Mobilization of PAHs by Wave-Induced Resuspension and Liquefaction in Silty Sediment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Material
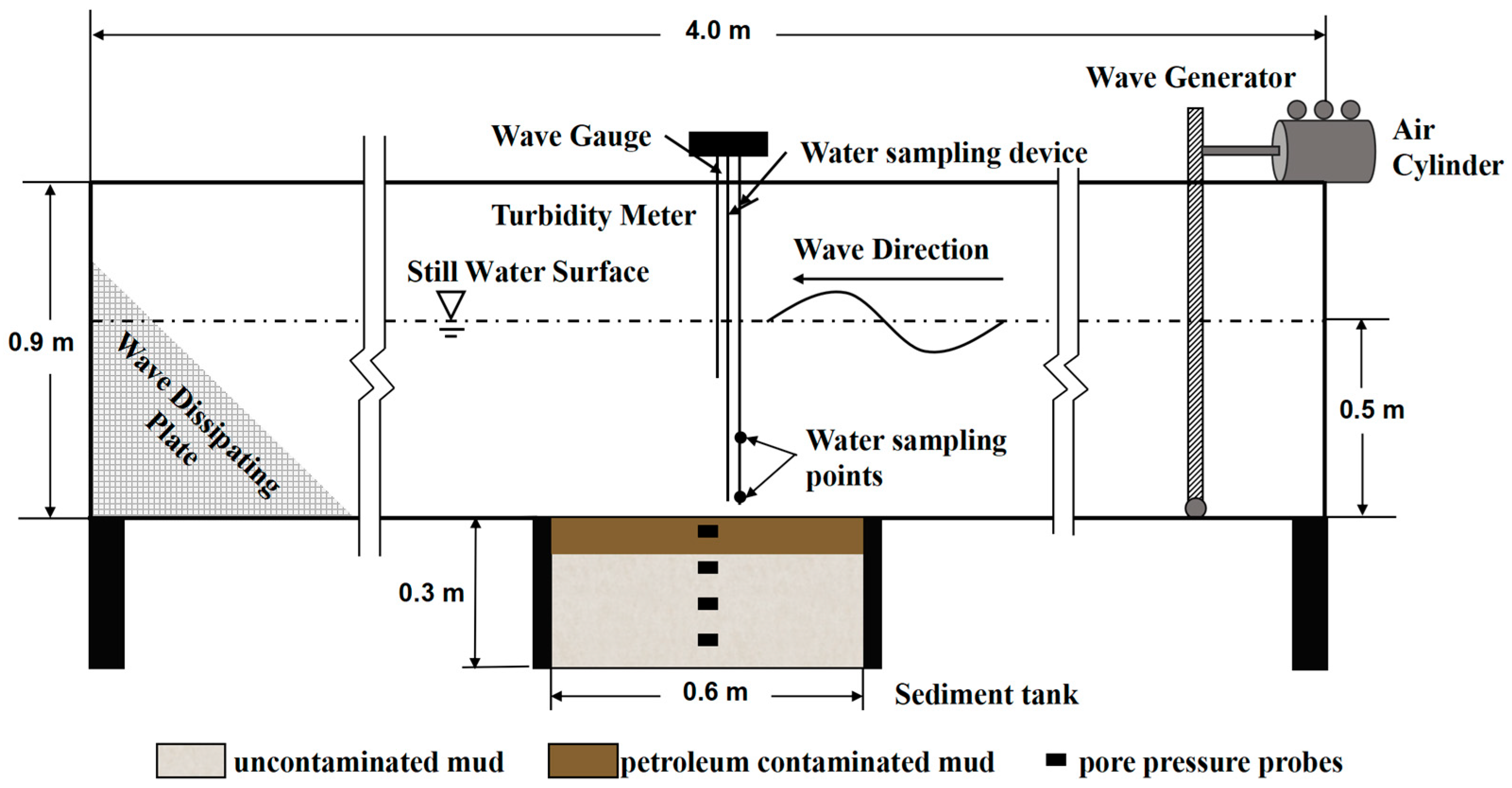
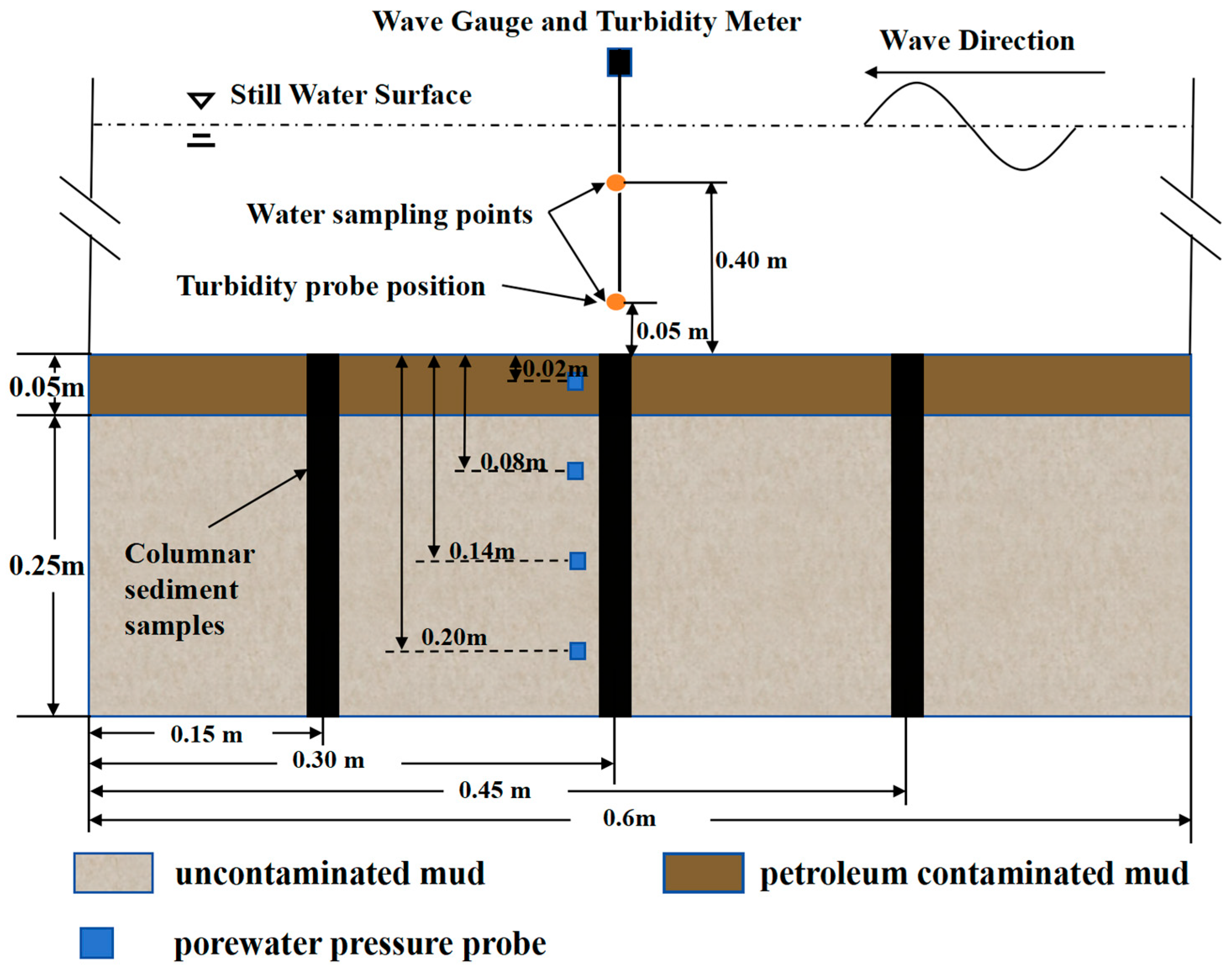
2.2. Configuration of Flume Experiment
2.3. Flume Experiment Procedure
2.4. Analytical Methods of the Samples
2.5. Data Statistical Analysis
2.6. Quality Control
3. Results
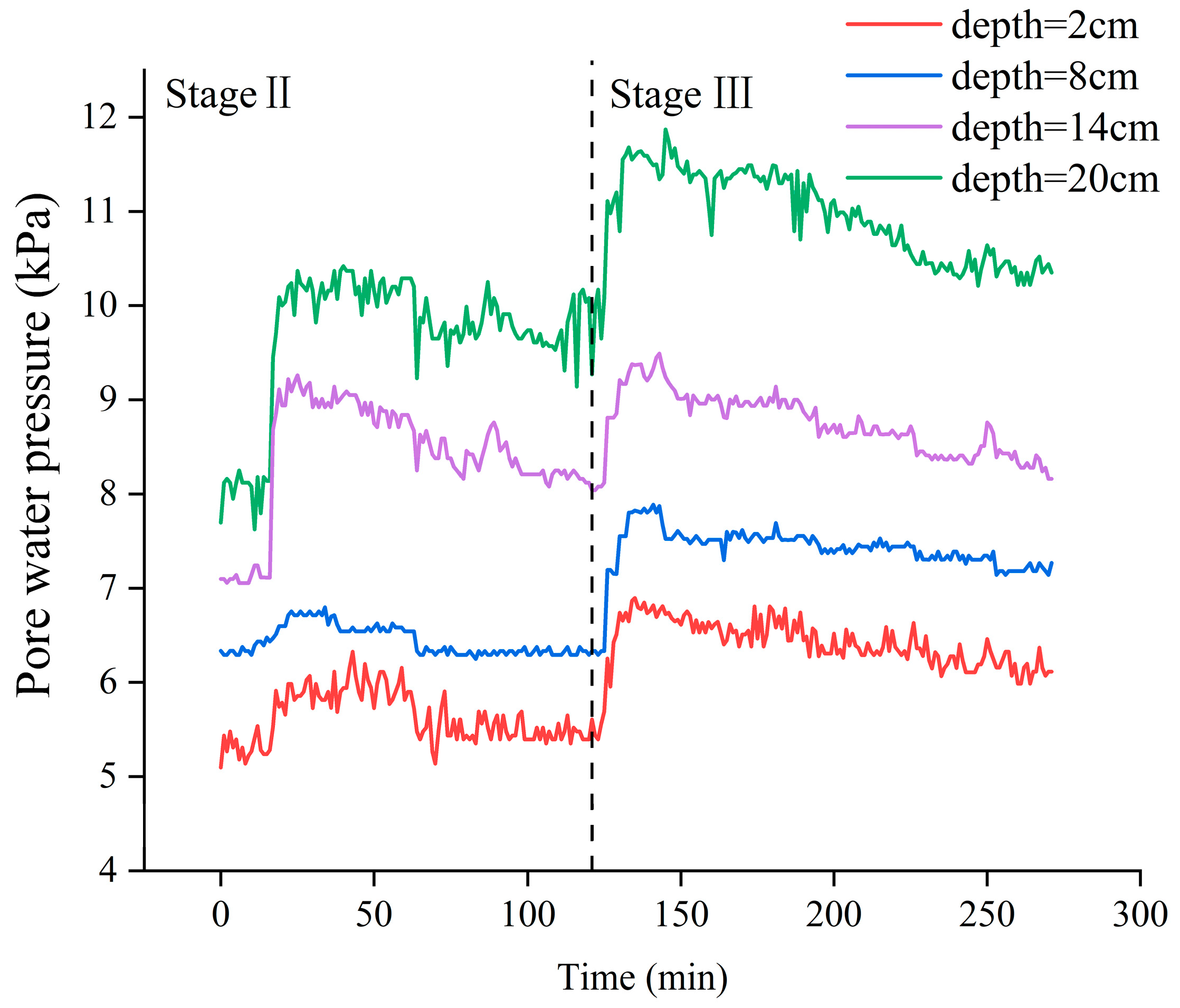
3.1. Characteristics of Porewater Pressure Changes in Sediments
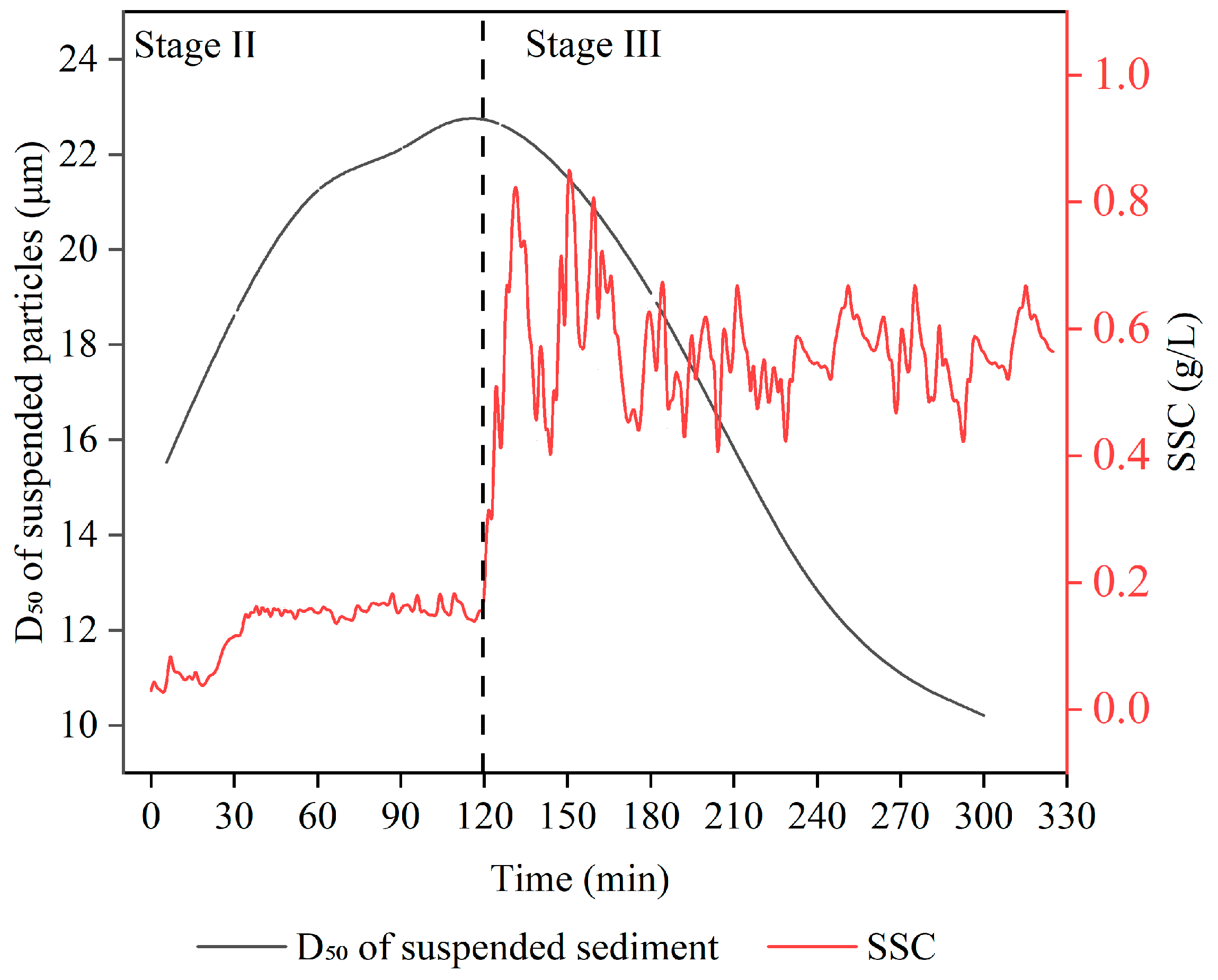
3.2. Variation Characteristics of Suspended Sediment Concentration and Median Particle Diameter of Suspended Particles in Overlying Water
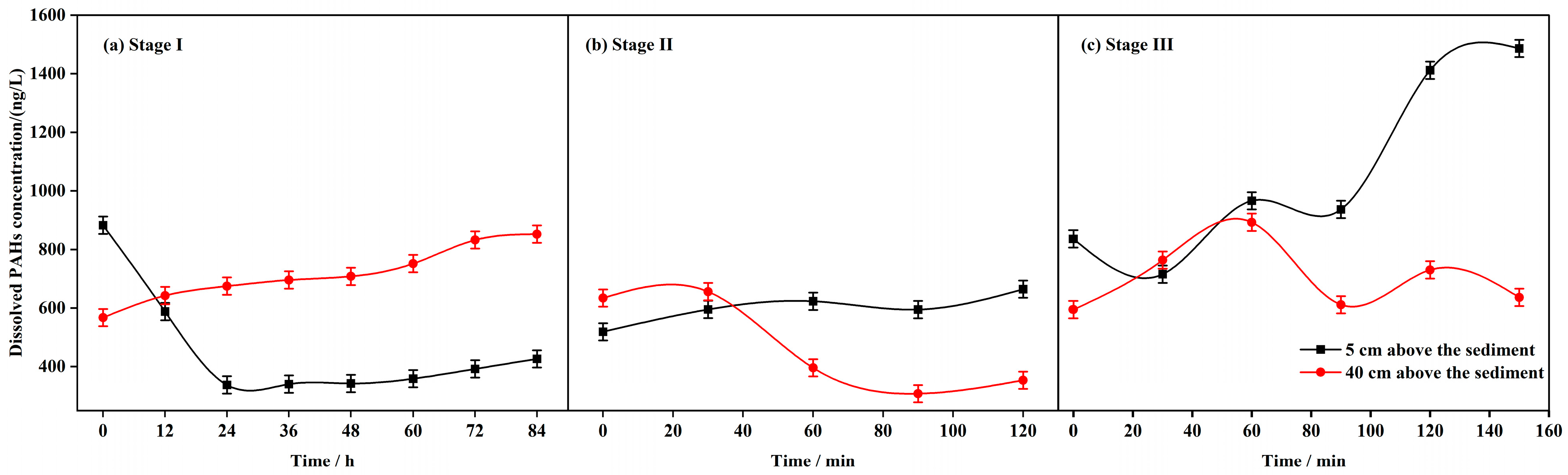
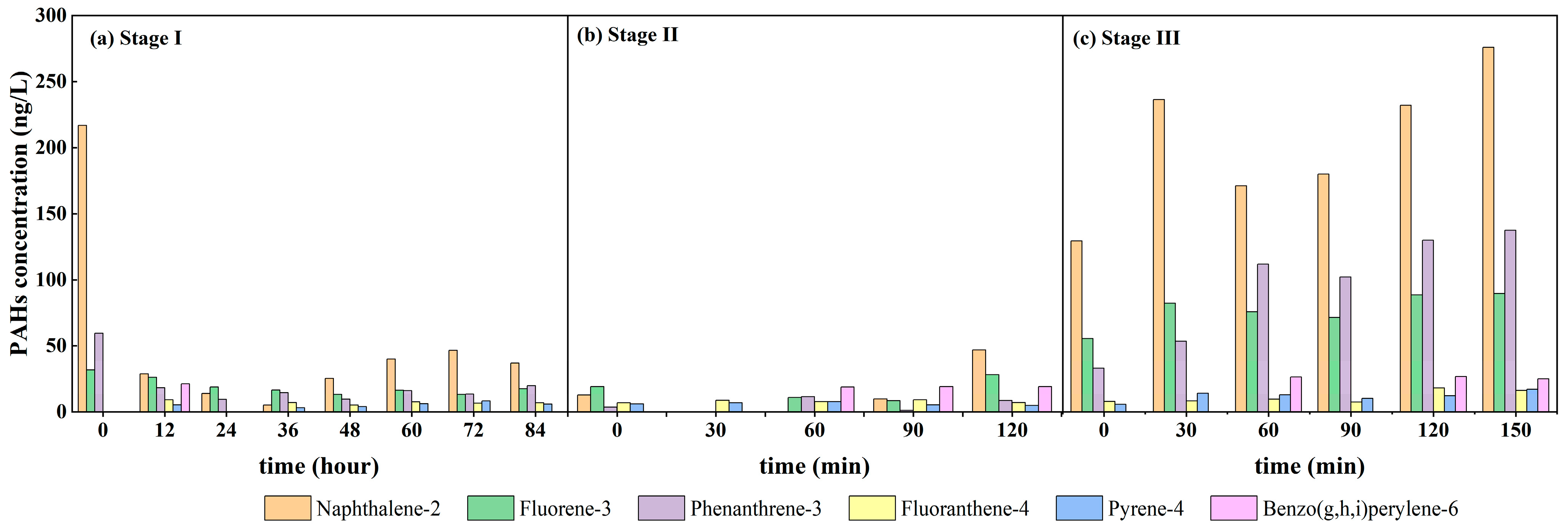
3.3. Variation Characteristics of PAHs Concentration and Composition in Overlying Water
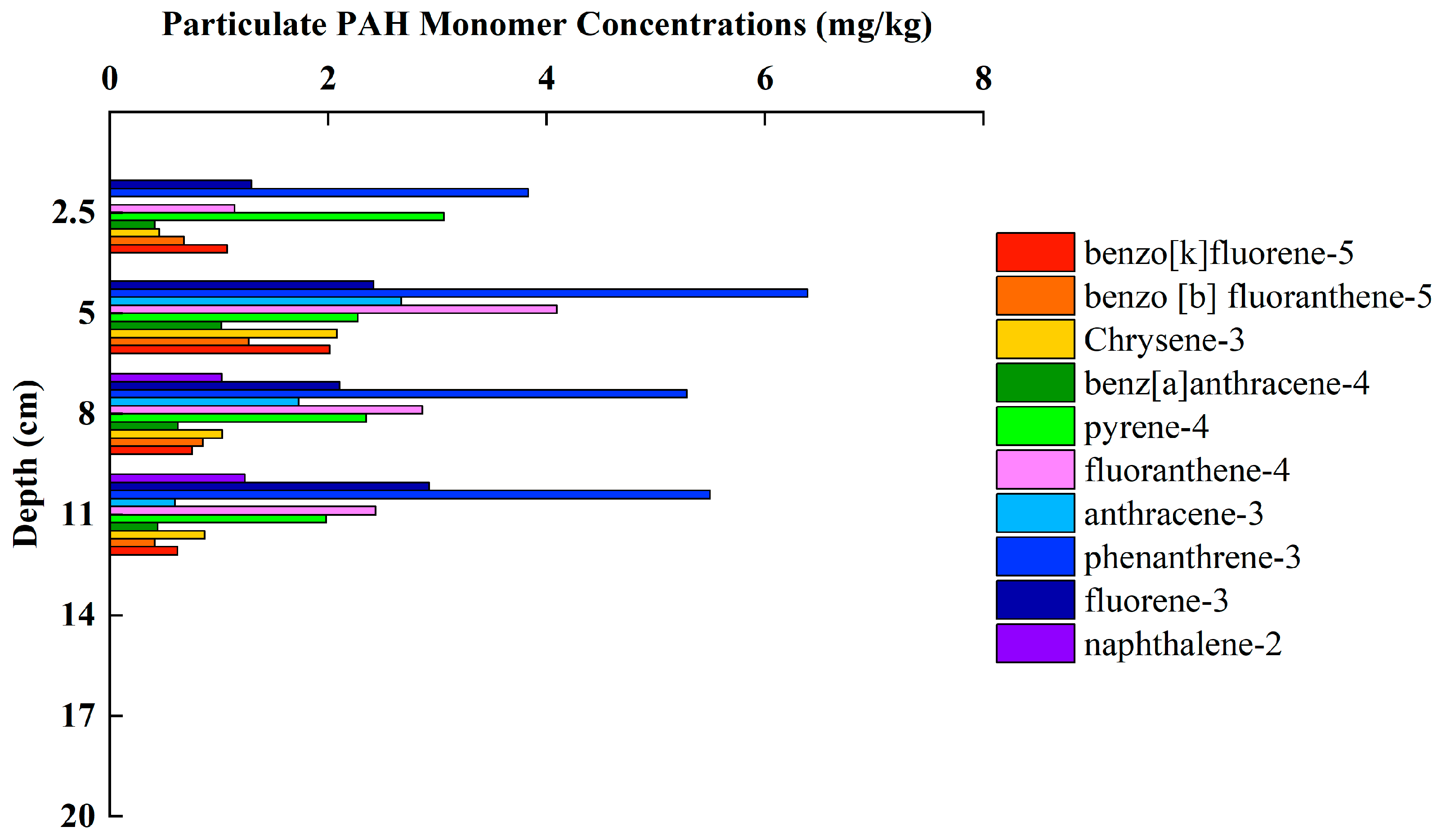
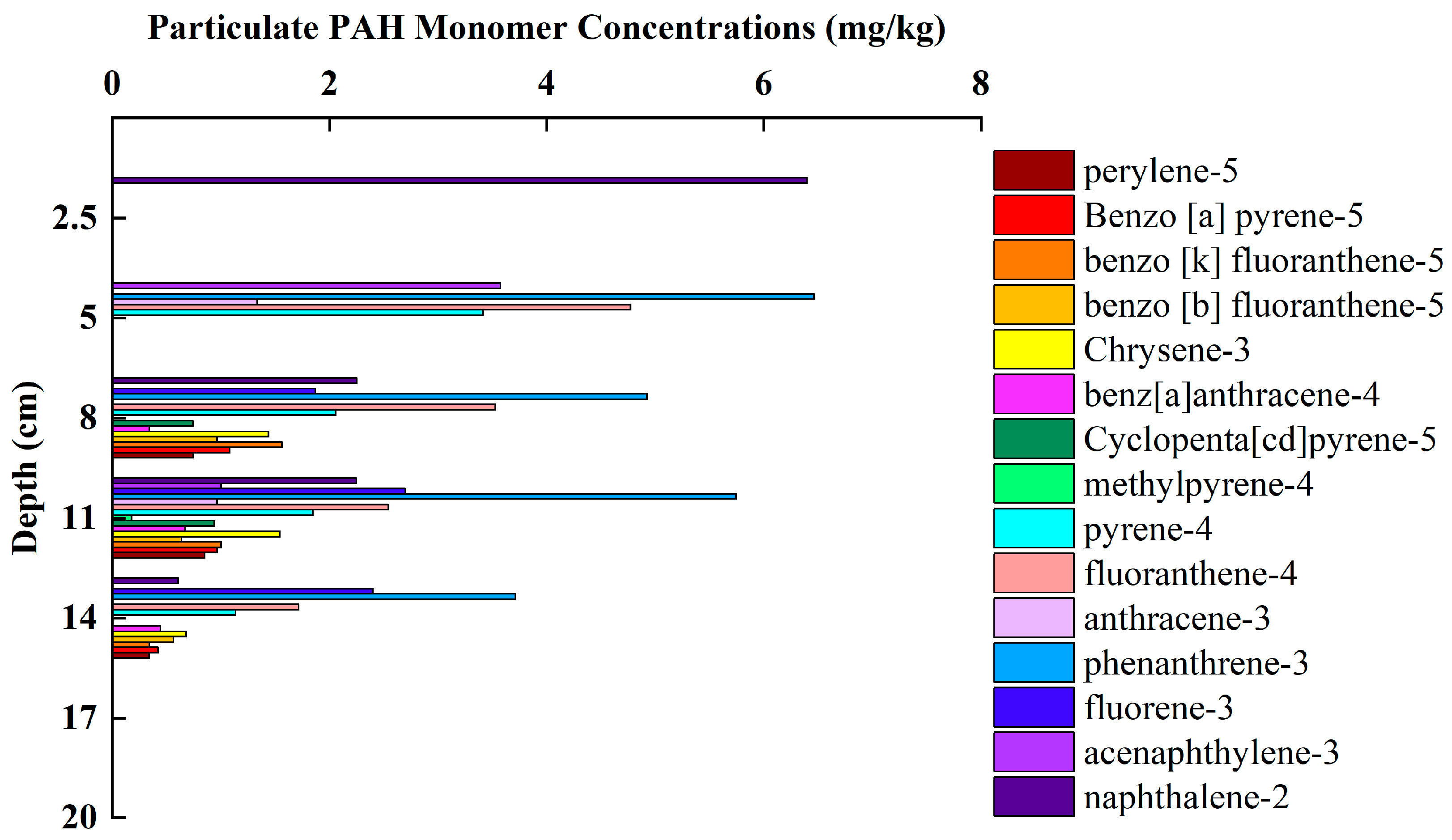
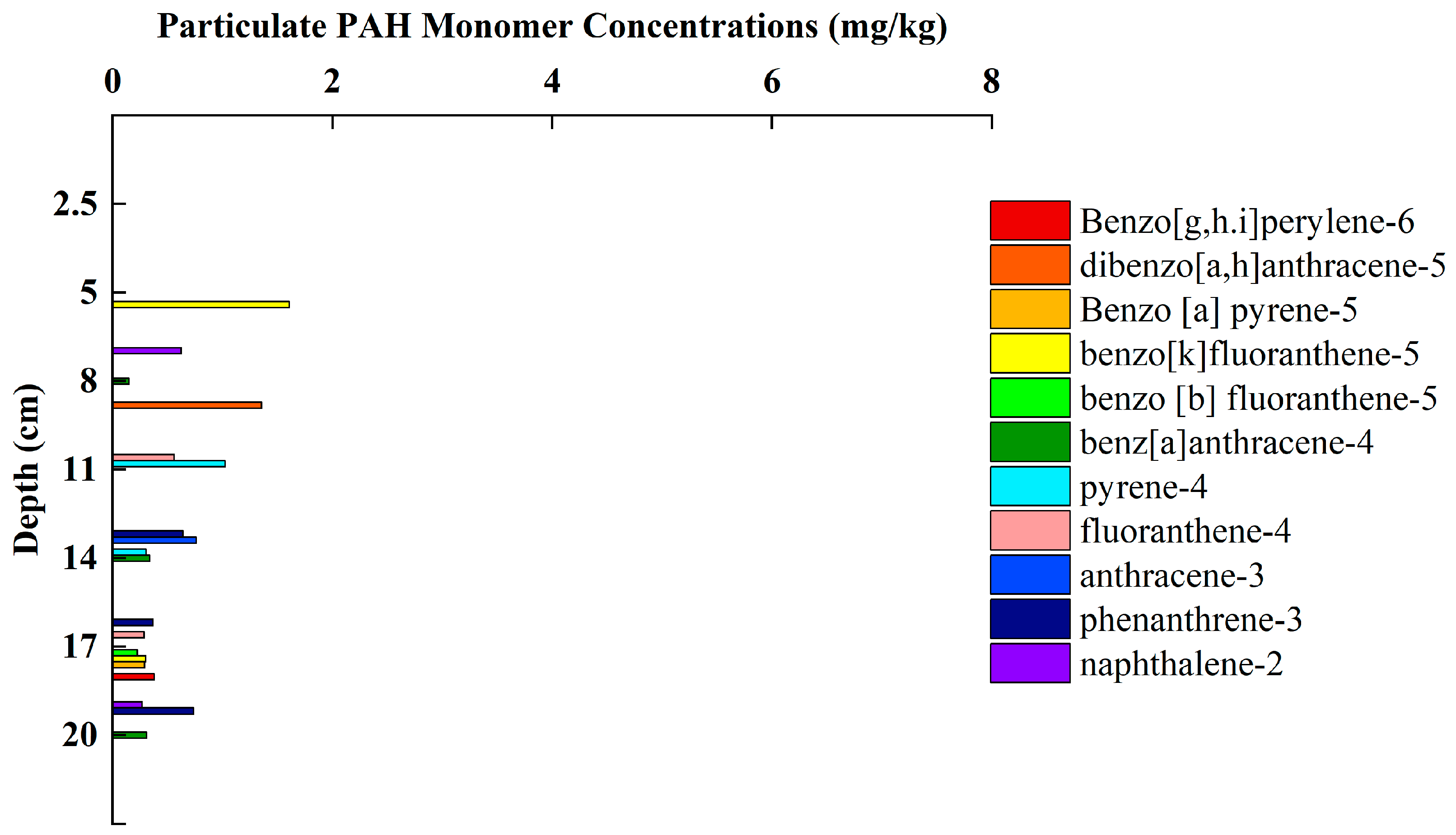
3.4. Variation Characteristics of PAHs Concentration and Composition in Sediments
4. Discussion
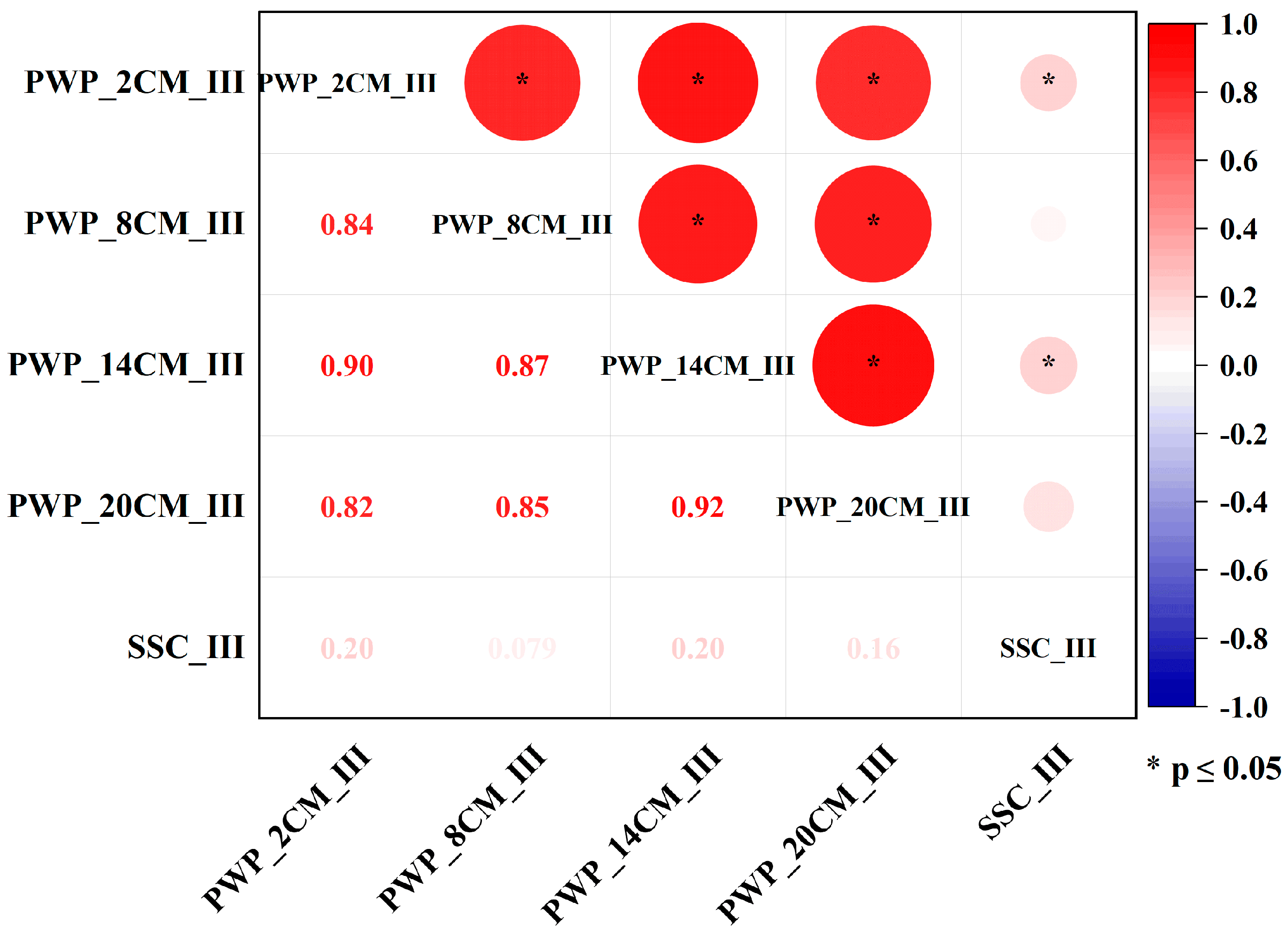
4.1. Correlation Analysis Between Porewater Pressure and Suspended Sediment Concentration Variations
4.2. Correlation Analysis Between Porewater Pressure and Suspended Sediment Grain Size Variations
4.3. Effects of Wave-Induced Disturbance on the Release of PAHs into the Overlying Water
4.4. Migration and Diffusion Processes of PAHs in Sediments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghandourah, M.A. An insightful overview of the distribution pattern of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in the marine sediments of the Red Sea. Open Chem. J. 2022, 20, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, P.; De Rosa, E.; Di Duca, F.; De Simone, B.; Scippa, S.; Russo, I.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Triassi, M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Dissolved Phase, Particulate Matter, and Sediment of the Sele River, Southern Italy: A Focus on Distribution, Risk Assessment, and Sources. Toxics 2022, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Tian, W.; Chen, Z.; Chu, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Zhao, J.; Zou, M.; Huo, B.; Xu, G. Release of PAHs from sediments to seawater under wave: Indoor microcosms and level IV fugacity models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletić, S.P.; Beljin, J.M.; Rončević, S.D.; Grgić, M.G.; Dalmacija, B.D. State of the art and future challenges for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments: Sources, fate, bioavailability and remediation techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xia, X.; Wang, M.; Xie, H.; Wen, J.; Bao, Y. Effect of recurrent sediment resuspension-deposition events on bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aquatic environments. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, C.; Wang, J.; Acharya, K.; Du, W.; Gao, X.; Luo, L.; Li, H.; Dai, S.; Mercy, J.; et al. Effect of wave-current interactions on sediment resuspension in large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4029–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, L.; Qin, B.; Wu, T.; Shen, X. Characteristics of sediment resuspension in Lake Taihu, China: A wave flume study. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, P.; Hua, Z.; Dong, Y.; Yu, L.; Huang, S. Field study on endogenous perfluoroalkyl acid release and their spatiotemporal distribution processes induced by inland navigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chai, J.; Xu, R.; Pang, Y. The effects of wind-wave disturbances on sediment resuspension and phosphate release in Lake Chao. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Jeng, D.S.; Guo, L.; Zheng, T. Numerical investigation of solute migration and release from sediments driven by wave-induced accumulation of porewater pressure. Adv. Water Resour. 2023, 179, 104508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Feng, C.; Wang, D.; Li, B.; Hu, L.; Shen, Z. Role of salinity in the multiphase redistribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediment suspension. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, Z.; Xu, M. Bioavailability of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and their Potential Application in Eco-risk Assessment and Source Apportionment in Urban River Sediment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, R.; Cravo-Laureau, C. Role of environmental factors and microorganisms in determining the fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the marine environment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 814–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Hui, K.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, W. Study on factors influencing the transport and transformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil-groundwater systems. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanand, M.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Subramanian, R.; Issac, P.K.; Nasr, M.; Khoo, K.S.; Rajagopal, R.; Greff, B.; Wan Azelee, N.I.; Jeon, B.-H.; et al. Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the water environment: A review on toxicity, microbial biodegradation, systematic biological advancements, and environmental fate. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Feng, C.; Huang, L.; Niu, J.; Shen, Z. Historical deposition behaviors of PAHs in the Yangtze River Estuary: Role of the sources and water currents. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 2020–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ailijiang, N.; Mamat, A.; Wu, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, M. Fugacity-based multimedia transport modeling and risk assessment of PAHs in Urumqi. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method 8260D (SW-846); Volatile Organic Compounds by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS), Revision 3. U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Method 8275A (SW-846); Semivolatile Organic Compounds in Soil/Sludges and Solid Wastes Using Thermal Extraction/Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (TE/GC/MS). U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Lu, F.; Zhang, H.Q.; Jia, Y.G.; Liu, W.; Wang, H. Migration and Diffusion of Heavy Metal Cu from the Interior of Sediment during Wave-Induced Sediment Liquefaction Process. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBT 26411-2010; Marine Water Quality—Determination of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons—Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- HJ 805-2016; Water Quality—Determination of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments—Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Liu, X.; Jia, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wen, M.; Shan, H. An Experimental Investigation of Wave-induced Sediment Responses in a Natural Silty Seabed: New Insights into Seabed Stratification. Sedimentology 2016, 64, 508–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.L.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, N.; Lin, X.F.; He, R.; Sun, L. Internal solitary wave-induced soil responses and its effects on seabed instability in the South China Sea. Ocean Eng. 2024, 310, 118697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jia, Y.; Zheng, J.; Hou, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Shan, H. Experimental evidence of wave-induced inhomogeneity in the strength of silty seabed sediments: Yellow River Delta, China. Ocean. Eng. 2013, 59, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzang, S.; Ou, S. Laboratory flume studies on monochromatic wave-fine sandy bed interactions: Part 1. Soil fluidization. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzang, S.; Ou, S.; Hsu, T. Laboratory flume studies on monochromatic wave-fine sandy bed interactions Part 2. Sediment suspensions. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Xu, J.; Dong, P.; Li, G. Porewater pressure responses in silty sediment bed under random wave action. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Xu, G.H.; Yang, J.J.; Xu, Z.Q.; Ren, Y.P. Field observation of the wave-induced pore pressure response in a silty soil seabed. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2021, 41, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Bian, C. In-Situ Observation of Storm-Induced Wave-Supported Fluid Mud Occurrence in the Subaqueous Yellow River Delta. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2021JC018190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lan, J.; Xie, Z.; Pu, J.; Yuan, D.; Yang, H.; Xing, B. Vertical migration from surface soils to groundwater and source appointment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in epikarst spring systems, southwest China. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, J.H.; Manica, R.; Puhl, E.; de Oliveira Borges, A.L. Thresholds of intrabed flow and other interactions of turbidity currents with soft muddy substrates. Sedimentology 2016, 63, 2002–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xu, J.; Li, G.; Li, A.; Zhang, S.; Niu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, L. Experimental Study on Silty Seabed Liquefaction and Its Impact on Sediment Resuspension by Random Waves. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Feng, C.; Wang, D.; Li, B.; Shen, Z. Multiphase redistribution differences of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) between two successive sediment suspensions. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Yang, L. Spatiotemporal evolution of excess pore pressures in a silty seabed under progressive waves during residual liquefaction. Appl. Ocean Res. 2022, 129, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jeng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, T. Experimental study on the dynamic response of a silty seabed under waves. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 269, 113554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Feng, J.; Niu, J.; Shen, Z. Release of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from Yangtze River sediment cores during periods of simulated resuspension. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 155, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Tian, W.; Zhang, S.; Chu, M.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, J.; Zou, M.; Liu, B. A study combining a sediment-seawater microcosm with multimedia fugacity model to evaluate the effect of tidal cycles on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon release from sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, G.; Liu, X.; Cui, H.; Han, J. Sources, transport and fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a typical river-estuary system in the North China: From a new perspective of PAHs loading. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 117, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usanase, G.; Azema, N.; El Bitouri, Y.; Souche, J.-C.; Gonzalez, C. Contribution of settling measurements to the study of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons’ (PAHs) mobilisation during resuspension of PAHs-associated sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 68349–68363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berríos-Rolón, P.J.; Cotto, M.C.; Márquez, F. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Freshwater Systems: A Comprehensive Review of Sources, Distribution, and Ecotoxicological Impacts. Toxics 2025, 13, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Meng, L.; Li, H.; Song, T.; Sun, P.; Bao, M.; Li, X. Petroleum hydrocarbon release behavior study in oil-sediment aggregates: Turbulence intensity and chemical dispersion effect. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7922–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigue, C.; Tedetti, M.; Dang, D.; Mullot, J.; Garnier, C.; Goutx, M. Remobilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organic matter in seawater during sediment resuspension experiments from a polluted coastal environment: Insights from Toulon Bay (France). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, D.; Shiu, W.Y.; Ma, K.C.; Lee, S.C. Handbook of Physical-Chemical Properties and Environmental Fate for Organic Chemical; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Ilabaca, C.; Gutiérrez, M.H.; Aranda, M.; Henríquez-Aedo, K.; Pereira, A.; Salamanca, M.; Galand, P.E.; Jessen, G.L.; Pantoja-Gutiérrez, S. PAH contamination in coastal surface sediments. Sci. Rep. 2024, 15, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z. Simulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon remobilization in typical active regions of river system under hydrodynamic conditions. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubhankar, B.; Ambade, B. A Review on Deposition, Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Different Environmental Matrix and Study Its Toxicity and Carcinogenic Effect. Asian J. Chem. 2016, 28, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minick, D.J.; Anderson, K.A. Diffusive flux of PAHs across sediment-water and water-air interfaces at urban Superfund sites. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Test Stage | Wave Parameters | Duration | Sampling Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wave Height (cm) | Period (s) | |||
| Static diffusion (Stage I) | - | - | 84 h | 12 h/session |
| 5 cm wave height (Stage II) | 5.0 | 2.4 | 120 min | 30 min/session |
| 12 cm wave height (Stage III) | 12.0 | 1.2 | 150 min | 30 min/session |
| Individual PAHs | Sediment | Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD (mg/kg, dw) | LOQ (mg/kg, dw) | LOD (ng/L) | LOQ (ng/L) | |
| Naphthalene | 0.09 | 0.36 | 20.00 | 80.00 |
| Acenaphthylene | 0.09 | 0.36 | 3.00 | 12.00 |
| Acenaphthene | 0.12 | 0.48 | 2.90 | 11.60 |
| Fluorene | 0.08 | 0.32 | 6.30 | 25.20 |
| Phenanthrene | 0.10 | 0.40 | 12.00 | 48.00 |
| Anthracene | 0.12 | 0.48 | 2.20 | 8.80 |
| Fluoranthene | 0.14 | 0.56 | 3.20 | 12.80 |
| Pyrene | 0.13 | 0.52 | 3.20 | 12.80 |
| Benzo[a]anthracene | 0.12 | 0.48 | 2.40 | 9.60 |
| Chrysene | 0.14 | 0.56 | 4.40 | 17.60 |
| Benzo[b]fluoranthene | 0.17 | 0.68 | 2.60 | 10.40 |
| Benzo[k]fluoranthene | 0.11 | 0.44 | 4.10 | 16.40 |
| Benzo[a]pyrene | 0.17 | 0.68 | 2.90 | 11.60 |
| Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene | 0.13 | 0.52 | 2.40 | 9.60 |
| Dibenzo[a,h]anthracene | 0.13 | 0.52 | 3.10 | 12.40 |
| Benzo[g,h,i]perylene | 0.12 | 0.48 | 4.10 | 16.40 |
| Shapiro–Wilk | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | Degrees of Freedom | Sig. (p-Value) | |
| PWP_2CM_II | 0.961 | 120 | 0.001 |
| PWP_8CM_II | 0.849 | 120 | 0.000 |
| PWP_14CM_II | 0.861 | 120 | 0.000 |
| PWP_20CM_II | 0.764 | 120 | 0.000 |
| SSC_II | 0.805 | 120 | 0.000 |
| PWP_2CM_III | 0.935 | 152 | 0.000 |
| PWP_8CM_III | 0.777 | 152 | 0.000 |
| PWP_14CM_III | 0.978 | 152 | 0.016 |
| PWP_20CM_III | 0.944 | 152 | 0.000 |
| SSC_III | 0.969 | 152 | 0.002 |
| Shapiro–Wilk Tests of Normality | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | Degrees of Freedom | Sig. (p-Value) | |
| SSC | 0.876 | 11 | 0.091 |
| PAHs | 0.837 | 11 | 0.029 |
| Spearman Correlations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SSC | PAHs | ||
| SSC | Correlation Coefficient ρ | 1.000 | 0.673 * |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.023 | ||
| N | 11 | 11 | |
| PAHs | Correlation Coefficient ρ | 0.673 * | 1.000 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.023 | ||
| N | 11 | 11 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, F.; Song, Q.; Liu, W. Mobilization of PAHs by Wave-Induced Resuspension and Liquefaction in Silty Sediment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091661
Lu F, Song Q, Liu W. Mobilization of PAHs by Wave-Induced Resuspension and Liquefaction in Silty Sediment. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091661
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Fang, Qian Song, and Wenquan Liu. 2025. "Mobilization of PAHs by Wave-Induced Resuspension and Liquefaction in Silty Sediment" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091661
APA StyleLu, F., Song, Q., & Liu, W. (2025). Mobilization of PAHs by Wave-Induced Resuspension and Liquefaction in Silty Sediment. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091661






