Effects of Nutrients on the Phytoplankton Community Structure in Zhanjiang Bay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
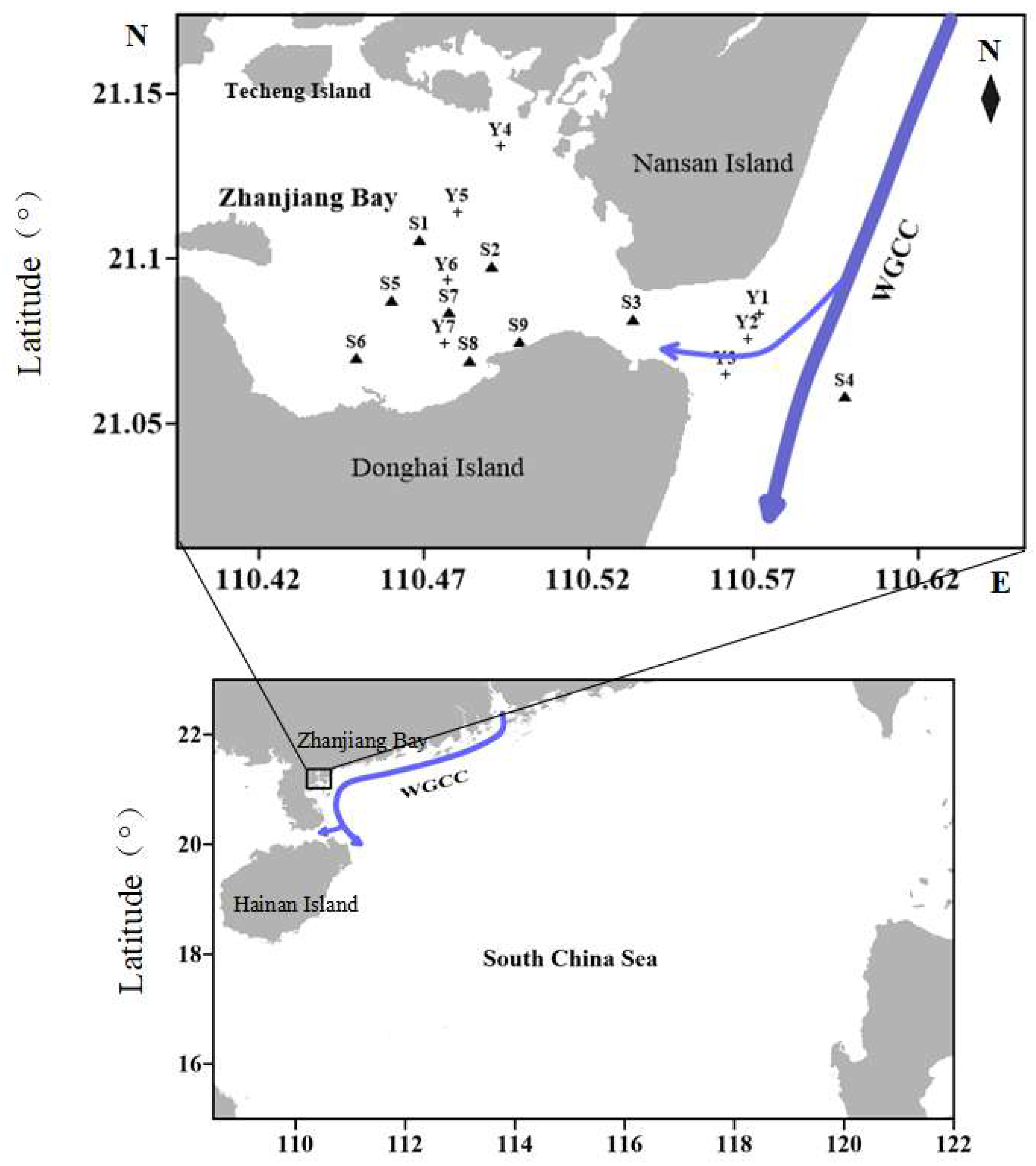
2.1. Study Area and Sample Analysis
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
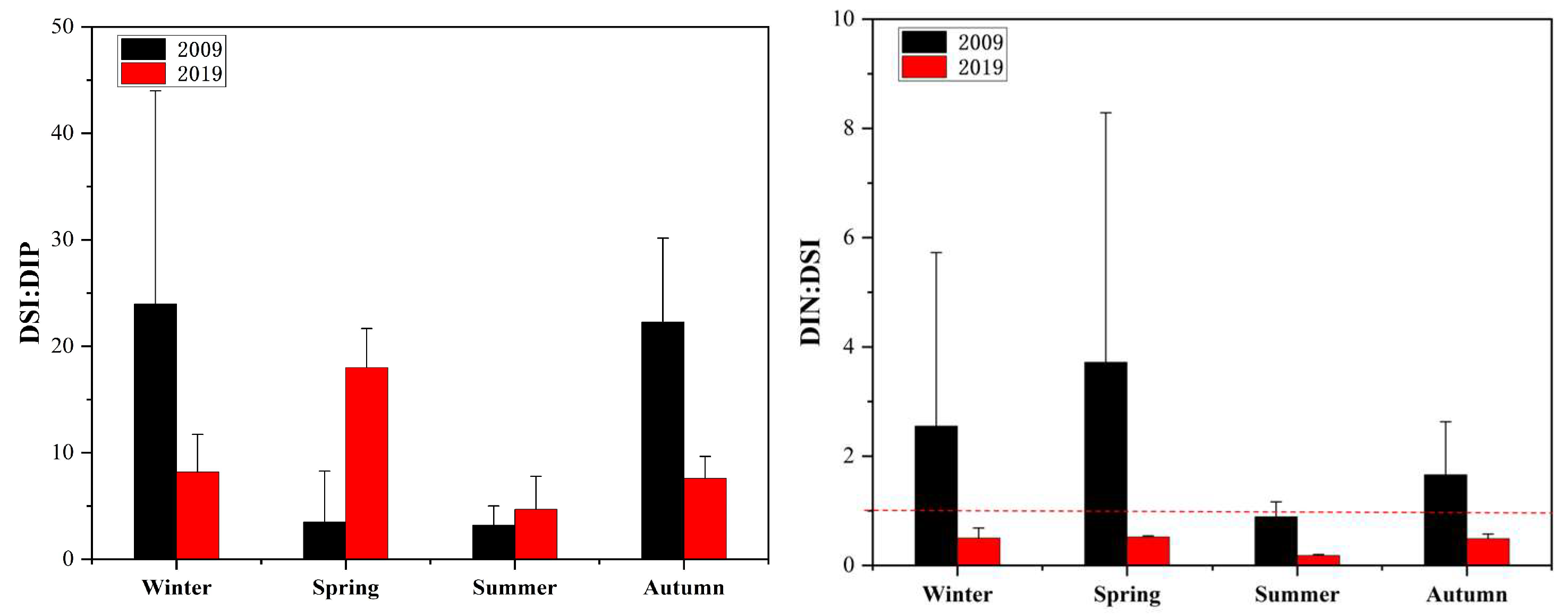
3.1. Variations in Environmental Factors
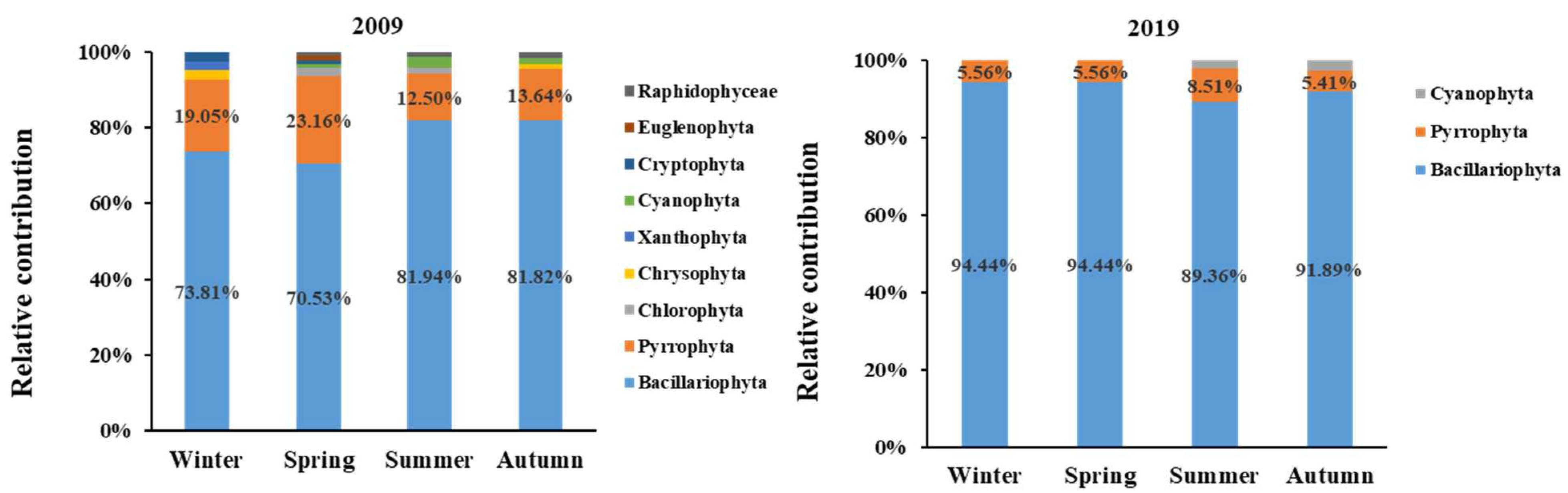
3.2. Variations in the Species Composition of Phytoplankton
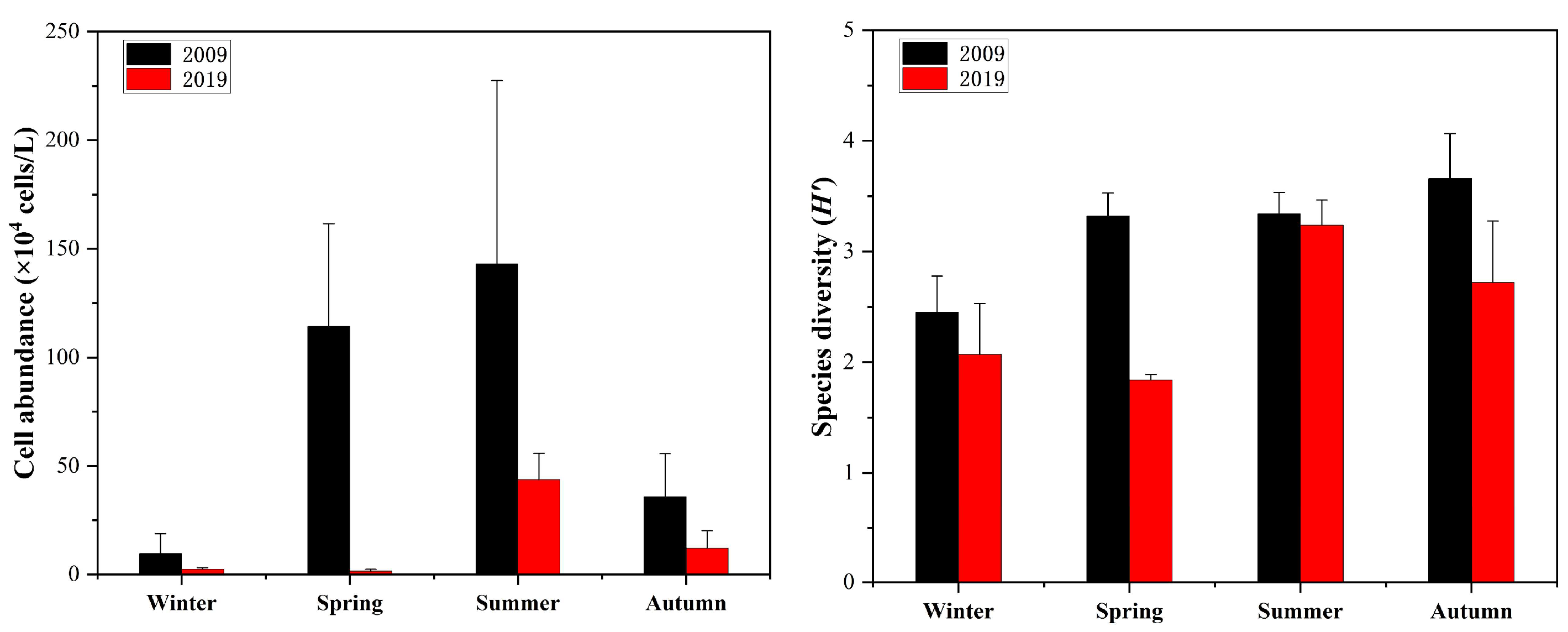
3.3. Variations in Phytoplankton Abundance and Species Diversity
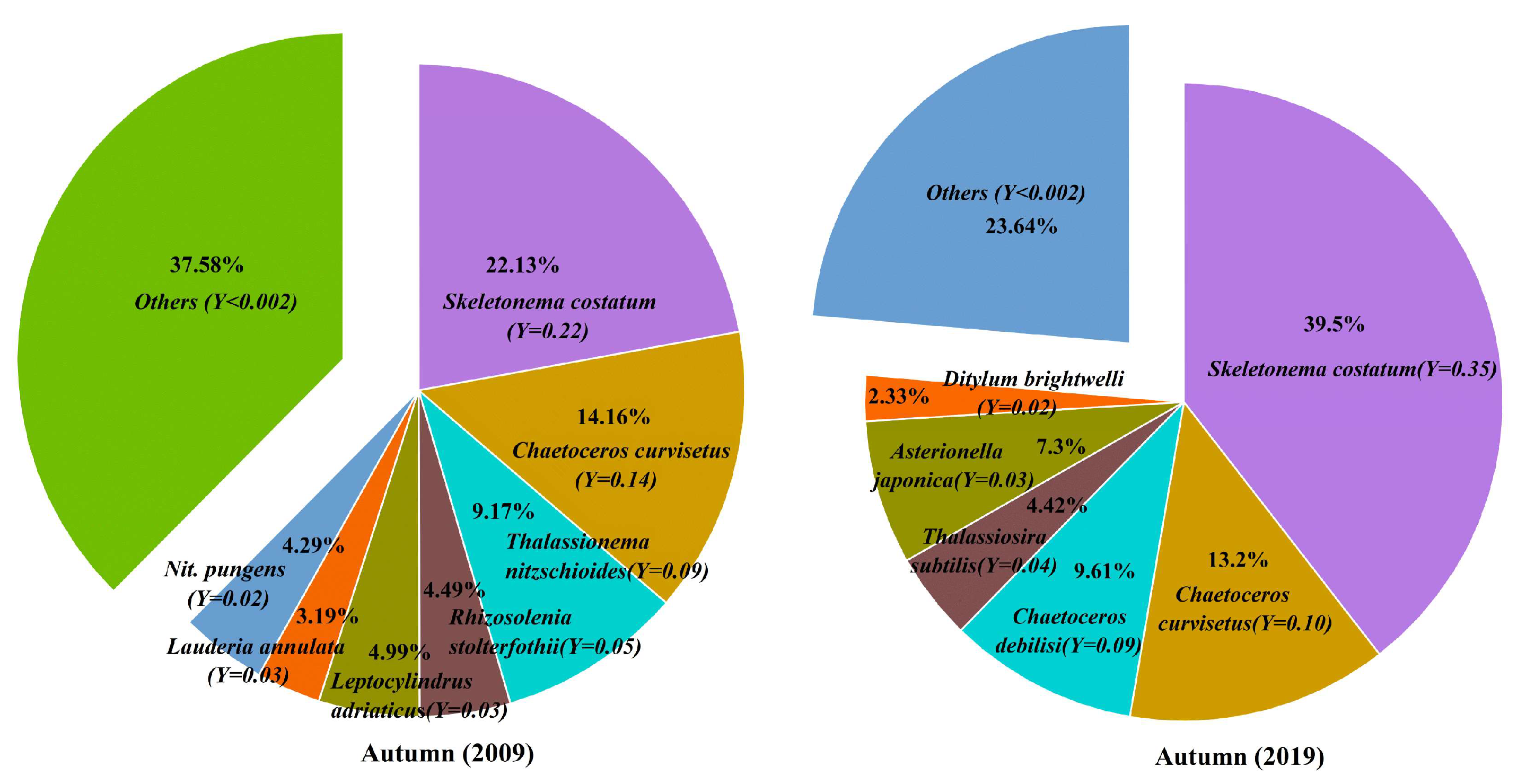
3.4. Dominant Species of Phytoplankton
4. Discussion
4.1. Variations in Nutrient Structure
4.2. Effects of Nutrient Concentration on Phytoplankton Cell Abundance
4.3. Effects of Nutrient Structure on Phytoplankton Community
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hattich, G.S.I.; Listmann, L.; Govaert, L.; Pansch, C.; Reusch, T.B.H.; Matthiessen, B. Experimentally decomposing phytoplankton community change into ecological and evolutionary contributions. Funct. Ecol. 2022, 36, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Cao, Y.; Pang, W.; Wang, L.; Song, K.; You, Q.; Wang, Q. Long-term plankton community dynamics and influencing factors in a man-made shallow lake, Lake Dishui, China. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 83, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-P, C.; Soudijn, F.; Visser, A.W.; Kiørboe, T.; Andersen, K.H. A general size-and trait-based model of plankton communities. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 189, 102473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Sun, J. Seasonal dynamics and key drivers of phytoplankton community structure in the Eastern Indian Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 212, 117548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Flores, R.; Garces, E.; Biox, D.; Badosa, A.; Brucet, S.; Maso, M.; Quintana, S.D. Comparative composition and dynamics of harmful dinoflagllates in Mediterranean saltmarshes and nearby external marine waters. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatharis, S.; Tsirtsis, G.; Danielidis, D.B.; Chi, T.D.; Mouillo, D. Effects of pulsed nutrient inputs on phytoplankton assemblage structure and blooms in an enclosed coastal area. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 73, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gle, C.; Amo, Y.D.; Sautour, B.; Laborde, P.; Chardy, P. Variability of nutrients and phytoplankton primary productionin a shallow macrotidal coastal ecosystem (Arcachon Bay, France). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Yang, Y.F. Heavy metal (Pb, Co, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn) concentrations in harvest-size white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei tissues from aquaculture and wild source. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, B.; Sun, X.L. Effects of a coastal power plant thermal discharge on phytoplankton community structure in zhanjiang bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Long, C.; Lu, C.; Wang, D.; et al. Unveiling the eutrophication crisis: 20 years of nutrient development in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1373716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, J.-L.; Zhang, J.-B.; Li, J.-X.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.-Q. Spatiotemporal dissolved silicate variation, sources, and behavior in the eutrophic zhanjiang bay, China. Water 2020, 12, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Q.; Deng, Z.; Li, J. Increasing intrusion of high salinity water alters the mariculture activities in zhanjiang bay during the past two decades identified by dual water isotopes. J. Environ. Manage 2022, 320, 115815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Lao, Q.; Jin, G.; Zhu Q and Chen, F. Increasing eutrophication driven by the increase of phosphate discharge in a subtropical bay in the past 30 years. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1184421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lu, K.; Hardison, A.K.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Gao, D.; Gong, J.; Gardner, W.S. Membrane inlet mass spectrometry method (REOX/MIMS) to measure 15N-nitrate in isotopeenrichment experiments. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, F.; Chen, F.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, Q. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Nutrients in the Drowned Tidal Inlet Under the Influence of Tides: A Case Study of Zhanjiang Bay, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Chen, C.; Lao, Q.; Chen, F. Thermal fronts in coastal waters regulate phytoplankton blooms via acting as barriers: A case study from western Guangdong, China. J. Hydrology 2024, 636, 131350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. The mathematical theory of communication. Bell Labs Tech. J. 1950, 3, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C.J. The Measurement of Diversity in Different Types of Biological Collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Khodaei, K.; Alnajar, N.; Shahsavari, A.; Ashja Ardalan, A. Cyanobacterial community patterns as water quality bioindicators. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2012, 11, 876–891. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Chen, F.; Zeng, Z. Nitrogen budget evolution in zhanjiang municipal district and its environmental effect during 2002–2013. Trop. Geogr. 2015, 35, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.C.; Lea, M.A.; Meyer, A.; Sall’ee, J.B.; Hindell, M. Defining Southern Ocean fronts and their influence on biological and physical processes in a changing climate. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, J.A.; Carreras-Carbonell, J.; Macpherson, E.; Pascual, M.; Roques, S.; Turner, G.F.; Rico, C. The influence of oceanographic fronts and early-life-history traits on connectivity among littoral fish species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, Q.; Chen, F.; Jin, G.; Lu, X.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Q. Characteristics and mechanisms of typhoon-induced decomposition of organic matter and its implication for climate change. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2023, 128, e2023JG007518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justić, D.; Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Dortch, Q. Changes in nutrient structure of river-dominated coastal waters: Stoichiometric nutrient balance and its consequences. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortch, Q.; Whitledge, T.E. Does nitrogen or silicon limit phytoplankton production in the Mississippi River plume and nearby regions. Cont. Shelf Res. 1992, 2, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Yang, D. Solar light, seawater temperature, and nutrients, which one is more important in affecting phytoplankton growth. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 27, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucha, R. Das gleichgewicht des limnischen Lebensraumes. Magy. Boil. Kut. Munkái. 1942, 14, 192–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Peng, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H. Long-Term Harmful Algal Blooms and Nutrients Patterns Affected by Climate Change and Anthropogenic Pressures in the Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 849819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, M. The new development of phytoplankton metabolism study. J. Oceanogr. Huanghai Bohai Seas. 1990, 3, 65–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Brzezinski, M.A.; Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W. Silicon availability and cell-cycle progression in marine diatoms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Series. 1990, 67, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, M.A. Cell-cycle effects on the kinetics of silicic acid uptake and resource competition among diatoms. J. Plankton Res. 1992, 14, 1511–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, G.E. Algal Cultures and Phytoplantkon Ecology. Madison; The University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Sverdrup, H.U.; Johnson, M.W.; Fleming, H. The Oceans. Prentice Hall, New York; Mao, H., Translator; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1959; pp. 665–676; 685–691. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Piehler, M.F.; Twomey, L.J.; Hall, N.S.; Paerl, H.W. Impacts of inorganic nutrient enrichment on phytoplankton community structure and function in Pamlico Sound, NC, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.F.; Wang, F.; Gao, Z.H.; Cui, W.L.; Huo, S.X. Ecological phenomena of phytoplankton in Jiaozhou Bay. Mar. Sci. 2004, 28, 71–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.D.; Liu, H.; Harrison, P.J. Sequential nutrient uptake as a potential mechanism for phytoplankton to maintain high primary productivity and balanced nutrient stoichiometry. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2469–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.K.; Rynearson, T.A. Identification and expression analyses of the nitrate transporter gene (NRT2) family among Skeletonema species (Bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, M.W.; Glibert, P.M. Comparisons of nitrate uptake, storage, and reduction in marine diatoms and flagellates. J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranon, E.; Lorenzo, M.P.; Cermeno, P.; Mourino-Carballido, B. Nutrient limitation suppresses the temperature dependence of phytoplankton metabolic rates. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Chen, F.; Mi, T.Z.; Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.G.; Zhen, Y. Responses of marine diatom Skeletonema marinoi to nutrient deficiency: Programmed cell death. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02460-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tem 1 | Salinity | pH | Chla | DIN | DIP | DSI | DIN/DIP | DSI/DIP | DIN/DSI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | - | - | mg/L | - | - | - | ||||
| 2009 | 26.14 | 28.34 | 8.15 | 7.95 ** | 0.302 * | 0.024 ** | 0.247 | 16.9 | 13.2 | 2.21 |
| 2019 | 25.62 | 28.52 | 7.96 | 3.97 ** | 0.196 * | 0.043 ** | 0.399 | 4.6 | 9.2 | 0.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Z.; Chen, F.; Lao, Q.; Zhu, Q. Effects of Nutrients on the Phytoplankton Community Structure in Zhanjiang Bay. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071202
Zeng Z, Chen F, Lao Q, Zhu Q. Effects of Nutrients on the Phytoplankton Community Structure in Zhanjiang Bay. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(7):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071202
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Zhen, Fajin Chen, Qibin Lao, and Qingmei Zhu. 2025. "Effects of Nutrients on the Phytoplankton Community Structure in Zhanjiang Bay" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 7: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071202
APA StyleZeng, Z., Chen, F., Lao, Q., & Zhu, Q. (2025). Effects of Nutrients on the Phytoplankton Community Structure in Zhanjiang Bay. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(7), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071202





