Duplication Detection When Evolving Feature Models of Software Product Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Software Product Line Evolution
2.1. Software Product Lines
2.2. SPL Evolution Challenges
2.3. Model Defects Caused by SPL Evolution
| Model Defect | Definition |
|---|---|
| Inconsistency | |
| The breaking of a rule between two partial specifications [14]. | |
| Incompleteness | The lack of necessary information related to a feature or requirement [15]. |
| Incorrectness | This describes the non-correspondence of a feature with the requirements imposed in the specification [5]. |
| Ambiguity | When a feature has more than one interpretation [15]. |
| Redundancy | The presence of reusable elements and variability constraints among them that can be omitted from the product line model (PLM) without loss of semantics on the PLM [16]. |
| Duplication | To have the same thing expressed in two or more places; duplication can happen in specifications, processes and programs [17]. |
| Unsafety | This happens when the behavior of existing products is affected by a new evolution [18]. |
2.4. Duplication of Features When Evolving SPLs
3. Modeling and Verifying SPL Features
3.1. Variability Modeling
3.2. Evolution Documentation
3.3. SPL Model Verification
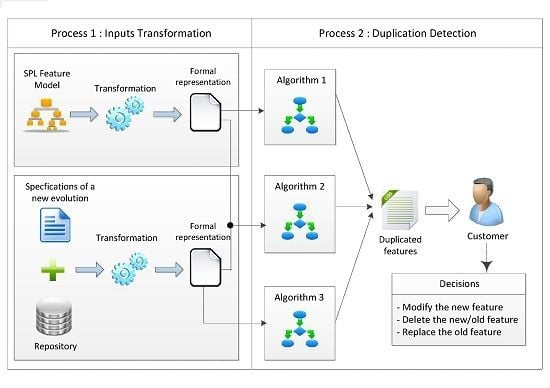
4. A Framework for Detecting Feature Duplication When Evolving SPLs
4.1. Process 1: Feature Model and Specification Transformation
4.1.1. Transforming Feature Models
4.1.2. Transforming Natural Language Specifications
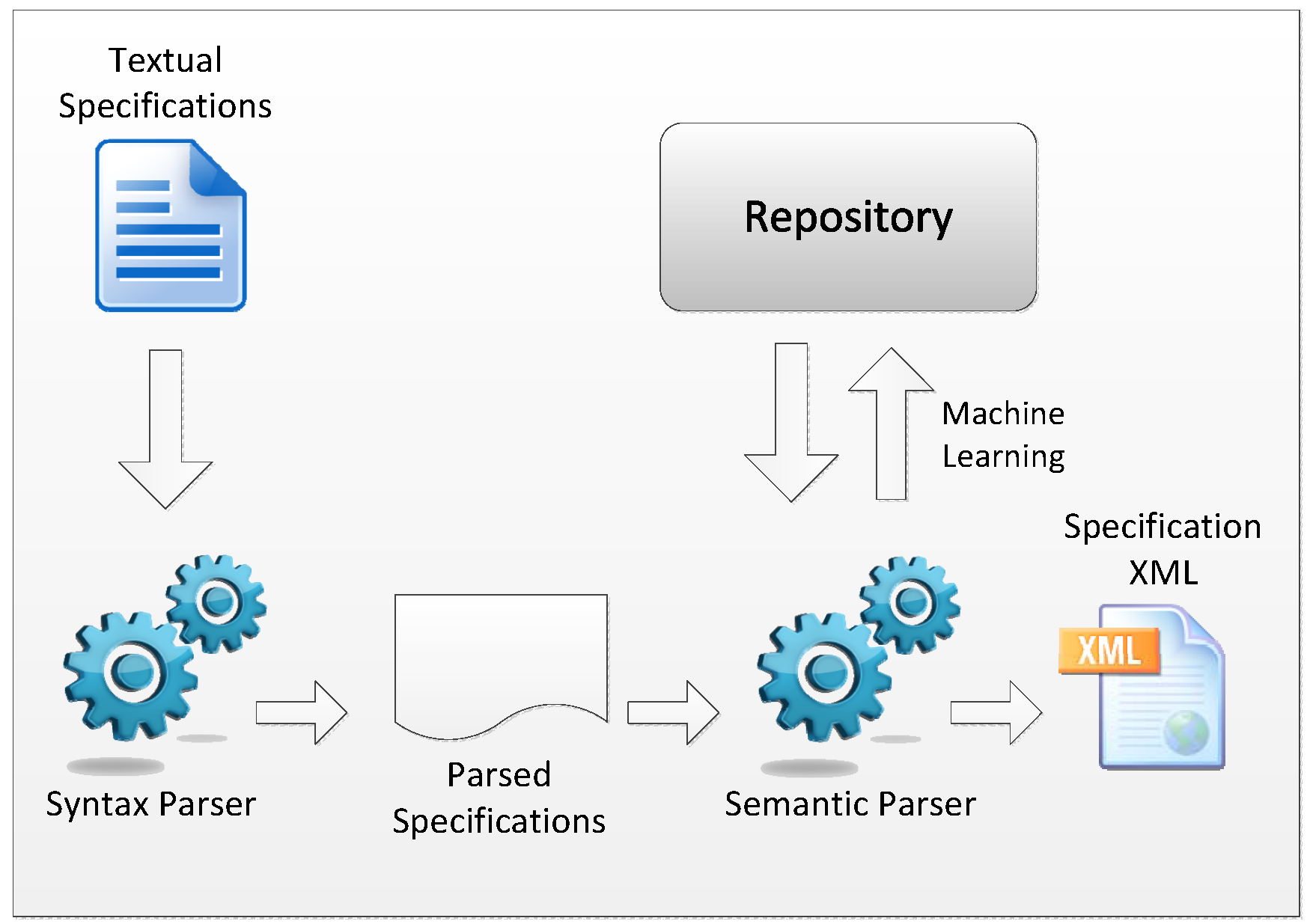
- Sentences detection: The first operation consists of detecting separate sentences in the specifications and writing each one in a different line.
- Tokenization: This action segments sentences into tokens. A token can be a word, punctuation, a number, etc. As an output of this action, all of the tokens of the specification are separated using whitespace characters, such as a space or line break, or by punctuation characters.
- Parsing: This step consists of analyzing each sentence of the specification in order to extract the words it contains and to determine their parts-of-speech based on the rules of the language grammar (e.g., noun, verb, adjective, adverb). A parser marks all of the words of a sentence using a POS tagger (part-of-speech tagger) and converts the sentence into a tree that represents the syntactic structure of the sentence. This action allows us to confirm whether the action of a verb is affirmative or negative and whether a requirement is mandatory or optional, etc.
- The glossary: This contains the different features used in the domain model, classified by different categories, especially “variant”.
- The dictionary: This corresponds to the definition of all of the features of the product line, their synonyms and the relationships between them. This dictionary is manually built and updated during system evolutions. In our test, we do not use an existing dictionary; we have created a new one based on the domain model of the SPL. It has to be noted that the current version is not final; we are still working on it. Moreover, we intend to import existing thesauri to enrich our dictionary. Based on this dictionary, we compare the key synonyms of the new and existing variants to automatically detect duplications. Thus, a dictionary is necessary in our approach, because it is based on a semantic comparison, so we necessarily need synonyms to detect the duplications.

4.2. Process 2: Duplication Detection
- Detecting duplication in the new specifications
- Detecting duplication in the existing feature models
- Detecting duplication between the specifications and the feature models
4.2.1. Formalizing the Basic Concepts
- Formalizing the domain model
- A variation point from the set is associated with a set of variants that contains the elements .
- is the union of all of the sets of variants associated with the variation points. It represents the set of all of the variants of the domain model.
- Formalizing the application model
- Formalizing the specification
4.2.2. The Algorithms of Duplication Detection
- Detecting Duplication in Specifications
| Step | Actions |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Definition of a key synonym for each set of synonyms, based on the dictionary. For example: The synonyms for “on-line sales” could be “e-sales”, “Internet sales” or “web sales”. The key synonym for these alternatives is “on-line sales”. |
| Generation of an equivalent XML, by replacing the name of every node (variation point or variant) with its associated key synonym in the dictionary. | |
| Step 2 | This step consists of putting in alphabetical order the variation points and the variants of each variation point. |
| Step 3 | For each variation point, the duplicated variants are detected and removed from the XML. |
| Step 4 | Comparison between the variants of all of the variation points, in order to detect duplication in the whole XML. |
- Detecting Duplication in Feature Models
- Detecting Duplication between Specifications and Feature Models
| Algorithm 1 Detecting duplication between the specification and the application model. |
| Principal Lookup : for each do for each do if then Secondary Lookup : for each do for each do if then Secondary Lookup end if end for end for Principal Lookup end if end for end for |
4.2.3. The Framework Outputs
4.3. Automated Tool
- Development environment: Eclipse
- Development language: Java
- Human-computer interface: SWT
- Database: PostGre SQL
- Feature models creation: FeatureIDE
- Natural language processing: OpenNLP
- Graph generation: Prefuse
- The processing of natural language specifications (a txt document) and their transformation to an XML document.
- The creation and modification of the repository.
- The detection of duplication in specifications.
- The detection of duplication in the XML source of a feature model.
- The detection of duplication between a feature model and a specification.
5. Results and Discussion
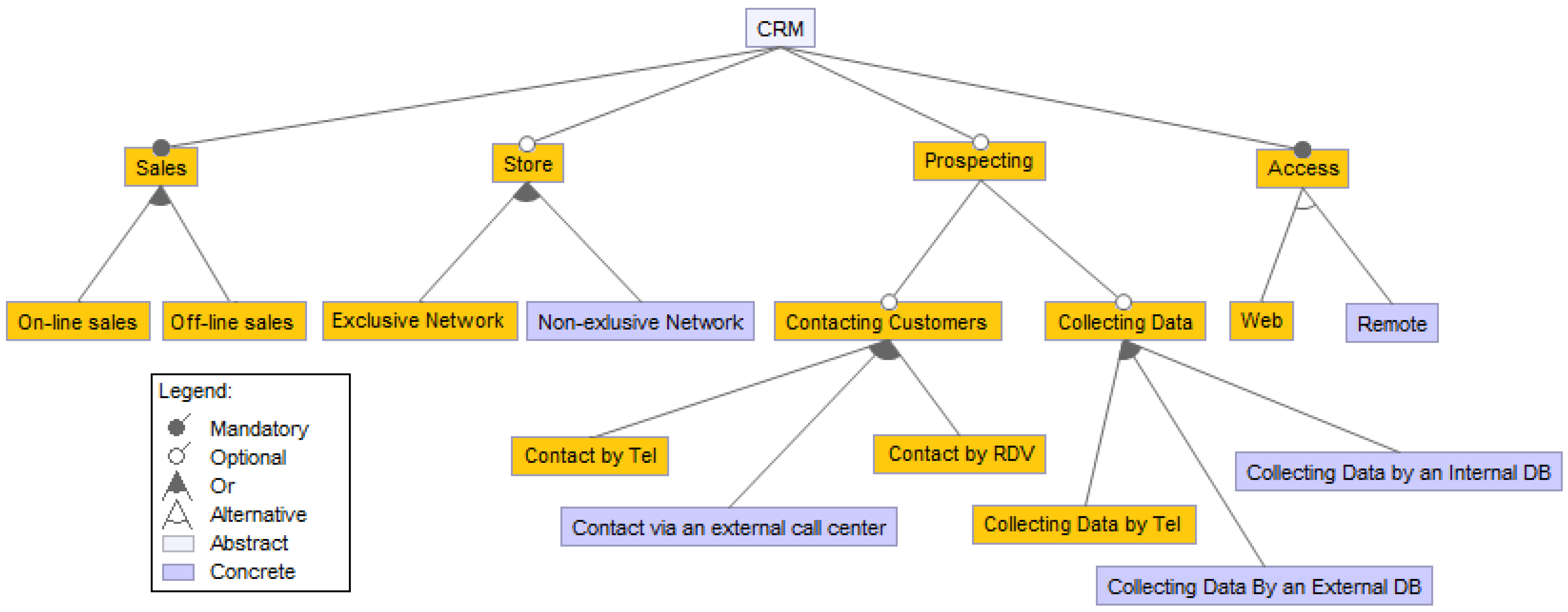

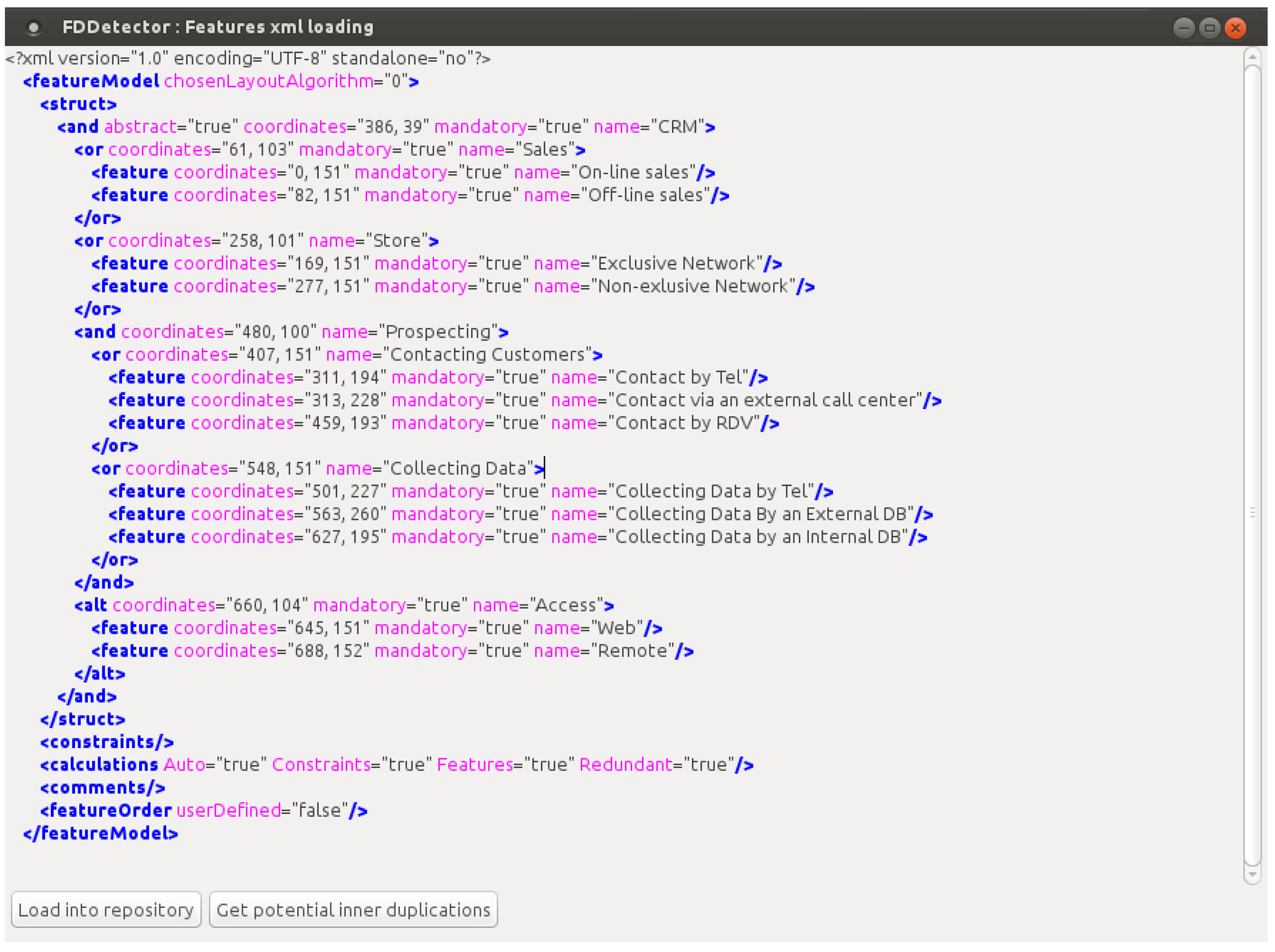
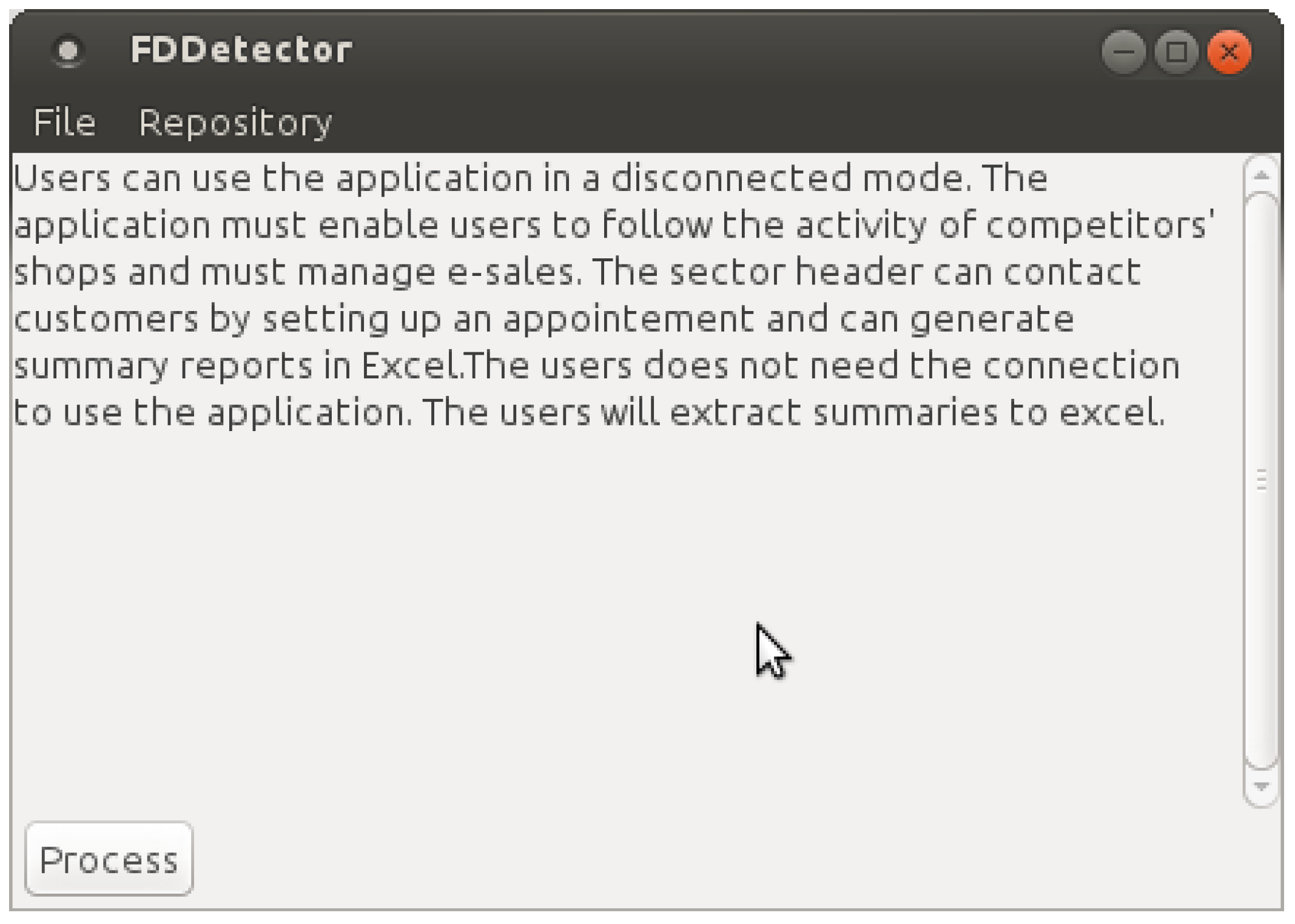
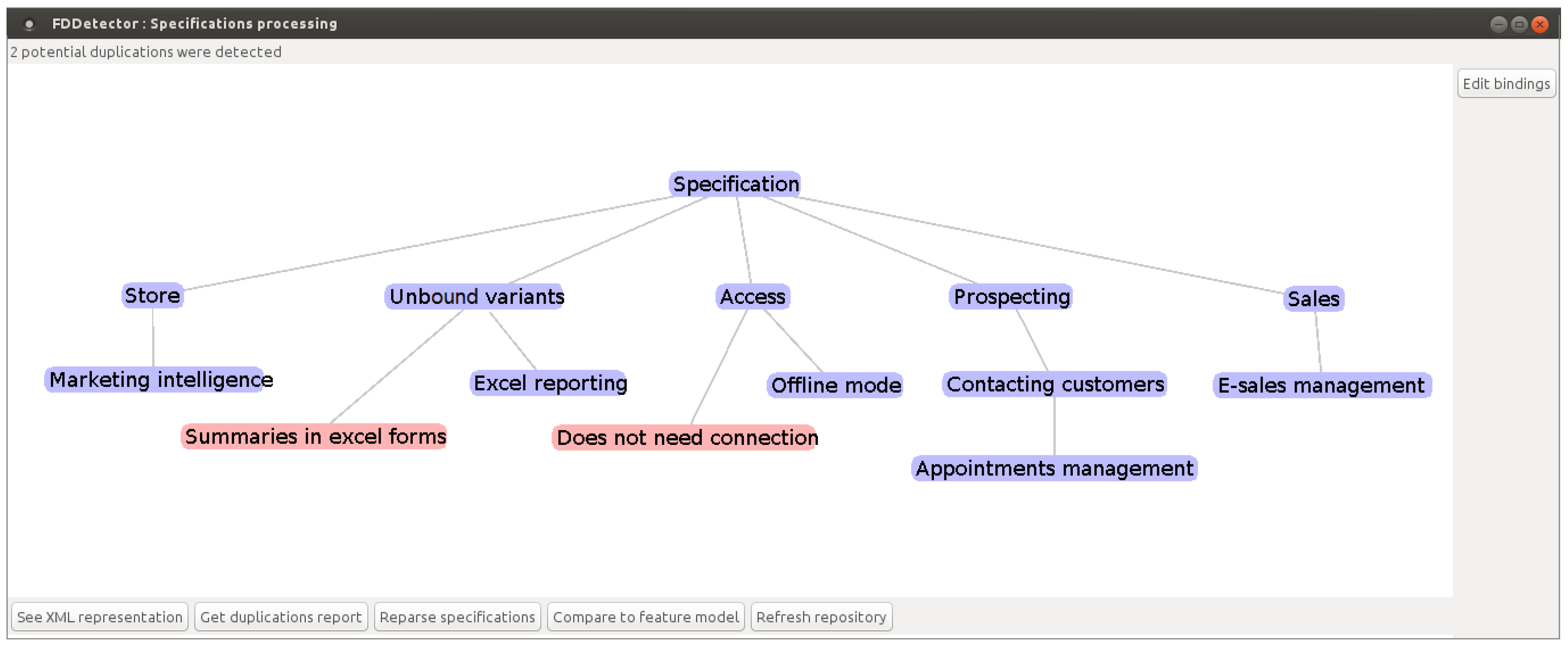
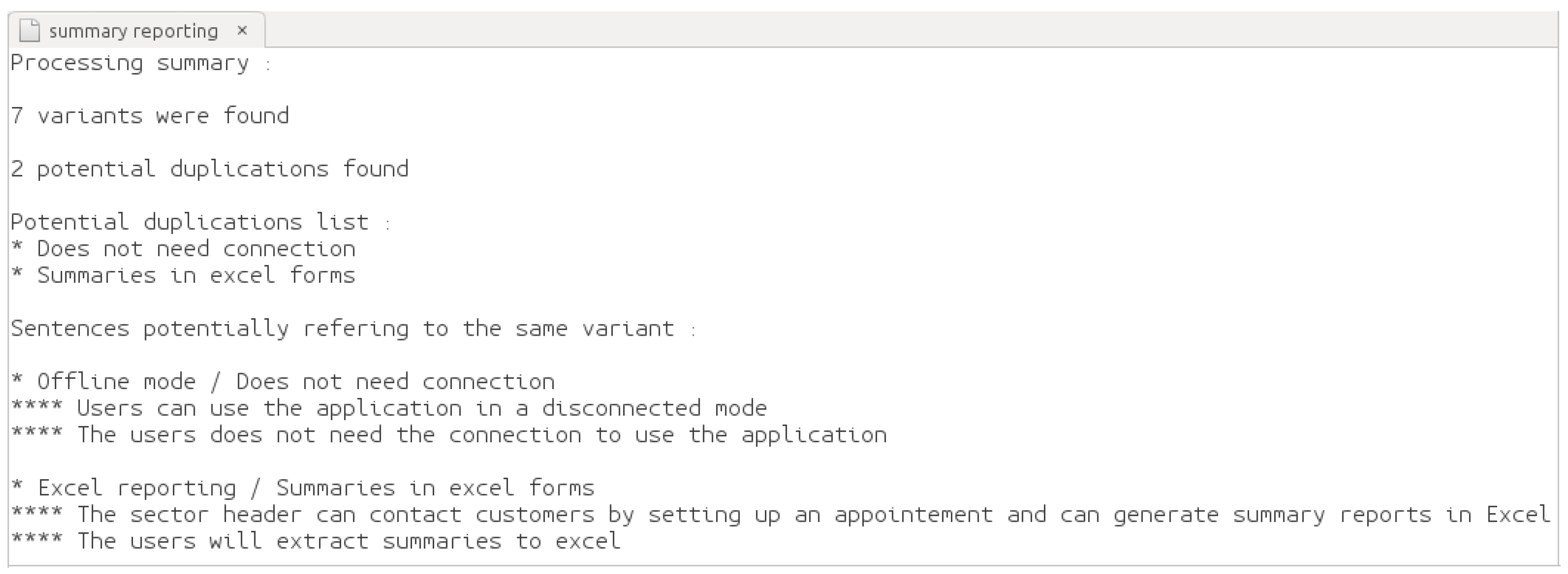
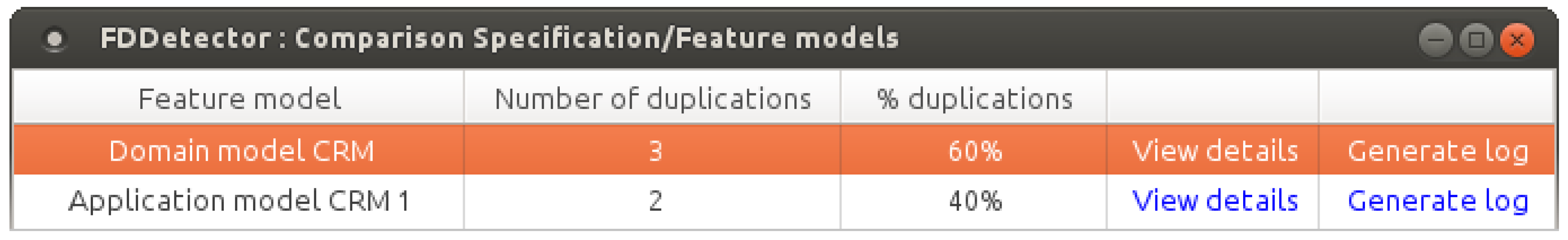
6. Related Work
6.1. Detecting Defects in Specifications
6.2. Detecting Defects in Feature Models
6.3. Detecting Duplication in SPLs
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clements, P.; Northop, L. Software Product Lines—Practices and Patterns; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Apel, S.; Kästner, C. An overview of feature-oriented software development. J. Object Technol. 2009, 8, 49–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Cohen, S.; Hess, J.; Novak, W.; Peterson, S. Feature-Oriented Domain Analysis (FODA) Feasibility Study; Technical Report CMU/SEI-90-TR-21; Software Engineering Institute: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, D.; Urli, S.; Quinton, C.; Blay-Fornarino, M.; Collet, P.; Duchien, L.; Mosser, S. SPLEMMA: A generic framework for controlled-evolution of software product lines. In Proceedings of the 17th International Software Product Line Conference Co-located Workshops, Tokyo, Japan, 26–30 August 2013; pp. 59–66.
- Zowghi, D.; Gervasi, V. On the interplay between consistency, completeness, and correctness in requirements evolution. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2004, 46, 763–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khtira, A.; Benlarabi, A.; El Asri, B. Towards duplication-free feature models when evolving software product lines. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Software Engineering Advances, Nice, France, 12–16 October 2014; pp. 107–113.
- Pohl, K.; Böckle, G.; van der Linden, F. Software Product Line Engineering Foundations, Principles, and Techniques; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Anquetil, N.; Kulesza, U.; Mitschke, R.; Moreira, A.; Royer, J.C.; Rummler, A.; Sousa, A. A model-driven traceability framework for software product lines. Softw. Syst. Model. 2010, 9, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleuss, A.; Botterweck, G.; Dhungana, D.; Polzer, A.; Kowalewski, S. Model-driven support for product line evolution on feature level. J. Syst. Softw. 2010, 85, 2261–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlarabi, A.; El Asri, B.; Khtira, A. A co-evolution model for software product lines: An approach based on evolutionary trees. In Proceedins of the IEEE Second World Conference on Complex Systems, Agadir, Morocco, 10–12 November 2014; pp. 140–145.
- Seidl, C.; Heidenreich, F.; Assmann, U. Co-evolution of models and feature mapping in software product lines. In Proceedings of the 16th International Software Product Line Conference, Salvador, Brazil, 2–7 September 2012; Volume 1, pp. 76–85.
- Tizzei, L.P.; Dias, M.; Rubira, C.M.; Garcia, A.; Lee, J. Components meet aspects: Assessing design stability of a software product line. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2011, 53, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuseibeh, B. To be and not to be: On managing inconsistency in software development. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Software Specification and Design, Schloss Velen, Germany, 22–23 March 1996; pp. 164–169.
- Easterbrook, S.; Nuseibeh, B. Managing inconsistencies in an evolving specification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Second IEEE International Symposium on Requirements Engineering, York, UK, 27–29 March 1995; pp. 48–55.
- Lami, G.; Gnesi, S.; Fabbrini, F.; Fusani, M.; Trentanni, G. An automatic tool for the analysis of natural language requirements. Comput. Syst. Eng. 2005, 20, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Mazo, R. A Generic Approach for Automated Verification of Product Line Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Pantheon-Sorbonne University, Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, A.; Thomas, D. The Pragmatic Programmer: From Journeyman to Master; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, L.; Teixeira, L.; Sena, D.; Alves, V.; Kulezsa, U.; Borba, P. Investigating the safe evolution of software product lines. ACM SIGPLAN Not. 2012, 47, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Aversano, L.; Cerulo, L.; Di Penta, M. How clones are maintained: An empirical study. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th European Conference on Software Maintenance and Reengineering, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 21–23 March 2007; pp. 81–90.
- Salinesi, C.; Mazo, R.; Djebbi, O.; Diaz, D.; Lora-Michiels, A. Constraints: The core of product line engineering. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Research Challenges in Information Science, Gosier, France, 19–21 May 2011; pp. 1–10.
- Kang, K.C.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Shin, E.; Huh, M. FORM: A feature-oriented reuse method with domain-specific reference architectures. Ann. Softw. Eng. 1998, 5, 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J. Design and Use of Software Architectures: Adopting and Evolving a Product-Line Approach; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA; Addison-Wesley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kästner, C.; Thüm, T.; Saake, G.; Feigenspan, J.; Leich, T.; Wielgorz, F.; Apel, S. FeatureIDE: A tool framework for feature-oriented software development. In Proceedings of the IEEE 31st International Conference on Software Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–27 May 2009; pp. 611–614.
- Meyer, B. On formalism in specifications. IEEE softw. 1985, 2, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtmann, J.; Meyer, J.; von Detten, M. Automatic validation and correction of formalized, textual requirements. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation Workshops, Berlin, Germany, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 486–495.
- Fatwanto, A. Software requirements specification analysis using natural language processing technique. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on QiR (Quality in Research), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 25–28 June 2013; pp. 105–110.
- Ilieva, M.G.; Ormandjieva, O. Automatic transition of natural language software requirements specification into formal presentation. In Natural Language Processing and Information Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 392–397. [Google Scholar]
- Khtira, A.; Benlarabi, A.; El Asri, B. An approach to detect duplication in software product lines using natural language processing. In Proceedings of the Mediterranean Conference on Information and Communication Technologies, Saidia, Morocco, 7–9 May 2015. in press.
- The Apache Software Foundation. OpenNLP. Available online: http://opennlp.apache.org/ (accessed on 5 October 2015).
- Khtira, A.; Benlarabi, A.; El Asri, B. Detecting feature duplication in natural language specifications when evolving software product lines. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering, Barcelona, Spain, 29–30 April 2015.
- Khtira, A. Towards a framework for feature deduplication during software product lines evolution. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, Stockholm, Sweden, 8–12 June 2015.
- Ambriola, V.; Gervasi, V. Processing natural language requirements. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, Incline Village, NV, USA, 1–5 November 1997; pp. 36–45.
- Guo, J.; Wang, Y. Towards consistent evolution of feature models. In Software Product Lines: Going Beyond; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Geng, P.; Wu, W. Constructing traceability between features and requirements for software product line engineering. In Proceedings of the 19th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference, Hong Kong, China, 4–7 December 2012; Volume 2, pp. 27–34.
- Schulze, S. Analysis and Removal of Code Clones in Software Product Lines. Ph.D. Thesis, Magdeburg University, Magdeburg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky, Y.; Rubin, J.; Berger, T.; Duszynski, S.; Becker, M.; Czarnecki, K. An exploratory study of cloning in industrial software product lines. In Proceedings of the IEEE 17th European Conference on Software Maintenance and Reengineering, Genova, Switzerland, 5–8 March 2013; pp. 25–34.
- Mende, T.; Beckwermert, F.; Koschke, R.; Meier, G. Supporting the grow-and-prune model in software product lines evolution using clone detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th European Conference on Software Maintenance and Reengineering, Athens, Greece, 1–4 April 2008; pp. 163–172.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khtira, A.; Benlarabi, A.; Asri, B.E. Duplication Detection When Evolving Feature Models of Software Product Lines. Information 2015, 6, 592-612. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6040592
Khtira A, Benlarabi A, Asri BE. Duplication Detection When Evolving Feature Models of Software Product Lines. Information. 2015; 6(4):592-612. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6040592
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhtira, Amal, Anissa Benlarabi, and Bouchra El Asri. 2015. "Duplication Detection When Evolving Feature Models of Software Product Lines" Information 6, no. 4: 592-612. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6040592
APA StyleKhtira, A., Benlarabi, A., & Asri, B. E. (2015). Duplication Detection When Evolving Feature Models of Software Product Lines. Information, 6(4), 592-612. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6040592