Physics-Guided Self-Supervised Learning Full Waveform Inversion with Pretraining on Simultaneous Source
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
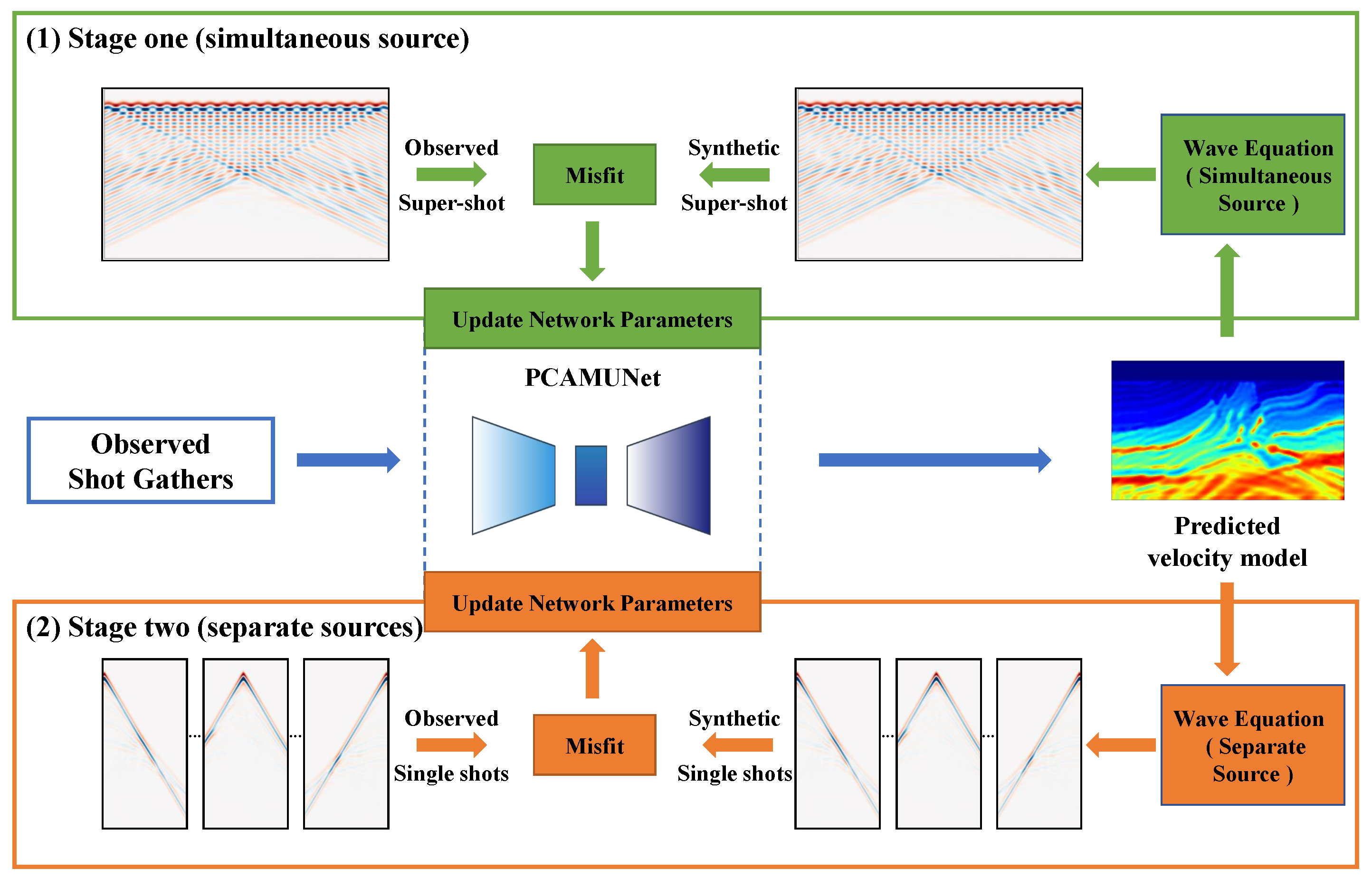
2.1. Physics-Guided Self-Supervised Inversion Framework
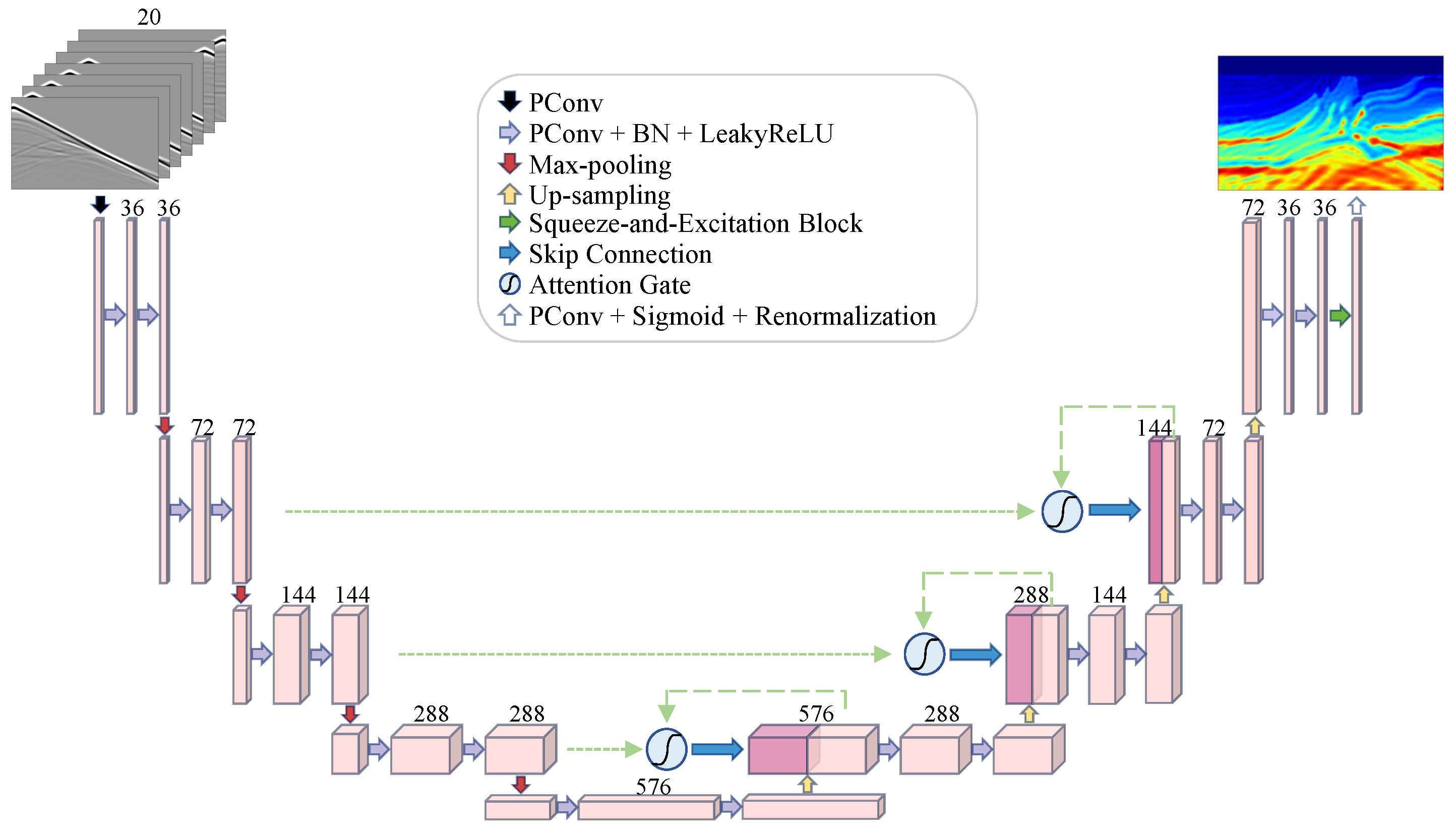
2.2. Inversion Network Architecture
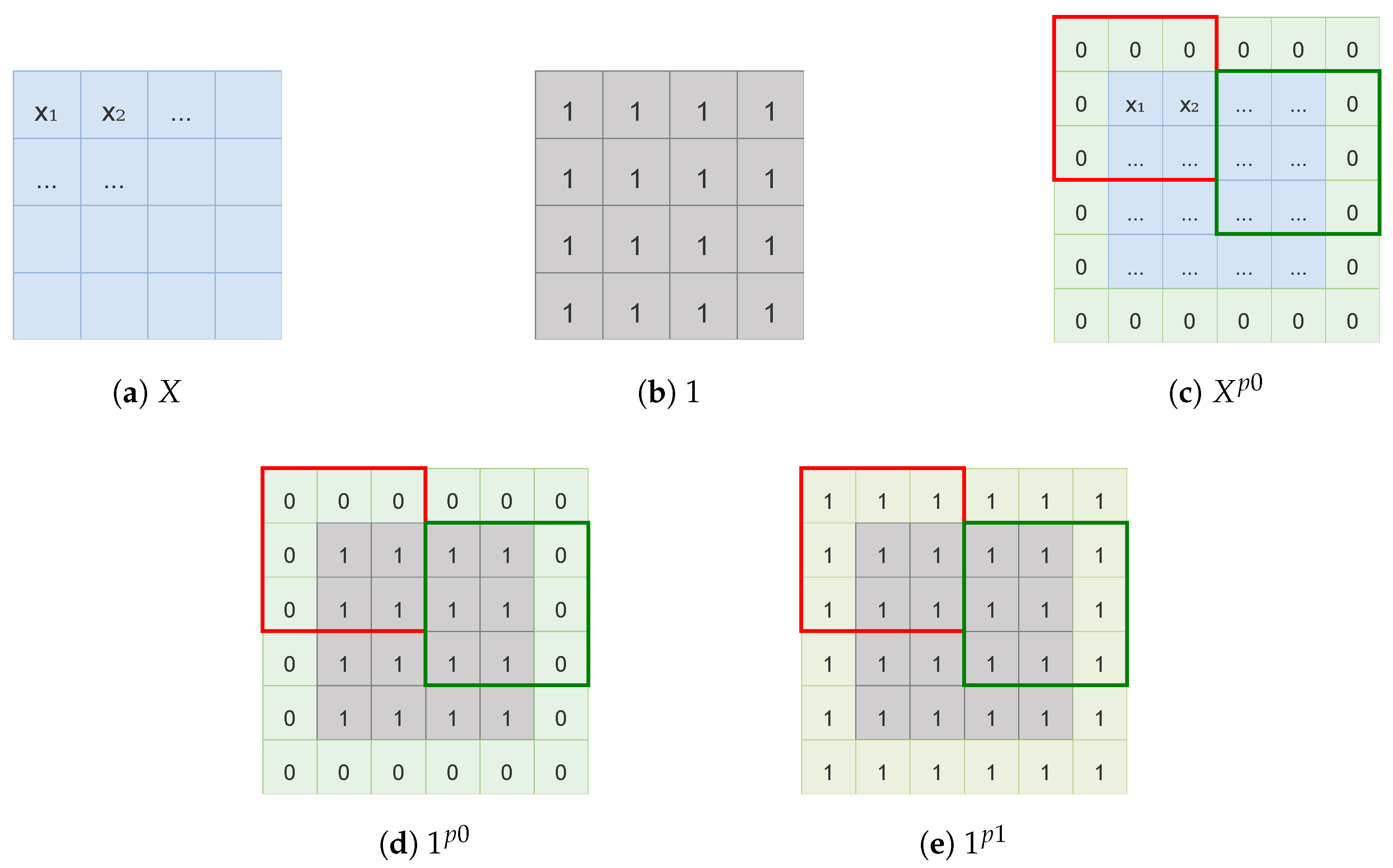
2.2.1. The Partial Convolution Component
2.2.2. The PConv Attention Modified UNet (PCAMUNet) Architecture
- Partial convolutions replacing standard convolutions enhances sensitivity to localized features on the data boundary;
- Attention mechanisms improves the identification of crucial geological structures and optimizes channel feature weighting;
- Designed skip connections effectively suppresses source footprint artifacts.
2.3. Wave Eqaution
2.4. Loss Functions
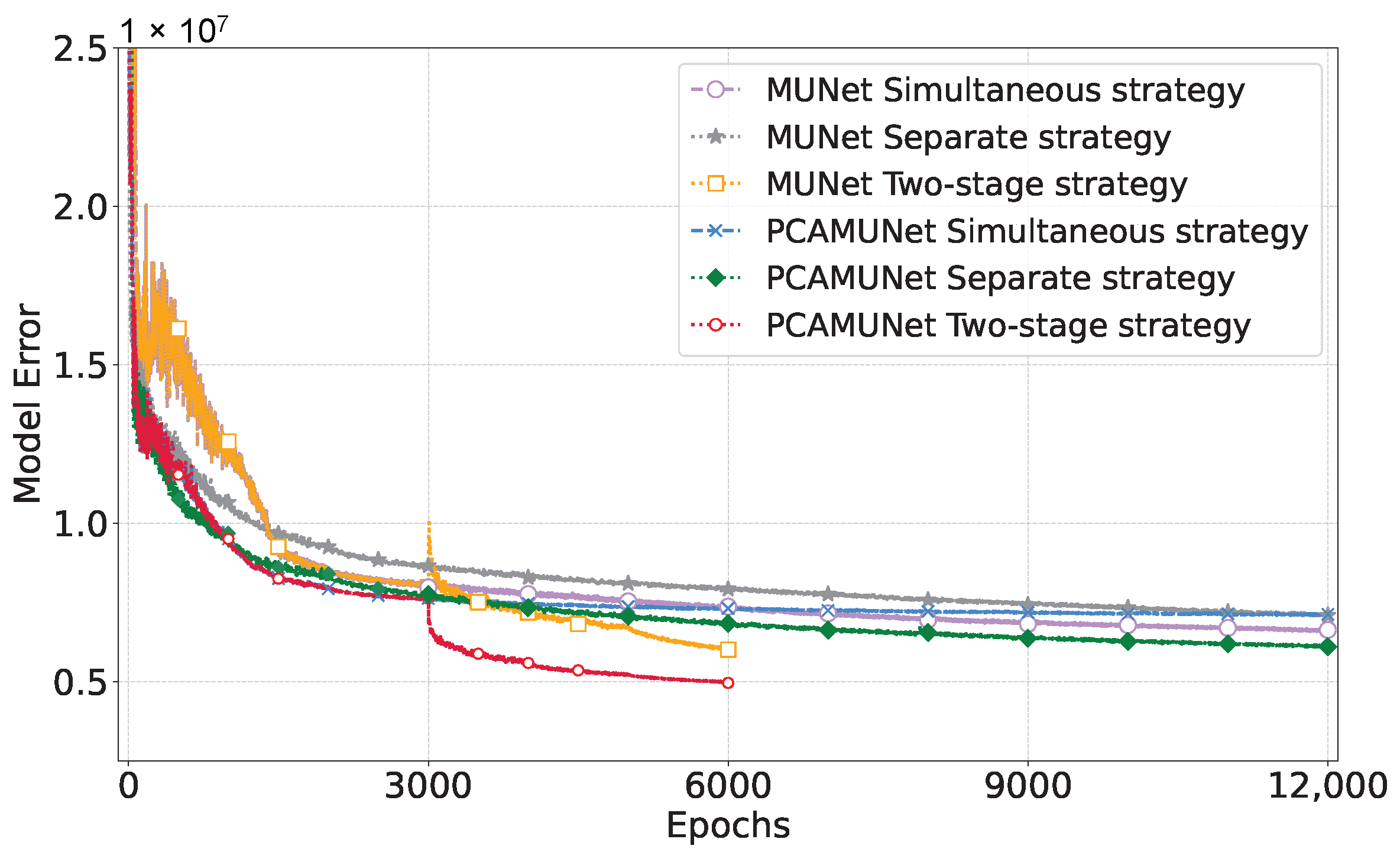
2.5. Two-Stage Training Strategy
2.6. Quantitative Indicators
- The normalized root mean square error (NRMSE, Equation (9)) quantifies absolute prediction errors normalized by the data range, with values closer to 0 indicating higher accuracy;
- The coefficient of determination (R2, Equation (10)) measures explained variance (1 is optimal);
- The Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC, Equation (11)) measures linear trend consistency between predictions and labels, with values near ±1 reflecting strong linear trend consistency.
3. Experiments and Results
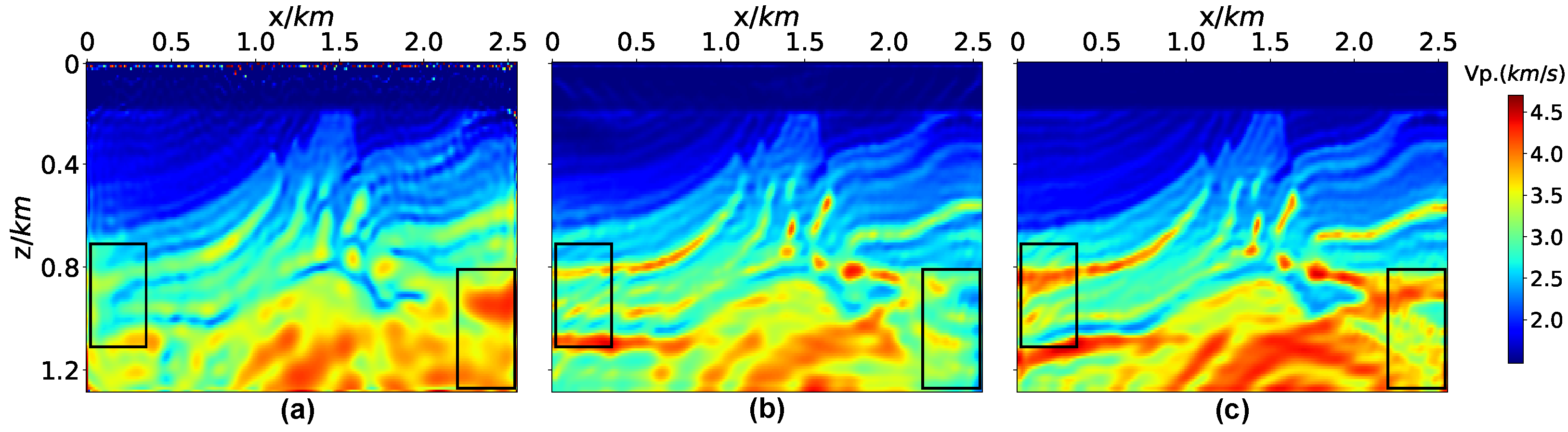
3.1. Marmousi2 Model
3.2. Overthrust Model
3.3. BP Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FWI | Full-Waveform Inversion |
| PCAMUNet | Partial Convolution Attention Modified UNet |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| MAU-Net | Multi-branch Attention UNet Network |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| MS-SSIM | Multiscale Structure Similarity |
| BCE | Binary Cross Entropy |
| MUNet | Modified UNet |
| AG | Attention Gate mechanism |
| SE | Squeeze-and-Excitation block |
| PConv | Partial Convolution |
| Conv | Standard Convolution |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| NRMSE | Normalized Root Mean Square Error |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| PCC | Pearson Correlation Coefficient |
References
- Tarantola, A. Inversion of seismic reflection data in the acoustic approximation. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjom, F.K.; Vaccarino, F.; Socco, L.V. Machine learning for seismic exploration: Where are we and how far are we from the holy grail? Geophysics 2024, 89, WA157–WA178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.D.; Alkhalifah, T. Regularized elastic full waveform inversion using deep learning. Geophysics 2019, 84, R741–R751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Alkhalifah, T. ML-descent: An optimization algorithm for full-waveform inversion using machine learning. Geophysics 2020, 85, R477–R492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.d.; Alkhalifah, T. High-resolution reservoir characterization using deep learning-aided elastic full-waveform inversion: The North Sea field data example. Geophysics 2020, 85, WA137–WA146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ma, J. Deep-learning inversion: A next-generation seismic velocity model building method. Geophysics 2019, 84, R583–R599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, Y. InversionNet: An efficient and accurate data-driven full waveform inversion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2019, 6, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, Y. VelocityGAN: Subsurface velocity image estimation using conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 705–714. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Guo, Z.; Pan, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, D. Deep learning with adaptive attention for seismic velocity inversion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Dong, H.; Xu, G.; Zhang, M. MAU-Net: A multi-branch attention U-Net for full-wavefom inversion. Geophysics 2024, 89, R119–R216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Lin, Y.; Wohlberg, B. Multiscale data-driven seismic full-waveform inversion with field data study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4506114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovcharenko, O.; Kazei, V.; Alkhalifah, T.A.; Peter, D.B. Multi-task learning for low-frequency extrapolation and elastic model building from seismic data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4510717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, M.; Hashemi, H.; Nabi-Bidhendi, M. Generalizable data driven full waveform inversion for complex structures and severe topographies. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 4025–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yang, W.; Li, C.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Ding, J.; Gao, J.; Xu, Z. Self-supervised deep learning for nonlinear seismic full waveform inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4509518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, P.; Feng, S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y. Simplifying full waveform inversion via domain-independent self-supervised learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.13314. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Innanen, K.; Zhang, T.; Trad, D. Implicit seismic full waveform inversion with deep neural representation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2023, 128, e2022JB025964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ma, J. FWIGAN: Full-Waveform Inversion via a Physics-Informed Generative Adversarial Network. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2023, 128, e2022JB025493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Alkhalifah, T.A. Wavefield reconstruction inversion via physics-informed neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5908012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, A.; Sen, M.K. Physics-guided deep autoencoder to overcome the need for a starting model in full-waveform inversion. Lead. Edge 2022, 41, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.X.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y. Unsupervised Learning of Full-Waveform Inversion: Connecting CNN and Partial Differential Equation in a Loop. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2110.07584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Yang, S.; Cohn, A.G. Physics-driven self-supervised learning system for seismic velocity inversion. Geophysics 2023, 88, R145–R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.P.; Costa, J.C.; Bom, C.R.; Klatt, M.; Faria, E.L.; de Albuquerque, M.P.; de Albuquerque, M.P. Deep pre-trained FWI: Where supervised learning meets the physics-informed neural networks. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 235, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustajab, A.H.; Lyu, H.; Rizvi, Z.; Wuttke, F. Physics-informed neural networks for high-frequency and multi-scale problems using transfer learning. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Cha, Y.H. Waveform inversion in the Laplace domain. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifah, T.; Song, C. An efficient wavefield inversion: Using a modified source function in the wave equation. Geophysics 2019, 84, R909–R922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdağ, E.; Trampert, J.; Tromp, J. Misfit functions for full waveform inversion based on instantaneous phase and envelope measurements. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 185, 845–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Cheng, S.; Mao, W. Deep-learning-based seismic variable-size velocity model building. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 3008305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Alkhalifah, T. ML-misfit: A neural network formulation of the misfit function for full-waveform inversion. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 1011825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, O.M.; Harsuko, R.; Alkhalifah, T. SiameseFWI: A deep learning network for enhanced full waveform inversion. J. Geophys. Res. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2024, 1, e2024JH000227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, T.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, Z. Frequency principle: Fourier analysis sheds light on deep neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.06523. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, K.; Darve, E.; Biondi, B.; Beroza, G.C. Integrating deep neural networks with full-waveform inversion: Reparameterization, regularization, and uncertainty quantification. Geophysics 2022, 87, R93–R109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Shih, K.J.; Wang, T.C.; Reda, F.A.; Sapra, K.; Yu, Z.; Tao, A.; Catanzaro, B. Partial convolution based padding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.11718. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, A. Deepwave. Zenodo 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.S.; Luo, J.; Wu, B. Seismic envelope inversion and modulation signal model. Geophysics 2014, 79, WA13–WA24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q. Digital Signal Processing; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Q.; Chen, J.; Wu, H. Multi-scale full waveform inversion based on logarithmic envelope of seismic data. Geophys. Prospect. Pet. 2018, 57, 584–591. [Google Scholar]
- You, K.; Long, M.; Wang, J.; Jordan, M.I. How does learning rate decay help modern neural networks? arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.01878. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.S.; Wiley, R.; Marfurt, K.J. Marmousi2: An elastic upgrade for Marmousi. Lead. Edge 2006, 25, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billette, F.; Brandsberg-Dahl, S. The 2004 BP velocity benchmark. In Proceedings of the 67th EAGE Conference & Exhibition, Madrid, Spain, 13–16 June 2005; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; p. cp–1–00513. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Ng, M.K.; Meng, D. Low-rank tensor function representation for multi-dimensional data recovery. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 3351–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




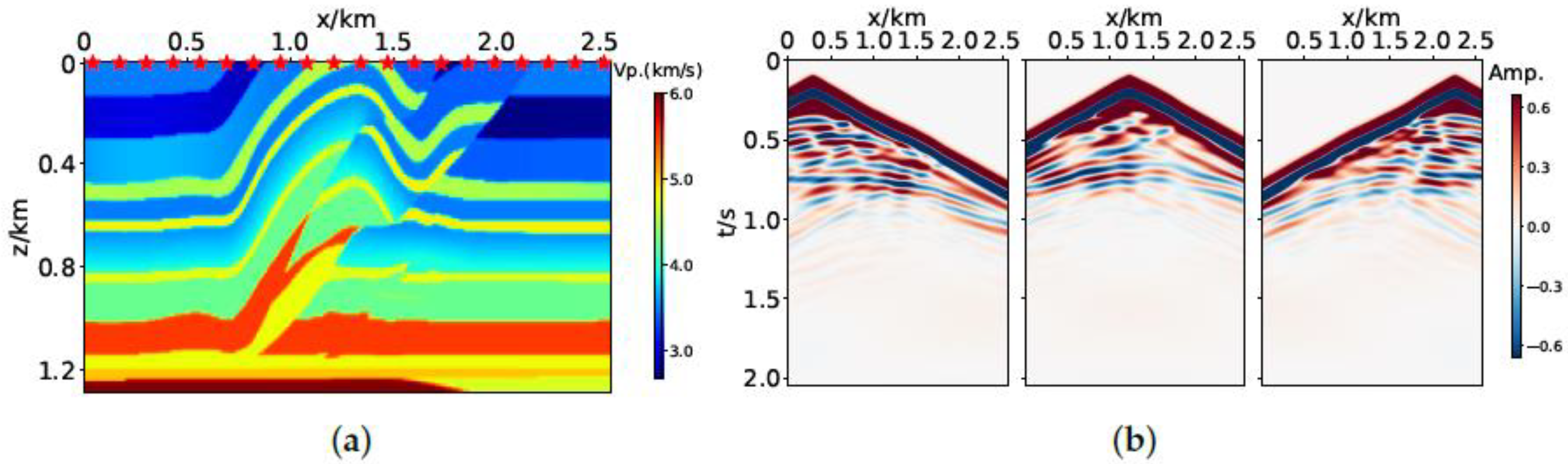

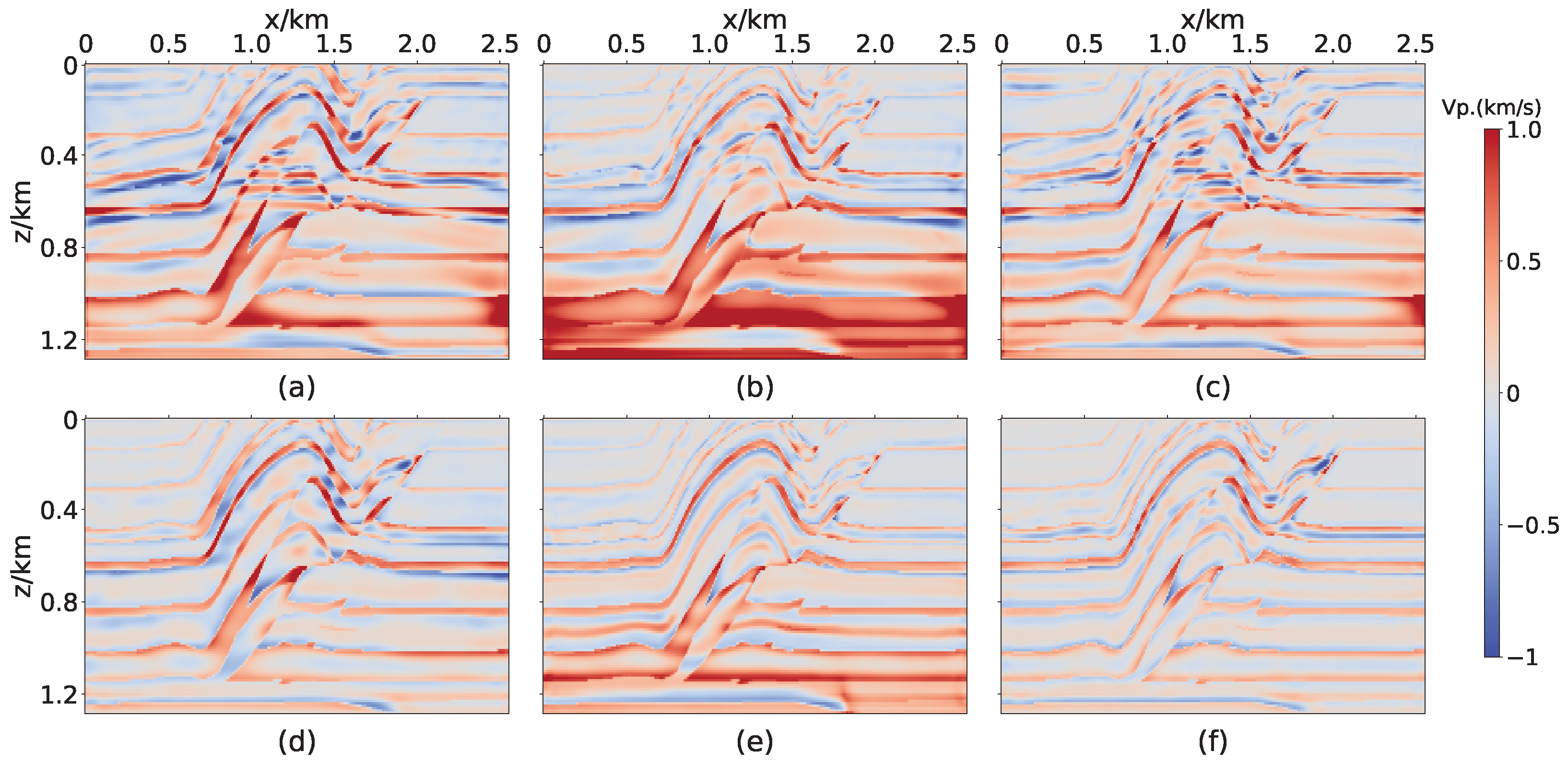
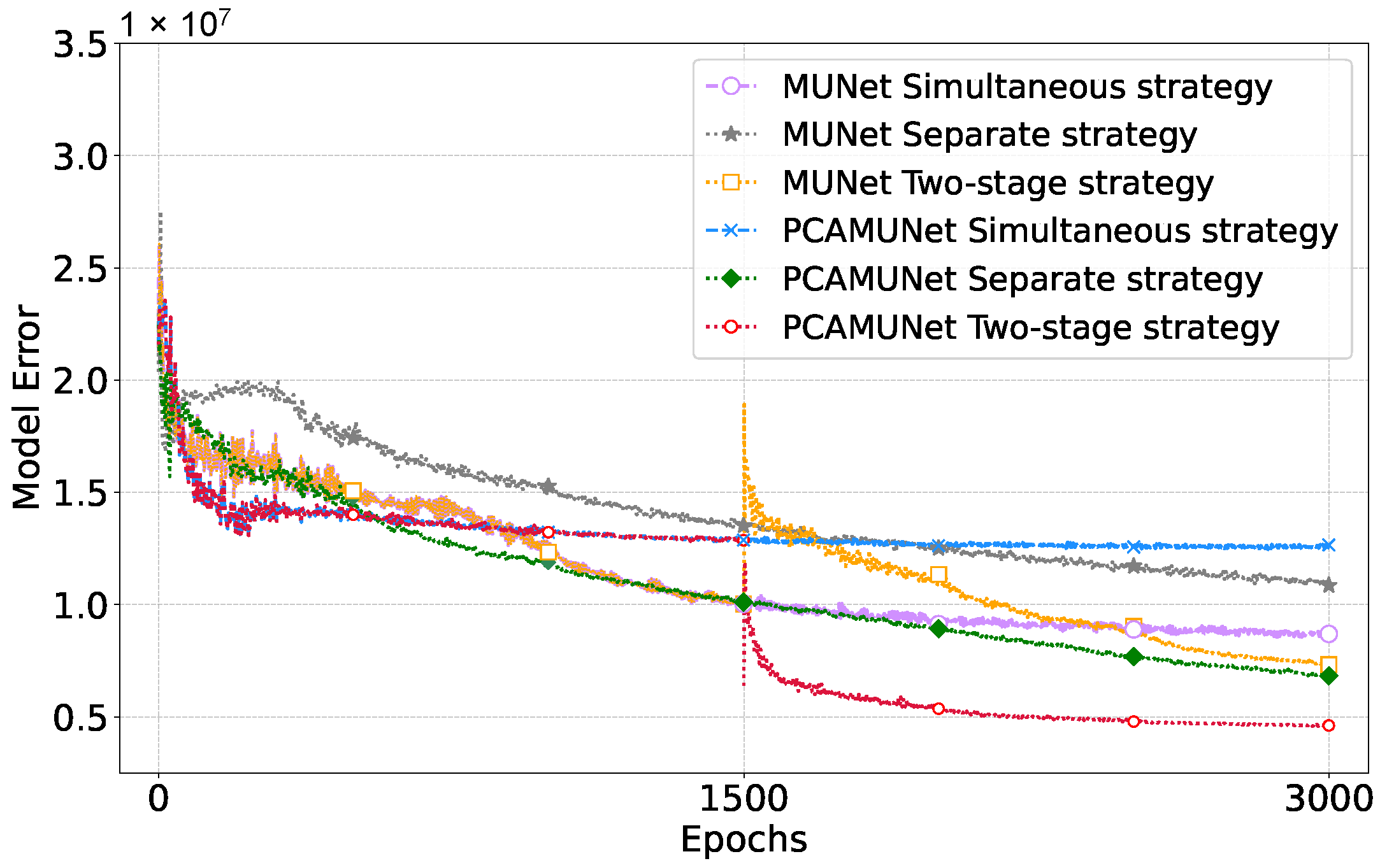
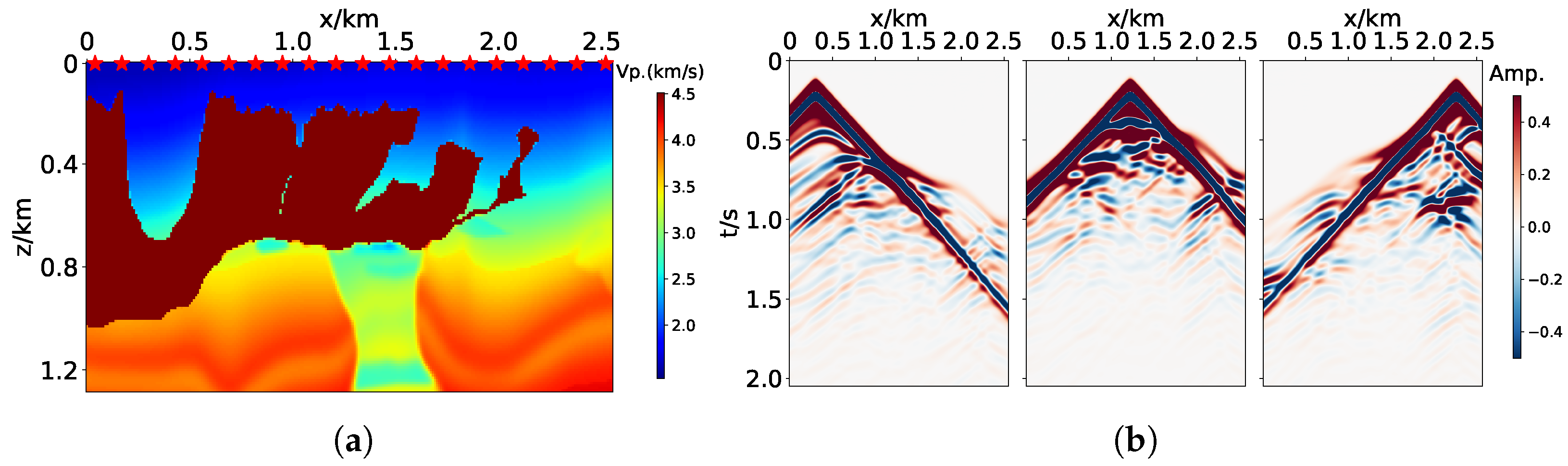
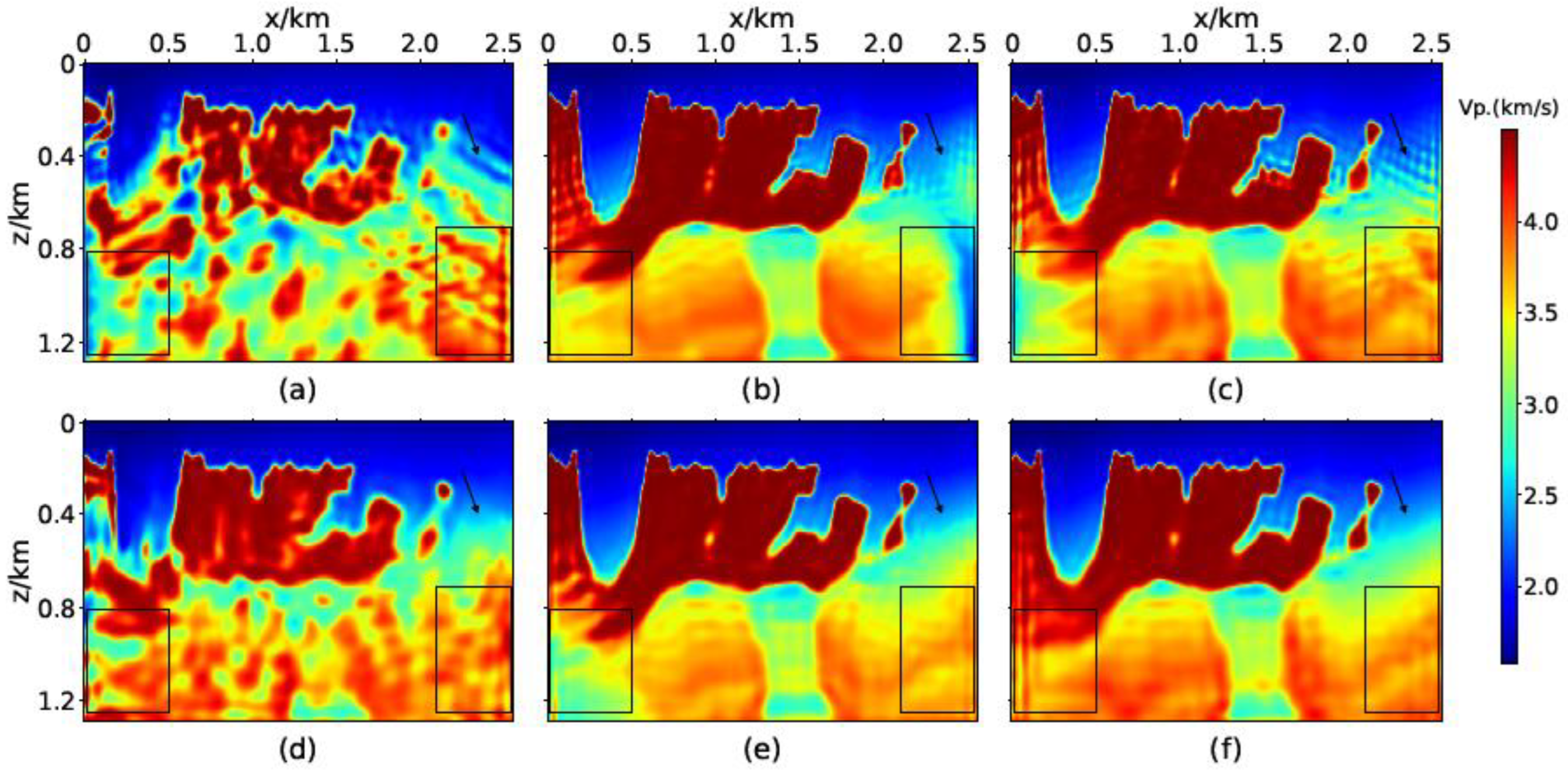
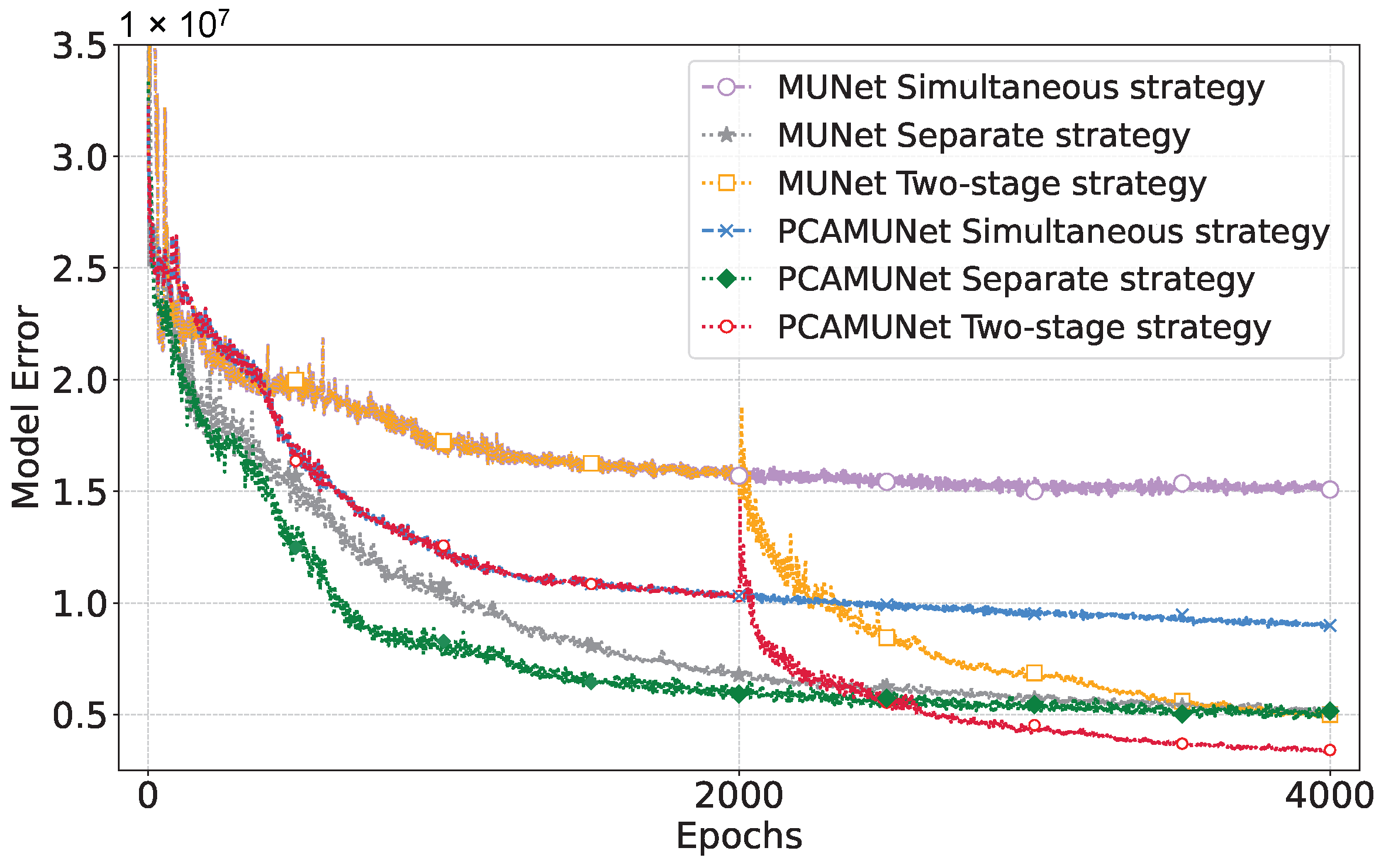
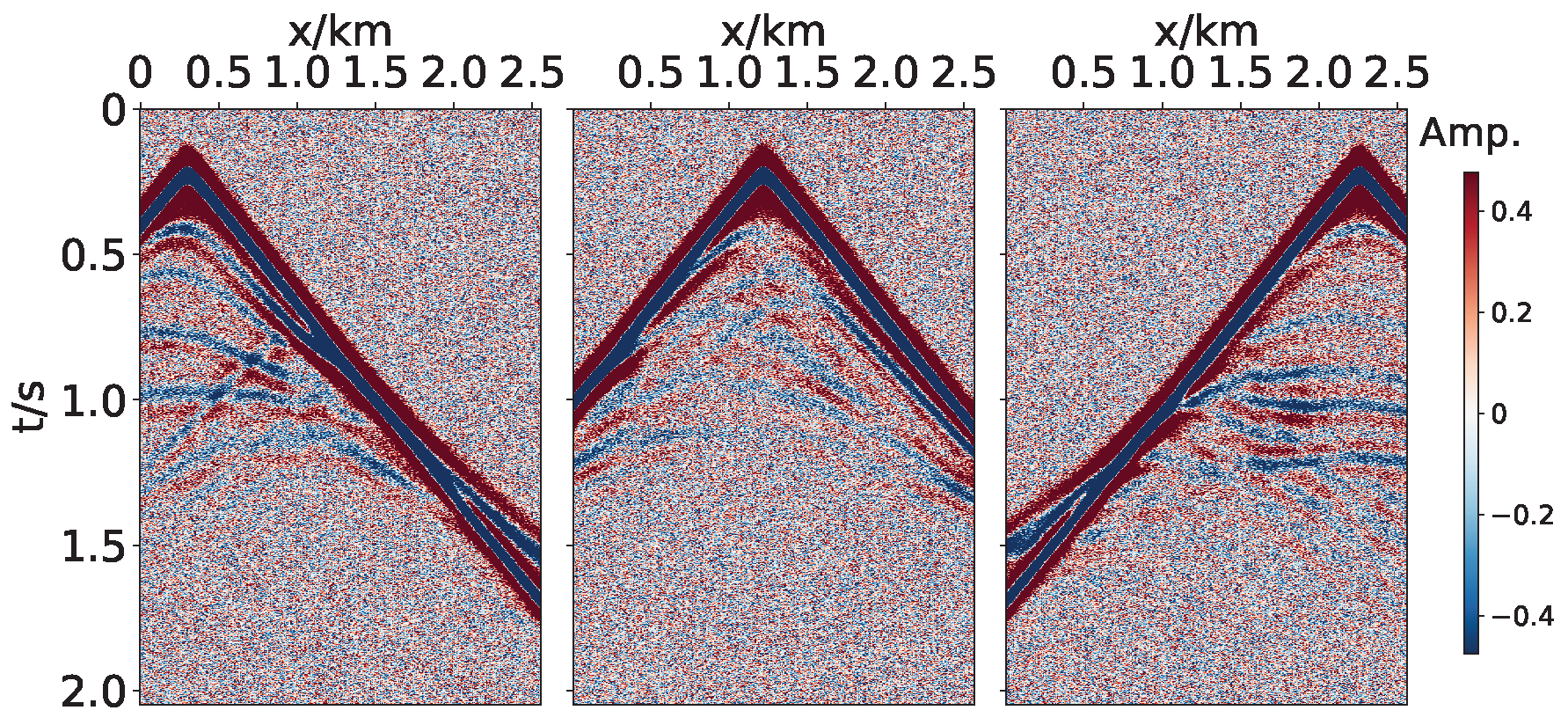

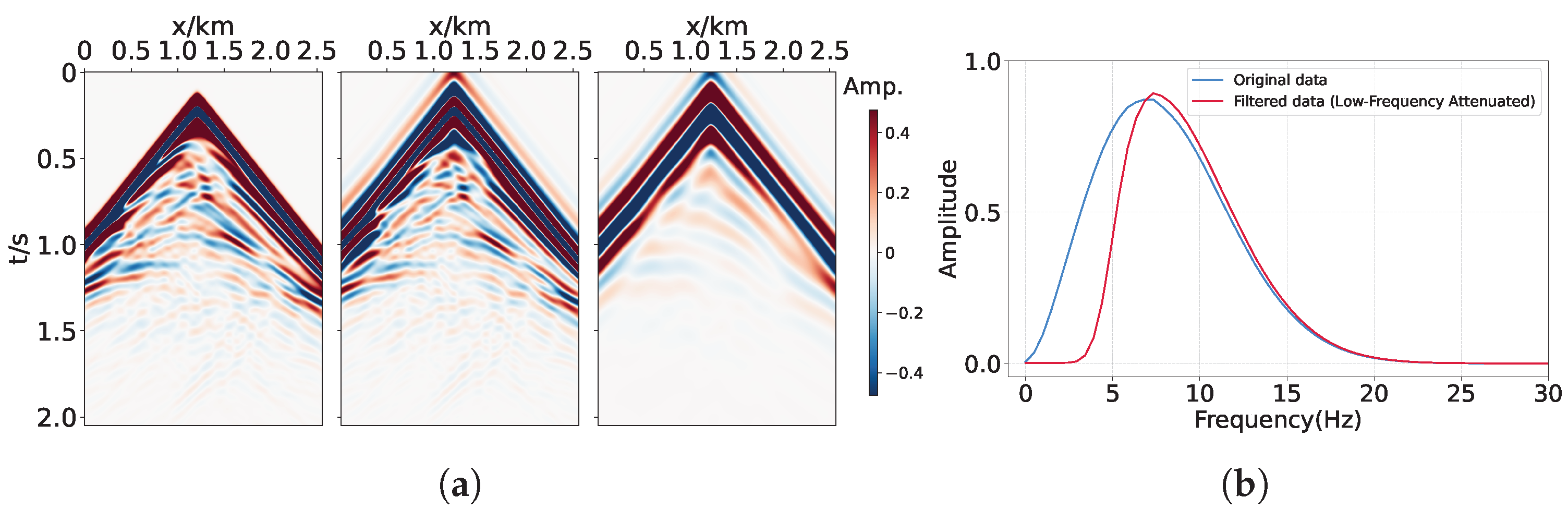
| Network | Strategy | NRMSE | R2 | PCC | Training Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MUNet | Simultaneous | 0.1115 | 0.8571 | 0.9323 | 1268 |
| Separate | 0.1209 | 0.8320 | 0.9157 | 5538 | |
| Two-stage | 0.1004 | 0.8840 | 0.9456 | 1615 | |
| PCAMUNet | Simultaneous | 0.0976 | 0.8905 | 0.9458 | 1796 |
| Separate | 0.1018 | 0.8809 | 0.9411 | 7185 | |
| Two-stage | 0.0794 | 0.9275 | 0.9637 | 1787 |
| Network | Strategy | NRMSE | R2 | PCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MUNet | Simultaneous | 0.1091 | 0.7905 | 0.8992 |
| Separate | 0.1421 | 0.6446 | 0.8643 | |
| Two-stage | 0.0924 | 0.8496 | 0.9291 | |
| PCAMUNet | Simultaneous | 0.0779 | 0.8933 | 0.9470 |
| Separate | 0.0865 | 0.8682 | 0.9440 | |
| Two-stage | 0.0616 | 0.9331 | 0.9667 |
| Network | Strategy | NRMSE | R2 | PCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MUNet | Simultaneous | 0.2405 | 0.5153 | 0.7746 |
| Separate | 0.1174 | 0.8845 | 0.9482 | |
| Two-stage | 0.1059 | 0.9060 | 0.9572 | |
| PCAMUNet | Simultaneous | 0.1645 | 0.7734 | 0.8887 |
| Separate | 0.1058 | 0.9063 | 0.9596 | |
| Two-stage | 0.0745 | 0.9535 | 0.9788 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, B. Physics-Guided Self-Supervised Learning Full Waveform Inversion with Pretraining on Simultaneous Source. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061193
Zheng Q, Li M, Wu B. Physics-Guided Self-Supervised Learning Full Waveform Inversion with Pretraining on Simultaneous Source. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061193
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Qiqi, Meng Li, and Bangyu Wu. 2025. "Physics-Guided Self-Supervised Learning Full Waveform Inversion with Pretraining on Simultaneous Source" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061193
APA StyleZheng, Q., Li, M., & Wu, B. (2025). Physics-Guided Self-Supervised Learning Full Waveform Inversion with Pretraining on Simultaneous Source. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061193








