Hierarchical Knowledge Distillation for Efficient Model Compression and Transfer: A Multi-Level Aggregation Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Hierarchical Knowledge Transfer: We introduce a novel hierarchical distillation process that enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of knowledge transfer by strategically leveraging intermediate assistant models to capture multi-level features from the teacher model.
- Model Aggregation and Distillation: Our method for recombining and distilling knowledge from multiple assistant models into a cohesive student model improves overall performance in VLM tasks. This process allows the student model to integrate knowledge across feature levels, leading to superior generalization.
- State-of-the-Art Performance: Through extensive experiments on benchmark remote sensing datasets, RSITMD and RSICD, we demonstrate that our hierarchical, multi-stage approach not only bridges the gap between high-performance models and resource-constrained deployment but also surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in image–text retrieval and zero-shot classification tasks. These results validate the effectiveness of the HIMS_KD framework in advancing efficient model transfer and, when a compact student is used, model compression for remote sensing applications.
2. Related Work
2.1. Knowledge Distillation on VLMs
2.2. Large VLMs for Remote Sensing
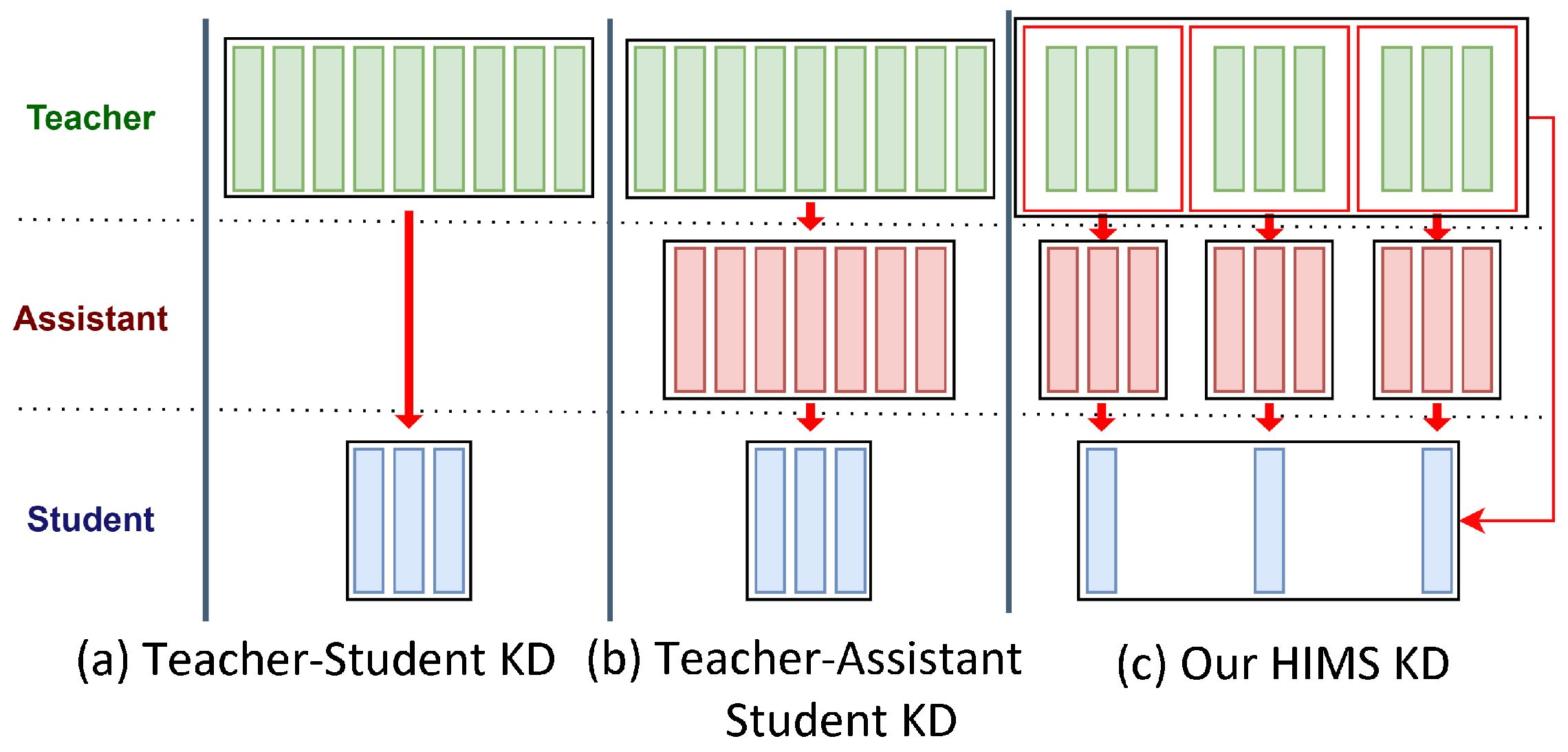
2.3. Assistant-Based Knowledge Distillation
3. Method
3.1. Problem Definition
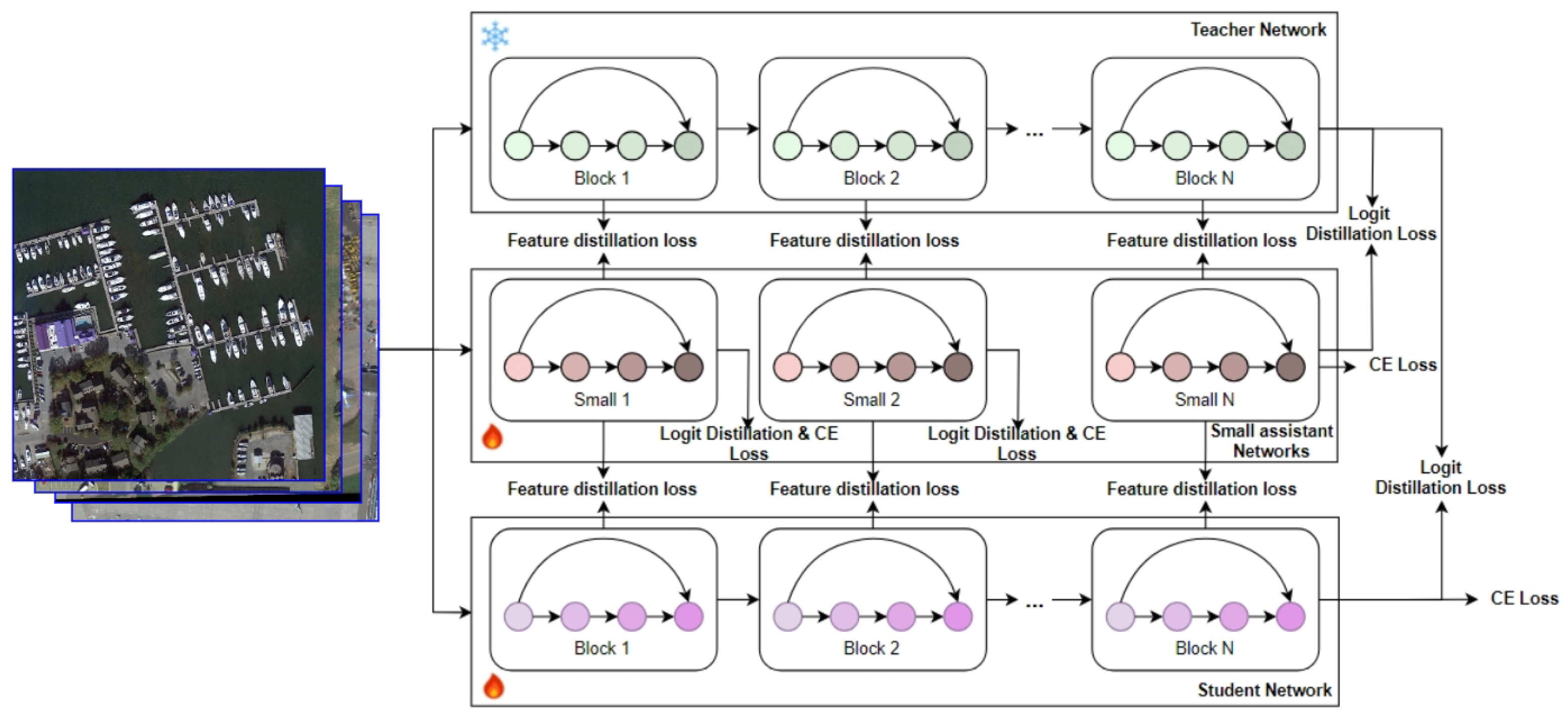
3.2. The Proposed HIMS_KD
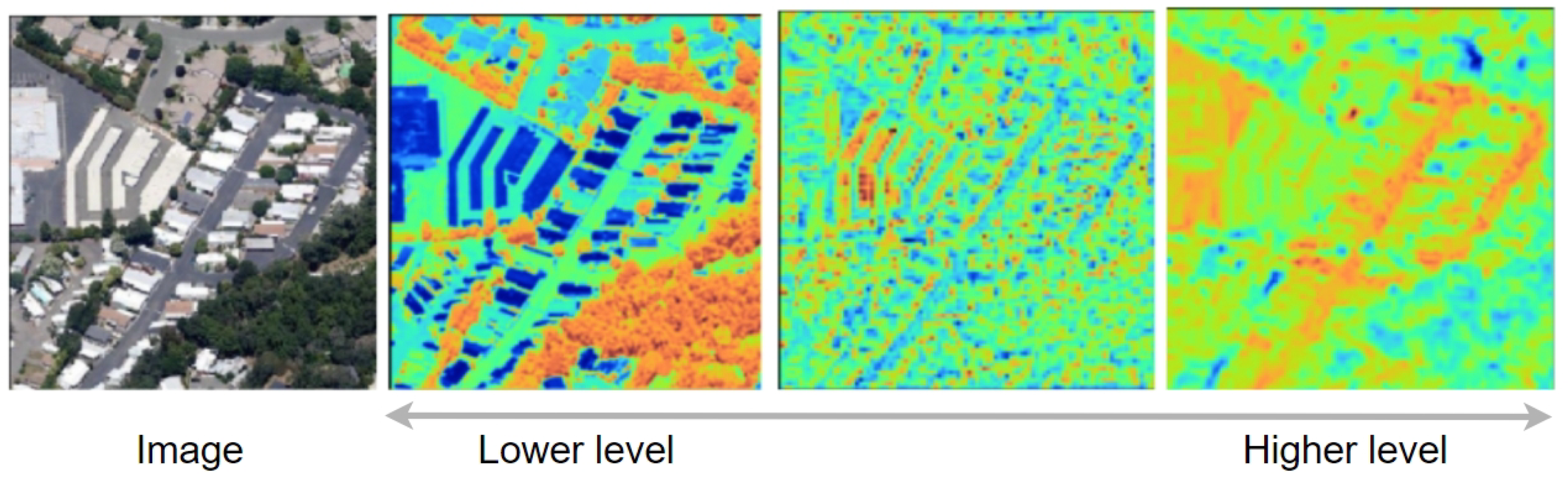
3.3. Multi-Level Feature Representations
3.4. Multi-Level Feature Combination for Student Model
3.4.1. Feature-Level Alignment
3.4.2. Logit-Based Alignment
3.4.3. Cross-Entropy Loss
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Zero-Shot Classification
4.2.1. Public Remote Sensing Classification Datasets
4.2.2. Knowledge Distillation Comparison
4.3. Image–Text Retrieval
4.3.1. Public Remote Sensing Retrieval Datasets
4.3.2. Results
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Assistant Configurations
4.4.2. Loss Components
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Wen, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, X.X. Vision-Language Models in Remote Sensing: Current progress and future trends. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024, 12, 32–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yao, J.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, B.; Chanussot, J. Deep Learning in Multimodal Remote Sensing Data Fusion: A Comprehensive Review. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.01380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Yu, B.; Maybank, S.J.; Tao, D. Knowledge Distillation: A Survey. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2021, 129, 1789–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Ballas, N.; Kahou, S.E.; Chassang, A.; Gatta, C.; Bengio, Y. FitNets: Hints for Thin Deep Nets. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1412.6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, S.I.; Farajtabar, M.; Li, A.; Levine, N.; Matsukawa, A.; Ghasemzadeh, H. Improved Knowledge Distillation via Teacher Assistant. Proc. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 5191–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Dong, L.; Wei, F.; Huang, M. MiniLLM: Knowledge Distillation of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kong, L.; CEN, J.; Chen, R.; Zhang, W.; Pan, L.; Chen, K.; Liu, Z. Segment Any Point Cloud Sequences by Distilling Vision Foundation Models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Oh, A., Naumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 36, pp. 37193–37229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, H. Distilling Out-of-Distribution Robustness from Vision-Language Foundation Models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Oh, A., Naumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 36, pp. 32938–32957. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, P.; Shah, H.; Saenko, K.; Xia, X. DIME-FM: DIstilling Multimodal and Efficient Foundation Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 15521–15533. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Yu, J.; Yang, M.H.; Brown, M.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, T.; Gong, B.; Zhou, T. Module-wise Adaptive Distillation for Multimodality Foundation Models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Oh, A., Naumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 36, pp. 69719–69735. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z. Compressing Visual-Linguistic Model via Knowledge Distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1428–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Peng, H.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, B.; Liu, M.; Yuan, L.; Xuan, H.; Valenzuela, M.; Chen, X.S.; Wang, X.; et al. Tinyclip: Clip distillation via affinity mimicking and weight inheritance. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 21970–21980. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; An, Z.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Yu, X.; Yang, H.; Diao, B.; Xu, Y. CLIP-KD: An Empirical Study of CLIP Model Distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 15952–15962. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Guo, Y.; Yin, J. RS5M and GeoRSCLIP: A Large Scale Vision-Language Dataset and A Large Vision-Language Model for Remote Sensing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2306.11300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Prabha, R.; Huang, T.; Wu, J.; Rajagopal, R. SkyScript: A Large and Semantically Diverse Vision-Language Dataset for Remote Sensing. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhtar, D.; Li, Z.; Gu, F.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, P. LHRS-Bot: Empowering Remote Sensing with VGI-Enhanced Large Multimodal Language Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.02544. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Yuan, Y. SkyEyeGPT: Unifying Remote Sensing Vision-Language Tasks via Instruction Tuning with Large Language Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.09712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wen, C.; Lu, X.; Li, X. RSGPT: A Remote Sensing Vision Language Model and Benchmark. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.15266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, D.; Guan, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, J.; Ye, Q.; Fu, L.; Zhou, J. RemoteCLIP: A Vision Language Foundation Model for Remote Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 5622216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cai, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhuang, Y.; Mao, X. EarthGPT: A Universal Multimodal Large Language Model for Multisensor Image Comprehension in Remote Sensing Domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5917820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuckreja, K.; Danish, M.S.; Naseer, M.; Das, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S. GeoChat: Grounded Large Vision-Language Model for Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 27831–27840. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wong, C.; Zhang, S.; Usuyama, N.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Naumann, T.; Poon, H.; Gao, J. LLaVA-Med: Training a Large Language-and-Vision Assistant for Biomedicine in One Day. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Oh, A., Naumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 36, pp. 28541–28564. [Google Scholar]
- Son, W.; Na, J.; Choi, J.; Hwang, W. Densely Guided Knowledge Distillation Using Multiple Teacher Assistants. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 9395–9404. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jia, Z. Teacher Assistant-Based Knowledge Distillation Extracting Multi-level Features on Single Channel Sleep EEG. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI, Macao, SAR, China, 19–25 August 2023; pp. 3948–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.S.; Hu, J.; Hu, F.; Shi, B.; Bai, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X. AID: A Benchmark Data Set for Performance Evaluation of Aerial Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helber, P.; Bischke, B.; Dengel, A.; Borth, D. EuroSAT: A Novel Dataset and Deep Learning Benchmark for Land Use and Land Cover Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, G.; Fendley, N.; Wilson, J.; Mukherjee, R. Functional Map of the World. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6172–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Xia, G.S.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.Y.; Zhu, X.X.; Zhang, L.; Li, D. On Creating Benchmark Dataset for Aerial Image Interpretation: Reviews, Guidances, and Million-AID. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4205–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Newsam, S.; Li, C.; Shao, Z. PatternNet: A benchmark dataset for performance evaluation of remote sensing image retrieval. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification: Benchmark and State of the Art. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dou, X.; Tao, C.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Peng, J.; Deng, M.; Zhao, L. RSI-CB: A Large-Scale Remote Sensing Image Classification Benchmark Using Crowdsourced Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghri, F.; Fleet, D.J.; Kiros, J.R.; Fidler, S. VSE++: Improving Visual-Semantic Embeddings with Hard Negatives. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1707.05612. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Chen, X.; Hua, G.; Hu, H.; He, X. Stacked Cross Attention for Image-Text Matching. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 212–228. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Hanjalic, A.; Shen, H.T.; Song, J. Matching Images and Text with Multi-modal Tensor Fusion and Re-ranking. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM ’19), Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, G.; Melgani, F.; Demir, B. Toward Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Under a Deep Image Captioning Perspective. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 4462–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahhal, M.M.A.; Bazi, Y.; Abdullah, T.; Mekhalfi, M.L.; Zuair, M. Deep Unsupervised Embedding for Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Using Textual Cues. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tian, C.; Rong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. Remote Sensing Cross-Modal Text-Image Retrieval Based on Global and Local Information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5620616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yao, F.; Lu, W.; Liu, N.; Li, P.; You, H.; Sun, X. Text-Image Matching for Cross-Modal Remote Sensing Image Retrieval via Graph Neural Network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Sun, X.; Liu, N.; Tian, C.; Xu, L.; Hu, L.; Ding, C. Hypergraph-Enhanced Textual-Visual Matching Network for Cross-Modal Remote Sensing Image Retrieval via Dynamic Hypergraph Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Gao, X.; Sun, X. Hypersphere-Based Remote Sensing Cross-Modal Text–Image Retrieval via Curriculum Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5621815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiong, W.; Cui, Y.; Xiong, Z. A fusion-based contrastive learning model for cross-modal remote sensing retrieval. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 3359–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Pan, J.; Bai, C. Direction-Oriented Visual–Semantic Embedding Model for Remote Sensing Image–Text Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4704014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ma, Q.; Bai, C. A Prior Instruction Representation Framework for Remote Sensing Image-text Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM ’23), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Fu, K.; Li, X.; Deng, C.; Wang, H.; Sun, X. Exploring a Fine-Grained Multiscale Method for Cross-Modal Remote Sensing Image Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, B.; Zheng, X.; Li, X. Exploring models and data for remote sensing image caption generation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 2183–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
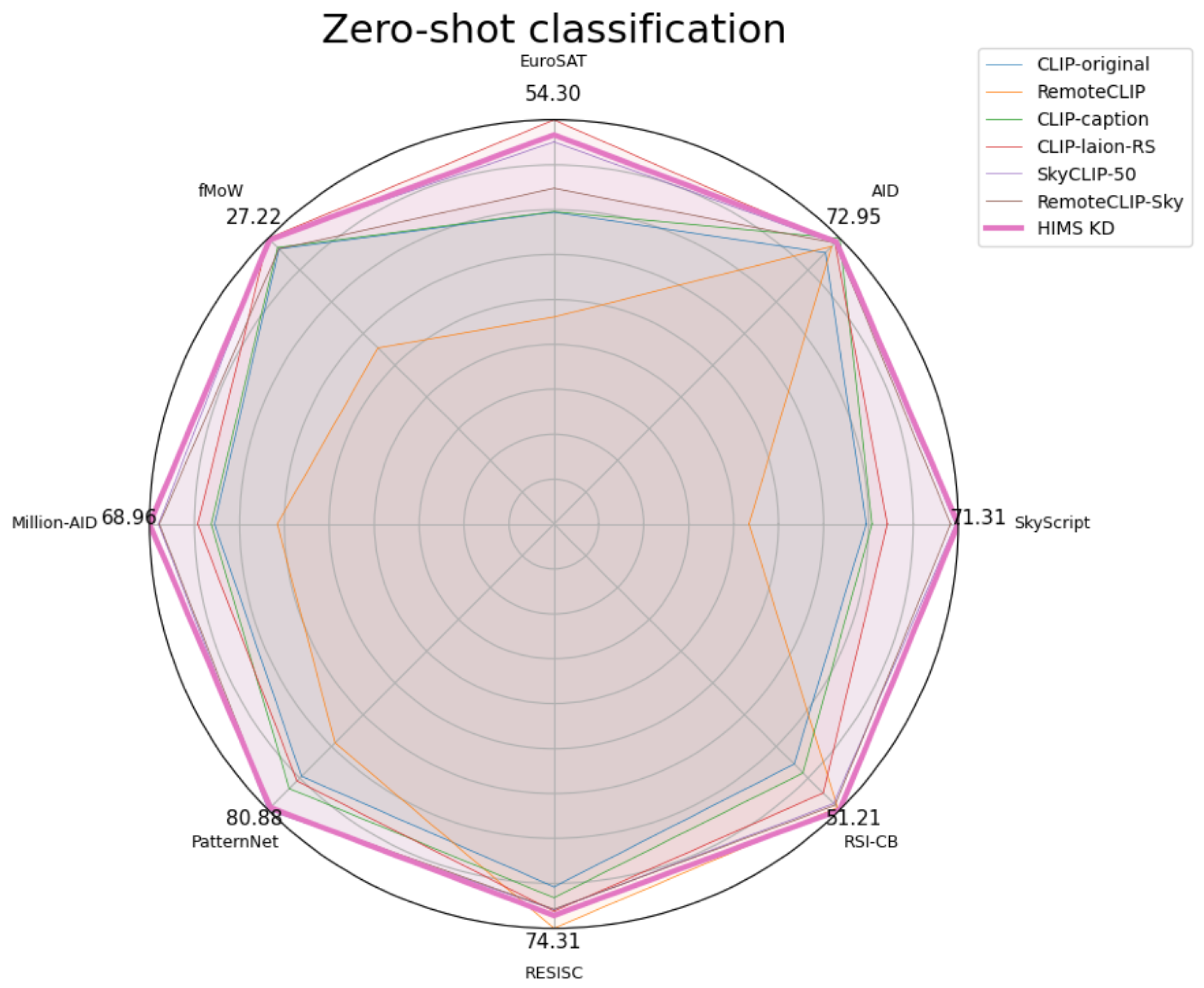
| ViT | Model | SkyScript | Zero-Shot Classification | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AID | EuroSAT | fMoW | Million-AID | PatternNet | RESISC | RSI-CB | |||
| L-14 | CLIP-original [15] | 55.06 | 69.25 | 41.89 | 26.19 | 57.88 | 71.39 | 66.70 | 43.02 |
| RemoteCLIP [21] | 34.40 | 70.85 | 27.81 | 16.77 | 47.20 | 61.91 | 74.31 | 50.79 | |
| CLIP-caption [17] | 56.09 | 72.95 | 41.96 | 26.33 | 58.47 | 74.86 | 68.70 | 44.60 | |
| CLIP-laion-RS [17] | 58.81 | 71.70 | 54.30 | 27.21 | 60.77 | 72.68 | 71.21 | 48.21 | |
| SkyCLIP-50 [17] | 70.89 | 71.70 | 51.33 | 27.12 | 67.45 | 80.88 | 70.94 | 50.09 | |
| RemoteCLIP-Sky | 69.98 | 71.74 | 45.11 | 26.20 | 67.29 | 80.35 | 70.84 | 50.37 | |
| HIMS_KD1 | 70.98 | 71.77 | 53.08 | 27.22 | 68.41 | 80.79 | 71.10 | 50.97 | |
| HIMS_KD2 | 71.31 | 72.05 | 52.29 | 27.07 | 68.96 | 80.24 | 71.97 | 51.21 | |
| Model | Training Method | SkyScript | Zero-Shot Classification | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AID | EuroSAT | fMoW | Million-AID | PatternNet | RESISC | RSI-CB | |||
| L-14 | Train | 70.89 | 71.70 | 51.33 | 27.12 | 67.45 | 80.88 | 70.94 | 50.09 |
| B-32 | Train | 52.98 | 70.90 | 33.30 | 19.24 | 62.69 | 72.18 | 66.67 | 46.20 |
| B-32 | KD-Logit [4] | 64.20 | 67.72 | 44.19 | 18.44 | 63.59 | 76.98 | 66.70 | 46.05 |
| KD-Feature [5] | 64.71 | 66.98 | 44.33 | 19.41 | 63.80 | 77.29 | 68.51 | 45.85 | |
| KD-TAKD [6] | 69.07 | 68.08 | 48.01 | 20.64 | 67.62 | 78.41 | 68.40 | 46.28 | |
| DGKD [25] | 67.56 | 67.58 | 46.89 | 20.23 | 67.77 | 78.43 | 67.97 | 46.59 | |
| B-32 | KD-Our | 68.93 | 69.47 | 49.20 | 20.71 | 66.96 | 79.61 | 69.01 | 47.23 |
| Model | Number of Params | Time (ms) | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Without KD | |||
| ViT-L14 | 305 m | 56 | 61.30% |
| ViT-B32 | 151 m | 48 | 53.02% |
| With KD | |||
| KD-Logit [4] | 151 m | 40 | 55.98% |
| KD-Feature [5] | 151 m | 42 | 56.36% |
| KD-TAKD [6] | 151 m | 45 | 58.31% |
| DGKD [25] | 151 m | 40 | 57.62% |
| HIMS_KD | 151m | 38 | 58.89% |
| Method | RSITMD | RSICD | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image to Text | Text to Image | Image to Text | Text to Image | |||||||||
| R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | R@1 | R@5 | R@10 | |
| VSE++ [34] | 10.38 | 27.65 | 39.60 | 7.79 | 24.87 | 38.67 | 3.38 | 9.51 | 17.46 | 2.82 | 11.32 | 18.10 |
| SCAN t2i [35] | 10.18 | 28.53 | 38.49 | 10.10 | 28.98 | 43.53 | 4.39 | 10.90 | 17.64 | 3.91 | 16.20 | 26.49 |
| SCAN i2t [35] | 11.06 | 25.88 | 39.38 | 9.82 | 29.38 | 42.12 | 5.85 | 12.89 | 19.84 | 3.71 | 16.40 | 26.73 |
| MTFN [36] | 10.40 | 27.65 | 36.28 | 9.96 | 31.37 | 45.84 | 5.02 | 12.52 | 19.74 | 4.90 | 17.17 | 29.49 |
| AMFMN-soft [37] | 11.06 | 25.88 | 39.82 | 9.82 | 33.94 | 51.90 | 5.05 | 14.53 | 21.57 | 5.05 | 19.74 | 31.04 |
| AMFMN-fusion [37] | 11.06 | 29.20 | 38.72 | 9.96 | 34.03 | 52.96 | 5.39 | 15.08 | 23.40 | 4.90 | 18.28 | 31.44 |
| AMFMN-sim [37] | 10.63 | 24.78 | 41.81 | 11.51 | 34.69 | 54.87 | 5.21 | 14.72 | 21.57 | 4.08 | 17.00 | 30.60 |
| LW-MRC-u [38] | 9.73 | 26.77 | 37.61 | 9.25 | 34.07 | 54.03 | 4.39 | 13.35 | 20.29 | 4.30 | 18.85 | 32.34 |
| GaLR [39] | 14.82 | 31.64 | 42.48 | 11.15 | 36.68 | 51.68 | 6.59 | 19.85 | 31.04 | 4.69 | 19.48 | 32.13 |
| CMFM-Net [40] | 10.83 | 28.76 | 40.04 | 10.00 | 32.83 | 47.21 | 5.40 | 18.66 | 28.55 | 5.31 | 18.57 | 30.03 |
| HyperMatch [41] | 11.73 | 28.10 | 38.05 | 9.16 | 32.31 | 46.64 | 7.14 | 20.04 | 31.02 | 6.08 | 20.37 | 33.82 |
| HVSA [42] | 13.20 | 32.08 | 45.58 | 11.43 | 39.20 | 57.45 | 7.47 | 20.62 | 32.11 | 5.51 | 21.13 | 34.13 |
| FBCLM [43] | 12.84 | 30.53 | 45.89 | 10.44 | 37.01 | 57.94 | 13.27 | 27.17 | 37.60 | 13.54 | 38.74 | 56.94 |
| DOVE [44] | 16.81 | 36.80 | 49.93 | 12.20 | 49.93 | 66.50 | 8.66 | 22.35 | 34.95 | 6.04 | 23.95 | 40.35 |
| PIR [45] | 18.14 | 41.15 | 52.88 | 12.17 | 41.68 | 63.41 | 9.88 | 27.26 | 39.16 | 6.97 | 24.56 | 38.92 |
| CLIP ViT-B-32 | 24.78 | 50.00 | 63.27 | 22.61 | 55.27 | 69.87 | 17.84 | 35.96 | 50.14 | 13.89 | 35.15 | 50.08 |
| HIMS_KD ViT-B-32 | 24.52 | 50.51 | 65.29 | 21.98 | 56.47 | 73.49 | 16.89 | 38.10 | 51.11 | 13.28 | 36.89 | 56.12 |
| Index | Number | Number of Params (M) | Feature Levels | Acc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 51 | Low | 52.83% |
| 2 | 1 | 51 | Mid | 51.23% |
| 3 | 1 | 51 | High | 52.75% |
| 4 | 1 | 102 | Low | 52.95% |
| 5 | 1 | 102 | Mid | 52.91% |
| 6 | 1 | 102 | High | 53.28% |
| 7 | 2 | 51 | Low + Mid | 56.51% |
| 8 | 2 | 51 | Low + High | 57.54% |
| 9 | 2 | 51 | Mid + High | 56.93% |
| 10 | 2 | 102 | Low + Mid | 57.61% |
| 11 | 2 | 102 | Low + High | 58.20% |
| 12 | 2 | 102 | Mid + High | 57.84% |
| 13 | 3 | 51 | All | 58.89% |
| 14 | 3 | 102 | All | 61.88% |
| Index | Logit KD | Feature KD | Cross-Entropy | Acc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✓ | - | - | 57.40% |
| 2 | - | ✓ | - | 57.64% |
| 3 | ✓ | ✓ | - | 58.42% |
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 58.89% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kitrungrotsakul, T.; Srichola, P. Hierarchical Knowledge Distillation for Efficient Model Compression and Transfer: A Multi-Level Aggregation Approach. Information 2026, 17, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/info17010070
Kitrungrotsakul T, Srichola P. Hierarchical Knowledge Distillation for Efficient Model Compression and Transfer: A Multi-Level Aggregation Approach. Information. 2026; 17(1):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/info17010070
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitrungrotsakul, Titinunt, and Preeyanuch Srichola. 2026. "Hierarchical Knowledge Distillation for Efficient Model Compression and Transfer: A Multi-Level Aggregation Approach" Information 17, no. 1: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/info17010070
APA StyleKitrungrotsakul, T., & Srichola, P. (2026). Hierarchical Knowledge Distillation for Efficient Model Compression and Transfer: A Multi-Level Aggregation Approach. Information, 17(1), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/info17010070






