Spray-Mediated Air-Sea Gas Exchange: The Governing Time Scales
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
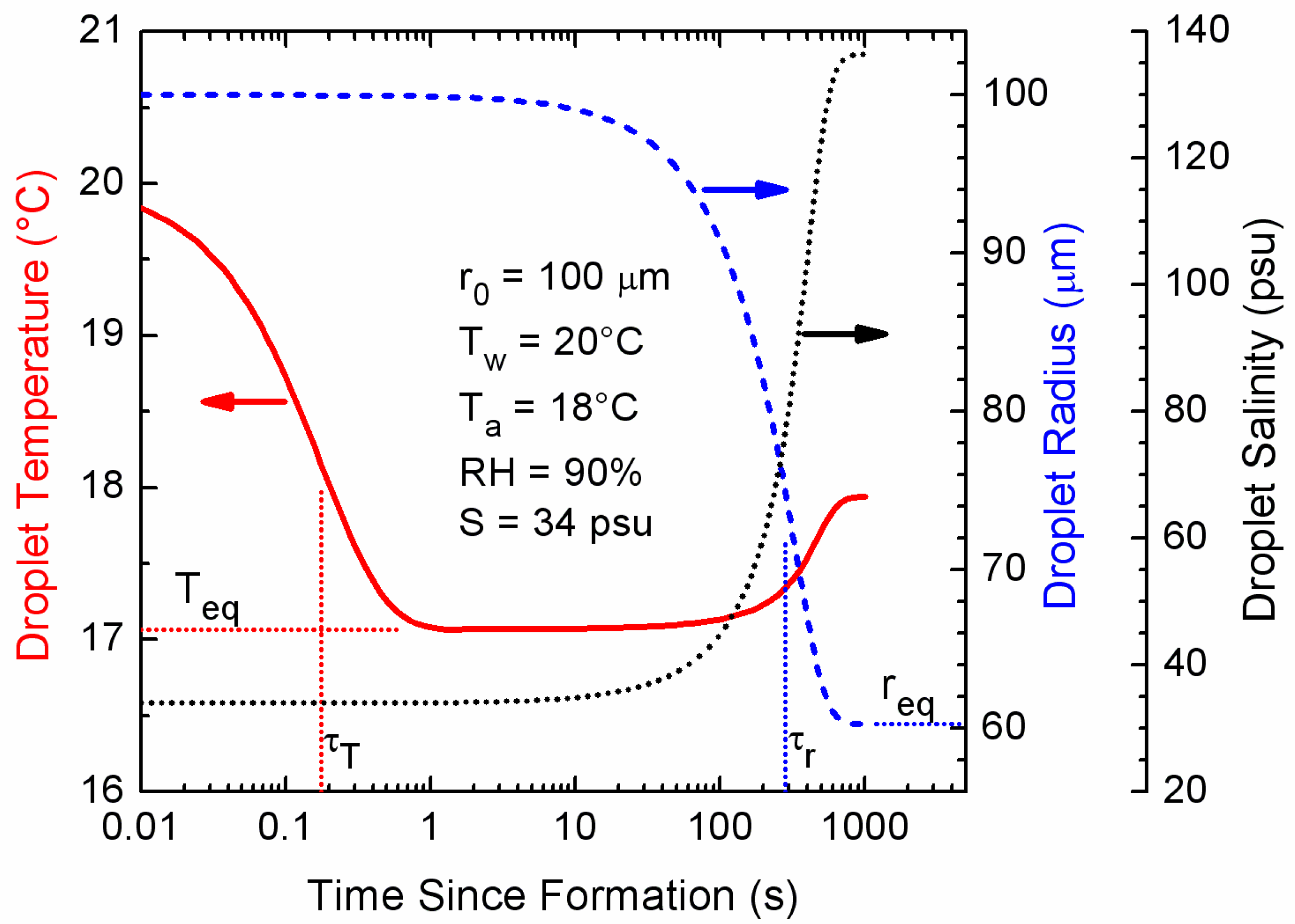
2.1. Spray Droplet Evolution
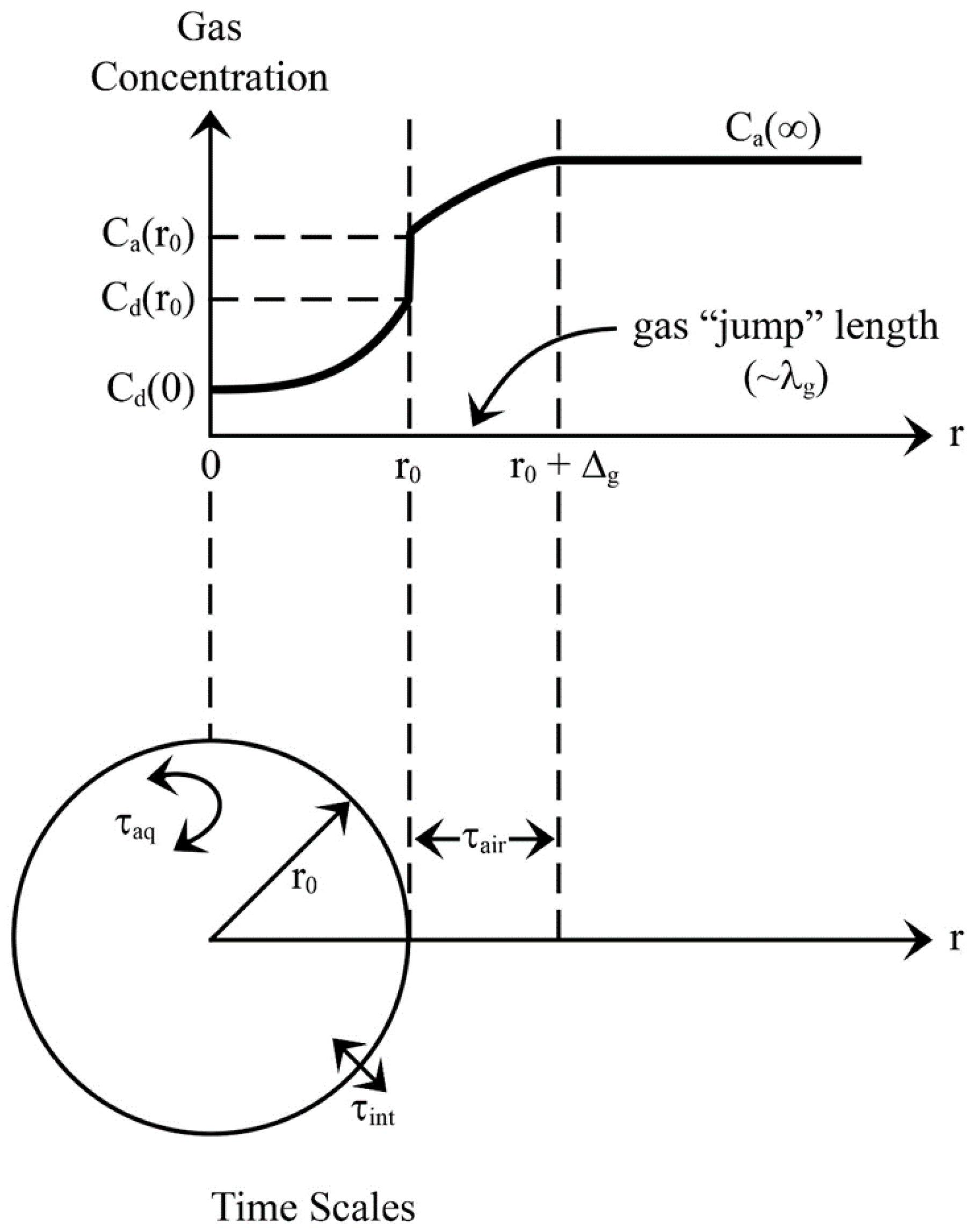
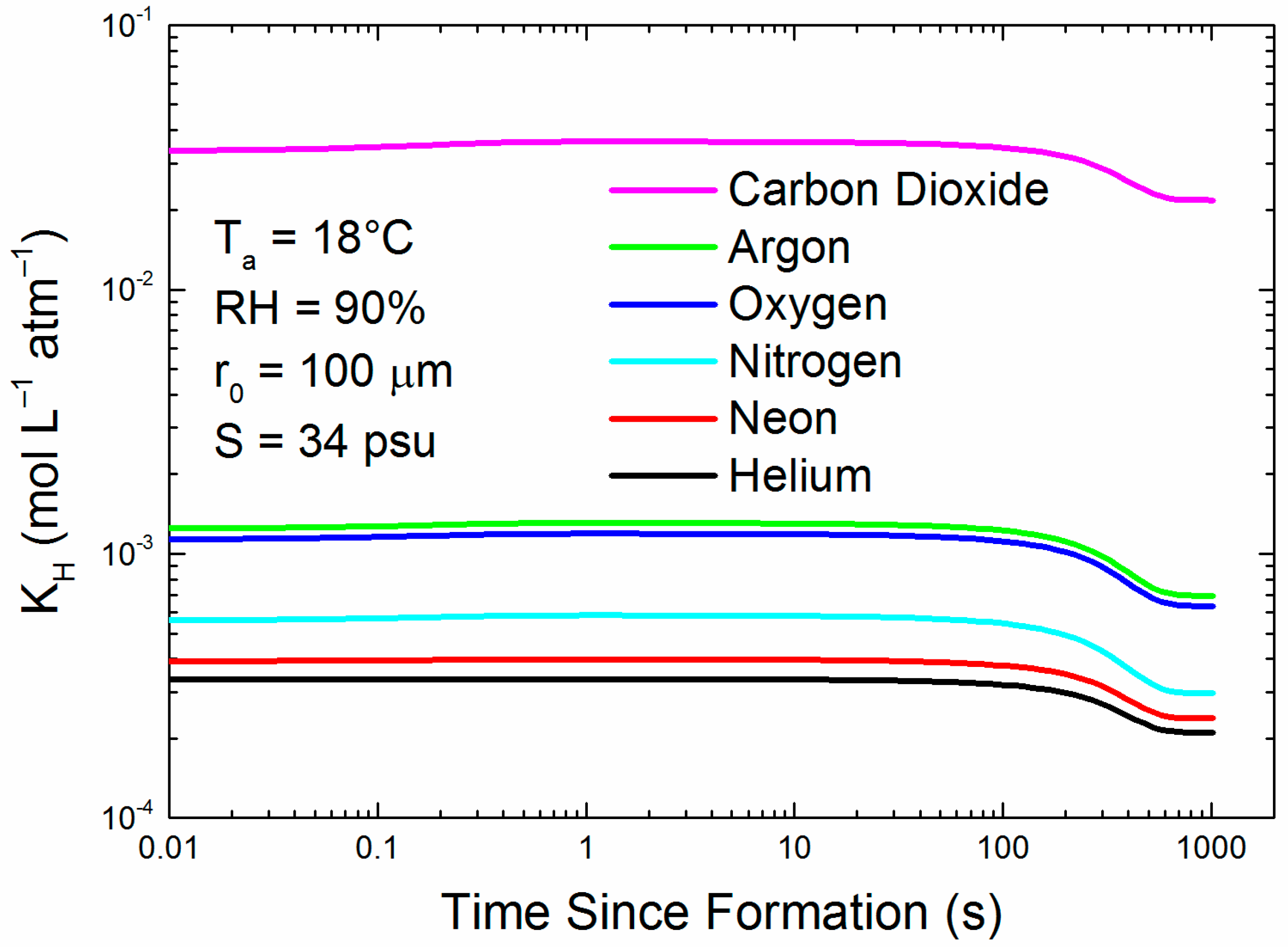
2.2. Gases and Spray Droplets
2.3. Microphysics
2.4. Droplet Residence Time
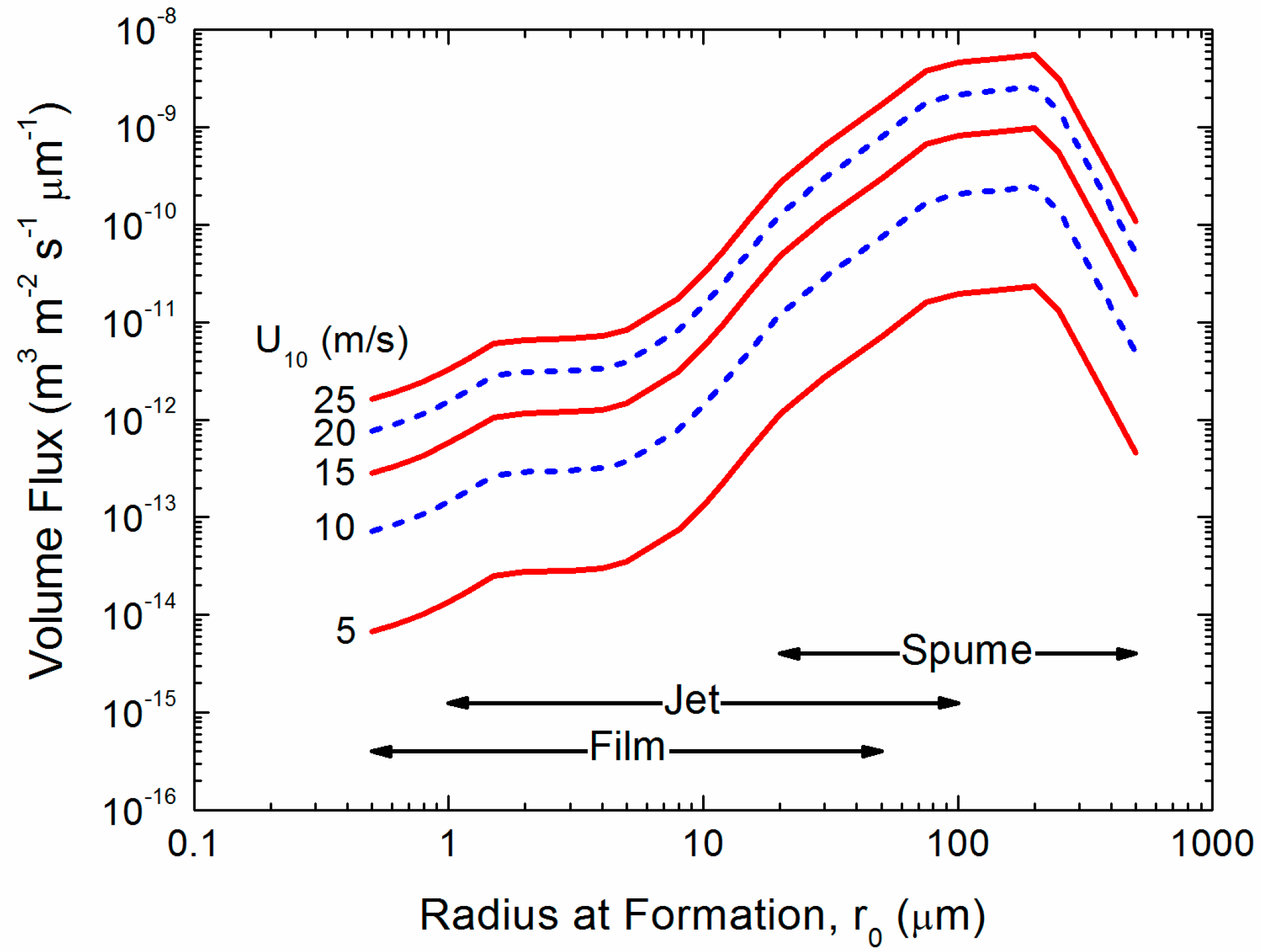
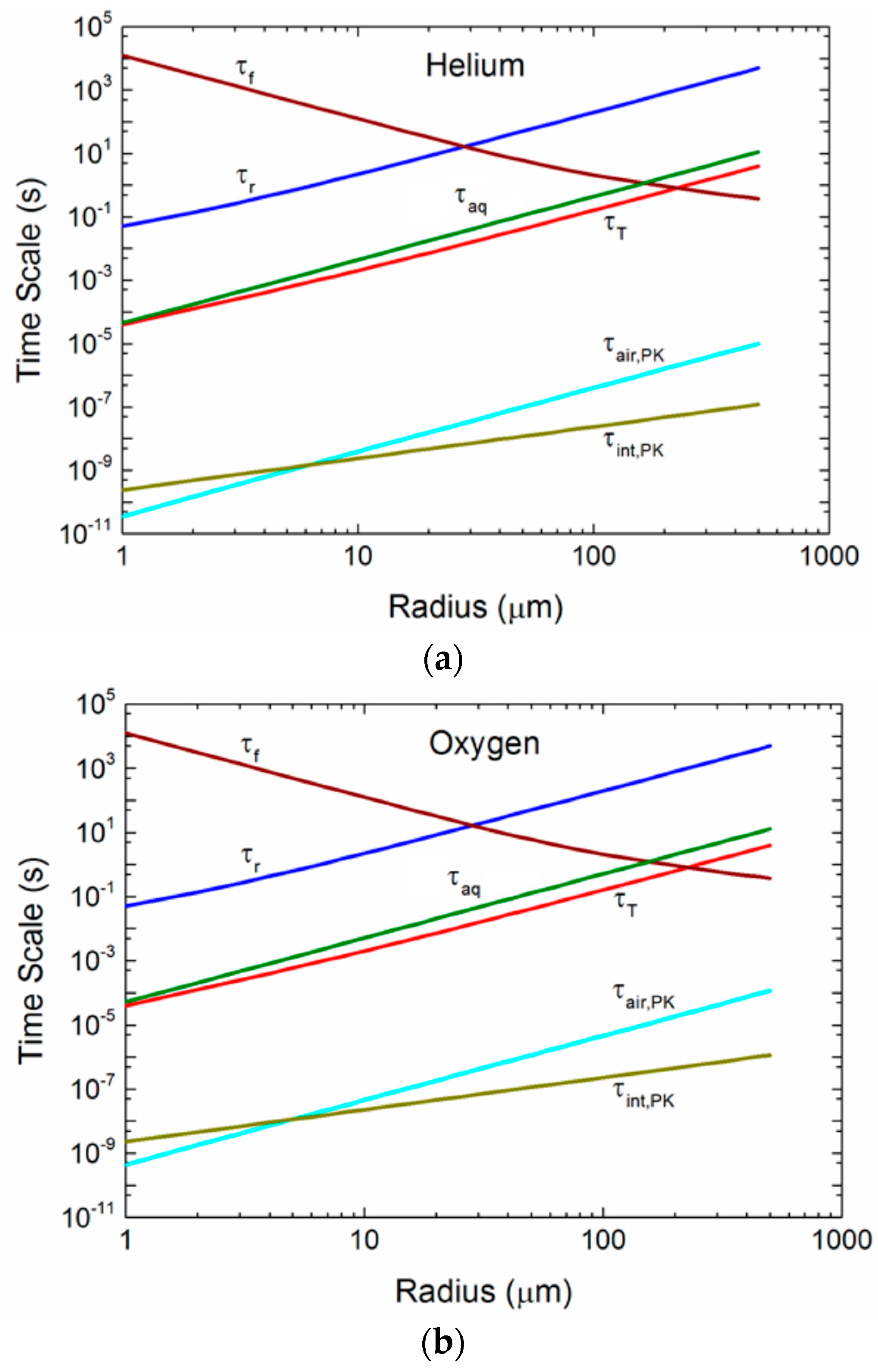
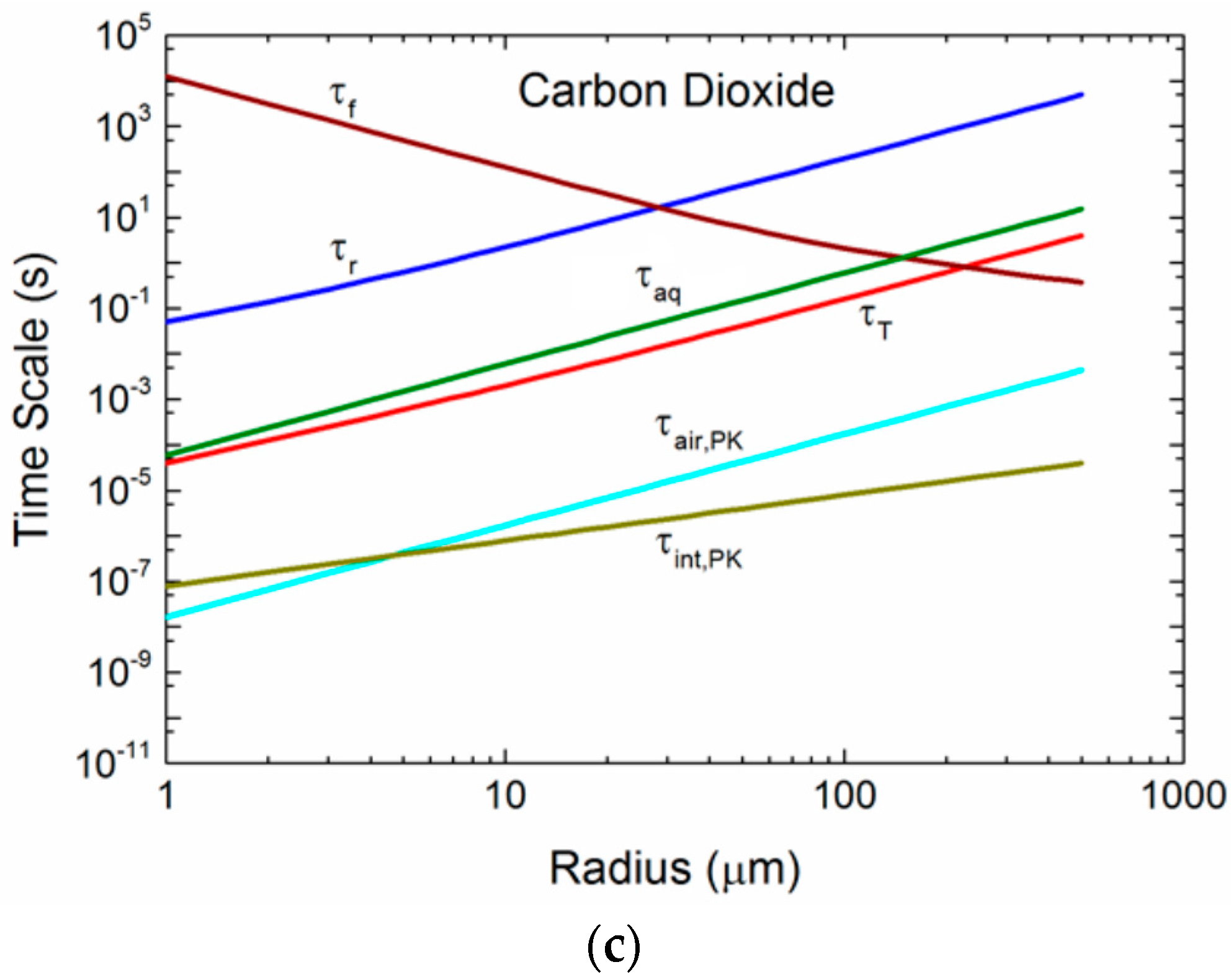
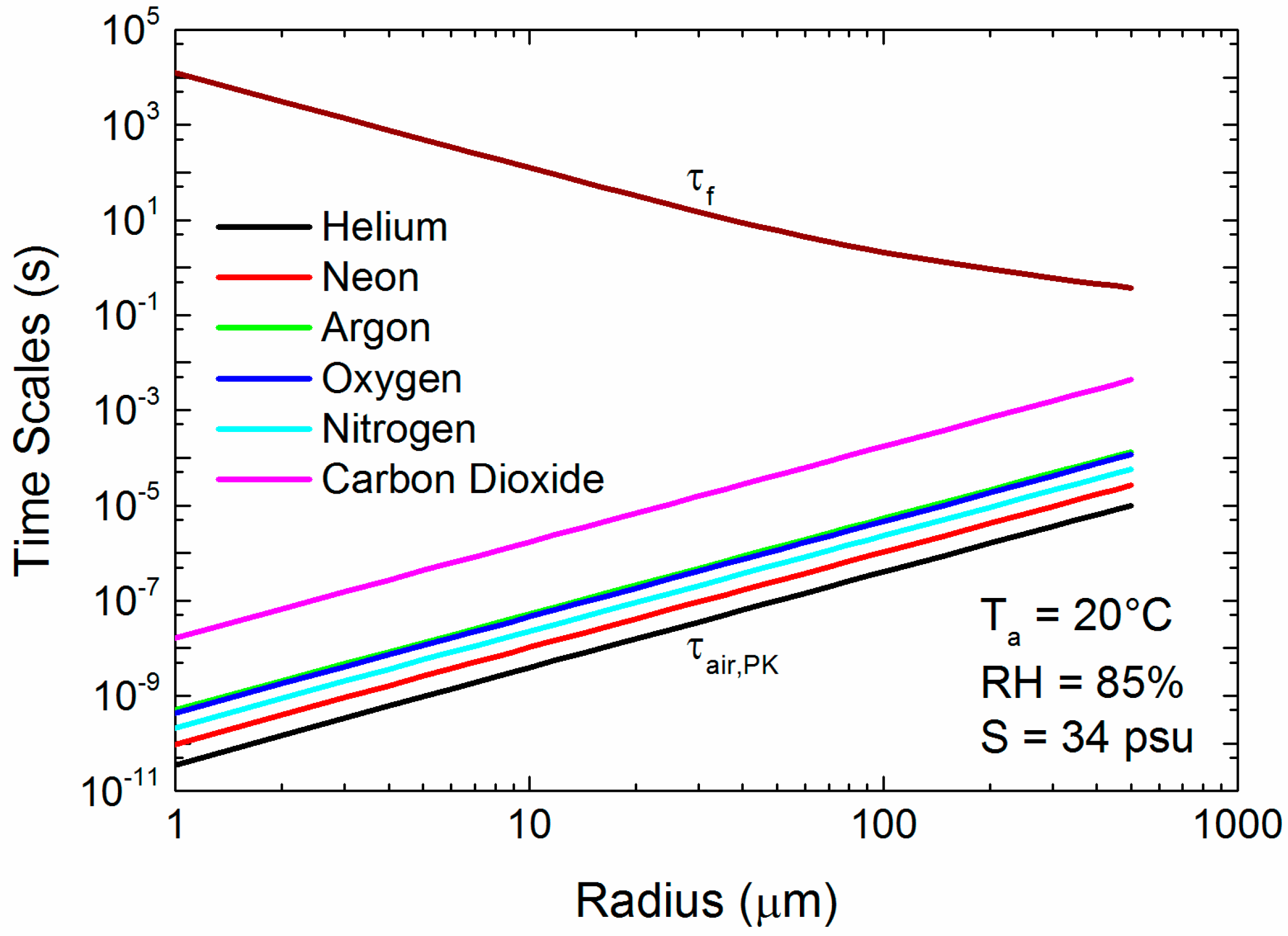
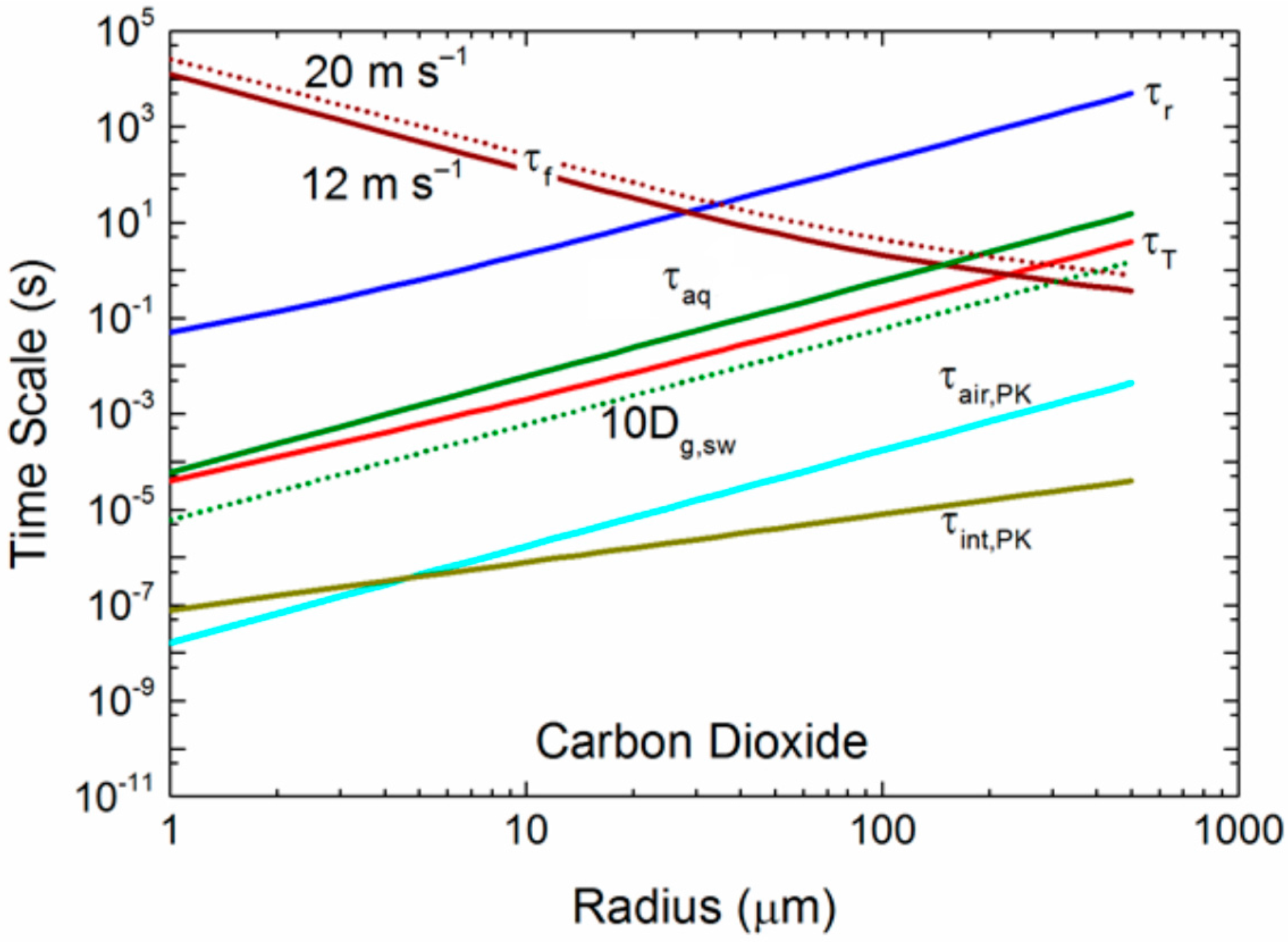
3. Spray Droplet Time Scales
3.1. Implications of the Time Scales
3.2. Initial Gas Concentration in Spray Droplets
3.3. Surface-Active Material
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Evaluating the Henry’s Law Coefficient, KH
References
- Monahan, E.C.; MacNiocaill, G. (Eds.) Oceanic Whitecaps and Their Role in Air-Sea Exchange Processes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; 294p. [Google Scholar]
- Bortkovskii, R.S. Air-Sea Exchange of Heat and Moisture during Storms; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; 194p. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, E.L.; Vlahos, P.; Monahan, E.C. The potential role of sea spray droplets in facilitating air-sea gas transfer. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.C. The electrification of the atmosphere by particles from bubbles in the sea. Prog. Ocenogr. 1963, 1, 71–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; Spiel, D.E.; Davidson, K.L. A model of marine aerosol generation via whitecaps and wave disruption. In Oceanic Whitecaps and Their Role in Air-Sea Exchange Processes; Monahan, E.C., MacNiocaill, G., Eds.; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Borisenkov, E.P. Some mechanisms of atmosphere-ocean interaction under stormy weather conditions. Probl. Arct. Antart 1974, 43–44, 330–347. [Google Scholar]
- Mestayer, P.G.; Lefauconnier, C. Spray droplet generation, transport, and evaporation in a wind wave tunnel during the Humidity over the Sea Experiments in the Simulation Tunnel. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Kepert, J.D.; Holland, G.J. The effect of sea spray on surface energy transports over the ocean. Glob. Atmos. Ocean Syst. 1994, 2, 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, E.L. Sea spray and the turbulent air-sea heat fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 11429–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, J.B.; Anquetin, S.; Mestayer, P.G.; Sini, J.F. Spray droplet modeling: 2. An interactive eulerian-lagrangian model of evaporating spray droplets. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Monahan, E.C. The role of whitecap bubbles in air-sea heat and moisture exchange. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2000, 30, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, L.P. Effect of air bubble solution on air-sea gas exchange. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A. On the clouds of bubbles formed by breaking wind waves in deep water and their role in air-sea gas transfer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1982, 304, 155–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlivat, L.; Memery, L. Gas exchange across an air-water interface: Experimental results and modeling of bubble contribution to transfer. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; Spillane, M.C. The role of oceanic whitecaps in air-sea gas exchange. In Gas Transfer at Water Surfaces; Brutsaert, W., Jirka, G.J., Eds.; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 495–503. [Google Scholar]
- Memery, L.; Merlivat, L. Modelling of gas flux through bubbles at the air-water interface. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 1985, 37, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, P.S.; Merlivat, L. Air-sea gas exchange rates: Introduction and synthesis. In The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling; Buat-Ménard, P., Ed.; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Lancaster, UK, 1986; pp. 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Woolf, D.K.; Thorpe, S.A. Bubbles and the air-sea exchange of gases in near-saturation conditions. J. Mar. Res. 1991, 49, 435–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.W.R.; Wirick, C.D. Large air-sea gas fluxes associated with breaking waves. Nature 1992, 356, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, R.F. On the role of large bubbles in air-sea gas exchange and supersaturation in the ocean. J. Mar. Res. 1993, 51, 237–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, D.K. Bubbles and the air-sea transfer velocity of gases. Atmos. Ocean 1993, 31, 517–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, W.E.; Wanninkhof, R. The effect of bubble-mediated gas transfer on purposeful dual-tracer gaseous transfer experiments. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 10555–10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, W.E.; Karle, L.M.; Higgins, B.J.; Farley, P.J.; Monahan, E.C.; Leifer, I.S. The influence of bubble plumes on air-seawater gas transfer velocities. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1996, 101, 12027–12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C. The physical and practical implications of a CO2 gas transfer coefficient that varies as the cube of the wind speed. In Gas Transfer at Water Surfaces; Donelan, M.A., Drennan, W.M., Saltzman, E.S., Wanninkhof, R., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Vlahos, P.; Monahan, E.C. A generalized model for the air-sea transfer of dimethyl sulfide at high wind speeds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L21605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahos, P.; Monahan, E.C.; Huebert, B.J.; Edson, J.B. Wind-dependence of DMS transfer velocity: Comparison of model with Southern Ocean observations. In Gas Transfer at Water Surfaces 2010; Komori, S., McGillis, W.R., Kurose, R., Eds.; Kyoto University Press: Kyoto, Japan, 2011; pp. 455–463. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, E.L. Spray-mediated enthalpy flux to the atmosphere and salt flux to the ocean in high winds. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; DeCosmo, J. The signature of sea spray in the HEXOS turbulent heat flux data. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2002, 103, 303–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Edson, J.B.; Monahan, E.C.; Rouault, M.P.; Smith, S.D. The spray contribution to net evaporation from the sea: A review of recent progress. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1995, 72, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Persson, P.O.G.; Hare, J.E. A bulk turbulent air-sea flux algorithm for high-wind, spray conditions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Mahrt, L.; Vickers, D. An improved bulk air-sea surface flux algorithm, including spray-mediated transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Time constants for the evolution of sea spray droplets. Tellus B 1990, 42, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Approximation formulas for the microphysical properties of saline droplets. Atmos. Res. 2005, 75, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Handbook of Physical Constants and Functions for Use in Atmospheric Boundary Layer Studies; ERDC/CRREL Monograph M-05-1; U.S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory: Hanover, NH, USA, 2005; 42p.
- Andreas, E.L.; DeCosmo, J. Sea spray production and influence on air-sea heat and moisture fluxes over the open ocean. In Air-Sea Exchange: Physics, Chemistry and Dynamics; Geernaert, G.L., Ed.; Kluwer: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 327–362. [Google Scholar]
- Twomey, S. The identification of individual hygroscopic particles in the atmosphere by a phase-transition method. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, I.N.; Munkelwitz, H.R. Composition and temperature dependence of the deliquescence properties of hygroscopic aerosols. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1993, 27, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; 1203p. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, E.L. Thermal and Size Evolution of Sea Spray Droplets; CRREL Rep. 89-11; U.S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory: Hanover, NH, USA, 1989; 37p.
- Smith, M.H.; Park, P.M.; Consterdine, I.E. Marine aerosol concentrations and estimated fluxes over the sea. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C. The ocean as a source of atmospheric particles. In The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling; Buat-Menard, P., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 129–163. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, E.L. Andreas, E.L. A review of the sea spray generation function for the open ocean. In Atmosphere-Ocean Interactions; Perrie, W., Ed.; WIT Press: Ashurst, UK, 2002; Volume 1, pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Pruppacher, H.R.; Klett, J.D. Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation, 2nd Revised ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; 954p. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, D.; Verlinde, J. Physics and Chemistry of Clouds; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; 584p. [Google Scholar]
- Pilson, M.E.Q. An Introduction to the Chemistry of the Sea, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; 524p. [Google Scholar]
- Bohren, C.F.; Albrecht, B.A. Atmospheric Thermodynamics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; 402p. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S. The characteristic time to achieve interfacial phase equilibrium in cloud drops. Atmos. Environ. 1989, 23, 2299–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; 510p. [Google Scholar]
- Mestayer, P.G.; Van Eijk, A.M.J.; de Leeuw, G.; Tranchant, B. Numerical simulation of the dynamics of sea spray over the waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 20771–20797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Wang, S. Predicting significant wave height off the northeast coast of the United States. Ocean Eng. 2007, 34, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakall, M.; Mitra, S.K.; Diehl, K.; Borrmann, S. Shapes and oscillations of falling raindrops—A review. Atmos. Res. 2010, 97, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, K.V.; Kubesh, R.J.; Ochs, H.T. Laboratory measurements of small raindrop distortion. Part I: Axis ratios and fall behavior. J. Atmos. Sci. 1991, 48, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeClair, B.P.; Hamielec, A.E.; Pruppacher, H.R.; Hall, W.D. A theoretical and experimental study of the internal circulation in water drops falling at terminal velocity in air. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, R.; Grace, J.; Weber, M.E. Bubbles, Drops, and Particles; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1978; 381p. [Google Scholar]
- Tennekes, H.; Lumley, J.L. A First Course in Turbulence; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972; 300p. [Google Scholar]
- Liss, P.S. Gas transfer: Experiments and geochemical implications. In Air-Sea Exchange of Gases and Particles; Liss, P.S., Slinn, W.G.N., Eds.; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 241–298. [Google Scholar]
- Donelan, M.A.; Wanninkhof, R. Gas transfer at water surfaces—Concepts and issues. In Gas Transfer at Water Surfaces; Donelan, M.A., Drennan, W.M., Saltzman, E.S., Wanninkhof, R., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Broecker, W.S.; Peng, T.-H. Gas exchange rates between air and sea. Tellus 1974, 26, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntyre, F. Flow patterns in breaking bubbles. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 5211–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntyre, F. The top millimeter of the ocean. Sci. Am. 1974, 230, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.C. The ejection of drops from the sea and their enrichment with bacteria and other materials: A review. Estuaries 1989, 12, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.C. Surface-active monolayers, bubbles, and jet drops. Tellus B 1990, 42, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, G.; Andreas, E.L.; Anguelova, M.D.; Fairall, C.W.; Lewis, E.R.; O’Dowd, C.; Schulz, M.; Schwartz, S.E. Production flux of sea spray aerosol. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49, RG2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970; 615p. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, R.T. The behavior of large, low-surface-tension water drops falling at terminal velocity in air. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1976, 15, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.F. The solubility of nitrogen, oxygen and argon in water and seawater. Deep-Sea Res. 1970, 17, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.F. Solubility of helium and neon in water and seawater. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1971, 16, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.F. Carbon dioxide in water and seawater: The solubility of a non-ideal gas. Mar. Chem. 1974, 2, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broecker, W.S.; Peng, T.-H. Tracers in the Sea; Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory, Columbia University: Palisades, NY, USA, 1982; 690p. [Google Scholar]
- Wanninkhof, R. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 7373–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J. The Physical Chemistry of Natural Waters; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2001; 654p. [Google Scholar]
| r0 | uf | Re | vs/uf a | vs | r0 vs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μm) | (m s−1) | (m s−1) | (m2 s−1) | ||
| 1 | 1.2 × 10−4 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 0.01 | 1.2 × 10−6 | 1.2 × 10−12 |
| 10 | 0.123 | 0.0164 | 0.01 | 1.2 × 10−4 | 1.2 × 10−9 |
| 50 | 0.254 | 1.69 | 0.012 | 3.1 × 10−3 | 1.9 × 10−7 |
| 100 | 0.725 | 9.65 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 1.2 × 10−6 |
| 200 | 1.67 | 44.4 | 0.024 | 0.030 | 1.0 × 10−5 |
| 500 | 4.10 | 272 | 0.042 | 0.16 | 1.0 × 10−5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andreas, E.L.; Vlahos, P.; Monahan, E.C. Spray-Mediated Air-Sea Gas Exchange: The Governing Time Scales. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5040060
Andreas EL, Vlahos P, Monahan EC. Spray-Mediated Air-Sea Gas Exchange: The Governing Time Scales. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2017; 5(4):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5040060
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndreas, Edgar L., Penny Vlahos, and Edward C. Monahan. 2017. "Spray-Mediated Air-Sea Gas Exchange: The Governing Time Scales" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 5, no. 4: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5040060
APA StyleAndreas, E. L., Vlahos, P., & Monahan, E. C. (2017). Spray-Mediated Air-Sea Gas Exchange: The Governing Time Scales. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 5(4), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5040060





