An Explainable Fake News Detector Based on Named Entity Recognition and Stance Classification Applied to COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Dataset
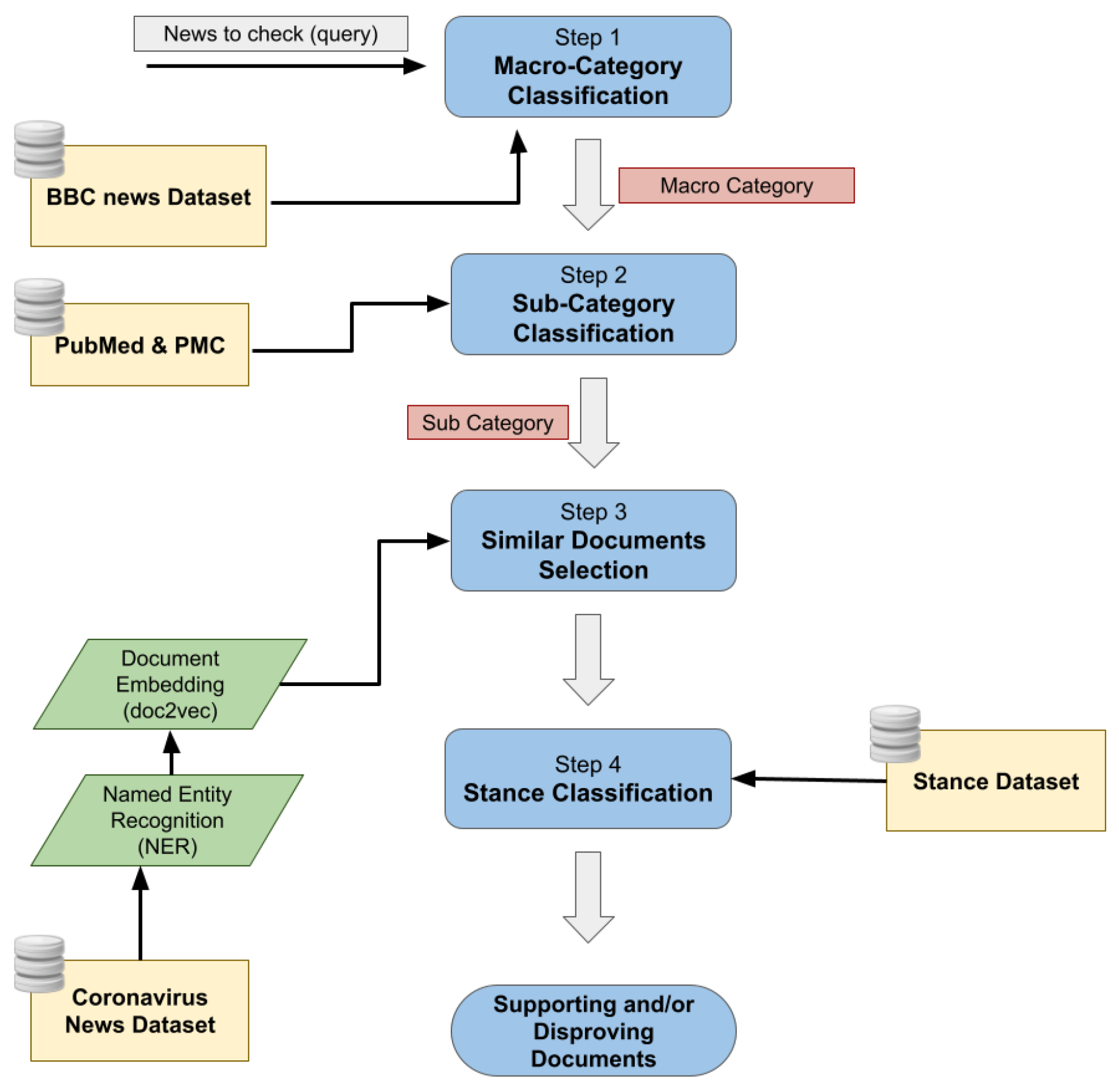
4. Method
4.1. Query Classification
4.2. Named Entity Recognition
4.3. Similar Documents Selection
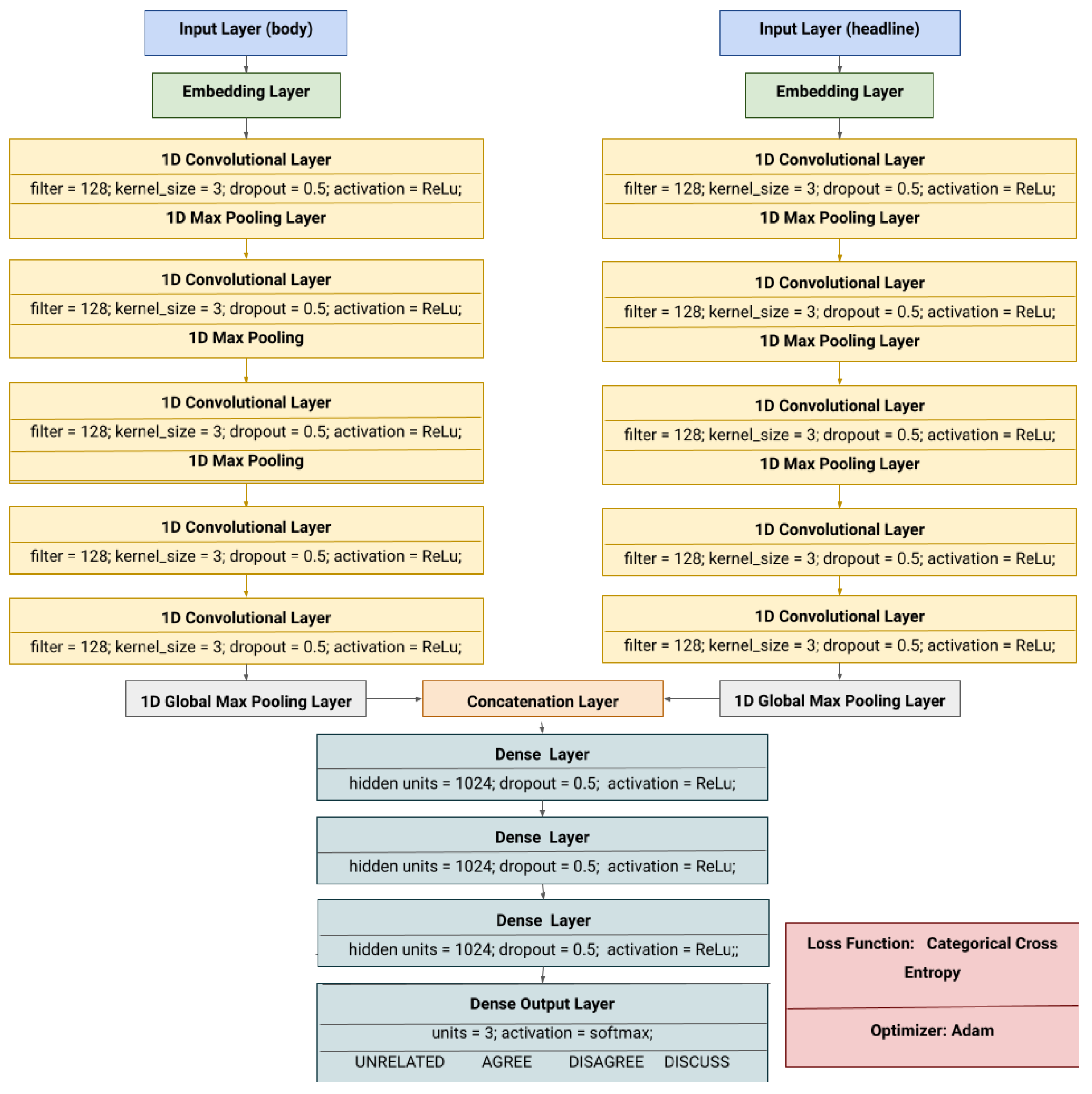
4.4. Stance Classification
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allcott, H.; Gentzkow, M. Social media and fake news in the 2016 election. J. Econ. Perspect. 2017, 31, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelfert, A. Fake news: A definition. Informal Log. 2018, 38, 84–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallè, F.; Veshi, A.; Sabella, E.A.; Çitozi, M.; Da Molin, G.; Ferracuti, S.; Liguori, G.; Orsi, G.B.; Napoli, C.; Napoli, C. Awareness and Behaviors Regarding COVID-19 among Albanian Undergraduates. Behav. Sci. 2021, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, D.; Stefik, M.; Choi, J.; Miller, T.; Stumpf, S.; Yang, G.Z. XAI—Explainable artificial intelligence. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaay7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oshikawa, R.; Qian, J.; Wang, W.Y. A survey on natural language processing for fake news detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.00770. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.Y. “ liar, liar pants on fire”: A new benchmark dataset for fake news detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.00648. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y. Fake news detection through multi-perspective speaker profiles. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 2: Short Papers), Taipei, Taiwan, 27 November–1 December 2017; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.T. A Study on Deep Learning for Fake News Detection. 2018. Available online: https://dspace.jaist.ac.jp/dspace/bitstream/10119/15196/3/paper.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Sliva, A.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Fake news detection on social media: A data mining perspective. ACM Sigkdd Explor. Newsl. 2017, 19, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, N.K.; Rubin, V.L.; Chen, Y. Automatic deception detection: Methods for finding fake news. Proc. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dungs, S.; Aker, A.; Fuhr, N.; Bontcheva, K. Can rumour stance alone predict veracity? In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; pp. 3360–3370. [Google Scholar]
- Tacchini, E.; Ballarin, G.; Della Vedova, M.L.; Moret, S.; de Alfaro, L. Some like it hoax: Automated fake news detection in social networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.07506. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Zhao, P.; Han, J. Evaluating event credibility on twitter. In Proceedings of the 2012 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, California, CA, USA, 25 January 2012; pp. 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Cao, J.; Jiang, Y.G.; Zhang, Y. News credibility evaluation on microblog with a hierarchical propagation model. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Shenzhen, China, 14–17 December 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 230–239. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J. News verification by exploiting conflicting social viewpoints in microblogs. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Cui, L.; Wang, S.; Lee, D.; Liu, H. Defend: Explainable fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, W.; Vlachos, A. Emergent: A novel data-set for stance classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016; pp. 1163–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Yufeng. BBC Articles Fulltext and Category. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/yufengdev/bbc-fulltext-and-category/code (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Byron Galbraith, D.R. Fake News Challenge FNC-1. Available online: http://www.fakenewschallenge.org/ (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble methods in machine learning. In International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sun, A.; Han, J.; Li, C. A survey on deep learning for named entity recognition. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; So, C.H.; Kang, J. BioBERT: A pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.; Mikolov, T. Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Bejing, China, 2–24 June 2014; pp. 1188–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, J.H.; Baldwin, T. An empirical evaluation of doc2vec with practical insights into document embedding generation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.05368. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A.M.; Olah, C.; Le, Q.V. Document embedding with paragraph vectors. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1507.07998. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, G.; Chitturi, B.; Poornachandran, P. Stance-in-depth deep neural approach to stance classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification. arXiv 2014, arXiv:cs.CL/1408.5882. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, T. pkudblab at SemEval-2016 Task 6: A Specific Convolutional Neural Network System for Effective Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2016), San Diego, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2016; Association for Computational Linguistics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julio, A.; Saenz, S.R.K.G.; Shukla, D. CoVID-19 Fake News Infodemic Research (CoVID19-FNIR) Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/open-access/covid-19-fake-news-infodemic-research-dataset-covid19-fnir-dataset (accessed on 4 January 2022).

| SVM | KNN | RF | NB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macro-category classification Precision | ||||
| Business | ||||
| Entertainment | ||||
| Medicine | ||||
| Politics | ||||
| Sports | ||||
| Tech | ||||
| Sub-category classification Precision | ||||
| Bones Diseases | ||||
| Cancer | ||||
| COVID-19 | ||||
| Depression | ||||
| Heart Diseases | ||||
| Hepatitis | ||||
| Nutrition Diseases | ||||
| STDs | ||||
| Query | |
|---|---|
| the indian embassy in tokyo has said that one more indian crew member on Diamond Princess has tested positive for covid | |
| Similar Documents | |
| Similarity | Text |
| 0.64 | 3rd indian tests positive for coronavirus on ship off coast Japan the indian embassy in Tokyo has said that one more indian crew member on Diamond Princess, the ship stranded off coast Japan, has tested positive for COVID-19. The person has been hospitalized for treatment […] |
| 0.60 | Four Indian crew members, who underwent tests for the coronavirus along with others still on board the cruise ship moored off the Japan coast, have tested positive for COVID-19, taking the total number of Indians infected with the virus on the vessel to 12, the Indian embassy said on Sunday. Passengers showing no signs of the deadly disease started deboarding the ship, Diamond Princess, after the quarantine period ended last week. |
| 0.58 | One more indian has been tested positive for the novel coronavirus disease. Covid on the quarantined cruise ship diamond princess off the japanese coast. The Indian embassy in Japan confirmed on friday this is the third confirmed case of indian nationals testing positive for the deadly coronavirus which has claimed lives of over […] |
| Example 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Query (ground = fake) | |||
| coronavirus has been found in broiler chicken | |||
| Explanation | |||
| Similarity | Stance | Text | url |
| 0.54 | Disagree | The Poultry Farm Association on Saturday organized this Chicken Mela to dispel rumours that the bird is a carrier of Coronavirus. Vineet Singh, president of the Poultry Farm Association said that people had stopped eating chicken since the past one month, due to fear of Coronavirus. “We organized this Mela where we invited people to eat chicken. We wanted to tell them that Coronavirus is not caused by eating chicken, mutton or fish. We cooked over a thousand kilograms of chicken for the Mela and the entire stock was finished”, he said. The Chicken Mela, held in front of the Gorakhpur railway station, proved to be a major crowd puller and left all roads leading to the railway station blocked for hours. | https://www.news18.com/news/india/free-chicken-mela-to-dispel-coronavirus-rumours-in-ups-gorakhpur-2520867.html (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
| 0.54 | Disagree | A full plate of chicken dishes for Rs 30 may sound unbelievable but it was a dream come true for chicken lovers in Gorakhpur. The Poultry Farm Association on Saturday organized this Chicken Mela to dispel rumours that the bird is a carrier of Coronavirus. Vineet Singh, president of the Poultry Farm Association said that people had stopped eating chicken since the past one month, due to fear of Coronavirus. “We organized this Mela where we invited people to eat chicken. We wanted to tell them that Coronavirus is not caused by eating chicken, mutton or fish. We cooked over a thousand kilograms of chicken for the Mela and the entire stock was finished”, he said. | https://www.hindustantimes.com/it-s-viral/gorakhpur-organizes-free-chicken-mela-to-shatter-coronavirus-myths/story-rtsaf0G5GvSmgopGjjLC9K.html (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
| 0.50 | Discuss | Coronavirus is reported to have started from Wuhan, China and in the wet markets where people come every day to shop for meats. In these markets, people sell and buy all kinds of meats—chicken, seafood, mutton, sheep, pig and even snakes. Because of this very reason, people in India are doubting if they should eat seafood. To put a rest to this confusion, it has been said that its safe to eat seafood in India as no such link between sea animals and coronavirus has been established. | https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/food-news/5-foods-linked-to-novel-coronavirus-and-the-truth/photostory/73935050.cms (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
| Example 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Query (ground = true) | |||
| an elderly chinese tourist hospitalised in france has died of the coronavirus covid | |||
| Explanation | |||
| Similarity | Stance | Text | url |
| 0.74 | Agree | France’s health minister on Saturday announced the first coronavirus death in Europe, an 80-year-old Chinese tourist who other French authorities say was initially turned away from two French hospitals when he first fell ill. Minister Agnes Buzyn said she was informed Friday night of the death of the patient, who had been in intensive care at Bichat Hospital in Paris after testing positive in late January. His daughter also tested positive for the virus that has spread across central China and was hospitalized. However, the health minister said she was doing well and should be leavin | https://www.france24.com/en/20200215-france-announces-first-coronavirus-death-outside-asia (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
| 0.66 | Agree | An 80-year-old Chinese tourist has died of the fast-spreading coronavirus in France, becoming the first fatality in Europe, French Health Minister Agnes Buzyn said on Saturday.France has recorded 12 cases of the virus, out of a global total of 67,000. The vast majority of those suffering from the virus are in China. The epidemic has killed more than 1500 people. Buzyn said she was informed on Friday that the patient, who had been treated at the Bichat hospital in northern Paris since 25 January, died of a lung infection due to the coronavirus. “This is the first fatality by the coronavirus outside Asia, the first death in Europe”, Buzyn told reporters. “We have to get our health system ready to face a possible pandemic propagation of the virus, and therefore the spreading of the virus across France”, she added. | https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-health-france-idUSKBN2090B0 (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
| 0.62 | Agree | France confirms fourth case of coronavirus in elderly Chinese tourist. France on Tuesday reported that a fourth person was infected with the coronavirus, an elderly Chinese tourist. Health Ministry director Jerome Salomon said the patient, hospitalized in Paris, was a Chinese tourist believed to be about 80 years old. “His medical situation is serious, as he is requiring resuscitation”, Salomon told reporters. | https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-health-france/france-confirms-fourth-case-of-coronavirus-in-elderly-chinese-tourist-idINKBN1ZR2CM?edition-redirect=in (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
| Example 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Query (ground = fake) | |||
| the asterix comic books and the simpsons predicted the coronavirus outbreak | |||
| Explanation | |||
| Similarity | Stance | Text | url |
| 0.52 | Agree | The Simpsons fans are convinced Tom Hanks’ coronavirus diagnosis was predicted by his cameo in the 2007 movie. The 63-year-old made an appearance in the animation, which also foresaw Donald Trump becoming president and The Shard being built. […] The Cast Away star said they suffered from aches, chills, and colds. And while the theory might seem a bit far-fetched, fans think it is The Simpsons’ way of predicting Tom’s isolation. It wasn’t long ago that The Simpsons fans believed that the show predicted the outbreak in 1993.Taking to social media one fan tweeted: ‘The Simpsons predicted The Coronavirus and Tom Hanks self-quarantine in 2 separate episodes? That show has predicted so many things!’ […] | https://metro.co.uk/2020/03/12/simpsons-fans-convinced-movie-predicted-tom-hanks-getting-coronavirus-2007-12390330/ (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
| 0.51 | Agree | ‘The Simpsons’ predicted the coronavirus outbreak over 20 years ago. The animated prophecies of “The Simpsons” have long been documented by fans of the series. Now in its 31st year, the cartoon created by Matt Groening predicted many a world-altering event long before they took place, including Donald Trump’s presidency, Greece’s economic meltdown and the underdog American Olympic curling team besting the Swedes. […] Speaking of “The Simpsons” predictions in general, Oakley said, “It’s mainly just coincidence because the episodes are so old that history repeats itself”. […] | https://nypost.com/2020/03/27/the-simpsons-predicted-the-coronavirus-outbreak-over-20-years-ago/ (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
| 0.49 | Discuss | […] Earlier this year, a 1993 episode called Marge in Chains made the rounds on social media. That’s the episode with the “Osaka Flu” and the hornets. Bill Oakley didn’t want people to use their show for nefarious purposes on social media. “I don’t like it being used for nefarious purposes”, Oakley told The Hollywood Reporter. “The idea that anyone misappropriates it to make coronavirus seem like an Asian plot is terrible. In terms of trying to place blame on Asia—I think that is gross. I believe the most antecedent to (Osaka Flu) was the Hong Kong flu of 1968. It was just supposed to be a quick joke about how the flu got here”. […] | https://comicbook.com/tv-shows/news/simpsons-classic-clip-fan-shares-wondering-will-this-horrible-year-end/ (accessed on 4 January 2022) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Magistris, G.; Russo, S.; Roma, P.; Starczewski, J.T.; Napoli, C. An Explainable Fake News Detector Based on Named Entity Recognition and Stance Classification Applied to COVID-19. Information 2022, 13, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13030137
De Magistris G, Russo S, Roma P, Starczewski JT, Napoli C. An Explainable Fake News Detector Based on Named Entity Recognition and Stance Classification Applied to COVID-19. Information. 2022; 13(3):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13030137
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Magistris, Giorgio, Samuele Russo, Paolo Roma, Janusz T. Starczewski, and Christian Napoli. 2022. "An Explainable Fake News Detector Based on Named Entity Recognition and Stance Classification Applied to COVID-19" Information 13, no. 3: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13030137
APA StyleDe Magistris, G., Russo, S., Roma, P., Starczewski, J. T., & Napoli, C. (2022). An Explainable Fake News Detector Based on Named Entity Recognition and Stance Classification Applied to COVID-19. Information, 13(3), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13030137








