Visitor Satisfaction at the Macau Science Center and Its Influencing Factors Based on Multi-Source Social Media Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Problem Statement and Objectives
2. Study Area and Methodology
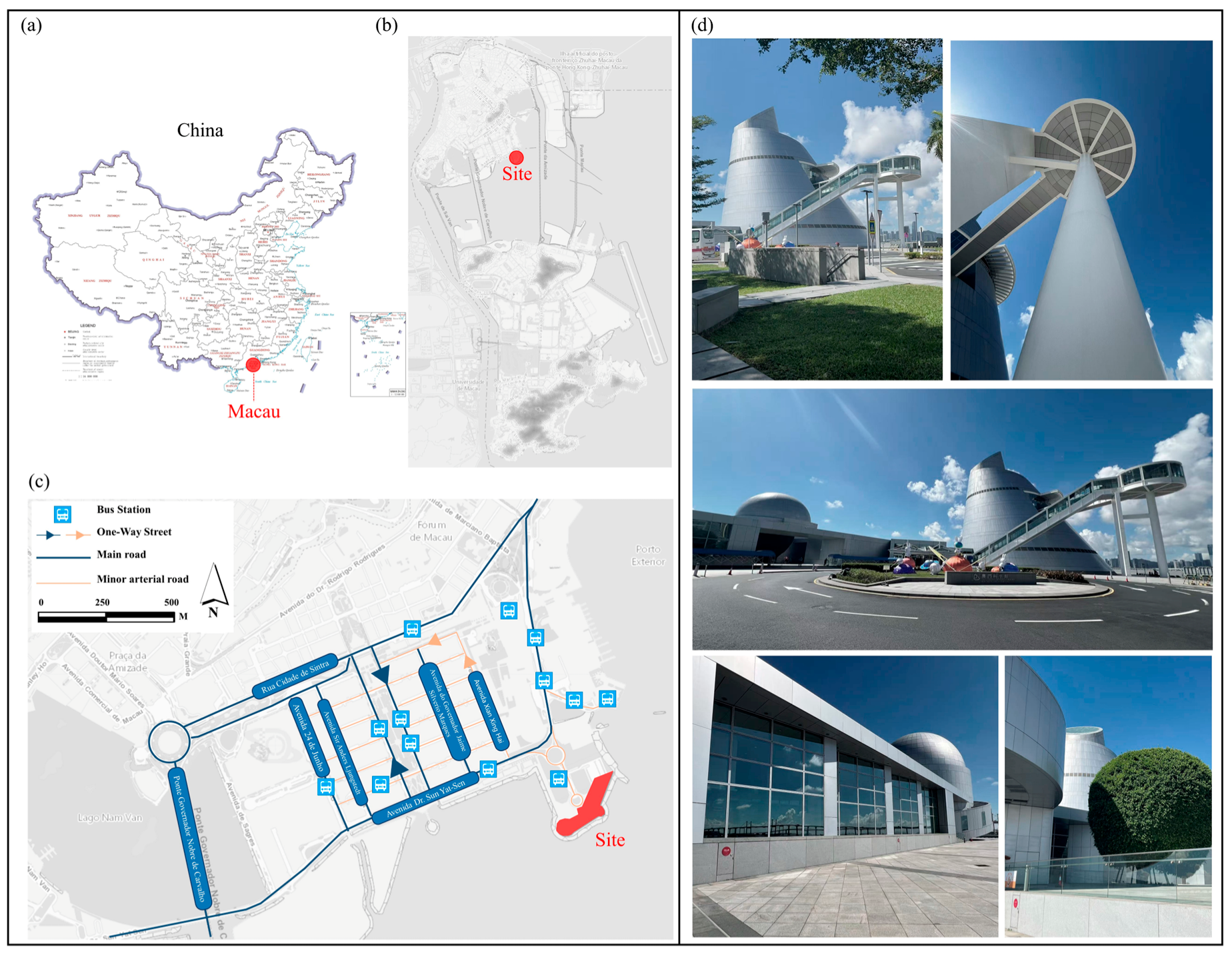
2.1. Study Area: Macau Science Center
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.2.1. Data Sources
2.2.2. Data Preprocessing
- (1)
- Field processing: Useless fields irrelevant to the research were deleted, including redundant identifiers and irrelevant system parameters. Core fields such as text content, publication time, and platform source were normalized to unify the data format.
- (2)
- Date filtering: The data time range was limited to January 2023 to November 2025 to ensure data timeliness.
- (3)
- Noise removal: Emojis, special symbols, topic tags, and web links were removed in batches from the text. Invalid content consisting of pure images without text was also filtered to reduce noise interference.
- (4)
- Deduplication: Duplicate data within and across platforms was removed to avoid data redundancy.
- (5)
- Data merging: Since only three valid data entries remained after filtering on the TripAdvisor platform, the sample size was too small for separate analysis. The main reason is that there are relatively few reviews on TripAdvisor from January 2023 to November 2025, which may be related to travel usage after the COVID-19 outbreak. Therefore, data on TripAdvisor reviews was merged with data on the Google Maps platform reviews to form a unified dataset.
- (6)
- This study uses Google Translate (https://translate.google.com/?hl=zh-TW&sl=auto&tl=en&op=translate, accessed on 4 January 2026) for the English translation of Chinese texts, and language detection is manually verified on the Google Translate platform. Due to differences in the consistency of text languages across different platforms (e.g., Chinese platforms are predominantly in Chinese, while international platforms are mainly in English), the target language for translation is uniformly set to English.
2.2.3. Data Statistics
2.3. Analysis Techniques
2.3.1. ROST CM6.0 Word Frequency Analysis
2.3.2. Semantic Network Analysis
2.3.3. LDA Model Analysis
- Number of topics (): Five; determined manually after a comprehensive analysis of coherence scores and perplexity scores for two to eight topics.
- Random seed (): 100; ensuring repeatable training results.
- Training epochs (): 10; improving the model’s traversal learning of the corpus.
- Number of iterations (): 50 per document; enhancing the model’s accuracy in topic assignment for individual documents.
- The alpha parameter: ; automatically optimizes the prior probability of topic distribution.
- Topic output setting (): True; outputs the probability distribution of each word in each topic.
2.3.4. VADER Sentiment Analysis
| def perform_semantic_analysis(text): |
| sid = SentimentIntensityAnalyzer() |
| sentiment_score = sid.polarity_scores(text) |
| if sentiment_score[‘compound’] ≥ 0.05: |
| return “Positive” |
| elif sentiment_score[‘compound’] ≤ −0.05: |
| return “Negative” |
| else: |
| return “Neutral” |
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Core Focus Dimensions
3.2. Keyword Association Network Features
3.3. LDA Topic Modeling Results: Potential Needs Topic Decomposition
3.4. VADER Sentiment Analysis Results: Correlation Patterns Between Sentiment and Influencing Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Existing Research
4.2. Interpretation of the Influencing Mechanism of Factors
4.3. Optimization Strategies for Venue Services
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
5.1. Key Findings
5.2. Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Stopwords.txt Files
| b | com | It’ | ours | ( | them | into | when | s | but | buy | do | below | since | while | where |
| c | the | it’ | their | I | when | even | where | t | was | through | does | beside | why | how | very |
| d | and | as | theirs | at | will | → | why | u | on | After | did | behind | well | now | then |
| e | a | . | these | how | day | 21:00 | me | v | you | just | have | before | once | twice | always |
| f | is | so | those | mine | all | don’ | mine | w | which | 14 | has | after | often | sometimes | never |
| g | to | your | such | yours | both | want | yours | x | not | Macau’ | had | because | ever | already | yet |
| h | of | A | some | he | about | 2 | he | y | this | do | having | since | still | almost | nearly |
| ii | for | There | any | him | by | 15 | him | z | that | had | will | while | hardly | scarcely | barely |
| iii | it | only | all | his | or | ! | his | ing | be | * | would | ; | : | ‘ | ) |
| j | are | , | each | she | up | M. | she | ed | from | you’ | shall | [ | ] | { | } |
| k | there | This | every | her | too | I. | her | -ing | were | I’ | should | / | \ | - | |
| l | s | 0 | no | hers | off | ? | hers | est | have | two | can | _ | @ | # | $ |
| m | i | – | none | us | out | 10:00 | us | er | more | ll | could | % | ^ | & | + |
| n | in | It | one | our | onto | off | our | ly | my | its | may | = | < | > | … |
| o | can | on- | ones | across | across | out | onto | ness | has | You | might | — | ‘’ | “” | th |
| p | with | We | am | between | between | among | above | ful | t | than | must | st | don | mop | avenida |
| q | also | each | been | among | below | beside | behind | “ | an | if | here | next | macau | Macau | there |
| r | many | There’ | being | above | before | after | because | The | we | If |
References
- Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Kim, H.S. Using Online Customer Reviews to Understand Customers’ Experience and Satisfaction with Integrated Resorts. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, A.M.W.; Yeh, S.S.; Zhou, Y.; Hung, C.W.; Huan, T.C. Exploring the influence of historical storytelling on cultural heritage tourists’ value co-creation using tour guide interaction and authentic place as mediators. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2024, 50, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, C.-K.; Liu, Y.; Kang, S.; Dai, A. The Role of Perceived Smart Tourism Technology Experience for Tourist Satisfaction, Happiness and Revisit Intention. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Suntikul, W.; King, B. Constructing an intangible cultural heritage experiences cape: The case of the Feast of the Drunken Dragon (Macau). Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2020, 34, 100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, L. Study on application of Ieoh Ming Pei’s design concept in landscape architecture design. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 981–987. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.Q. World Architecture in China; Joint Publishing: Hong Kong, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Feng, J.; Wu, R.; Jia, M. Tourists’ Perception of Macau’s City Image: Based on the Analysis of User-Generated Content (UGC) Text Data. Buildings 2023, 13, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, C.; Liu, J. Research on Tourist Satisfaction Evaluation of Macau’s Built Heritage Space Under the Genius Loci. Buildings 2025, 15, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, P. Unraveling Tourist Behavioral Intentions in Historic Urban Built Environment: The Mediating Role of Perceived Value via SOR Model in Macau’s Heritage Sites. Buildings 2025, 15, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, C.K.; Chen, T.; Lee, T.J.; Wu, X.D. Hotel brand signature, brand attitude, subject norm, and perceived behavior control. J. Vacat. Mark. 2025, 31, 904–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, A.M.W.; Yeh, S.S.; Chen, H.B.; Lee, C.L.; Huan, T.C. Does gender make a difference in heritage tourism experience? Searching for answers through multi-group analysis. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2024, 52, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Luo, J.M. Impact of generativity on museum visitors’ engagement, experience, and psychological well-being. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2022, 42, 100958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.M.; Ye, B.H. Role of generativity on tourists’ experience expectation, motivation and visit intention in museums. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2020, 43, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, F.; Tang, Y.K.; Xi, L.; Xu, H.F. Analysis of tourist perception and emotion in ethnic minority village tourist destinations based on network text: A case study of Xijiang Qianhu Miao Village. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2025, 1–12. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/51.1448.N.20250729.1650.002 (accessed on 30 December 2025). (In Chinese).
- Wei, Y.Z.; Li, F.L. Study on the perception of Guangxi’s tourism image based on web text analysis: A case study of Xingping Ancient Town. J. Hezhou Univ. 2024, 40, 116–124. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=OfZxIIxxsvDB9LQp9vXX8QeWFvSdWit934Q0qwgEgIjSH9cDP3OjiwxAWxvyy-3eJ_LDNC7_GqtwcQAtHtRmpXiq3F8dgnVPmMuRDTE5461yJW3ZVOUyjJZgZXjN-FKzWaCjY8xosTbD83yTiK78jItBS3B6CwEmkq2tEO-avr82PwqwdbVSp7hoMnbqu3cc&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 30 December 2025). (In Chinese).
- Zhang, H.C.; Wang, S.S.; Fan, Q.; Tang, W.Z. A study on audience satisfaction in science and technology museums based on service-dominant logic: A case study of the audience satisfaction survey of the China Science and Technology Museum. Sci. Pop. Res. 2022, 17, 57–64+95+104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L. Analysis of tourist reviews in movie theme parks based on the LDA model: A case study of Huayi Brothers Movie World (Suzhou). North. Econ. Trade 2025, 10, 136–141. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=OfZxIIxxsvAFjrqY5j6xi5-rP7EuxRcP55D-1NDVsb0WznbmQ_ZBy3e4tnyW5yzPDU9tkEVm7o3dSbpF-KWLDM1W1dwLAr8oqH02Ldoef2UWMnV7biDFhUE2zimrzoDnovs1AaIXy_sKEO-WM885HzIFzbA68tV77oOvNjdtkwKMcOcul1xX85gFRgiVbMG-&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 30 December 2025). (In Chinese).
- Tian, S.M.; Ding, Y. Study on the improvement of tourism service quality in famous historical and cultural towns based on the LDA topic model: A case study of Qingyan Ancient Town in Guiyang City. Inn. Mong. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2025, 19, 54–59+94. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=OfZxIIxxsvDrXXD5bCvk_Qx90gdlgBELl866Pi6QO4lmlSep-1OocgiNA5nrZQWJ18rbvqeu-TFBdD-N6hKQ4NaMEAayZFf9OB6LFNbKuzYyKzLieNCxNGIBWLbATMFbADOgFIlqT3HN2HLjomMV_tk68XCyryq4sXdOYYXC8bBpFXiAvab0sQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 30 December 2025). (In Chinese).
- Saoualih, A.; Safaa, L.; Bouhatous, A.; Bidan, M.; Perkumienė, D.; Aleinikovas, M.; Šilinskas, B.; Perkumas, A. Exploring the Tourist Experience of the Majorelle Garden Using VADER-Based Sentiment Analysis and the Latent Dirichlet Allocation Algorithm: The Case of TripAdvisor Reviews. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Feng, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C. Visual Analysis of Social Media Data on Experiences at a World Heritage Tourist Destination: Historic Centre of Macau. Buildings 2024, 14, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, L. Analyzing online reviews of foreign tourists to destination attractions in China: A novel text mining approach. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2023, 28, 647–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.B. Study on the perception of the image of mountain tourism destinations based on the LDA model: A case study of Maling River Canyon Scenic Area in Guizhou Province. Commer. Exhib. Econ. 2025, 21, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.C.; Guo, X.J.; Yin, R.Q.; Rong, X. Emotional mining and analysis of online reviews in Xingwen Stone Forest Scenic Area based on the LDA topic model. China Mark. 2025, 21, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xie, Z.Y.; Zhang, G.P.; Hao, Z.C.; Xiang, Z. Topic classification of tourist online reviews based on LDA: A case study of the Forbidden City. J. Inf. Eng. 2017, 3, 55–63. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=Ow72tX7v2w325cZxPfs-j0jhaOUqwEaA7UWh-5agyYBIX33AFCqTHT7YLhxqraHf-qACBGZfH5Xb6nTwW30OAbpREt5j0up4ZnjFMBkmHjrjLHILLT1Im47NufsYK5Q3aiyBdUP-xb3zjveL_7QpE1lF6VpXKHLzacneZsFNrI5Yv3JSEXLM4nNPEJCnaH3w&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 30 December 2025). (In Chinese).
- Lili, I.; Xhina, E.; Kosta, A.; Ceni, A.; Ulqinaku, M. Comparing VADER and BERT for Short-Text Sentiment Analysis: Challenges and Observed Variations. In Pioneer and Innovative Studies in Computer Sciences and Engineering; Chapter 94; All Sciences Academy: Konya, Turkey, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Youvan, D.C. Understanding Sentiment Analysis with VADER: A Comprehensive Overview and Application. AI Data Sci. J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macau Science Center. Available online: https://www.Macautourism.gov.mo/en/events/whatson/9920/ (accessed on 12 December 2025).
- National Science Popularization and Education Base. Available online: https://www.msc.org.mo/en/article-detail/140/1b27706a08be2dae0142cf7c0226eba9 (accessed on 12 December 2025).
- Borrego, Á.; Comalat Navarra, M. What users say about public libraries: An analysis of Google Maps reviews. Online Inf. Rev. 2021, 45, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Loan, F.A. Exploring the reviews of Google Maps to assess the user opinions about public libraries. Libr. Manag. 2022, 43, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnone, M.R.; Fiorentino, G. TripAdvisor and tourism: The linguistic behaviour of consumers in the tourism industry 2.0. In Strategies of Adaptation in Tourist Communication; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 270–294. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Niu, K.; He, Z.; He, X. Microblog user interest modeling based on feature propagation. In Proceedings of the 2013 Sixth International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design, Hangzhou, China, 28–29 October 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibo Released Its Q4 and Full-Year 2024 Financial Report, with Total Revenue of 12.61 Billion Yuan. Available online: https://finance.sina.com.cn/tech/2025-03-13/doc-ineppeui0597904.shtml?finpagefr=p_108 (accessed on 14 December 2025).
- Ning, K.X. Research on Brand Marketing Strategies on the Xiaohongshu Platform. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on E-Business, Management and Economics, Beijing, China, 19–21 July 2024; pp. 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Tong, L.; Knearem, T.; Li, T.J.J.; Huang, T.H.K.; Wu, Q. Hashtag re-appropriation for audience control on recommendation-driven social media Xiaohongshu (rednote). In Proceedings of the 2025 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 26 April–1 May 2025; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2025 “Active Users” Research Report (Xiaohongshu Platform). Available online: https://www.qian-gua.com/information/detail/3149 (accessed on 14 December 2025).
- Chen, J. Research on the Ctrip Tourism Market Analysis and Marketing Strategy Optimization. In SHS Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2024; Volume 207, p. 03003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Man, T.; He, L.; He, Y.; Qian, Y. Delineating Landscape Features Perception in Tourism-Based Traditional Villages: A Case Study of Xijiang Thousand Households Miao Village, Guizhou. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ding, F.; Ding, Z.; Zheng, Y. Study on Multidimensional Perception of National Forest Village Landscape Based on Digital Footprint Support—Anhui Xidi Village as an Example. Forests 2023, 14, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. Impact of Short Video Marketing on Tourist Destination Perception in the Post-pandemic Era. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, L.; Yuan, J. Research on Zhanjiang’s Leisure Sports Tourism Development Strategy in Coastal Recreational Areas. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 111, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Barnes, S.J.; Jia, Q. Mining meaning from online ratings and reviews: Tourist satisfaction analysis using latent dirichlet allocation. Tour. Manag. 2017, 59, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Z.P.; Zhang, J. Wisdom of crowds: Conducting importance-performance analysis (IPA) through online reviews. Tour. Manag. 2019, 70, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Study on the conservation and renewal of traditional rural tourism spaces: A perspective based on tourists’ revisit intention. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 499, 145184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lin, D.; Xiao, H. The collision of tradition and fashion: How anthropomorphizing museum exhibits influences cultural inheritance. Tour. Manag. 2025, 109, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, W.; You, J. Evaluation of tourism elements in historical and cultural blocks using machine learning: A case study of Taiping Street in Hunan Province. NPJ Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhang, C.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z. Enhancement of Harbin ice and snow tourism destination competitiveness: A large-scale data study based on sentiment analysis and Latent Dirichlet Allocation. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wang, T.; Li, H. Segmenting tourists’ motivations via online reviews: An exploration of the service strategies for enhancing tourist satisfaction. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, M. Tracing the Evolution of Tourist Perception of Destination Image: A Multi-Method Analysis of a Cultural Heritage Tourist Site. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, R.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, S. Exploring cross-cultural disparities in tourists’ perceived images: A text mining and sentiment analysis study using LDA and BERT-BILSTM models. Data Technol. Appl. 2024, 58, 669–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Fu, H.; Xiong, C. Evaluating Perceived Cultural Ecosystem Services in Urban Green Spaces Using Big Data and Machine Learning: Insights from Fragrance Hill Park in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sharudin, S.A.; Lv, H.L. A novel product shape design method integrating Kansei engineering and whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 62, 102847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hasna, M.F.; Aziz, F.A. Integrating LDA thematic model, FCE, and QFD methods for consumer-centered visual planning of the creative tourism destination: A macrosystem decision approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 177, 113299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, P.; Cagliyor, S.I.; Gurce, M.Y. Reducing Consumer-Brand Incongruity Through Corporate Social Responsibility and Brand Trust: Exploring Negative Word-of-Mouth (NWOM). Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2024, 48, e13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Rahman, M.F. Customer Sentiment Analysis and Prediction of Insurance Products’ Reviews Using Machine Learning Approaches. FIIB Bus. Rev. 2023, 12, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarraf, S.; Kushwaha, A.K.; Kar, A.K.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Giannakis, M. How did online misinformation impact stockouts in the e-commerce supply chain during COVID-19—A mixed methods study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 267, 109064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Cui, S.; Knieling, V.; Khanna, K.; Shao, M. Investigation of the Misinformation about COVID-19 on YouTube Using Topic Modeling, Sentiment Analysis, and Language Analysis. Computation 2024, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Platforms | Comments | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Google Maps | A great place for children, youngsters. They refurbished new topics such as Data Science, Network Security, AI and so on. By the way, the MacDonald inside the exhibition hall also provides the great sea view. | (The content itself is already in English and does not require translation.) |
| TripAdvisor | 我们今天下午去了这里,以后去澳门一定会回来的。孩子们可以做的事情太多了,他们很喜欢。我们看到了一些画廊,但还没有尝试游乐区或天文馆,这两个看起来惊人。太值钱了! | We went here this afternoon and will definitely come back when we go to Macau in the future. There are so many things kids can do and they love it. We saw some galleries but have not tried the play area or planetarium, these two look amazing. It is worth a lot! |
| Sina Weibo | 澳门科学馆真是个溜娃的好地方!特别在台风过后,没什么游客,空调也够足,设施也非常好,工作人员的服务态度也是很好,完美!!! | The Macau Science Center is a great place to take the kids! Especially after the typhoon, there were not many tourists. The air conditioning was great, the facilities were excellent, and the staff were very friendly and helpful—perfect!!! |
| Xiaohongshu (rednote) | 光是看着贝聿铭设计的澳门科学馆都是视觉享受 内部空间设计非常值得体验(麦当劳有种泡沫经济时代的感觉)。 | Just looking at I.M. Pei’s design for the Macau Science Center is a visual treat, and the interior design is definitely worth experiencing (McDonald’s has a bubble economy vibe). |
| Ctrip | 位于澳门半岛的澳门科学馆值得花时间一游,旁边就是观音莲花苑休息区,有大型的免费儿童游乐场,两者体验都体验非常好,澳门科学馆逛下来起码三四小时,推荐。 | The Macau Science Museum, located on the Macau Peninsula, is worth a visit. It is right next to the leisure area of Kun Iam Statue Waterfront, which has a large, free children’s playground. Both offer excellent experiences. A visit to the Macau Science Museum will take at least three to four hours. This is highly recommended. |
| Core Words After Merging | Synonyms | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| child | “kid” “children” “kids” | Both represent “child” and are unified into the basic word form “child” |
| museum | “science museum” “Macau Science Center” “MSC” | All refer to the research object, unified as “museum” |
| exhibition | “exhibit” “exhibits” exhibition hall” | All indicate “exhibition/exhibit/exhibition hall”, unified as “exhibition” |
| view | “scenery” “scene” “seaside view” “landscape” | All represent “scenery/landscape”, unified as “view” |
| play | “playing” “played” “fun play” “enjoy playing” | All represent “play/entertainment”, unified as “play” |
| family | “family trip” “parent–child” “family visit” “family group” | All related to family travel, unified as “family” |
| experience | “visit experience” “interactive experience” “tour experience” | All represent “experience”, unified as “experience” |
| ticket | “tickets” “ticket price” “admission ticket” | All related to tickets, unified as “ticket” |
| No. | Word | Word Frequency | No. | Word | Word Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | child | 754 | 31 | show | 113 |
| 2 | hall | 414 | 32 | interactive | 112 |
| 3 | museum | 389 | 33 | photo | 110 |
| 4 | exhibition | 347 | 34 | McDonald | 107 |
| 5 | ticket | 346 | 35 | adult | 106 |
| 6 | take | 237 | 36 | family | 106 |
| 7 | time | 228 | 37 | minute | 105 |
| 8 | visit | 224 | 38 | exhibit | 105 |
| 9 | experience | 212 | 39 | see | 101 |
| 10 | view | 202 | 40 | light | 99 |
| 11 | firework | 182 | 41 | new | 97 |
| 12 | free | 176 | 42 | worth | 95 |
| 13 | area | 168 | 43 | site | 95 |
| 14 | play | 163 | 44 | display | 94 |
| 15 | sea | 161 | 45 | close | 93 |
| 16 | great | 160 | 46 | trip | 93 |
| 17 | go | 152 | 47 | learn | 92 |
| 18 | good | 150 | 48 | hotel | 92 |
| 19 | recommend | 146 | 49 | open | 90 |
| 20 | fun | 142 | 50 | perfect | 90 |
| 21 | planetarium | 138 | 51 | enjoy | 90 |
| 22 | year | 130 | 52 | world | 90 |
| 23 | first | 128 | 53 | get | 89 |
| 24 | floor | 127 | 54 | Zhuhai | 89 |
| 25 | make | 127 | 55 | art | 87 |
| 26 | place | 125 | 56 | build | 87 |
| 27 | pm | 123 | 57 | movie | 82 |
| 28 | walk | 118 | 58 | suitable | 79 |
| 29 | hour | 116 | 59 | space | 76 |
| 30 | design | 115 | 60 | activity | 75 |
| Type | Topic 1 | Topic 2 | Topic 3 | Topic 4 | Topic 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword 1 (Weight 1) | museum | children | hall | museum | bus |
| (0.009) | (0.013) | (0.028) | (0.013) | (0.011) | |
| Keyword 2 (Weight 2) | sea | fireworks | children | children | children |
| (0.006) | (0.013) | (0.022) | (0.011) | (0.009) | |
| Keyword 3 (Weight 3) | first | exhibition | exhibition | kids | tickets |
| (0.005) | (0.012) | (0.016) | (0.01) | (0.009) | |
| Keyword 4 (Weight 4) | art | hall | tickets | great | free |
| (0.005) | (0.008) | (0.015) | (0.008) | (0.008) | |
| Keyword 5 (Weight 5) | coffee | museum | museum | experience | zhuhai |
| (0.005) | (0.007) | (0.011) | (0.008) | (0.008) | |
| Keyword 6 (Weight 6) | year | experience | halls | fireworks | take |
| (0.005) | (0.005) | (0.008) | (0.007) | (0.007) | |
| Keyword 7 (Weight 7) | time | time | kids | worth | museum |
| (0.005) | (0.005) | (0.008) | (0.006) | (0.007) | |
| Keyword 8 (Weight 8) | exhibition | october | planetarium | visit | sea |
| (0.005) | (0.005) | (0.007) | (0.006) | (0.007) | |
| Keyword 9 (Weight 9) | city | interactive | fun | time | view |
| (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.006) | (0.005) | (0.006) | |
| Keyword 10 (Weight 10) | children | halls | ticket | free | walk |
| (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.006) | (0.005) | (0.006) |
| Research Questions (RQs) | Core Research Findings | Corresponding Analysis Methods | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) What are the core dimensions of user attention to the Macau Science Center? | Five core dimensions:
| Word frequency analysis, word cloud visualization | Table 3, Figure 4 |
| (2) What is the correlation strength and network structure of the core attention keywords? |
| Semantic network analysis | Figure 5 |
| (3) What are the underlying needs and themes hidden behind user feedback? | Five major potential demand themes:
| LDA topic modeling | Table 4 |
| (4) What are the correlation patterns between various influencing factors and user emotional tendencies? |
| VADER sentiment analysis | Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Liang, J.; Deng, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, J.; Wu, C.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Y. Visitor Satisfaction at the Macau Science Center and Its Influencing Factors Based on Multi-Source Social Media Data. Information 2026, 17, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/info17010057
Liang J, Deng Q, Zhu Y, Liang J, Wu C, Zheng L, Chen Y. Visitor Satisfaction at the Macau Science Center and Its Influencing Factors Based on Multi-Source Social Media Data. Information. 2026; 17(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/info17010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Jingwei, Qingnian Deng, Yufei Zhu, Jiahai Liang, Chunhong Wu, Liang Zheng, and Yile Chen. 2026. "Visitor Satisfaction at the Macau Science Center and Its Influencing Factors Based on Multi-Source Social Media Data" Information 17, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/info17010057
APA StyleLiang, J., Deng, Q., Zhu, Y., Liang, J., Wu, C., Zheng, L., & Chen, Y. (2026). Visitor Satisfaction at the Macau Science Center and Its Influencing Factors Based on Multi-Source Social Media Data. Information, 17(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/info17010057












