Abstract
Covert channel communications are of vital importance for the ill-motivated purposes of cyber-crooks. Through these channels, they are capable of communicating in a stealthy way, unnoticed by the defenders and bypassing the security mechanisms of protected networks. The covert channels facilitate the hidden distribution of data to internal agents. For instance, a stealthy covert channel could be beneficial for the purposes of a botmaster that desires to send commands to their bot army, or for exfiltrating corporate and sensitive private data from an internal network of an organization. During the evolution of Internet, a plethora of network protocols has been exploited as covert channel. DNS protocol however has a prominent position in this exploitation race, as it is one of the few protocols that is rarely restricted by security policies or filtered by firewalls, and thus fulfills perfectly a covert channel’s requirements. Therefore, there are more than a few cases where the DNS protocol and infrastructure are exploited in well-known security incidents. In this context, the work at hand puts forward by investigating the feasibility of exploiting the DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) as a covert channel. We demonstrate that is beneficial and quite straightforward to embed the arbitrary data of an aggressor’s choice within the DNSKEY resource record, which normally provides the public key of a DNSSEC-enabled domain zone. Since DNSKEY contains the public key encoded in base64 format, it can be easily exploited for the dissemination of an encrypted or stego message, or even for the distribution of a malware’s binary encoded in base64 string. To this end, we implement a proof of concept based on two prominent nameserver software, namely BIND and NDS, and we publish in the DNS hierarchy custom data of our choice concealed as the public key of the DNS zone under our jurisdiction in order to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed covert channel.
1. Introduction
Undoubtedly, Domain Name System (DNS) is one of the most fundamental elements of Internet infrastructure. In fact, after IP protocol, DNS is the most used network protocol. The main purpose of DNS is to provide the mapping of a domain name to the corresponding IP address. This IP address or any other resource of a domain name are represented in the form of resource records (RR). This simple resolving process constitutes the cornerstone of the Internet due to the fact that it is essential before any other network transaction takes place. For this reason, DNS transactions are rarely restricted by security policies or filtered by firewalls. In the initial version of DNS, security considerations were not an issue, so a provision for the protection of the DNS data integrity and authenticity has not been considered. Therefore at some point of the DNS evolution, DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) [1] was proposed with the aim to secure the integrity of DNS data and verify their origin. DNSSEC deploys a public key infrastructure within the DNS infrastructure, where each domain zone contains one or multiple public keys in the form of DNSKEY RR, with which the clients authenticate the digital signatures of the DNS data.
Despite the significance of DNS protocol, there are documented many incidents where DNS protocol and/or infrastructure is exploited for malicious purposes. In some well-known security incidents, DNS protocol was used as a covert channel to exfiltrate corporate or sensitive private data from an internal network [2,3], for the coordination of botnets [4,5] or for the distribution of the malicious behavior in the case of fileless malwares [6,7]. In the aforementioned cases, usually the TXT type of RR was misused. TXT RR allows the association of an arbitrary string with a domain name. Traditionally, it is used for the publication of human readable information, such as in the case of Sender Policy Framework (SPF) [8] where the TXT record is used for the detection of email spoofing. The corresponding RFC 1035 [9] does not define a specific structure of the resource data, allowing thus an adversary to publish plaintext string with length that could reach several KBs. In overall, TXT records are used on specific cases with explicit structure format. Hence, the usage of a non-conforming TXT record can easily raise suspicions. On the contrary, DNSSEC-related records contain cryptographic material encoded in base64 format, making them a perfect place to conceal hidden messages. The detection of the hidden data requires deep inspection of the DNS message and cryptographic operations in order to deduce that the based64 data is not valid cryptographic material of the DNSSEC-enabled zone.
The exploitation of the DNSSEC protocol as a covert channel has not been investigated by the security community nor reported as a security incident so far. However, we consider it necessary to discuss and examine the feasibility of such an approach proactively in order to raise the awareness of the community for the potential of the threat. In the literature, the focus of the security community concerning security issues caused by the DNSSEC mechanism focus solely on the case of DNS amplification attacks, where the attackers take advantage of the hefty size of the DNSSEC-related RR in order to increase the effectiveness of the Denial of Service (DoS) attack in terms of bandwidth consumption [10].
To our knowledge, the work at hand is the first to demonstrate that is feasible to publish arbitrary (custom) data within the DNSKEY RR. This possibility could be beneficial for an attacker compared with the typical case of TXT records, for three main reasons: (1) The DNSKEY record contains the public key of the zone in the form of a base64 encoded string, thus it can embed indistinguishable from a legitimate public key an encrypted or stego message, or even the executable of a malware, (2) Typically a DNSKEY RR carries a public key of RSA algorithm with a size of at least 1024 bytes, so the capacity of the covert channel is increased compared with the typical case, and (3) The abuse of TXT records is more trivial to be detected, as TXT records are used for specific purposes and hence it will be suspicious to carry non-conforming strings. At the contrary, the detection of malicious DNSKEY records, as demonstrated in this work, will require a deep inspection of the DNS responses and further (cryptographic) analysis of the contained data. The overall capacity of the DNSKEY-based covert channel depends solely on the size of the carried public key. It is recommended that the size of the public key used in DNSSEC should vary from 1024 to 4096 bits. Thus, the proposed covert channel can transfer in the typical case a maximum of 3072 bit per packet encoded in base64 format.
In our work, we implement a proof of concept based on two prominent nameserver softwares, namely BIND and NDS, and we show that is feasible and quite straightforward to embed arbitrary data of one’s choice in the resource data of the DNSKEY RR. This way, an adversary can exploit the DNSKEY RR with the goal to establish a covert channel. The proposed architecture could be beneficial for the purposes of a botherder to coordinate their botnet, for exfiltration of sensitive data or even for disseminating fileless malware. The main purpose of this work is to alert the community regarding new variations of DNS-based covert channels, which may allow an adversary to cloak their action and substantially increase the resilience of their malicious infrastructure.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. The next section presents related cases where the DNS protocol and infrastructure is exploited as covert channel. Section 3 presents the architecture of the proposed DNSKEY-based covert channel, while Section 4 elaborates on the implementation of the proof of concept and discusses the results of our experiments. The last section concludes the paper.
2. DNS as a Covert Channel
DNS protocol and infrastructure are exploited in multiple occasions for achieving the malicious purposes of aggressors. In the following section, we explore the main types of these violations.
2.1. DNS-Based C&C
Botnets constitute a growing threat to the Internet as they are capable of disrupting the normal operation of services, networks and systems at will of their botmaster. These armies of bots are used for launching Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, sending spam emails on a massive scale, identity theft, and so forth [11]. To coordinate their network of bots effectively and in a stealthy manner, the botherders rely on advanced Command and Control (C&C) channels [12]. Specifically, the infected devices, called bots, receive and execute the commands of the botherder, through this covert C&C channel. In this respect, the C&C channel enables a bot to acquire new instructions and malicious capabilities, as injected by the remote botmaster. Therefore, the most critical requirement for maintaining control of the entire botnet is the botmaster’s ability to constantly stay in touch and disseminate their orders through the C&C infrastructure to the bots. For this purpose, the botmaster may take advantage of DNS protocol and infrastructure to build stealthy and resilient C&C channels [13].
The key benefit for exploiting DNS over other network protocols, such as HTTP or IRC, as C&C channel is that it is one of the few protocols rarely filtered out by firewalls. Moreover, even in the case a bot is restricted to communicate directly with the outside network due to the organization’s security policy, the local DNS recursive resolver will deliver the command on the botherder’s behalf through the DNS hierarchy to the bot [14]. Dietrich et al. [15] were the first to investigate botnets that take advantage of DNS for C&C purposes. The authors analysed by reverse engineering the Feederbot, a botnet malware, which disseminates the attack parameters in DNS responses. Actually, Feederbot creates an end-to-end communication channel among the bots and botherder in the form of DNS messages.
A representative example of a botnet with DNS C&C capabilities is Morto worm. As Symantec reported [5], this worm tries to resolve a DNS TXT RR. The text embedded in the RDATA field of the response contains the encrypted IP address where the bot could find and download a binary executable.
2.2. DNS Tunneling
DNS has been exhaustively exploited as a carrier protocol for establishing a covert channel for obscure exchange of messages. By leveraging a technique called DNS tunneling, malicious agents are capable of transferring data embedded within the RRs of a DNS query or response packet [14]. Usually, the leftmost labels of the domain name in the query are used by insiders for exfiltrating data to the outside network, while text-based RRs in the DNS response carry data to the internal agents. For instance, the latter case can be used to provide an update to their malware capabilities or actions that they should perform [15]. The most convenient RR type in this case is the TXT type, as it is able to convey large amount of data [15]. However, record types, such as CNAME or MX which include textual data on their RDATA field, have also been misused for similar purposes [16].
An extensive investigation about the practicality of DNS protocol as a covert channel was conducted by Xu et al. [16]. The authors identified the so-called tunneled communication mode, which permits the two-way transfer of arbitrary binary data between the inside and outside networks. In the downstream communication, the external agent encodes the data in base32 format and embed them to a record of the DNS response, for example in a CNAME record. All the downstream DNS responses should have minimal TTL value for avoiding their caching. Certainly, this communication mode requires the deployment of an DNS authoritative names server (ANS) under the attacker’s control and the registration of a domain zone in the DNS hierarchy.
In the recent notorious case of Equifax, sensitive and private data of almost 150M of US citizens were leaked through DNS tunneling (and other similar tunneling techniques) after the attackers took advantage of an unpatched Apache Struts vulnerability that US-CERT warned about two months earlier [3].
2.3. Fileless Malware
Another way to take advantage of DNS RDATA field is in the case of fileless malware. This type of malware is a stealthy variant of malicious software where the binary of the malware exists solely on the volatile computer memory, such as RAM or the system’s registry, and does not leave any trace of activity on the hard disk [17]. This way, fileless malware is resistant to the existing anti-virus strategies. Specifically, the typical anti-virus mechanisms fail to detect them, as does not exist any payload file stored in the hard disk for analysis. In general, a fileless malware can exploit the DNS protocol by retrieving the binary or execution commands through a DNS request for TXT records types. For instance, in a recent incident, DNSMesseger [7], a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) malware, employs DNS transactions to receive and following execute in the compromised devices malicious PowerShell commands. The malware has a hardcoded list of domains, and issues DNS queries about TXT records, which contain the commands encoded in base64 format.
3. Proposed Architecture: DNSKEY as a Covert C&C Channel
In the following section, we introduce our threat model and detail how an adversary is able to exploit the DNSKEY RR of the DNSSEC protocol as a covert C&C channel.
3.1. Threat Model
In our model, we assume that an adversary successfully compromised a device in the internal network of an organization. The objective of the adversary is to stealthy communicate with the compromised host, i.e., bot, without using a direct communication channel, which could be easily detected by the intrusion detection system. Furthermore, we assume that the adversary has not the ability to modify the network policy of the host network, while any use of unauthorized protocols or connections with entities not defined in the network policy would be blocked. For this reason, they opt to use the DNS protocol as a covert channel, which usually is not restricted by the firewall policy of the host network.
According to our model, the adversary conceals the existence of the exchanged messages by embedding them within the DNSKEY RR. To establish the communication between the bot and the C&C server, we assume that the adversary has the capability to force the compromised device to issue DNS request towards the local DNS recursive resolver and receive the corresponding DNS responses. We also assume that the local DNS recursive resolver forwards unknowingly the DNS request on the bot’s behalf to the ANS under the control of the adversary. Furthermore, we assume that the adversary has full control of one or multiple ANS hosting the domain zone that contains the crafted DNSKEY RR. We finally assume that the adversary has the ability to update and modify the contains of the zone, and restart the DNS service in the ANS at will.
3.2. Covert Channel
Figure 1 illustrates the setup of the proposed covert channel. In the initialization phase, the malicious entity publishes the latest version of the message embedded in the DNSKEY record (step A). Namely, they insert in the zone file of the ANS under their jurisdiction the custom DNSKEY RR containing the hidden message. This entry has a minimum TTL value in order to avoid the caching of the RR in the cache memory of the recursive resolver. For the dissemination of the hidden message a pulled approach is followed. This means that the internal actors should trigger the DNS transaction each time they desire to receive the hidden message. To do so, the internal actor sends a DNS query for the DNSKEY RR to the local recursive resolver (step 1). The resolver in turn traverses the DNS hierarchy to locate the corresponding DNSKEY record (steps 2–7) and returns the response back to the internal agent (step 8). In this illustration, as well as in our implementation, we use a fixed domain name. However, a more sophisticated attacker could employ a domain generation algorithm (DGA) technique for producing constantly changing random domain zones [18]. Thus, they will have better chances to evade the correlation of the used domain names to the covert channel.
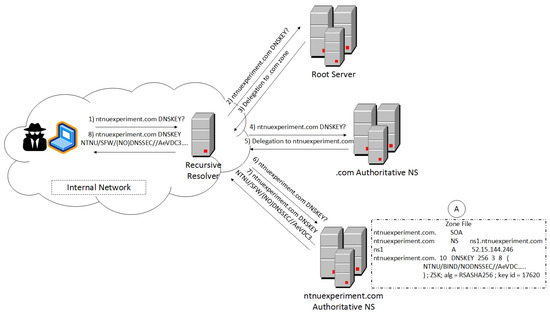
Figure 1.
Proposed covert channel transactions.
4. Implementation and Results
To prove the validity of our research question, i.e., whether is feasible to publish arbitrary (custom) data within the DNSKEY RR, we consider two prominent nameserver softwares that operate as ANS and support DNSSEC on their domain zones, these are BIND and NSD. Both of the software under consideration are distributed as open source and support the DNSSEC extension. BIND [19] is the most widely used DNS software and essentially constitutes the de facto standard of DNS software for Unix-based operating systems. BIND is able to operate both as recursive resolver and ANS. NSD [20] developed by the NLnet Labs is designed to operate solely as ANS with the purpose to increase the performance of heavily loaded ANS. For the purpose of our experiment, we register a domain name, that is ntnuexperiment.com, in the .com zone. We use the management console of the registrar to easily administer and upload the necessary nameserver (NS) and glue RR on the parental zone. Furthermore, we deploy for each different software and scenario, as explained in the following paragraphs, a distinct virtual machine (VM) in a commercial cloud computing provider. In total we created four VMs.
For each software, we deploy two different scenarios, an unsigned and a DNSSEC-enabled domain zone respectively. To each of these zones, we introduce a DNSKEY RR with a custom RDATA field. Specifically, we set as the public key a string conforming with the base64 format encoding. As we can observe in the example snippet , extracted from the zone file of the BIND without DNSSEC installation, the string contains a message regarding the specific scenario of the experiment followed by random characters and looks like a legitimate DNSKEY record.
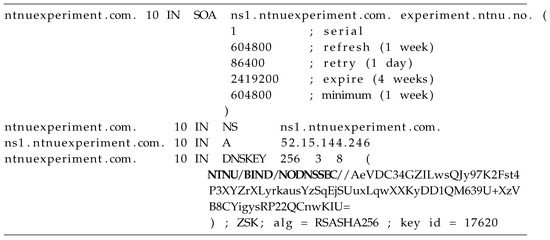
Listing 1.
Zone file of the BIND without DNSSEC scenario.
For the convenience of our experiment, in the case of the DNSSEC-enabled domain zones, we configure the DNSKEY as zone signing key (ZSK), while we generate a key signing key (KSK)—with the use of the software’s embedded tools—for the creation of the delegation signer (DS) RR, which in turn was published on the parental domain zone. Bear in mind, that the custom DNSKEY RR was directly inserted (hardcoded) in the zone file, and thus any insertion of a crafted DNSKEY RR requires the restart of the service in order the modification to be applied in the DNS hierarchy. An on-the-fly modification of the zone through dynamic DNS update is not possible, since the software requires the corresponding private key for creating the digital signatures of the resources. Obviously, such private key does not exist and cannot be generated. Therefore, an attacker should only rely on the hardcoded way for publishing crafted DNSKEY records. After the setup of the zone and the relaunch of the service, we verify that the DNSKEY RR was successfully published with a dig query.
For all the considered software and both scenarios, we observe that the crafted DNSKEY records were published in the DNS hierarchy and were accessible from a third network. An initial observation for the first scenario is that even though the zones were not signed, the nameserver software allowed the publication of a DNSKEY RR. In the case of the second scenario of DNSSEC-enabled domain zones, the valid KSK record was used to produce the digital signatures of the resources and the DS record for the parental zone, while the crafted DNSKEY record was included in the DNSKEY record set without getting involved in any cryptographic operation. Obviously, if the key was involved, then the generation of the digital signatures would fail, as the attacker does not possess the corresponding private key. Moreover, there is no way to check that a crafted DNSKEY is present in the zone, as there is not any digital signature associated with the fake public key. Furthermore, all the examined DNS software allow publishing a custom length string as long as it contains valid base64 characters. Actually, the only restriction for the crafted RDATA is to include the correct padding characters at the end of the string. An apparent drawback is that the aggressor cannot use the dynamic update to publish on-the-fly crafted DNSKEY records. However, rather, they have to restart the DNS service each time a modification is taking place. In any case, it will be straightforward to automate this process since the abused domain zone will serve the specific purpose and is not expected to host other legitimate DNS resources that will be rendered unavailable due to a restart of the service.
5. Conclusions
A covert communication channel that could go unnoticed by the defenders and bypass the security mechanisms of any network is of vital importance for malicious entities. In this work, we investigate the feasibility to exploit the RDATA part of the DNSKEY record as a carrier for transferring custom messages of independent length masqueraded as public keys. With the contributed proof of concept, we demonstrate that an aggressor is able to publish arbitrary data, such as encrypted or stego messages, or even the binary executable of malwares, in the DNS hierarchy and disseminate them via legitimate DNS transactions. As future work, we intend to investigate the DNS infrastructure to examine whether crafted DNSKEY, as described in this work, are currently used for malicious purposes and determine their intentions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing: M.A.; Contribution to the execution of the experiment: J.A.S.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially supported by the CREATE project, of the Department of Information Security and Communication Technology, Norwegian University of Science and Technology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ANS | Authoritative NameServer |
| C&C | Command and Control |
| DDoS | Distributed Denial of Service |
| DNS | Domain Name System |
| DNSSEC | DNS Security extention |
| DoS | Denial of Service |
| DS | Delegation Signer |
| KSK | Key Signing Key |
| NS | NameServer |
| RR | Resource Record |
| RDATA | Resource Data |
| ZSK | Zone Signing Key |
| VM | Virtual Machine |
References
- Arends, R.; Austein, R.; Larson, M.; Massey, D.; Rose, S. RFC 4033: DNS Security Introduction and Requirements. 2005. RFC Editor. Available online: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4033 (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Nadler, A.; Aminov, A.; Shabtai, A. Detection of malicious and low throughput data exfiltration over the DNS protocol. Comput. Secur. 2019, 80, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D. Protecting Networks from DNS Exfiltration. 2017. Help Net Security. Available online: https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2017/10/02/dns-exfiltration/ (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Kara, A.M.; Binsalleeh, H.; Mannan, M.; Youssef, A.; Debbabi, M. Detection of malicious payload distribution channels in DNS. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Sydney, Australia, 10–14 June 2014; pp. 853–858. [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney, C. Morto Worm Sets a (DNS) Record. 2011. Symantec. Available online: https://www.symantec.com/connect/blogs/morto-worm-sets-dns-record (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Ahmed, J.; Gharakheili, H.H.; Raza, Q.; Russell, C.; Sivaraman, V. Real-Time Detection of DNS Exfiltration and Tunneling from Enterprise Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM), Washington, DC, USA, 8–12 April 2019; pp. 649–653. [Google Scholar]
- Brumaghin, E.; Grady, C. Covert Channels and Poor Decisions: The Tale of DNSMessenger. 2017. Talos. Available online: https://blog.talosintelligence.com/2017/03/dnsmessenger.html (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Kitterman, S. RFC 7208: Sender Policy Framework (SPF) for Authorizing Use of Domains in Email. 2014. RFC Editor. Available online: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7208 (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Mockapetris, P. RFC 1035: Domain Names—Implementation and Specification. 1987. RFC Editor. Available online: https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1035.txt (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Anagnostopoulos, M.; Kambourakis, G.; Kopanos, P.; Louloudakis, G.; Gritzalis, S. DNS Amplification Attack Revisited. Comput. Secur. 2013, 39, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianelli, N.; Hackworth, A. Botnets as a Vehicle for Online Crime; White Paper; CERT Coordination Center: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos, M.; Kambourakis, G.; Drakatos, P.; Karavolos, M.; Kotsilitis, S.; Yau, D. Botnet Command and Control Architectures Revisited: Tor Hidden Services and Fluxing. In Proceedings of the Web Information Systems Engineering (WISE 2017), Puschino, Russia, 7–11 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos, M.; Kambourakis, G.; Gritzalis, S. New facets of mobile botnet: architecture and evaluation. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2015, 15, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, L.; Neyron, P.; Richard, O. On Robust Covert Channels Inside DNS. In Proceedings of the 24th IFIP TC 11 International Information Security Conference (SEC 2009); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, C.J.; Rossow, C.; Freiling, F.C.; Bos, H.; van Steen, M.V.; Pohlmann, N. On Botnets That Use DNS for Command and Control. In Proceedings of the Seventh European Conference on Computer Network Defense (EC2ND), Gothenburg, Sweden, 6–7 September 2011; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Butler, P.; Saha, S.; Yao, D. DNS for Massive-Scale Command and Control. IEEE Trans. Depend. Secur. Comput. 2013, 10, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield-Devine, S. Fileless attacks: Compromising targets without malware. Netw. Secur. 2017, 2017, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Reddy, A.K.K.; Reddy, A.N.; Ranjan, S. Detecting Algorithmically Generated Malicious Domain Names. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM SIGCOMM IMC ’10, Melbourne, Australia, 1–3 November 2010; pp. 48–61. [Google Scholar]
- Internet Systems Consortium; BIND 9. Available online: https://www.isc.org/bind/ (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- NLnet Labs; Name Server Daemon (NSD). Available online: https://www.nlnetlabs.nl/projects/nsd/about/ (accessed on 17 July 2019).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).