Abstract
The rapid development of mobile Internet technology has brought about the flourishing growth of social media live streaming. This study employs social presence theory as the primary framework to investigate the impact of Facebook Live’s features of sociality, immediacy, and entertainment on users’ sense of presence. These features were then considered within the dimensions of awareness, emotion, and cognition. The influence of social presence on user engagement behaviors was divided into browsing behavior, interactive behavior, and creative behavior. Using snowball sampling, an online survey was administered to Facebook Live users, and 416 valid responses were collected. The research team used software to analyze the data, primarily encompassing descriptive statistics, reliability and validity analyses, structural equation modeling, and mediation effects testing. The research findings are as follows. First, the media characteristics of Facebook Live significantly influence the sense of presence. Specifically, sociality, immediacy, and entertainment on Facebook Live have a notable impact on users’ awareness, emotion, and cognition. Second, different dimensions of social presence have distinct effects on various user engagement behaviors. Notably, the dimensions of awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence positively affect users’ browsing and interactive behaviors, while emotion influences users’ creative behavior. The third finding was that awareness, emotion, and cognition act as intermediates between Facebook Live’s media characteristics and user engagement behaviors. Implications are discussed.
1. Introduction
With the widespread adoption of 4G networks, the development of 5G technology, the improvement of basic mobile communication infrastructure, and the reduction in mobile tariffs, the information ecosystem of the Internet era is seeing significant advancement. This has fostered the emergence of numerous media formats, with one of the most notable being live streaming. With the rise of numerous live-streaming platforms, a “triopoly” situation has formed among global live-streaming platforms, including Facebook Live, the Periscope application acquired by Twitter, and YouTube Live. Among these, nearly 80% of the audience watches live videos through the Facebook platform [1]. Due to its leading role in live streaming, Facebook Live serves as the primary research entity for this study.
In the academic community, social media live streaming has garnered attention from scholars who have primarily focused on media scenes, uses, and gratifications theories, but the scholarship has not revisited users’ perceived sense of presence. Initially rooted in sociology, the sense of presence has been regarded as a key design principle for media attributes and communication systems, particularly in the context of computer-mediated communication [2]. Variations in the sense of presence also exist across different media platforms. With technological advancements and further theoretical developments, there is potential for applying and extending the sense of presence theory. For example, social media scholars have studied the sense of presence in e-commerce and short videos. But research that specifically focuses on the sense of presence in the context of social media live-streaming platforms remains scarce.
This study recognizes the sense of presence as a critical theoretical framework for understanding user behavior in social media live streaming and investigates whether the sense of presence is influenced by the media’s characteristics, and how those attributes, in turn, affect user engagement behavior. Existing research on the sense of presence often treats it either as a dependent variable or an independent variable and explores factors that enhance the sense of presence, such as its impact on user satisfaction, its stickiness, and similar aspects. However, as a psychological state that reflects users’ internal activity, the sense of presence should also be examined as a mediating variable and offer a holistic understanding of how it works.
In summary, this study investigates social media live streaming, via the sense of presence, to better understand users’ participatory behavior in live streaming. Specifically, it focuses on Facebook Live, analyzes the media characteristics inherent to Facebook Live, explores the impact of these variables on users’ sense of presence, and investigates how this sense of presence influences user engagement behavior. This study delves deeply into the platform’s users by investigating the relationship between user engagement behavior and the sense of presence on Facebook Live. This not only extends the scenarios of the sense of presence but also enriches the realm of research related to social media live streaming. It also enables user experience designers to better understand their customers, appropriately guide user engagement behavior, and enhance user stickiness and interaction on the platform.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Media Characteristics of Facebook Live
Johnson et al. [3] asserted that Facebook Live is an information exchange platform characterized by its entertainment, real-time interaction, and social engagement. The application of Facebook Live is user-friendly and straightforward, with a simple requirement of users to only click a button to initiate live streaming and engage with other users. The content on Facebook Live is also diverse, which allows users access based on personal interests. Apart from intriguing live content, Facebook Live also offers various engaging features, such as sending stars to favorite broadcasters, using emoticons in the comments section, and participating in real-time interactions with broadcasters.
Haimson and Tang [4] argued that Facebook Live’s media characteristics—immersion, immediacy, interactivity, and sociality—enhance user experiences. Within the Facebook Live platform, users can communicate with other users through comments, private messages, likes, and shares, which fulfils emotional and social needs during their platform usage. Furthermore, the live videos in Facebook Live are unedited, real-time, and on-site, which provides users with an immersive experience. Facebook Live also allows broadcasters to engage in real-time interactions with the audience during the live broadcast. Once the live stream ends, the Facebook platform automatically publishes the live video to the broadcaster’s page, which facilitates repeated viewing and continued discussions among users.
Based on the considerations mentioned above, the present study utilizes social engagement, immediacy, and entertainment as the measured indicators for media characteristics of Facebook Live. They are defined as follows:
- Social Engagement: Users of the content can comprehend the feedback from other audiences and promptly respond in a targeted manner to facilitate communication.
- Immediacy: Content recipients can promptly receive the intended message of the live content, as all information is collected and presented in real-time synchronization.
- Entertainment: The content is designed to capture the audience’s interest, typically by encompassing two aspects: first, content that is inherently amusing and interesting to the general audience and second, an engaging and vivid expression that captivates the audience with its lively and humorous presentation style.
2.2. Social Presence
Social presence theory is a theoretical framework within the realm of communication studies, particularly at the intersection of technology and society. Proposed by Short et al. [5], the theory defines social presence as the degree to which an individual is perceived as a “real person” and the level of perceived connection with others when engaging in communication through a medium. The scope of social presence continues to expand, and its conceptual framework is progressively enriched and refined. Nevertheless, its core definition consistently revolves around the notions of co-presence, connectedness, and perception. Most scholars concur that social presence primarily describes the psychological state of “being there” in virtual environments. Therefore, within the context of social media live streaming, this study defines social presence as the psychological sense of co-presence and perceived connectedness between users and other participants during their engagement on Facebook Live.
Considering that Facebook Live serves as a social platform encompassing entertainment and communication, its social attributes cannot be overlooked. This study posits that social presence through social media live streaming can influence users, as evidenced in their psychological states, cognitive behaviors, and even perceptual attitudes. Given that this study focuses on the social presence of users on Facebook Live and in order to align with the research needs and the defined concept of social presence, this study adopts the three-dimensional framework proposed by Shen and Khalifa [6]. This framework divides social presence into three levels: awareness, emotions, and cognition. Awareness-based social presence refers to the extent to which users perceive the presence of other users on Facebook Live. Emotional social presence relates to the emotional connections and mutual influence among users during Facebook Live sessions. Cognitive social presence pertains to users’ awareness and understanding of other participants on Facebook Live.
2.3. User Engagement
“User” is a collective term for the widely diverse individuals on the Internet, and different types of users may exhibit distinct engagement behaviors. Chen [6] divided engagement behavior among self-media users into two categories: browsing behavior and creative behavior. The former mainly refers to users taking actions like saving and liking content they enjoy after browsing self-media content, while the latter includes joining fan groups, reposting content, and participating in various online and offline activities, which signifies a proactive exploration and involvement in content-related matters. In the context of mobile social platforms, Dai and Gu [7] indicated that user engagement behavior primarily includes browsing behavior, interactive behavior, and creative behavior. Pang and Yang [8] suggested that user engagement behavior in virtual communities involves various interactive and content-creative actions, including browsing, commenting, reposting, and sharing.
The study of user engagement behavior holds significance for the continuous development of social media live streaming and the enhancement of user experiences. In line with the specific research context of this paper, it draws inspiration from Dai and Gu [7] regarding the measurement of user engagement. Based on actual user behaviors on the platform, this study categorizes user engagement in Facebook Live into three dimensions: browsing behavior, interactive behavior, and creative behavior:
- Browsing Behavior: actions like reading text and watching videos on the platform;
- Interactive Behavior: actions like liking, commenting, sharing, and leaving messages on the live stream;
- Creative Behavior: producing and publishing videos, as well as participating in platform activities.
3. Research Framework and Hypotheses
The S-O-R (Stimulus–Organism–Response) model was initially established in the field of environmental psychology and is commonly used to explain the influence of various environmental stimuli on an individual’s intrinsic cognition, consciousness, and emotions and, thereby, their behavioral responses [9]. This model posits that the environment does not directly impact an individual’s behavior; rather, it indirectly affects behavior by stimulating an individual’s psychological processes. A complete S-O-R model comprises three fundamental components: stimulus variables, organism variables, and response variables. Stimulus refers to various elements that influence an individual and can evoke intrinsic psychological reactions, encompassing various external environmental factors. Organism primarily refers to the psychological state in which individuals experience emotions and cognition. In the S-O-R model, organism variables act as an intermediary between stimulus variables and response variables, often by occupying the position of a mediating variable. Response pertains to the internal or external behaviors exhibited by an individual in response to the influencing stimulus factors. Intrinsic responses often manifest as individual attitudes, while extrinsic responses are observed in an individual’s behaviors (Figure 1).
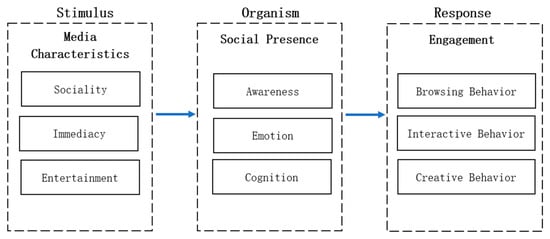
Figure 1.
Research model.
Based on the S-O-R model, this research considers the media features of social media live streaming as stimuli that evoke users’ intrinsic cognition and emotions and, thereby, influence their behavioral responses. Specifically, stimuli represent the media features created by Facebook Live; organism represents users’ perceived psychological state or subjective feelings, in this study referred to as social presence; and response represents users’ participation behavior. This study investigates the impact of Facebook Live’s media features as independent variables on three different dimensions of social presence. It further explores social presence as a mediating variable, while user engagement serves as the dependent variable. The study examines whether varying degrees of social presence influence user participation behavior.
Based on the relevant variables in this research, the proposed hypotheses are as follows:
H1.
The sociality, immediacy, and entertaining features of Facebook Live positively influence the awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence.
H2.
The awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence positively influence user browsing, interactive, and creative behavior.
H3.
Social presence mediates the effects of media features on user engagement.
4. Research Method
This study employed an online questionnaire survey to investigate the relationship among media characteristics, social presence, and user engagement in Facebook Live. The study used cross-sectional data rather than longitudinal data, mainly because the participants in this study were already users of Facebook Live. Due to the fact that the study population is not first-time users of Facebook Live, longitudinal data are not very valuable because changes in users’ social presence, engagement behaviors, or perceptions over time cannot be scientifically manipulated and examined.
4.1. Scale Design and Questionnaire Structure
Drawing upon relevant literature and considering the specific context of Facebook Live, this study established the variables under investigation. Table 1 presents the specific design of the scale items.

Table 1.
The design of measurement scales.
Afterward, this study designed a survey questionnaire using 7-point Likert scales ranging from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree” for measurement. The questionnaire consists of three parts:
- The first part includes an introduction and concept explanations. The introduction details the purpose of the survey to provide participants with an initial understanding, reduce concerns, and thus encourage participation. The concept explanations are provided to ensure that participants have a clear understanding of the terms and concepts used in the questionnaire.
- The second part focuses on collecting basic demographic information about participants, including gender, age, education level, occupation, and more, to serve as control variables. Additionally, information about participants’ current usage of Facebook Live was collected. The data were used to assess the demographic characteristics of the surveyed users to enhance the accuracy and generalizability of the sample.
- The third part comprises measurement items related to the variables, including media characteristics of Facebook Live, social presence, and user engagement. The selection of items was based on prior research literature and the analyses of the research objects.
In order to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of the questionnaire and to prevent significant biases during the formal research, this study conducted a pilot study with a small sample size. Initially, the questionnaire was distributed to users who had previously used Facebook Live through an online survey platform in order to assess their comprehension of the questionnaire items. During this process, a total of 151 valid questionnaires were collected. Subsequently, based on participants’ feedback, modifications were made to address issues and other concerns in the questionnaire items. For example, a questionnaire item was revised from “the Facebook Live platform allows me and other users to follow each other” to “the Facebook Live platform allows me and other users to follow each other and expand my network of relationships” due to its incomplete scenario description. Lastly, the collected valid questionnaires from the pilot study were analyzed to assess reliability and construct validity, all of which led to the creation of the final version of the questionnaire for the main study.
Reliability analysis assesses the stability and consistency of various items within a variable in a questionnaire, which provides a measure of the instrument’s internal consistency and reliability [14]. As shown in Table 2, the Cronbach’s α coefficients for all variables are above 0.7, which suggests the questionnaire’s reliability is at a good level.

Table 2.
Pilot questionnaire’s reliability analysis.
In the pilot study of this research, the validity of the questionnaire’s indicators was explored through the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) test and Bartlett’s test of sphericity. For Bartlett’s test, if p < 0.05, the null hypothesis is rejected, which indicates that factor analysis can be performed. As given in Table 3, the KMO values are all above 0.7, a suitable level for factor analysis. Additionally, the result of Bartlett’s test of sphericity shows significant p-values of 0.000 ***, which indicates that the data are suitable for factor analysis [15] (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Pilot questionnaire’s validity analysis.
4.2. Data Collection
After the pilot study, the questionnaire was distributed through online survey platforms and collected data using a snowball sampling technique that targeted users who had used or are currently using Facebook Live for broadcasting and ensured the questionnaire reached users from various educational backgrounds, age groups, and professional levels. To ensure data quality and reliability, the study analyzed the completion rate of the survey and considered any surveys with partially missing responses as invalid. Furthermore, the research monitored specific response patterns to eliminate random responses. If respondents uniformly provided identical ratings for all questions, their surveys were also deemed invalid. In total, 430 surveys were collected, of which 416 were considered valid. This resulted in an effective response rate of 96.74%. The collected data were analyzed using IBM SPSS to determine the distribution of samples and assess the validity of the research objects.
5. Results
To ensure the explanatory power of the research model concerning users’ social presence and engagement behavior, this study conducted reliability and validity analyses on the measurement variables of the conceptual model.
5.1. Reliability and Validity Analyses
Following the optimization of certain items affecting questionnaire reliability during the pilot testing phase, this study continued to use Cronbach’s α coefficient to assess the reliability of the formal survey. Table 4 shows that the Cronbach’s α coefficients of each variable are all greater than 0.7. This indicates that the scales meet the requirement for reliability and are ready for the next stage of analysis.

Table 4.
Reliabilities of measured variables.
After conducting the reliability analysis on the valid samples, a validity analysis was carried out to assess whether each item accurately reflected the latent variables. The convergent validity analysis presented in Table 5 reveals that the factor loading coefficients of each item are all above 0.7, composite reliability (CR) values exceed 0.7, and the average variance extracted (AVE) values are also greater than 0.5. This suggests that all the data meet the criteria, and the convergent validity of the scale is ideal [16].

Table 5.
Convergent validity.
In terms of discriminant validity, if the square root of the average variance extracted (AVE) of a variable is greater than the correlation coefficient values with other variables, it indicates that the variable possesses good discriminant validity. In the analysis below, the diagonal values represent the square root of AVE, and the series of values below the diagonal are the Pearson correlation coefficients between variables. It can be observed that the Pearson correlation coefficients between variables are all smaller than the square roots of AVE for each variable, and the square roots of AVE are greater than 0.7. This indicates that there is good discriminant validity among the variables [16] (see Table 6).

Table 6.
Discriminant validity.
5.2. Structural Equation Modeling and Hypotheses Testing
Structural equation modeling is a statistical method based on the covariance matrix of variables to analyze the relationships between variables. It serves as a crucial tool in multivariate data analysis. This study used SPSSAU to create the model.
Building upon reliability and validity analyses, this study proceeded to assess the model fit. As indicated in Table 7, the χ2/df is less than 3 and RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error of Approximation) is less than 0.08. The GFI (Goodness-of-Fit Index), NFI (Normed Fit Index), NNFI (Non-Normed Fit Index), CFI (Comparative Fit Index), and IFI (Incremental Fit Index) all exceed 0.8, which falls within an acceptable range. This implies that the variables in this study meet the criteria for model fit [17].

Table 7.
Model fit examination.
Given the acceptable model fit of the variables, this study proceeded to test the hypotheses within the model. The determination of the validity of the hypothesis testing in this study relies on the path coefficients and p-values within the model. The non-standardized coefficients (Estimates) indicate the degree of influence of independent variables on the dependent variable. A positive value suggests a positive effect, while a negative value indicates a negative effect. p-value represents the significance level. In this study, the threshold for significance is set at p < 0.10. Therefore, if the p-value is less than 0.10, it indicates a significant correlation between variables.
As shown in Table 8, the path coefficients between variables in this study are mostly positive, with the exception of the paths between “Awareness of Social Presence” and “Creative Behavior” and between “Cognitive Social Presence” and “Creative Behavior,” where the p-values exceed 0.10. For the remaining paths, the p-values are less than 0.10. Notably, variables like “Sociality”, “ Immediacy”, and “Entertainment” have significant positive effects on the awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence. Regarding the relationship between social presence and user engagement, awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence have a significant impact on user browsing behavior. This implies that a stronger social presence corresponds to more pronounced browsing behavior. The awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence also positively influence user interactive behavior. Emotion positively influences creative behavior, but awareness and cognition do not impact creative behavior.

Table 8.
Path coefficients and hypotheses testing.
5.3. Mediation Effects Testing
The mediation effect model analyzes the process and mechanisms through which the independent variable influences the dependent variable. This study follows the mediation effect testing method proposed by Wen et al. [18]. The independent variable is denoted as X, the dependent variable as Y, and M is the mediator variable. The mediation effect is tested through three successive regression equations as follows:
- (a)
- Y = cX + e1: This equation represents the extent to which the independent variable explains the dependent variable. Here, c is the coefficient to be tested. If this coefficient is not significant, it indicates the absence of a mediation effect, and the testing is stopped. If significant, the testing proceeds to the next step.
- (b)
- M = aX + e2: This equation represents the extent to which the independent variable explains the mediator variable. Similarly, a is the coefficient to be tested. If this coefficient is not significant, it implies the absence of a mediation effect, and the testing is halted. If significant, the testing proceeds to the next step.
- (c)
- Y = c′X + bM + e3: This equation represents the combined effect of the independent variable and the mediator variable on the dependent variable. The coefficients in this regression equation are tested for significance.
In the above process, it is typically assumed that there is a significant effect between the independent and dependent variables. However, some scholars argue that in certain situations, a mediation effect might still exist even if c is not significant [19]. Therefore, this study employed the Bootstrap method to revalidate the mediation effect and mitigate the situations in which the c coefficient is not significant or when the assumption of normal distribution is not met, which enhances statistical power. The Bootstrap method involves repeatedly sampling from the original dataset, treating the original sample as the sampling population, and drawing samples with replacements to obtain similar data to the original [18]. The obtained Bootstrap samples are then analyzed to generate a set of estimates. These estimates form a distribution that can be sorted, and a 95% confidence interval is established. The upper limit of the interval is the 97.5th percentile-based coefficient product estimate, while the lower limit is the 2.5th percentile-based coefficient product estimate. In this method, a significant mediation effect is indicated when the confidence interval of the coefficient product estimate does not include 0; if it includes 0, the mediation effect is deemed insignificant.
5.3.1. The Mediation Effects of Awareness of Social Presence
As indicated in Table 9, when using “Sociality”, “Immediacy”, and “Entertainment” as independent variables, user browsing as the dependent variable, and introducing “Awareness of Social Presence” as a mediator, all the confidence intervals of the coefficient estimates do not include 0. This implies that “Awareness of Social Presence” has mediation effects between these independent variables and the dependent variable. Similarly, for user interactive behavior, the confidence intervals also exclude 0, which indicates significant mediation effects of “Awareness of Social Presence”. For “Immediacy”, using “Awareness of Social Presence” as a mediator and browsing behavior and interactive behavior as dependent variables, the confidence intervals also exclude 0, which suggests mediation effects of “Awareness of Social Presence”. However, for “Immediacy” and creative behavior, the confidence interval (−0.102, 0.123) includes 0, which indicates that a mediation effect of “Awareness of Social Presence” does not exist between these variables.

Table 9.
The mediation effects of awareness of social presence.
5.3.2. The Mediation Effects of Emotional Social Presence
According to Table 10, when using “Sociality”, “Immediacy”, and “Entertainment” as independent variables and browsing behavior, interactive behavior, and creative behavior as dependent variables, all the confidence intervals of the coefficient estimates do not include 0. This suggests that “Emotional Social Presence” exhibits mediation effects between these independent variables and the dependent variables.

Table 10.
The mediation effects of emotional social presence.
5.3.3. The Mediation Effects of Cognitive Social Presence
As indicated in Table 11, when considering “Sociality”, “Immediacy”, and “Entertainment” of Facebook Live as independent variables and user browsing behavior and interactive behavior as dependent variables, introducing “Cognitive Social Presence” as a mediator leads to all confidence intervals of the coefficient estimates that do not include 0. This suggests that “Cognitive Social Presence” has mediation effects between these independent variables and the dependent variables. Similarly, when “Cognitive Social Presence” is considered a mediator between creative behavior and “Immediacy” and “Entertainment”, the confidence interval again excludes 0, which indicates the mediation effects of “Cognitive Social Presence” between these variables. However, when “Cognitive Social Presence” acts as a mediator between creative behavior and “Sociality” as an independent variable, the confidence interval (−0.100, 0.067) includes 0, which demonstrates the lack of a significant mediation effect of cognitive social presence in this case.

Table 11.
The mediation effects of cognitive social presence.
6. Conclusion and Future Research
This study, focused on the context of Facebook Live, examined the impact of the media attributes of Facebook Live—sociality, immediacy, and entertainment—on different dimensions of social presence. It also investigated how these dimensions of social presence influence user engagement, including browsing, interactive, and creative behaviors. The specific conclusions of this study are as follows.
6.1. The Impact of Media Attributes on Social Presence
The study findings reveal that the sociality of Facebook Live significantly positively influences users’ awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence. This conclusion aligns with the initial research hypotheses. Sociality facilitates interactions between users and live broadcasters or other users and fosters connections. The immersive nature of Facebook Live allows for quick and natural interaction, as well as a perception of the presence of other users. Users can engage by liking, sharing, commenting, and using emojis when they encounter interesting content. Even after the live broadcast ends, users can maintain connections and interactions through private messages and mutual following in ways that nurture social relationships and emotions. Interaction and communication enable users to understand and know each other better, which fosters deeper connections.
The immediacy of Facebook Live also significantly influences users’ awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence positively. These results support the hypotheses proposed earlier. Due to the user-friendly nature of Facebook Live, people from various backgrounds can easily share real-time experiences with their audience by hitting the “Go Live” button. Unlike traditional media, Facebook Live broadcasts offer users an immersive experience because they are unedited and uncut. Both live broadcasters and users feel like they are engaging in a face-to-face conversation. This immediacy helps users become aware of the presence of others, which enhances emotional connections and cognition among users.
Furthermore, the entertaining aspect of Facebook Live has a significant positive influence on users’ awareness, emotion, and cognition of social presence. The platform offers diverse and captivating content spanning topics, such as gaming, e-commerce, sports, and education. Facebook Live’s entertaining features, such as sending emojis and sharing content, allow users to experience pleasure and emotion in a way that facilitates the establishment of social relationships. In this process, Facebook Live triggers the generation of users’ social presence across awareness, emotion, and cognition.
In summary, the sociality, immediacy, and entertainment of Facebook Live all have significant positive effects on users’ dimensions of social presence—awareness, emotion, and cognition. This study supports the research hypotheses put forth earlier concerning the relationship between Facebook Live media attributes and social presence.
6.2. The Influence of Different Dimensions of Social Presence on User Engagement
The results indicate that social presence in the dimensions of awareness, emotion, and cognition significantly positively influences user browsing behavior. Drawing on the theory of use and gratification, Facebook Live’s social presence fulfils users’ perceptual needs and enables them to experience interactions as if they were face-to-face. Simultaneously, it satisfies users’ emotional values and enhances their cognitive awareness of themselves and popular trends on social media platforms. When these needs are met, users certainly become more inclined to browse content on Facebook Live and invest more time and energy.
Moreover, social presence in the dimensions of awareness, emotion, and cognition also significantly influences users’ interactive behavior. User interactive behavior on Facebook Live includes actions like liking, commenting, messaging, and sharing. As users engage with Facebook Live, they become aware of the presence of other users and establish emotional connections and mutual understanding, which in turn fosters more profound interactive behaviors on the platform. When users perceive value from social presence across different dimensions while using Facebook Live, they become more willing to interact and engage. This observation is consistent with the research hypotheses initially proposed in this study.
Interestingly, the emotional dimension of social presence significantly influences users’ creative behavior. Unexpectedly, the awareness and cognition of social presence do not have a significant impact on users’ creative behavior. This result contradicts the initial research hypotheses. This discrepancy might be attributed to the possibility that creative behavior does not necessarily require the activation of awareness or cognitive social presence. Instead, users may engage in creative behavior simply when they experience pleasant emotions while using the medium. The specific reasons behind this outcome warrant further exploration.
6.3. The Mediation Effect of Social Presence
Based on the results of the mediation analysis, it was found that among the three dimensions of social presence, the awareness dimension mediated the effects of both sociality and entertainment on browsing behavior, interactive behavior, and creative behavior. Awareness mediated the effects of immediacy on browsing and interactive behavior but not on creative behavior. This could be attributed to the fact that the extent to which users perceive the presence of other users on Facebook Live satisfies users’ activities like browsing and interactive behavior on the platform, whereas some aspects of creative behavior are less demanding in terms of sensing the presence of others.
Emotional social presence represents the emotional connections and resonances formed among users. The sociality, immediacy, and entertainment of Facebook Live influence users’ browsing, interactive, and creative behavior through emotional social presence. This indicates that users experience pleasure and emotion from Facebook Live’s media characteristics, which subsequently motivates them to engage and participate more on the platform. This highlights the significance of emotional social presence in facilitating user engagement.
Cognitive social presence represents the process of understanding among users. When introducing cognitive social presence as a mediating variable along with the media characteristics, it was found that cognitive social presence mediated the effects of immediacy and entertainment of Facebook Live on browsing and interactive behavior. However, the effect of cognitive social presence did not mediate the effect of social aspects on creative behavior. While existing literature suggests that cognitive social presence could enhance user engagement through platform usage [20], this study found that cognitive social presence did not significantly impact users’ creative behavior, and its mediation effect was not significant. This implies that users’ creative behavior might not necessarily require cognitive social presence to be activated.
In conclusion, the results of this study suggest that emotional social presence plays the most significant mediating role between the media characteristics of Facebook Live and user engagement behavior. Meanwhile, the mediation effects of awareness and cognitive social presence on user engagement behavior are limited to browsing and interactive behavior.
6.4. Contributions and Implications
This study confirms the relationship between the media characteristics of Facebook Live and user engagement, while also exploring the mediating role of social presence. The generalizability of the results of this study is not limited to Facebook Live but can also be applied to other similar platforms, such as Periscope and YouTube Live. The media characteristics of Facebook Live examined in this study, such as sociality, immediacy, and entertainment, are common characteristics among various platforms. Based on the research findings mentioned earlier, the following recommendations and implications are suggested.
- Emphasizing the platform value and optimizing its media characteristics: As indicated by the study, sociality, immediacy, and entertainment are important factors influencing user social presence and engagement behavior. Therefore, operators of the platform should invest more in enhancing its media characteristics. In terms of sociality, regular large-scale online or offline fan events could be organized and invite well-known live broadcasters to participate. Through such activities, more opportunities for interaction could be created, which would allow for a better understanding of user thoughts and preferences, enhance users’ sense of belonging and identification, and ultimately boost engagement behavior. Additionally, the platform’s operators should enhance the technical capabilities to enable more interactive real-time features, such as allowing users to apply for co-broadcasting with live broadcasters. Regarding the aspect of entertainment, operators need to focus on catering to users’ entertainment and relaxation needs. For example, platforms should provide users with flexible and dynamically entertaining sections based on social trends to expand platform content and encourage actual user engagement.
- Focusing on enhancing users’ social presence and optimizing the platform from the perspective of improving social presence: As evident from the previous discussions, the media characteristics positively influence user engagement through social presence. Therefore, platforms should prioritize social presence that simulates face-to-face communication. On the one hand, presenting users with a more convenient, vivid, personified, and immersive platform—such as exquisite interfaces, the use of virtual reality technology, and the presentation of 3D visual effects—can contribute to the formation of users’ sense of presence and enable them to feel as if they are engaging in face-to-face communication. On the other hand, the platform should provide a relaxed online environment for communication among users to create a pleasant and social-media-friendly atmosphere. Features like bullet comments and virtual gifts could be introduced to compensate for the emotional absence in the virtual environment. Establishing users’ social presence is no longer solely a technological challenge; it has become an indispensable aspect that platform operators need to closely address in their development.
6.5. Limitations and Future Research
Like other studies, this study has its limitations. First, empirical results may be affected by self-report data because study participants may suffer from memory errors. Other data collection methods, such as biological indices, could be used in future studies. Second, other social factors, such as social norms and peer pressure, may also be related to the variables examined in this study. Future research could consider developing an original live-streaming platform and employing laboratory studies. Third, this study uses the S-O-R model as the research framework to examine social presence as a mediating factor. However, other potential mediating factors, such as user demographics or usage patterns, deserve further exploration. Fourth, future research may consider other research methods, such as qualitative interviews and focus groups, to gather more in-depth information related to this topic. Studies may also consider conducting longitudinal studies to examine the relationships of variables over time. Furthermore, our findings warrant further exploration in the context of different cultural and demographic contexts. As social media and new media develop very rapidly, future research needs to examine how new media characteristics might affect the results of this study. Last, this study used snowball sampling because of the ease and feasibility of data collection since not everyone is an active user of Facebook Live. Future research may consider other sampling methods to prevent potential bias from snowball sampling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L.; methodology, Y.L.; formal analysis, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.; writing—review and editing, C.-W.C.; supervision, C.-W.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This article was subsidized by the National Taiwan Normal University (NTNU), Taiwan, ROC.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mao, Y. Enlightenment of Facebook Live+ Model to Domestic Online Live Broadcasting. China Media Sci. 2017, 5, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Biocca, F.; Harms, C.; Gregg, J. The networked minds measure of social presence: Pilot test of the factor structure and concurrent validity. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual International Workshop on Presence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 21–23 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.T.; Thomas, R.B.; Fishman, E.K. Facebook Live: A free real-time interactive information platform. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2018, 15, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimson, O.L.; Tang, J.C. What makes live events engaging on Facebook Live, Periscope, and Snapchat. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Short, J.; Williams, E.; Christie, B. The Social Psychology of Telecommunications; Wiley: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.M. Study on the Use Behavior and Satisfaction of Fashion Self-Media Users. Master’s Thesis, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, D.B.; Gu, X.H. User Participation Behavior, Perceived Value, and Loyalty: An Analysis Based on Mobile Short Video Social Application. Consum. Econ. 2017, 33, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L.J.; Yang, Z. Influence of Information Interaction on User Participation Behavior in Virtual Brand Community. Inf. Stud. Theory Appl. 2021, 41, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J.A. An Approach to Environmental Psychology; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, L. Research on Influencing Factors of Bilibili User Participation Behavior Based on SOR Model. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, Kunming, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.J.; Jiang, X.Y.; Ni, R.R.; Dong, X.B. Impact of Interaction and Entertainment on Impulse Purchase Intention in Livestreaming. J. Syst. Manag. 2020, 29, 294–307. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.K.; Choi, H.J. Broadcasting upon a shooting star: Investigating the success of Afreeca TV’s livestream personal broadcast model. Int. J. Web Based Communities 2017, 13, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, S. Mechanism of Interaction and Entertainment Impact on Impulse Purchase Intention in Shopping Livestream. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on E-Commerce, E-Business and E-Government, Plymouth, UK, 27–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, P.; Priest, H. Reliability and validity in research. Nurs. Stand. 2006, 20, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, L.S.; Gamst, G.; Guarino, A.J. Applied Multivariate Research: Design and Interpretation; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, J.P.; Verma, P. Understanding Structural Equation Modeling: A Manual for Researchers; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Subudhi, R.N.; Mishra, S. (Eds.) Methodological Issues in Management Research: Advances, Challenges, and the Way ahead; Emerald Publishing Limited: Leeds, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Hou, J.T.; Liu, H.Y. Mediating Effect Test Procedure and Its Application. Biotechnol. World 2004, 2014, 216. [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon, D.P.; Krull, J.L.; Lockwood, C.M. Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect. Prev. Sci. 2000, 1, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.Q. Research on User Participation Behavior of Mobile Short Video Based on Social Presence Theory. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, Kunming, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).