Acoustic Analysis of Fish Tanks for Marine Bioacoustics Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ▪
- Determination of the acoustic normal modes of a water-filled fish tank both theoretically and experimentally.
- ▪
- Analysis of the sound field spatial distribution for these frequencies over horizontal planes at different depths.
- ▪
- Study of the influence of modifying the water level and the sound source intensity on the sound pressure level frequency spectrum.
- ▪
- Perform a preliminary exploration of the vibroacoustic behavior and the uncertainty in the low-frequency analysis of fish tanks.
2. Background Theory
2.1. Importance of Fish Tanks in Bioacoustics
2.2. Sound Field in Water-Filled Rectangular Tanks
3. Materials and Methods
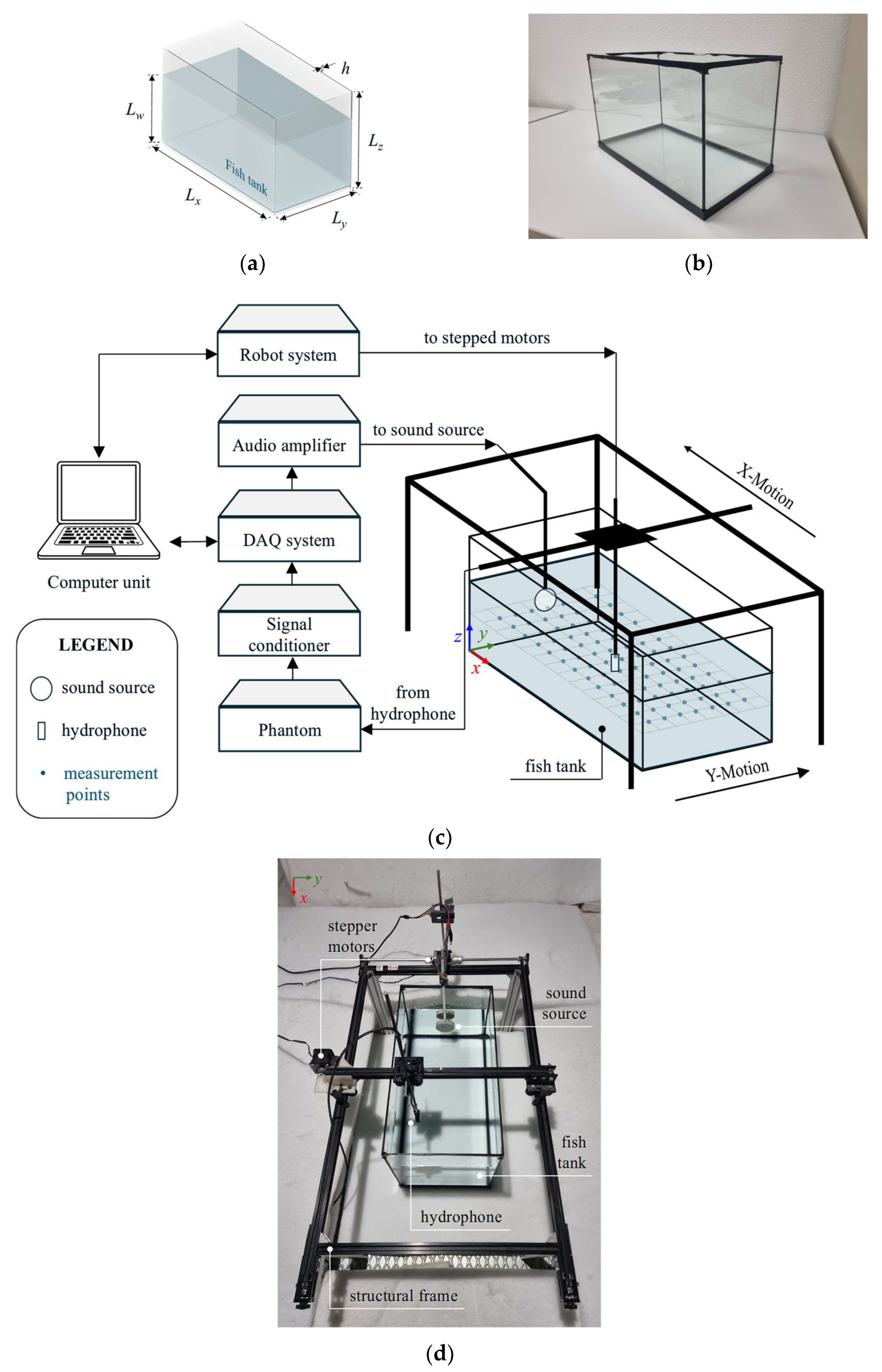
3.1. Fish Tank
3.2. Measurement System
3.3. Novak et al. [14] Model for Water-Filled Rectangular Tanks
4. Results and Discussion
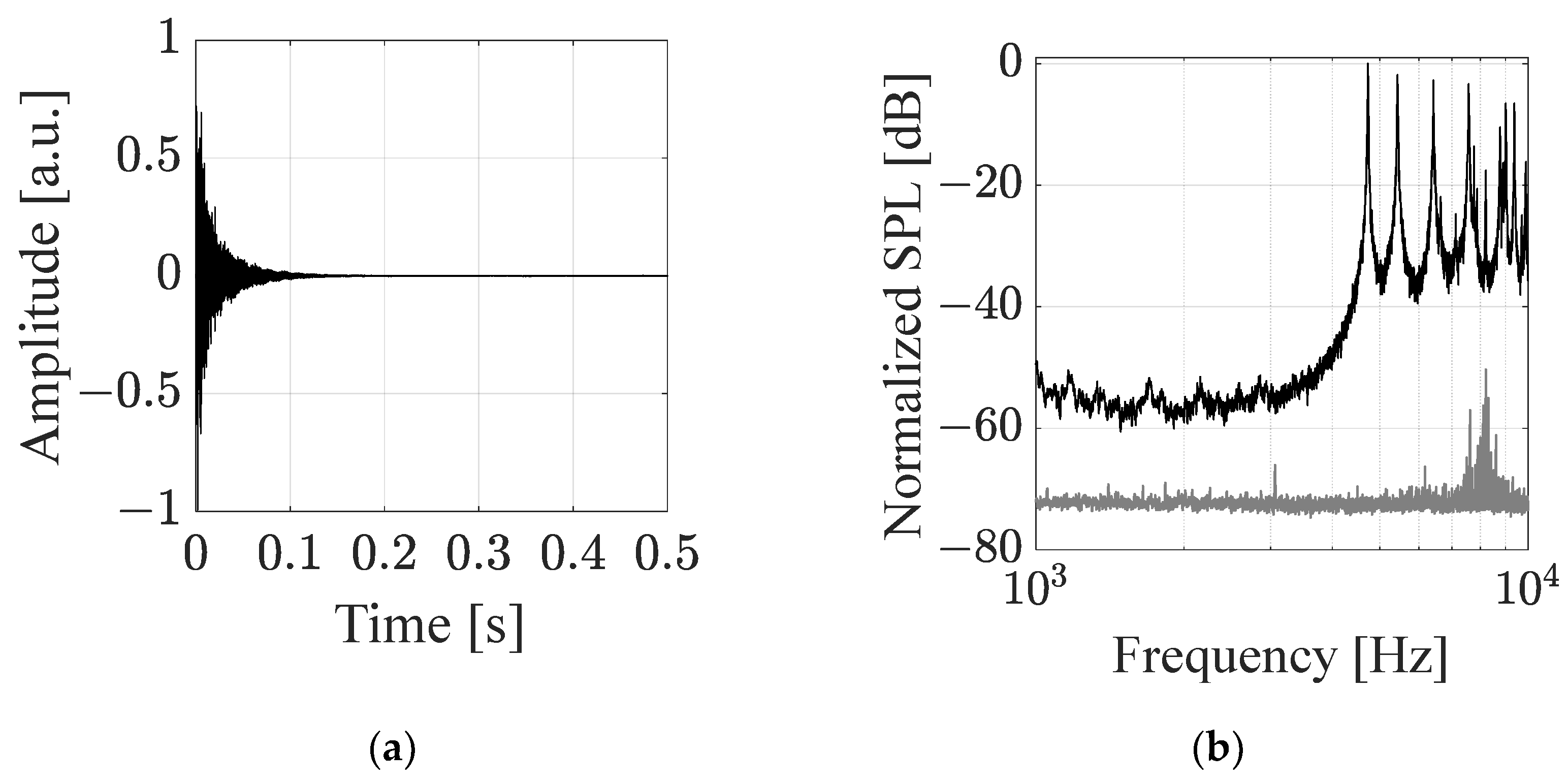
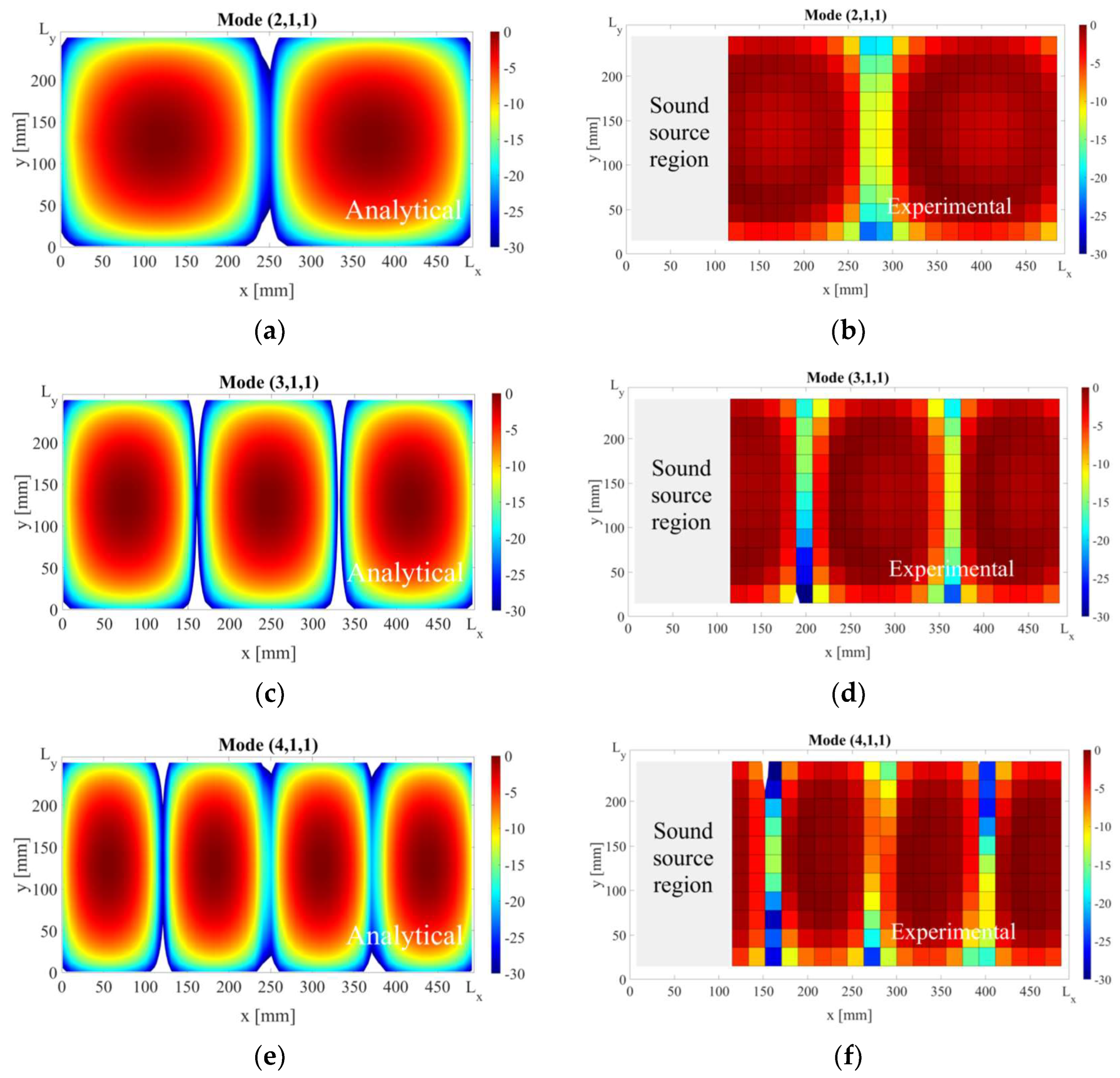
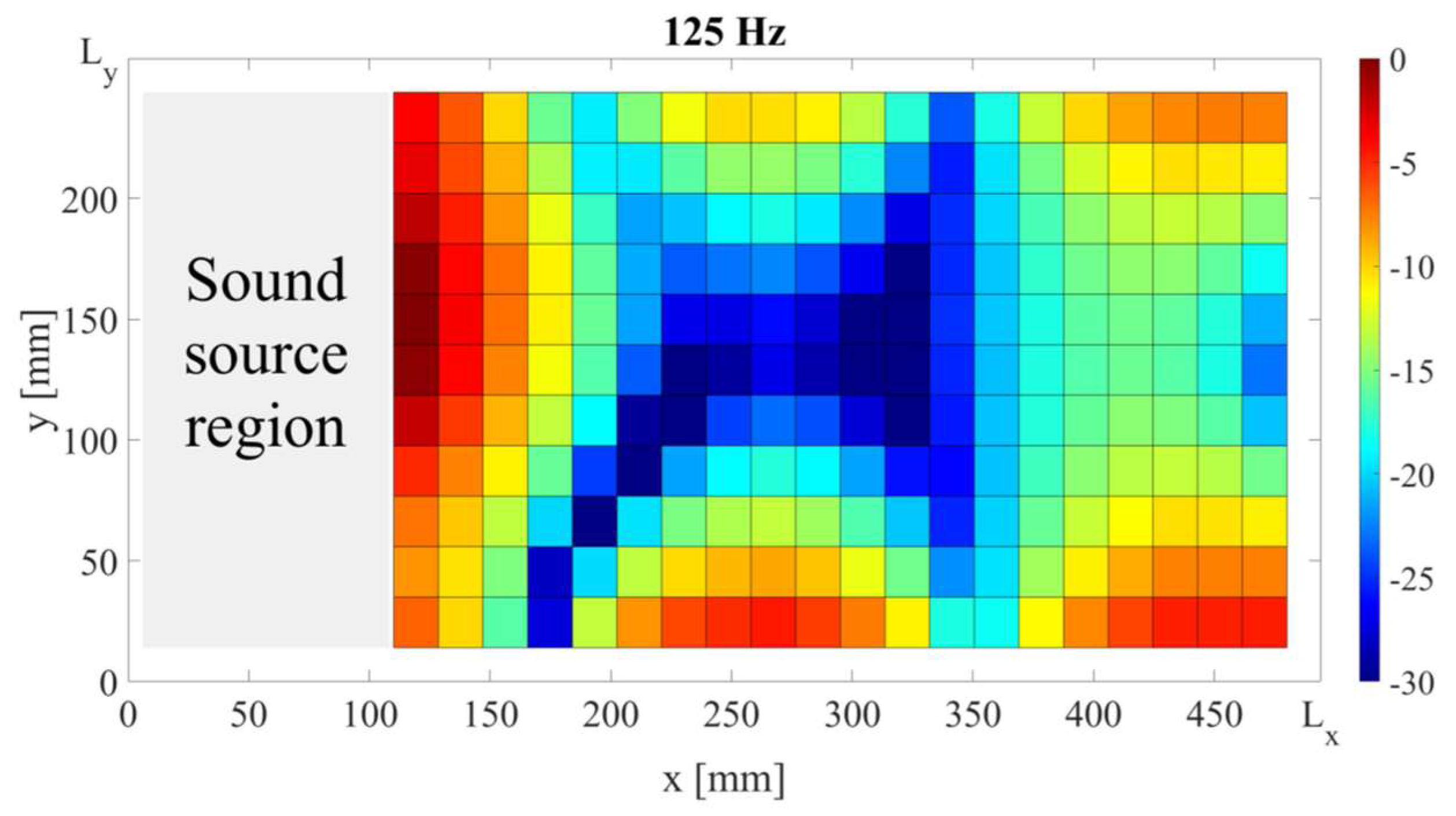
4.1. Normal Modes
4.2. Parametric Analysis
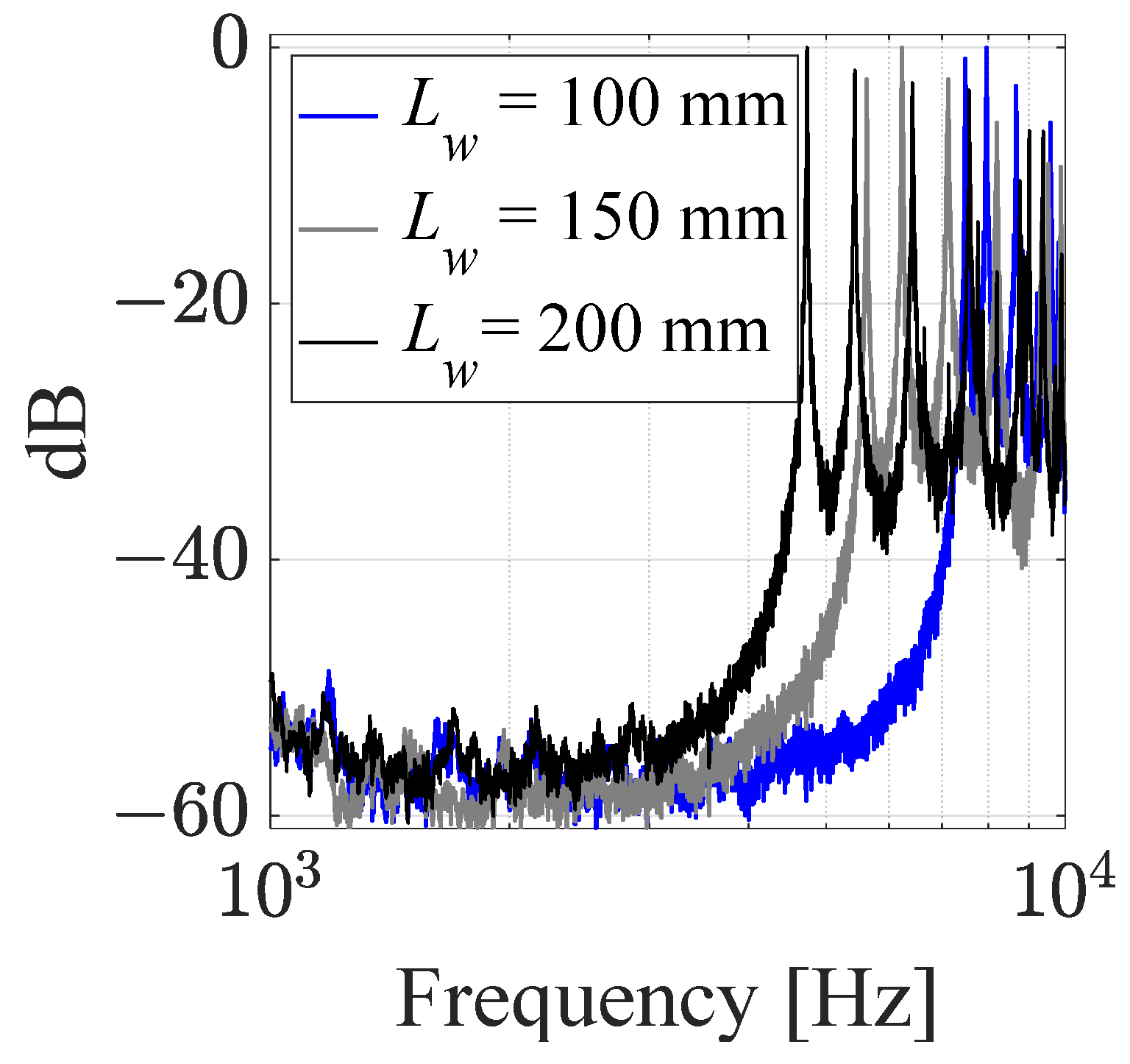
4.2.1. Water Level
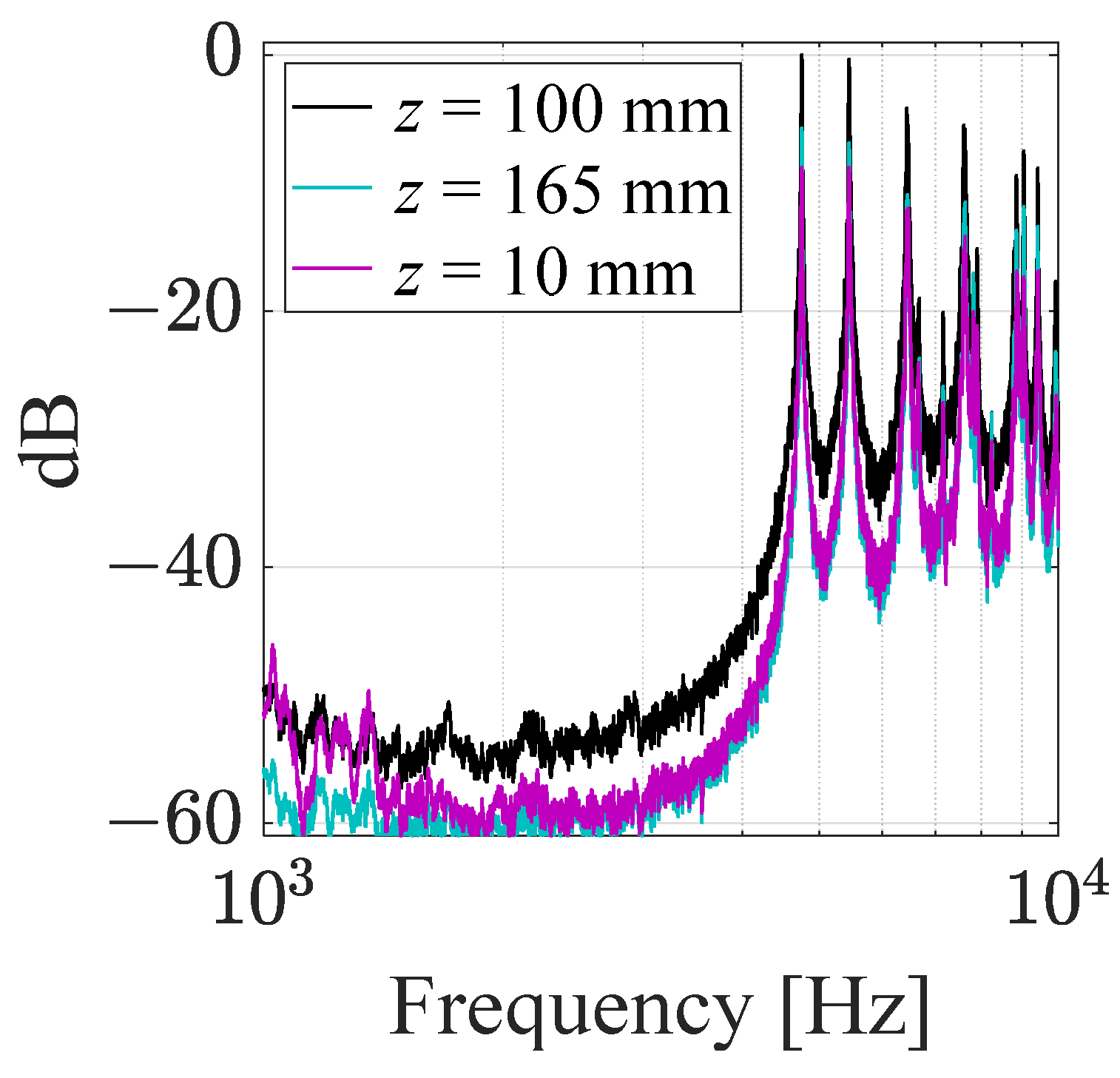
4.2.2. Measurement Depth
4.2.3. Sound Source Power
4.3. Remarks on the Low-Frequency Behavior of Fish Tanks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Popper, A.; Hastings, M. The effects of anthropogenic sources of sound on fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 75, 455–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popper, A.N.; Hawkins, A.D. An overview of fish bioacoustics and the impacts of anthropogenic sounds on fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 692–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J.A. Anthropogenic and natural sources of ambient noise in the ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 395, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilgart, L. The impacts of anthropogenic ocean noise on cetaceans and implications for management. Can. J. Zool. 2007, 85, 1091–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jézéquel, Y.; Julien, B.; Coston-Guarini, J.; Chauvaud, L. Revisiting the bioacoustics of European spiny lobsters Palinurus elephas: Comparison of antennal rasps in tanks and in situ. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 615, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, S.; Zhao, J.; Ji, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, F.; Ding, X.; Ye, Z. Impact of underwater noise on the growth, physiology and behavior of Micropterus salmoides in industrial recirculating aquaculture systems. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.A. Acoustic characterization of seahorse tank environments in public aquaria: A citizen science project. Aquacult. Eng. 2013, 54, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L.; Hastings, M.C. Principles of Marine Bioacoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Parvulescu, A. The acoustics of small tanks. Mar. Bioacoustics 1967, 2, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lucke, K.; MacGillivray, O.; Halvorsen, M.B.; Ainslie, M.A.; Zeddies, D.G.; Sisneros, J.A. Recommendations on bioacoustical metrics relevant for regulating exposure to anthropogenic underwater sound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2024, 156, 2508–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, P.H.; Hawkins, A.D.; Popper, A.N.; Fay, R.R.; Gray, M.D. Parvulescu revisited: Small tank acoustics for bioacousticians. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II; Popper, A.N., Hawkins, A.D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 933–941. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Xing, J.; Tang, R.; Zhang, Y. Finite-element method for calculating the sound field in a tank with impedance boundaries. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6794760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.J.; Lucke, K.; Erbe, C.; McCauley, R.D. Issues associated with sound exposure experiments in tanks. Proc. Mtgs. Acoust. 2016, 27, 070008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, A.; Bruneau, M.; Lotton, P. Small-sized rectangular liquid-filled acoustical tank excitation: A modal approach including leakage through the walls. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2018, 104, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Shafiei Sabet, S.; Slabbekoorn, H. Particle motion and sound pressure in fish tanks: A behavioral exploration of acoustic sensitivity in the zebrafish. Behav. Process. 2019, 164, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiciotto, F.; Vazzana, M.; Celi, M.; Maccarrone, V.; Ceraulo, M.; Buffa, G.; Di Stefano, V.; Mazzola, S.; Buscaino, G. Behavioral and biochemical stress responses of Palinurus elephas after exposure to boat noise pollution in tank. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Kabir, I.; Yeoh, G.H.; Peng, Z. A review on polymer-based materials for underwater sound absorption. Polym. Test. 2021, 96, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, T.; Okumura, T.; Novarini, N.; Yan, H.Y. Empirical refinements applicable to the recording of fish sounds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 3073–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Shang, D. The investigation of the methods for predicting the sound field in a non-anechoic tank with elastic boundary. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 9–11 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pieniazek, R.H.; Mickle, F.; Higgs, D.M. Comparative analysis of noise effects on wild and captive freshwater fish behavior. Anim. Behav. 2020, 168, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda-Martínez, P.; Carbajo-San-Martín, J.; Martínez-Iranzo, J.; Segovia-Eulogio, G.; Tinivella, U.; Cianferra, M.; Ramis-Soriano, J. Primeros pasos en el diseño de sistema radiante del tipo DML para acústica submarina. In Tecniacústica 2023; Sociedad Española de Acústica (SEA): Cuenca, Spain, 2023. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Vorländer, M.; Kob, M. Practical aspects of MLS measurements in building. Appl. Acoust. 1997, 52, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Svensson, O.; Swartz, T.; Manera, J.L.; Bertram, M.G.; Blom, E.L. Increased noise levels cause behavioral and distributional changes in Atlantic cod and saithe in a large public aquarium—A case study. Aquacult. Fish Fish. 2023, 3, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranek, L.; Mellow, T. Acoustics: Sound Fields and Transducers; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Tang, R.; Li, Q.; Shang, D.J. The investigation of the method for measuring the low-frequency radiated sound power in a reverberation tank. Proc. Mtgs. Acoust. 2016, 29, 070002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaiee-Pajand, M.; Aftabi S, A.; Kazemiyan, M. Analytical solution for free vibration of flexible 2D rectangular tanks. Ocean Eng. 2016, 122, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, F.; Gardonio, P. Sound and Structural Vibration: Radiation, Transmission and Response, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, F.; Gigot, M.; Mathias, D.; Jezequel, Y.; Meziane, T.; L’Her, C.; Chauvaud, L.; Bonnel, J. Assessing the impacts of anthropogenic sounds on early stages of benthic invertebrates: The “Larvosonic system. ” Limnol. Oceanogr. Meth. 2022, 21, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgate, A.; White, P.R.; Leighton, T.; Kemp, P.S. Sound fields in two small experimental test arenas: A comparison. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life: Principles and Practical Considerations; Popper, A.N., Sisneros, J.A., Hawkins, A.D., Thomsen, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ramis, J.; Poveda, P.; Carbajo, J.; Ullah, N.; Ramis, E.; Forcada, A.; Valle, C.; Espinosa, V.; Pérez-Arjona, I.; Ortega, A.; et al. Estudio del efecto del ruido antropogénico en atunes en cautividad. In FIA 2024; Sociedad Chilena de Acústica (SOCHA): Santiago de Chile, Chile, 2024. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, E.; Cao, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Fang, N.X.; Zhang, Y. Underwater acoustic metamaterials. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegerink, J.; Baldock, T.; Callaghan, D.; Wang, C. Experimental study on hydrodynamic response of a floating rigid fish tank model with slosh suppression blocks. Ocean Eng. 2023, 273, 113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Wang, C.; Park, J.; Lader, P. Review of cage and containment tank designs for offshore fish farming. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mode * | Normal Frequency (Hz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mx | my | mz | Analytical | Experimental | Relative Error (%) |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 4757 | 4752 | 0.11 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 5396 | 5456 | 1.10 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 6319 | 6449 | 2.02 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 6710 | 6682 | 0.42 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 7178 | 7162 | 0.22 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 7421 | 7628 | 2.71 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 7895 | 7903 | 0.10 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 8252 | 8250 | 0.02 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 8802 | 8855 | 0.60 |
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 9075 | 9051 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carbajo, J.; Poveda, P.; Ullah, N.; Ramis, J. Acoustic Analysis of Fish Tanks for Marine Bioacoustics Research. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071253
Carbajo J, Poveda P, Ullah N, Ramis J. Acoustic Analysis of Fish Tanks for Marine Bioacoustics Research. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(7):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071253
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarbajo, Jesús, Pedro Poveda, Naeem Ullah, and Jaime Ramis. 2025. "Acoustic Analysis of Fish Tanks for Marine Bioacoustics Research" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 7: 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071253
APA StyleCarbajo, J., Poveda, P., Ullah, N., & Ramis, J. (2025). Acoustic Analysis of Fish Tanks for Marine Bioacoustics Research. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(7), 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071253









