Mobile Mixed Reality for Experiential Learning and Simulation in Medical and Health Sciences Education
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Experimental Design
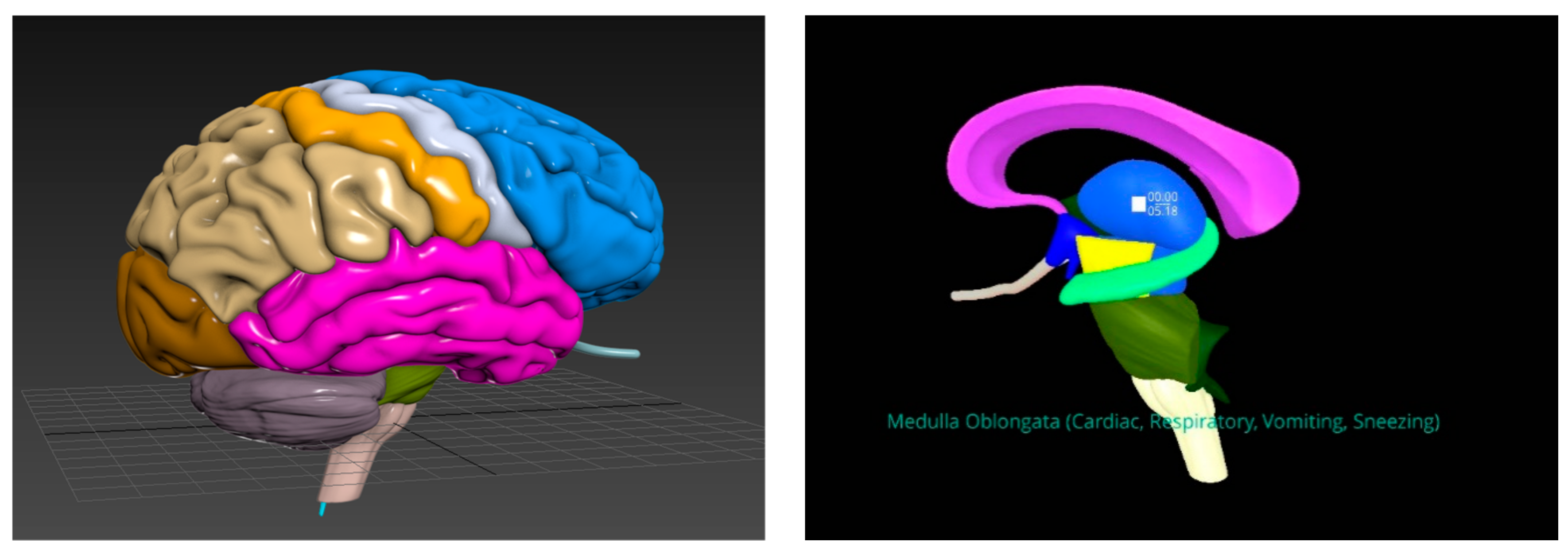
3.1. Knowledge Acquisition
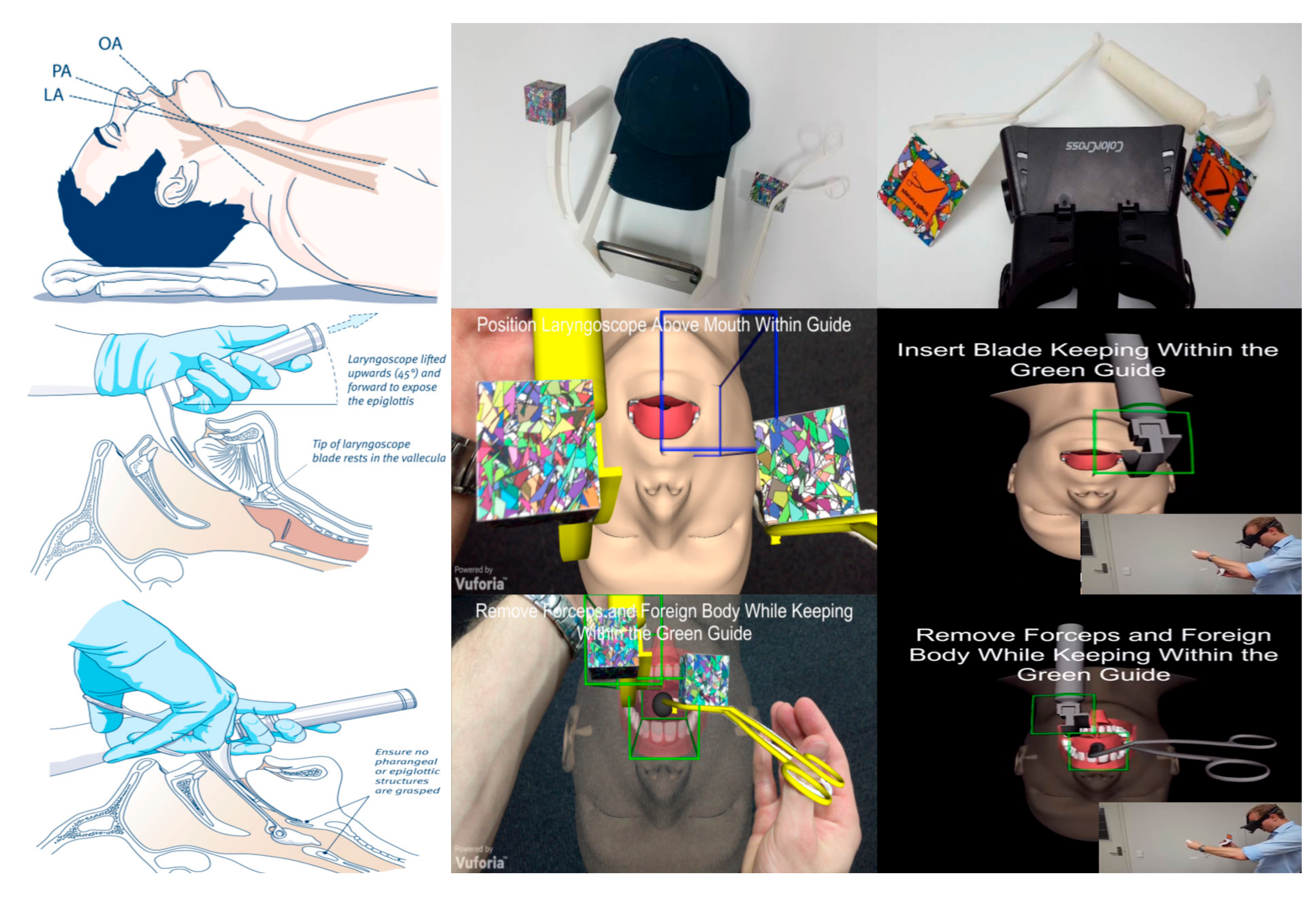
3.2. Skills Development
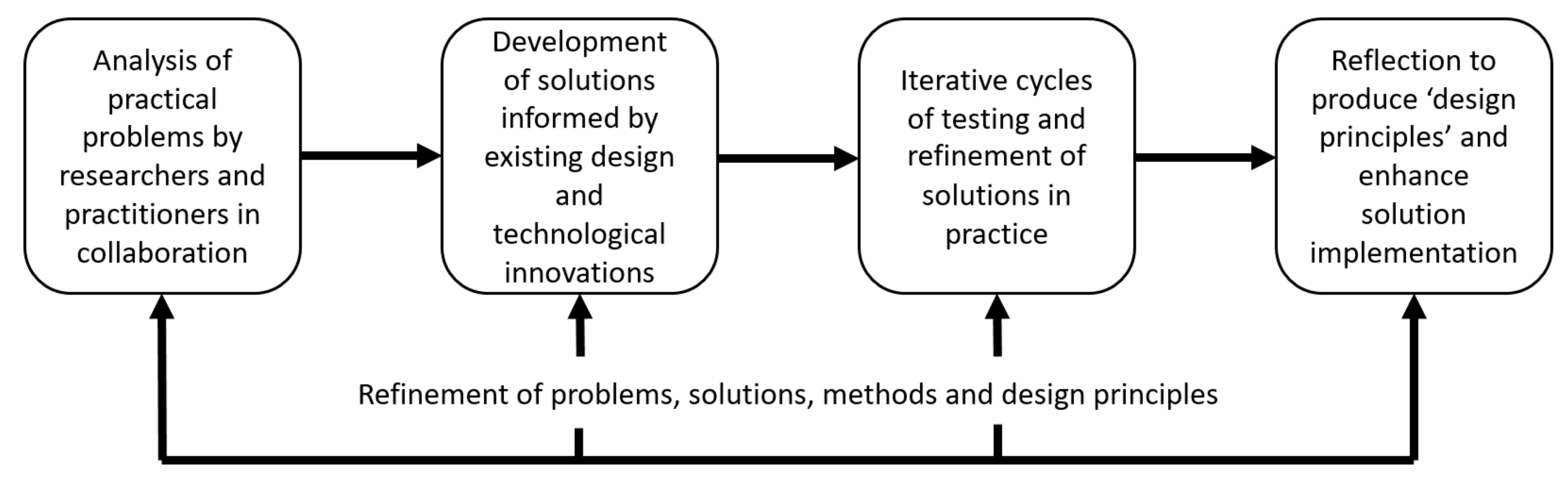
4. Methodology
5. Results
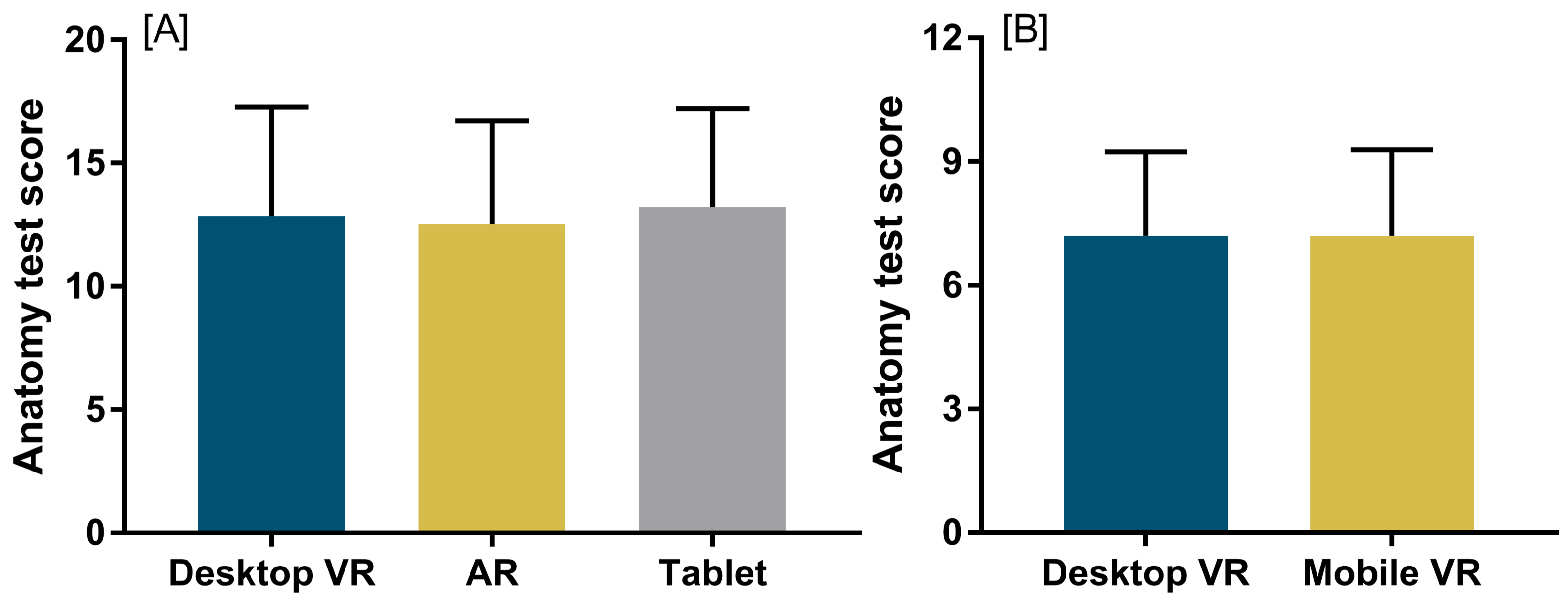
5.1. Knowledge Acquisition and Student Perceptions
5.1.1. Mobile-Based VR
5.1.2. Mobile Augmented Reality
5.1.3. Mobile Learning Environment
5.2. Skills Development
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moro, C.; McLean, M. Supporting students’ transition to university and problem-based learning. Med. Sci. Educ. 2017, 27, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirling, A.; Birt, J. An enriched multimedia ebook application to facilitate learning of anatomy. Anat. Sci. Educ. 2014, 7, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, M.H.; Coto-Yglesias, F.; Varkey, P.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, A.L. The effectiveness of self-directed learning in health professions education: A systematic review. Med. Educ. 2010, 44, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.C.; Mayer, R.E. E-Learning and the Science of Instruction: Proven Guidelines for Consumers and Designers of Multimedia Learning; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.A.; Brydges, R.; Hamstra, S.J.; Zendejas, B.; Szostek, J.H.; Wang, A.T.; Erwin, P.J.; Hatala, R. Comparative effectiveness of technology-enhanced simulation versus other instructional methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Simul. Healthc. 2012, 7, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.A.; Hamstra, S.J.; Brydges, R.; Zendejas, B.; Szostek, J.H.; Wang, A.T.; Erwin, P.J.; Hatala, R. Comparative effectiveness of instructional design features in simulation-based education: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Teach. 2013, 35, e867–e898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendejas, B.; Wang, A.T.; Brydges, R.; Hamstra, S.J.; Cook, D.A. Cost: The missing outcome in simulation-based medical education research: A systematic review. Surgery 2013, 153, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birt, J.; Cowling, M. Toward future ‘mixed reality’ learning spaces for steam education. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Math. Educ. 2017, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cowling, M.; Moore, E.; Birt, J. Augmenting distance education skills development in paramedic science through mixed media visualisation. In Proceedings of the EUROMEDIA’2015, Lisbon, Portugal, 27–29 April 2015; pp. 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Milgram, P.; Kishino, F. A taxonomy of mixed reality visual displays. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 1994, 77, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Magana, A.J. Learning strategies and multimedia techniques for scaffolding size and scale cognition. Comput. Educ. 2014, 72, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Adams Becker, S.; Cummins, M.; Estrada, V.; Freeman, A.; Hall, C. Nmc Horizon Report: 2016 Higher Education Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Adams Becker, S.; Cummins, M.; Estrada, V.; Freeman, A.; Ludgate, H. Nmc Horizon Report: 2013 Higher Education Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Adams Becker, S.; Estrada, V.; Freeman, A. Nmc Horizon Report: 2014 Higher Education Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Adams Becker, S.; Estrada, V.; Freeman, A. Nmc Horizon Report: 2015 Higher Education Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cowling, M.; Tanenbaum, J.; Birt, J.; Tanenbaum, K. Augmenting reality for augmented reality. Interactions 2016, 24, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C.; Štromberga, Z.; Stirling, A. Virtualisation devices for student learning: Comparison between desktop-based (Oculus Rift) and mobile-based (Gear VR) virtual reality in medical and health science education. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2017, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birt, J.; Moore, E.; Cowling, M. Improving paramedic distance education through mobile mixed reality simulation. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2017, 33, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birt, J.; Moore, E.; Cowling, M.A. Piloting mobile mixed reality simulation in paramedic distance education. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 5th International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health (SeGAH), Perth, Australia, 2–4 April 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birt, J.; Hovorka, D.; Nelson, J. Interdisciplinary translation of comparative visualization. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1606.03551. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, C.; Štromberga, Z.; Raikos, A.; Stirling, A. The effectiveness of virtual and augmented reality in health sciences and medical anatomy. Anat. Sci. Educ. 2017, 10, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Densen, P. Challenges and opportunities facing medical education. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2011, 122, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alper, B.S.; Hand, J.A.; Elliott, S.G.; Kinkade, S.; Hauan, M.J.; Onion, D.K.; Sklar, B.M. How much effort is needed to keep up with the literature relevant for primary care? J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2004, 92, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Druss, B.G.; Marcus, S.C. Growth and decentralization of the medical literature: Implications for evidence-based medicine. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2005, 93, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corrin, L.; Bennett, S.; Lockyer, L. Digital natives: Exploring the diversity of young people’s experience with technology. In Reshaping Learning: Frontiers of Learning Technology in a Global Context; Huang, R., Kinshuk, Spector, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 113–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, S. The multiple representation principle in multimedia learning. In The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning, 2nd ed.; Mayer, R.E., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 464–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgarno, B.; Lee, M.J. What are the learning affordances of 3-D virtual environments? Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2010, 41, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Carrera, C.; Saorin, J.L. Virtual learning environments to enhance spatial orientation. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2017, 14, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.A.; Weller, J.M.; Greenland, K.B.; Riley, R.H.; Merry, A.F. Education in airway management. Anaesthesia 2011, 66, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, C.C.; Cannon, E.K.; Warner, D.O.; Cook, D.A. Advanced airway management simulation training in medical education: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butchart, A.G.; Tjen, C.; Garg, A.; Young, P. Paramedic laryngoscopy in the simulated difficult airway: Comparison of the venner A.P. Advance and glidescope ranger video laryngoscopes. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2011, 18, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalese, R.J.; Obeso, V.T.; Issenberg, S.B. Simulation technology for skills training and competency assessment in medical education. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2008, 23, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.D.; Ken, B.; Syroid, M.S.; Noah, D.; Drews, P.D.; Frank, A.; Ogden, M.D.L.L.; Strayer, P.D.; David, L.; Pace, M.D.M.S.; et al. Part task and variable priority training in first-year anesthesia resident educationa combined didactic and simulation-based approach to improve management of adverse airway and respiratory events. Anesthesiology 2008, 108, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.Q.; Van Merrienboer, J.; Durning, S.; Ten Cate, O. Cognitive load theory: Implications for medical education: Amee guide no. 86. Med. Teach. 2014, 36, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickens, C.D.; Hutchins, S.; Carolan, T.; Cumming, J. Effectiveness of part-task training and increasing-difficulty training strategies: A meta-analysis approach. Hum. Factors 2013, 55, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, P. State-of-the-art research into multimedia learning: A commentary on Mayer’s handbook of multimedia learning. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2015, 29, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydges, R.; Manzone, J.; Shanks, D.; Hatala, R.; Hamstra, S.J.; Zendejas, B.; Cook, D.A. Self-regulated learning in simulation-based training: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Educ. 2015, 49, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamstra, S.J.; Brydges, R.; Hatala, R.; Zendejas, B.; Cook, D.A. Reconsidering fidelity in simulation-based training. Acad. Med. 2014, 89, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, G.; Dore, K.; Grierson, L. The minimal relationship between simulation fidelity and transfer of learning. Med. Educ. 2012, 46, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queensland Ambulance Service, C.U. Clinical Practice Procedures: Airway Management. Available online: https://www.ambulance.qld.gov.au/CPPtable.html. (accessed on 29 January 2018).
- Anderson, T.; Shattuck, J. Design-based research: A decade of progress in education research? Educ. Res. 2012, 41, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, T.C. Design research from a technology perspective. Educ. Des. Res. 2006, 1, 52–66. [Google Scholar]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birt, J.; Stromberga, Z.; Cowling, M.; Moro, C. Mobile Mixed Reality for Experiential Learning and Simulation in Medical and Health Sciences Education. Information 2018, 9, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9020031
Birt J, Stromberga Z, Cowling M, Moro C. Mobile Mixed Reality for Experiential Learning and Simulation in Medical and Health Sciences Education. Information. 2018; 9(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirt, James, Zane Stromberga, Michael Cowling, and Christian Moro. 2018. "Mobile Mixed Reality for Experiential Learning and Simulation in Medical and Health Sciences Education" Information 9, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9020031
APA StyleBirt, J., Stromberga, Z., Cowling, M., & Moro, C. (2018). Mobile Mixed Reality for Experiential Learning and Simulation in Medical and Health Sciences Education. Information, 9(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9020031





