Evaluating Interaction Techniques in XR Environments Through the Prism of Four EduGames
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample—Short Description of the Four Developed XR Edugames
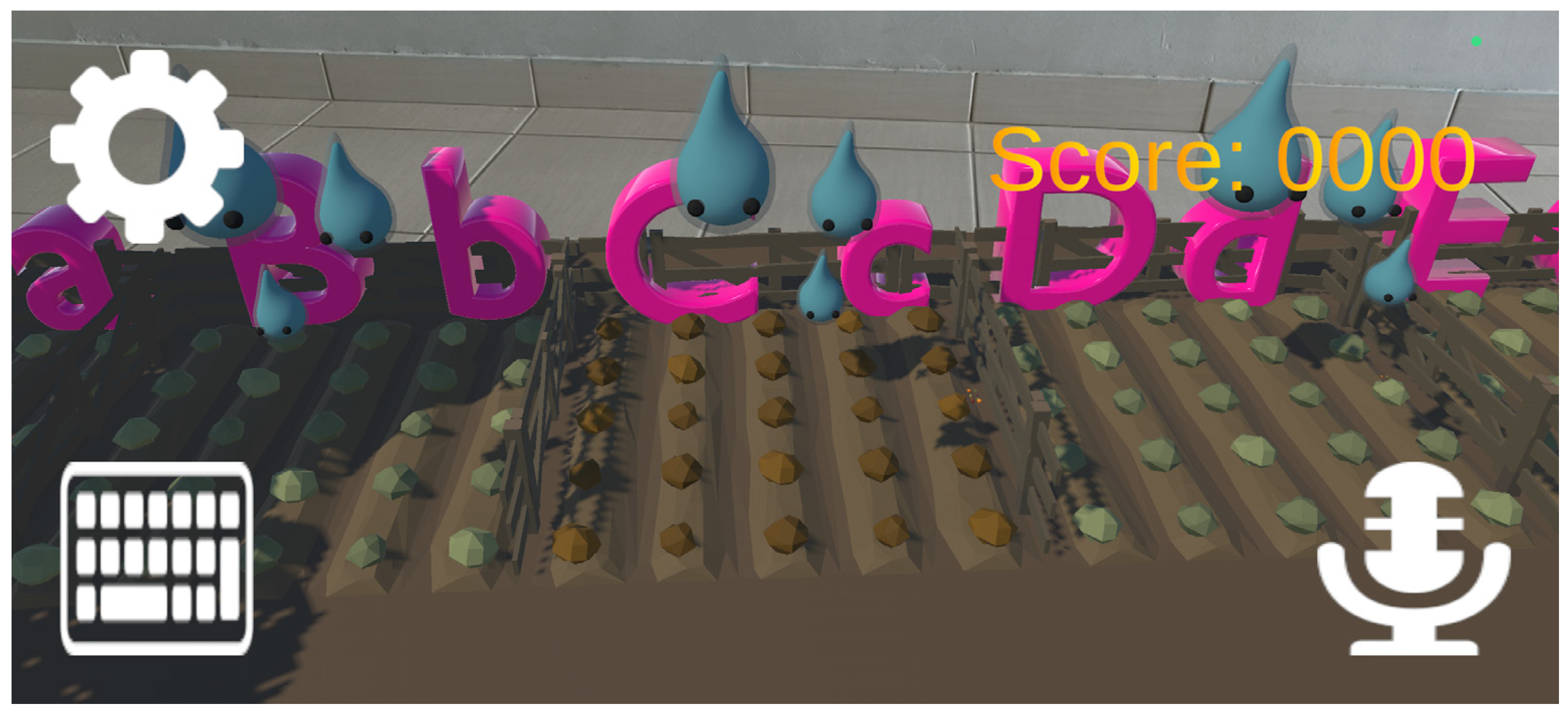
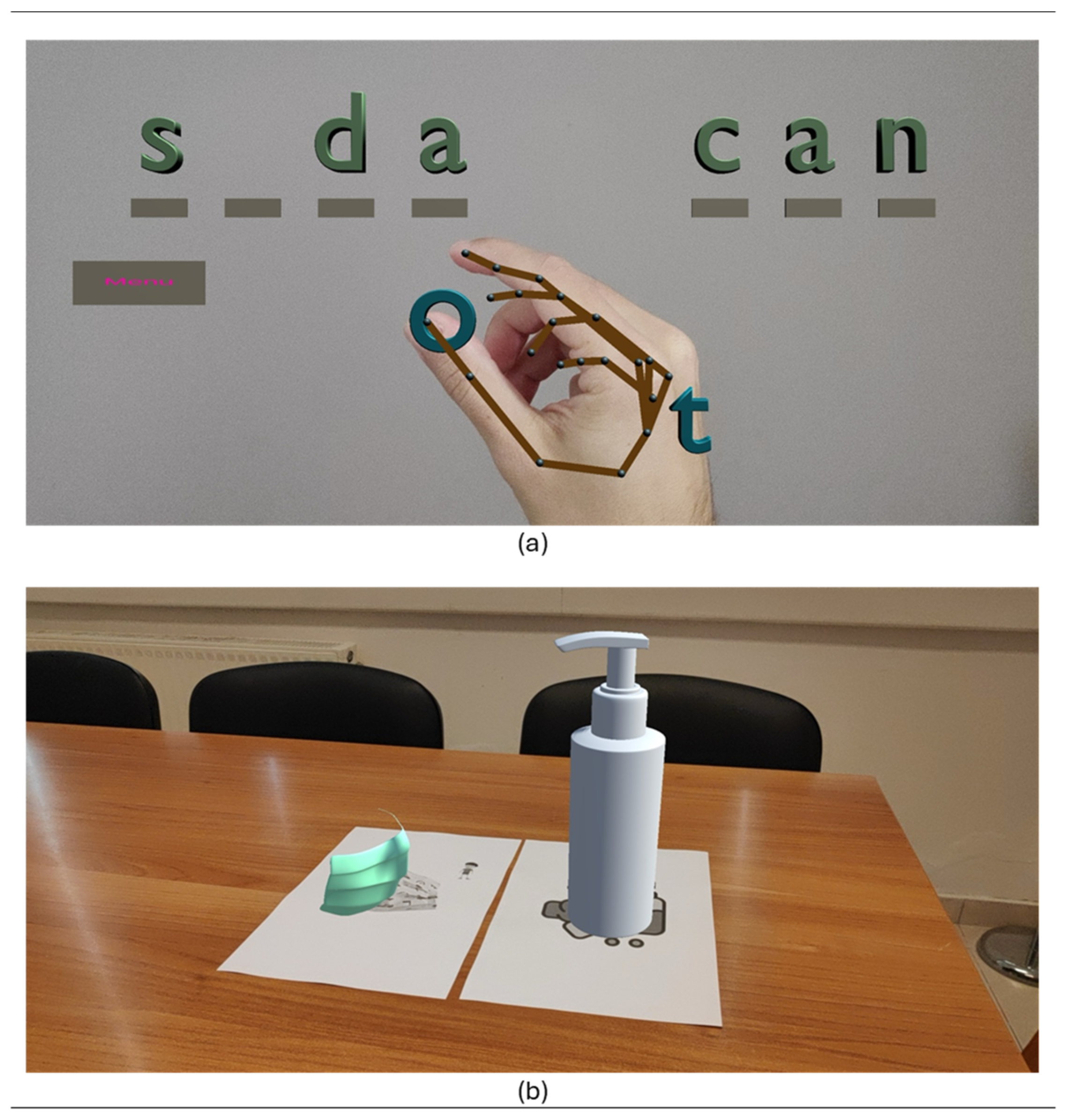
2.1.1. Game 1—Garden Words Game
2.1.2. Game 2—Hangman Game
2.1.3. Game 3—AR Geography Map Puzzle Game
2.1.4. Game 4—3D Map of Eastern Crete Puzzle and Matching Mini-Games
2.2. User Testing Observations
3. Results
3.1. Input and Interaction Techniques
3.2. Gamification and Game Mechanics
3.3. Educational Theories
3.4. Learning Subjects and Objectives
3.5. Proposed Theoretical Framework
4. Discussion
- Multimodal input libraries should be developed to enable flexible integration and switching of input types.
- Adaptive interfaces that detect user behavior and dynamically suggest the optimal input method can enhance usability.
- Developer dashboards should include configurations for task-input mapping, enabling educators to customize interaction based on learners’ profiles.
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| MR | Mixed Reality |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| XR | Extended Reality |
References
- Alnagrat, A.J.; Che Ismail, R.; Syed Idrus, S.Z.; Abdulhafith Alfaqi, R.M. A Review of Extended Reality (XR) Technologies in the Future of Human Education: Current Trend and Future Opportunity. HumEnTech 2022, 1, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Giorgio, A.; Monetti, F.M.; Maffei, A.; Romero, M.; Wang, L. Adopting extended reality? A systematic review of manufacturing training and teaching applications. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 71, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meccawy, M. Creating an Immersive XR Learning Experience: A Roadmap for Educators. Electronics 2022, 11, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crogman, H.T.; Cano, V.D.; Pacheco, E.; Sonawane, R.B.; Boroon, R. Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality in Experiential Learning: Transforming Educational Paradigms. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, K.R.; Rogers, J.A.; Ko, S.H. Materials and devices for immersive virtual reality. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Oveissi, F.; Langrish, T. Applications of augmented reality (AR) in chemical engineering education: Virtual laboratory work demonstration to digital twin development. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2024, 188, 108784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.V.; Carberry, D.; Beenfeldt, C.; Andersson, M.P.; Mansouri, S.S.; Gallucci, F. Virtual reality in chemical and biochemical engineering education and training. Educat. Chem. Eng. 2021, 36, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoropoulou, H.G.; Kiourt, C.; Lalos, A.S.; Koutsoudis, A.; Paxinou, E.; Kalles, D.; Pavlidis, G. Exploiting Extended Reality Technologies for Educational Microscopy. In Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality; Bourdot, P., Interrante, V., Kopper, R., Olivier, A.H., Saito, H., Zachmann, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; p. 12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocente, C.; Ulrich, L.; Moos, S.; Vezzetti, E. A framework study on the use of immersive XR technologies in the cultural heritage domain. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 62, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudintseva, A. Virtual reality affordances for oral communication in English as a second language classroom: A literature review. CEXR 2023, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samala, A.D.; Bojic, L.; Rawas, S.; Howard, N.J.; Arif, Y.M.; Tsoy, D.; Coelho, D.P. Extended reality for education: Mapping current trends, challenges, and applications. J. Pendidik. Teknol. Kejuru. 2024, 7, 140–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhattabi, M. Augmented reality as e-learning tool in primary schools’ education: Barriers to teachers’ adoption. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2017, 12, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.; Nguyen, M. An Online Platform for Enhancing Learning Experiences with Web-Based Augmented Reality and Pictorial Bar Code. In Augmented Reality in Education: A New Technology for Teaching and Learning; Geroimenko, V., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilovas, E. Evaluation of quality and personalisation of VR/AR/MR learning systems. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2016, 35, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spittle, B.; Frutos-Pascual, M.; Creed, C.; Williams, I. A Review of Interaction Techniques for Immersive Environments. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2023, 29, 3900–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Sasikumar, P.; Yang, J.; Billinghurst, M. A user study on mixed reality remote collaboration with eye gaze and hand gesture sharing. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI 2020, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad Nizam, S.S.; Zainal Abidin, P.; Che Hashim, N.; Lam, M.C.; Arshad, H.; Abd Majid, N.A. A review of multimodal interaction technique in augmented reality environment. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2018, 8, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliprantis, J.; Konstantakis, M.; Nikopoulou, R.; Mylonas, P.; Caridakis, G. Natural interaction in augmented reality context. In Proceedings of the VIPERC@IRCDL, Piza, Italy, 30 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Luo, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, J. Augmented Reality in Higher Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature from 2000 to 2023. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G.; Keramopoulos, E.; Diamantaras, K.; Evangelidis, G. Augmented Reality and Gamification in Education: A Systematic Literature Review of Research, Applications, and Empirical Studies. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, I.; Katsaris, I.; Vidakis, N. GardenWords—A Garden Watering AR Game for Learning Vocabulary Using Speech. In Extended Reality. XR Salento 2024; De Paolis, L.T., Arpaia, P., Sacco, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 15030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, I.; Papadourakis, G.; Katsaris, I.; Katsios, K.; Vidakis, N. Transforming Classic Learning Games with the Use of AR: The Case of the Word Hangman Game. In Learning and Collaboration Technologies: Games and Virtual Environments for Learning (HCII 2021); Zaphiris, P., Ioannou, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, I.; Katsaris, I.; Sfyrakis, M.; Vidakis, N. 3D Geography Course Using AR: The Case of the Map of Greece (HCII 2023). In Learning and Collaboration Technologies; Zaphiris, P., Ioannou, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, I.; Mari, I.; Vidakis, N. Towards a Digital Twin Implementation of Eastern Crete: An Educational Approach. In Extended Reality. XR Salento 2023; De Paolis, L.T., Arpaia, P., Sacco, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilo, C.; DiVerdi, S.; Bowman, D. Goldilocks Zoning: Evaluating a Gaze-Aware Approach to Task-Agnostic VR Notification Placement. In Proceedings of the SUI ‘24: ACM Symposium on Spatial User Interaction, ACM, Trier, Germany, 7–8 October 2024; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostal, J.; Hinrichs, U.; Kristensson, P.O.; Quigley, A. SpiderEyes: Designing Attention- and Proximity-Aware Collaborative Interfaces for Wall-Sized Displays. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Haifa, Israel, 24–27 February 2014; pp. 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, K. The integration of extended reality for student-developed games to support cross-curricular learning. Front. Virtual Real. 2022, 3, 888689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawde, V.; Dostálová, N.; Cigánová, E.; Kriglstein, S. Exploring the Fit: Analysing Material Selection for Interactive Markers in MAR Games through Co-Design. In Proceedings of the 2025 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 26 April–1 May 2025; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.C.; Ribeiro, J.M. Marker-based Tangible Interfaces for Smartphone-based Virtual Reality. EAI Endorsed Trans. Mob. Commun. Appl. 2022, 6, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawde, V.; Kriglstein, S. Mobile Augmented Reality: A Systematic Review of Current Research and the Untapped Potential of Interactive Marker-Based Games. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games, Graz, Austria, 15–18 April 2025; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Game | Game 1 | Game 2 | Game 3 | Game 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XR technologies | AR | AR | AR | AR |
| Input | ||||
| Freehand | x | x | ||
| Touch | x | x | x | |
| Speech | x | |||
| Markers | x | |||
| Spatial proximity | x | |||
| Spatial navigation | x | x | ||
| Gaze | x | |||
| Actions | ||||
| Pointing | x | x | ||
| Selection | x | x | x | |
| Translation | x | x | x | |
| Trigger/keyword | x | |||
| Learning Subject | ||||
| Geography | x | |||
| Foreign Language | x | x | ||
| Cultural heritage | x | |||
| Gamification Elements | ||||
| Points | x | |||
| Levels | x | x | ||
| Rewards | x | x | ||
| Game Mechanics | ||||
| Matching | x | x | x | x |
| Puzzles | x | x | ||
| Storytelling | x | |||
| Quests | x | x | ||
| Mini-games | x | |||
| Educational Theories | ||||
| Revised Bloom Taxonomy | x | x | x | x |
| Learning Styles | x | |||
| Multimodal learning | x | x | x | x |
| Blended Learning | x | x | ||
| Flipped classroom | x | |||
| Game-based Learning | x | |||
| 21st-century skills | x | x | x | x |
| Cognitive theory | x | |||
| Flow theory | x | |||
| Interaction Techniques | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Hand | natural, immersive, encourages movement | sensitive to lighting conditions, less precise, physically demanding |
| Touch | familiar, precise, easy to use | less immersive, less engaging |
| Voice | hands-free, accessible | needs a quiet environment, difficulties in pronunciation |
| Gaze | fast, hands-free (possible if HMDs) | potential accuracy issues |
| Markers | tangible, enhances storytelling | requires physical preparation, less flexible |
| Spatial proximity | easier placement, improves feedback | may reduce precision if tolerance is too high |
| Spatial navigation | promotes movement, spatial awareness, supports embodied learning | needs physical space, may limit accessibility |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Logothetis, I.; Chatzea, V.E.; Katsaris, I.; Papadakis, A.; Kontoulis, V.; Pirpiris, D.; Sfyrakis, M.; Stamatakis, A.; Vidakis, N. Evaluating Interaction Techniques in XR Environments Through the Prism of Four EduGames. Information 2025, 16, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070572
Logothetis I, Chatzea VE, Katsaris I, Papadakis A, Kontoulis V, Pirpiris D, Sfyrakis M, Stamatakis A, Vidakis N. Evaluating Interaction Techniques in XR Environments Through the Prism of Four EduGames. Information. 2025; 16(7):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070572
Chicago/Turabian StyleLogothetis, Ilias, Vasiliki Eirini Chatzea, Iraklis Katsaris, Alexandros Papadakis, Vasileios Kontoulis, Dimitris Pirpiris, Myron Sfyrakis, Antonios Stamatakis, and Nikolaos Vidakis. 2025. "Evaluating Interaction Techniques in XR Environments Through the Prism of Four EduGames" Information 16, no. 7: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070572
APA StyleLogothetis, I., Chatzea, V. E., Katsaris, I., Papadakis, A., Kontoulis, V., Pirpiris, D., Sfyrakis, M., Stamatakis, A., & Vidakis, N. (2025). Evaluating Interaction Techniques in XR Environments Through the Prism of Four EduGames. Information, 16(7), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070572









