Abstract
Infrared small target detection is crucial for military surveillance and autonomous driving. However, complex scenes and weak signal characteristics make the identification of such targets particularly difficult. This study proposes YOLO-SSFA, an enhanced You Only Look Once version 11 (YOLOv11) model with three modules: Scale-Sequence Feature Fusion (SSFF), LiteShiftHead detection head, and Noise Suppression Network (NSN). SSFF improves multi-scale feature representation through adaptive fusion; LiteShiftHead boosts efficiency via sparse convolution and dynamic integration; and NSN enhances localization accuracy by focusing on key regions. Experiments on the HIT-UAV and FLIR datasets show mAP50 scores of 94.9% and 85%, respectively. These findings showcase YOLO-SSFA’s strong potential for real-time deployment in challenging infrared environments.
1. Introduction
Detecting small targets in infrared imagery is crucial for a range of applications, including remote sensing monitoring, intelligent security systems, and autonomous UAV navigation [1,2]. However, factors such as low target-to-background contrast, complex backgrounds, and sensor noise significantly hinder detection performance [3,4]. Moreover, infrared images are further affected by sensor noise, false targets, and environmental interference [5]. Therefore, improving the detection accuracy of infrared small targets in complex backgrounds remains a critical challenge. To tackle this issue, researchers have proposed a variety of enhancements in feature extraction, feature fusion, and object detection head design [6,7,8,9]. Nevertheless, current approaches still exhibit certain limitations.
Firstly, in multi-scale feature fusion, traditional methods such as Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) and Path Aggregation Network (PAN) enhance multi-scale features through top-down and bottom-up information flow. However, these approaches rely on simple feature concatenation or weighted fusion, making it challenging to accurately extract key information from small targets. To address this issue, HRNet [10] employs a parallel high-resolution feature extraction mechanism, improving the detection of small targets. The Dynamic Feature Pyramid (DFP) proposed by Zhang et al. [11] adopts a dynamic attention mechanism, enabling the model to automatically optimize feature representations for different target categories and sizes. Nevertheless, these methods still struggle to fully capture contextual information across feature layers, limiting further improvements in detection performance.
Secondly, in suppressing background noise, recent studies have primarily employed attention mechanisms to enhance the representation of key target regions. For instance, the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) [12] integrates channel and spatial attention to improve the network’s focus on essential features. The Simple Attention Module (SimAM) [13] enhances target representation by explicitly computing the response distribution of neurons. Despite these developments, current infrared small target detection approaches continue to suffer from high computational overhead and limited cross-domain generalizability. A key challenge is effectively suppressing background interference while enhancing small target feature representation.
Finally, regarding detection head optimization, YOLO series detectors (e.g., YOLOv1 [14], YOLOv4 [15], and YOLOv7 [16]) use various architectures for different scenarios. For example, the PANet detection head in YOLOv4 enhances target localization capabilities, while YOLOv5 further improves detection accuracy by refining activation functions and regularization strategies. In recent years, research on lightweight detection heads has gained significant attention. For instance, NanoDet [17] employs a more compact network architecture to accommodate edge computing devices. However, these methods still struggle to balance computational efficiency and detection precision in infrared small target tasks.
To overcome the aforementioned limitations, this paper proposes an infrared small target detection method based on Scale-Sequence Feature Fusion (SSFF) and the LiteShiftHead detection head. Specifically, the key contributions of this study can be outlined as follows:
- We designed a Scale-Sequence Feature Fusion (SSFF) neck to improve multi-scale feature representation for accurate small target detection.
- We develop LiteShiftHead, a lightweight detection head that significantly reduces computational cost, enabling deployment on resource-constrained platforms.
- We designed a Noise Suppression Network (NSN) that enhances attention to salient features by effectively mitigating interference from irrelevant background regions.
2. Related Work
In traditional deep learning-based object detection models, Feature Pyramid Networks (FPN) and Path Aggregation Networks (PANs) are two typical multi-scale feature fusion methods. FPN utilizes a simple additive fusion approach, which results in insufficient feature representation for small target areas. PAN [18], proposed by Liu et al., further enhances feature flow based on FPN. However, the feature fusion method in PAN remains relatively coarse. To improve accuracy in complex scenarios, researchers have developed novel feature fusion techniques [19,20,21,22,23]. BiFPN [24] enhances feature fusion efficiency by introducing adaptive weighting to optimize information flow. Tang et al. [25] introduced Light-YOLO, which enhances small ship detection through multi-scale feature fusion, but involves deeper backbone structures. However, these methods still fall short in complex scenarios. To address this, this paper proposes a feature fusion neck structure that employs Scale-Sequence Feature Fusion (SSFF) methods. This structure establishes stronger connections between multi-level features, thereby better capturing detailed information of the targets.
In infrared target detection, background noise often interferes with small target recognition. Traditional methods use techniques like background modeling or filtering to suppress noise [26,27,28]. The Top-Hat transform proposed by Bai et al. [29] enhances target features through morphological operations, but it is prone to noise interference. The mean smoothing filter proposed by Gao et al. [30] reduces high-frequency noise but may blur target edges [31]. MST-Net, proposed by Li et al. [32], utilizes a multi-scale Transformer to extract global context information, effectively mitigating background interference. Sun et al. [33] applied non-convex weighted tensor rank minimization for small target detection, achieving strong accuracy at the cost of higher computational load. Xiong et al. [34] presented an adaptive dynamic fusion network to address complex backgrounds, though lacking deployment considerations. Li et al.’s Adaptive Background Modeling (ABM) constructs a feature distribution model via adversarial learning but struggles with rapidly changing backgrounds [35]. To address this, this paper proposes a noise suppression network that combines channel and spatial attention to effectively enhance feature representation in the target area while suppressing background interference. It significantly improves the detection performance of infrared small targets without notably increasing computational cost.
The detection head is a crucial component of the object detection framework, responsible for classifying the output of the feature extraction network and performing bounding box regression. Early detection heads often used dense connections, such as the fully connected detection heads in Faster R-CNN [36] proposed by Ren et al. and YOLOv3 [14] by Redmon et al., but these methods are computationally expensive and unsuitable for real-time detection tasks. To improve efficiency, lightweight detection heads have been proposed [37]. For instance, Yi et al.’s Efficient Detection Head (EDH) uses depth-wise separable convolutions to minimize parameter count and computation, though at the cost of weaker feature representation and limited adaptability in complex scenarios [38]. To address this, this paper designs a lightweight detection head, LiteShiftHead, which significantly reduces the computational complexity of the model while maintaining high detection performance, making it suitable for resource-constrained devices.
Transformer-based detectors have emerged as powerful tools in infrared target detection. DETR [39] and Swin Transformer-based models [40] offer global context modeling and strong feature representation, which are beneficial for small target recognition in complex backgrounds. However, their computational cost and slower inference speed limit their deployment in real-time UAV applications. Our proposed YOLO-SSFA is designed to address this trade-off by offering competitive detection performance with significantly higher FPS and fewer parameters. In addition to transformer-based architectures, recent anchor-free detectors such as YOLOX [41] have demonstrated improved performance and training stability in object detection tasks, including infrared target detection. YOLOX eliminates the need for anchor box design by predicting center points and object dimensions directly, which can simplify training and enhance generalization. However, its computational load remains significant compared to lightweight alternatives, limiting deployment on real-time UAV platforms. In contrast, YOLO-SSFA is optimized for low-latency environments while maintaining competitive accuracy.
YOLOv11 [42] is a recent evolution in the YOLO series, designed to further improve inference speed and deployment efficiency on edge devices. Compared with earlier versions like YOLOv5 and YOLOv8, YOLOv11 emphasizes lightweight architecture while preserving detection accuracy, making it a promising baseline for real-time tasks. However, YOLOv11 still suffers from limitations in handling small infrared targets and complex backgrounds, as it lacks dedicated modules for fine-grained feature fusion and attention-based noise suppression. In this work, we build upon YOLOv11n by integrating a lightweight multi-scale fusion neck (SSFF), a denoising attention module (NSN), and an efficient detection head (LiteShiftHead), aiming to enhance both accuracy and real-time performance in infrared small target detection scenarios. To facilitate a concise comparison of typical methods used in infrared small target detection, Table 1 summarizes representative architectures and attention modules, along with their respective performance trade-offs.

Table 1.
Performance comparison with advanced algorithms based on the HIT-UAV dataset.
3. Method
3.1. YOLO-SSFA
The proposed architecture employs YOLOv11n as the base backbone due to its lightweight design and favorable speed–accuracy trade-off. YOLO-SSFA is a lightweight model for infrared small object detection. The model optimizes the backbone network for enhanced multi-scale feature extraction by integrating convolutional neural networks and NSNs. It also includes a novel fusion mechanism in the neck structure for better feature fusion and LiteShiftHead. This lightweight detection head reduces computational complexity while improving small target detection accuracy. Figure 1 shows the overall model structure.
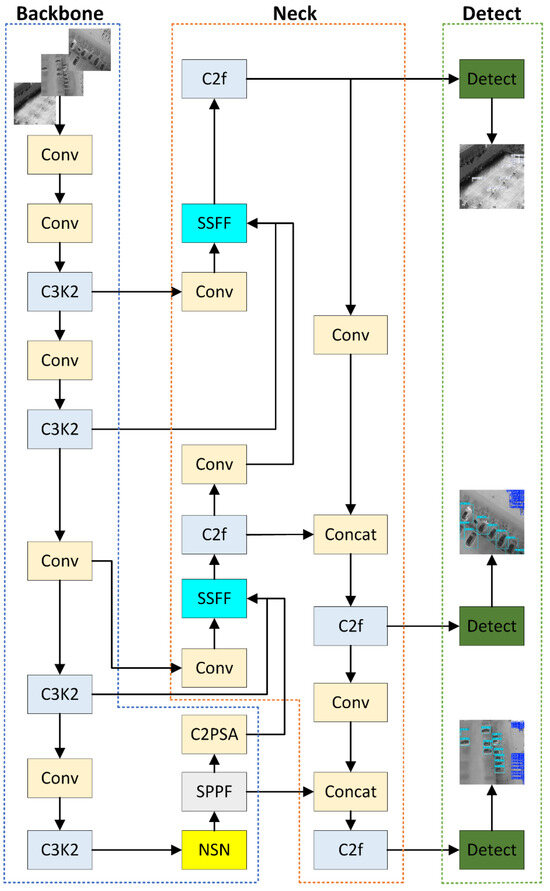
Figure 1.
The architectural diagram of the YOLO-SSFA network. The model consists of three main components: the Scale-Sequence Feature Fusion (SSFF) neck, the LiteShiftHead detection head, and the Noise Suppression Network (NSN) module. The framework is designed to enhance multi-scale feature representation, reduce computational complexity, and improve robustness in infrared small target detection tasks.
3.1.1. Feature Fusion Structure
Traditional object detection networks have limitations. For example, upsampling can lead to detail loss in high-resolution feature maps, and simple concatenation or weighted fusion methods struggle to capture contextual information across layers, resulting in insufficient feature representation for small targets. To address these issues, we propose an SSFF module. It uses a sequential fusion strategy to dynamically integrate low-, mid-, and high-level features via an adaptive mechanism. Depth-wise separable convolutions and attention mechanisms further enhance fusion effectiveness. The structure is shown in Figure 2, with the workflow consisting of three steps: First, global enhancement aligns low-resolution features L with mid-resolution features M using adaptive pooling, strengthening global context. Second, nearest neighbor interpolation upsamples high-resolution features to match M’s resolution, preserving details better than bilinear interpolation. Finally, aligned features L, M, and S are concatenated along the channel axis to generate a fused feature map LMS, which is input to the detection head. This enables efficient integration of multi-scale features, thereby producing richer semantic representations for accurate detection.
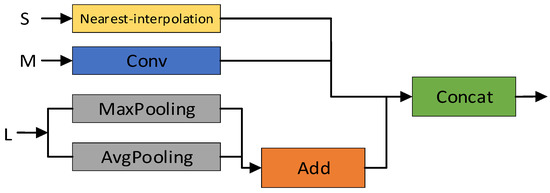
Figure 2.
The architecture of the SSFF module. The module fuses feature maps of different resolutions (L, M, and S) via sequential alignment and attention-weighted fusion. This enhances the detection of small-scale targets by retaining spatial details while capturing contextual semantics. The output fused feature LMS is passed to the detection head.
The proposed SSFF can be viewed as an efficiency-oriented variant of BiFPN [24]. While BiFPN adopts iterative bidirectional paths and learnable fusion weights, it incurs additional computational overhead due to repeated refinement. In contrast, SSFF performs scale-sequential fusion in a single pass, omitting complex attention layers. This simplification reduces the number of floating-point operations (FLOPs) by approximately 8.7% compared to BiFPN under the same input resolution and feature depth, as shown in Table 2. Thus, SSFF is more suitable for real-time applications on resource-limited platforms, such as UAVs and edge devices.

Table 2.
Performance comparison with advanced algorithms based on the HIT-UAV dataset.
3.1.2. Noise Suppression Network
To improve model performance, YOLO-SSFA designed a Noise Suppression Network (NSN). NSN is a lightweight attention module that enhances key feature capture by interactively integrating channel and spatial features. Unlike traditional modules, NSN uses feature grouping and shuffling to reduce computational complexity and parameter count while leveraging inter-group correlations, making it ideal for resource-constrained scenarios. Specifically, NSN groups channels into sub-features, processes them in parallel, models dependencies using a Shuffle Unit, aggregates the sub-features, and applies channel shuffling for cross-sub-feature communication. The NSN architecture is shown in Figure 3.
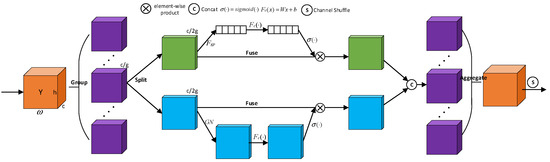
Figure 3.
An overview of the NSN module. NSN applies channel grouping, attention-based sub-feature weighting, and spatial modulation to suppress irrelevant background information. The channel shuffle mechanism at the end facilitates cross-group feature exchange, enhancing the feature focus on valid target regions.
The following is the detailed processing flow of the NSN module:
- Input Features. Let represent the input feature map, where B, C, H, and correspond to the batch size, channel count, height, and width, respectively.
- Feature grouping and channel segmentation. The feature map is reorganized into G groups, denoted as , where each sub-feature learns distinct semantic representations during training. An attention unit is then applied to each sub-feature to compute importance weights. Specifically, each is split into two branches along the channel dimension, denoted as .
- Channel attention calculation. The final output is computed as
Here, and denote the scaling and shifting parameters applied within the functions.
Spatial attention computation. The final output is
Here, and are parameters with a shape of . The outputs of the two branches are merged to reestablish the original channel dimensionality.
- 4.
- Fusion. Finally, a “channel shuffling” strategy is applied to enhance inter-group feature interaction along the channel axis. The resulting output preserves the same shape as the input , allowing seamless integration of the NSN module into modern detection architectures.
The NSN module shares the idea of spatial and channel-wise attention with CBAM [12] but introduces group-wise attention blending and a lightweight channel shuffle mechanism. This design allows efficient feature modulation while maintaining low parameter complexity, enhancing applicability on edge devices.
3.1.3. LiteShiftHead Detection Head
To overcome the balance challenge between detection precision and efficiency, we introduce LiteShiftHead, a lightweight detection head. It achieves precise and efficient target detection through feature fusion and target box regression. The overall structure is shown in Figure 4, with key components including convolution layer (Conv), regression layer (REG), classification layer (CLS), sparse convolution (SPConv), and distributed focal loss (DFL). The SPConv module structure is shown in Figure 5.
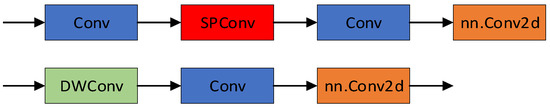
Figure 4.
Architecture design of the LiteShiftHead module. The module integrates SPConv for efficient multi-scale feature refinement, a REG module for bounding box regression, a CLS module for object classification, and a DFL (Distribution Focal Loss) unit for precise localization. LiteShiftHead significantly reduces computational overhead while maintaining high accuracy in small target scenarios.
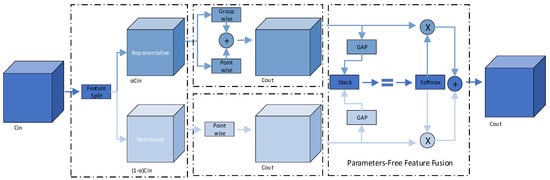
Figure 5.
Structural components of the SPConv module used in LiteShiftHead. SPConv employs parallel convolutional kernels of varying sizes to extract multi-scale spatial features. This design improves detection adaptability across different target scales while keeping parameter count low.
The operational mechanism of the LiteShiftHead module is structured as follows: The input feature map undergoes processing via a cascade of 3 × 3 and 1 × 1 convolutional layers, enabling the capture of multi-scale feature representations. These layers reduce dimensionality and extract semantic information for bounding box regression and object classification. Next, LiteShiftHead fuses multi-scale features using the REG module. After convolutional operations, the SPConv module optimizes each feature map by reducing parameters and enhancing efficiency. SPConv uses varying kernel sizes to extract multi-scale information, improving adaptability to targets of different sizes. The REG module predicts bounding box coordinates, ensuring detection accuracy, while the CLS module predicts object classes to enhance classification accuracy. Finally, DFL optimizes the distribution of bounding box predictions, improving localization precision. The LiteShiftHead module attains superior detection performance while minimizing computational burden, making it highly adaptable for deployment on resource-constrained platforms, including mobile devices, UAVs, and autonomous driving systems.
LiteShiftHead adopts a streamlined detection head inspired by NanoDet [17] but introduces a modular SPConv layer and DFL optimization, resulting in higher localization accuracy under constrained resources.
3.2. Datasets
This study leverages two publicly accessible datasets, HIT-UAV and FLIR, for model validation and performance evaluation. To improve the model’s generalization performance, the categories “Other Vehicles” and “DontCare” were excluded from the dataset [43]. Only the categories “Person”, “Car”, and “Bicycle” were retained. The resulting dataset comprises 2898 infrared images, each featuring a resolution of 640 × 512 pixels. Stratified sampling was employed to partition the dataset into training (2008 images), testing (571 images), and validation (287 images) sets at a ratio of 7:2:1. Additionally, the FLIR-provided infrared scene dataset was utilized for comparative and ablation experiments. This dataset consists of 10,548 infrared images, each featuring a resolution of 640 × 512 pixels, and includes three labels categorized as “pedestrian”, “bicycle”, and “car.” The same partitioning strategy was applied, dividing the dataset into training (7381 images), testing (2111 images), and validation (1056 images) sets in a 7:2:1 ratio.
3.3. Data Augmentation
To increase dataset diversity and improve model generalization, this study adopts data augmentation strategies by applying two specific augmentation schemes to the HIT-UAV dataset. For random rotation augmentation, images are rotated by +90°, −90° or remain in their original orientation with equal probability (p = 1/3). The random cropping approach simulates viewpoint variations by applying random shifts of ±10° along both the horizontal and vertical axes. After applying the above augmentation methods, the total dataset size increases to 5649 images. Specifically, the training, testing, and validation subsets are expanded to 5223, 112, and 314 images, respectively, while maintaining the original 7:2:1 partitioning ratio. The resolution of the images remains unchanged at 640 × 512 pixels, and the original three categories, “Person”, “Bicycle” and “Car” are retained.
3.4. The Evaluation Criteria
To tackle the distinct challenges of infrared small target detection—including low target–background contrast, cluttered thermal noise, and real-time inference requirements on edge devices—YOLO-SSFA is evaluated using a combination of accuracy, efficiency, and robustness metrics, with specific emphasis on small target representation and computational feasibility for UAV-based deployment. Mean Average Precision (mAP50) functions as the core metric to quantify the model’s localization accuracy for infrared small targets (particularly those ≤ 32 pixels, accounting for 70% of the HIT-UAV dataset). Precision and Recall are used to analyze false positives and false negatives in complex backgrounds. The F1 score, as the harmonic mean of Precision and Recall, reflects the model’s stability in mixed-scale infrared scenarios. Parameter count and floating-point operations (FLOPs) directly reflect the model’s lightweight design. The following equations define the evaluation metrics:
where TP refers to true positive instances, FN is false negative, and FP stands for false positive.
Additionally, frames per second (FPS) measures the processing throughput of the model, reflecting both detection speed and real-time recognition capability. The formula for calculating FPS is given by
where N denotes the total number of processed images, and T denotes the overall processing time.
4. Results of the Experiments
4.1. Experiment Environment
To validate the efficacy of the YOLO-SSFA framework, a series of comparative tests and ablation analyses were conducted. The experimental hardware configuration is detailed in Table 3. The model was trained for 300 epochs, with a batch size of 16 and an input resolution of 640 × 640 pixels. The SGD optimizer was used with an initial learning rate of 0.01, momentum of 0.937, and a weight decay of 5 × 10−4. No dropout was applied. A fixed learning rate schedule was used without cosine decay or warm restarts. The loss functions consisted of Complete IoU (CIoU) loss for bounding box regression, Binary Cross-Entropy (BCE) loss for classification, and Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) for improved localization accuracy. Early stopping was enabled with a patience of 100 epochs, and model checkpoints were selected based on the best validation mean Average Precision (mAP). Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) training was enabled to accelerate convergence. Most importantly, all training did not use pretrained weights. Each model results are averaged over three independent runs with different random seeds. The reported performance includes mean ± standard deviation.

Table 3.
Experimental platform and parameter configuration.
4.2. Comparison Studies and Analysis
To comprehensively evaluate the applicability and effectiveness of YOLO-SSFA in UAV-based infrared target detection, extensive comparisons were made against multiple state-of-the-art algorithms using the HIT-UAV and FLIR datasets under consistent experimental settings.
As shown in Table 4, while YOLOv8s achieved the second-highest mAP50 of 94.2%, the YOLO-SSFA model demonstrated superior real-time capability, with a detection speed of 217.6 FPS, which is 34.6% faster than YOLOv8s (122.5 FPS) and 31.5% faster than the baseline YOLOv11n (165.5 FPS). Notably, YOLO-SSFA achieved the highest mAP50 of 94.9%, outperforming YOLOv11n by 0.8% and YOLOv5n by 1.5% while maintaining lightweight characteristics with only 3.3 M parameters—a 28% increase over YOLOv11n (2.58 M) but with 70% fewer parameters than YOLOv8s (11.13 M). In terms of computational efficiency, YOLO-SSFA’s GFLOPs (8.1) are comparable to YOLOv8n (8.1) but achieve 0.7% higher mAP50. Compared to heavier models like YOLOv3-tiny (18.9 GFLOPs), YOLO-SSFA reduces computational complexity by 57% while improving mAP50 by 8.9%. The model also outperforms YOLOv9t (93.9% mAP50) by 1.0% in accuracy and 41.3% in FPS, demonstrating a superior balance of Precision and speed. Notably, YOLO-SSFA’s F1 score (91%) and Precision (0.913) are the highest among all tested models, indicating strong generalization ability in infrared small-target scenarios. Its lightweight architecture (3.3 M parameters, 8.1 GFLOPs) enables a 217.6 FPS inference speed, making it 1.3× faster than YOLOv10n (191.6 FPS) and 1.5× faster than YOLOv5n (158.3 FPS) while maintaining competitive detection accuracy. Figure 6 shows the visualization results and heatmaps on the HIT-UAV dataset.

Table 4.
Performance comparison with advanced algorithms based on the HIT-UAV dataset.
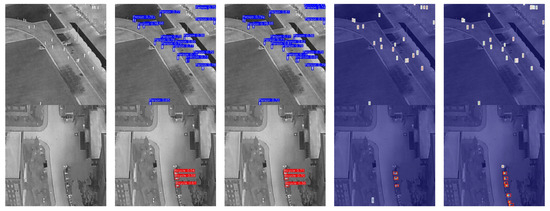
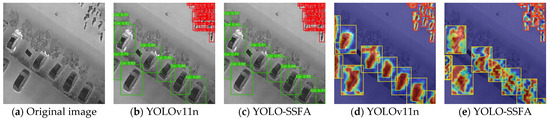
Figure 6.
Visualization of detection outcomes produced by YOLOv11n and YOLO-SSFA on the HIT-UAV dataset. (a) Original infrared image prior to detection. (b) Detection output generated by YOLOv11n. (c) Detection output generated by YOLO-SSFA. (d) Heatmaps of YOLOv11n. (e) Heatmaps of YOLO-SSFA. The inference time for each image corresponding to (b) is 7.5 ms, 6.5 ms, and 9.3 ms. The inference time for each image corresponding to (c) is 6.0 ms, 5.5 ms, and 6.5 ms.
To further evaluate the detection performance of the proposed YOLO-SSFA model, we plotted the Precision–Recall (P–R) curves for both the HIT-UAV and FLIR datasets, comparing them with the baseline YOLOv11n. As shown in Figure 7, YOLO-SSFA consistently exhibits superior Precision and Recall trade-offs across both datasets.
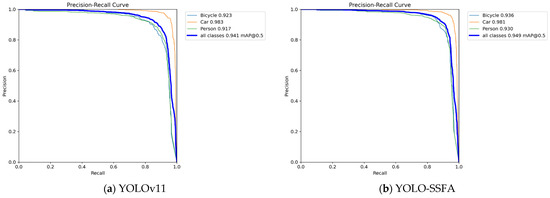
Figure 7.
Precision–Recall curve of YOLOv11n and YOLO-SSFA on the HIT-UAV dataset.
These curves demonstrate that the integration of SSFF, NSN, and LiteShiftHead modules not only improves overall accuracy but also enhances stability across varying detection thresholds.
The performance comparison on the FLIR dataset (dominated by complex backgrounds and medium–small targets) in Table 5 highlights YOLO-SSFA’s robustness and efficiency. With an mAP50 of 85.0%, YOLO-SSFA outperforms YOLOv11n (83.8%) by 1.2% and YOLOv5n (83.6%) by 1.4% while achieving a detection speed of 319.4 FPS—6.8% faster than YOLOv11n (299 FPS) and 68.7% faster than YOLOv8s (189.4 FPS). The model’s lightweight architecture (3.3 M parameters, 8.1 GFLOPs) ensures low computational overhead, with a parameter count 70% lower than YOLOv8s (11.13 M) and GFLOPs 71.5% lower than YOLOv3-tiny (18.9 GFLOPs). Notably, YOLO-SSFA’s F1 score (80%) and Precision (0.867) surpass YOLOv6n (78%, 0.819) and YOLOv10n (78%, 0.829), demonstrating stronger target–background discrimination in cluttered infrared scenes. The NSN module plays a critical role here, reducing false alarms by suppressing background noise, while the LiteShiftHead maintains high throughput via sparse convolution. Compared to the HIT-UAV dataset, YOLO-SSFA’s mAP50 decreases slightly (−0.9%) on FLIR but achieves a 15.5% higher FPS, reflecting its adaptability to mixed-scale target scenarios. Figure 8 shows the visualization results and heatmaps on the HIT-UAV dataset.

Table 5.
Performance comparison with advanced algorithms based on the FLIR dataset.
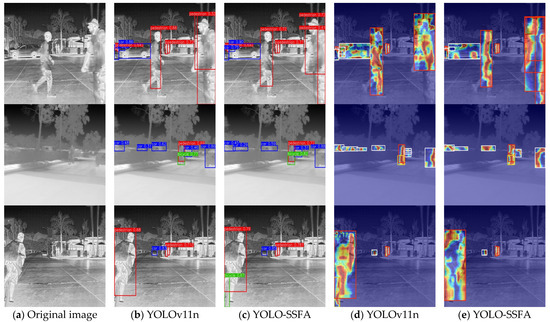
Figure 8.
Visualization of detection outcomes produced by YOLOv11n and YOLO-SSFA on the FLIR dataset. (a) Original infrared image prior to detection. (b) Detection output generated by YOLOv11n. (c) Detection output generated by YOLO-SSFA. (d) Heatmaps of YOLOv11n. (e) Heatmaps of YOLO-SSFA. The inference time for each image corresponding to (b) is 116.1 ms, 107.1 ms, and 143.7 ms. The inference time for each image corresponding to (c) is 104.5 ms, 101.4 ms, and 95.9 ms.
Figure 9 shows the Precision–Recall curve of YOLOv11n and YOLO-SSFA on the FLIR dataset.
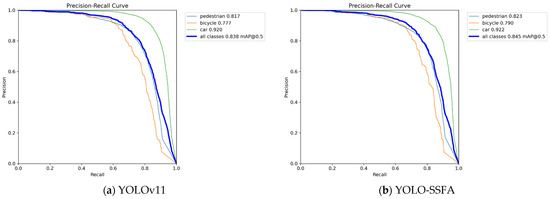
Figure 9.
Precision–Recall curve of YOLOv11n and YOLO-SSFA on the FLIR dataset.
To further evaluate the performance and generalization of YOLO-SSFA, we conducted comparative experiments with transformer-based and anchor-free detectors on both the HIT-UAV and FLIR datasets. As shown in Table 6 (HIT-UAV), we included DETR [39], Swin Transformer [40], and YOLOX [41] as baselines. All models were trained from scratch under the following identical conditions: input resolution of 640 × 640 pixels, batch size 16, and 300 epochs.

Table 6.
Performance comparison with advanced algorithms based on the HIT-UAV dataset.
As shown in Table 7 (FLIR), these results across both datasets confirm that YOLO-SSFA not only achieves competitive accuracy compared to recent transformer and anchor-free models, but also surpasses them in inference speed and efficiency, demonstrating its suitability for real-time, resource-constrained infrared target detection scenarios.

Table 7.
Performance comparison with advanced algorithms based on the FLIR dataset.
As depicted in Figure 10, this study conducts a comprehensive evaluation of three critical metrics, mAP50, FPS, and model size, from the standpoint of model practicality. These metrics correspond to detection accuracy, inference speed, and resource efficiency, respectively. The experimental findings indicate that YOLO-SSFA attains superior detection accuracy and inference speed while preserving a compact architectural design. This outcome substantiates that YOLO-SSFA strikes an optimal balance between accuracy and speed, with its lightweight structure providing substantial benefits for mobile deployment. In summary, YOLO-SSFA exhibits exceptional overall performance in infrared target detection, positioning it as a robust and practical solution for real-world deployments.
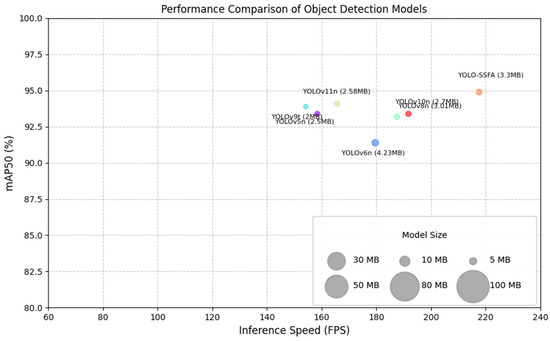
Figure 10.
Comprehensive performance comparison of models.
4.3. Ablation Studies and Analysis
To assess the impact of the proposed YOLO-SSFA model, extensive ablation tests were performed using both the HIT-UAV and FLIR datasets. The objective was to analyze how each individual component contributes to the model’s overall performance. The corresponding experimental results are summarized in Table 8. On the HIT-UAV dataset, which predominantly contains small targets, the SSFF module alone improves mAP50 from 94.1% (baseline YOLOv11n) to 94.4%, validating its effectiveness in enhancing multi-scale feature representation for tiny objects. Adding the NSN module boosts FPS by 33.3% (from 165.5 to 220.5), indicating its role in optimizing computational efficiency without significant accuracy loss. Integrating SSFF, LiteShiftHead, and NSN achieves the highest mAP50 of 94.9% (+0.8% over the baseline), with a parameter increase of only 27.9%, demonstrating the synergistic effect of multi-module design for small-target scenarios.

Table 8.
Ablation analysis conducted on the HIT-UAV dataset.
On the FLIR dataset, characterized by complex backgrounds, Table 9 indicates that the LiteShiftHead alone improves FPS by 7.8% (from 299 to 312.2), with a mAP50 gain (+0.6%), highlighting its efficiency in inference acceleration. The NSN module significantly enhances F1 score from 79% to 80% and Precision from 0.85 to 0.844, likely due to its ability to suppress background noise in cluttered scenes. When all modules are integrated, YOLO-SSFA maintains 85.0% mAP50 (comparable to YOLOv8s) while achieving 319.4 FPS (+6.8% over the baseline), proving the robustness of the lightweight architecture across diverse infrared scenarios.

Table 9.
Ablation analysis conducted on the FLIR dataset.
Figure 11 demonstrates the enhanced performance of the YOLO-SSFA model over the original algorithm in detecting infrared vehicle targets. Consequently, the YOLO-SSFA model represents a more suitable and effective solution for detecting weak small targets in infrared environments.
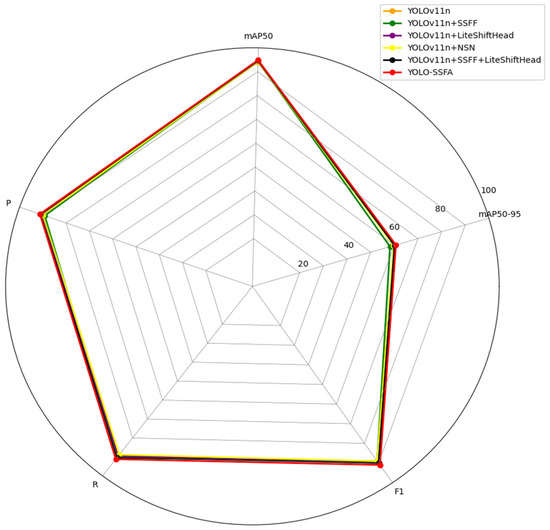
Figure 11.
Performance comparison chart of ablation modules.
4.4. Comparative Analysis of Various Attention Mechanisms
To further verify the validity of the proposed YOLO-SSFA model, a comparative experiment on attention mechanisms was conducted using the HIT-UAV dataset. This experiment included several widely used attention mechanisms, and only the attention mechanism was modified during the experiment.
Table 10 presents a performance comparison of the YOLO-SSFA model integrated with different attention mechanisms on the HIT-UAV dataset, highlighting the NSN module’s superior lightweight design and detection efficiency. With an mAP50 of 94.9% and a detection speed of 217.6 FPS, NSN outperforms all comparative schemes; its mAP50 exceeds CBAM [12] (94.2%), GAM [44] (93.6%), SimAM [13] (93.9%), SK [45] (94.5%), and EMA [46] (93.9%) by 0.7%, 1.3%, 1.0%, 0.4%, and 1.0%, respectively. Meanwhile, NSN achieves a 47.7% increase in FPS compared to SK (147.3 FPS) and a 31.6% increase compared to EMA (165.3 FPS), demonstrating significant real-time performance advantages. In terms of lightweight design, NSN introduces only 0.72 M parameters (total parameters: 3.3 M), reducing the parameter count by 77% compared to SK (14.4 M) and 21% compared to GAM (4.2 M) while achieving a 1.3% mAP50 improvement over GAM. By partitioning channels into subgroups and introducing Shuffle Units, NSN effectively suppresses background noise while avoiding the computational redundancy of traditional attention modules (e.g., CBAM’s sequential convolutions). Experimental data show that NSN achieves the highest F1 score (91%) and Precision (0.913), indicating superior discrimination between small targets and cluttered backgrounds, especially in low-contrast scenarios. In summary, NSN achieves an optimal balance of accuracy, speed, and parameter efficiency through channel-group sparse computation and dynamic feature shuffling. These results validate NSN’s effectiveness in enhancing feature representation and suppressing noise for infrared small-target detection, making it an ideal solution for real-time deployment on edge devices.

Table 10.
Comparative analysis of attention mechanisms conducted on the HIT-UAV dataset.
In addition, to verify the effectiveness of the NSN module, we used Grad CAM to visualize the spatial attention map of YOLO-SSFA. Figure 12 and Figure 13 show the comparison of attention response between our model and YOLO-SSFA without attention mechanism.
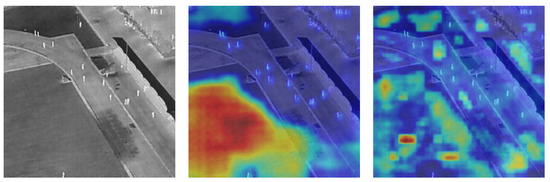
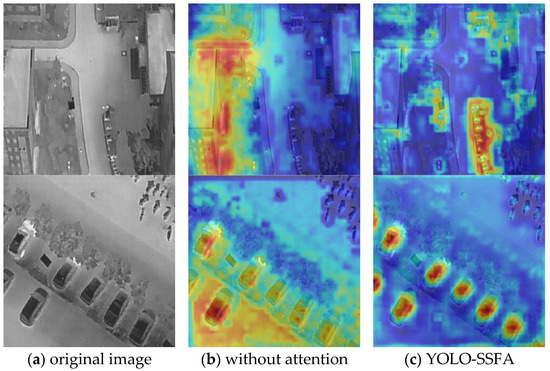
Figure 12.
Attention visualization on the HIT-UAV dataset. (a) Original infrared image prior to detection. (b) Visualization output generated by YOLO-SSFA without attention mechanism. (c) Visualization output generated by YOLO-SSFA.
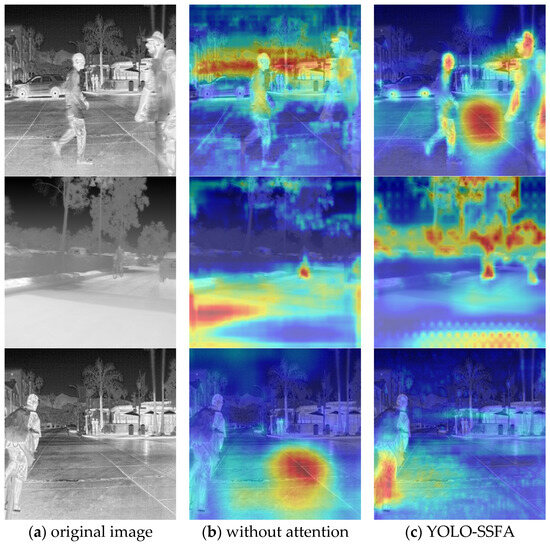
Figure 13.
Attention visualization on the FLIR dataset. (a) Original infrared image prior to detection. (b) Visualization output generated by YOLO-SSFA without attention mechanism. (c) Visualization output generated by YOLO-SSFA.
The results demonstrate that YOLO-SSFA exhibits more concentrated and target-focused activation regions. In particular, small objects such as distant pedestrians or bicycles generate clear, localized responses, while background clutter is largely suppressed. This suggests that the integration of channel–spatial grouping and channel shuffle in NSN enhances the network’s ability to focus on semantically meaningful areas, contributing to improved precision.
5. Conclusions
This study presents the YOLO-SSFA model, which enhances infrared small target detection through multi-module optimization. It achieves mAP50 scores of 94.9% and 85% on the HIT-UAV and FLIR datasets, respectively. By integrating three key modules, SSFF, LiteShiftHead, and NSN, the model enhances detection accuracy and robustness. The SSFF module strengthens feature extraction for weak and small targets via multi-scale fusion. The LiteShiftHead module reduces computational cost while maintaining accuracy and accelerating inference through sparse convolution. The NSN module focuses on salient features and suppresses background noise using attention mechanisms. Experimental results indicate that the YOLO-SSFA model surpasses traditional methods in both detection accuracy and computational efficiency, demonstrating strong potential for real-world deployment.
Although the proposed YOLO-SSFA model demonstrates high inference speed and accuracy in experimental evaluations, it is important to note that the current testing setup does not fully replicate a real-world real-time deployment scenario, such as on embedded systems or UAVs with limited computational resources. To implement the model in an actual real-time environment, further optimizations would be necessary, including quantization, pruning, and hardware-specific deployment. Additionally, real-time data acquisition, thermal noise adaptation, and latency control in embedded pipelines should be addressed in future work.
The proposed method has potential applications in both civilian and security-related domains. All datasets used in this study are publicly available (HIT-UAV and FLIR), and no sensitive or military data were involved. We fully comply with ethical guidelines and data-sharing policies as outlined by the respective dataset providers and journal requirements. The code is available at the following URL: https://github.com/dd001217/YOLO-SSFA.git, accessed on 1 June 2025.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W., M.C. and Q.Y.; Methodology, Y.W., M.C. and Y.Z.; Validation, M.C., Q.Y. and Y.W.; Investigation, Y.W. and Z.W.; Resources, Y.W.; Data Curation, Y.W.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.C. and Y.W.; Writing—Review and Editing, M.C., Y.W., Q.Y. and Y.Z.; Visualization, Y.W. and Z.W.; Supervision, M.C. and Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62265010; Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province under Grant 24JRRA183.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable for studies not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying this study’s findings can be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their heartfelt appreciation to the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their insightful comments and constructive feedback, which have greatly enhanced the quality of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, C.L.P.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xia, T.; Tang, Y. A Local Contrast Method for Small Infrared Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Hu, J.; Ma, P.; Tao, R. Single-Frame Infrared Small-Target Detection: A Survey. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 10, 87–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, S.; Niu, S.; Zhang, K. Detection of Infrared Small Targets Using Feature Fusion Convolutional Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146081–146092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L. Miss Detection vs. False Alarm: Adversarial Learning for Small Object Segmentation in Infrared Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8508–8517. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Deng, B.; Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, K.; Cai, S.; Ciampa, F. Infrared machine vision and infrared thermography with deep learning: A review. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 116, 103754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Luo, H.; Cheng, B.; Sun, H. Infrared LSS-Target Detection Via Adaptive TCAIE-LGM Smoothing and Pixel-Based Background Subtraction. Photonic Sens. 2019, 9, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lv, G.; Xu, L. Infrared dim target detection based on visual attention. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2012, 55, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y. Multi-Stage Multi-Scale Local Feature Fusion for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Hu, H.; Li, B.; Tan, W.; Lu, H.; Xiao, J.; Ren, Y.; Pu, S. Dynamic Feature Pyramid Networks for Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, (ICME), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Xie, X. SimAM: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2004, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, J. Generalized focal loss: Learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; pp. 21002–21012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Chan, J.; Krouss, M.; Furlich, G.; Martens, P.; Chan, M.; Comer, M.; Delp, E. Infrared Small Target Detection Enhancement Using a Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 3513405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A Single-Stage Object Detection Framework for Industrial Applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Gao, Y.; Wan, M.; Gu, G.; Chen, Q. Infrared small target detection via region super resolution generative adversarial network. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 11725–11737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qin, S. Adaptive detection method of infrared small target based on target-background separation via robust principal component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 69, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. EfficientDet: Scalable and Efficient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10778–10787. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Hu, X.M.; Jeon, S.W.; Chen, W.N. Light-YOLO: A lightweight detection algorithm based on multi-scale feature enhancement for infrared small ship target. Complex Intell. Syst. 2025, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Liu, G.; Tang, H.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, J. Multi-level adaptive perception guidance based infrared and visible image fusion. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023, 171, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Tong, X.; Wei, J.; Su, S.; Wu, P.; Guo, R.; Sun, B. AFFPN: Attention Fusion Feature Pyramid Network for Small Infrared Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kim, S. Small infrared target detection by data-driven proposal and deep learning-based classification. In Proceedings of the Conference on Infrared Technology and Applications XLIV, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–19 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F. Analysis of new top-hat trans formation and the application for infrared dim small target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Meng, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hauptmann, A.G. Infrared Patch-Image Model for Small Target Detection in a Single Image. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Yoshida, I.; Kondo, Y.; Numada, M.; Koshimizu, H.; Oshiro, K.; Saito, R. Edge-preserving smoothing filter using fast M-estimation method with an automatic determination algorithm for basic width. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Y.; Tong, L.; Lu, R.; Yan, B. MST-net: A multi-scale swin transformer network for EEG-based cognitive load assessment. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 206, 110834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, B.; Yin, Q.; Chen, Y.; Dai, Y. Infrared Small Target Detection via Nonconvex Weighted Tensor Rank Minimization and Adaptive Spatial-Temporal Modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5003918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Sheng, Z.; Mao, Y. Feature Multi-Scale Enhancement and Adaptive Dynamic Fusion Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Siddique, A.; Liu, Y.; Yu, K. Infrared Small Target Detection Based on Adaptive Region Growing Algorithm With Iterative Threshold Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5003715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Cao, L.; Zhou, P.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, D. Infrared Small-Target Detection Based on Radiation Characteristics with a Multimodal Feature Fusion Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, P.; Wang, G.; Mo, L.; Wu, B.; Yi, Y.; Fu, X.; Qian, P. Light-FC-YOLO: A Lightweight Method for Flower Counting Based on Enhanced Feature Fusion with a New Efficient Detection Head. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLO. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Zhao, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Z. YOLO-ViT-Based Method for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Infrared Vehicle Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Hoffmann, N. Global attention mechanism: Retain information to enhance channel-spatial interactions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.05561. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective kernel networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).