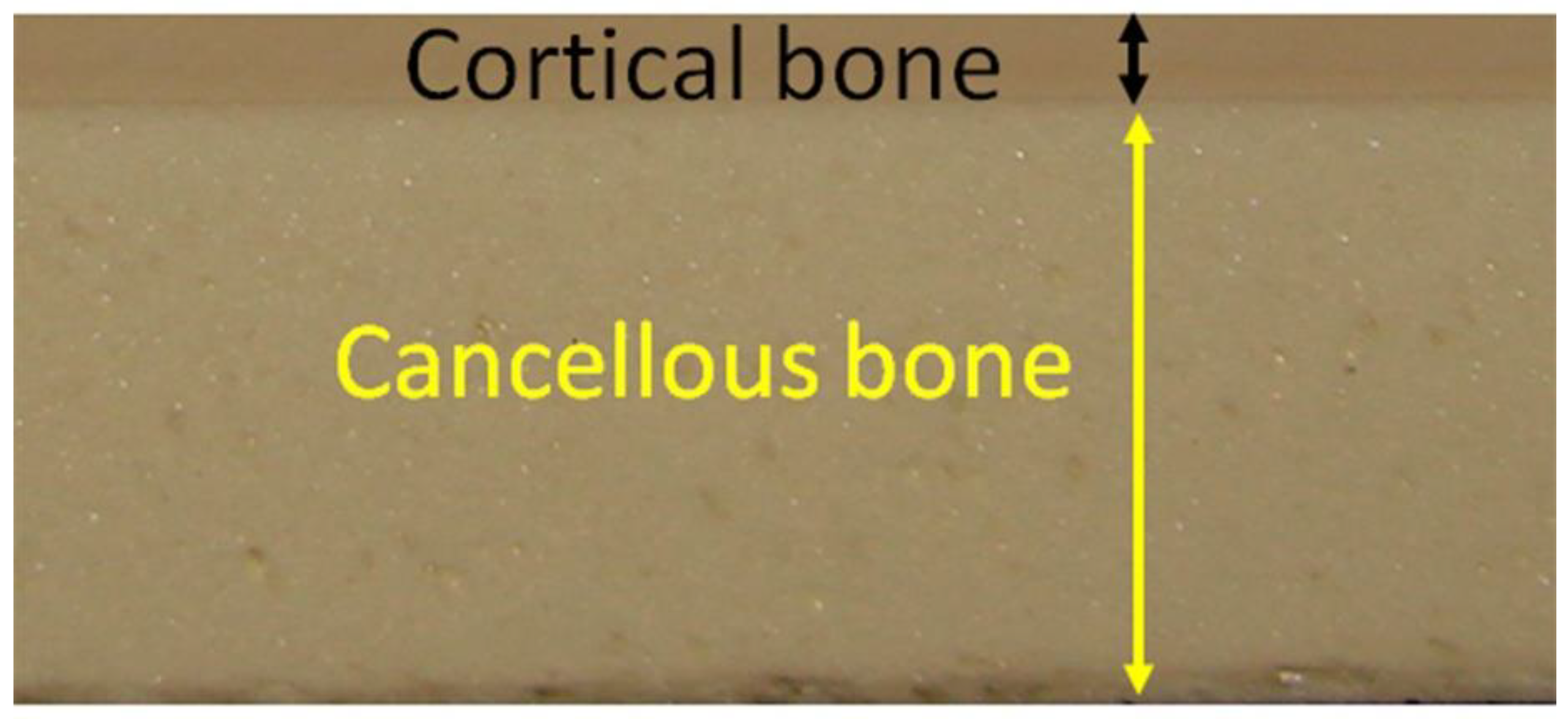
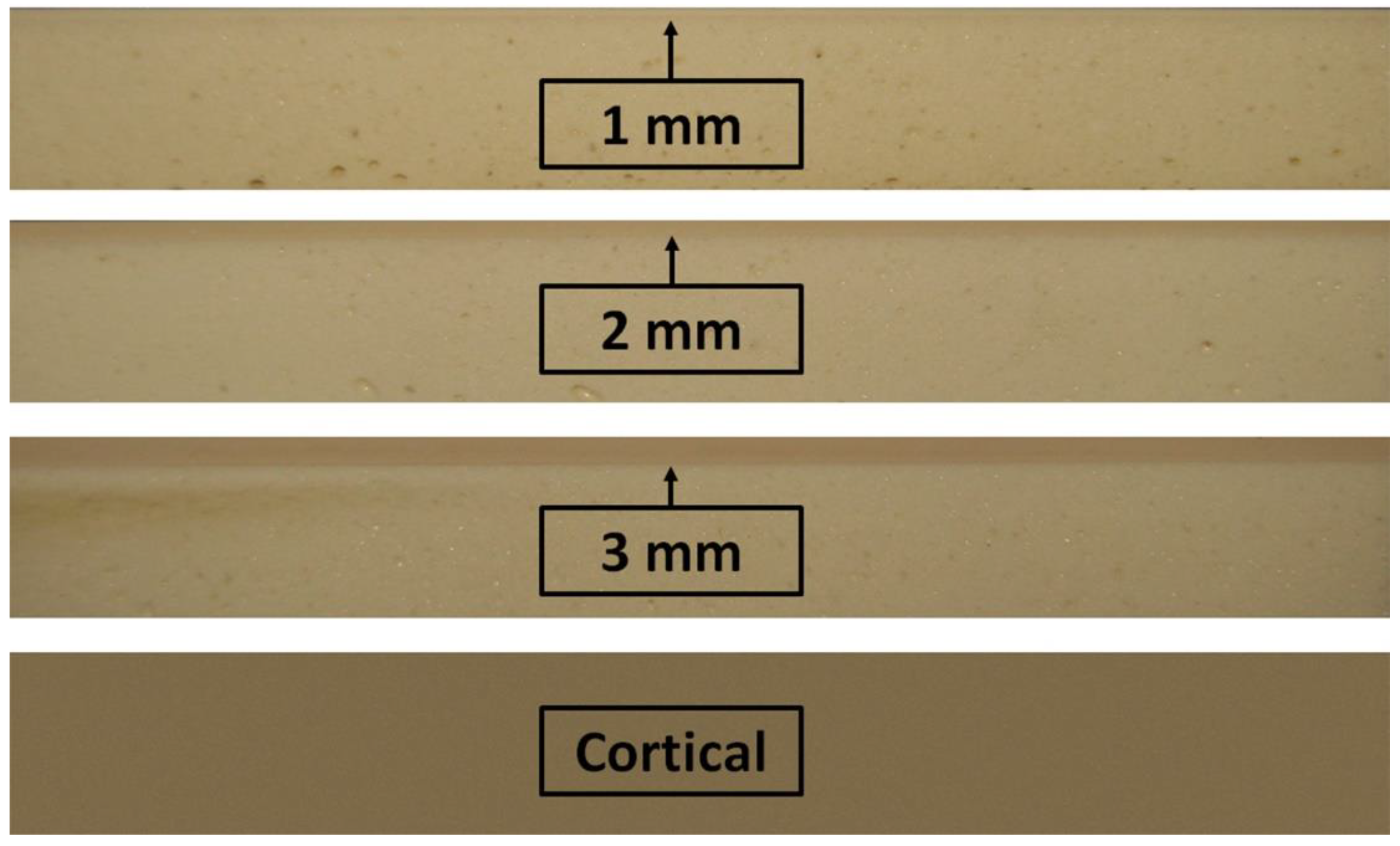
2.1. Synthetic Bone Characteristics
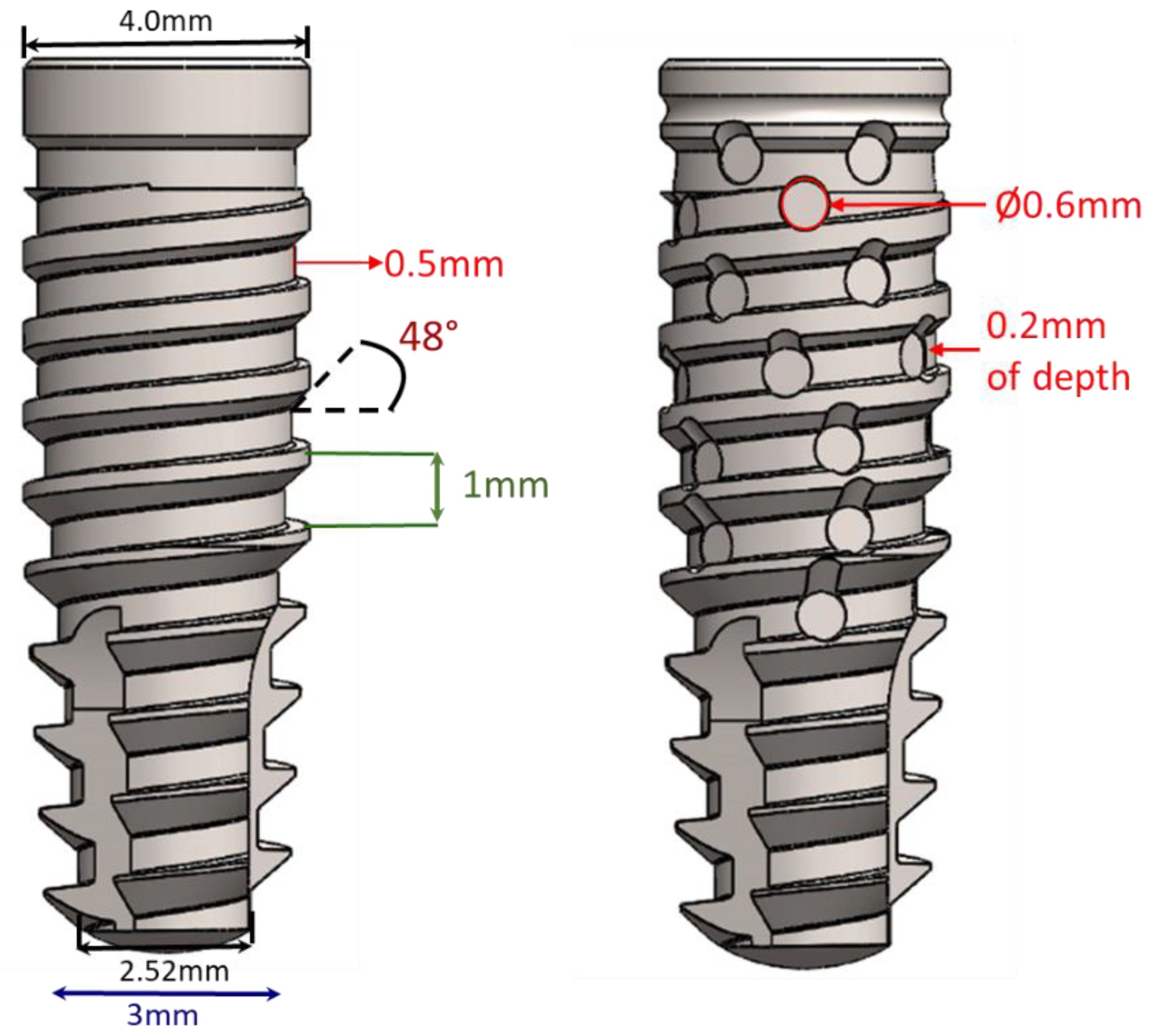
2.2. Implant Characteristics and Group Distribution
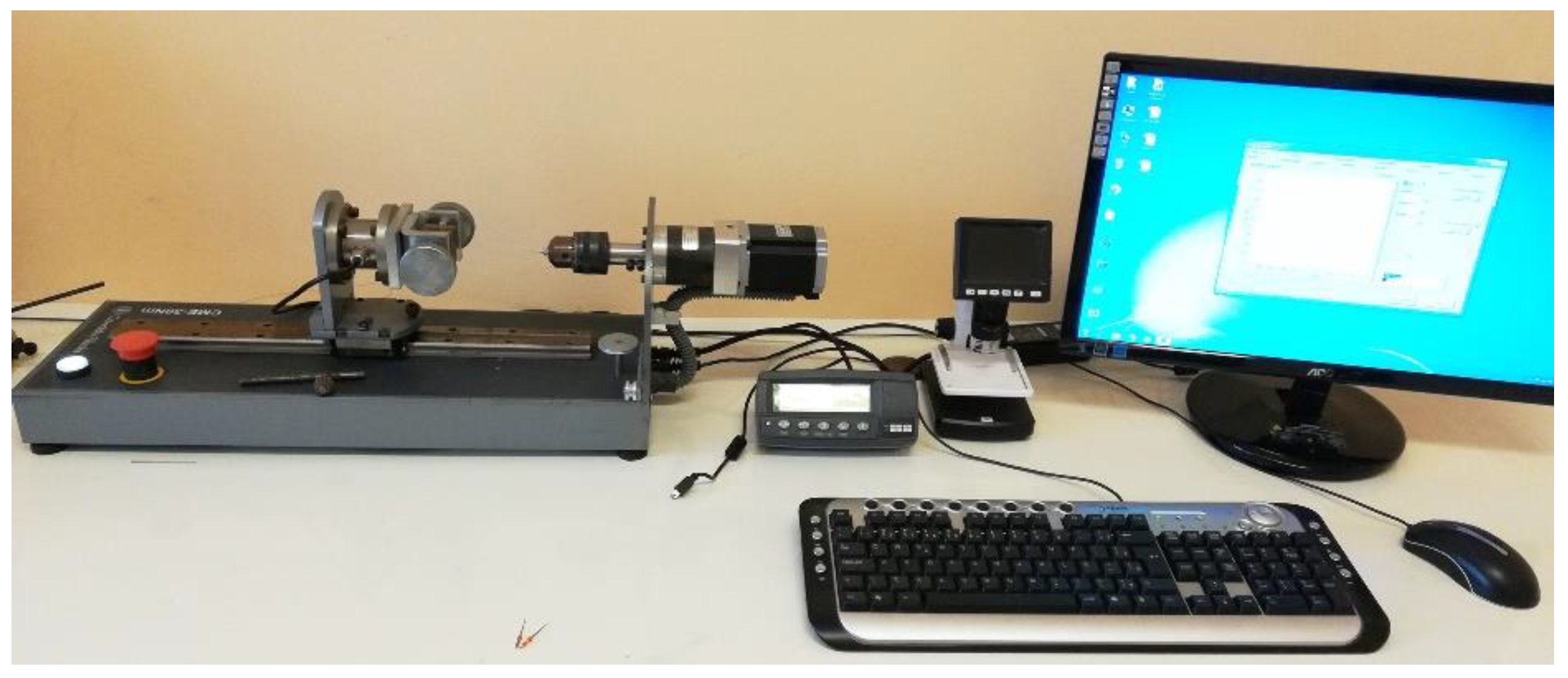
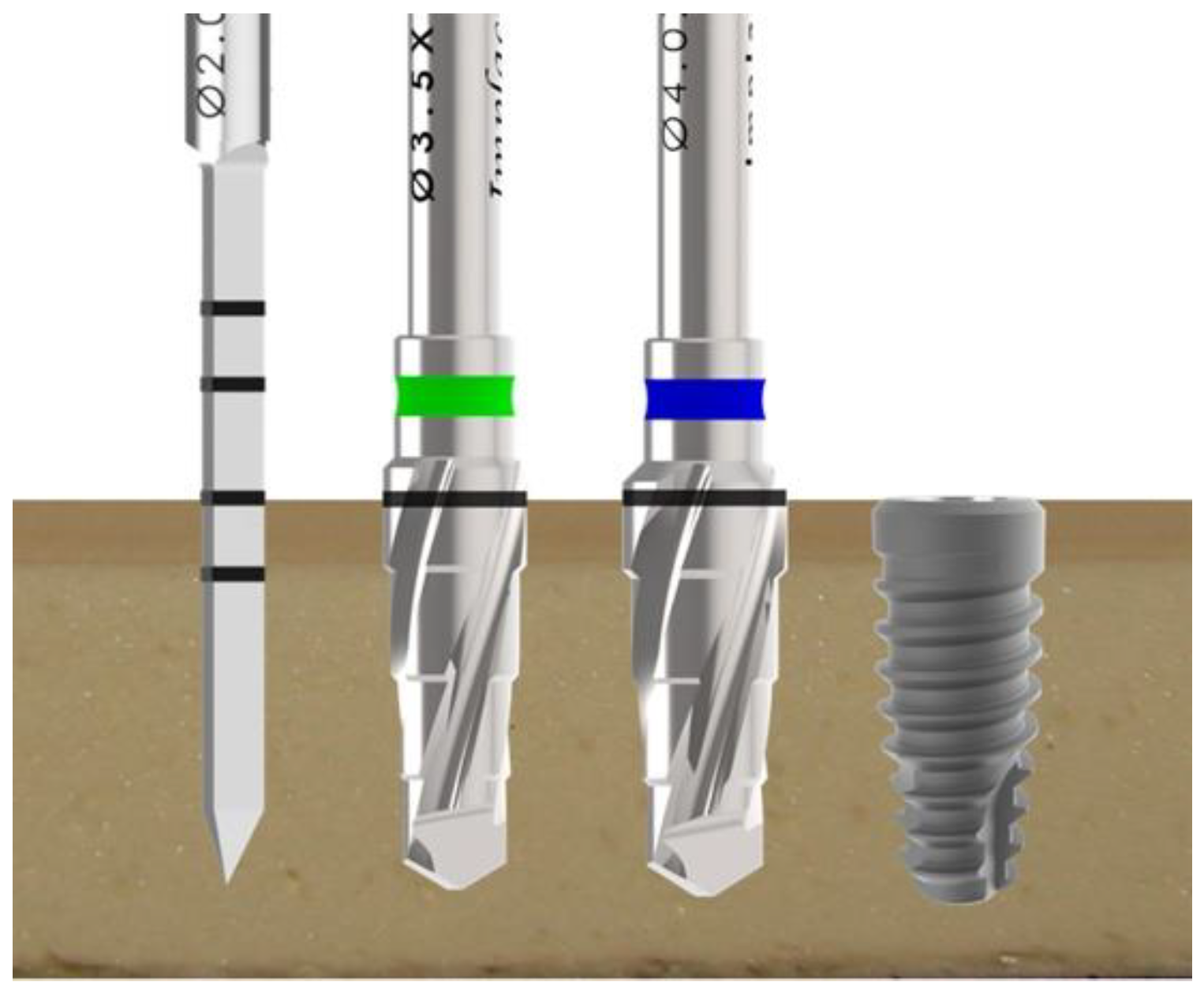
2.3. Implant Management and Biomechanical Analysis
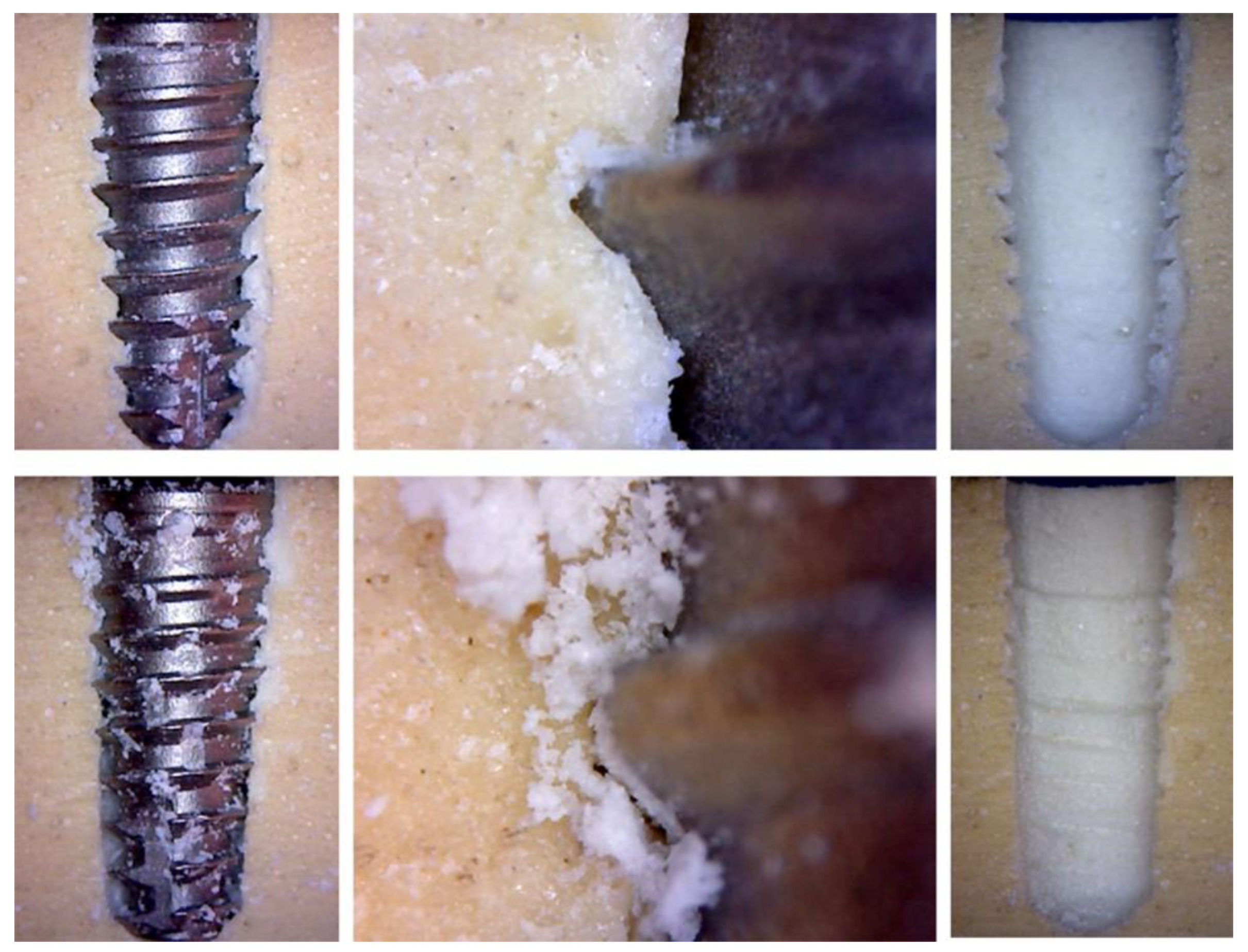
2.4. Analysis of the Effect of the Threads Passage
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Degidi, M.; Daprile, G.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Development of a new implant primary stability parameter: Insertion torque revisited. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matys, J.; Świder, K.; Grzech-Leśniak, K.; Dominiak, M.; Romeo, U. Photobiomodulation by a 635nm Diode Laser on Peri-Implant Bone: Primary and Secondary Stability and Bone Density Analysis-A Randomized Clinical Trial. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matys, J.; Świder, K.; Flieger, R.; Dominiak, M. Assessment of the primary stability of root analog zirconia implants designed using cone beam computed tomography software by means of the Periotest® device: An ex vivo study. A preliminary report. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilek, O.; Tezulas, E.; Dincel, M. Required minimum primary stability and torque values for immediate loading of mini dental implants: An experimental study in nonviable bovine femoral bone. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2008, 105, e20–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchi, C.; Vercellotti, T.; Torelli, L.; Furlan, F.; Di Lenarda, R. Changes in implant stability using different site preparation techniques: Twist drills versus piezosurgery: A single-blinded, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matys, J.; Flieger, R.; Tenore, G.; Grzech-Leśniak, K.; Romeo, U.; Dominiak, M. Er:YAG laser, piezosurgery, and surgical drill for bone decortication during orthodontic mini-implant insertion: Primary stability analysis-an animal study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedir, R.; Bischof, M.; Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Bernard, J.P.; Samson, J. Predicting osseointegration by means of im¬plant primary stability. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 15, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoda, K.; Ayukawa, Y.; Tsukiyama, Y.; Sogo, M.; Matsushita, Y.; Koyano, K. Relationship between the bone density estimated by cone-beam computed tomography and the primary stability of dental implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilhan, H.; Geckili, O.; Mumcu, E.; Bozdag, E.; Sunbuloglu, E.; Kutay, O. Influence of surgical technique, implant shape and diameter on the primary stability in cancellous bone. J. Oral Rehabil. 2010, 37, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, A.; Meijer, G.J.; Walboomers, X.F.; Jansen, J.A. Evaluation of primary and secondary stability of titanium implants using different surgical techniques. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimbo, R.; Tovar, N.; Anchieta, R.B.; Machado, L.S.; Marin, C.; Teixeira, H.S.; Coelho, P.G. The combined effects of undersized drilling and implant macrogeometry on bone healing around dental implants: An experimental study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, F.; Romanos, G.E. The role of primary stability for successful immediate loading of dental implants. A literature review. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makary, C.; Menhall, A.; Zammarie, C.; Lombardi, T.; Lee, S.Y.; Stacchi, C.; Park, K.B. Primary Stability Optimization by Using Fixtures with Different Thread Depth According to Bone Density: A Clinical Prospective Study on Early Loaded Implants. Materials 2019, 12, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Hirsch, J.M.; Lekholm, U.; Thomsen, P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (II). Etiopathogenesis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1998, 106, 721–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsumi, M.; Park, S.H.; Wang, H.L. Methods used to assess implant stability: Current status. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2007, 22, 743–754. [Google Scholar]
- Bayarchimeg, D.; Namgoong, H.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, M.D.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.I.; Seol, Y.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Ku, Y.; Rhyu, I.C.; et al. Evaluation of the correlation between insertion torque and primary stability of dental implants using a block bone test. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013, 43, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, H.; Horner, K.; Ledgerton, D. A comparison of maxillary and mandibular bone mineral densities. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1998, 79, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Chen, P.Q.; Lu, T.W.; Wu, S.S.; Shih, K.S.; Lin, S.C. Comparison and prediction of pullout strength of conical and cylindrical pedicle screws within synthetic bone. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarioli, A.; Simões, P.A.; Shimano, A.C.; Defino, H.L.A. Insertion torque and pullout strength of vertebral screws with cylindrical and conic core. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2008, 43, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofolini, L.; Viceconti, M.; Cappello, A.; Toni, A. Mechanical validation of whole bone composite femur models. J. Biomech. 1996, 29, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofolini, L.; Viceconti, M. Mechanical validation of whole bone composite tibia models. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatti, D.B.; Pelegrine, A.A.; Gehrke, S.; Teixeira, M.L.; Moshaverinia, A.; Moy, P.K. Is there a need for standardization of tightening force used to connect the transducer for resonance frequency analysis in determining implant stability? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, D.; Sennerby, L.; Meredith, N. Measurements comparing the initial stability of five designs of dental implants: A human cadaver study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 2, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandriello, R.; Tomatis, M.; Rangert, B. Immediate functional loading of Brånemark System implants with enhanced initial stability: A prospective study 1 to 2-year clinical and radiographic study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2003, 5 (Suppl. 1), 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, A.; Gahleitner, A.; Holm, A.; Tschabitscher, M.; Homolka, P. Correlation of insertion torques with bone mineral density from dental quantitative CT in the mandible. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2003, 14, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoh, J.; Wahlmann, U.; Stender, E.; Al-Nawas, B.; Wagner, W. Primary stability of a conical implant and a hybrid, cylindric screw-type implant in vitro. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2006, 21, 560–566. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, F.E.; Gomes, J.B.; Marin, C.; Teixeira, H.S.; Suzuki, M.; Witek, L.; Zanetta-Barbosa, D.; Coelho, P.G. Effect of drilling dimension on implant placement torque and early osseointegration stages: An experimental study in dogs. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, e43–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.-J.; Leesungbok, R.; Lee, S.-W.; Heo, Y.-K.; Kang, K.L. Differences in implant stability associated with various methods of preparation of the implant bed: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2012, 107, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM F1839-97. Standard Specification for Rigid Polyurethane Foam for Use as a Standard Material for Testing Orthopaedic Devices and Instruments; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Misch, C.E. Bone density: A key determinant for clinical success. Contemp. Implant Dent. 1999, 8, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Comuzzi, L.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A.; Tumedei, M. An In Vitro Evaluation, on Polyurethane Foam Sheets, of the Insertion Torque (IT) Values, Pull-Out Torque Values, and Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) of NanoShort Dental Implants. Polymers 2019, 11, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Aramburú Júnior, J.; Pérez-Díaz, L.; Eirles Treichel, T.L.; Dedavid, B.A.; De Aza, P.N.; Prados-Frutos, J.C. New Implant Macrogeometry to Improve and Accelerate the Osseointegration: An In Vivo Experimental Study. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.H.; Nimphius, S.; Rantalainen, T.; Ireland, A.; Siafarikas, A.; Newton, R.U. Mechanical basis of bone strength: Influence of bone material, bone structure and muscle action. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2017, 17, 114–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Pérez-Albacete Martínez, C.; Piattelli, A.; Shibli, J.A.; Markovic, A.; Calvo Guirado, J.L. The influence of three different apical implant designs at stability and osseointegration process: Experimental study in rabbits. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Tavares da Silva Neto, U. Does the time of osseointegration in the maxilla and mandible differ? J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, 2117–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; da Silva, U.T.; Del Fabbro, M. Does Implant Design Affect Implant Primary Stability? A Resonance Frequency Analysis-Based Randomized Split-Mouth Clinical Trial. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, e281–e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manresa, C.; Bosch, M.; Echeverría, J.J. The comparison between implant stability quotient and bone-implant contact revisited: An experiment in Beagle dog. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, H.; Davarpanah, M.; Missika, P.; Celletti, R.; Lazzara, R. Optimal implant stabilization in low density bone. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2001, 12, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N.; Book, K.; Friberg, B.; Jemt, T.; Sennerby, L. Resonance frequency measurements of implant stability in vivo. A cross-sectional and longitudinal study of resonance frequency measurements on implants in the edentulous and partially dentate maxilla. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1997, 8, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatvaratthana, K.; Thaworanunta, S.; Seriwatanachai, D.; Wongsirichat, N. Correlation between the thickness of the crestal and buccolingual cortical bone at varying depths and implant stability quotients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açil, Y.; Sievers, J.; Gülses, A.; Ayna, M.; Wiltfang, J.; Terheyden, H. Correlation between resonance frequency, insertion torque and bone-implant contact in self-cutting threaded implants. Odontology 2017, 105, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lages, F.S.; Douglas-de Oliveira, D.W.; Costa, F.O. Relationship between implant stability measurements obtained by insertion torque and resonance frequency analysis: A systematic review. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, A.; Meijer, G.J.; Wolke, J.G.C.; Jansen, J.A. Influence of surgical technique and surface roughness on the primary stability of an implant in artificial bone with different cortical thickness: A laboratory study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2010, 21, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, R.R.M.; Novaes, A.B., Jr.; Papalexiou, V.; Souza, S.L.S.; Taba, M., Jr.; Palioto, D.B.; Grisi, M.F. Effect of biofunctionalized implant surface on osseointegration—A histomorphometric study in dogs. Braz. Dent. J. 2009, 20, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Kim, M.-R.; Rim, J.-S.; Chung, S.-M.; Shin, S.W. Comparison of implant stability after different implant surface treatments in dog bone. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2010, 18, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.F. Factors influencing primary dental implant stability remain unclear. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2012, 12 (Suppl. 3), 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodanov, L.; Lamers, E.; Wolke, J.; Huiberts, R.; Jansen, J.A.; Frank Walboomers, X. In vivo comparison between laser-treated and grit blasted/acid etched titanium. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, H.; Francischone, C.E.; Filho, H.N.; Oliveira, R.C.G. A comparison between insertion torque and resonance frequency in the assessment of primary stability and final torque capacity of standard and TiUnite single-tooth implants under immediate loading. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2004, 19, 578–585. [Google Scholar]
- Elmengaard, B.; Bechtold, J.E.; Soballe, K.S. In vivo study of the effect of treatment on bone on growth on press-fit titanium alloy implants. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3521–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabel, A.; Köhler, S.G.; Schmidt-Westhausen, A.M. Clinical study on the primary stability of two dental implant systems with resonance frequency analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2007, 11, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedrange, T.; Hietschold, V.; Mai, R.; Wolf, P.; Nicklish, M.; Harzer, W. An evaluation of resonance frequency analysis for the determination of the primary stability of orthodontic palatal implants. A study in human cadavers. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozé, J.; Babu, S.; Saffarzadeh, A.; Gayet-Delacroix, M.; Hoornaert, A.; Layrolle, P. Correlating implant stability to bone structure. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.V.; Elias, C.N.; Cavalcanti Lima, J.H. The effects of superficial roughness and design on the primary stability of dental implants. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2011, 13, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleo, E.; Varvara, G.; Scarano, A.; Sinjari, B.; Murmura, G. Comparison of the primary stabilities of conical and cylindrical endosseous dental implants: An in-vitro study. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, F.; Ribeiro, E.D.P.; Sousa, S.B.; Lenharo, A. Influence of macro-geometry in the primary stability of implants. Innov. Implant J. Biomater. Esthet. 2010, 15, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, S.; Bal, B.T.; Asar, N.V.; Turkyilmaz, I.; Tözüm, T.F. Clinical study on the insertion torque and wireless resonance frequency analysis in the assessment of torque capacity and stability of self-tapping dental implants. J. Oral Rehabil. 2009, 36, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennerby, L.; Meredith, N. Implant stability measurements using resonance frequency analysis: Biological and biomechanical aspects and clinical implications. Periodontology 2000 2008, 47, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

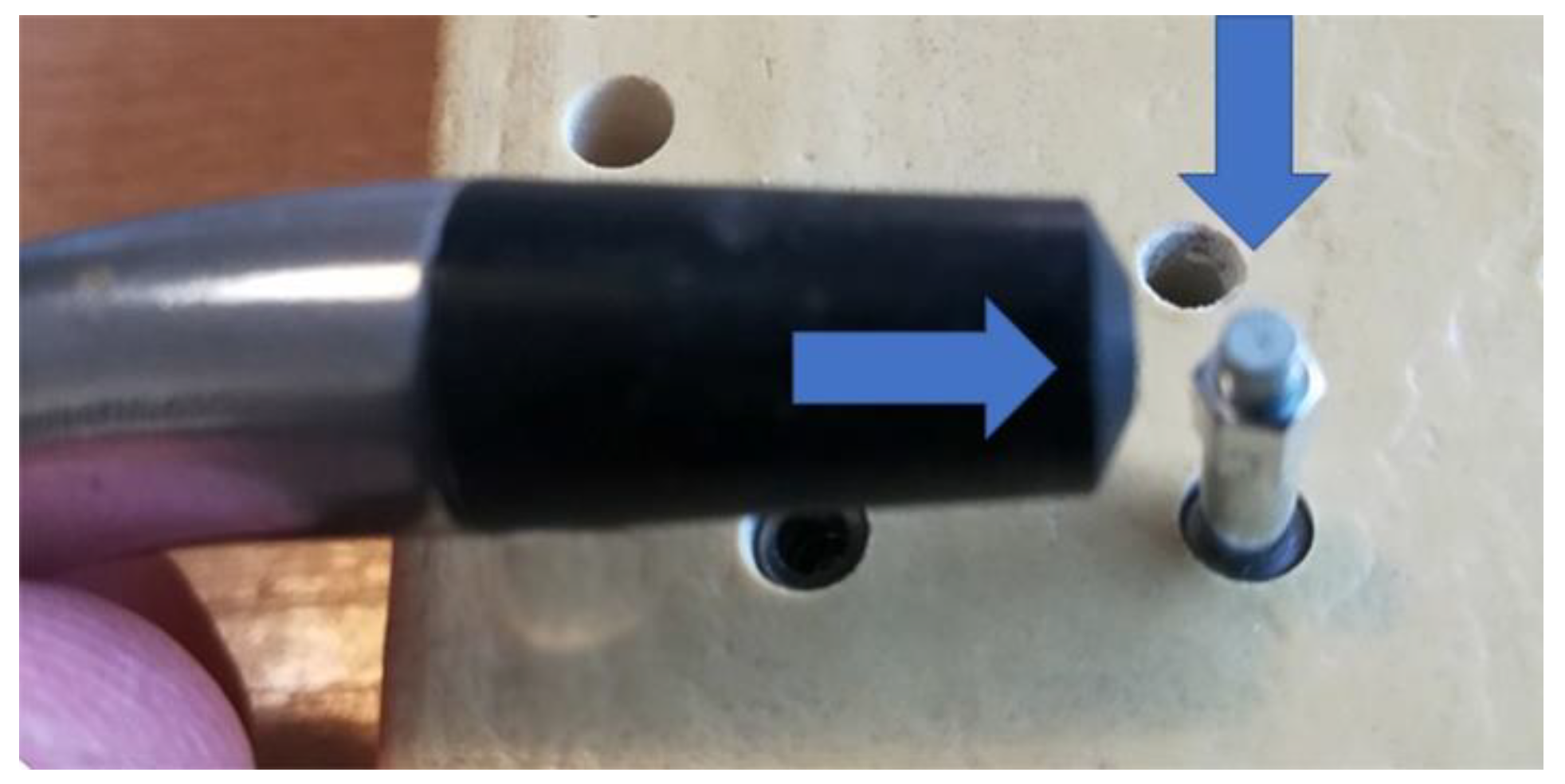
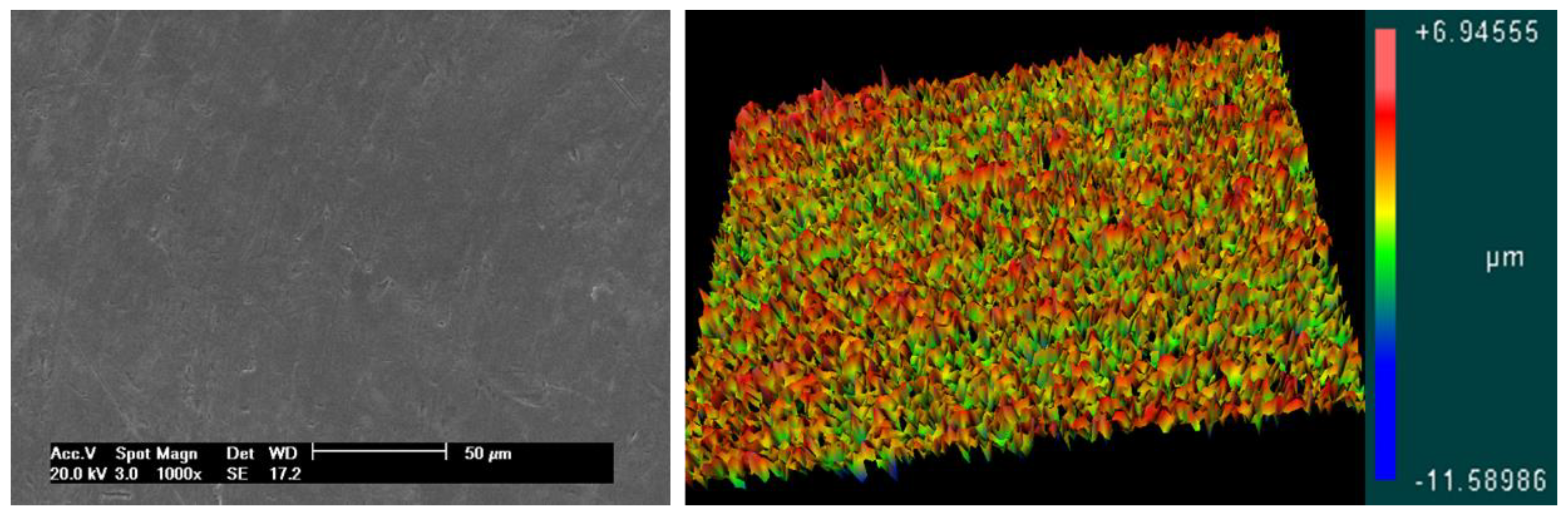

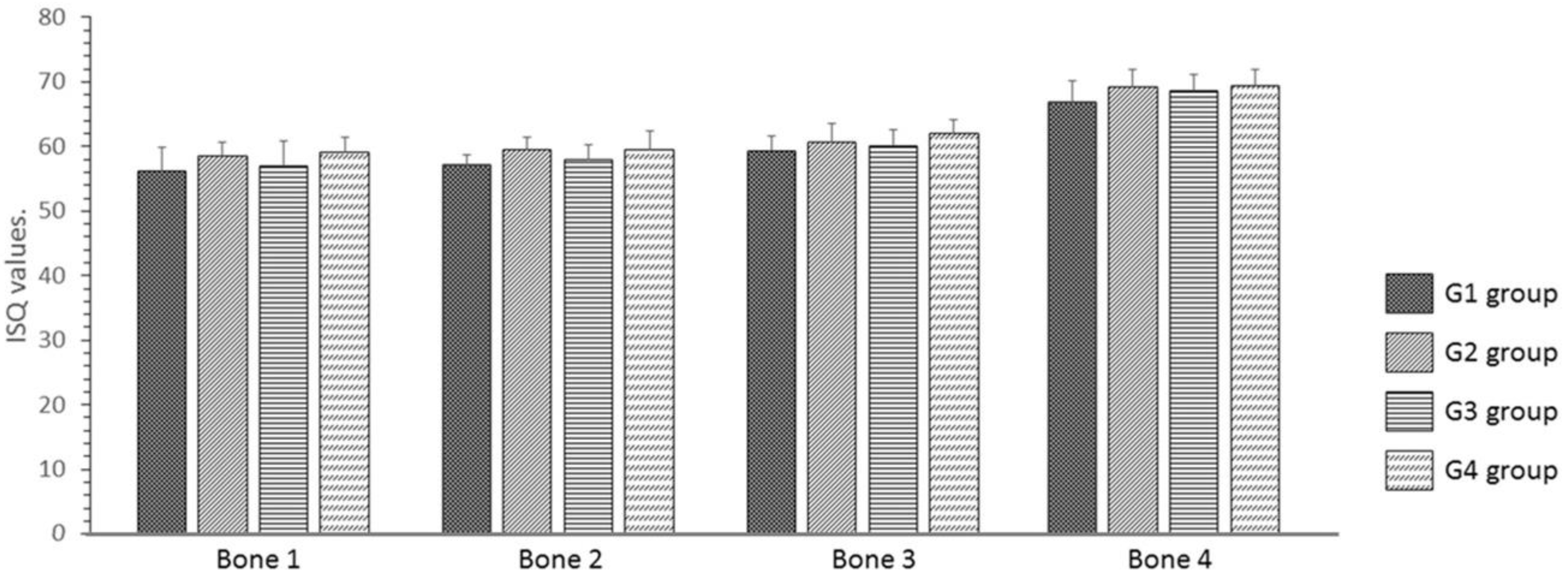
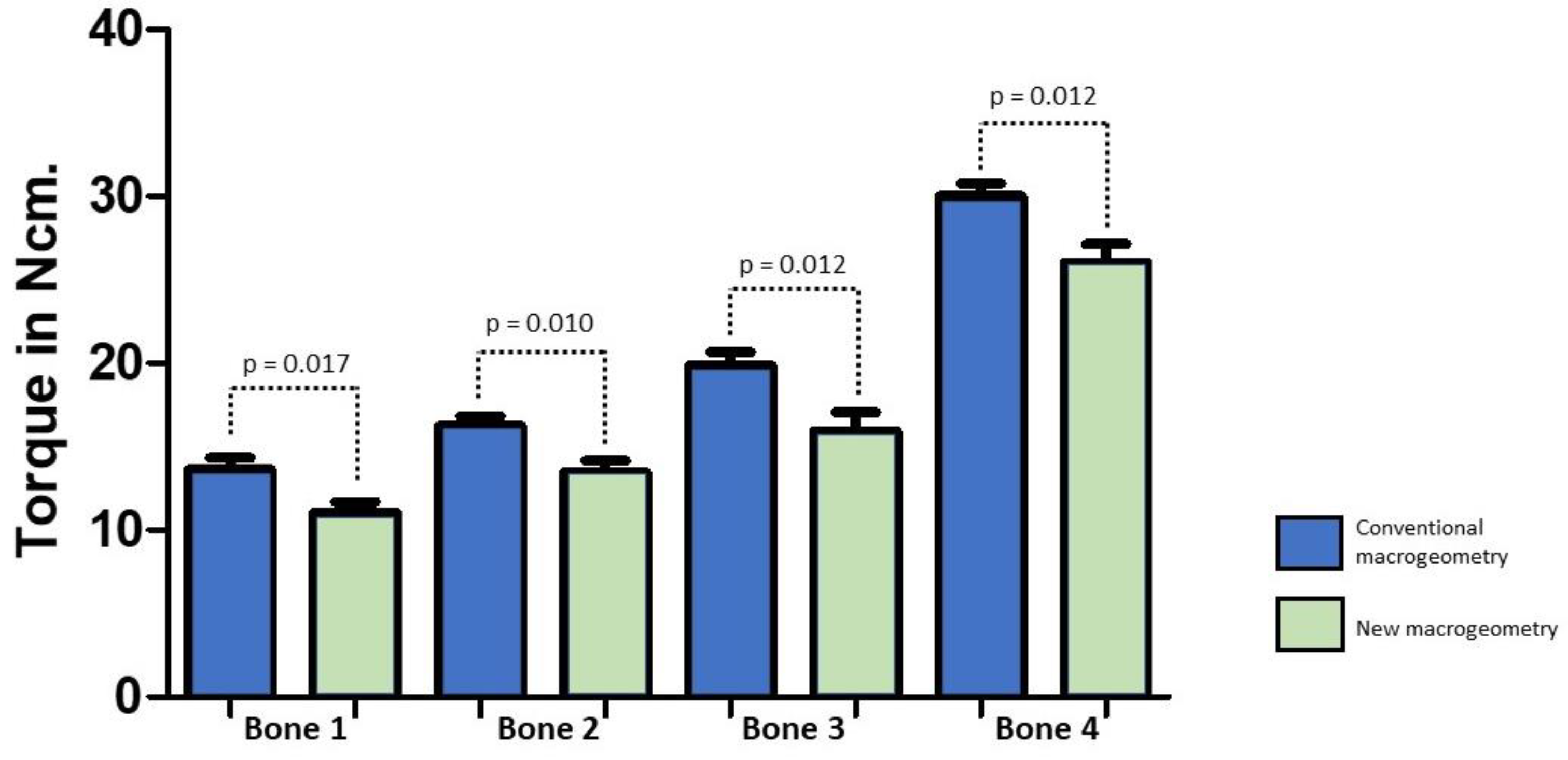
| Parameter | Group G1 | Group G2 | Group G3 | Group G4 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone 1 | 56.2 ± 3.71 | 58.5 ± 2.17 | 57.0 ± 3.79 | 59.2 ± 2.32 | 0.4093 |
| Bone 2 | 57.2 ± 1.60 | 59.5 ± 1.87 | 58.0 ± 2.28 | 59.5 ± 2.88 | 0.4842 |
| Bone 3 | 59.3 ± 2.34 | 60.7 ± 2.17 | 60.2 ± 2.48 | 62.0 ± 2.10 | 0.2105 |
| Bone 4 | 66.8 ± 3.25 | 69.2 ± 2.79 | 68.7 ± 2.42 | 69.3 ± 2.66 | 0.2551 |
| Parameter | Group G1 | Group G2 | Group G3 | Group G4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone 1 | 13.4 ± 2.04 | 13.8 ± 2.55 | 11.0 ± 2.06 | 11.2 ± 2.19 |
| Bone 2 | 16.0 ± 1.93 | 16.4 ± 1.98 | 13.1 ± 2.58 | 13.8 ± 2.03 |
| Bone 3 | 19.5 ± 2.39 | 20.2 ± 2.89 | 15.7 ± 3.99 | 16.2 ± 3.36 |
| Bone 4 | 29.6 ± 2.33 | 30.4 ± 2.85 | 25.8 ± 3.89 | 26.2 ± 3.32 |
| Parameter | Group G1 | Group G2 | Group G3 | Group G4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone 1 | 6.72 ± 1.43 | 6.92 ± 1.44 | 6.50 ± 1.52 | 6.94 ± 1.32 |
| Bone 2 | 7.46 ± 1.52 | 7.84 ± 1.46 | 7.10 ± 1.57 | 7.48 ± 1.54 |
| Bone 3 | 8.46 ± 1.50 | 9.78 ± 1.70 | 8.34 ± 1.97 | 8.58 ± 1.72 |
| Bone 4 | 20.22 ± 1.86 | 20.78 ± 2.05 | 17.14 ± 1.85 | 18.38 ± 1.40 |
| Group | Bone 1 | Bone 2 | Bone 3 | Bone 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | r = 0.334/p = 0.497 | r = −0.395/p = 0.419 | r = −0.348/p = 0.497 | r = −0.486/p = 0.053 |
| G2 | r = 0.358/p = 0.497 | r = 0.086/p = 0.919 | r = −0.717/p = 0.136 | r = −0.152/p = 0.803 |
| G3 | r = 0.029/p = 1.000 | r = −0.541/p = 0.058 | r = −0.429/p = 0.419 | r = 0.435/p = 0.419 |
| G4 | r = 0.086/p = 0.919 | r = 0.486/p = 0.356 | r = −0.058/p = 0.919 | r = −0.395/p = 0.419 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gehrke, S.A.; Pérez-Díaz, L.; Mazón, P.; De Aza, P.N. Biomechanical Effects of a New Macrogeometry Design of Dental Implants: An In Vitro Experimental Analysis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb10040047
Gehrke SA, Pérez-Díaz L, Mazón P, De Aza PN. Biomechanical Effects of a New Macrogeometry Design of Dental Implants: An In Vitro Experimental Analysis. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2019; 10(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb10040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleGehrke, Sergio Alexandre, Leticia Pérez-Díaz, Patricia Mazón, and Piedad N. De Aza. 2019. "Biomechanical Effects of a New Macrogeometry Design of Dental Implants: An In Vitro Experimental Analysis" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 10, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb10040047
APA StyleGehrke, S. A., Pérez-Díaz, L., Mazón, P., & De Aza, P. N. (2019). Biomechanical Effects of a New Macrogeometry Design of Dental Implants: An In Vitro Experimental Analysis. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 10(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb10040047








