Microbial Abundance and Enzyme Activity Patterns: Response to Changing Environmental Characteristics along a Transect in Kongsfjorden (Svalbard Islands)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Collection of Samples
2.2. Physical and Chemical Variables
2.3. Microbial Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
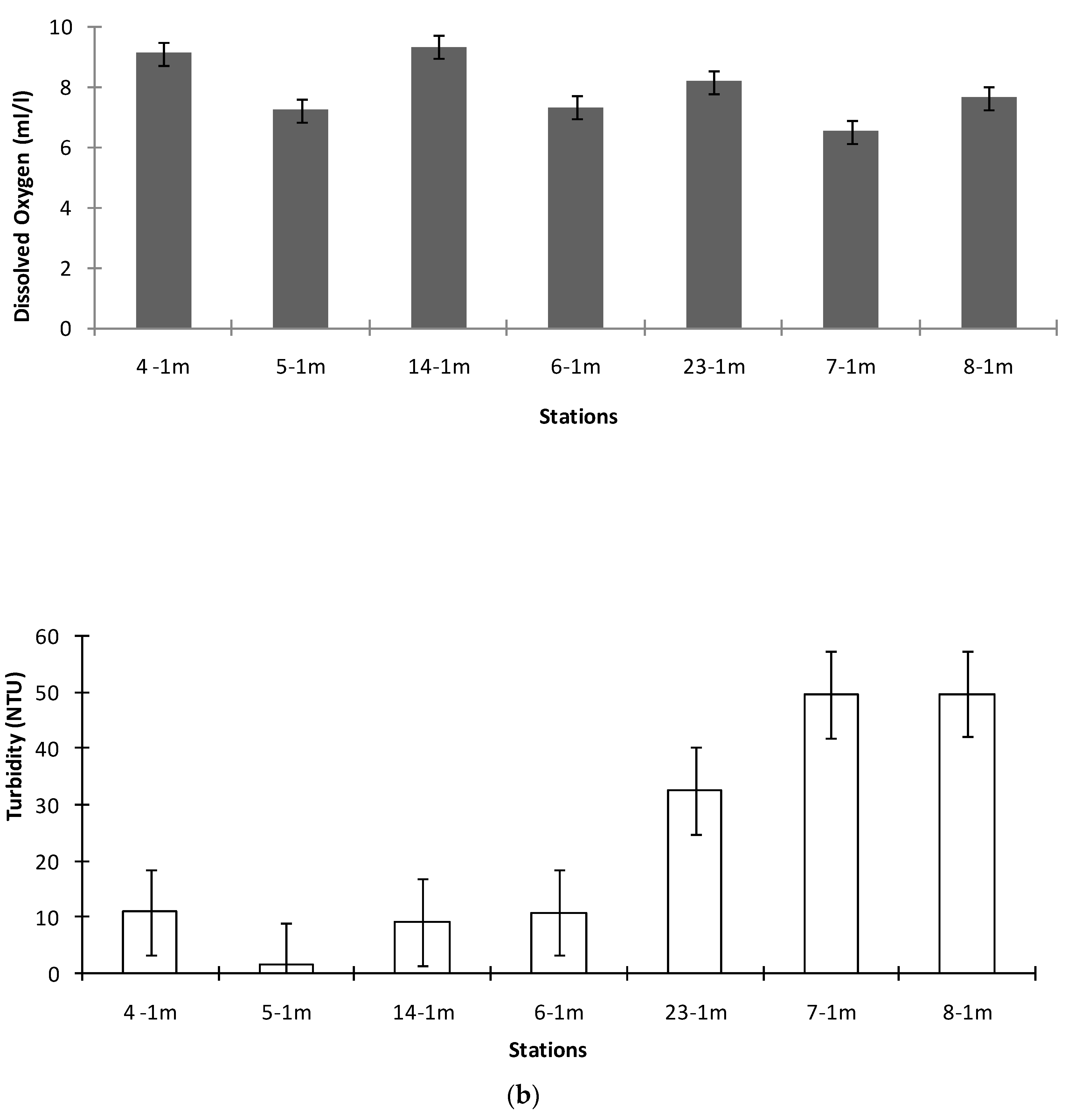
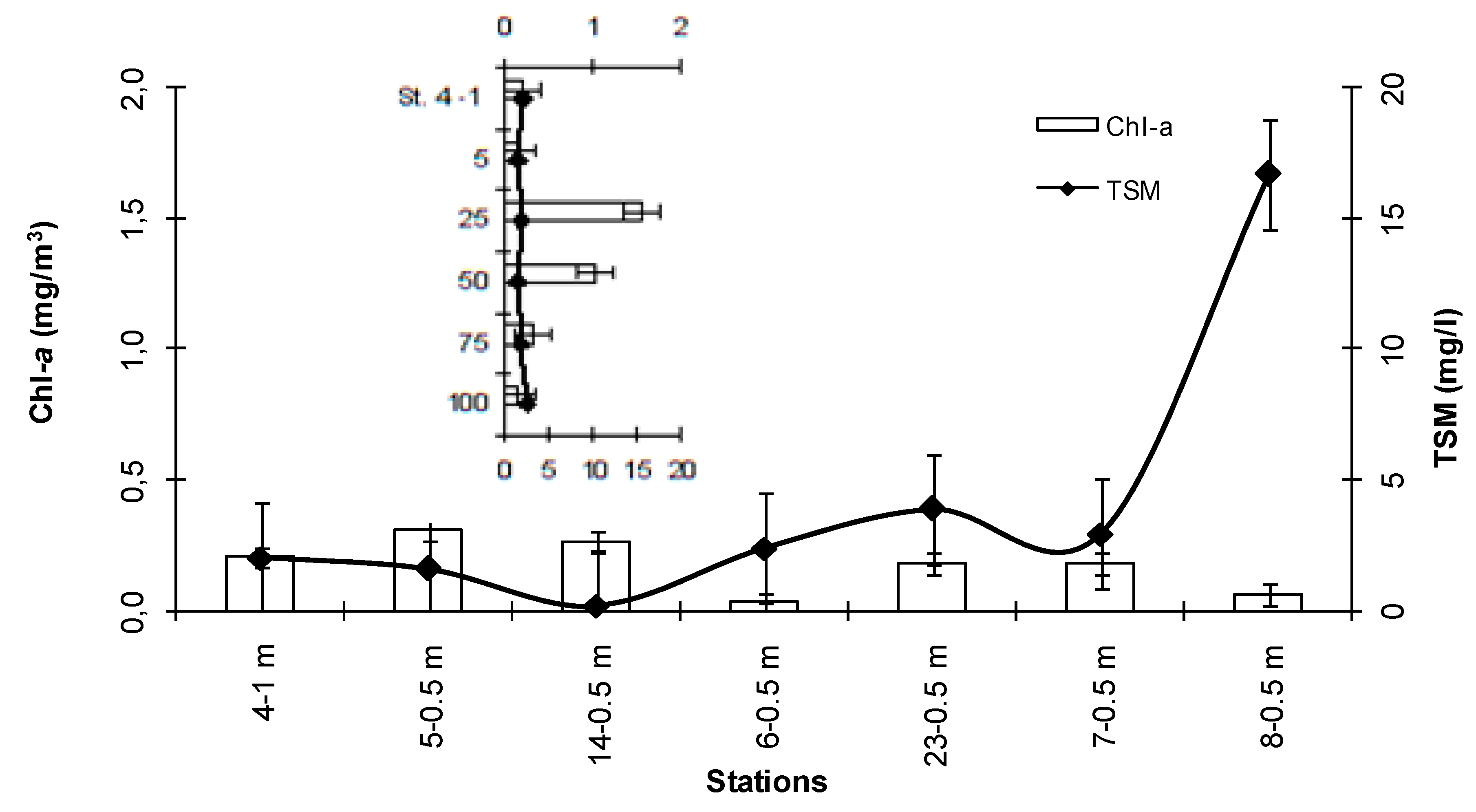
3.1. Environmental Conditions
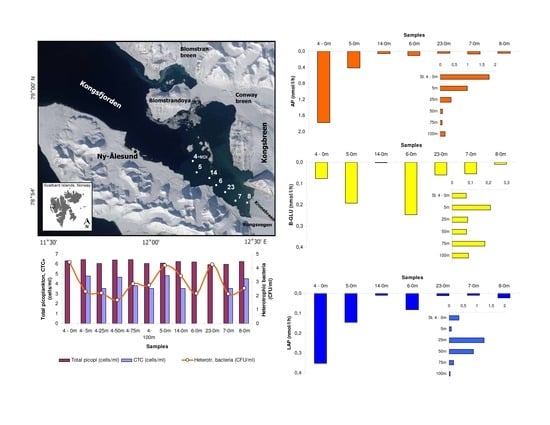
3.2. Microbial Variables
3.3. Statistical Data Elaboration
4. Discussions
4.1. Environmental Characterization
4.2. Microbial Variables and Their Response to Natural Forcings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boy, M.; Thomson, E.S.; Acosta-Navarro, J.C.; Arnalds, O.; Batchvarova, E.; Bäck, J.; Berninger, F.; Bilde, M.; Brasseur, Z.; Dagsson-Waldhauserova, P.; et al. Interactions between the atmosphere, cryosphere, and ecosystems at northern high latitudes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2015–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnosti, C. Functional differences between Arctic seawater andsedimentary microbial communities: Contrasts in microbialhydrolysis of complex substrates. FEMS Microb. Ecol. 2008, 66, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teske, A.; Durbin, A.; Ziervogel, K.; Cox, C.; Arnosti, C. Microbial community composition and function in permanently cold seawater and sediments from an Arctic fjord of Svalbard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnosti, C.; Steen, A.D. Patterns of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial metabolism in an Arctic fjord of Svalbard and in the northern Gulf of Mexico: Contrasts in carbon processing by pelagic microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, A.D.; Arnosti, C. Extracellular peptidase and carbohydrate hydrolase activities in an Arctic fjord (Smeerenburgfjord, Svalbard). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 69, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, A.D.; Arnosti, C. Picky, hungry eaters in the cold: Persistent substrate selectivity among polar pelagic microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnosti, C. Contrasting patterns of peptidase activities in seawater and sediments: An example from Arctic fjords of Svalbard. Mar. Chem. 2015, 168, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmonte, J.P.; Teske, A.; Arnosti, C. Structure and function of high Arctic pelagic, particle associated and benthic bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2941–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmonte, J.P.; Hasler-Sheetal, H.; Glud, R.N.; Andersen, T.J.; Sejr, M.K.; Middelboe, M.; Teske, A.; Arnosti, C. Sharp contrasts between freshwater and marine microbial enzymatic capabilities, community composition, and DOM pools in a NE Greenland fjord. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boras, J.A.; Sala, M.M.; Arrieta, J.M.; Sà, E.L.; Felipe, J.; Agustí, S.; Duarte, C.M.; Vaqué, D. Effect of ice melting on bacterial carbon fluxes channelled by viruses and protists in the Arctic Ocean. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielsen, G.W.; Hop, H.; Hübner, C.; Kallenborn, R.; Weslawski, J.M.; Wiencke, C. (Eds.) The Kongsfjorden System-a Flagship Programme for Ny-Ålesund, a Concluding Document from Workshop 28–31 March 2008; Brief Report Series No. 11; Norwegian Polar Institute: Tromsø, Norway, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, H.; Dutta, A. The microbial aspect of climate change. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2016, 1, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Azzaro, M.; Caroppo, C.; Decembrini, F.; Monticelli, L.S.; Leonardi, M.; Maimone, G.; Zaccone, R.; La Ferla, R. Microbial community and its potential as descriptor of environmental status. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 2174–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganà, P.; Votano, L.; Caruso, G.; Azzaro, M.; Lo Giudice, A.; Delia, S.A. Bacterial isolates from the Arctic region (Pasvik river, Norway). biofilm production and antibiotic susceptibility. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, E.; Forchhammer, M.C.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Callaghan, T.V.; Christensen, T.R.; Elberling, B.; Fox, A.D.; Gilg, O.; Hik, D.S.; Høye, T.T.; et al. Ecological dynamics across the arctic associated with recent climate change. Science 2009, 325, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, W. Microbial ecosystem responses to rapid climate change in the Arctic. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D.L.; Moran, X.; Ducklow, H. Microbial growth in the polar oceans-role of temperature and potential impact of climate change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.R.; Macko, S.A.; Ostrom, P.H.; Dunphy, J. The microbial food web in Arctic seawater: Concentration of dissolved free amino acids and bacterial abundance and activity in the Arctic Ocean and in Resolute Passage. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 61, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, H.; Montoya, J.M.; Vazquez-Dominguez, E.; Vaqué, D.; Gasol, J.M. Warming effects on marine microbial food web processes: How far can we go when it comes to predictions? Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2137–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beszczynska-Møller, A.; Weslawski, J.M.; Walczowski, W.; Zajaczkowski, M. Estimation of glacial meltwater discharge into Svalbard coastal waters. Oceanologia 1997, 39, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Cottier, F.R.; Tverberg, V.; Inall, M.E.; Svendsen, H.; Nilsen, F.; Griffiths, C. Water mass modification in an Arctic fjord through cross-shelf exchange: The seasonal hydrography of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2005, 110, 12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, H.; Pearson, T.; Hegseth, E.H.; Kovacs, K.M.; Wiencke, C.; Kwasniewski, S.; Eiane, K.; Mehlum, F.; Gulliksen, B.; Wlodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; et al. The marine ecosystem of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Polar Res. 2002, 21, 167–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, H.; Wiencke, C. The Ecosystem of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. In The Ecosystem of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard; Hop, H., Wiencke, C., Eds.; Advances in Polar Ecology 2; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Chapter 1; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, H.; Beszczynska-Moller, A.; Hagen, J.O.; Lefauconnier, B.; Tverberg, V.; Gerland, S.; Ørbøk, J.B.; Bischof, K.; Papucci, C.; Zajaczkowski, M.; et al. The physical environment of Kongsfjorden–Krossfjorden, an Arctic fjord system in Svalbard. Polar Res. 2002, 21, 133–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husum, K.; Howe, J.A.; Baltzer, A.; Forwick, M.; Jensen, M.; Jernas, P.; Korsun, S.; Miettinen, A.; Mohan, R.; Morigi, C.; et al. The marine sedimentary environments of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard: An archive of polar environmental change. Polar Res. 2019, 38, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksen, K.; Nordli, Ø.; Førland, E.J.; Łupikasza, E.; Eastwood, S.; Niedźwiedź, T. Recent warming on Spitsbergen-Influence of atmospheric circulation and sea icecover. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2016, 121, 11913–11931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, S.; Kerhervé, P.; Calleja, M.L.; Many, G.; Morata, N. Glacier inputs influence organic matter composition and prokaryotic distribution in a high Arctic fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard). J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 164, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M.; Archambault, P.; Renaud, P.E.; März, C. The changing Arctic Ocean: Consequence for biological communities, biogeochemical processes and ecosystem functioning. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20200266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, K.R.; Seuthe, L. Seasonal microbial processes in a high-latitude fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard): I. Heterotrophic bacteria, picoplankton and nanoflagellates. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 731–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Padinchati Krishnan, K.; Singh, A.; Thomas., F.A.; Begum, N.; Tiwari, M.; Parli Bhaskar, V.; Gopinath, A. Biochemical composition of particles shape particle-attached bacterial community structure in a high Arctic fjord. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, C.; Pagliara, P.; Azzaro, F.; Miserocchi, S.; Azzaro, M. Late summer phytoplankton blooms in the changing polar environment of the Konsfjorden (Svalbard, Arctic). Cryptogam. Algol. 2017, 38, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuliński, K.; Kedra, M.; Legezyńska, J.; Gluchowska, M.; Zaborska, A. Particulate organic matter sinks and sources in high Arctic fjord. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 139, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, S.; Darecki, M. Inherent optical properties and particulate matter distribution in summer season in waters of Hornsund and Konsfjorden, Spitsbergen. Oceanologia 2018, 60, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliani, S.; Sciascia, R.; Conese, I.; D’Angelo, A.; Del Bianco, F.; Giglio, F.; Langone, L.; Miserocchi, S. Characterization of seawater properties and ocean heat content in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard Archipelago. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2016, 27, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya David, T.; Krishnan, K.P. Recent variability in the Atlantic water intrusion and water masses in Kongsfjorden, an Arctic fjord. Polar Sci. 2017, 11, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parson, T.R. A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 1972, 167, 1–311. [Google Scholar]
- Aminot, A.; Chaussepied, M. Manuel des Analyses Chimiques en Milieu Marin; CNEXO (Centre National pour l’Exploration des Oceans): Brest, France, 1983; pp. 1–395. [Google Scholar]
- Yentsch, C.S.; Menzel, D.W. A method for the determination of phytoplankton chlorophyll and phaeophytin by fluorescence. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1963, 10, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Stern, J.H. Carbon and nitrogen determination of carbonate-containing solids. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1984, 19, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, A.; Courp, T.; Heussner, S.; Carbonne, J.; Fowler, S.W.; Deniaux, B. Seasonality and composition of particulate fluxes during ECOMARGE-I, western Gulf of Lions. Cont. Shelf Res. 1990, 10, 959–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.G.; Kahru, M.; Wieland, J.; Stramska, M. Determination of spectral absorption coefficients of particles, dissolved material and phytoplankton for discrete water samples. In Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation, Revision 3; Muller, J.L., Fargion, G.S., Eds.; NASA: Hanover, NH, USA, 2002; Chapter 15; Volume 2, pp. 231–257. [Google Scholar]
- Twardowski, M.S.; Boss, E.; Sullivan, J.M.; Donaghay, P.L. Modeling the spectral shape of absorption by chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Mar. Chem. 2004, 89, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Absorption by dissolved organic matter of the sea (yellow substance) in the UV and visible domains 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.G.; Feig, Y.S. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G. Leucine aminopeptidase, beta-glucosidase and alkaline phosphatase activity rates and their significance in nutrient cycles in some coastal Mediterranean sites. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 916–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappalà, G.; Bruzzone, G.; Caruso, G.; Azzaro, M. Development of an automatic sampler for extreme environments: First in situ application in Svalbard. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2016, 27, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Furhman, J.A. Relationship between biovolume and biomass of naturally derived marine bacterioplankton. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Monticelli, L.; Azzaro, F.; Azzaro, M.; Decembrini, F.; La Ferla, R.; Leonardi, M.; Zaccone, R. Dynamics of extracellular enzymatic activities in a shallow Mediterranean ecosystem (Tindari ponds, Sicily). Mar. Freshw. Res. 2005, 56, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiencke, C.; Hop, H. Ecosystem Kongsfjorden: New views after more than a decade of research. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.; Seuthe, L.; Bratbak, G.; Paulsen, M.L. Bacterial response to permafrost derived organic matter input in an Arctic fjord. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinasquet, J.; Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Lovejoy, C.; Obernosterer, I. Editorial: Microbiology of the Rapidly Changing Polar Environments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallot, D.; Pettersson, R.; Luckman, A.; Benn, D.J.; Zwinger, T.; van Pelt, W.J.J.; Kohler, J.; Schafer, M.; Claremar, B.; Hulton, N.R.J. Basal dynamics of Kronebreen, a fast-flowing tidewater glacier in Svalbard: Non-local spatio-temporal response to water input. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, M.L.; Nielsen, S.E.B.; Müller, O.; Møller, E.F.; Stedmon, C.A.; Juul-Pedersen, T.; Markager, S.; Sejr, M.K.; Delgado Huertas, A.; Larsen, A.; et al. Carbon Bioavailability in a High Arctic Fjord Influenced by Glacial Meltwater, NE Greenland. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, F.A.; Kirchner, N.; Kuttenkeuler, J.; Krutzfeldt, J.; Noonnets, R. Relating ocean temperatures to frontal ablation rates at Svalbard tidewater glaciers: Insights from glacier proximal datasets. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darlington, E. Meltwater Delivery from the Tidewater Glacier Kronebreen to Kongsfjorden, Svalbard: Insights from In Situ and Remote-Sensing Analyses of Sediment Plumes. Ph.D. Thesis, Loughborough University, Loughborough, UK, November 2015; p. 230. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/288374364.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Jiang, X.; Jianfeng, H.E.; Caim, I. Abundance and biomass of heterotrophic microbes in the Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2005, 24, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska, K.; Wiodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Wieczorek, P. Abundance and biomass of bacteria in two glacial fjords. Pol. Polar Res. 2005, 26, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor, J.; Wojciechowska, K. Differences in taxonomic composition of summer phytoplankton in two fjords of West Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Pol. Polar Res. 2005, 26, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Thingstad, T.F.; Bellerby, R.G.; Bratbak, G.; Børsheim, K.Y.; Egge, J.K.; Heldal, M.; Larsen, A.; Neill, C.; Nejstgaard, J.; Norland, S.; et al. Counteractive carbon-to-nutrient coupling in an Arctic pelagic ecosystem. Nature 2008, 455, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwosz, K.; Walkusz, W.; Hapter, R.; Wieczorek, P.; Hop, H.; Wiktor, J. Comparison of productivity and phytoplankton in a warm (Kongsfjorden) and a cold (Hornsund) Spitsbergen fjord in mid-summer 2002. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Guo, C.; Luo, W.; Cai, M.; He, J. The distribution of picoplanktonand nanoplankton in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard during late summer 2006. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Piquet, A.M.-T.; Scheepens, J.F.; Bolhuis, H.; Wiencke, C.; Buma, A.G.J. Variability of protistan and bacterial communities in two Arctic fjords (Spitsbergen). Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1521–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Piquet, A.M.-T.; van de Poll, W.H.; Visser, R.J.W.; Wiencke, C.; Bolhuis, H.; Buma, A.G.J. Springtime phytoplankton dynamics in Arctic Krossfjorden and Kongsfjorden (Spitsbergen) as a function of glacier proximity. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 2263–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquet, A.M.-T.; Maat, D.S.; Confurius-Guns, V.; Sintes, E.; Herndl, G.J.; van de Poll, W.H.; Wiencke, C.; Buma, A.G.J.; Bolhuis, H. Springtime dynamics, productivity and activity of prokaryotesin two Arctic fjords. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 1749–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.K.; Krishnan, K.P.; Kerkar, S.; David, T.D. Spatio-temporal monitoring and ecological significance of retrievable pelagic heterotrophic bacteria in Konsfjorden, an Arctic Fjord. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 57, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carmack, E.; Wassmann, P. Food webs and physical-biological coupling on pan-Arctic shelves: Unifying concepts and comprehensive perspectives. Progr. Oceanogr. 2006, 71, 446–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalande, C.; Moriceau, B.; Leynaert, A.; Morata, N. Spatial and temporal variability in export fluxes of biogenic matter in Kongsfjorden. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborska, A.; Pempkowiak, J.; Papucci, C. Some sediment characteristics and sedimentation rates in an Arctic Fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard). Annu. Environ. Prot. 2006, 8, 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, F.; Malfatti, F. Microbial structuring of marine ecosystems. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajączkowska, B.; Zajączkowski, M. Quantitative microbiological survey in Hornsund, SW Spitsbergen. Reconnaissance study in summer 1985. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. 1989, 37, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, E.F.; Nielsen, T.G. Plankton community structure and carbon cycling off the western coast of Greenland, with emphasis on sources of DOM for the bacterial community. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 22, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota, G.F.; Pomeroy, L.R.; Harrison, W.G.; Jones, E.P.; Peters, F.; Sheldon, W.M., Jr.; Weingartner, T.R. Nutrients, primary production and microbial heterotrophy in the southeastern Chukchi Sea: Arctic summer nutrient depletion and heterotrophy. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 135, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, A.; Ameryk, A.; Jankowska, K. Microbiological Survey in Two Arctic Fjords: Total Bacterial Number and Biomass Comparison of Hornsund and Kongsfjorden. In Impact of Climate Changes on Marine Environments; Zielinski, T., Weslawski, M., Kuliński, K., Eds.; GeoPlanet: Earth and Planetary Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichot, C.G.; Benner, R. The spectral slope coefficient of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (S 275–295) as a tracer of terrigenous dissolved organic carbon in river-influenced ocean margins. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Markager, S.; Kaas, H. Optical Properties and Signatures of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Danish Coastal Waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.B.; Carlson, C.A.; Steinberg, D.K. Production of chromophoric dissolved organic matter by Sargasso Sea microbes. Mar. Chem. 2004, 89, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, E.B.; Sherr, B.F.; Wheeler, P.A.; Thompson, K. Temporal and spatial variation in stocks of autotrophic and heterotrophic microbes in the upper water column of the central Arctic Ocean. Deep Sea Res. I 2003, 50, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard-Jones, M.H.; Ballard, V.D.; Allen, A.E.; Frischer, M.E.; Verity, P.G. Distribution of bacterial biomass and activity in the marginal ice zone of the central Barents Sea during summer. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 38, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, L.; Kevan, P.G.; Trevors, J.T. Viable bacterial biomass and functional diversity in fresh and marine waters in the Canadian Arctic. Polar Biol. 2003, 26, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Smith, D.C.; Steward, G.F.; Hagström, Å. Bacteria-organic matter coupling and its significance for oceanic carbon cycling. Microb. Ecol. 1994, 28, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Long, R.A. Sea snow microcosms. Nature 2001, 414, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.; Robinson, C.; Azam, F.; Thomas, H.; Baltar, F.; Dang, H.; Hardman-Mountford, N.J.; Johnson, M.; Kirchman, D.L.; Koch, B.P.; et al. Mechanisms of microbial carbon sequestration in the ocean—Future research directions. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 5285–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, M.M.; Terrado, R.; Lovejoy, C.; Unrein, F.; Pedrós-Alió, C. Metabolic diversity of heterotrophic bacterioplankton over winter and spring in the coastal Arctic Ocean. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnosti, C.; Steen, A.D.; Ziervogel, K.; Ghobrial, S.; Jeffrey, W.H. Latitudinal gradients in degradation of marine dissolved organic carbon. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, A.L.; Deming, J.W. Relationships between microbial extracellular enzymatic activity and suspended and sinking particulate organic matter: Seasonal transformations in the North Water. Deep-Sea Res. II 2002, 49, 5211–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, C.T.E.; Carpenter, S.D.; Renfro, A.A.; Sallon, A.; Michel, C.; Cochran, J.K.; Deming, J.W. Evidence for microbial attenuation of particle flux in the Amundsen Gulf and Beaufort Sea: Elevated hydrolytic enzyme activityon sinking aggregates. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 2007–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaro, M.; Aliani, S.; Azzaro, F.; Decembrini, F.; Caroppo, C.; Giglio, F.; Langone, L.; Maimone, G.; Rappazzo, A.C.; Mancuso, M.; et al. Short-term dynamics of nutrients, planktonic abundances and microbial respiratory activity in the Arctic Kongsfjorden (Svalbard, Norway). Polar Biol. submitted.
- Sala, M.M.; Arrieta, J.M.; Boras, J.A.; Duarte, C.M.; Vaqué, D. The impact of ice melting on bacterioplankton in the Arctic Ocean. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappalà, G.; Bruzzone, G.; Azzaro, M.; Caruso, G. New advanced technology devices for operational oceanography in extreme conditions. Int. J. Sus. Dev. Plann. 2017, 12, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
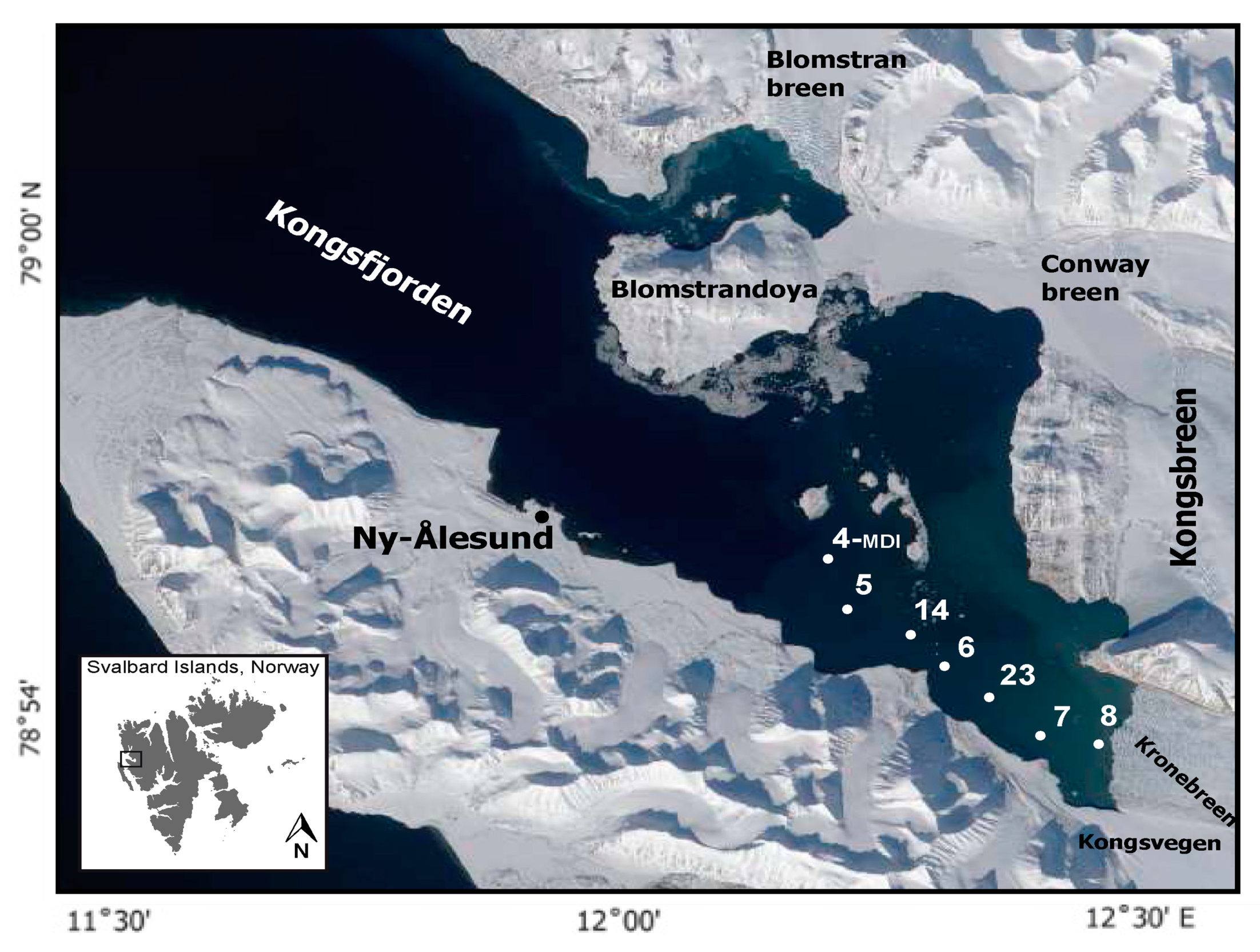


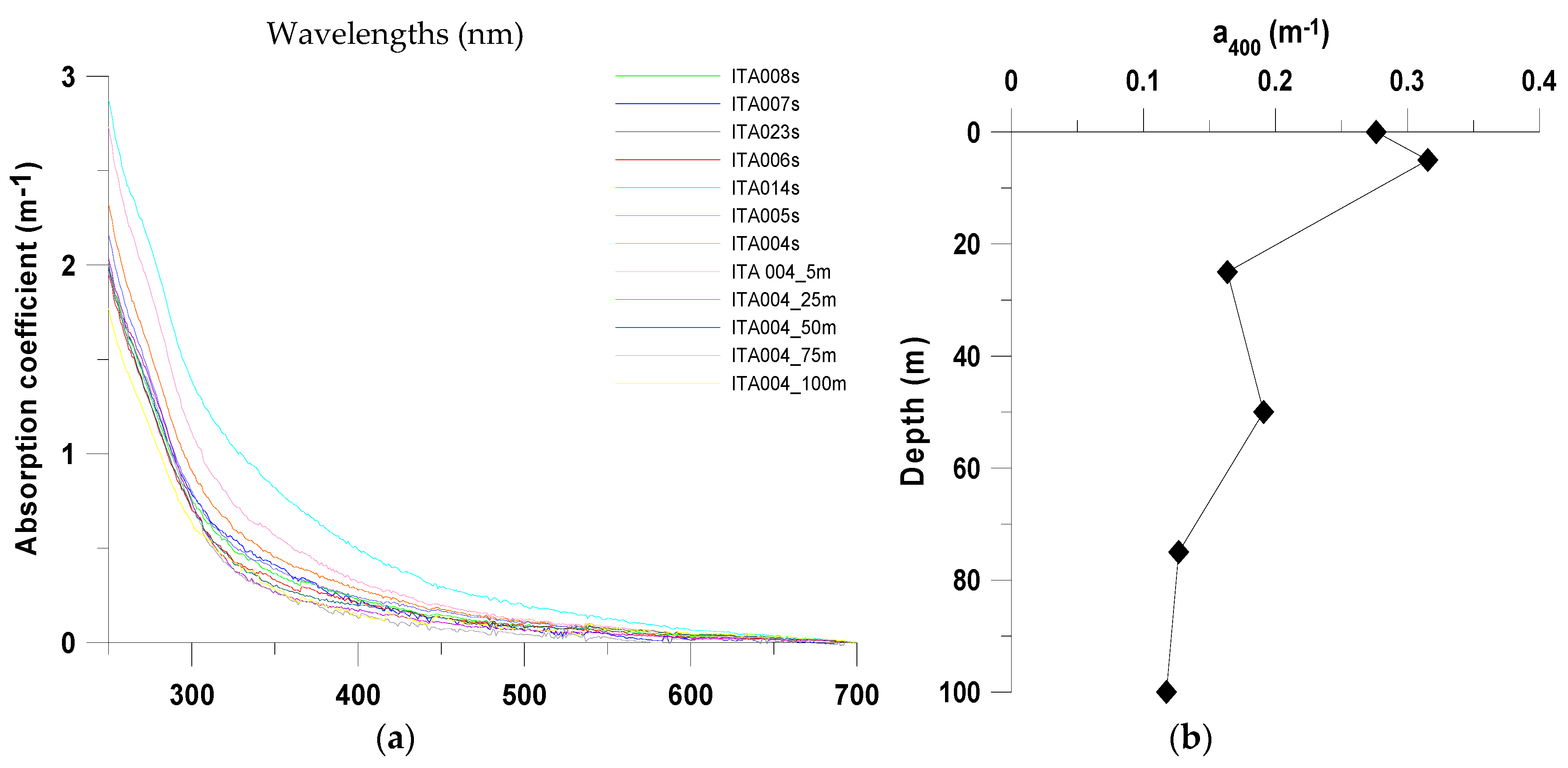
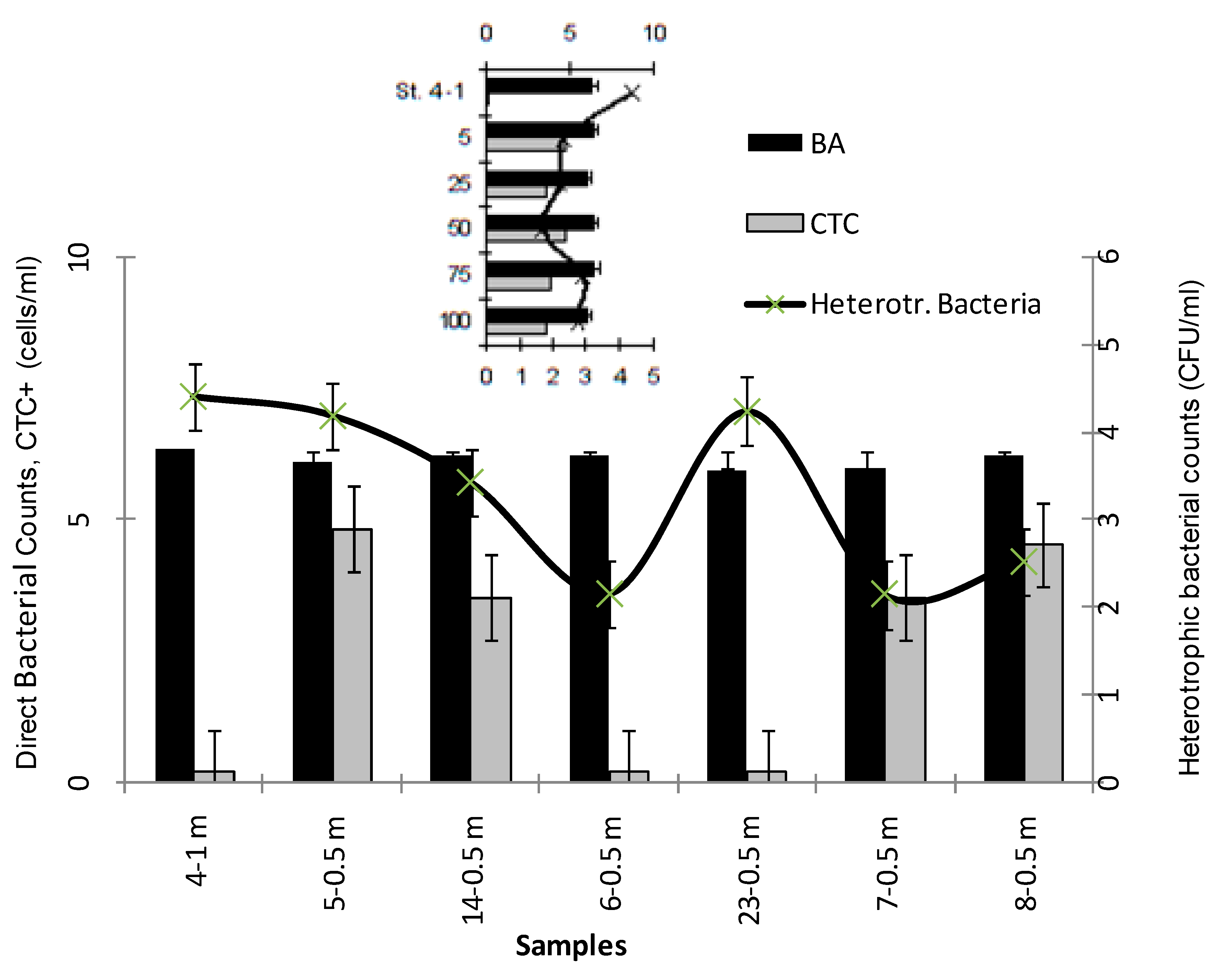


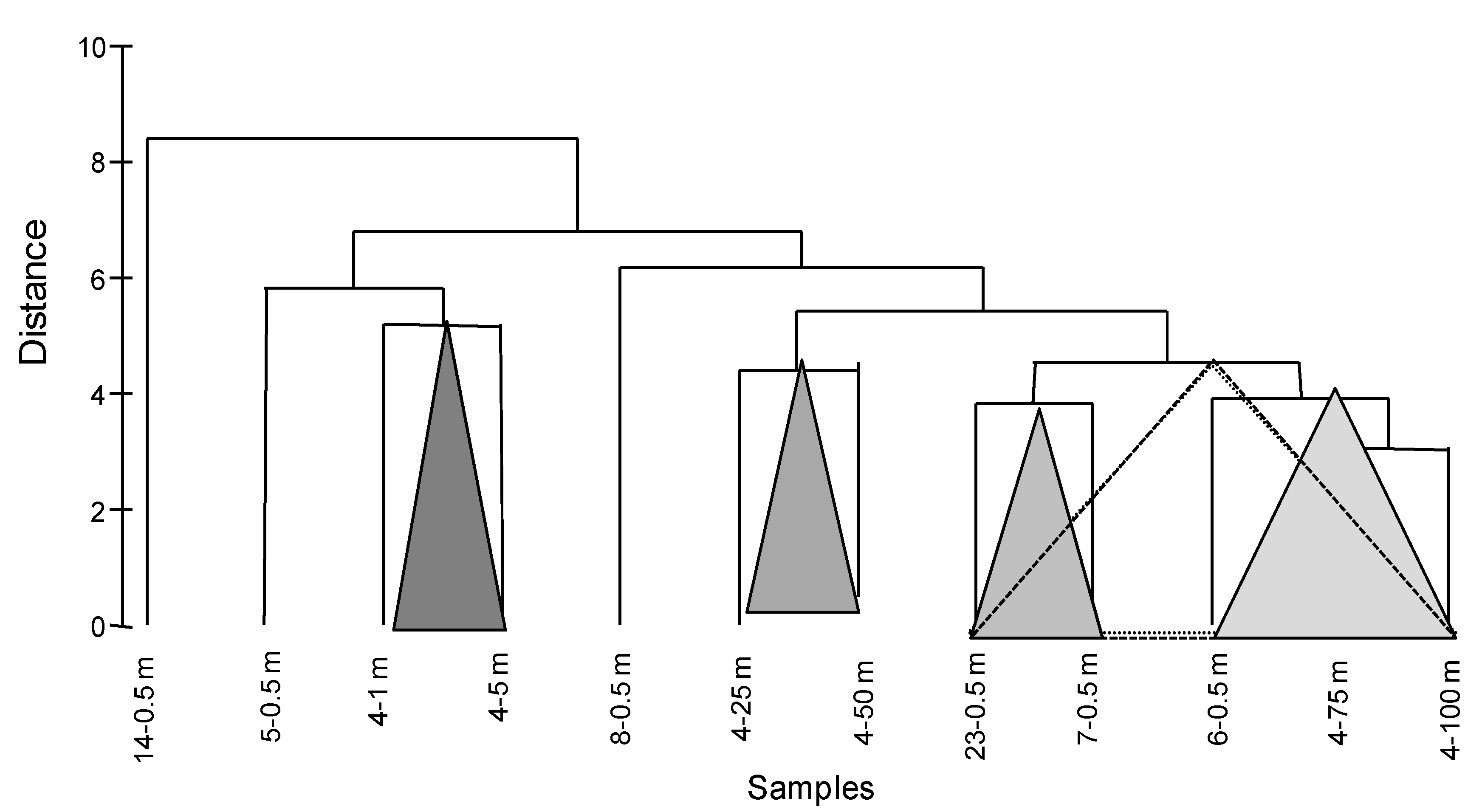
| Stations | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 78°54′ 36.00″ N | 12°15′ 0.00″ E |
| 5 | 78°54′ 0.00″ N | 12°16′ 12.00″ E |
| 14 | 78°53′ 24.00″ N | 12°19′ 12.00″ E |
| 6 | 78°53′ 24.00″ N | 12°22′ 12.00″ E |
| 23 | 78°52′ 48.00″ N | 12°25′ 12.00″ E |
| 7 | 78°52′ 12.00″ N | 12°28′ 12.00″ E |
| 8 | 78°52′ 12.00″ N | 12°31′ 48.00″ E |
| Sample | NH4 | NO2+NO3 | PO4 | Total C | Inorganic C | POC | PON | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Station-Depth) | µM | µM | µM | µgC/L | µgC/L | µgC/L | µg/L | Molar Ratio |
| 4–1 m | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 173.60 | 26.19 | 147.41 | 28.20 | 6.10 |
| 4–5 m | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 249.28 | 38.23 | 211.05 | 43.73 | 5.63 |
| 4–25 m | 0.76 | 0.14 | 0.19 | - | - | 397.20 | 60.69 | 7.64 |
| 4–50 m | 1.44 | 1.87 | 0.40 | 204.46 | 52.50 | 151.96 | 30.79 | 5.76 |
| 4–75 m | 0.99 | 3.12 | 0.48 | 188.58 | 12.57 | 176.01 | 27.15 | 7.56 |
| 4–100 m | 1.30 | 5.60 | 0.46 | 170.14 | 44.26 | 125.88 | 15.38 | 9.55 |
| 5–0.5 m | 0.45 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 165.41 | 29.62 | 135.79 | 26.54 | 5.97 |
| 14–0.5 m | 0.61 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 293.93 | 140.35 | 153.58 | 31.61 | 5.67 |
| 6–0.5 m | 0.73 | 1.05 | 0.19 | 103.86 | 19.06 | 84.79 | 14.78 | 6.69 |
| 23–0.5 m | 0.98 | 3.36 | 0.34 | 154.22 | 62.59 | 91.64 | 14.48 | 7.38 |
| 7–0.5 m | 1.05 | 2.62 | 0.33 | 112.83 | 39.52 | 73.31 | 12.50 | 6.84 |
| 8–0.5 m | 1.15 | 2.67 | 0.39 | 174.53 | 47.25 | 67.94 | 13.43 | 5.90 |
| Sample | Phyto-B (mg/l) | % of POC | BB (mg/l) | % of POC | Detritus (mg/l) | % of POC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4–1 m | 8.28 | 5.62 | 42.32 | 28.71 | 96.81 | 65.68 |
| 4–5 m | 5.64 | 2.67 | 55.31 | 26.21 | 150.10 | 71.12 |
| 4–25 m | 62.52 | 15.74 | 21.98 | 5.53 | 312.70 | 78.73 |
| 4–50 m | 40.64 | 26.74 | 50.55 | 33.26 | 60.77 | 39.99 |
| 4–75 m | 12.44 | 7.07 | 57.42 | 32.62 | 106.15 | 60.31 |
| 4–100 m | 5.6 | 4.45 | 22.93 | 18.21 | 97.35 | 77.34 |
| 5–0.5 m | 12.4 | 9.13 | 25.24 | 18.59 | 98.14 | 72.28 |
| 14–0.5 m | 10.52 | 6.85 | 34.83 | 22.68 | 108.23 | 70.47 |
| 6–0.5 m | 1.32 | 1.56 | 33.13 | 39.07 | 50.34 | 59.37 |
| 23–0.5 m | 7.2 | 7.86 | 16.60 | 18.12 | 67.84 | 74.03 |
| 7–0.5 m | 7.2 | 9.82 | 19.12 | 26.08 | 46.99 | 64.10 |
| 8–0.5 m | 2.48 | 3.65 | 34.22 | 50.37 | 31.24 | 45.98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caruso, G.; Madonia, A.; Bonamano, S.; Miserocchi, S.; Giglio, F.; Maimone, G.; Azzaro, F.; Decembrini, F.; La Ferla, R.; Piermattei, V.; et al. Microbial Abundance and Enzyme Activity Patterns: Response to Changing Environmental Characteristics along a Transect in Kongsfjorden (Svalbard Islands). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8100824
Caruso G, Madonia A, Bonamano S, Miserocchi S, Giglio F, Maimone G, Azzaro F, Decembrini F, La Ferla R, Piermattei V, et al. Microbial Abundance and Enzyme Activity Patterns: Response to Changing Environmental Characteristics along a Transect in Kongsfjorden (Svalbard Islands). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(10):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8100824
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaruso, Gabriella, Alice Madonia, Simone Bonamano, Stefano Miserocchi, Federico Giglio, Giovanna Maimone, Filippo Azzaro, Franco Decembrini, Rosabruna La Ferla, Viviana Piermattei, and et al. 2020. "Microbial Abundance and Enzyme Activity Patterns: Response to Changing Environmental Characteristics along a Transect in Kongsfjorden (Svalbard Islands)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 10: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8100824
APA StyleCaruso, G., Madonia, A., Bonamano, S., Miserocchi, S., Giglio, F., Maimone, G., Azzaro, F., Decembrini, F., La Ferla, R., Piermattei, V., Piazzolla, D., Marcelli, M., & Azzaro, M. (2020). Microbial Abundance and Enzyme Activity Patterns: Response to Changing Environmental Characteristics along a Transect in Kongsfjorden (Svalbard Islands). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(10), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8100824